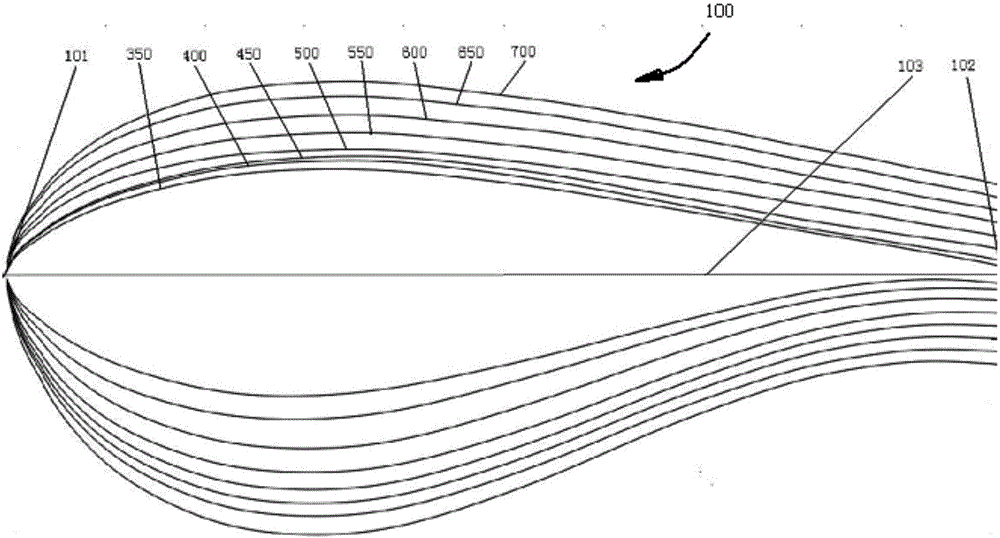
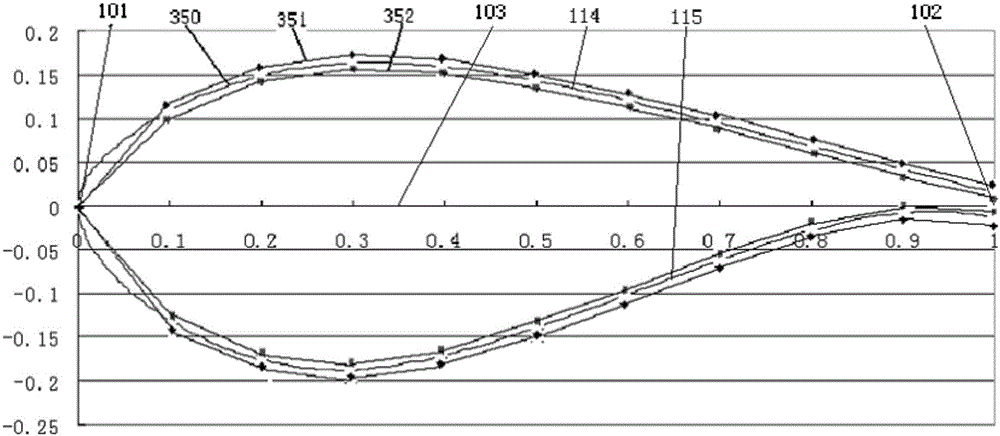
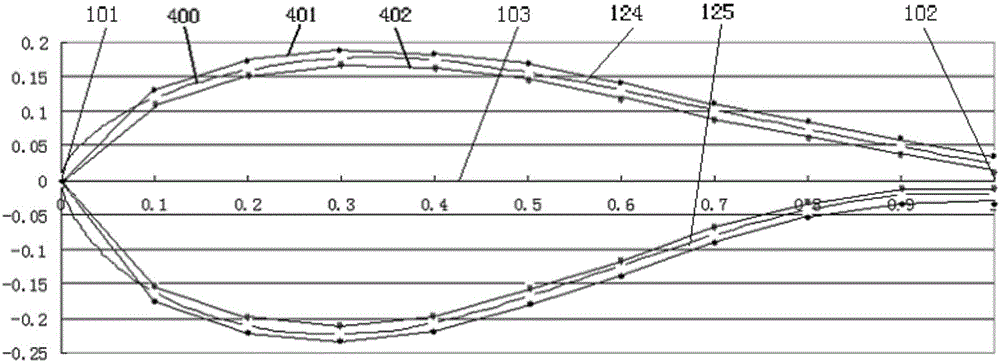
Thick wing group of large turbine blade
A wind turbine blade and airfoil family technology, applied in the field of horizontal axis wind turbine airfoil design, can solve the problems of deviation from optimal torsion angle, unfavorable blade structural strength and rigidity, and poor performance, so as to reduce pressure gradient and save materials Amount and cost, effect of increased strength and structural rigidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0083] In order to achieve the above goals, the present invention is aimed at each airfoil in the above-mentioned airfoil family, which is characterized in that the suction surface of the airfoil is lower, the pressure surface is more convex, the thickness of the trailing edge is larger, the pressure surface is S-shaped after loading, and the leading edge Larger radius. According to the above-mentioned basic idea, the present invention uses the Profil i Pro based on Xfoil (the software based on the vortex surface element method of viscous-inviscid iteration developed by the U.S. MIT, the airfoil calculation in the state before the subsonic speed stall has sufficient precision) The software constructs a new airfoil, including relative camber size and position change, relative thickness size and position change, leading edge radius and trailing edge thickness change, etc., and performs performance calculation under smooth conditions under the condition of Re=3000000 , and finall...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com