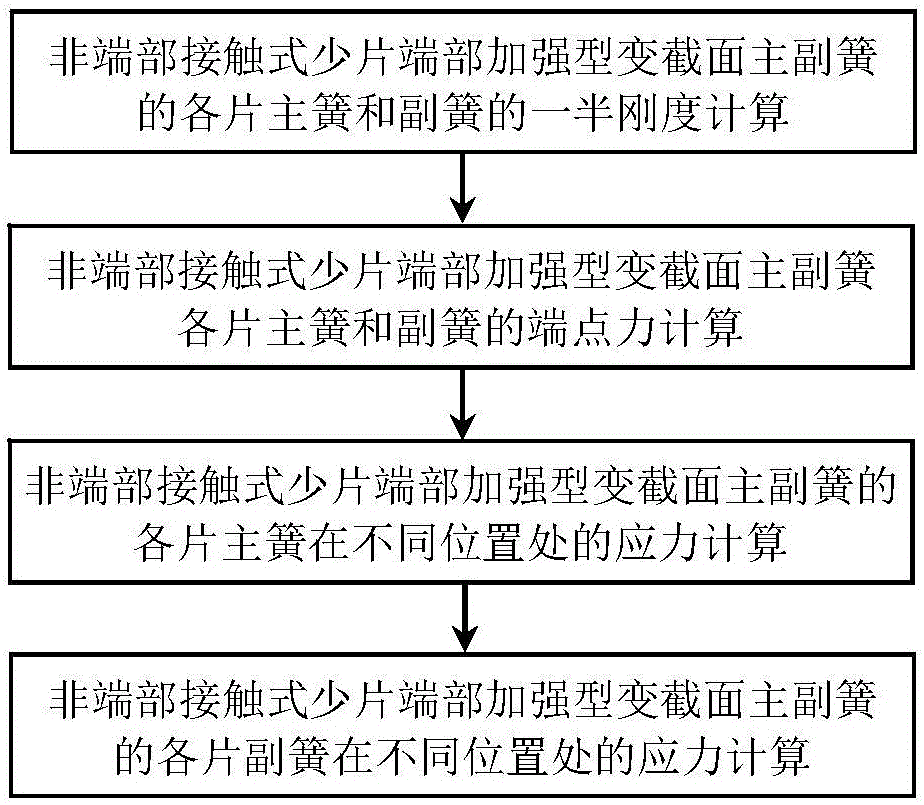
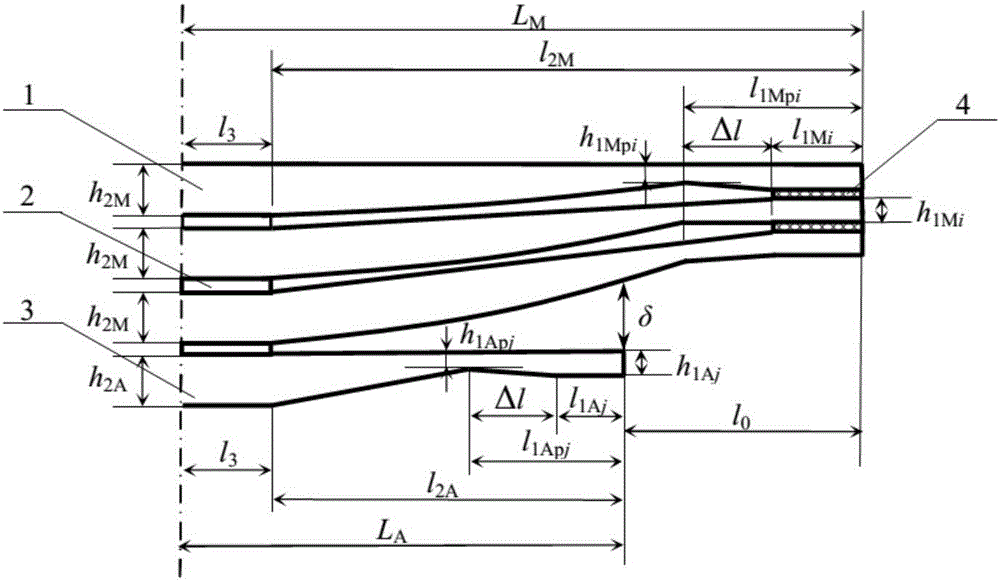
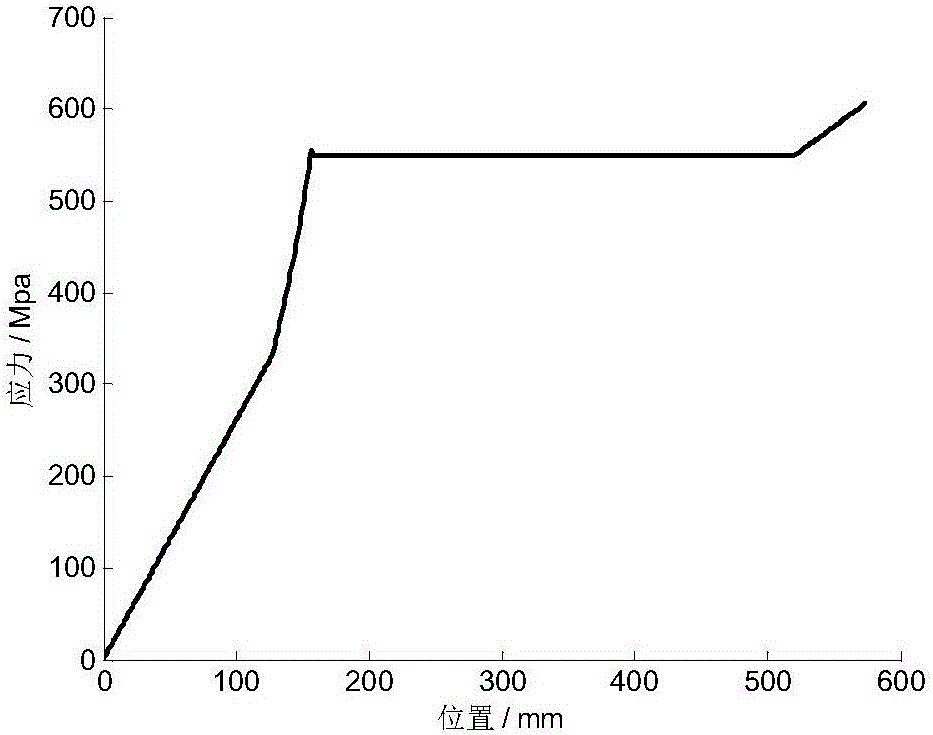
Calculation method for stress of each leaf of non-end-contact few-leaf end-enhanced main spring and sub-spring
A calculation method and contact technology, which is applied in calculation, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to meet the requirements of non-end contact type, few-piece end-reinforced variable-section primary and secondary springs, and the inability to provide accurate stress analysis calculation formulas. And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0062] Example: The width b of a non-end contact type few-piece end-reinforced variable-section primary and secondary springs = 60 mm, half of the installation distance l 3 =55mm, length Δl of oblique line segment=30mm, elastic modulus E=200GPa. Half the length L of the main spring M =575mm,, the distance from the root of the main spring parabola segment to the end point of the main spring l 2M =L M -l 3 =520mm; the thickness h of the straight section at the root of each piece of main spring 2M =11mm, the number of main reeds m=2, where the end thickness h of the parabolic segment of the first main spring 1Mp1 =6mm, that is, the thickness ratio of the parabola segment β 1 =h 1Mp1 / h 2M =0.55, the distance l from the end of the parabola segment to the end point of the main spring 1Mp1 = l 2M beta1 2 =157.30mm, the thickness h of the straight section at the end 1M1 =7mm, that is, the thickness ratio of the oblique line segment γ M1 = h 1M1 / h 1Mp1 =1.17, the length...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com