A master-slave replication method of an in-memory database and an in-memory database system
A replication method and database technology, applied in the field of in-memory databases, can solve problems such as decreased processing efficiency, achieve the effect of efficient processing and ensure consistency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
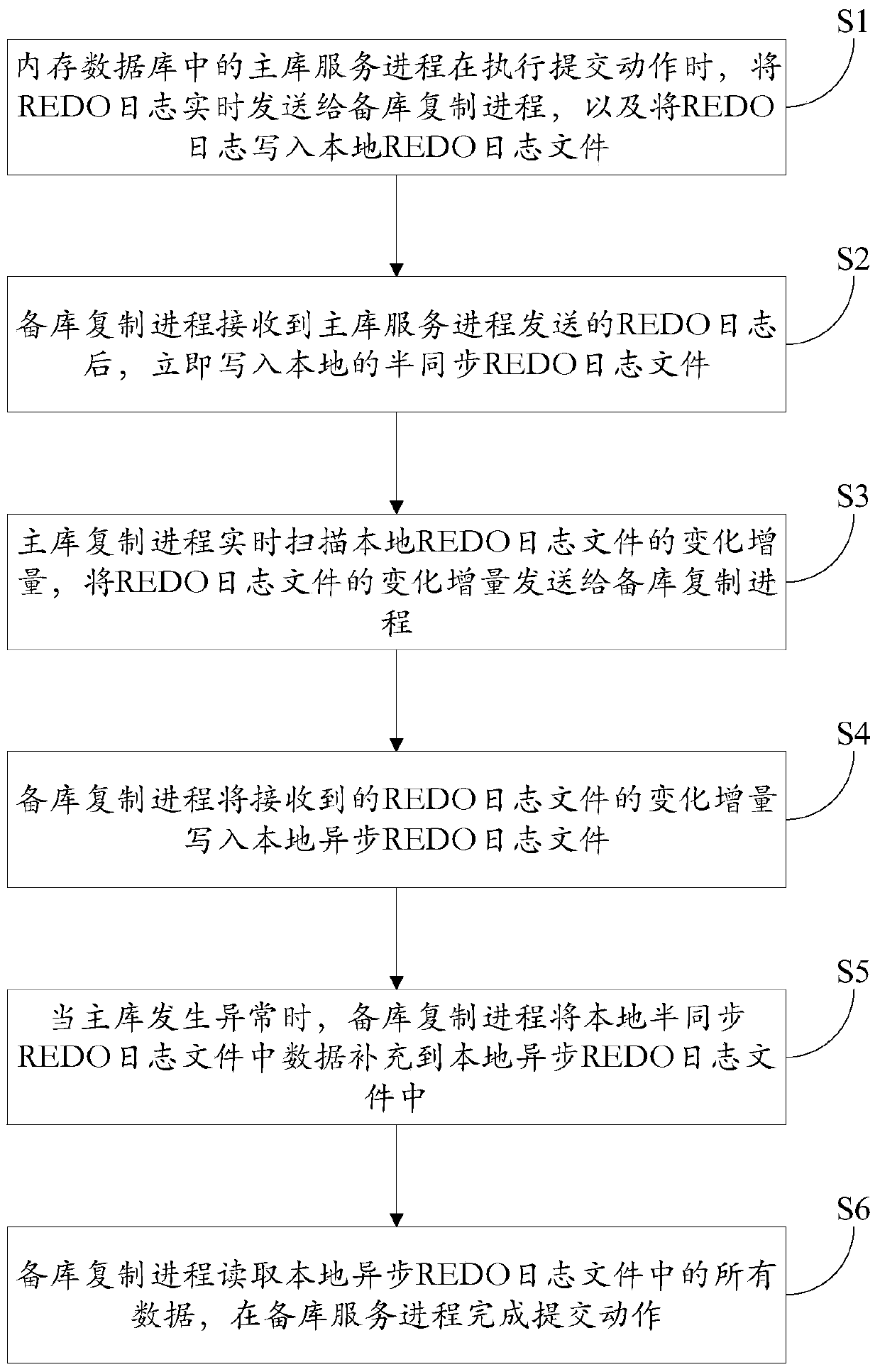
[0025] Embodiment 1. A method for master-backup replication of an in-memory database. Combine below figure 1 The method provided in this embodiment will be described.
[0026] join figure 1 , the method provided by this embodiment includes: S1. When the main library service process in the memory database executes the submission action, the REDO log is sent to the backup library replication process in real time, and the REDO log is written into the local REDO log file;
[0027] S2. After the standby database replication process receives the REDO log sent by the main database service process, it immediately writes the local semi-synchronous REDO log file;
[0028] S3. The master database replication process scans the change increment of the local REDO log file in real time, and sends the change increment of the REDO log file to the standby database replication process;
[0029] S4. The copy process of the standby database writes the change increment of the received REDO log f...
Embodiment 2
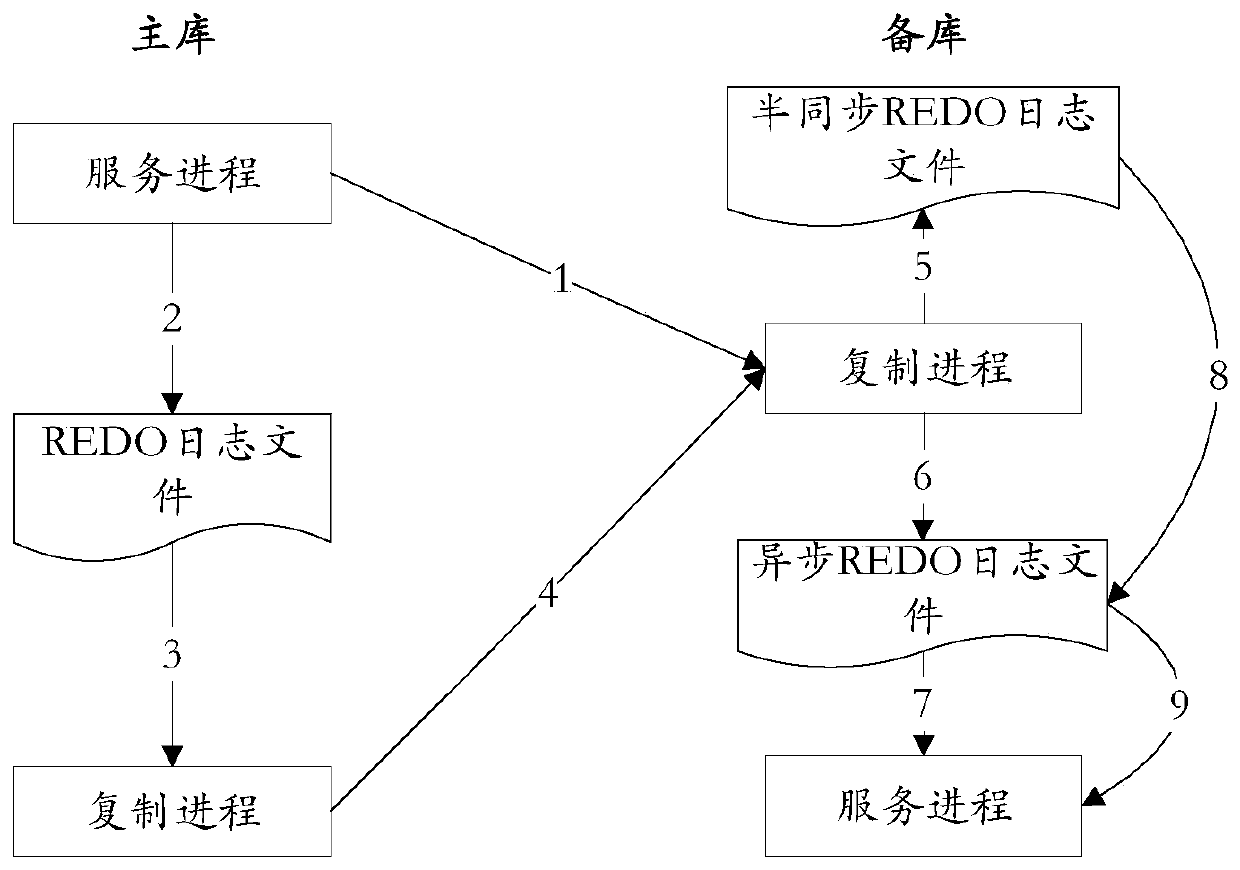
[0045] Embodiment 2, an in-memory database system. Combine below figure 2 The system provided by this embodiment is described.
[0046] see figure 2 , the in-memory data system provided in this embodiment includes a master database and a standby database, wherein the master database has a master database replication process and a master database service process, and the standby database has a standby database replication process and a standby database service process.
[0047] The main library service process is used to send the REDO log to the standby library replication process in real time when performing the submission action, and write the REDO log to the local REDO log file;
[0048] Described master database replication process is used to scan the change increment of local REDO log file in real time, and the change increment of REDO log file is sent to standby database replication process;
[0049] Described standby library copying process is used to write into the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com