A Mass Spectrometry System That Can Improve Ion Detection Efficiency
A mass spectrometry and ion technology, applied in the field of mass spectrometry, can solve the problems of increasing the detection circuit, increasing the manufacturing cost, increasing the volume and power consumption of the mass spectrometer, and achieving the effect of economical miniaturization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] In order to better understand the asymmetric structure, a symmetric structure is first described below.
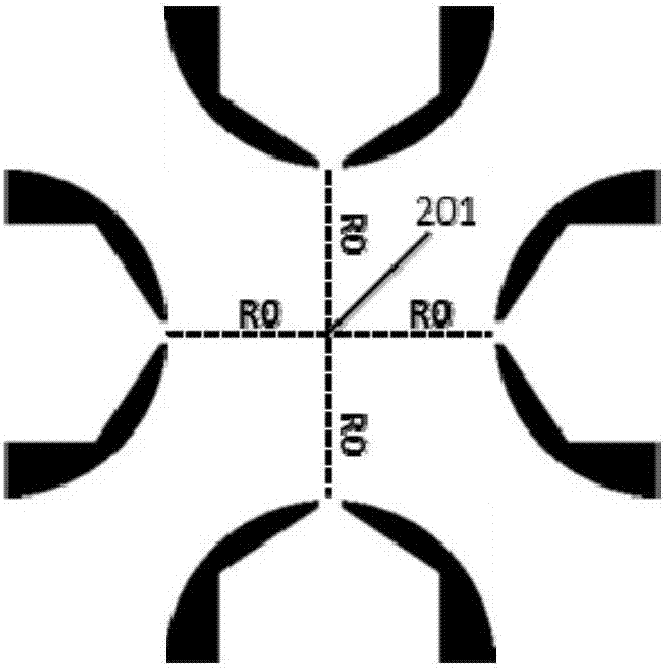
[0040] see figure 2 , figure 2 It is a structural schematic diagram of a semi-cylindrical columnar electrode linear ion trap with a symmetrical structure. Such as figure 2 As shown, the distance (R0) of the two pairs of columnar electrodes (X electrode and Y electrode) relative to the central axis 201 of the ion trap is equal.
Embodiment 2
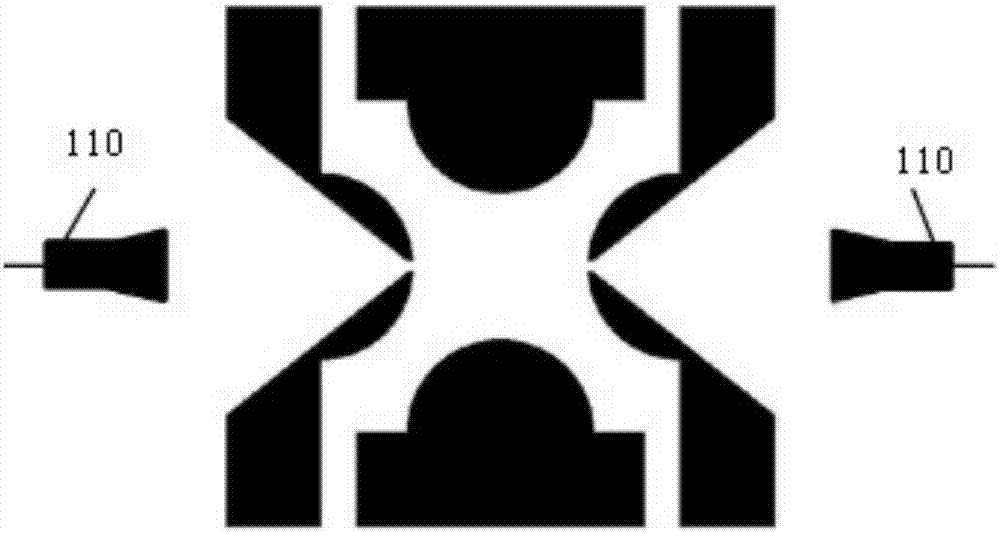
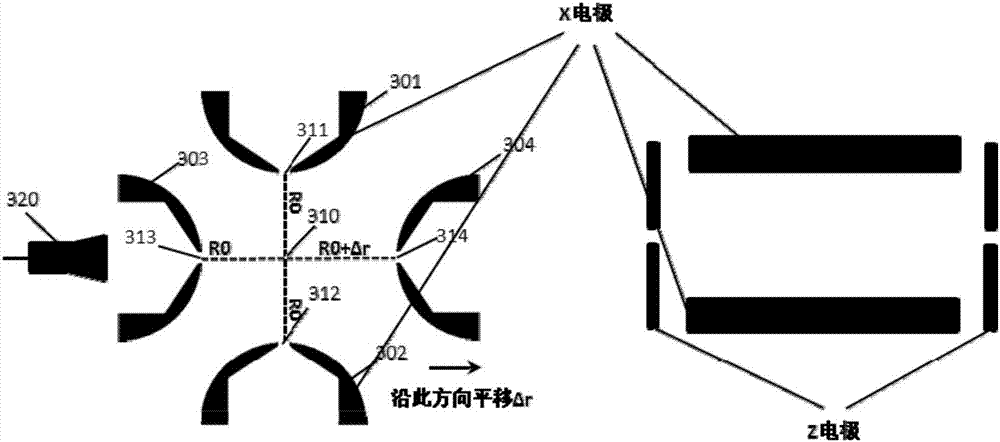
[0042] see image 3 , image 3 It is a structural schematic diagram of a mass spectrometry system based on a linear ion trap with asymmetric semi-cylindrical electrodes. Such as image 3 As shown, it consists of two pairs of columnar electrodes (X electrodes 301, 302 and Y electrodes 303, 304) placed in parallel and a pair of end cap sheet electrodes (Z electrodes). The X electrodes 301, 302, Y electrodes 303 , 304 is a semi-cylindrical columnar electrode. The X right terminal electrode 304 is shifted to the right by Δr in the direction away from the central axis 310 of the ion trap, so that the distance from the central axis 310 of the original symmetrical structure is increased to R0+Δr, forming an asymmetric linear ion trap. Ion extraction slots 311 , 312 , 313 , 314 are located in the center of the semi-cylindrical columnar electrode, and the width of the ion extraction slots 311 , 312 , 313 , 314 is between 0.3 mm and 2 mm. The end cap sheet electrodes (Z electrodes) ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] see Figure 4 , Figure 4 It is a structural schematic diagram of a mass spectrometry system based on an asymmetrical triangular columnar electrode linear ion trap. Such as Figure 4 As shown, it consists of two pairs of relatively parallel columnar electrodes (X electrodes 401, 402 and Y electrodes 403, 404) and a pair of end cap sheet electrodes (Z electrodes). The Z electrode structures in the three are the same, so Figure 4 The Z electrode is omitted in , and only a cross-sectional view of the system is given. The X electrodes 401 , 402 and Y electrodes 403 , 404 are triangular columnar electrodes with an isosceles triangle cross section and a vertex angle ranging from 90° to 180° (excluding 180°). The X right terminal electrode 404 is shifted to the right by Δr in the direction away from the central axis 410 of the ion trap, so that the distance from the central axis 410 of the original symmetrical structure is increased to R0+Δr, forming an asymmetric linear ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com