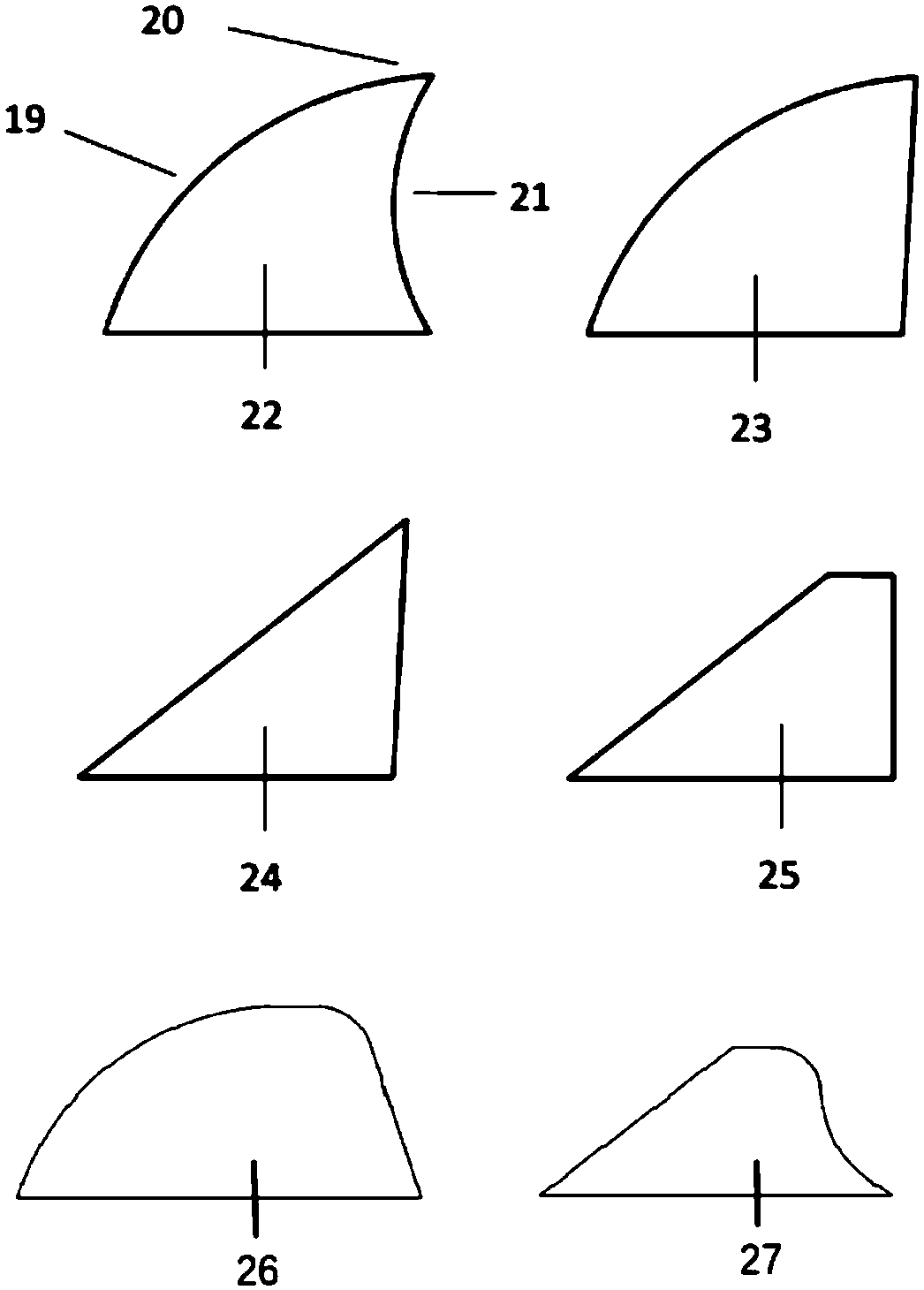Patents
Literature
149 results about "Wind turbine design" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
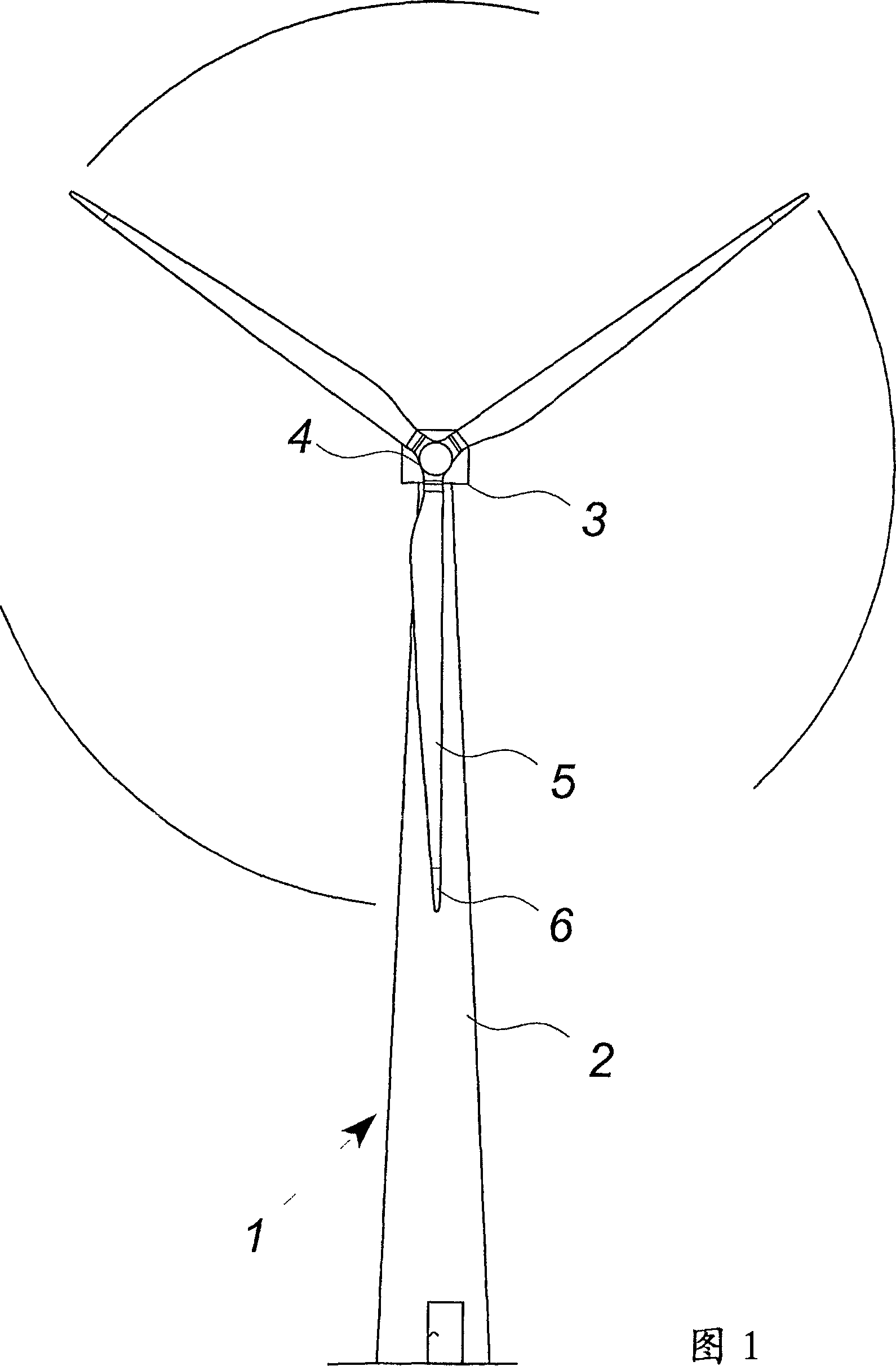
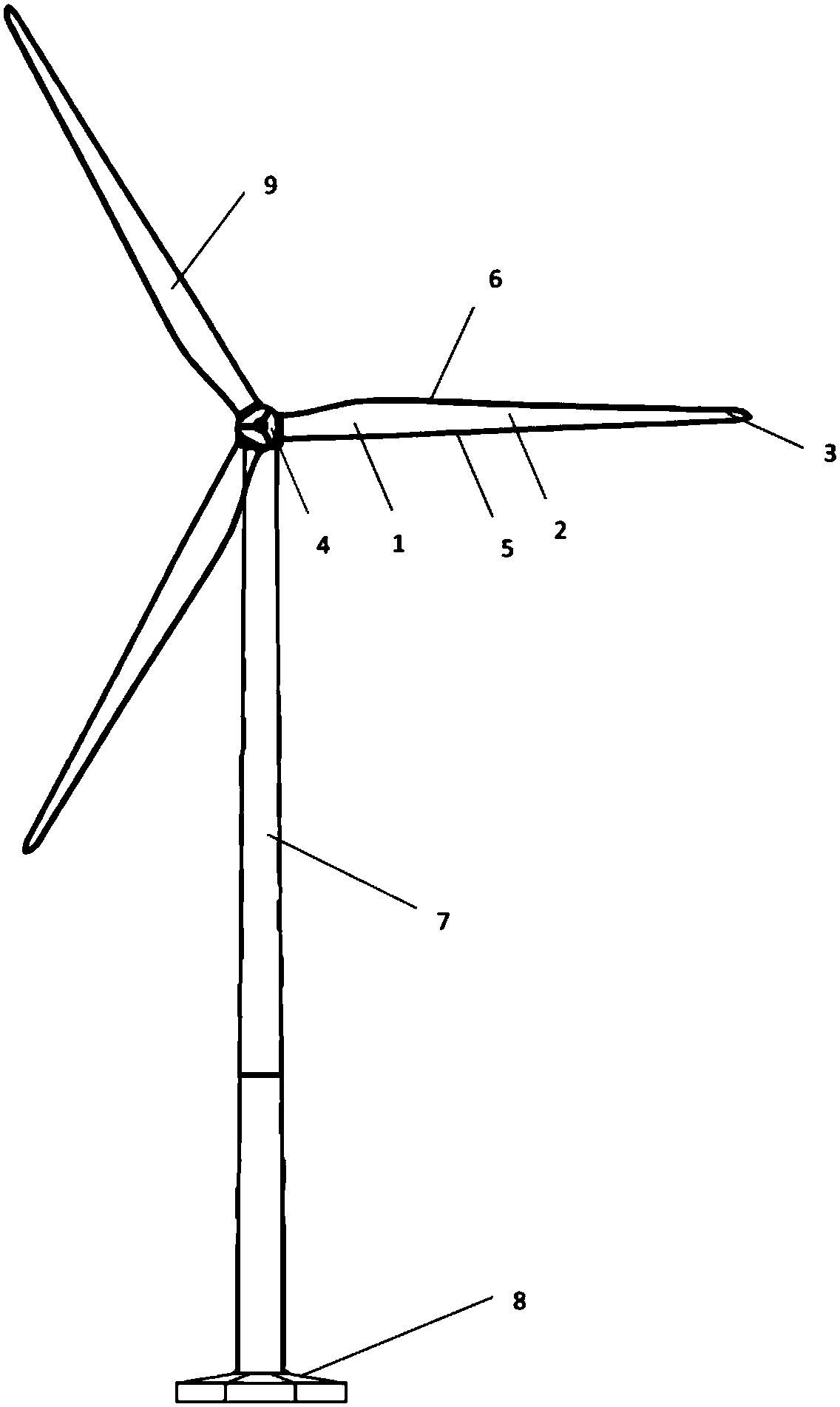
Wind turbine design is the process of defining the form and specifications of a wind turbine to extract energy from the wind. A wind turbine installation consists of the necessary systems needed to capture the wind's energy, point the turbine into the wind, convert mechanical rotation into electrical power, and other systems to start, stop, and control the turbine.
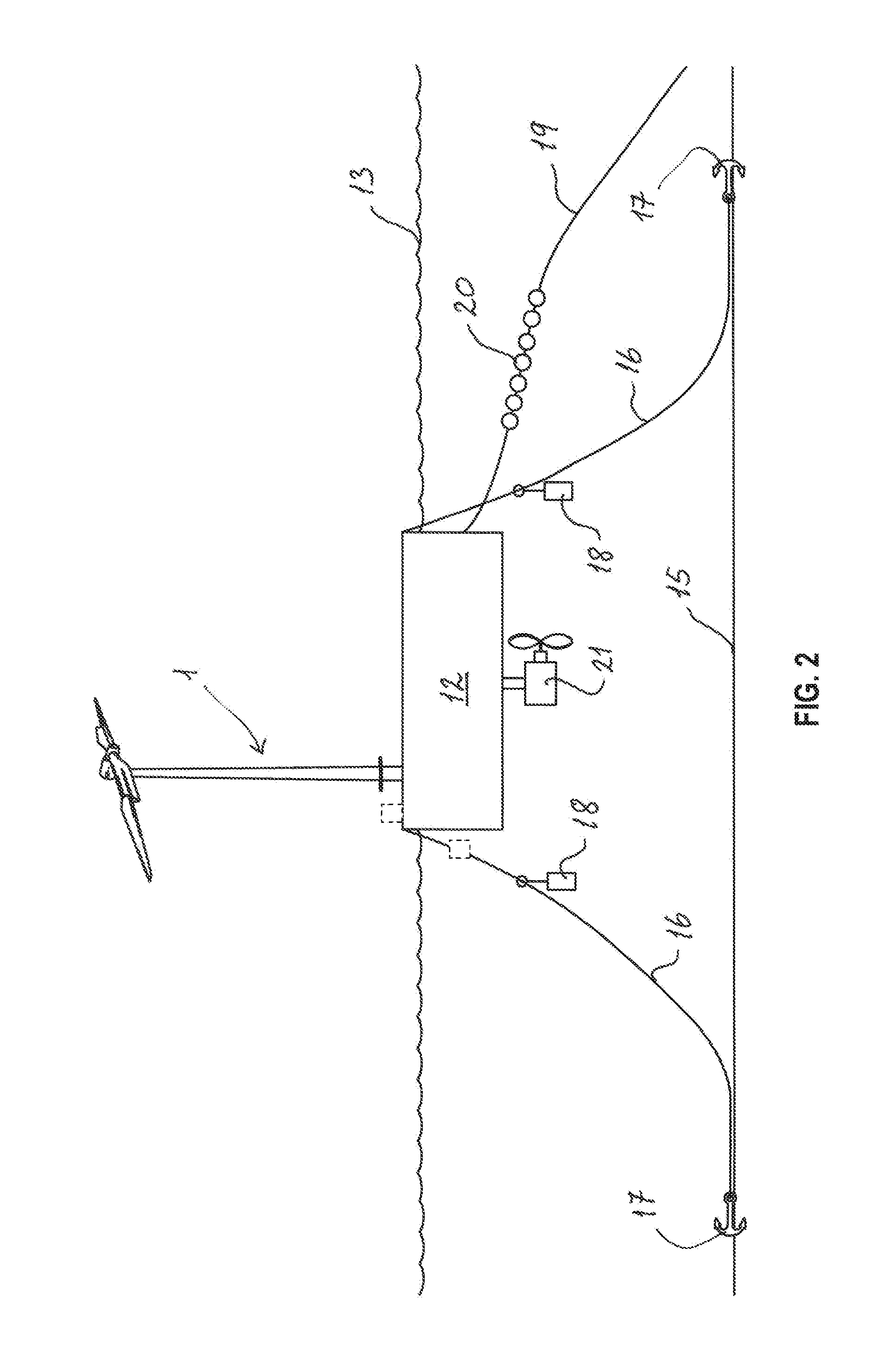
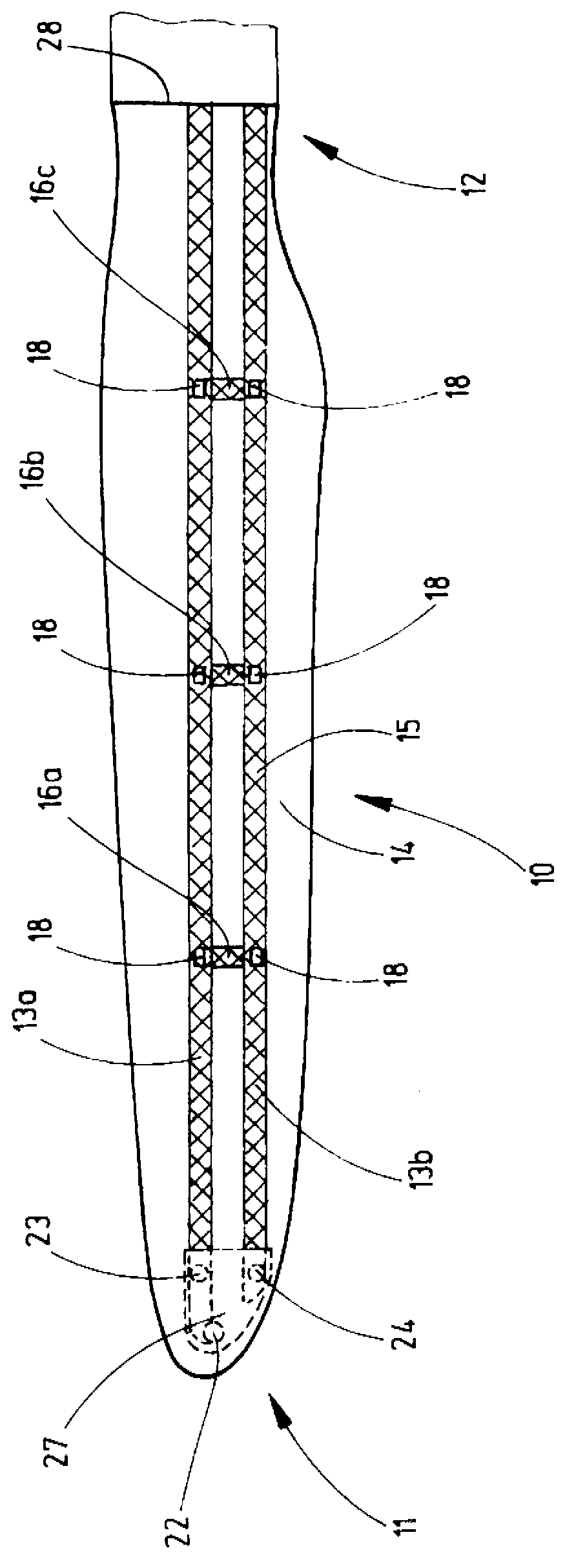
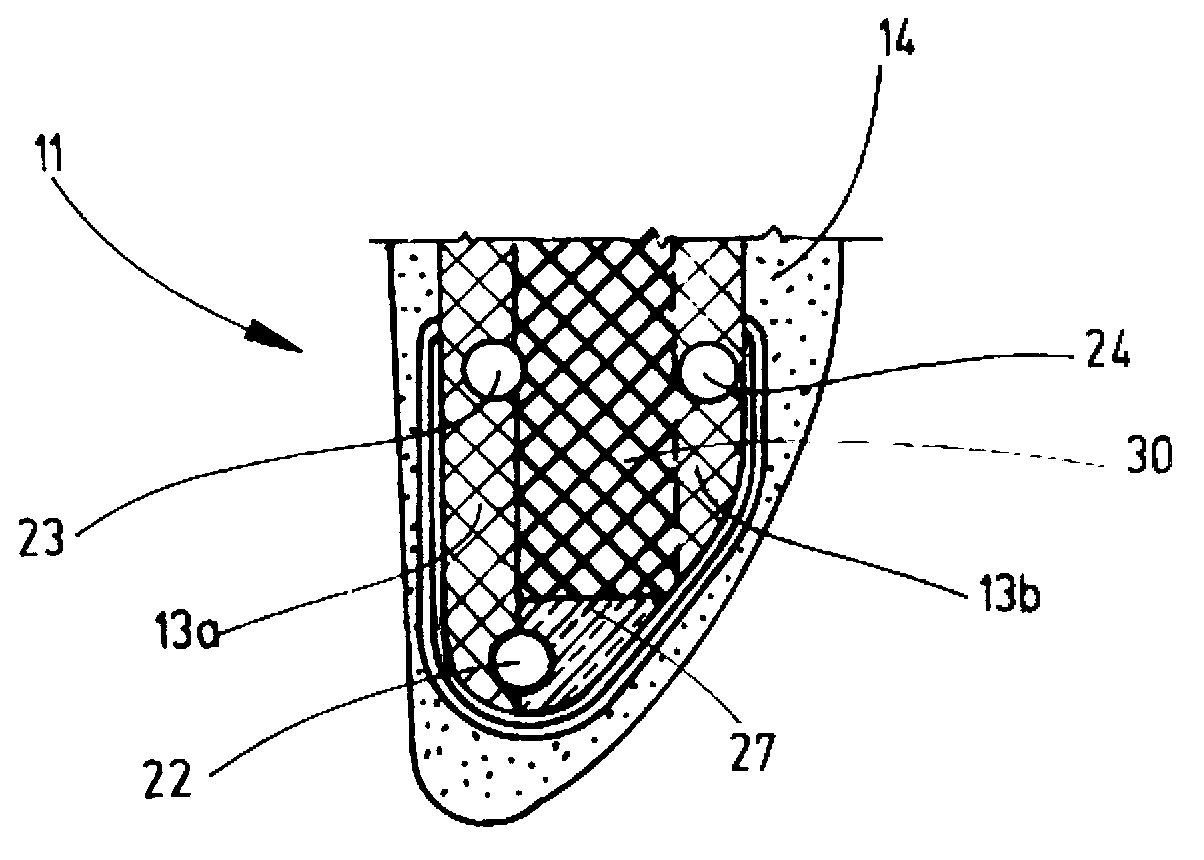
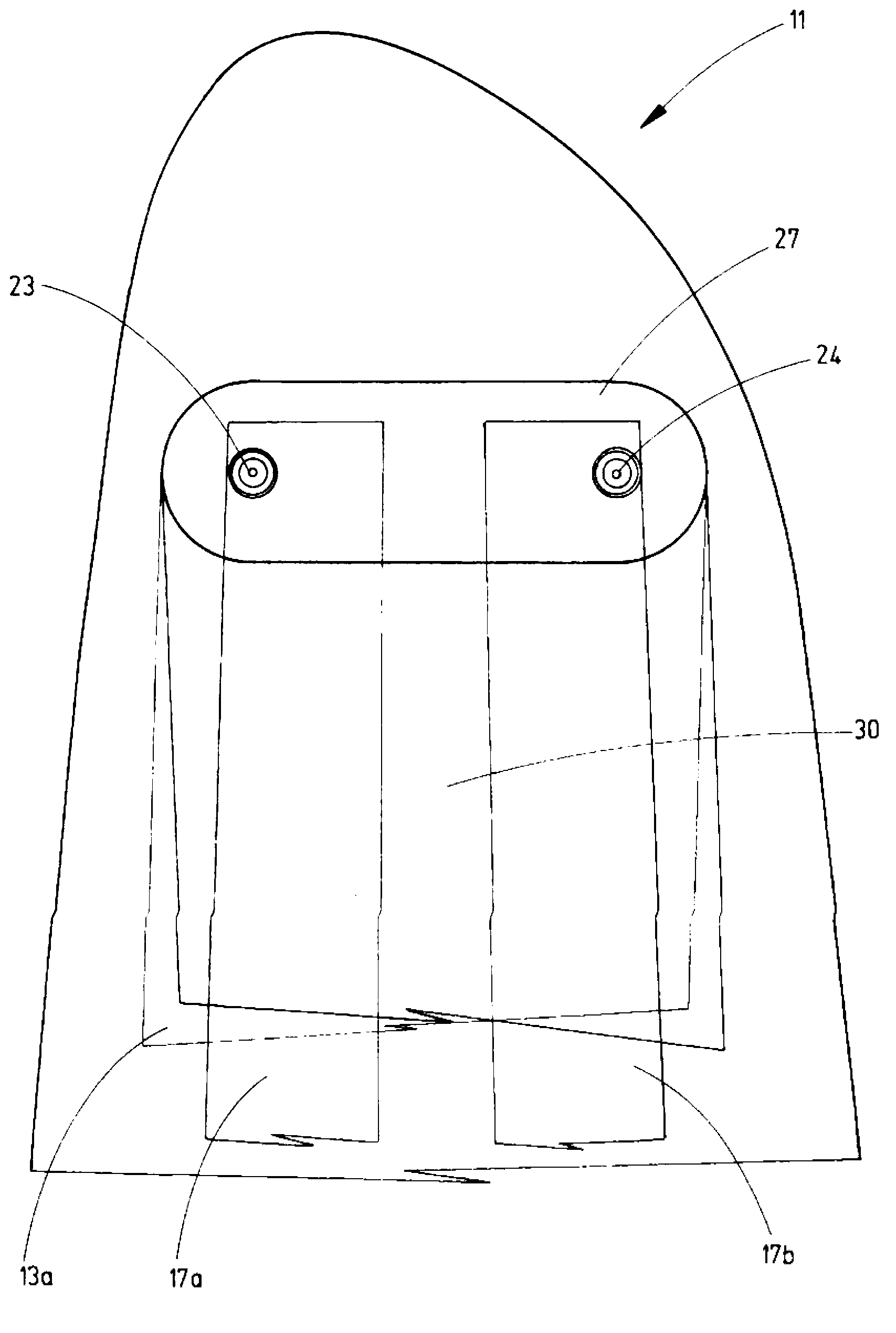
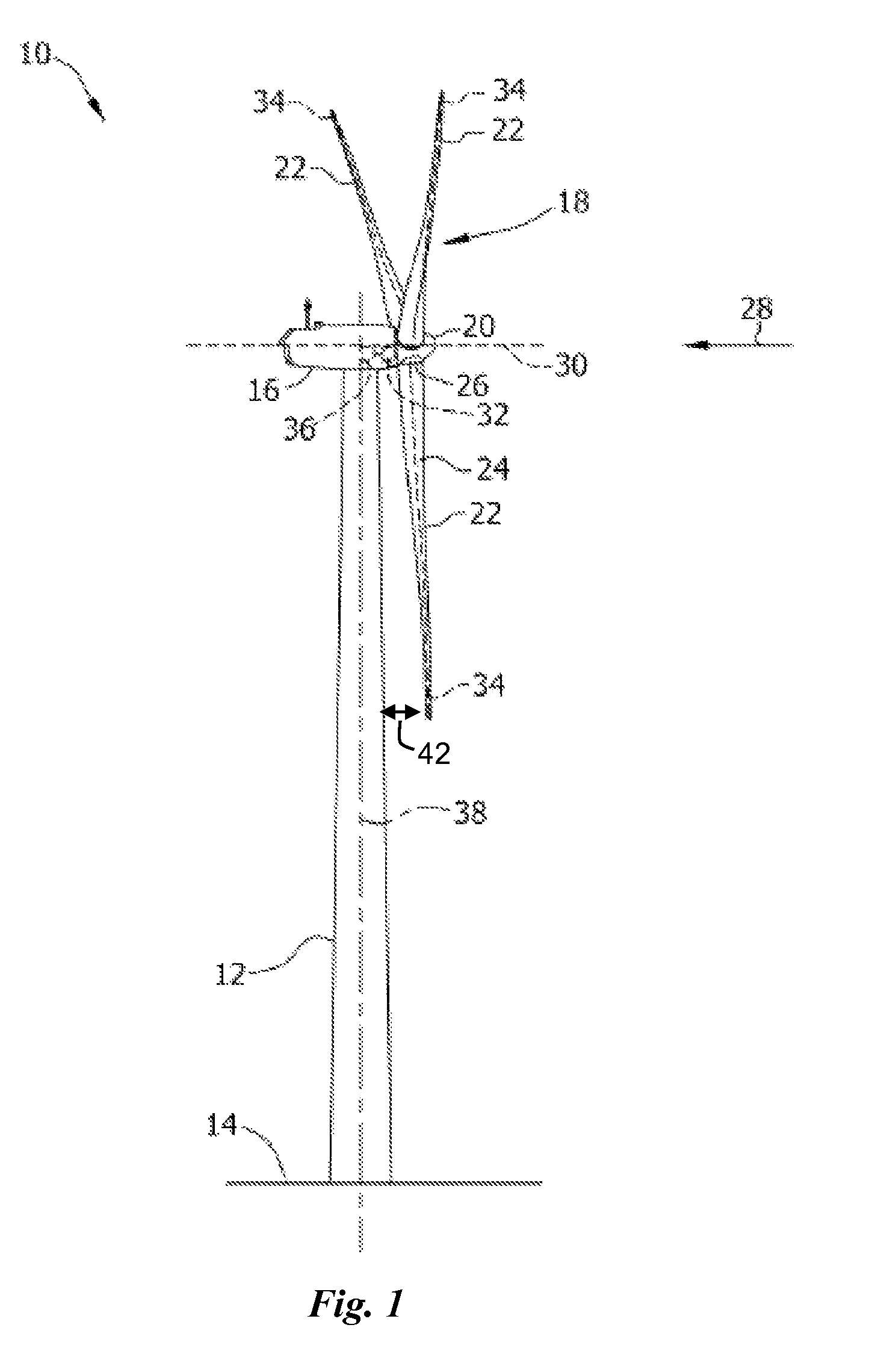
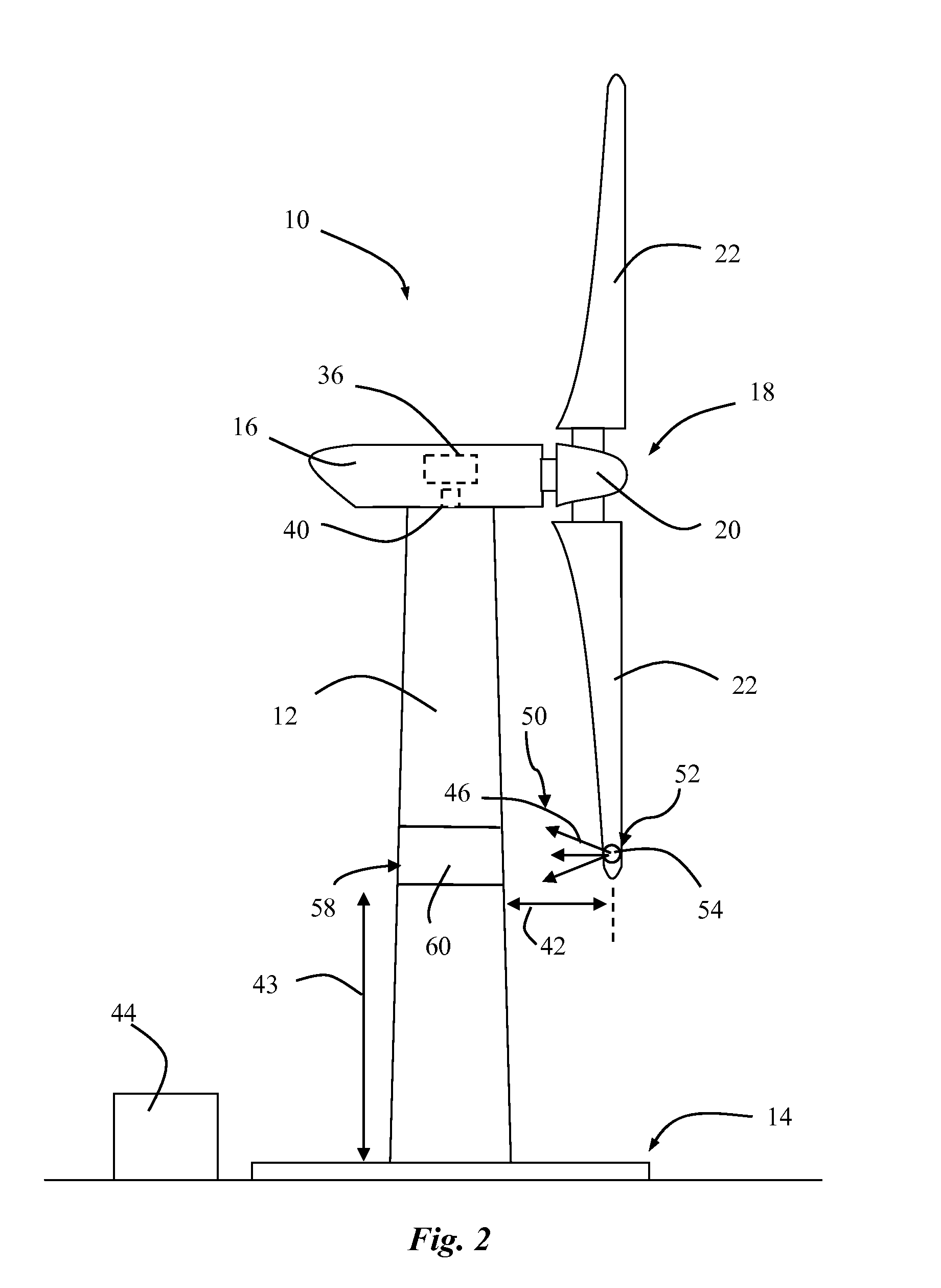
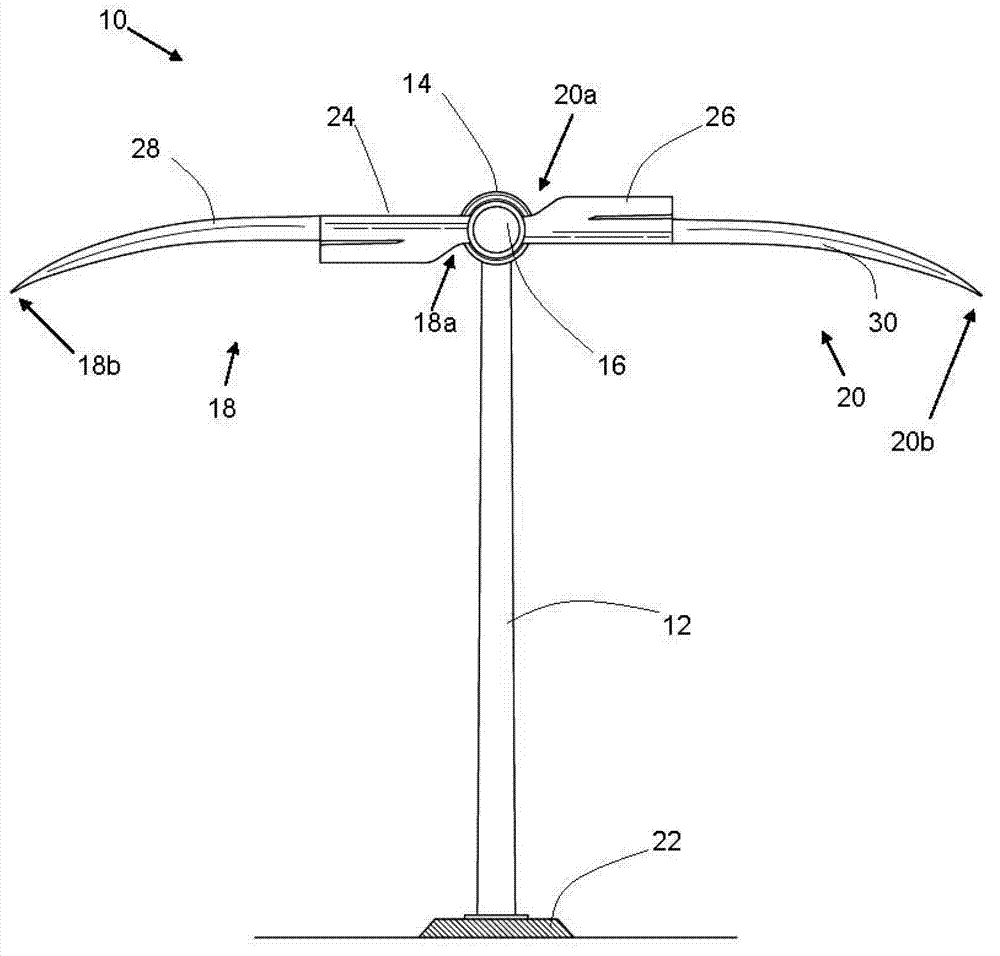
Wind turbine device
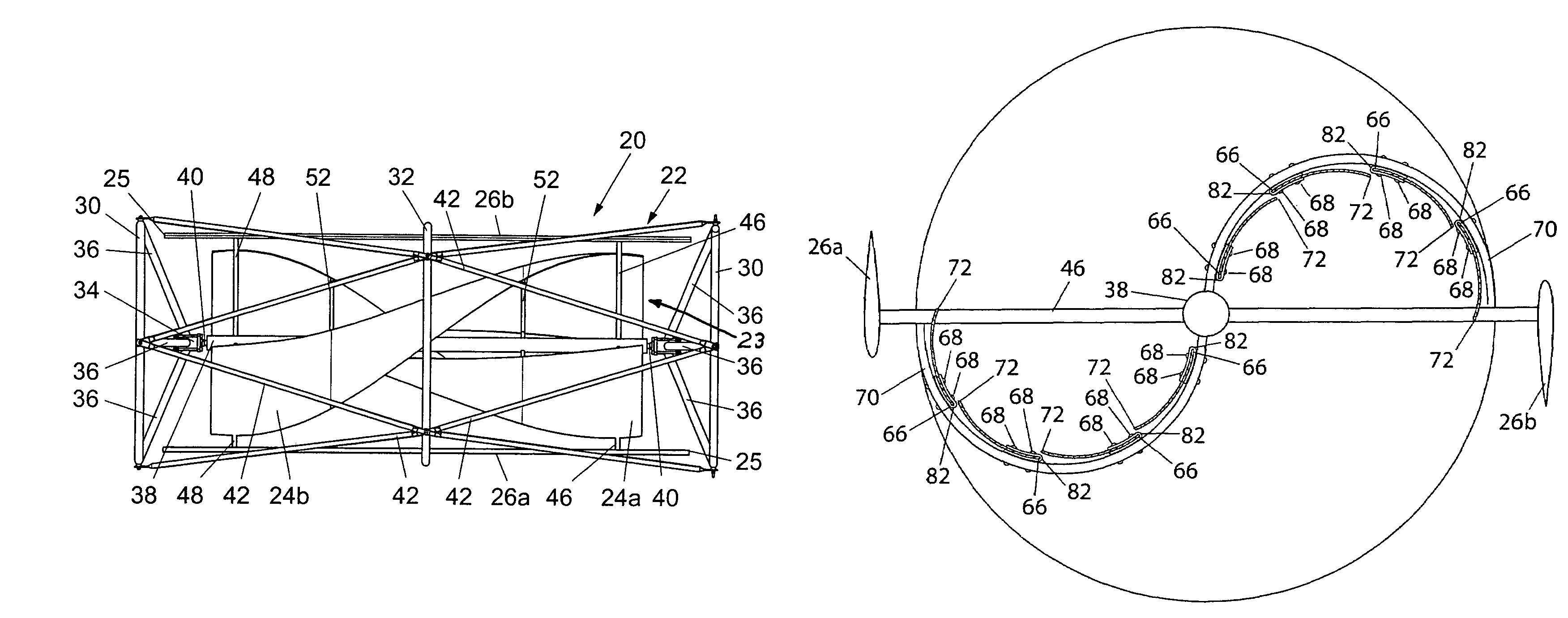
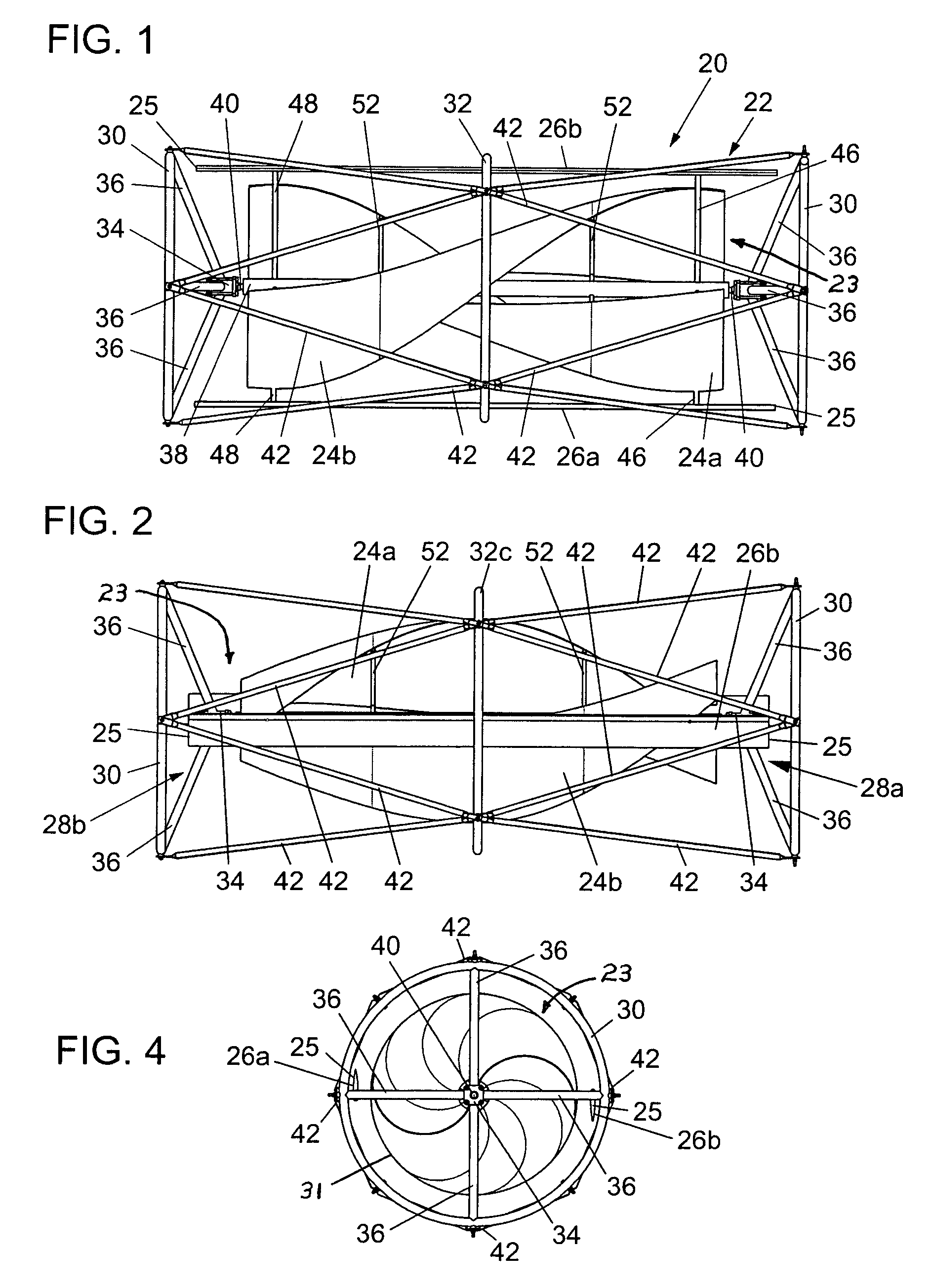
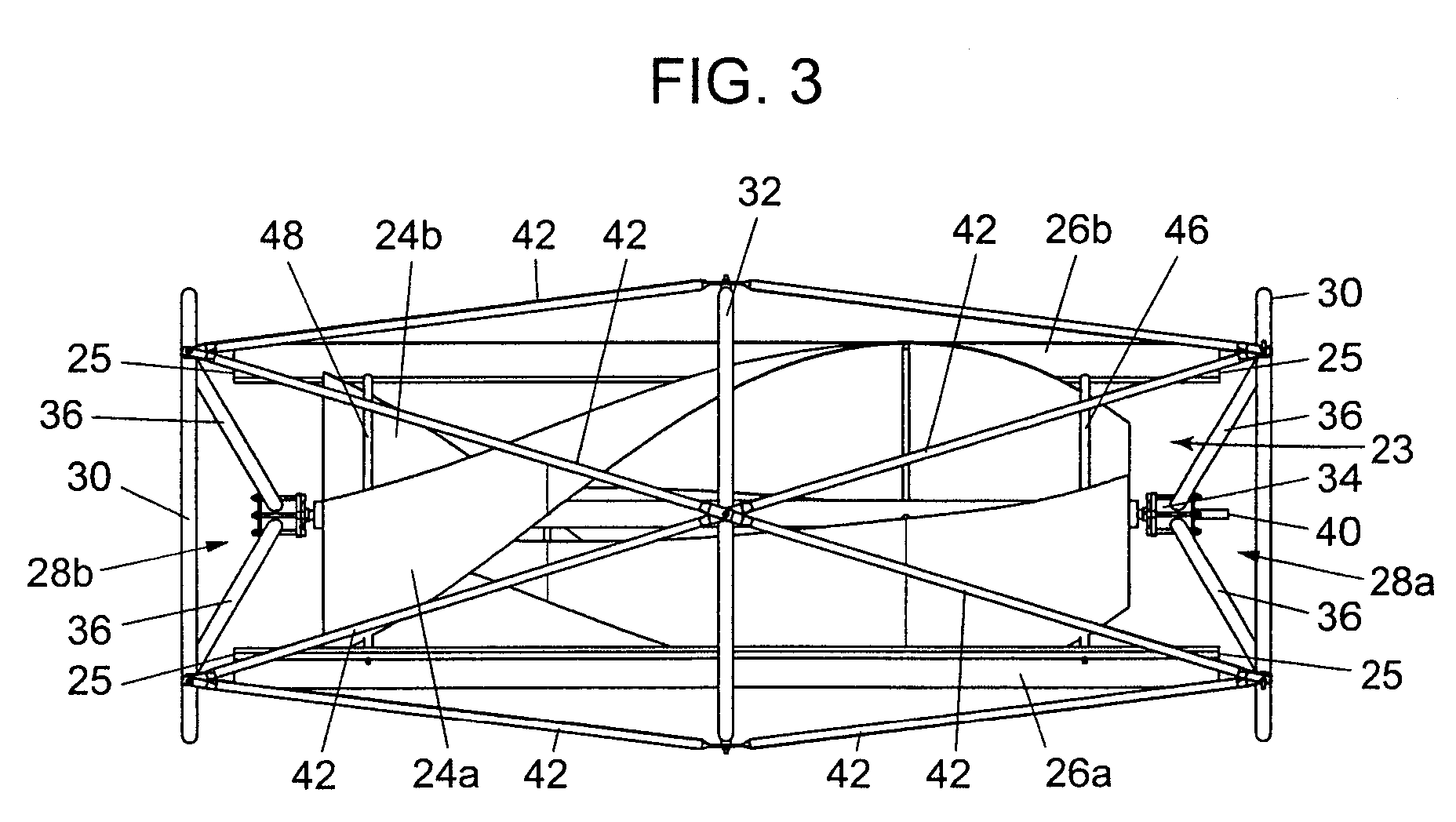
ActiveUS7132760B2Reduce blade dragConvenient lengthPropellersRotary propellersDevice formOperational capabilities
Owner:BECKER WILLIAM S
Methods and apparatus for advanced wind turbine design
ActiveUS20070024058A1Eliminate needReduced pressure levelWind motor controlEngine fuctionsHigh energyHydraulic pump
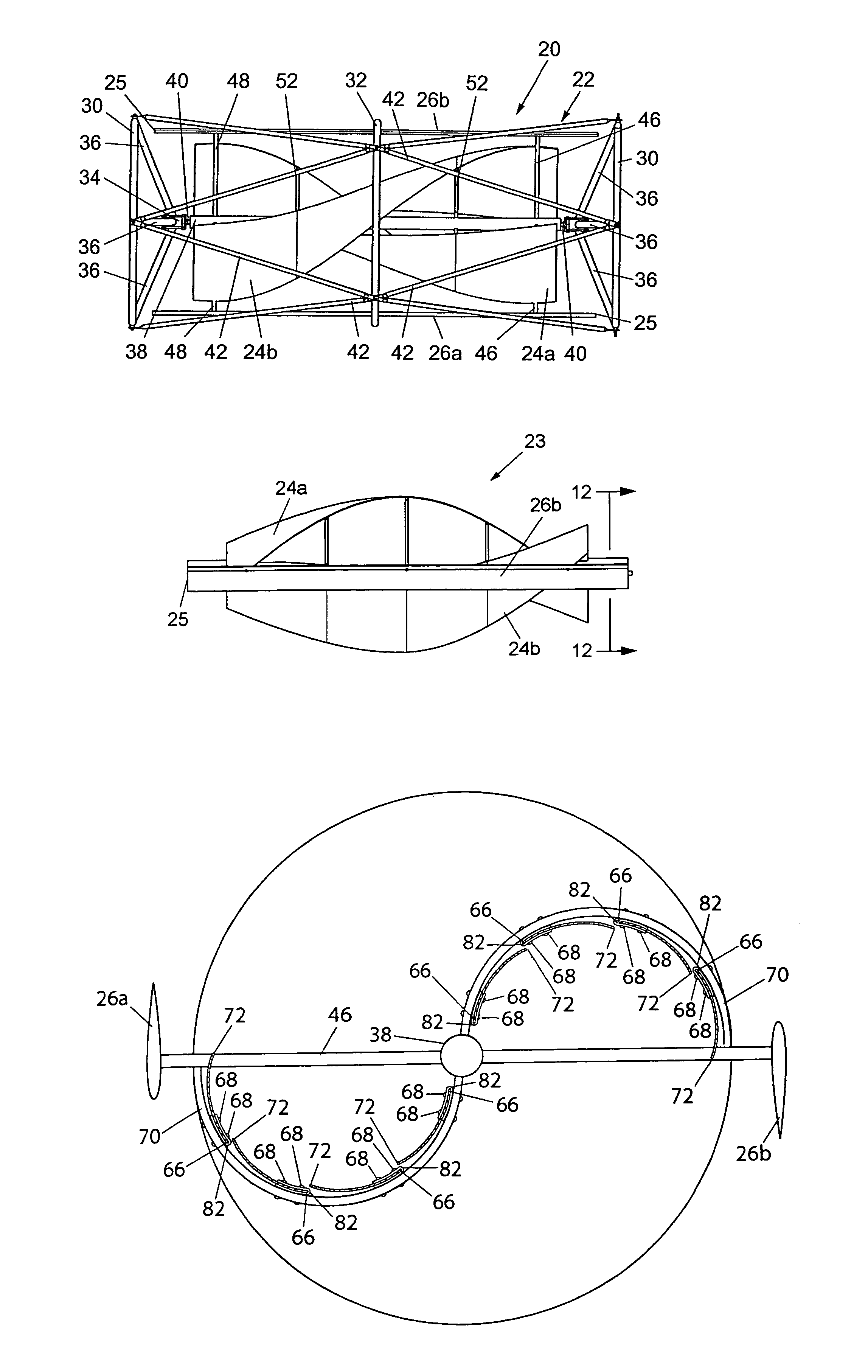
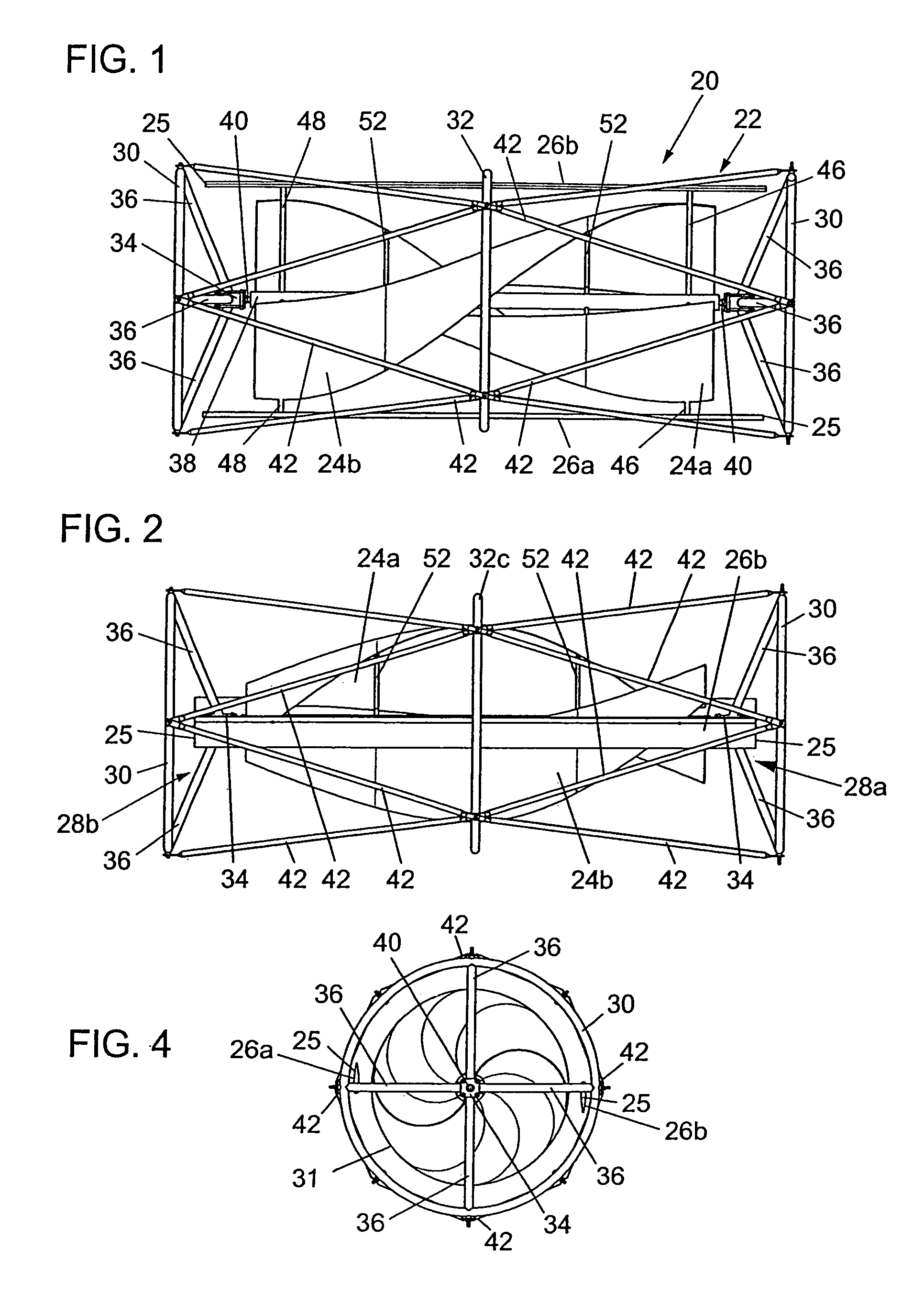
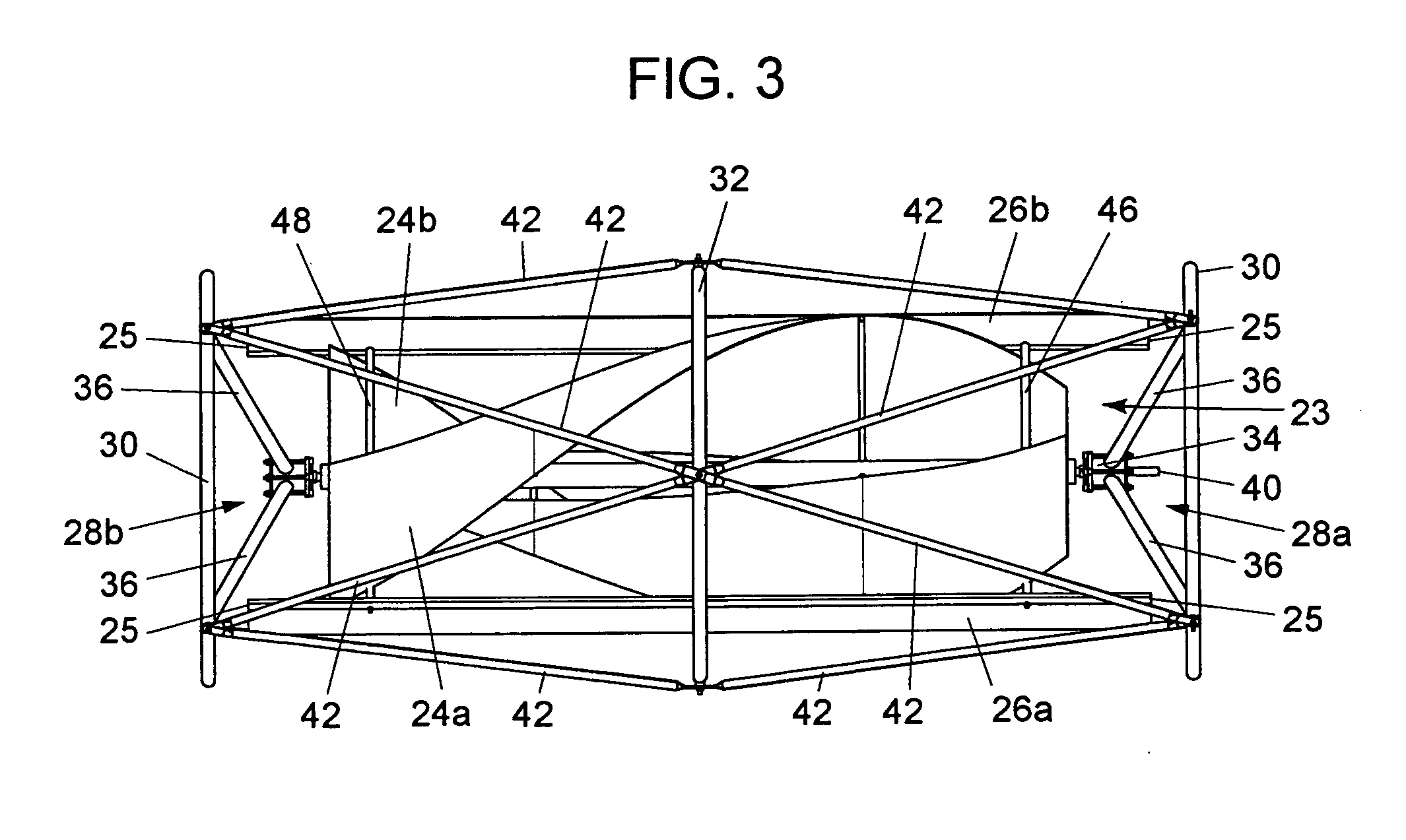
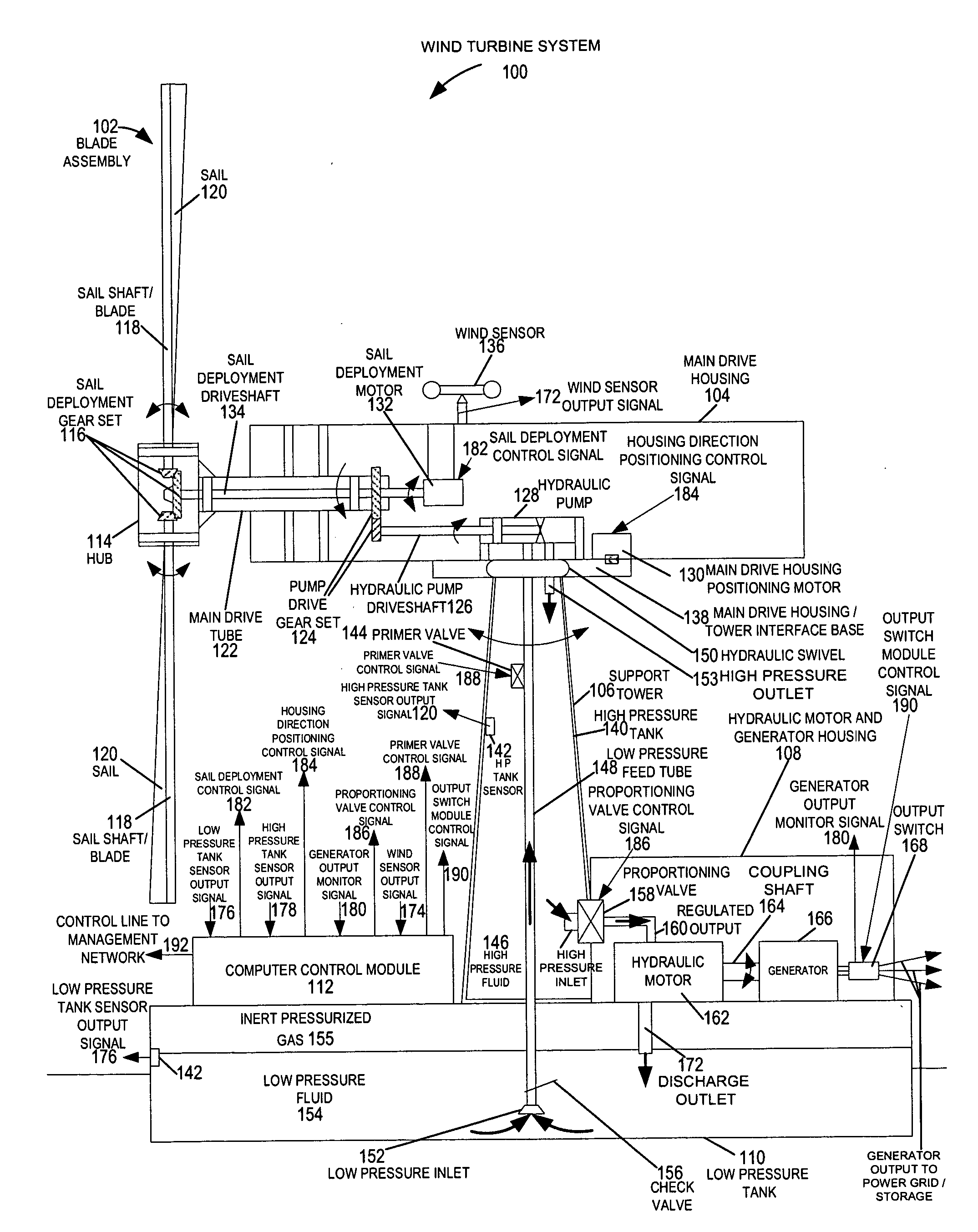
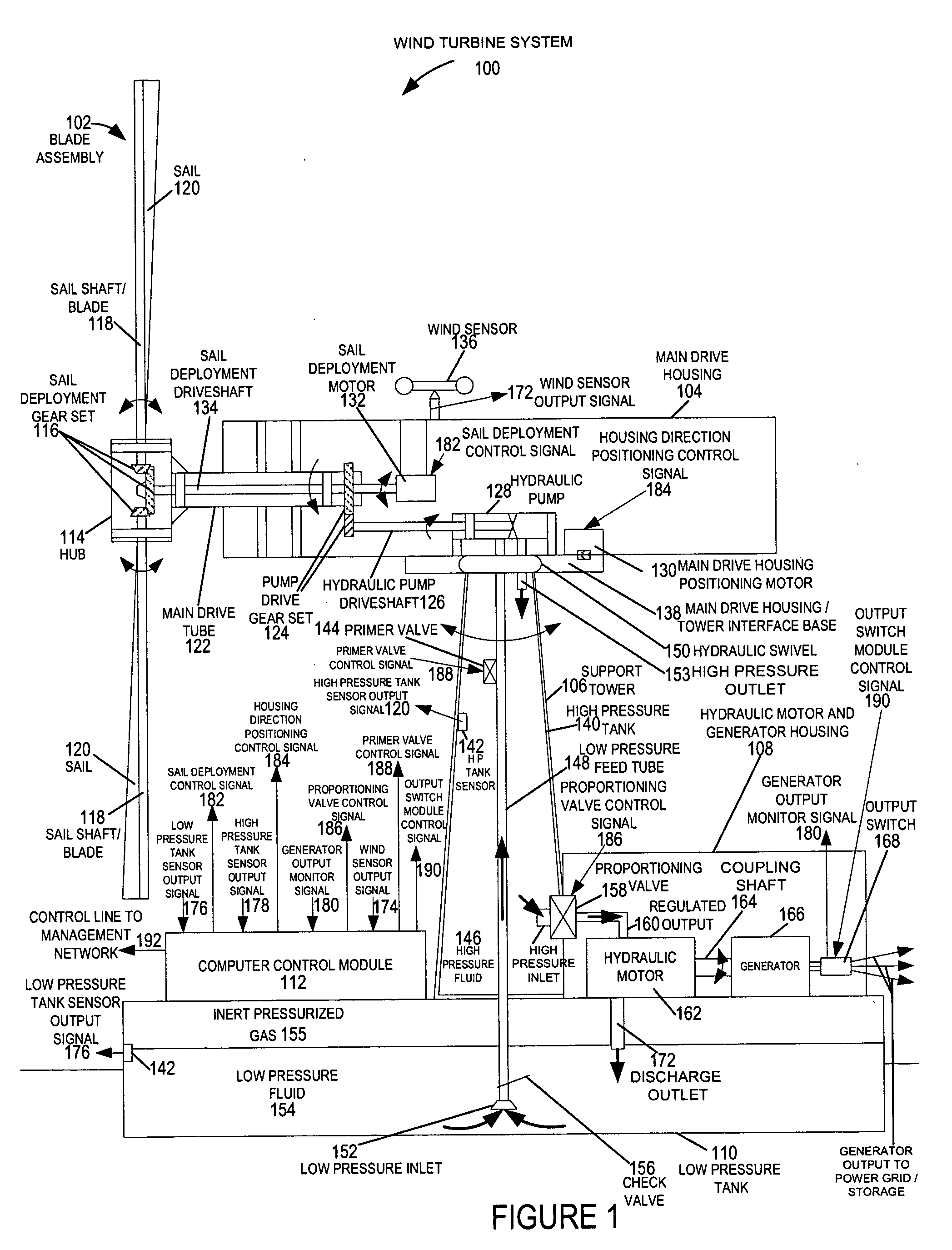
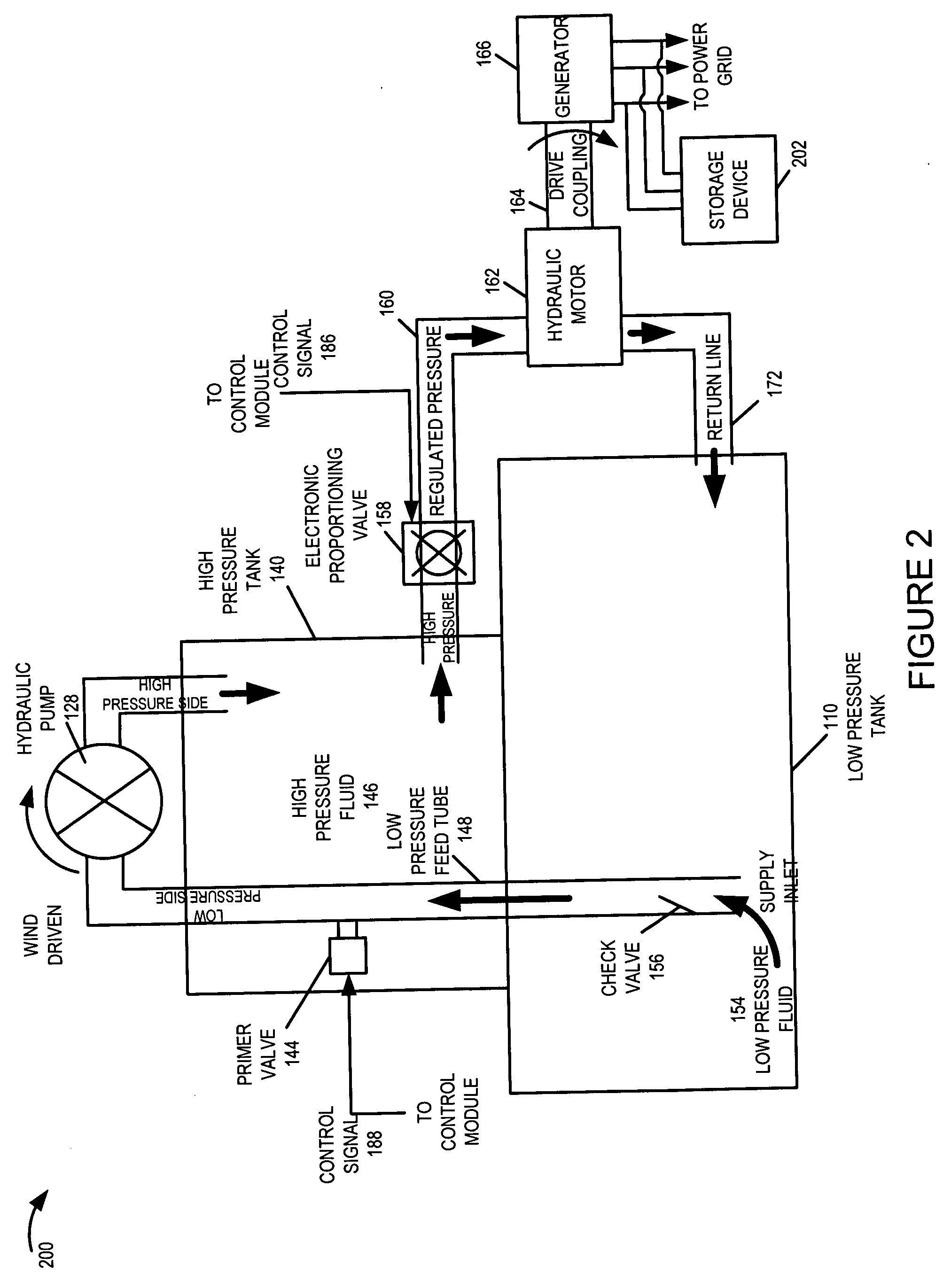
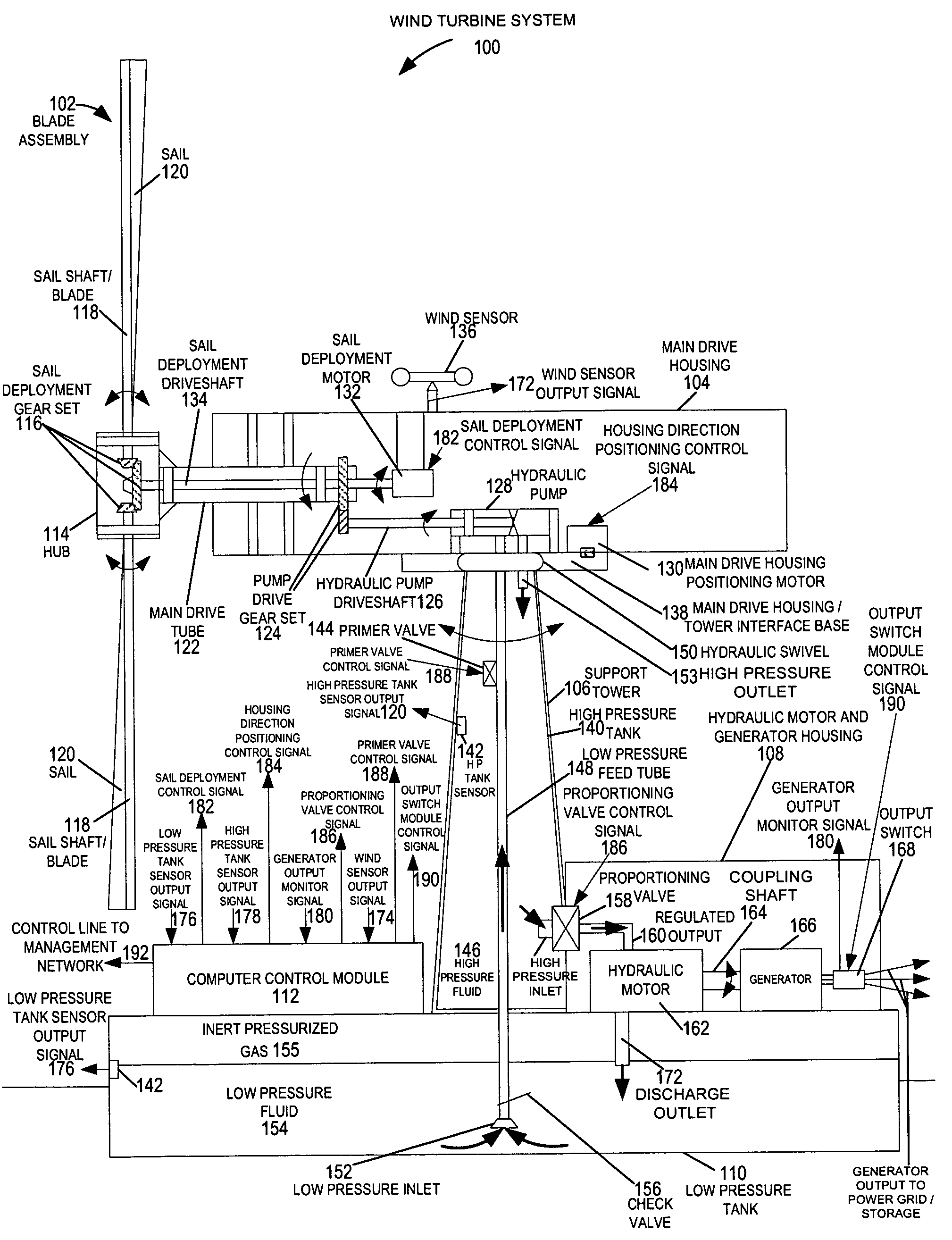
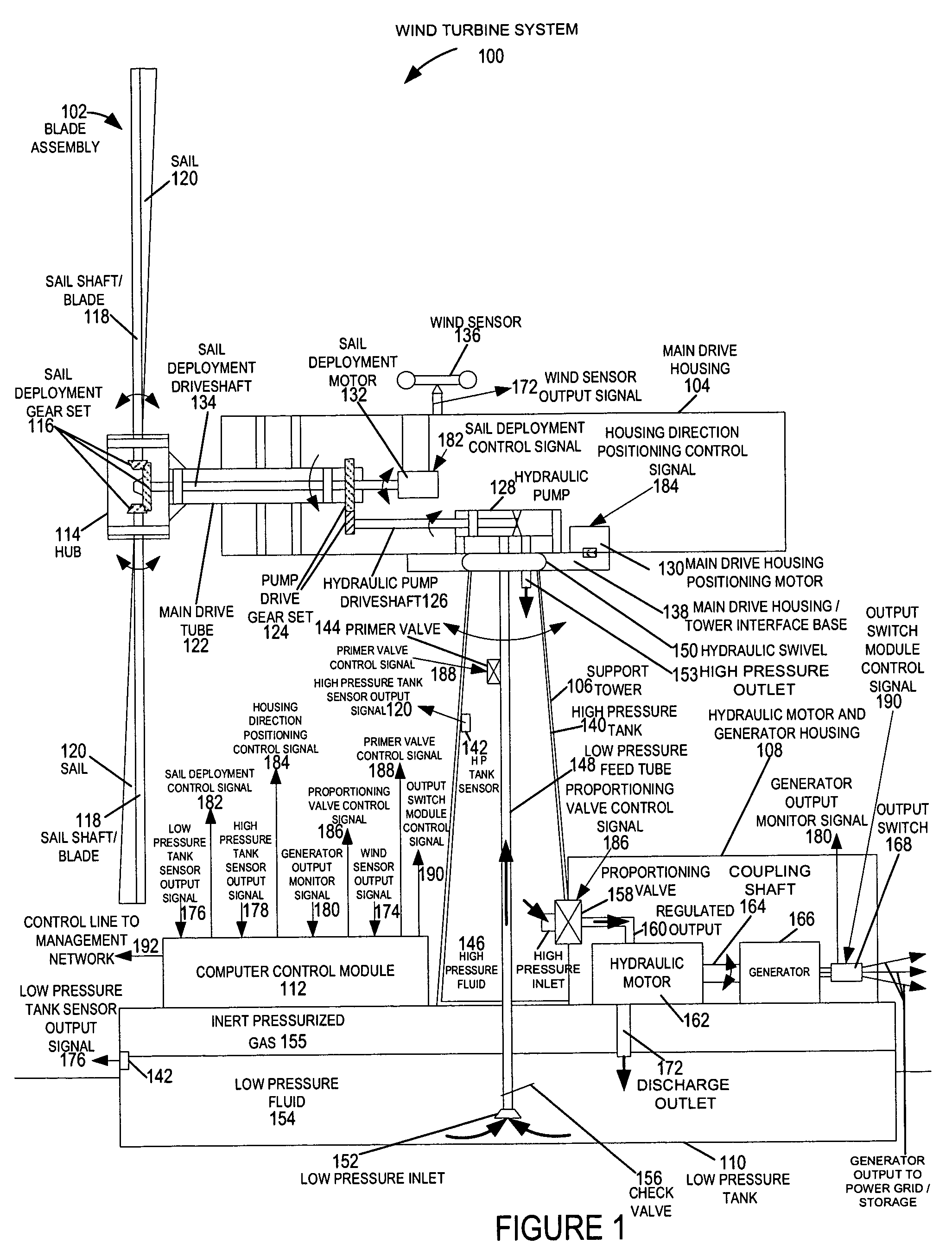
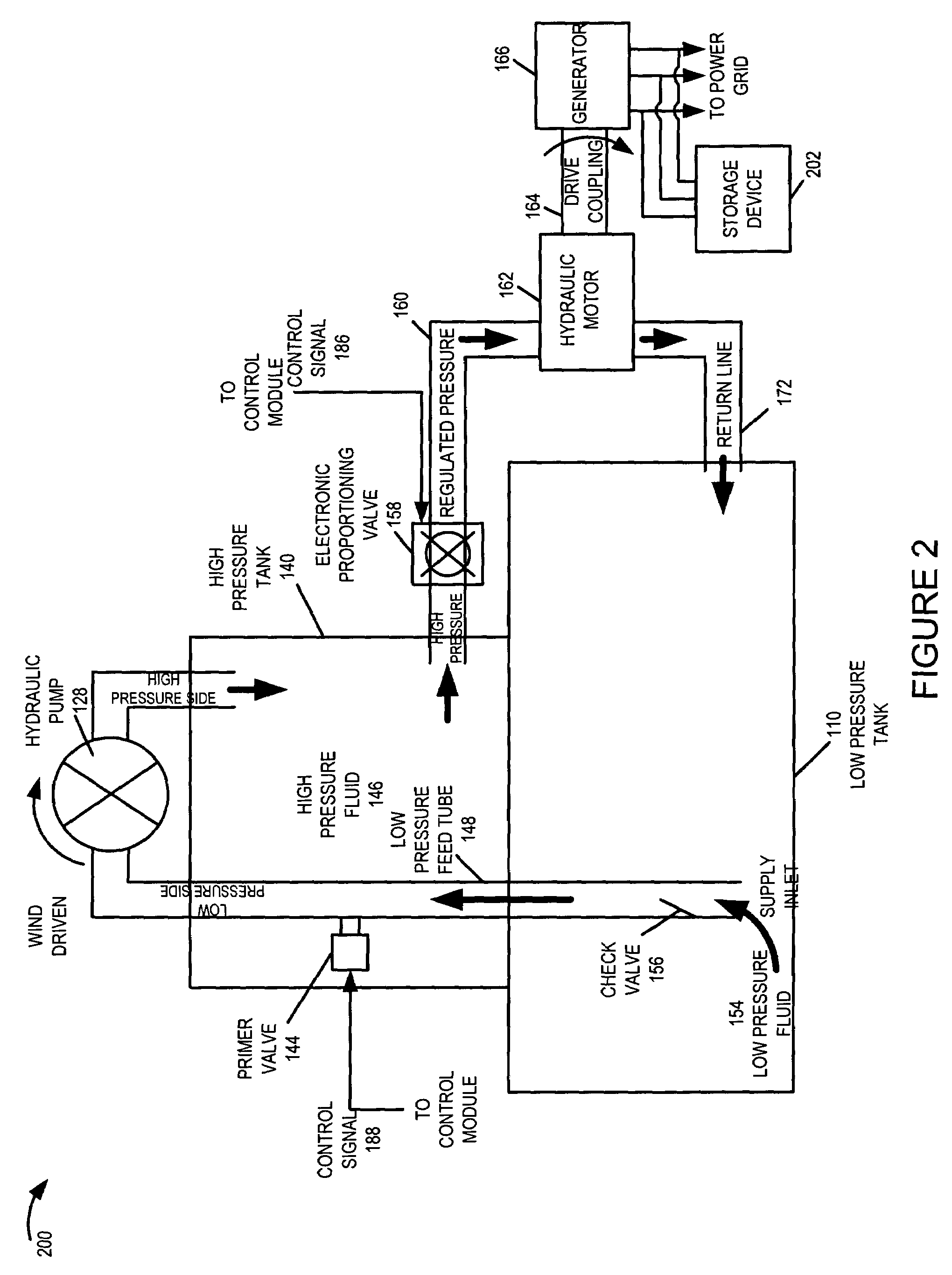
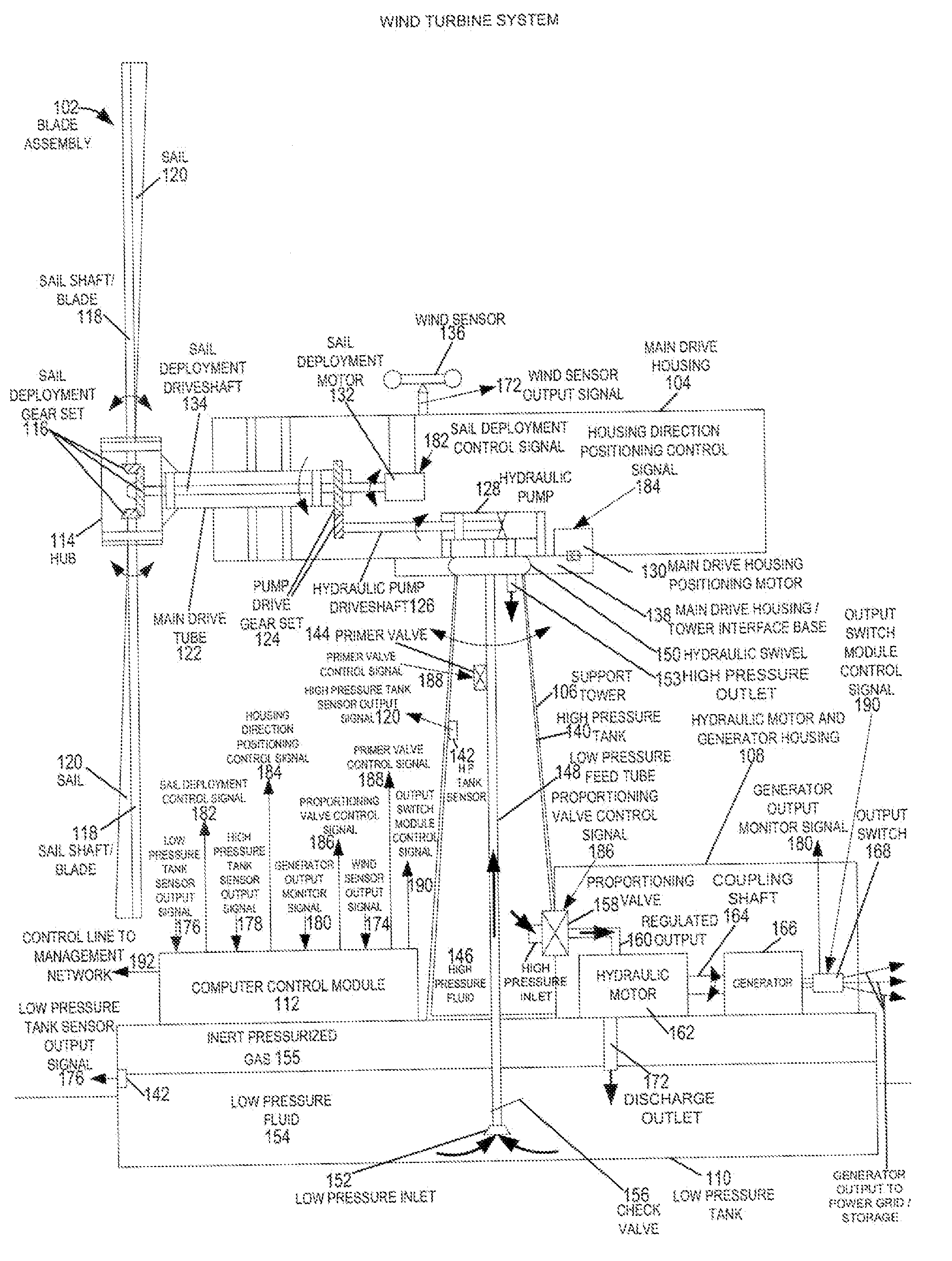
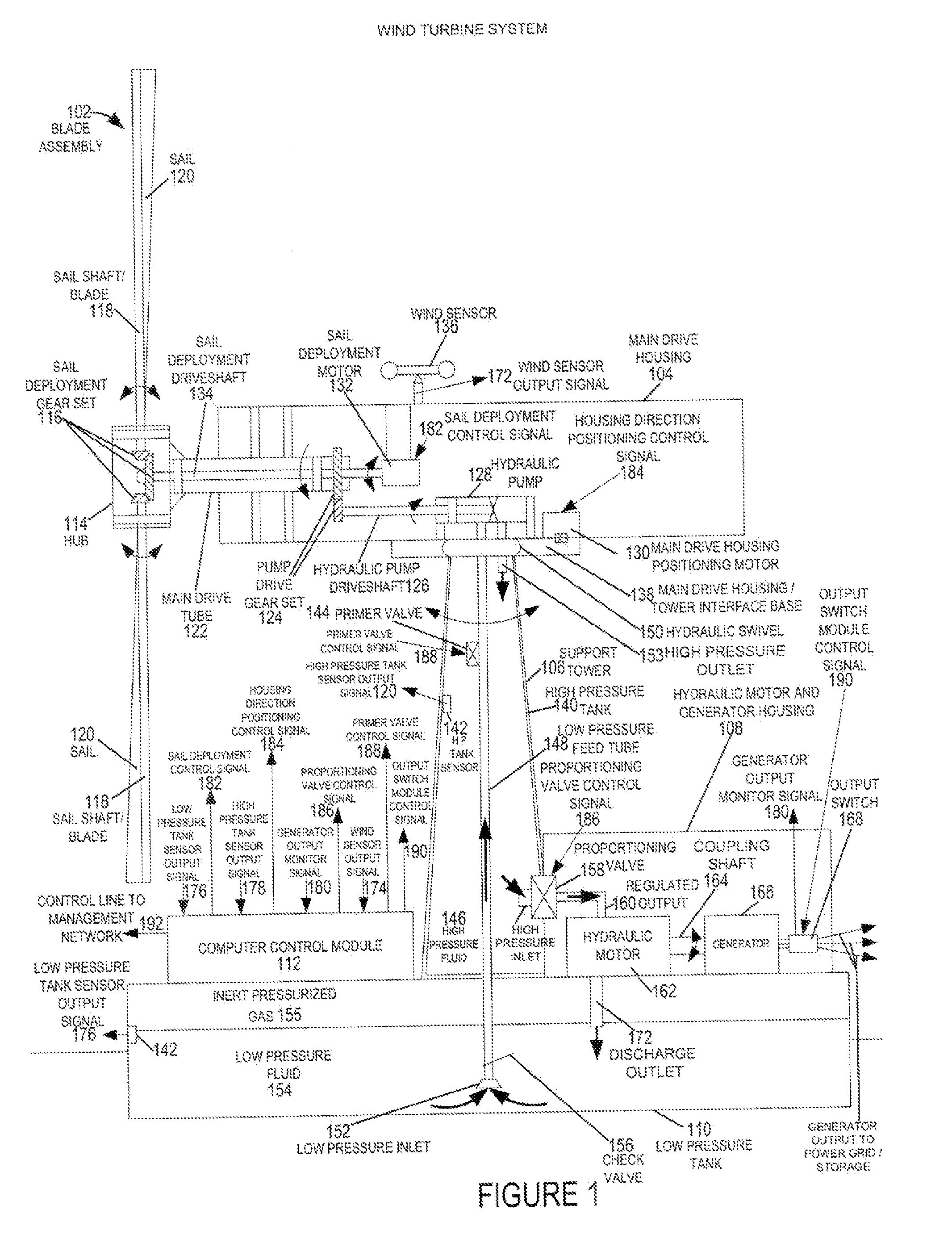
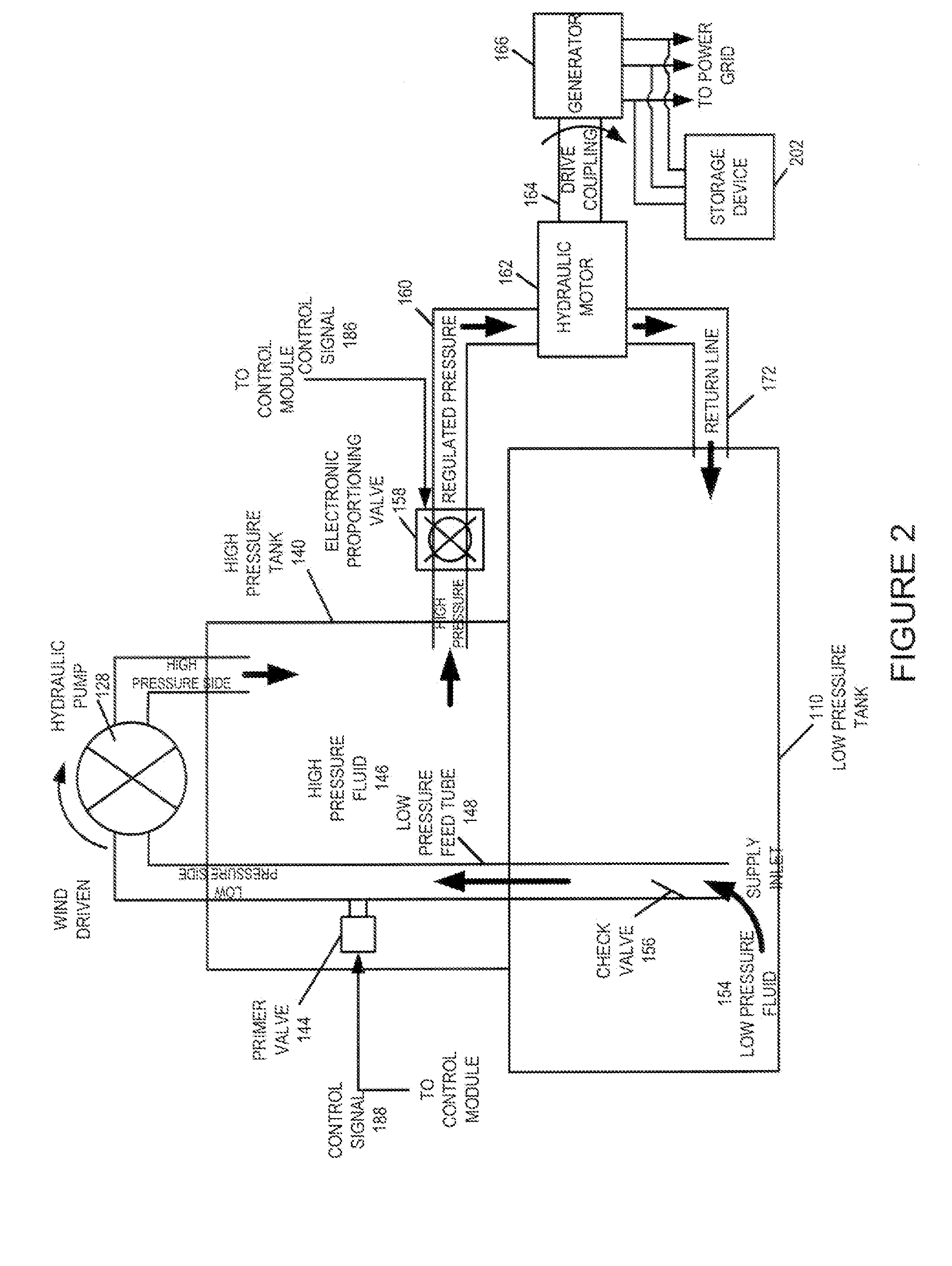
A wind turbine system includes a variable blade assembly including adjustable sails and wing shaped masts expanding the wind velocity capture envelope. The blade assembly turns a hydraulic pump, which pressurizes fluid and stores the pressurized fluid in a chamber in the support tower. Pressurized fluid is directed via an electronically controllable proportioning valve to a hydraulic motor which is coupled to an electric generator. A computer control module operates the proportioning valve regulating pressure to the hydraulic motor, maintaining generator rotational speed, and providing consistent output frequency to the power grid. Stored energy in the high pressure tank is used to continue generator operation after the winds cease, allowing early warning notification to the power management system of impending power loss. Residual pressure maintained in the high pressure tank allows restart operations via hydraulic pressure rather than power grid energy drain. On site high energy capacitors store additional energy.
Owner:MCCLINTIC FRANK
Methods and apparatus for advanced wind turbine design
ActiveUS7183664B2Eliminate needReduce pressureWind motor controlEngine fuctionsHigh energyHydraulic pump
A wind turbine system includes a variable blade assembly including adjustable sails and wing shaped masts expanding the wind velocity capture envelope. The blade assembly turns a hydraulic pump, which pressurizes fluid and stores the pressurized fluid in a chamber in the support tower. Pressurized fluid is directed via an electronically controllable proportioning valve to a hydraulic motor which is coupled to an electric generator. A computer control module operates the proportioning valve regulating pressure to the hydraulic motor, maintaining generator rotational speed, and providing consistent output frequency to the power grid. Stored energy in the high pressure tank is used to continue generator operation after the winds cease, allowing early warning notification to the power management system of impending power loss. Residual pressure maintained in the high pressure tank allows restart operations via hydraulic pressure rather than power grid energy drain. On site high energy capacitors store additional energy.
Owner:MCCLINTIC FRANK
Methods of handling wind turbine blades and mounting said blades on a wind turbine, system and gripping unit for handling a wind turbine blade
The invention relates to methods of handling wind turbine blades and mounting said blades on a wind turbine, said method comprising the steps of lifting a wind turbine hub to the nacelle of wind turbine with a lifting system and mounting the hub on the nacelle. Further, the method comprises the steps of gripping at least one wind turbine blade with a lifting system including at least one gripping unit for handling wind turbine blades, lifting said at least one wind turbine blade into close proximity to said hub, and mounting said at least one wind turbine blade on said hub. The invention also relates to a gripping unit for handling a wind turbine blade during transport.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Wind turbine device
InactiveUS7362004B2Reduce blade dragConvenient lengthWind energy with electric storageWind motor supports/mountsDevice formOperational capabilities
A hybrid blade wind turbine device formed of at least a pair of straight outer airfoil blades, and a pair of inner helical wing blades, as supported for rotation within a safety protective cage structure, which wind turbine can be mounted in the vertical, horizontal, or other aligned operational positions. The inner helical half wing blades, being preferably somewhat shorter than the length of the outer airfoil blades, act to “regularize” the swirling wind regime flowing through the hybrid wind turbine, so as to maximize the efficiency of the outer airfoil blades. The helical half wing blades can be formed of individual segmented vane segments to provide improved operational capabilities for the overall hybrid wind turbine. To best harness annualized available wind conditions, the hybrid wind turbine can be customized, through modification of the number of vane segments, the selection of the specific shape of the outer airfoil blades, and the specific operational positioning of the outer airfoil blades. Alternatively, the helical half wing blades can be formed as generally smooth-walled blades.
Owner:BECKER WILLIAM S
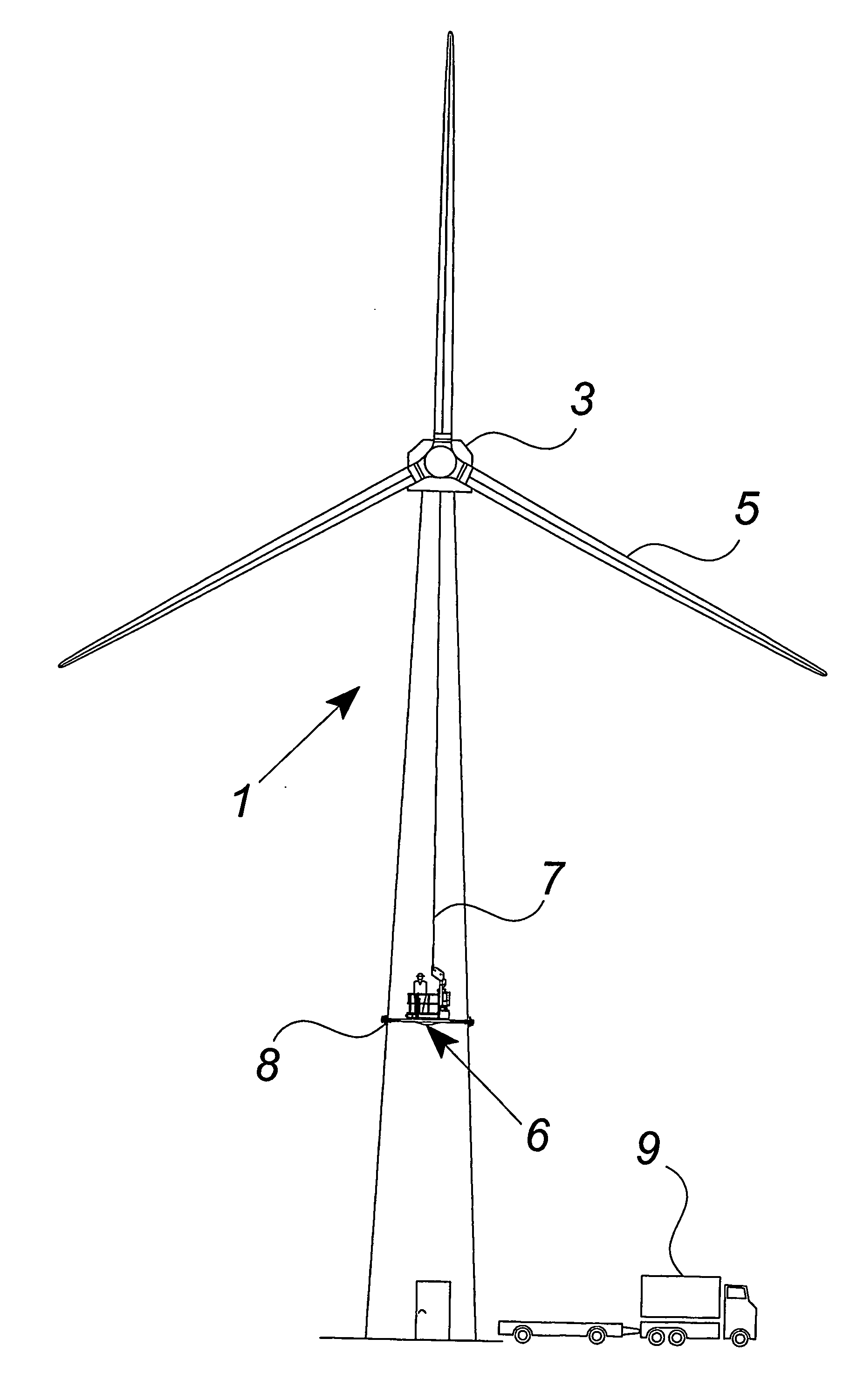
Method of servicing the outer components of a wind turbine such as the wind turbine blades and the tower with a work platform and work platform
The invention relates to a method of servicing the outer components of a wind turbine such as the wind turbine blades and the tower with a work platform, said method comprises the steps of: positioning the work platform at the wind turbine tower and connecting the work platform to an upper part of the wind turbine with at least one cable. Further the method comprises the steps of raising the work platform with the cable and cable winding means to a position of use, and holding the work platform to the side of the wind turbine tower with holding means. The invention also relates to a work platform for servicing the outer components of a wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Wind turbine blade
InactiveUS20130149153A1Facilitate conductionImprove protectionPropellersInstallation of lighting conductorsElectrical conductorMetal foil
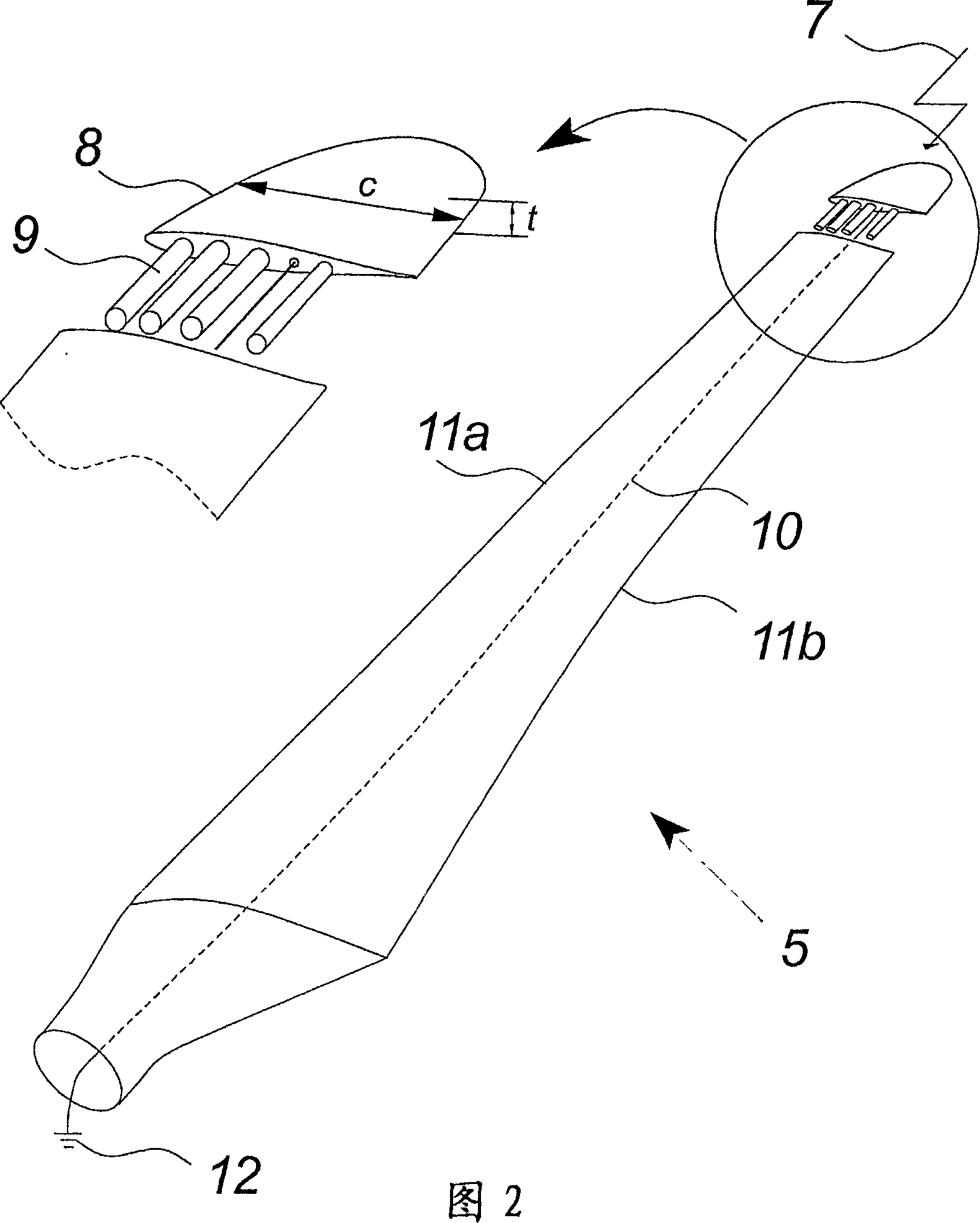
The invention relates to a wind turbine blade for a wind turbine, having a tip end area and a root end area, and a lightning protection system, said lightning protection system comprising at least one metal foil, wherein said metal foil extends continuously from the tip end area to the root end area of the blade and wherein the metal foil is arranged in proximity to the outer surface of the blade, so that the metal foil is adapted to function as a receptor of a stroke of lightning and as a down conductor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD +1
Lightning protection of a pitch-controlled wind turbine blade
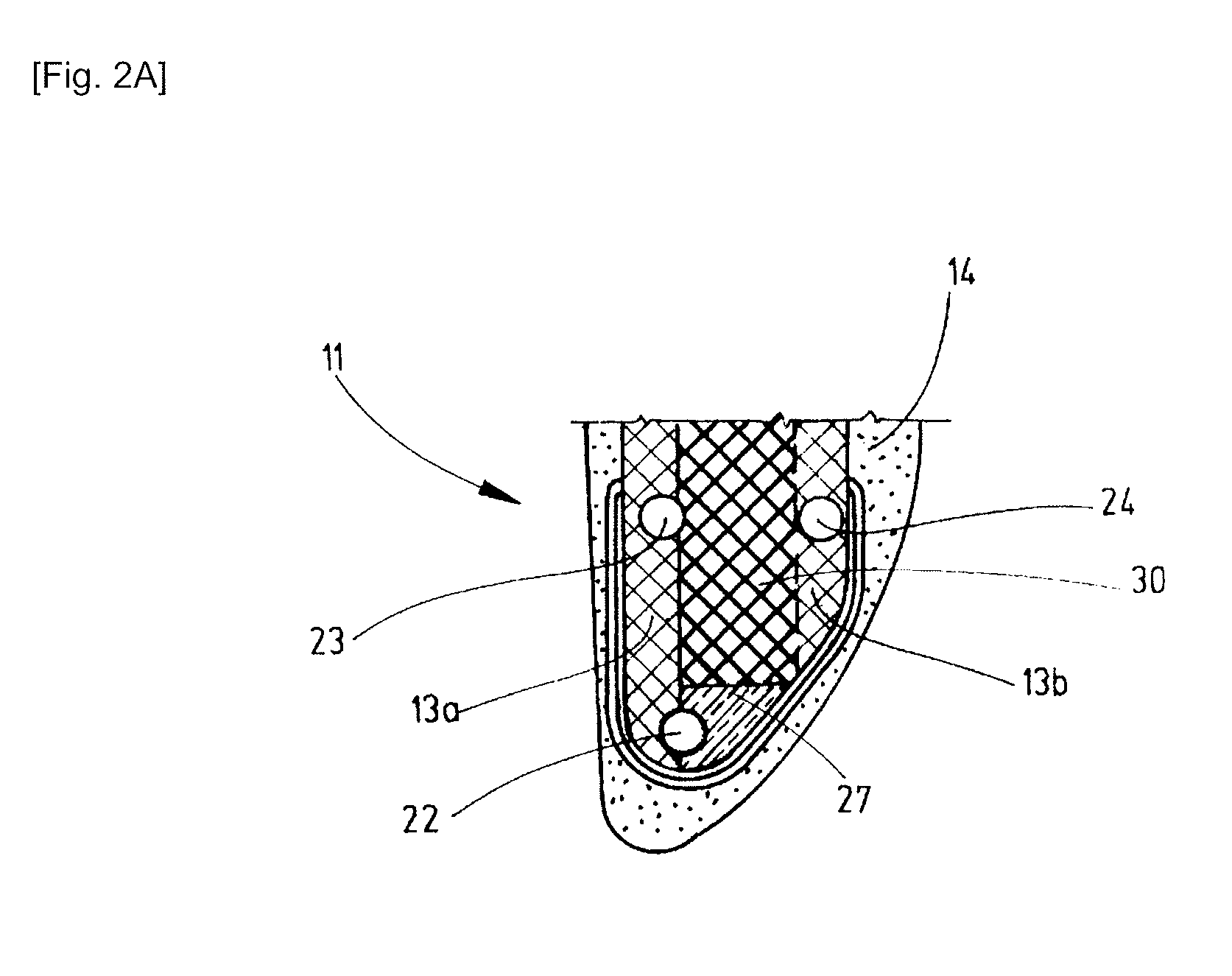
ActiveUS7390169B2Current protectionReduce resistancePropellersPump componentsTurbine bladeBlade pitch
A wind turbine rotor including a rotor hub (3) and a plurality of blades (4), and where each blade root (16) is connected to said rotor hub through a pitch bearing (5) in such a manner that the pitch angle of the blade is adjustable by a turning of the blade about its longitudinal axis relative to the rotor hub. The blade is provided with at least one electrically conducting lightening down-conductor (6) extending in the longitudinal direction of the blade to the blade root and being electrically isolated from the pitch bearing (5). A spark gap (15) is provided between the lightning down-conductor and the rotor hub, said spark gap (15) being adapted to conduct a lightning current passing through the lightning down-conductor. A sliding contact connection (7, 12) is provided parallel to the spark gap (15) between the lightning down-conductor (6) and the rotor hub (3), said sliding contact connection ensuring electrical contact between said lightening down-conductor (6) and said rotor hub (3) irrespective of the pitch angle of the blade. The invention also relates to a wind turbine including such a rotor.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
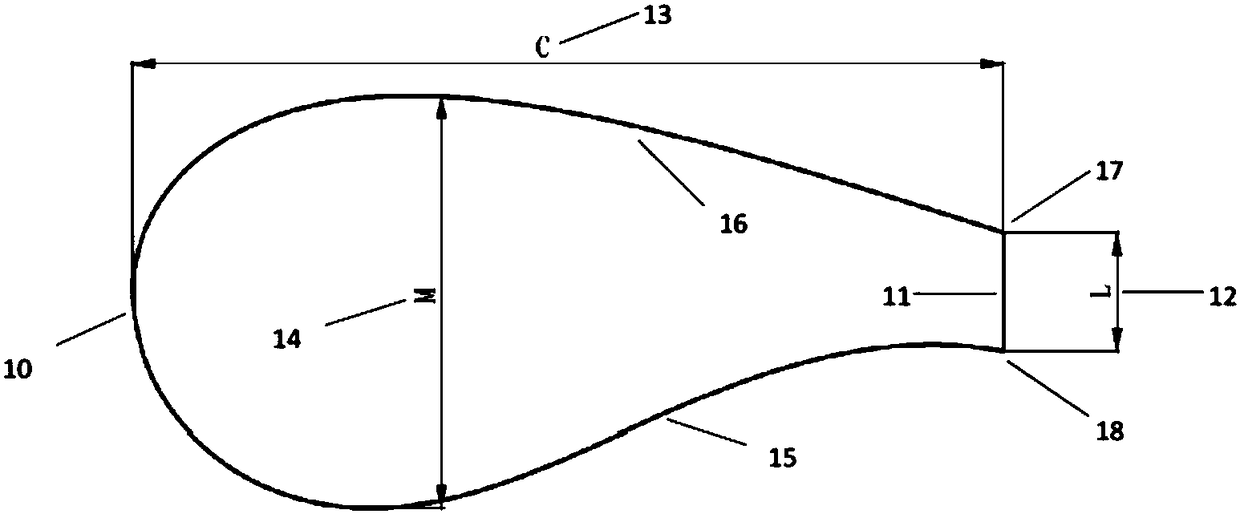
Wind Turbine Blade
ActiveUS20080206055A1Extreme and fatigue loadIncreased durabilityPropellersRotary propellersTurbine bladeSolidity
A wind turbine comprising a wind turbine blade with high lift and / or low solidity is provided. The blade is directed towards pitch regulated wind turbines, which are operated at variable rotor speed and have blades longer than about 30 meters. The blade is for example advantageous in that it may provide reduced extreme and fatigue loads at the same or near the same power production.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Methods and apparatus for advanced wind turbine design
ActiveUS20070138798A1Eliminate needReduce pressureWind motor controlEngine fuctionsHigh energyHydraulic pump
A wind turbine system includes a variable blade assembly including adjustable sails and wing shaped masts expanding the wind velocity capture envelope. The blade assembly turns a hydraulic pump, which pressurizes fluid and stores the pressurized fluid in a chamber in the support tower. Pressurized fluid is directed via an electronically controllable proportioning valve to a hydraulic motor which is coupled to an electric generator. A computer control module operates the proportioning valve regulating pressure to the hydraulic motor, maintaining generator rotational speed, and providing consistent output frequency to the power grid. Stored energy in the high pressure tank is used to continue generator operation after the winds cease, allowing early warning notification to the power management system of impending power loss. Residual pressure maintained in the high pressure tank allows restart operations via hydraulic pressure rather than power grid energy drain. On site high energy capacitors store additional energy.
Owner:MCCLINTIC FRANK
Off-shore wind turbine generator and off-shore wind farm
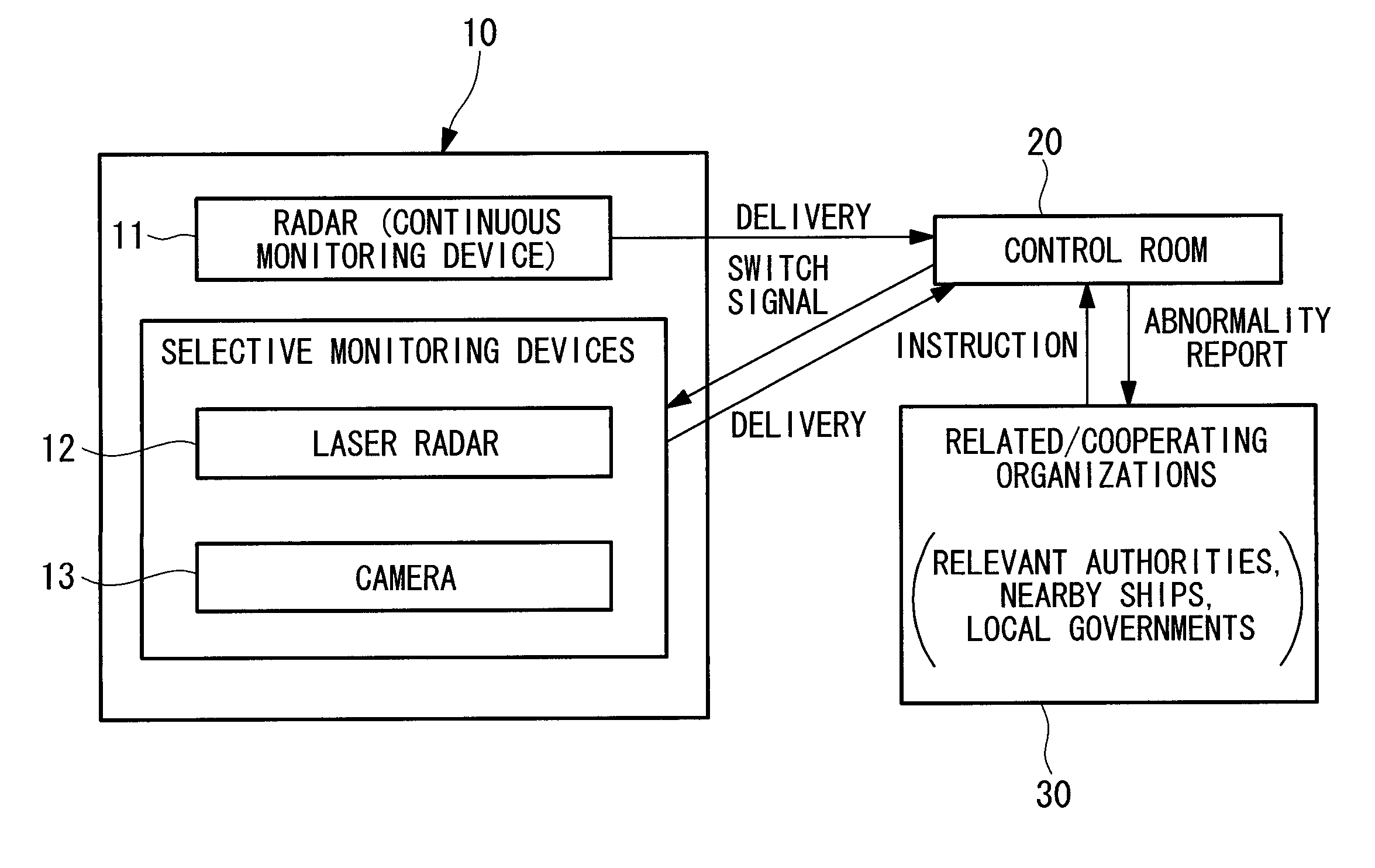
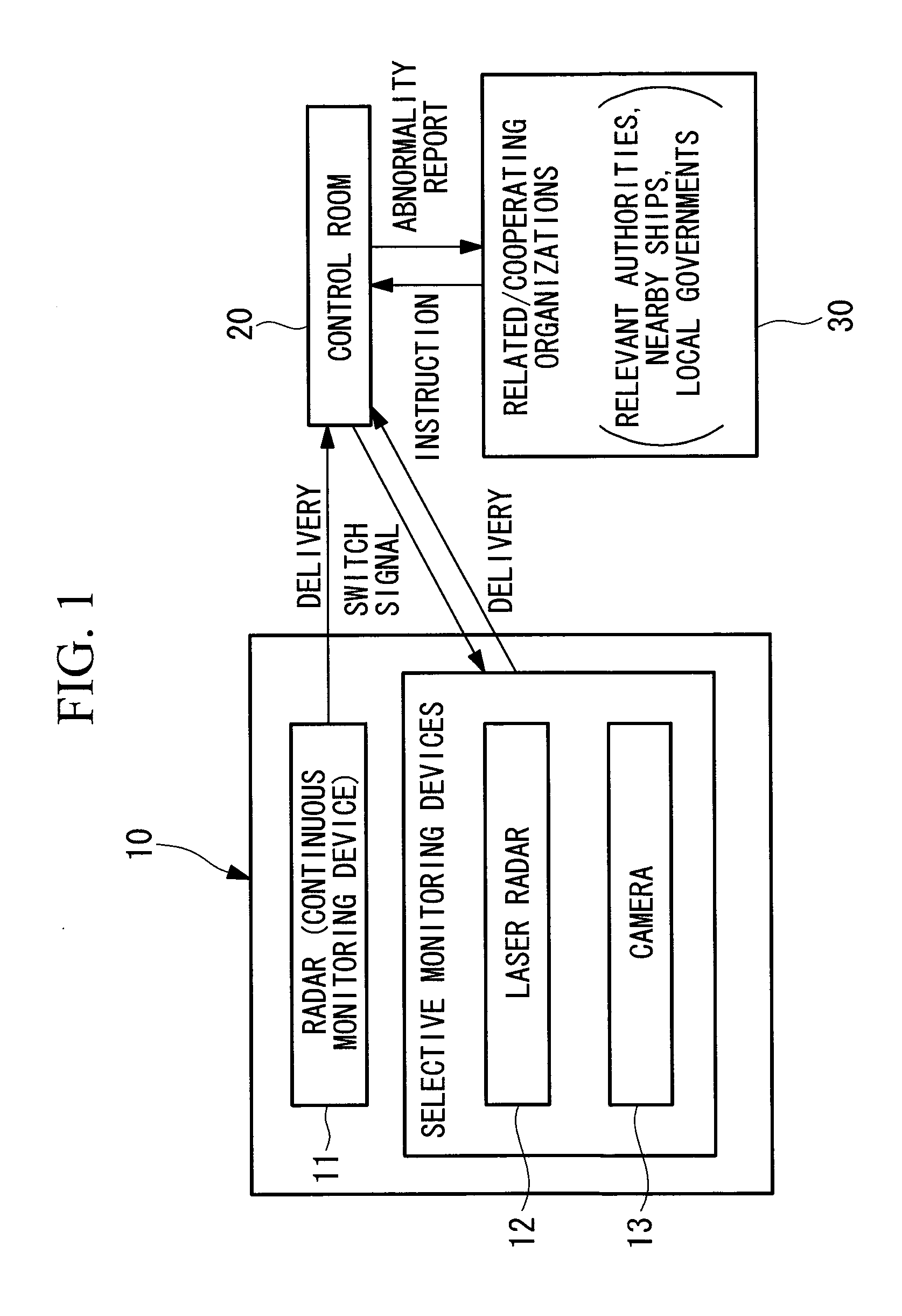
InactiveUS20110084486A1Accurate informationUseful accuracyWind motor controlEngine fuctionsTurbine bladeShore
An object is to provide an off-shore wind turbine generator capable of obtaining accurate information about the situation of a wind turbine itself, surrounding weather conditions, and the like. The off-shore wind turbine generator of the present invention generates power by driving a generator mechanism through the rotation of a rotor head to which wind turbine blades are attached and includes a monitoring apparatus for monitoring the wind turbine generator itself and its surrounding circumstances.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Wind turbine with different size blades for a diffuser augmented wind turbine assembly
InactiveUS20090280009A1Improve efficiencyEvenly distributedPump componentsWind motor assemblyWind forceWind turbine design
A wind turbine for a diffuser augmented wind turbine assembly is provided. The wind turbine comprises a wind turbine housing, a hub mounted within the wind turbine housing, and a plurality of blades rotatably coupled with the hub and radially extending from the hub. The plurality of blades includes a first blade and a second blade, wherein the first blade includes a surface area and / or a maximum width that is greater than a surface area and / or a maximum width of the second blade to increase the efficiency of the diffuser augmented wind turbine assembly in variable speed winds.
Owner:WINDTAMER
Method for operating a wind turbine at improved power output
ActiveUS20130140819A1Increased riskIncrease productionOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlTurbine bladeTower
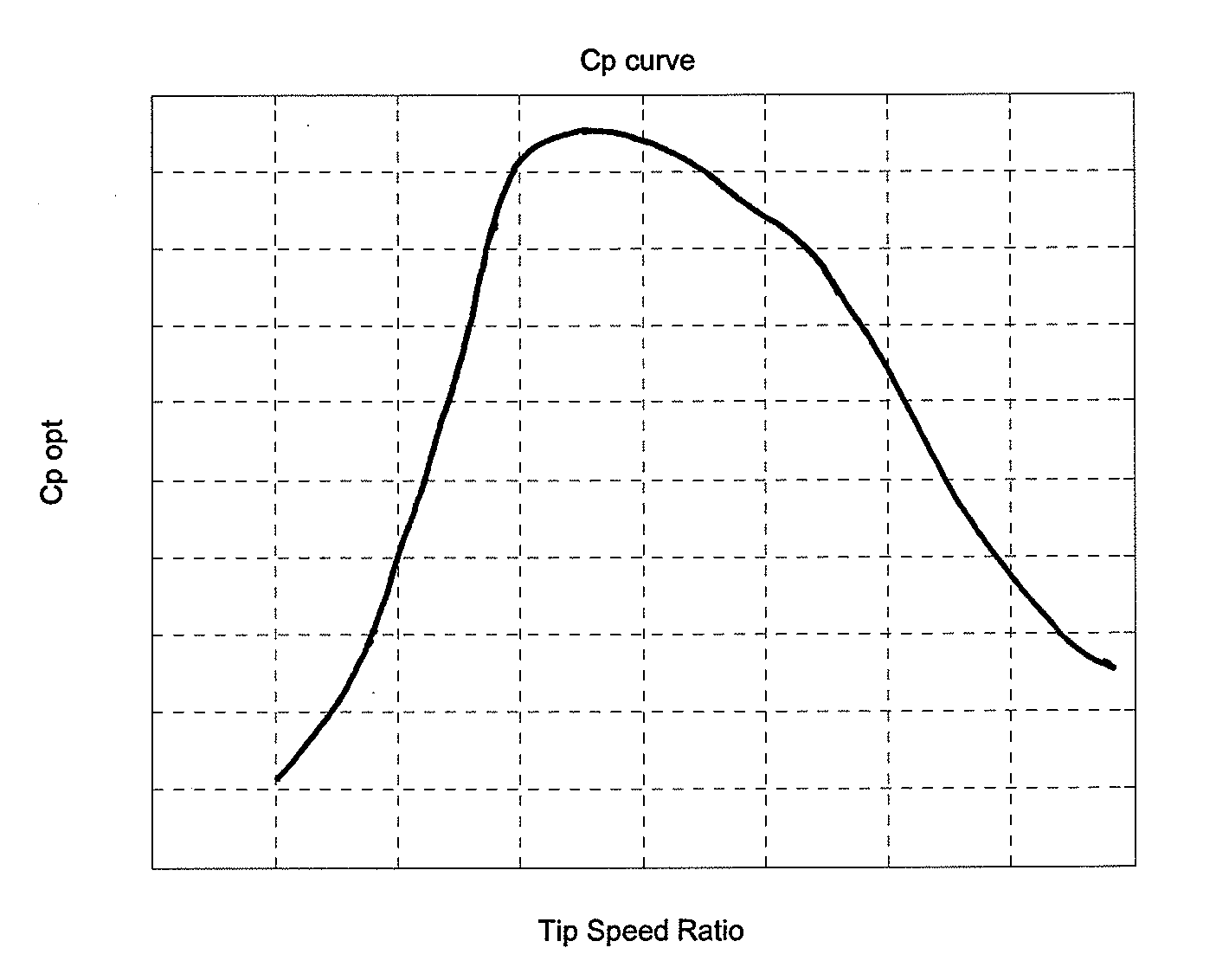
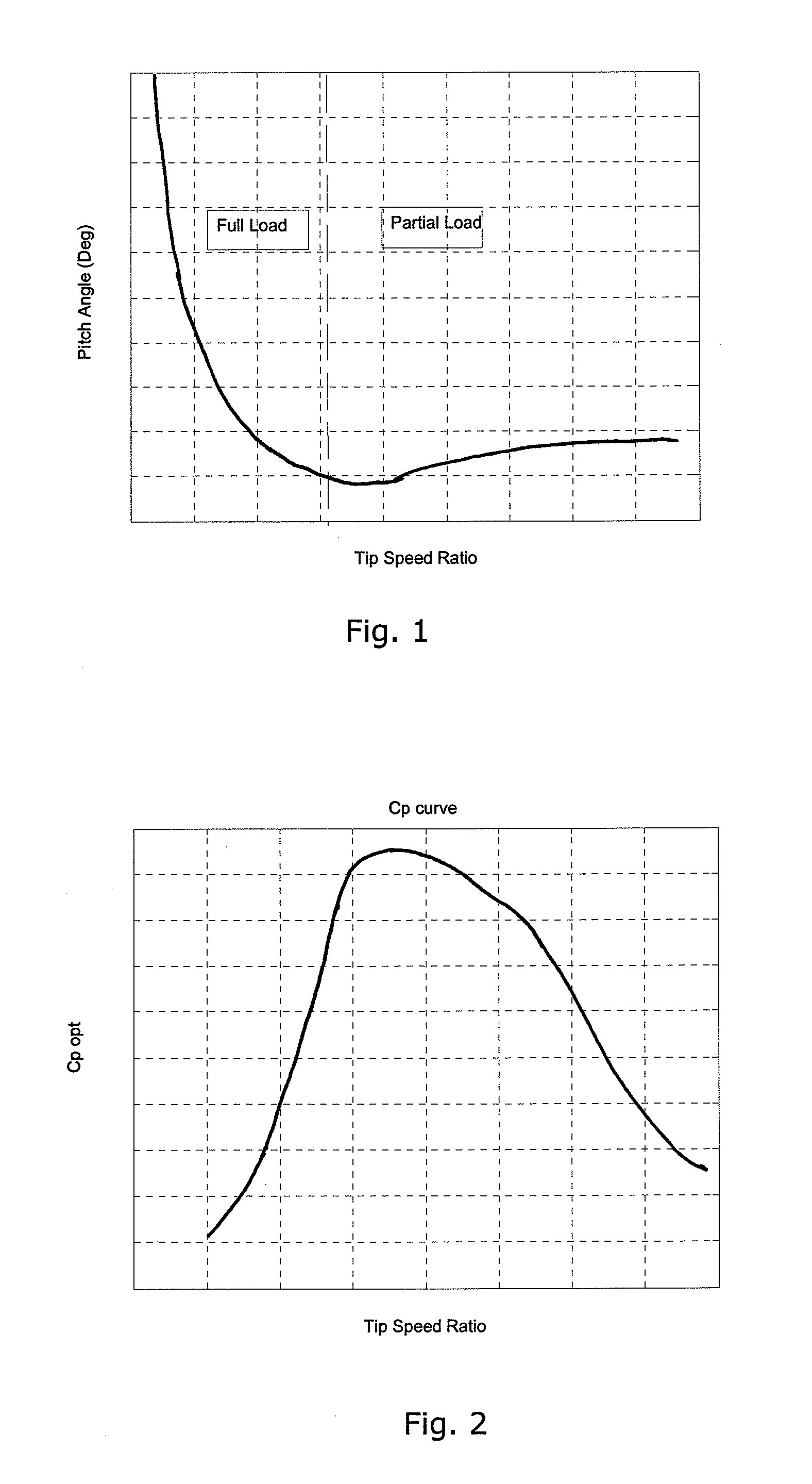
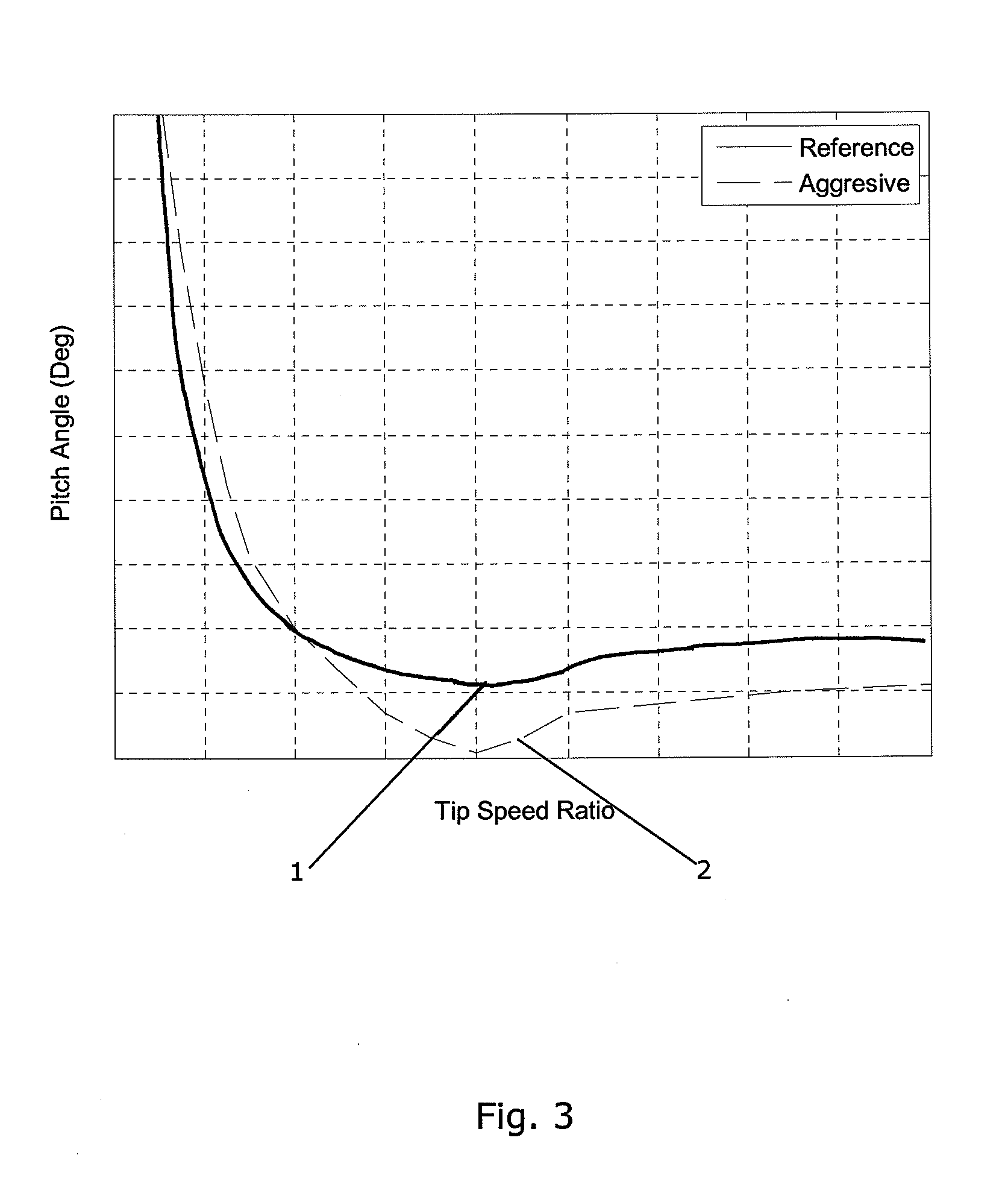
A method for operating a wind turbine is disclosed. The wind turbine comprises a rotor having a set of wind turbine blades, said rotor being mounted on a tower. The method comprises the steps of: Providing a curve defining optimal pitch angle as a function of tip speed ratio for the wind turbine blades or as a function of wind speed. Modifying at least a part of said optimal pitch angle curve by applying a safety buffer, e.g. at tip speed ratios and / or pitch angles where there is a risk that the blades may stall and / or that overload is caused to the wind turbine, thereby obtaining a safety modified pitch angle curve. Operating the wind turbine in accordance with the safety modified pitch angle curve. Measuring one or more parameters providing information regarding wind conditions and / or loads on one or more components of the wind turbine, during operation of the wind turbine. Adjusting the safety buffer, based on said measurements, thereby obtaining an adjusted pitch angle curve, and operating the wind turbine in accordance with the adjusted pitch angle curve. The safety buffer is applied in order to ensure that the blades of the wind turbine do not stall and / or that the wind turbine is not overloaded, but it has the effect that the wind turbine is operated in a suboptimal manner from an energy production view. Since the safety buffer is adjusted based on measured parameters, it can be reduced if it is detected that the actual operating conditions are less severe than expected. This allows the wind turbine to be operated in a more optimal manner, thereby increasing the energy production of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
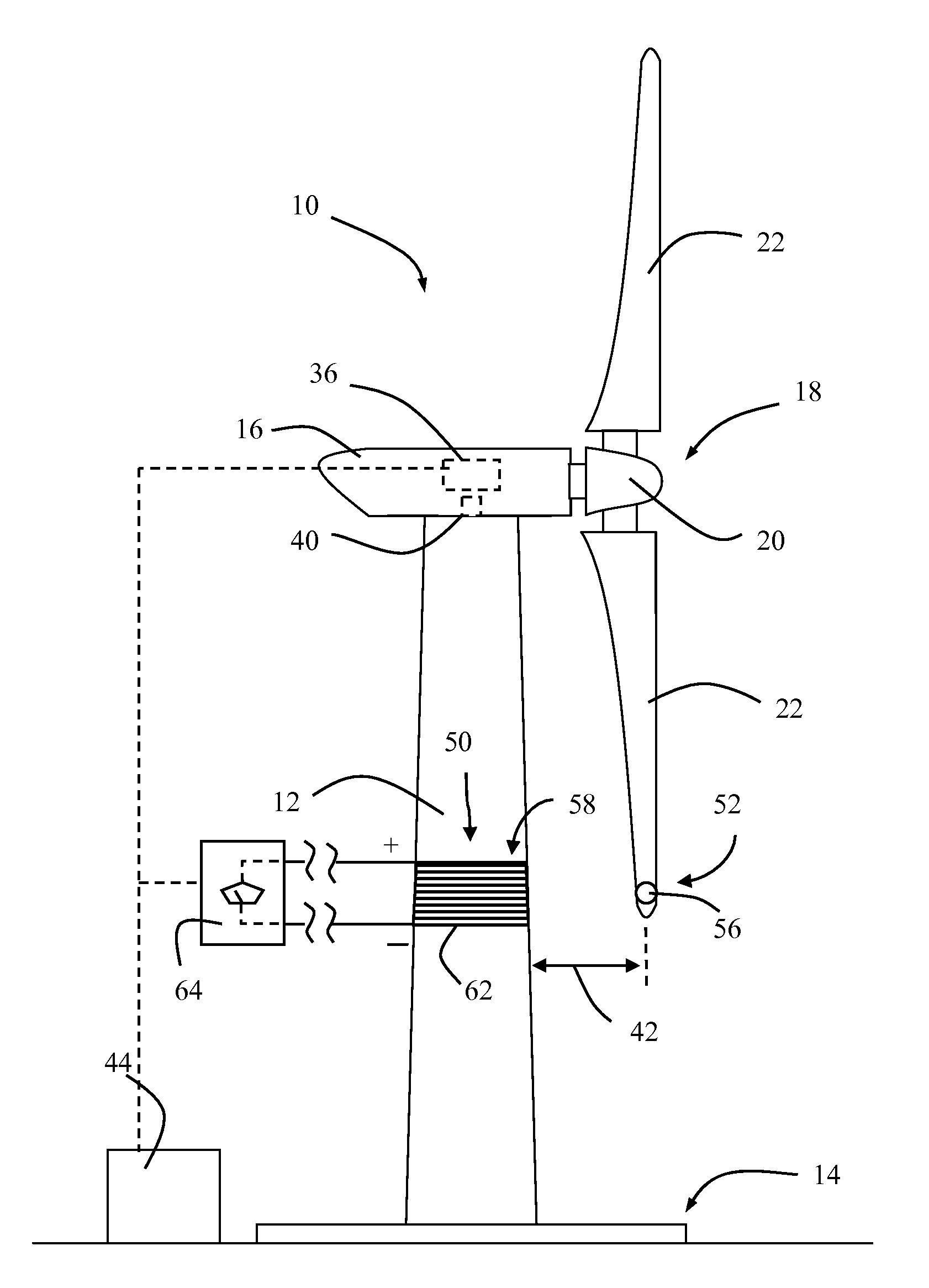
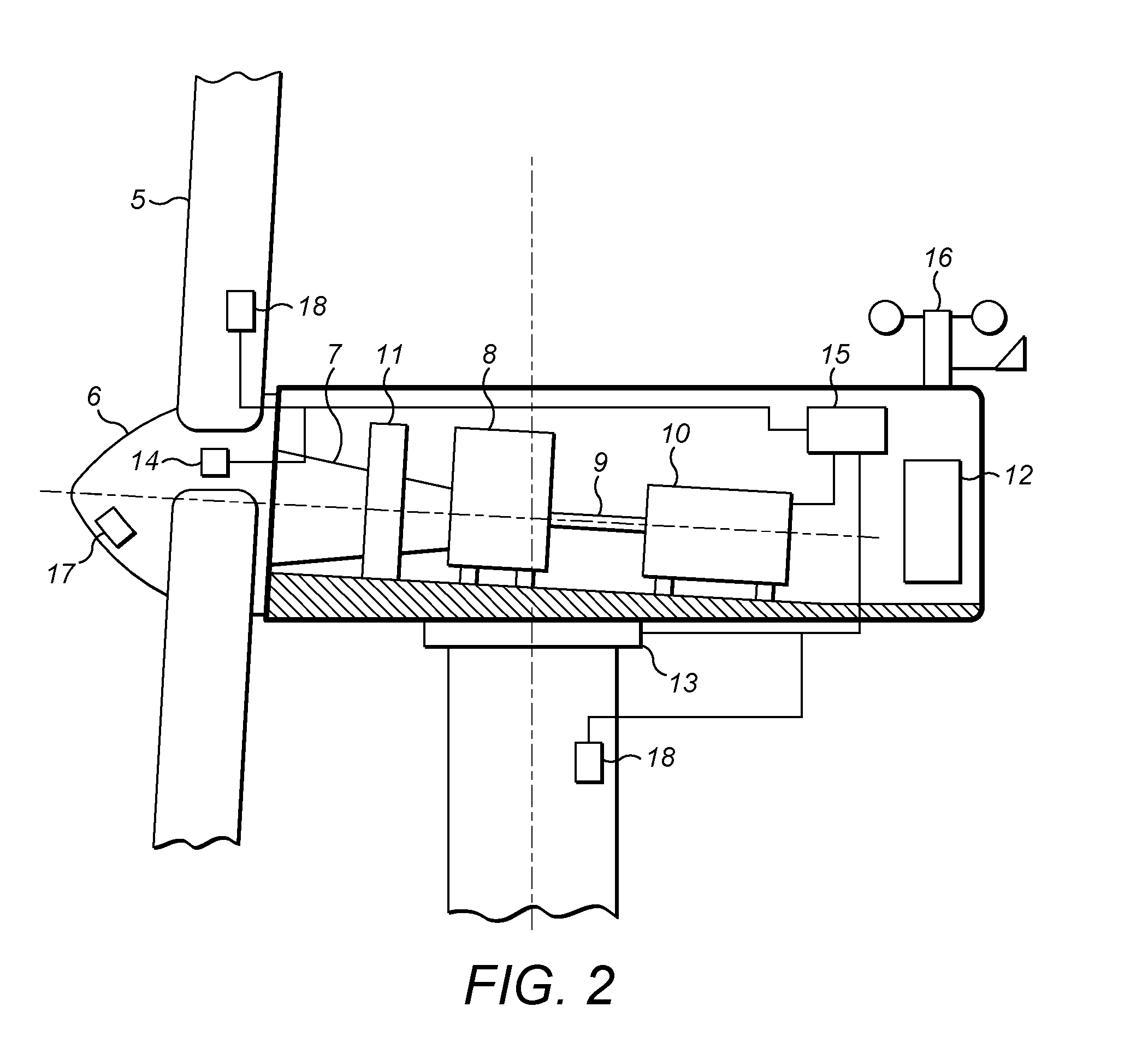
System for detecting proximity between a wind turbine blade and a tower wall
The invention provides a system for detecting proximity between a wind turbine blade and a tower wall. A sensor system monitors deflection of turbine blades of a wind turbine. The system includes a first component configured on the turbine blades. A second component is configured on the tower at a height so as to detect the presence of the first component as the blades rotate past the tower. The second component generates a corresponding measurable parameter or value that is indicative of distance between the blades and tower. The second component is disposed substantially completely around the circumference of the tower so as to detect the first components at any rotational position of the turbine nacelle relative to the tower.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC RENOVABLES ESPANA SL
Wind Turbine with Floating Foundation and Position Regulating Control System and Method Thereof
InactiveUS20170037832A1Dampens oscillating forceDampens force generatedWind motor controlSteering by propulsive elementsNacelleControl system
The present invention relates to a wind turbine structure comprising a wind turbine tower with a nacelle arranged on the top to which a rotor hub with one or more rotatable mounted wind turbine blades are mounted which form a rotor plane. A floating foundation is mounted to the bottom of the wind turbine tower and the pitch and / or yaw system are used to regulate the position of the wind turbine structure. A control unit detects the relative movement of the wind turbine structure in two axial directions and activates the pitch or yaw system to move the wind turbine structure into an equilibrium position. This reduces the directional movement of the wind turbine structure so that it remains in a stable equilibrium position. This also reduces the oscillating movement and tension forces in the anchor chains.
Owner:ENVISION ENERGY DENMARK
Wind turbine blade
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD +1
Thunderbolt protection device of wind turbine blade
ActiveCN1839259AFirmly connectedHigh strengthInstallation of lighting conductorsEngine manufactureTurbine bladeWind turbine design
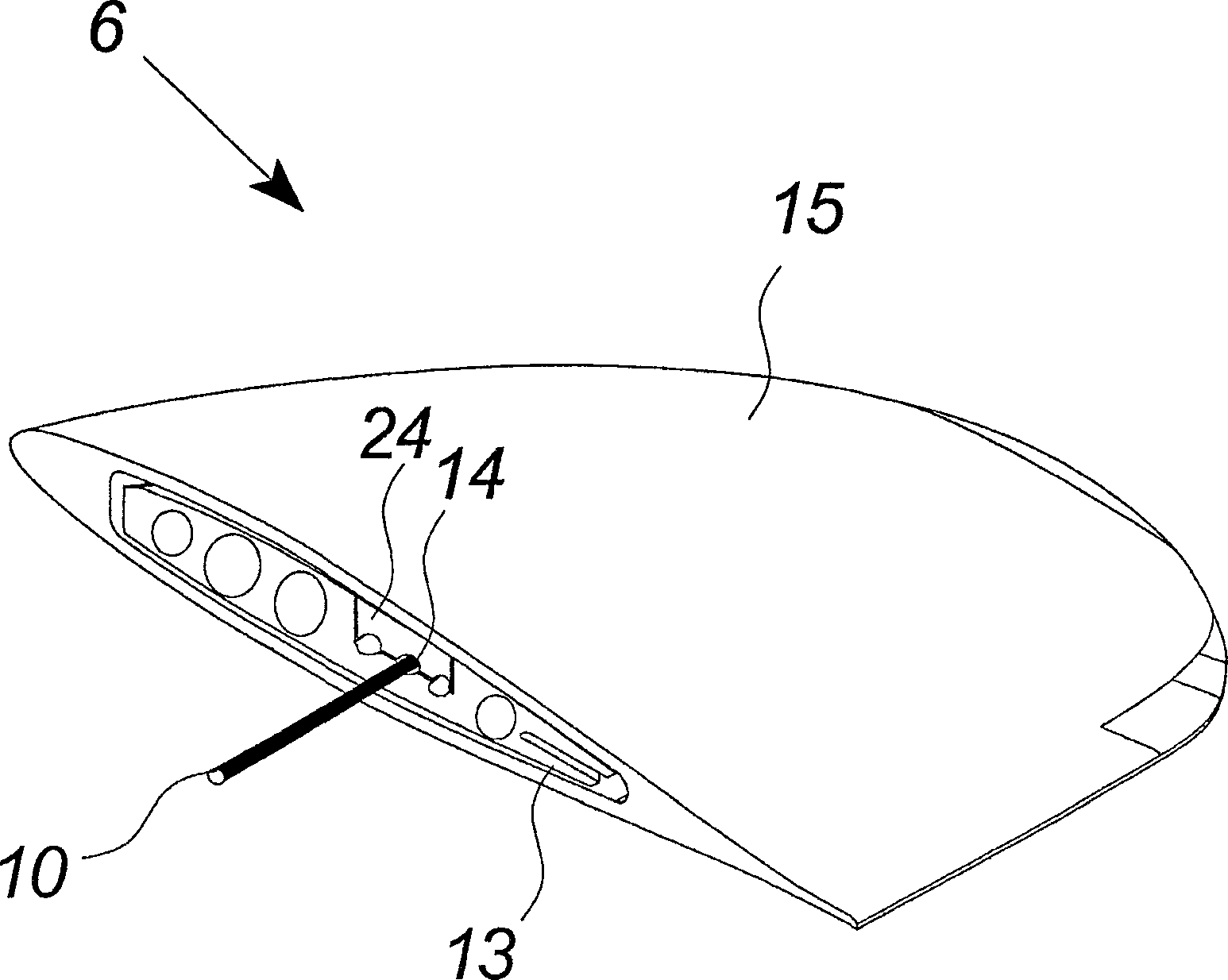
The invention relates to a wind turbine blade comprising lightning protection means. At least one section of the tip of said blade is made in solid metal and is included as part of said lightning means. The invention also relates to a wind turbine, a method of providing lightning receptor means to a wind turbine blade and use hereof.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
System for detecting proximity between a wind turbine blade and a tower wall
A sensor system monitors deflection of turbine blades of a wind turbine. The system includes a first component configured on the turbine blades. A second component is configured on the tower at a height so as to detect the presence of the first component as the blades rotate past the tower. The second component generates a corresponding measurable parameter or value that is indicative of distance between the blades and tower. The second component is disposed substantially completely around the circumference of the tower so as to detect the first components at any rotational position of the turbine nacelle relative to the tower.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Wind power device
A new reduced cost easily manufactured light weight wind turbine design combining the use of downwind passive yaw, large take off rim on the outside of the semi rigid sails, a new method of furling or changing sail AOA, new semi rigid sail design, and new tower design that allows passive yaw for high installation of wind wheels to gain energy from higher wind speeds.Combining these features dramatically lowers weight / simplifies manufacture / avoids need for expensive composite materials / avoids the need for heavy high reduction gearboxes / reduces friction losses to air / reduces noise / reduces bird strikes / catches more energy per area of sails / and ultimately reduces cost in US$ per kwh generated ratio.
Owner:DAWOUD GUIRGUIS SAAD +1
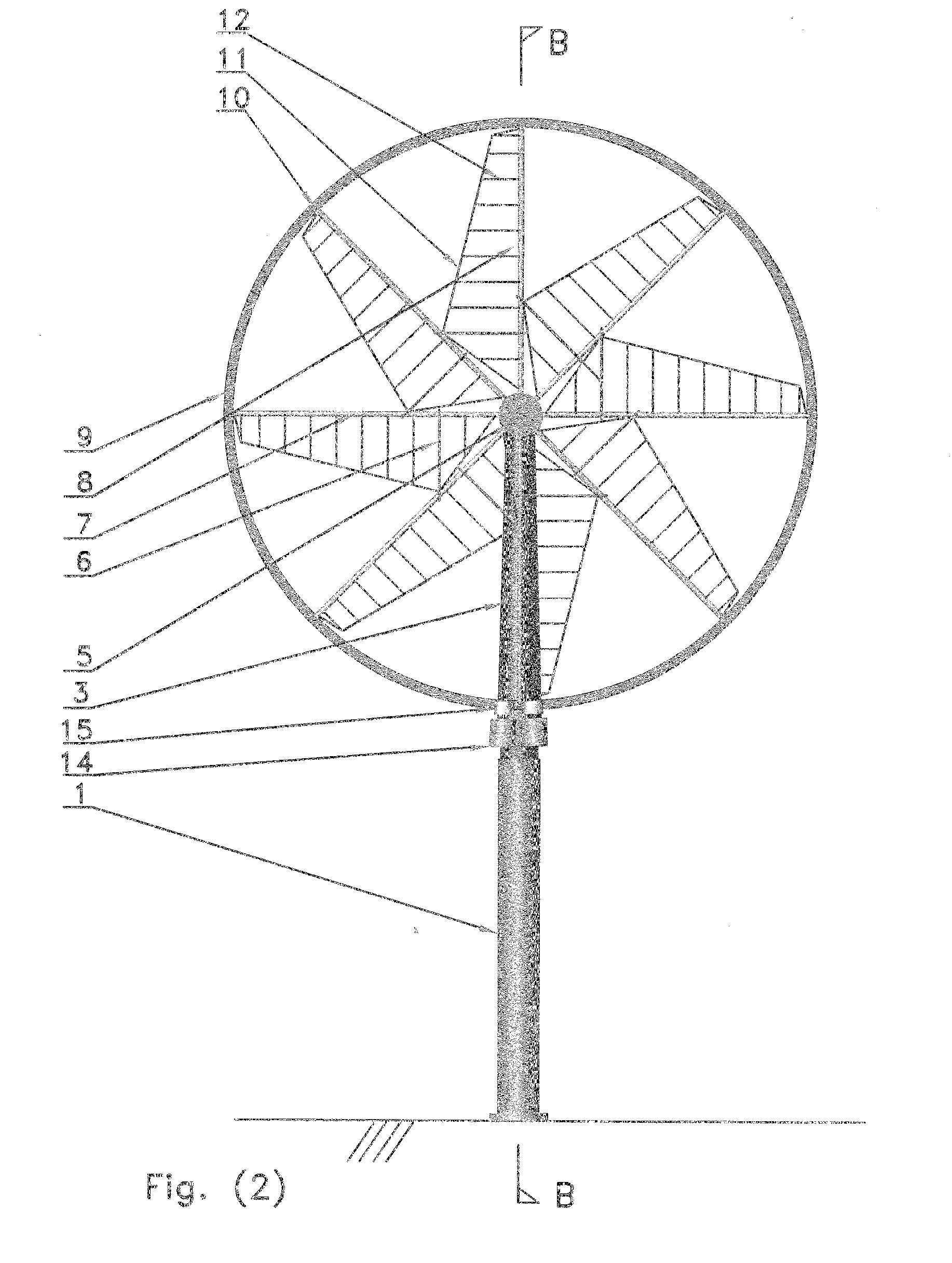
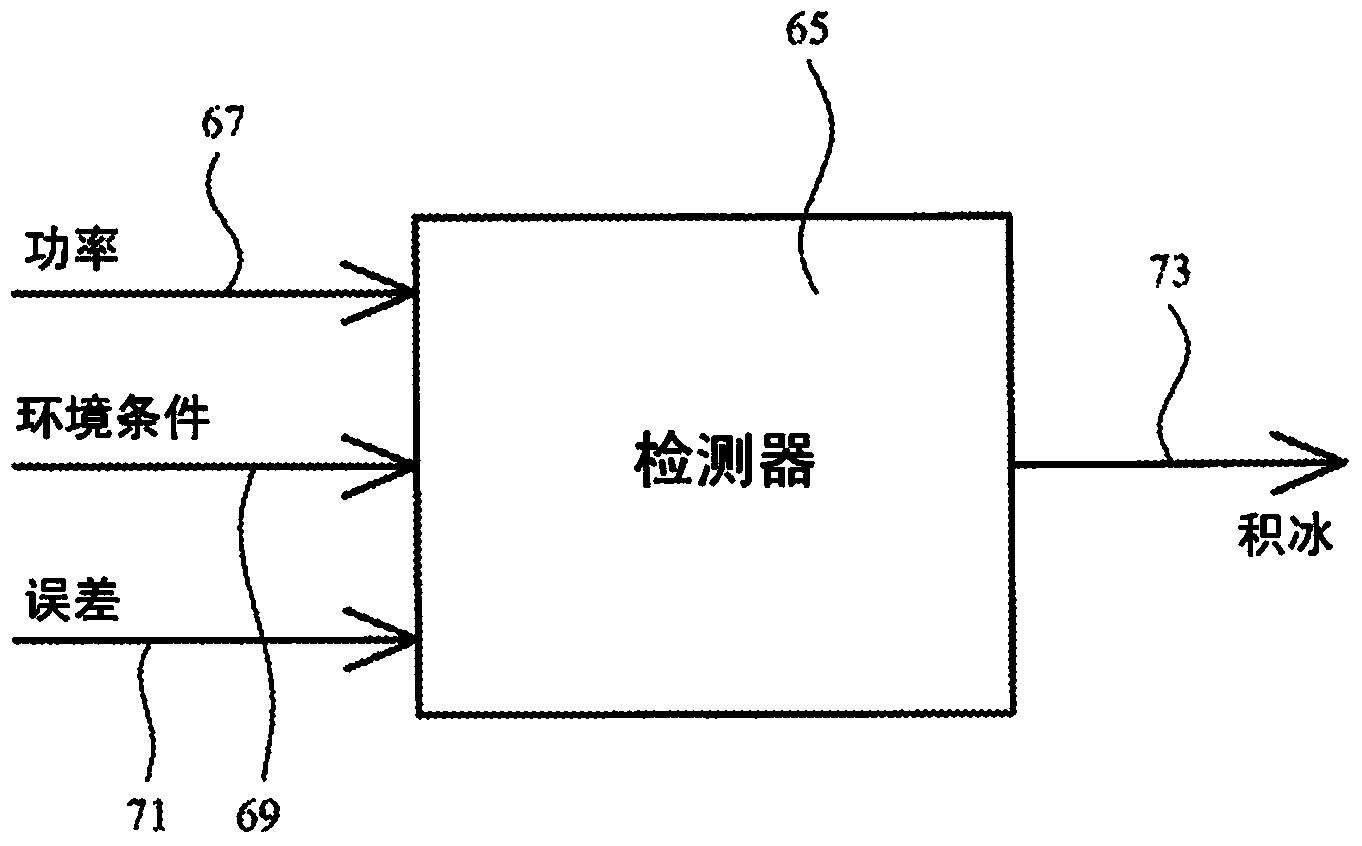
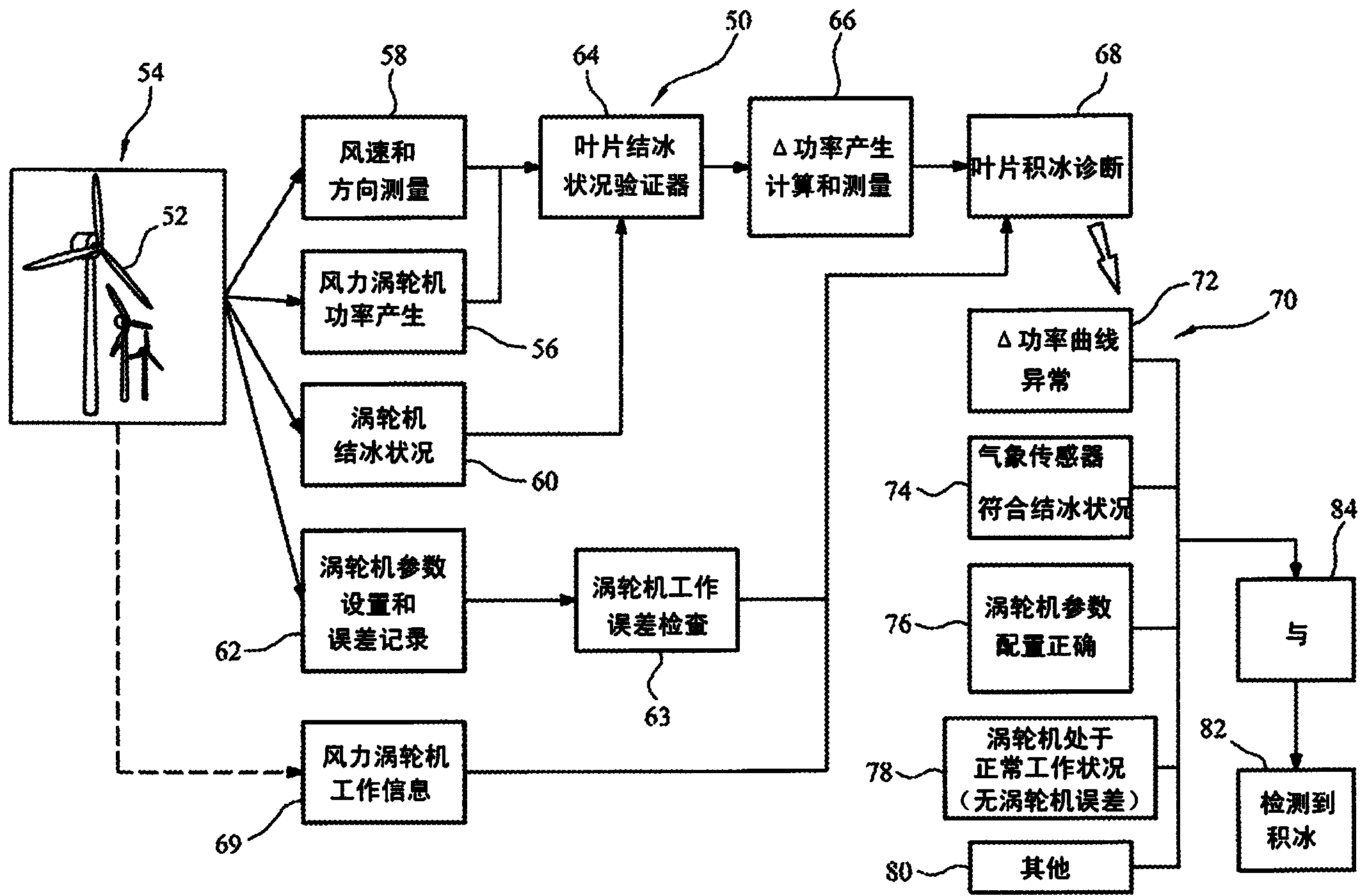
A wind turbine blade ice accretion detector
A wind turbine blade ice accretion detector 65 is configured to receive an indication of power generated by a wind turbine 67 and an indication of a plurality of environmental conditions of the wind turbine 69. It is also configured to receive an indication of an error relating to the operation of the wind turbine 71. These indications are processed by the detector 65 to provide an indication of ice accretion of a wind turbine blade. In addition to or as an alternative, the wind turbine blade ice accretion detector 65 is configured to receive an indication of power generated by a wind turbine 67 in a plurality of different time periods and an indication of a plurality of environmental conditions of the wind turbine 69 in the plurality of different time periods; and to process these to provide an indication of ice accretion of a wind turbine blade.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Fairing for wind turbine blade
The invention relates to a fairing adapted to be mounted on a wind turbine blade (2), wherein the outer surface of said fairing is arranged so as to reduce, when mounted on the blade, the aerodynamic drag in a flapwise (z) direction of the blade. In this way a reduction of the exciter power required in a flatwise fatigue test of the blade is achieved.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Transport system for a wind turbine blade
InactiveUS9011054B2Preventing unwanted cargo movementVehicle to carry long loadsTransport systemTurbine blade
Owner:SIEMENS AG
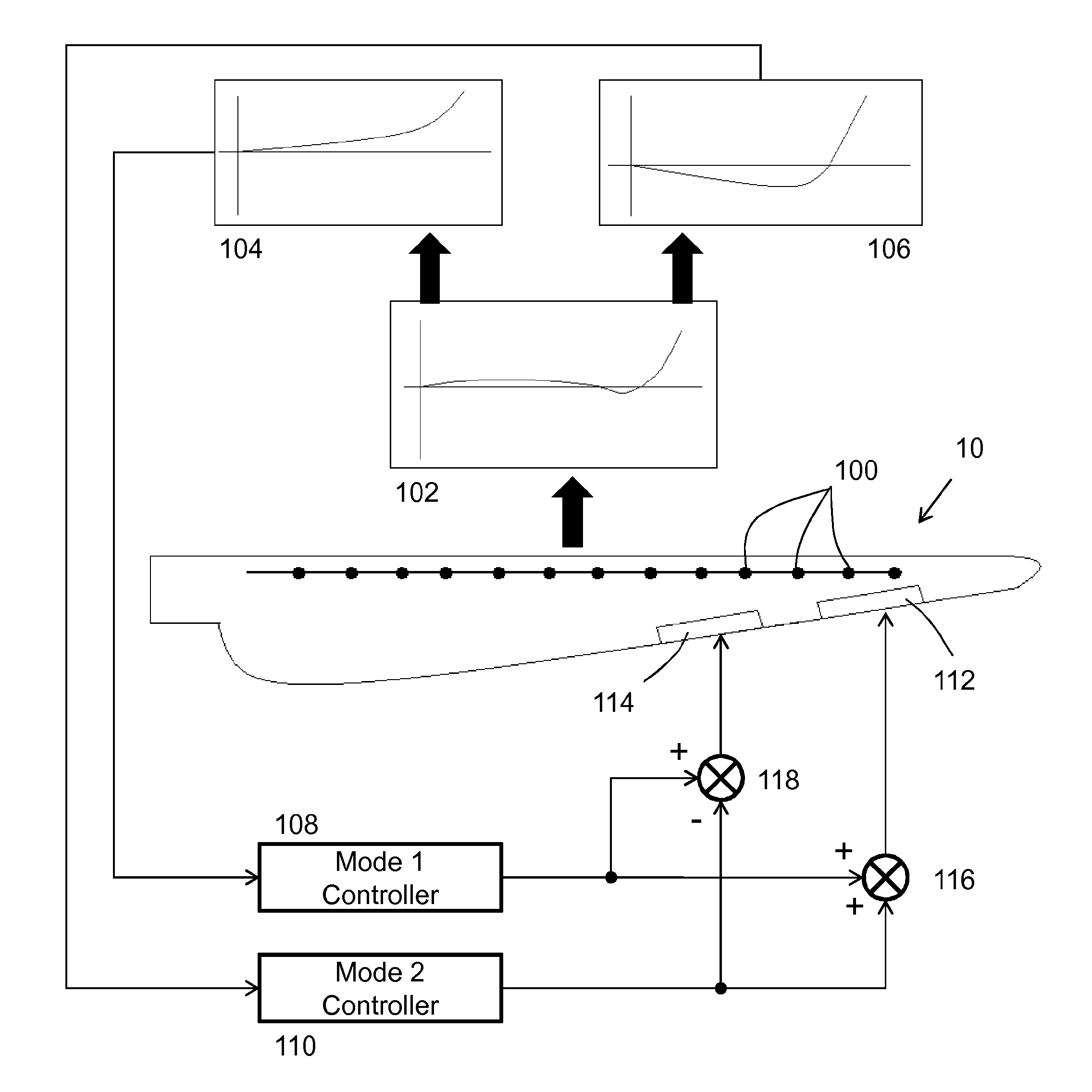
Rotor blade control for high winds
ActiveUS20160305402A1Reduce loadMaximize efficiencyWind motor controlCircuit arrangementsTurbine bladeRotation velocity
The invention relates to a control apparatus and method for controlling the rotor blades of a wind turbine, and in particular to controlling the rotor blades during an extreme wind event. An extended mode of operation of the wind turbine rotor beyond the cut-out wind speed is provided. In the extended mode of operation, the pitch of the wind turbine blades is actively controlled so that the rotor and the generator idle at a designated rotational speed. The rotational speed may be relatively high, say 15 to 20% of the nominal speed, compared with minimal speeds experienced by purely feathered wind turbine blades, and may be further controlled as a function of the incident wind speed. Output power control in the extended mode may be zero but is preferably a low, but non-zero value. The output power so produced may then be used as an auxiliary power source for controlling the wind turbine in situations where the utility grid fails.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Wind turbine blade control method
A control method for a wind turbine, in particular for a wind turbine blade is described. The control method makes use of the blade mode shapes, or natural vibration shapes, of the blade to detect the excitement level of the blade natural vibrations, and controls active lift devices on the blade in an effort to reduce the excitement levels, to reduce loading in the blade and the overall wind turbine structure. There is also provided a method of designing a wind turbine blade for use in such a method.
Owner:LM WP PATENT HLDG
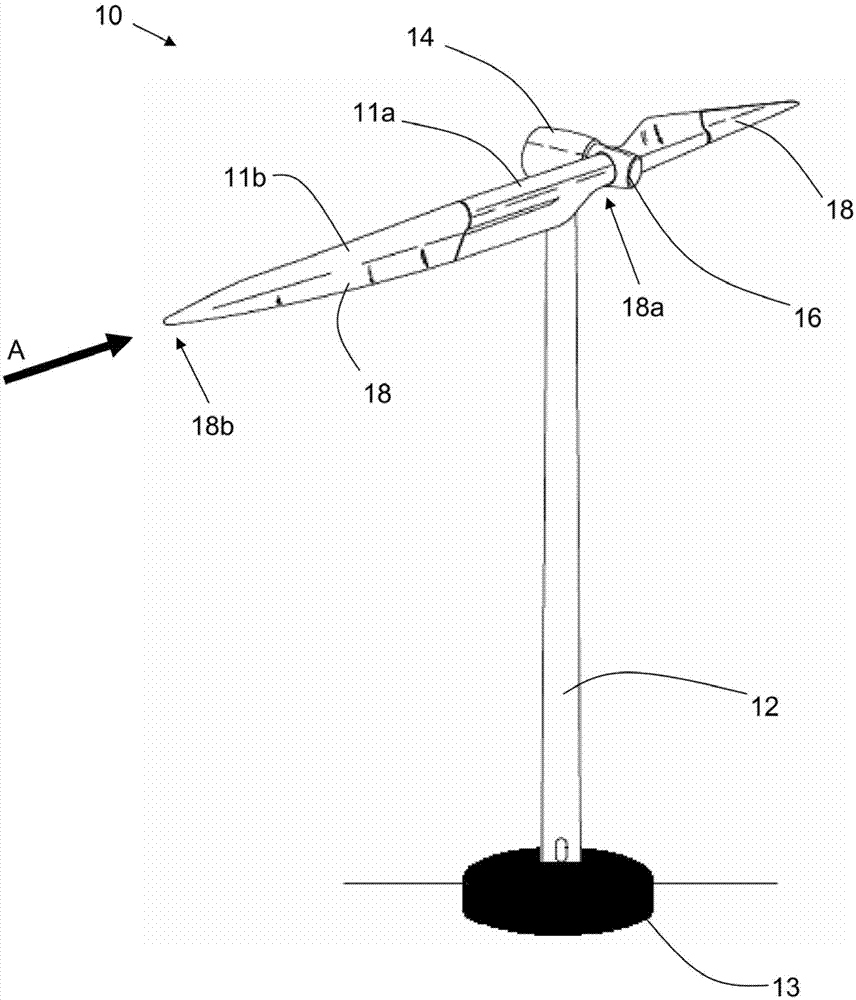
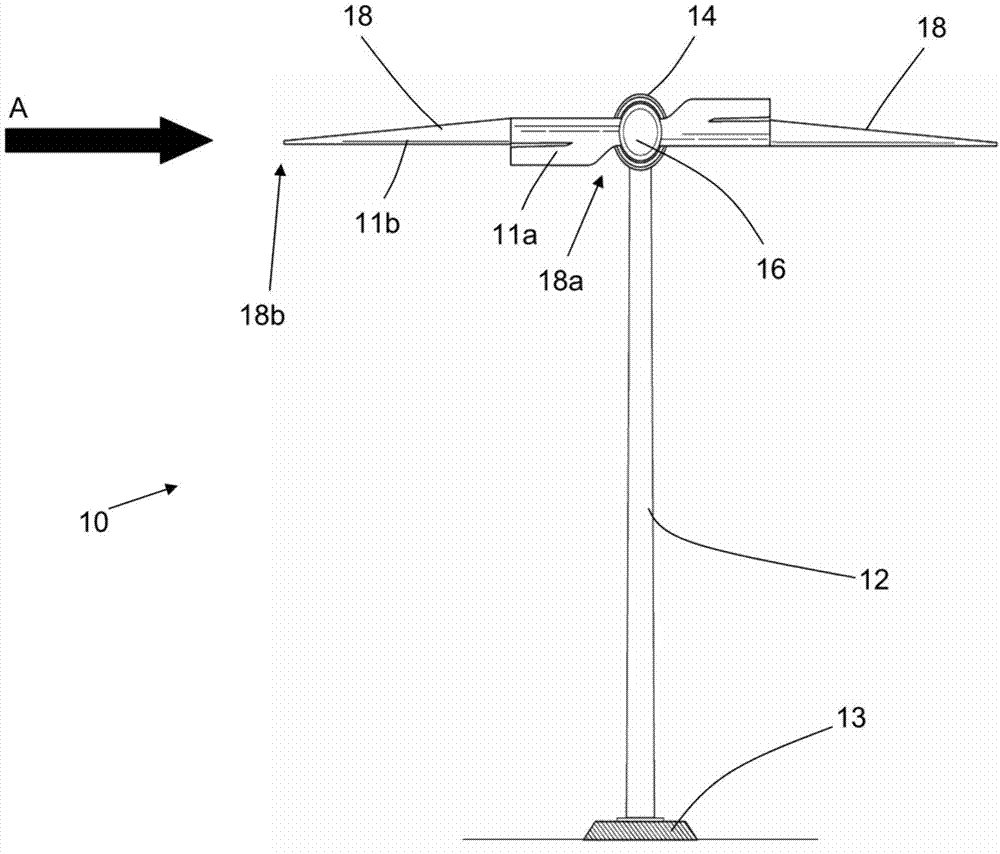
A wind turbine and associated control method
A method for controlling a two-bladed wind turbine in extreme wind conditions is described, wherein when extreme conditions are detected or forecast for the wind turbine, the wind turbine blades are positioned in a horizontal arrangement, and actively yawed such that a tip of one of the wind turbine blades points into the wind direction. The blades are yawed such as to actively follow the changing wind direction, resulting in a reduced surface area of the blades exposed to the extreme wind forces, due to the spear-like arrangement of the turbine blades. This reduced surface area provides for a reduction in the extreme loads which may be experienced by the wind turbine in such extreme wind conditions.
Owner:YUANJIAN WIND POWER JIANGYINENVISION ENERGY CO LTD
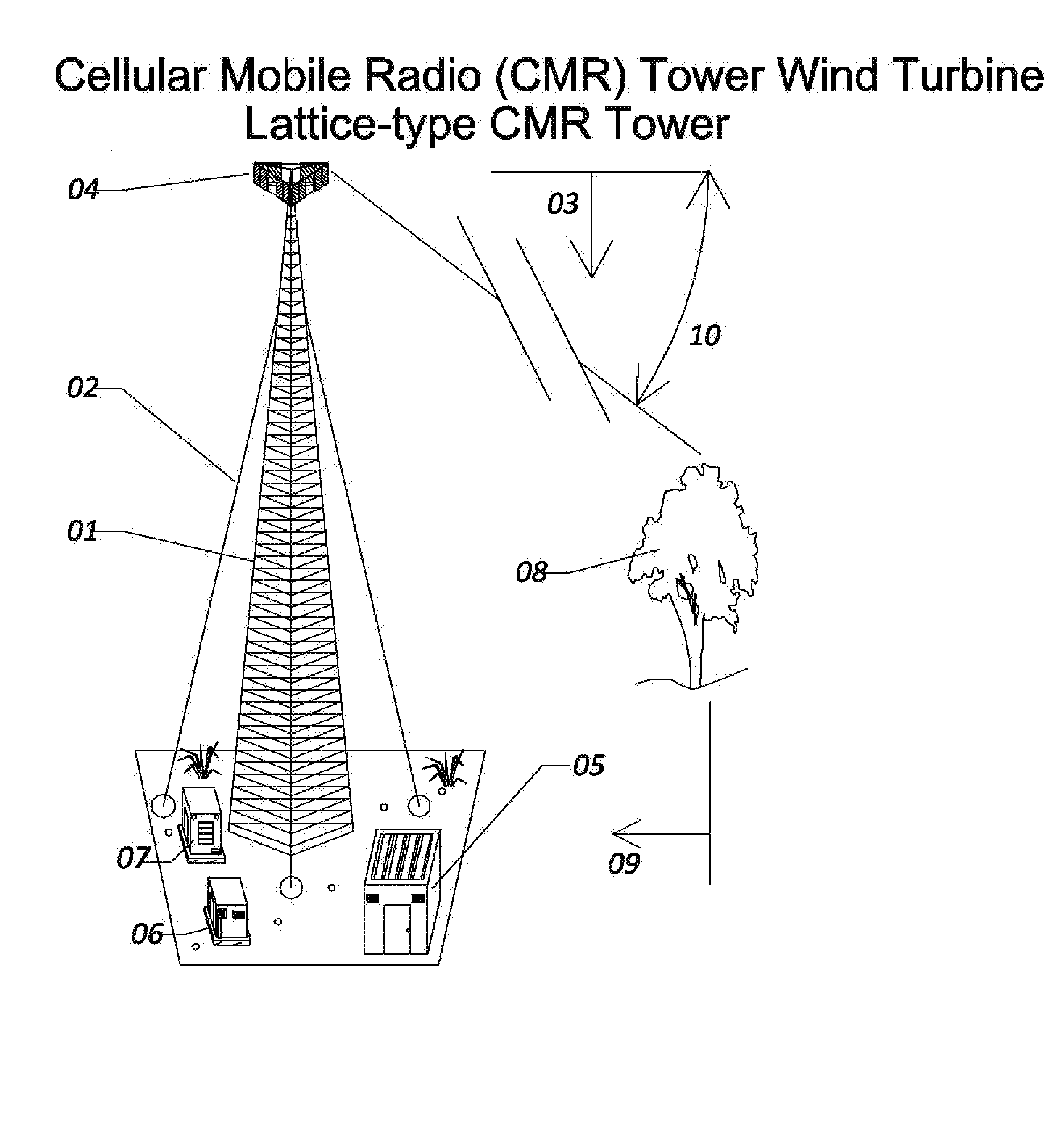
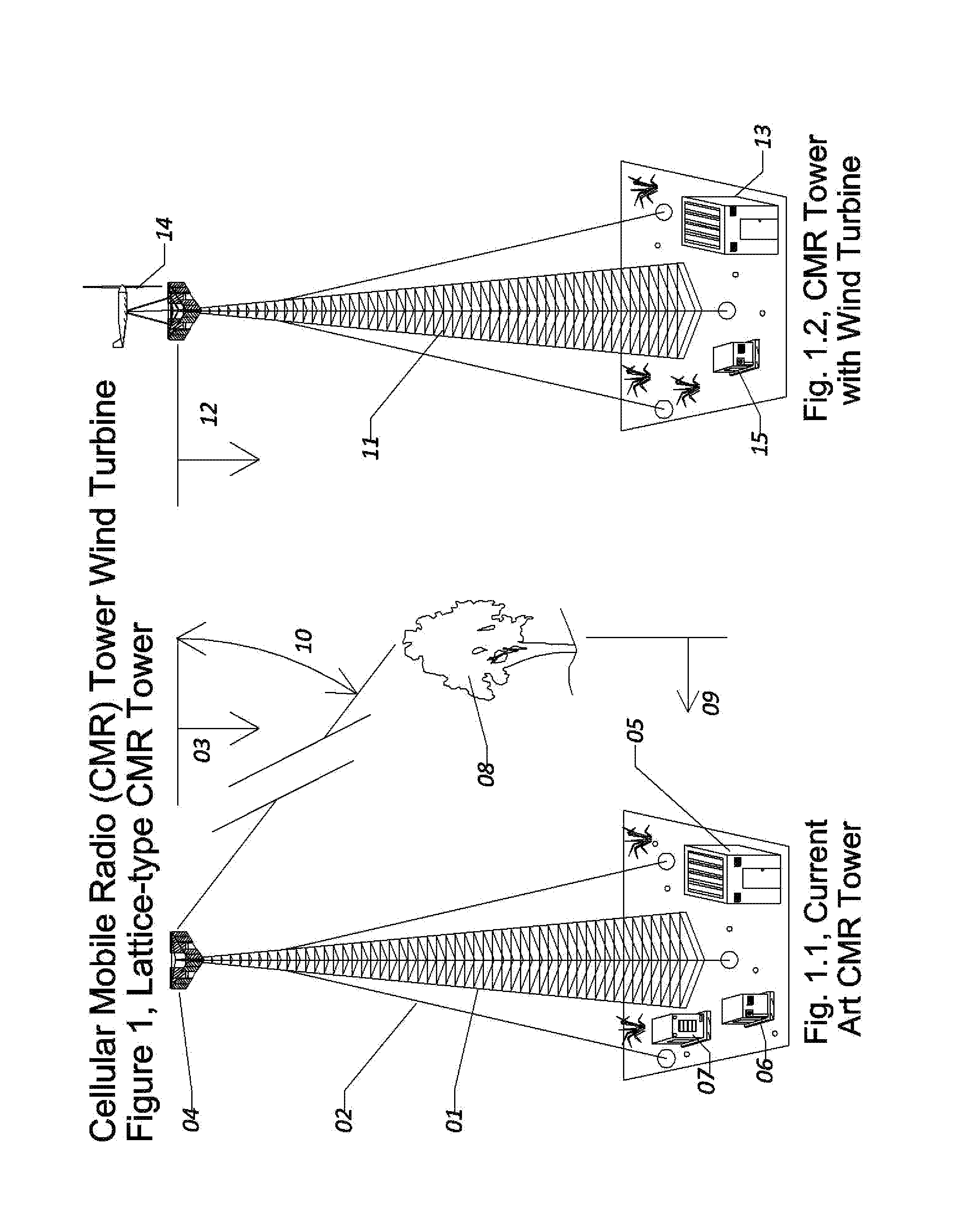
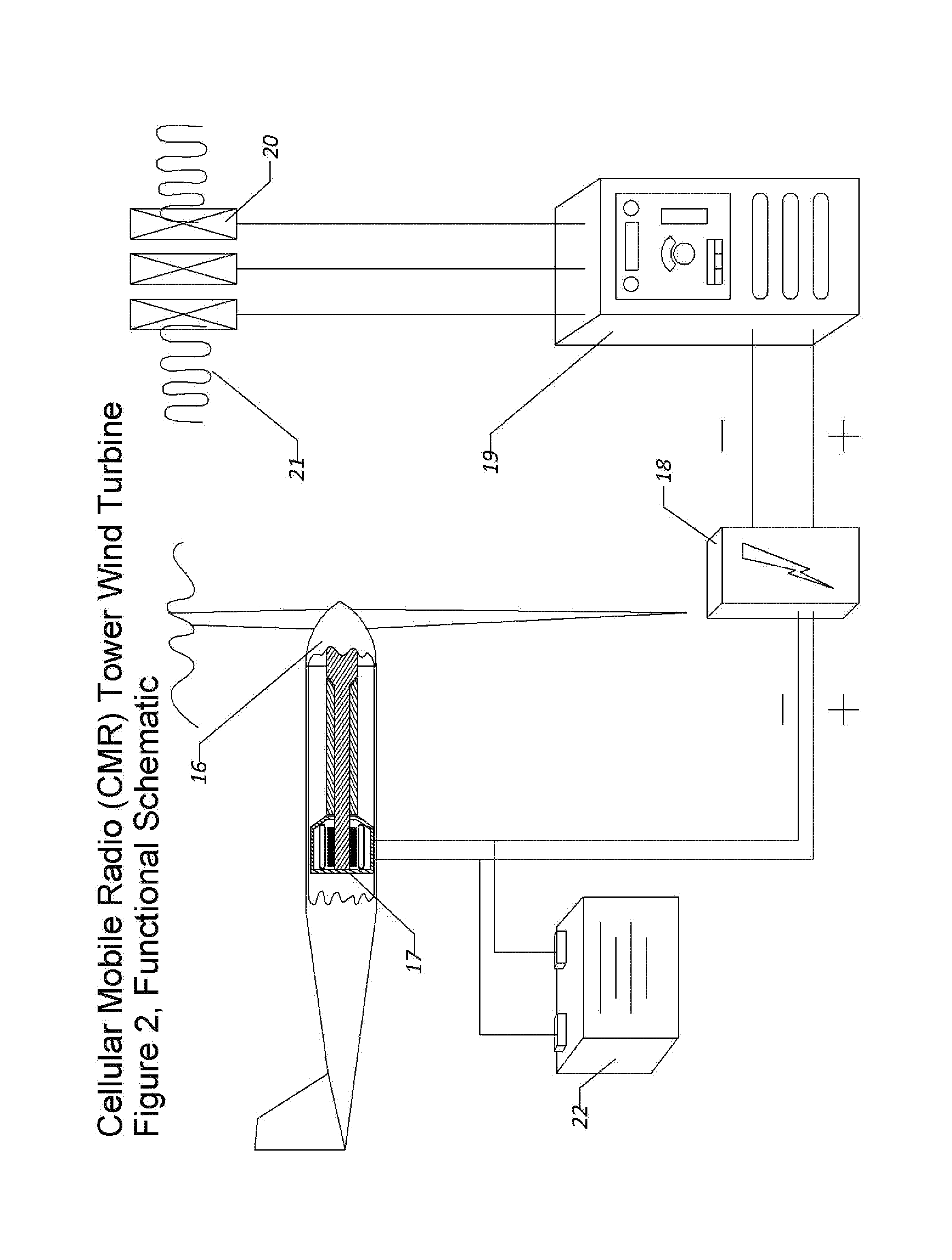
Cellular Mobile Radiotelephone Tower Wind Turbine
InactiveUS20110177844A1Maximize power generationPower managementWind energy with electric storageConstant powerNetwork connection
The Cellular Mobile Radiotelephone Tower Wind Turbine (CMRTTWT) specifically is an innovative method of harvesting available wind power around CMRT towers. The CMRTTWT addresses the base station power needs of the Cellular Mobile Radiotelephone (CMRT or Cell Phone) industry, providing clean on-site power generation for reduced environmental impact and for improved availability during disasters (natural or man-made). This invention extends the design of the CMRT tower to include a wind turbine and the associated structural and electrical modifications to accommodate that wind turbine. This wind turbine is designed to provide approximately the daily power demands for the CMRT tower system; thus the turbine would be small enough to be mounted on the tower without interfering with the operations of the antennas. By using the turbine as a constant power source, clean electricity is directly harvested from suitable velocity winds at the higher altitudes of the tower. Once the invention is installed, the electricity required from the power grid is reduced significantly. By designing the system to vary the number of network connections based upon the power available from the turbine, constant operation of at least some capacity is possible even without power from the electrical grid; this is a tremendous advantage for maintaining communication capability during and immediately following disasters (both natural and man-made). The invention creates a low-cost way to harness readily available wind power to generate much needed electrical power for the CMRT industry.
Owner:LOWAS III ALBERT FR
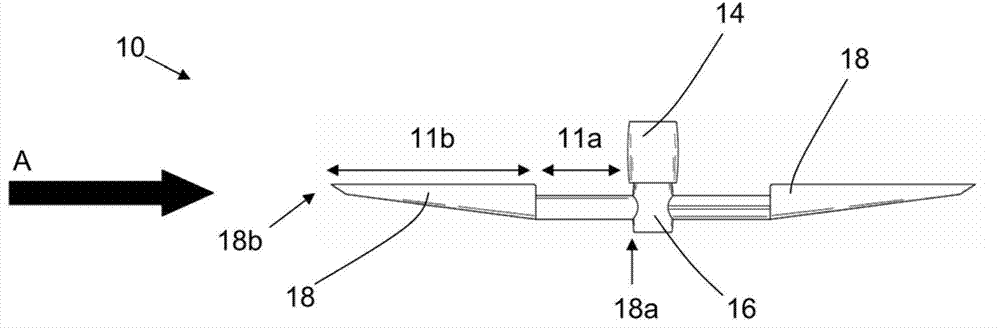
A wind turbine and wind turbine blade
A method for controlling a two-bladed pitchable swept-blade wind turbine in extreme wind conditions is described, wherein when extreme conditions are detected or forecast for the wind turbine, the wind turbine blades are pitched such that they will stabilise in a substantially horizontal arrangement. The blades can be yawed such that the tip ends of the wind turbine blades point in the same direction towards the surface level, thereby lowering the centre of mass of the rotor assembly of the wind turbine blades and the rotor hub. The lower centre of mass of the assembly results in the stabilisation of the blades in a substantially horizontal position, resulting in a reduced surface area of the blades exposed to the extreme wind forces. This reduced surface area provides for a reduction in the extreme loads which may be experienced by the wind turbine in such extreme wind conditions.
Owner:YUANJIAN WIND POWER JIANGYINENVISION ENERGY CO LTD
Eddy generator, wind turbine blade with eddy generator and installation method of eddy generator
PendingCN109386424ADelayed stallImprove aerodynamic performanceWind motor controlWind motor assemblyTurbine bladeWind turbine design
The invention relates to an eddy generator for a wind turbine blade. The eddy generator comprises multiple fins, and each fin is a triangular plate part with a circular corner as a top corner. According to the eddy generator, stalling can be effectively delayed, the pneumatic performance of the blade is improved, the situation can be reduced that the power generation loss of a wind turbine is caused by blade surface pollution, and the eddy generator can be applied to power increase transformation of the wind turbine blade which is operated. The invention further relates to a method for determining the mounting position of the eddy generator on the wind turbine blade and a method for installing the eddy generator on the wind turbine blade. According to the methods, the mounting and positioning process is precise and reliable, and the mounting efficiency is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRIC WIND POWER GRP CO LTD
Method Of Controlling The Pitch Velocity Of A Wind Turbine Blade And Control System Therefore
ActiveUS20110040413A1Quick stopPrecise and swiftly reactingRotational speed controlPropellersControl systemTurbine blade
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com