Patents
Literature
66results about "Avoid excessive blade deflection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
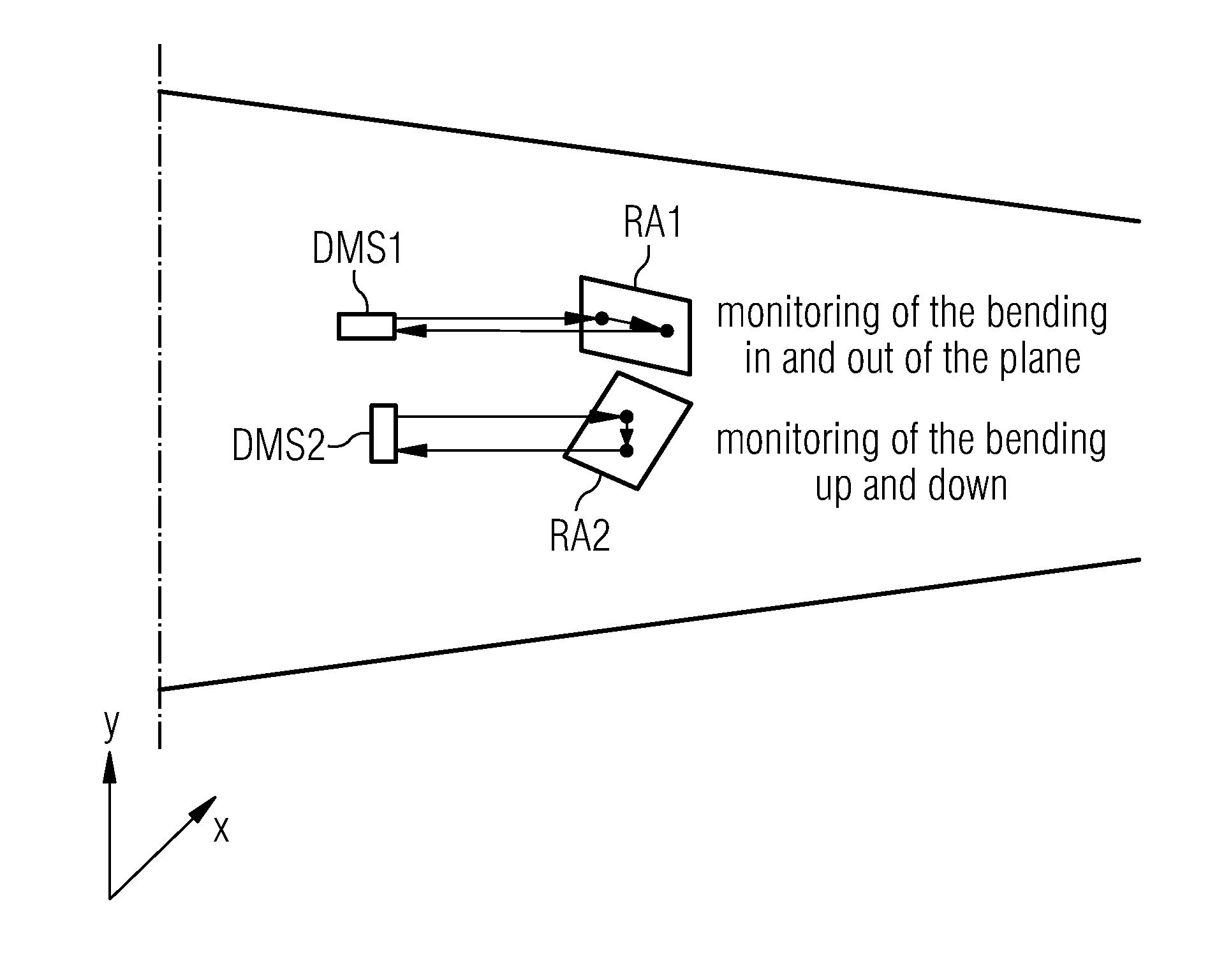
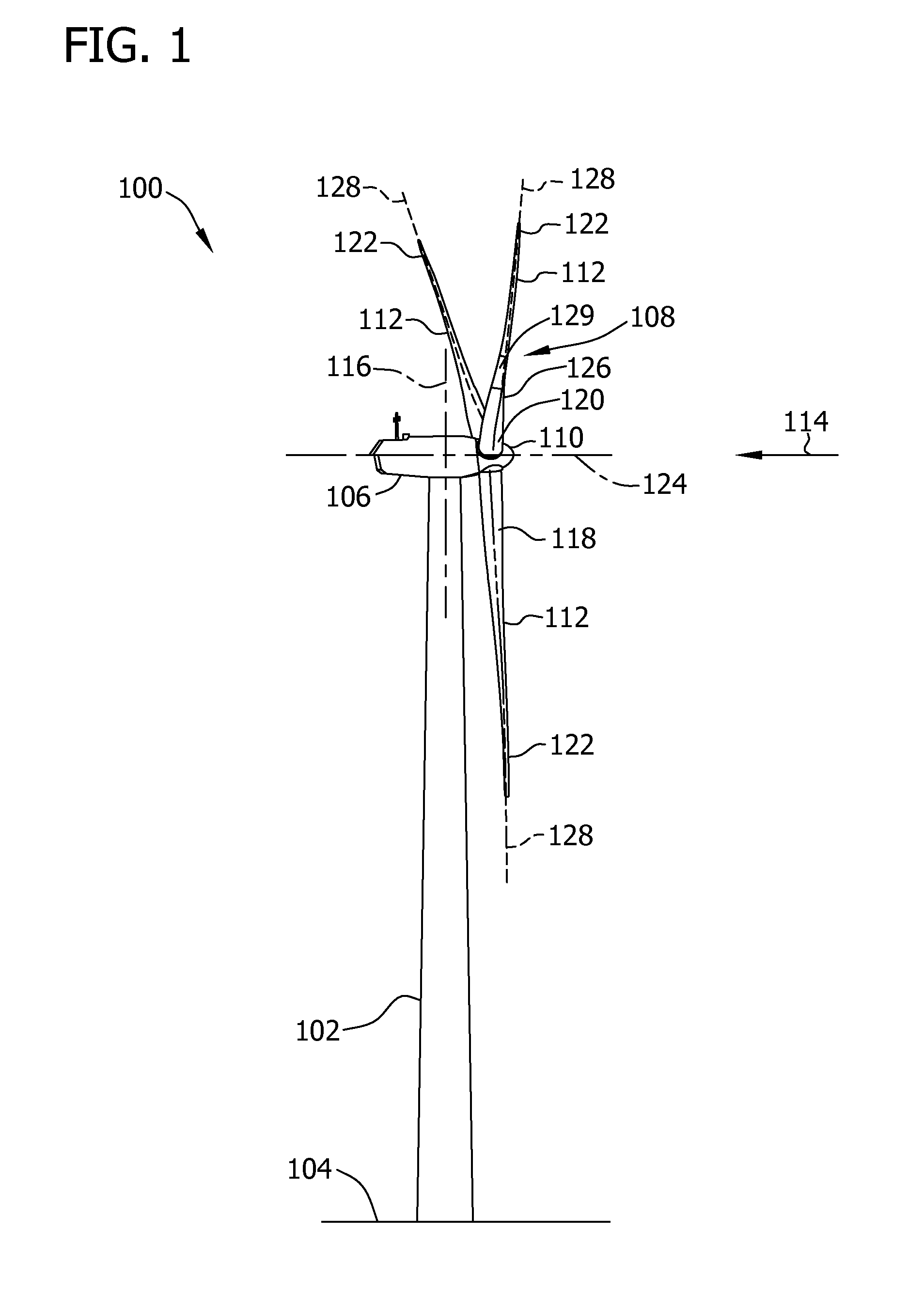
Wind turbine blade deflection control system
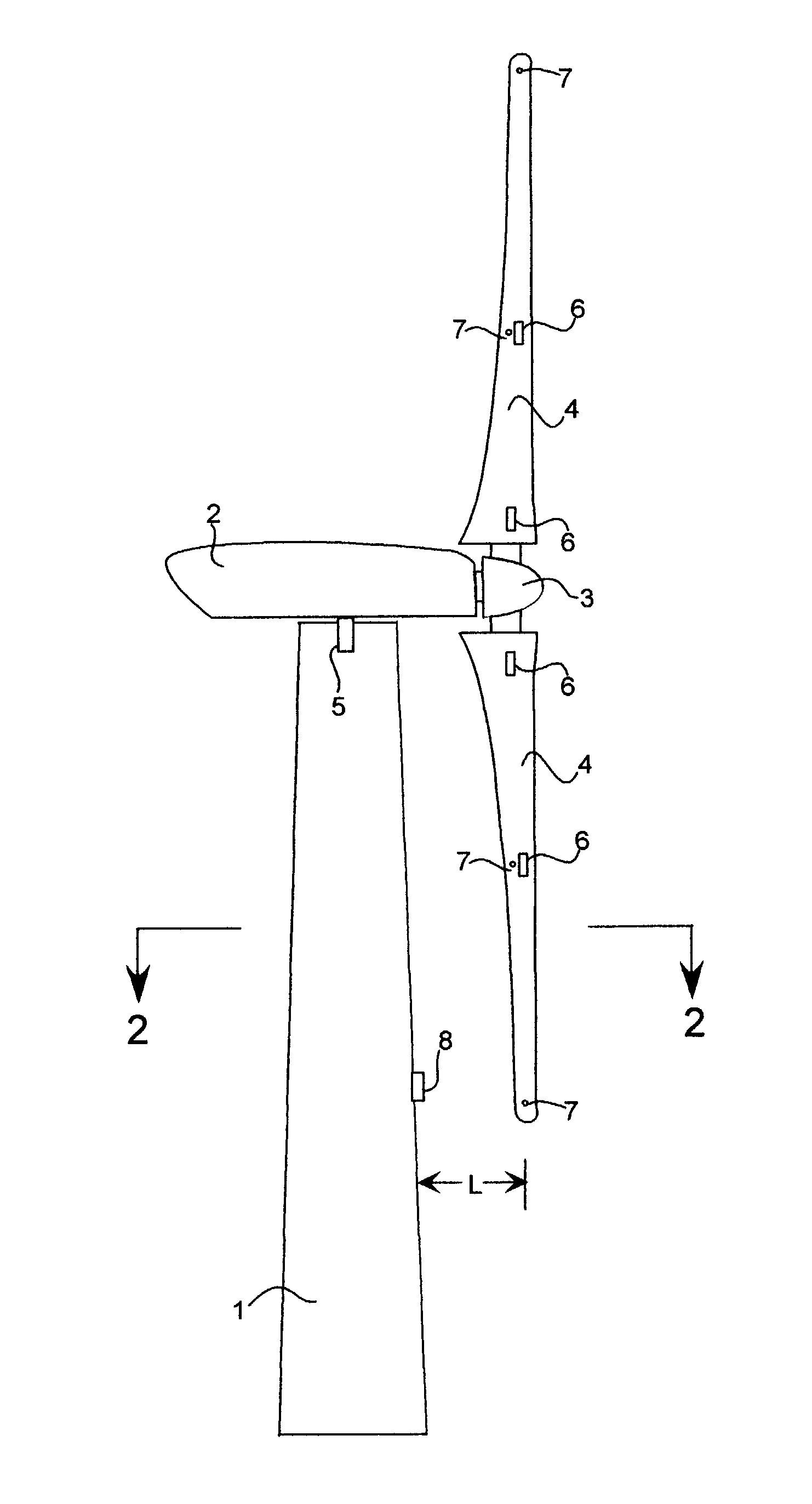
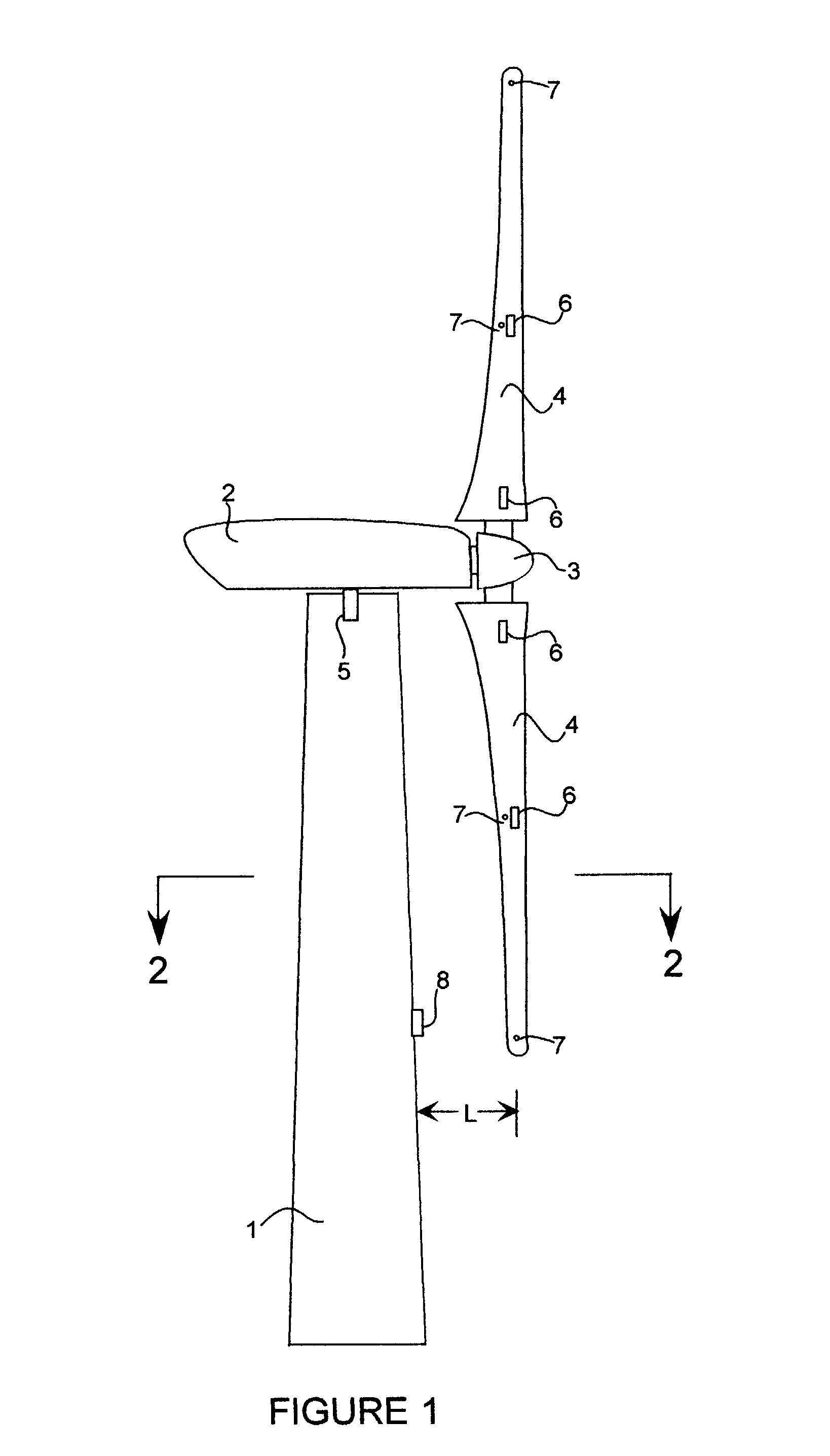
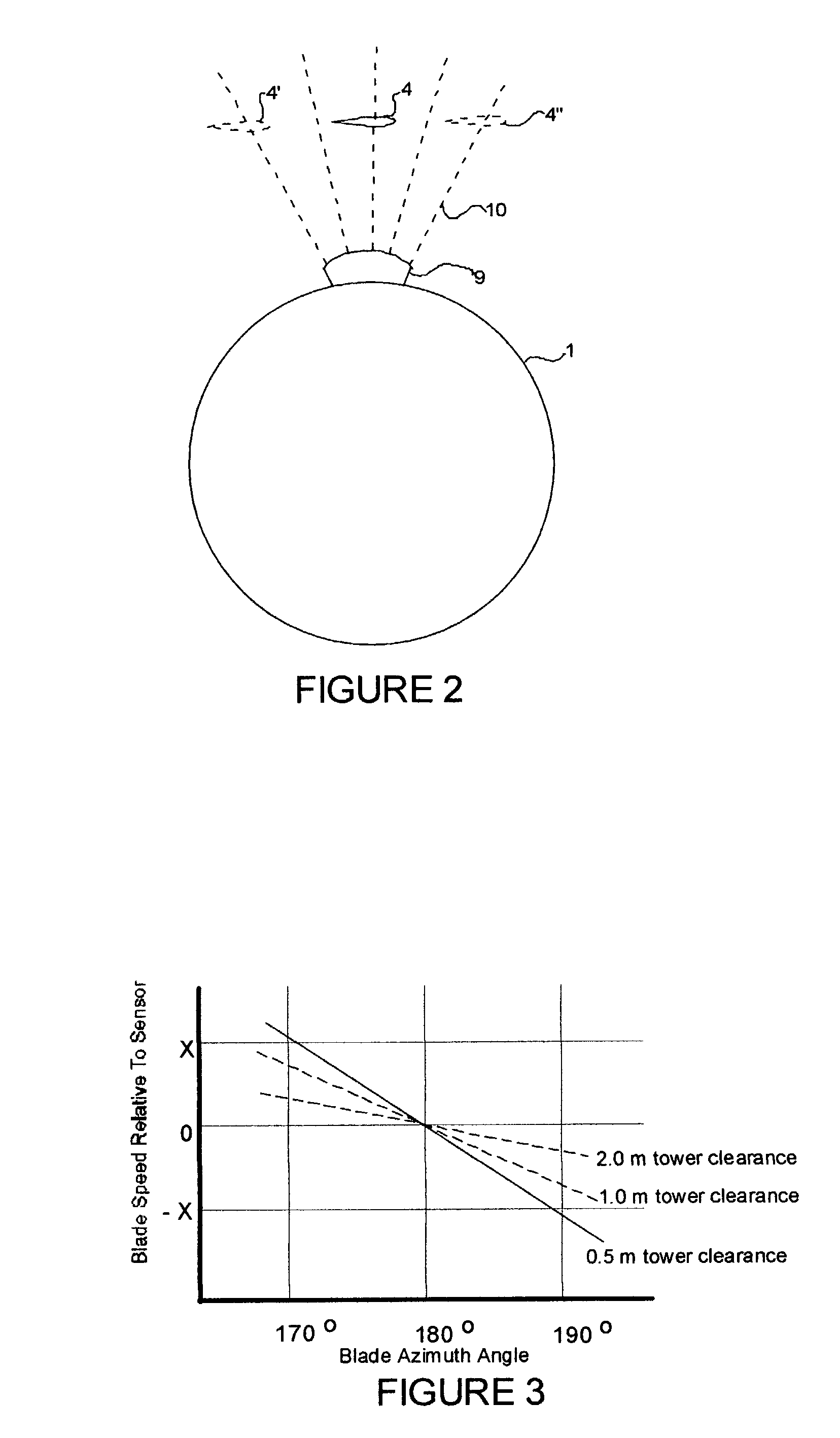
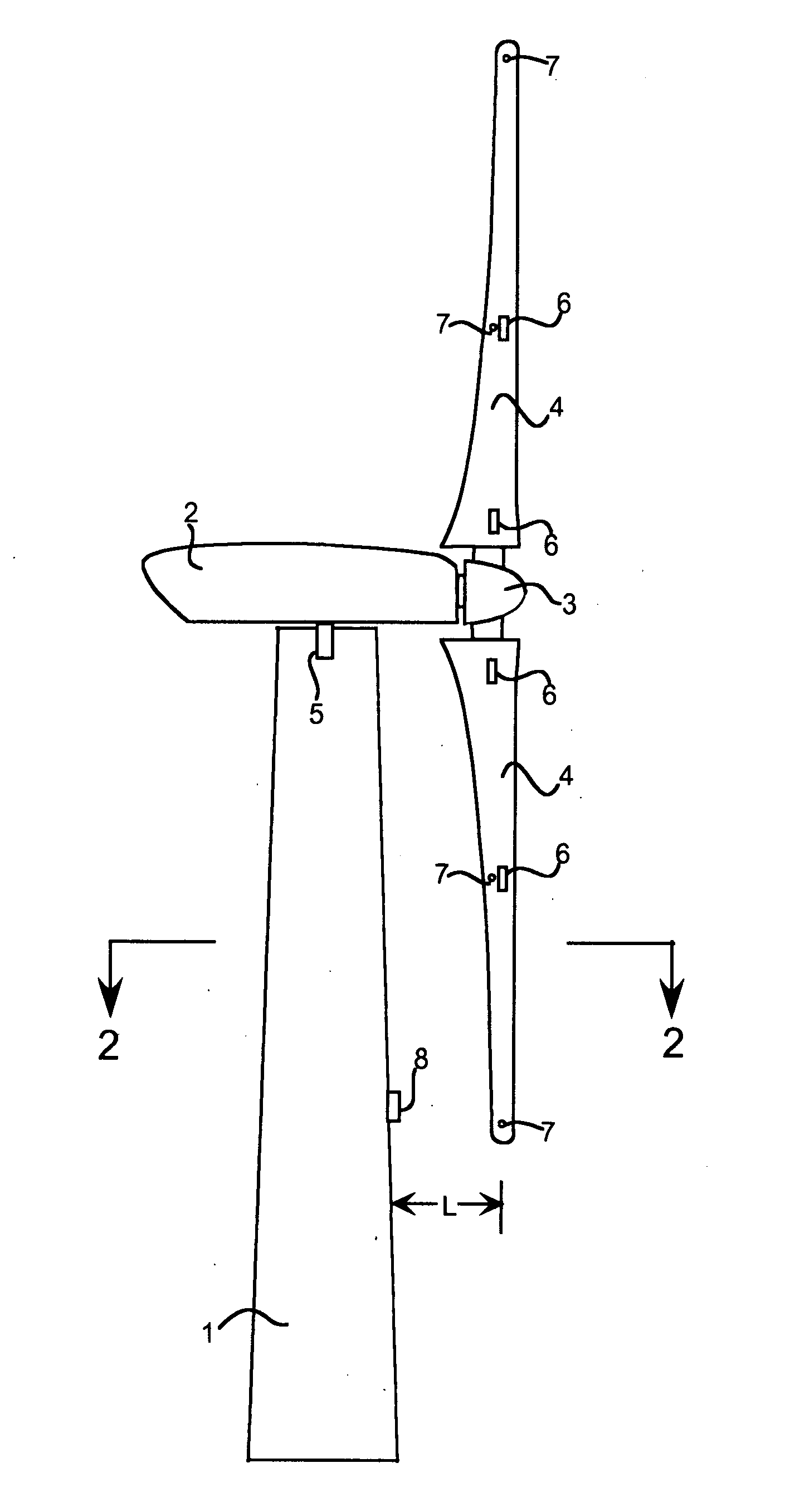
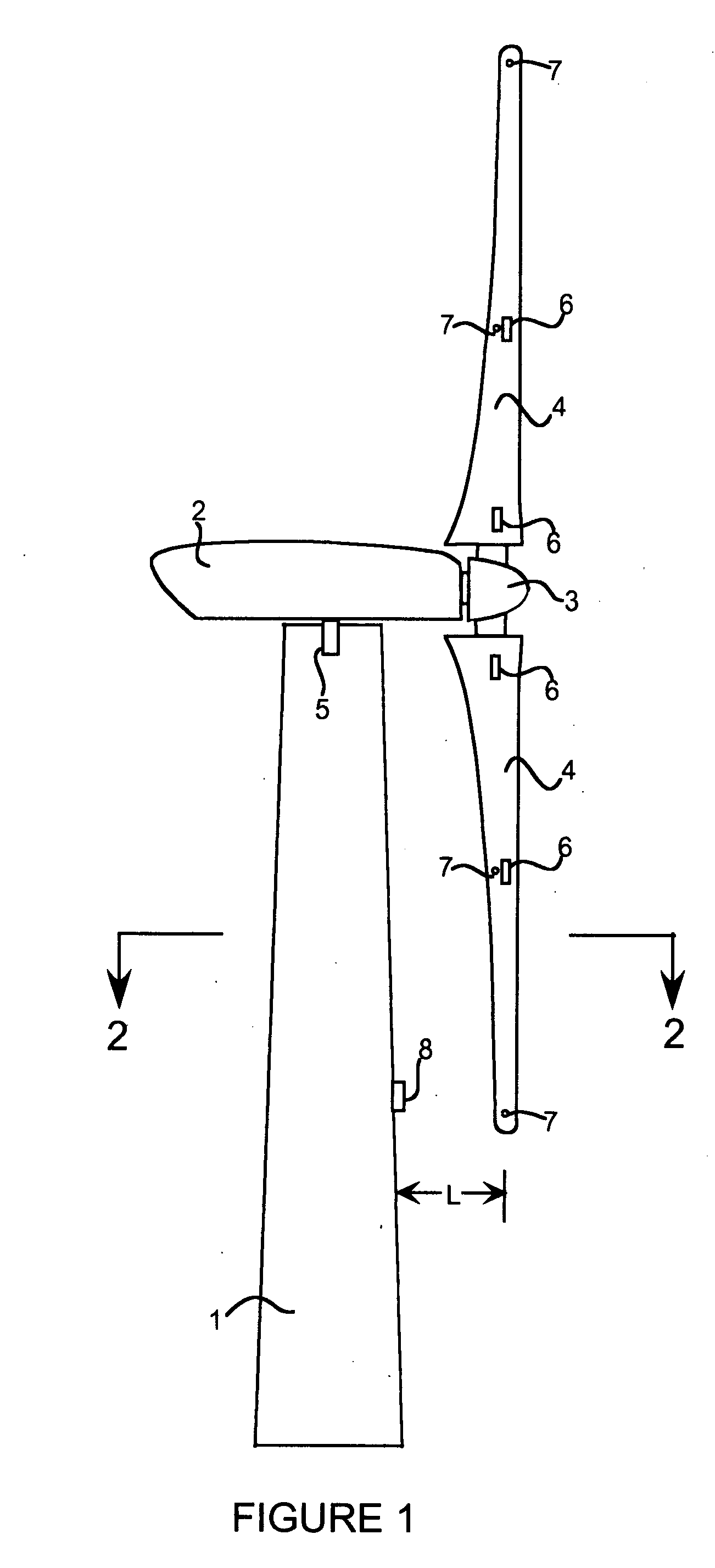
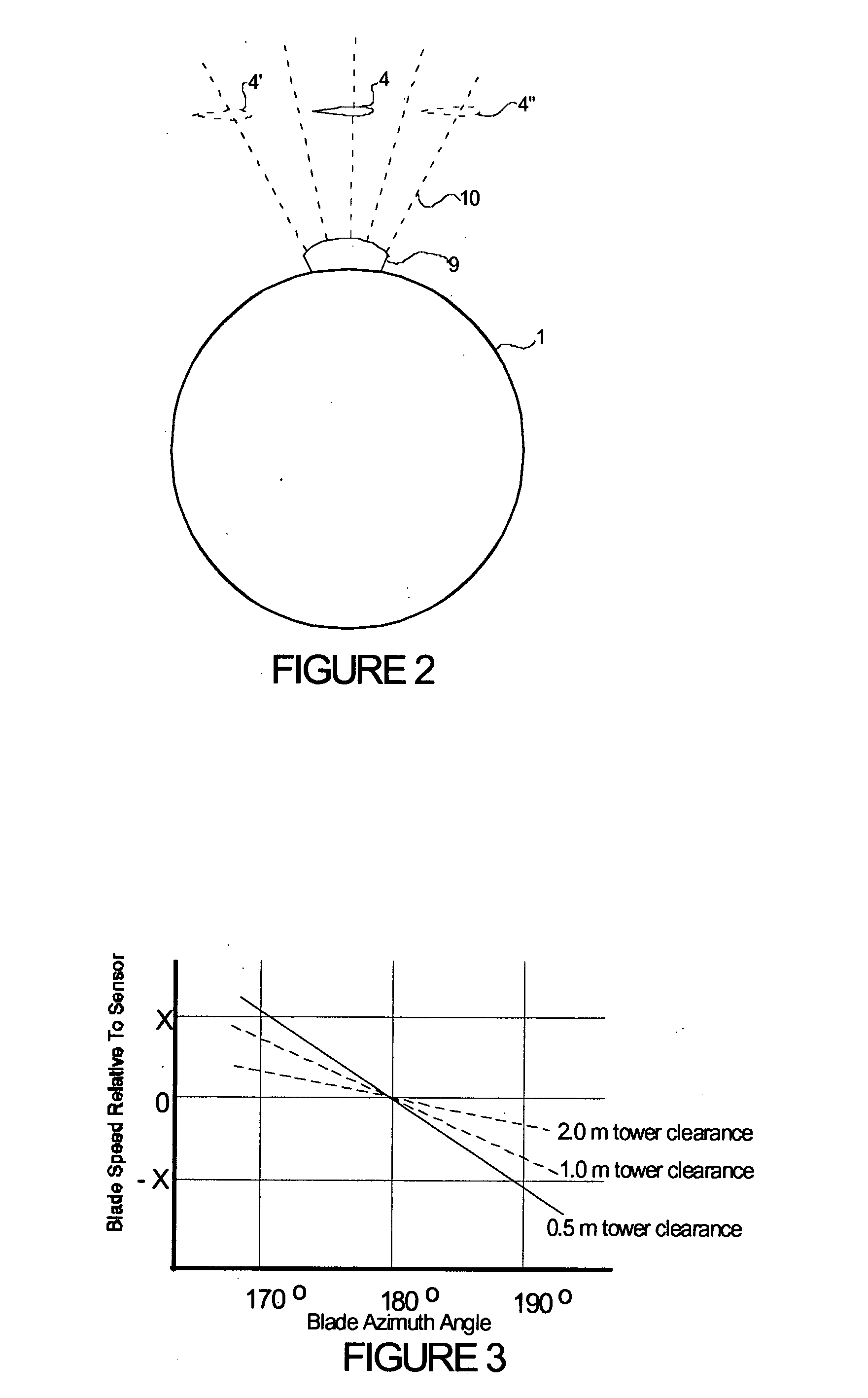
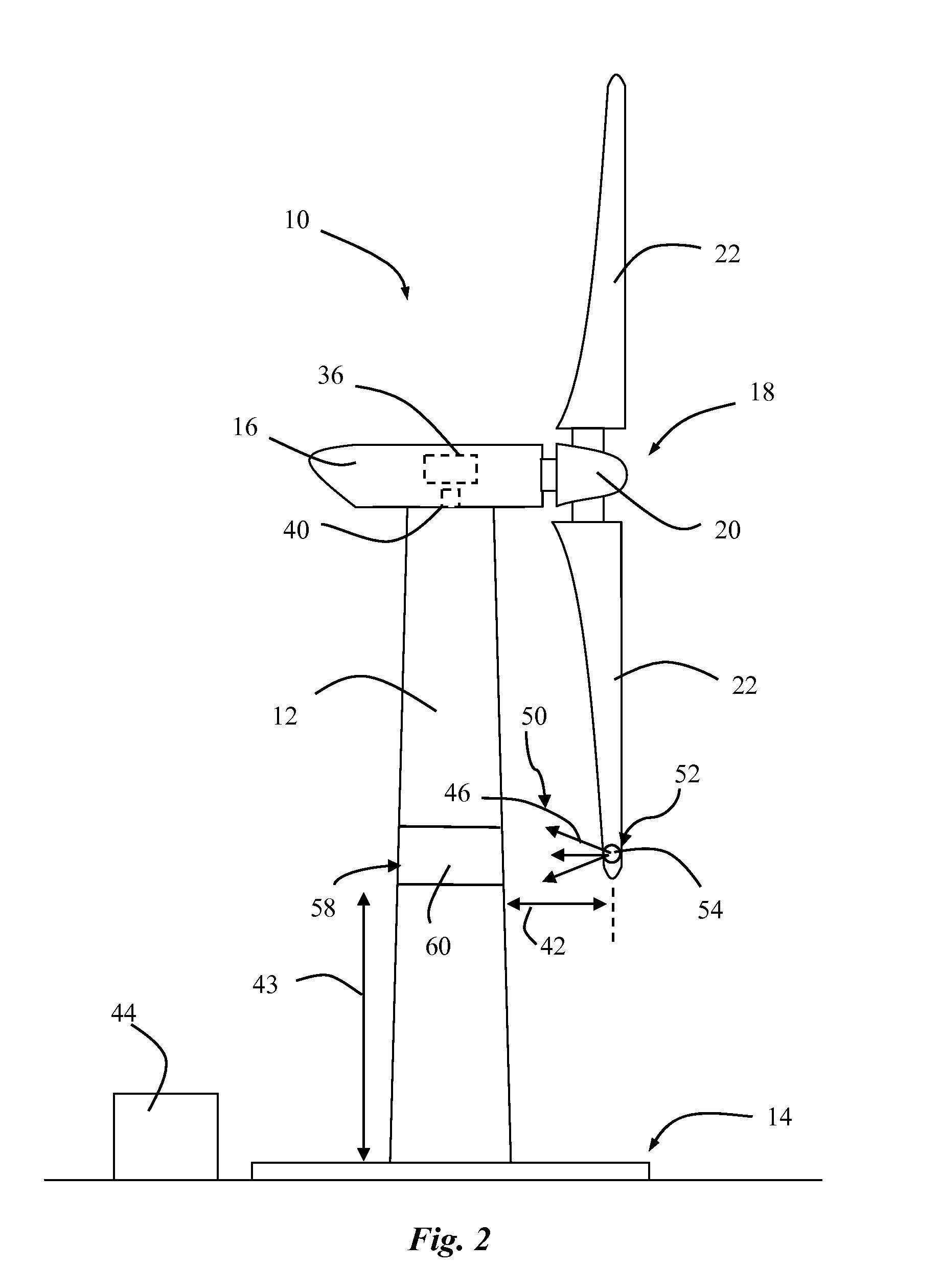
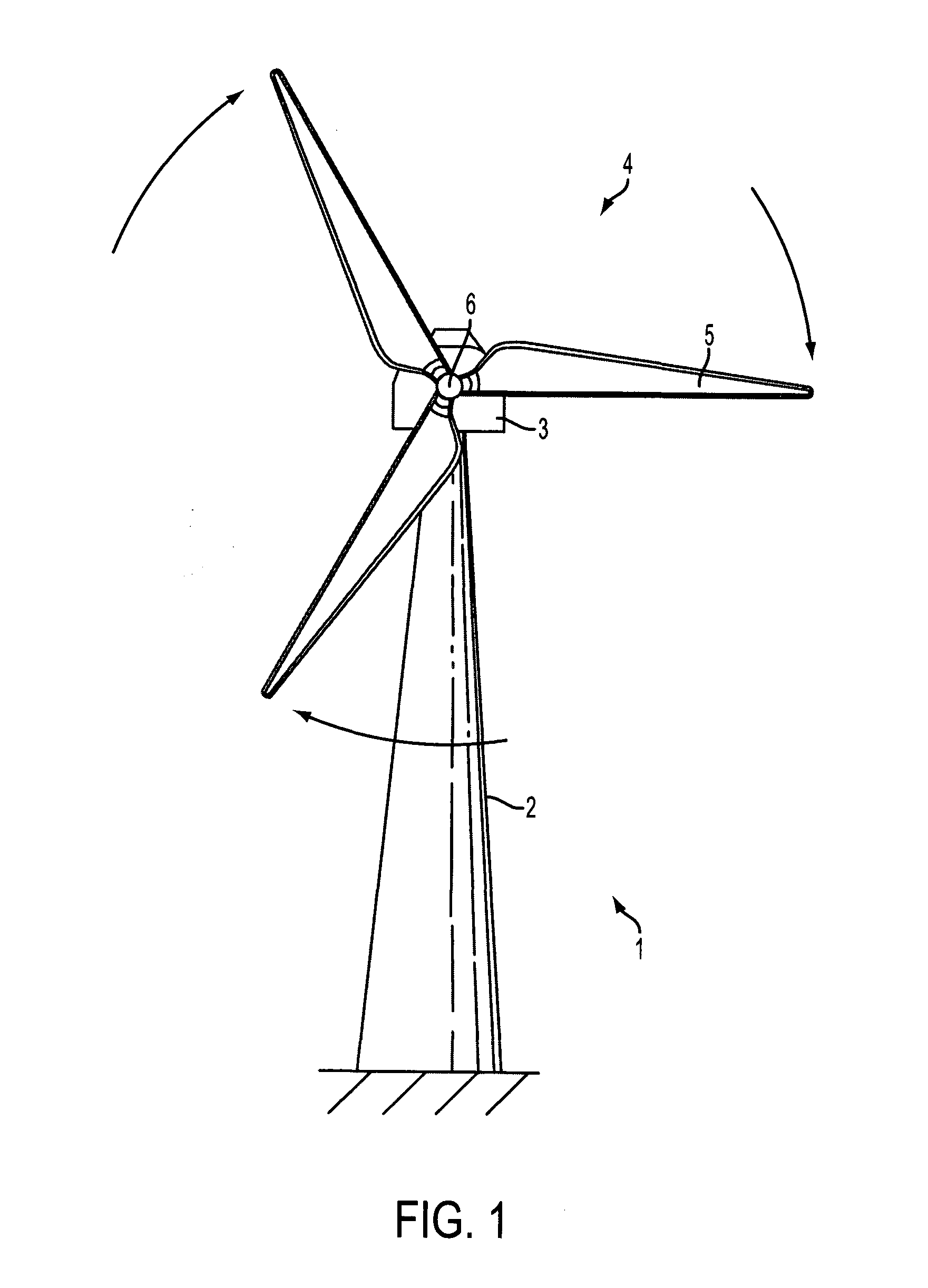
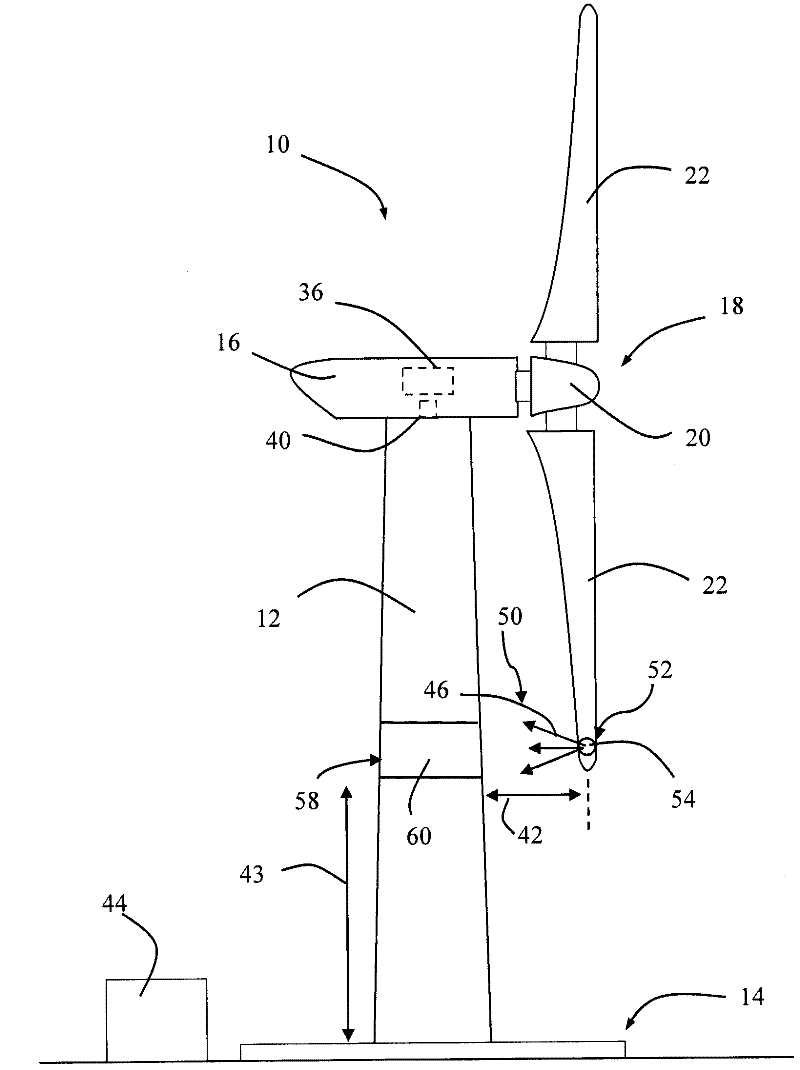
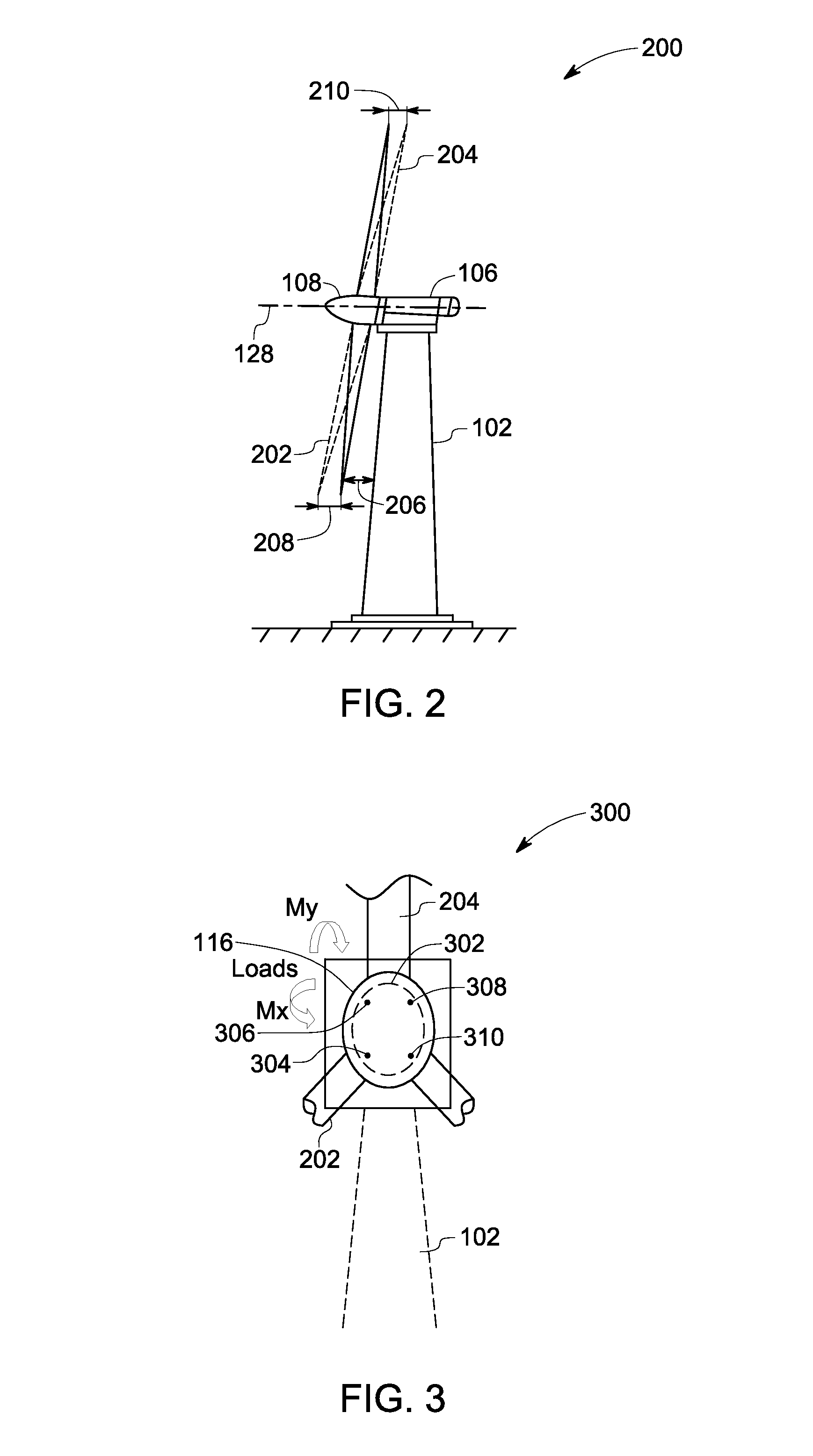
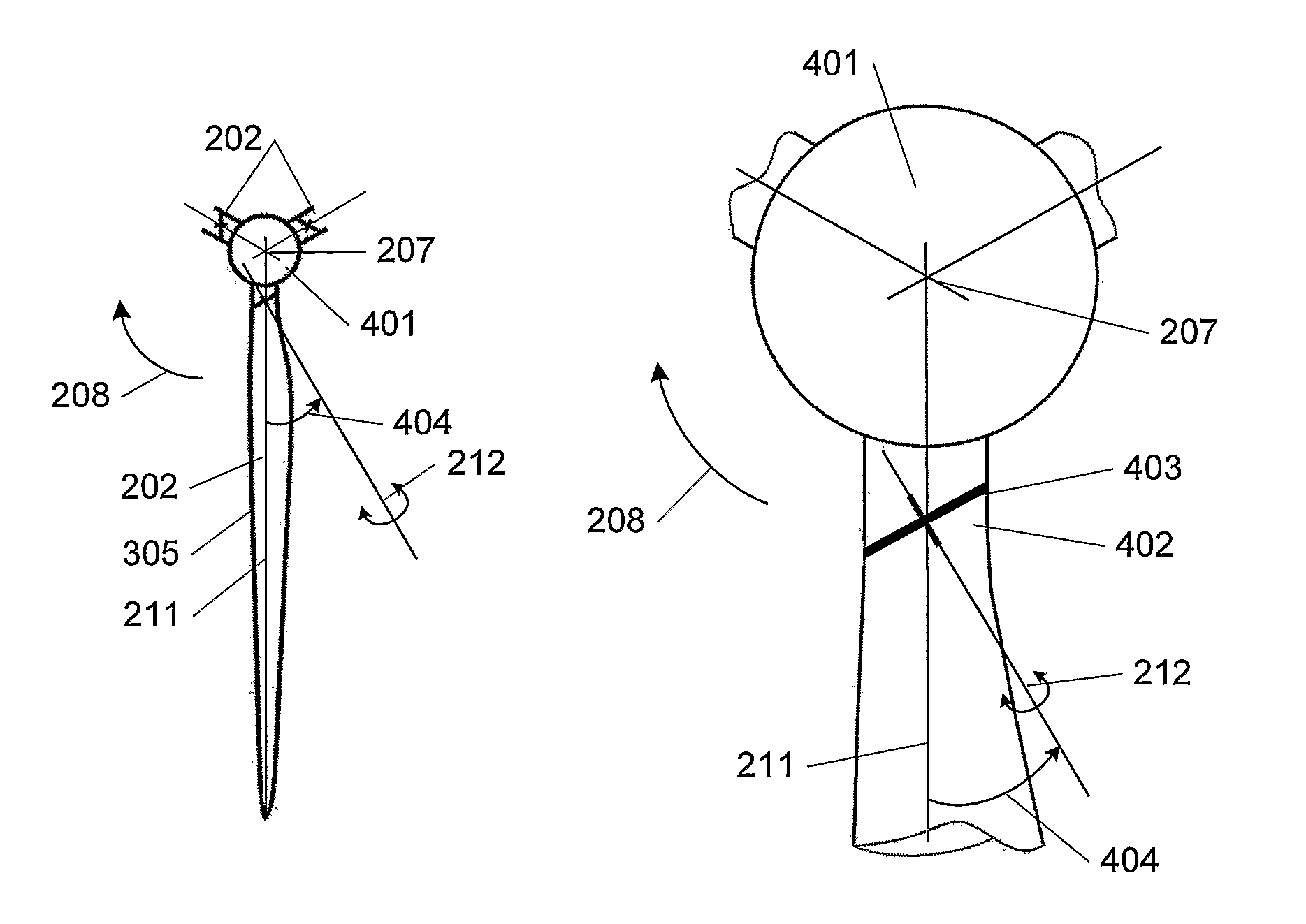
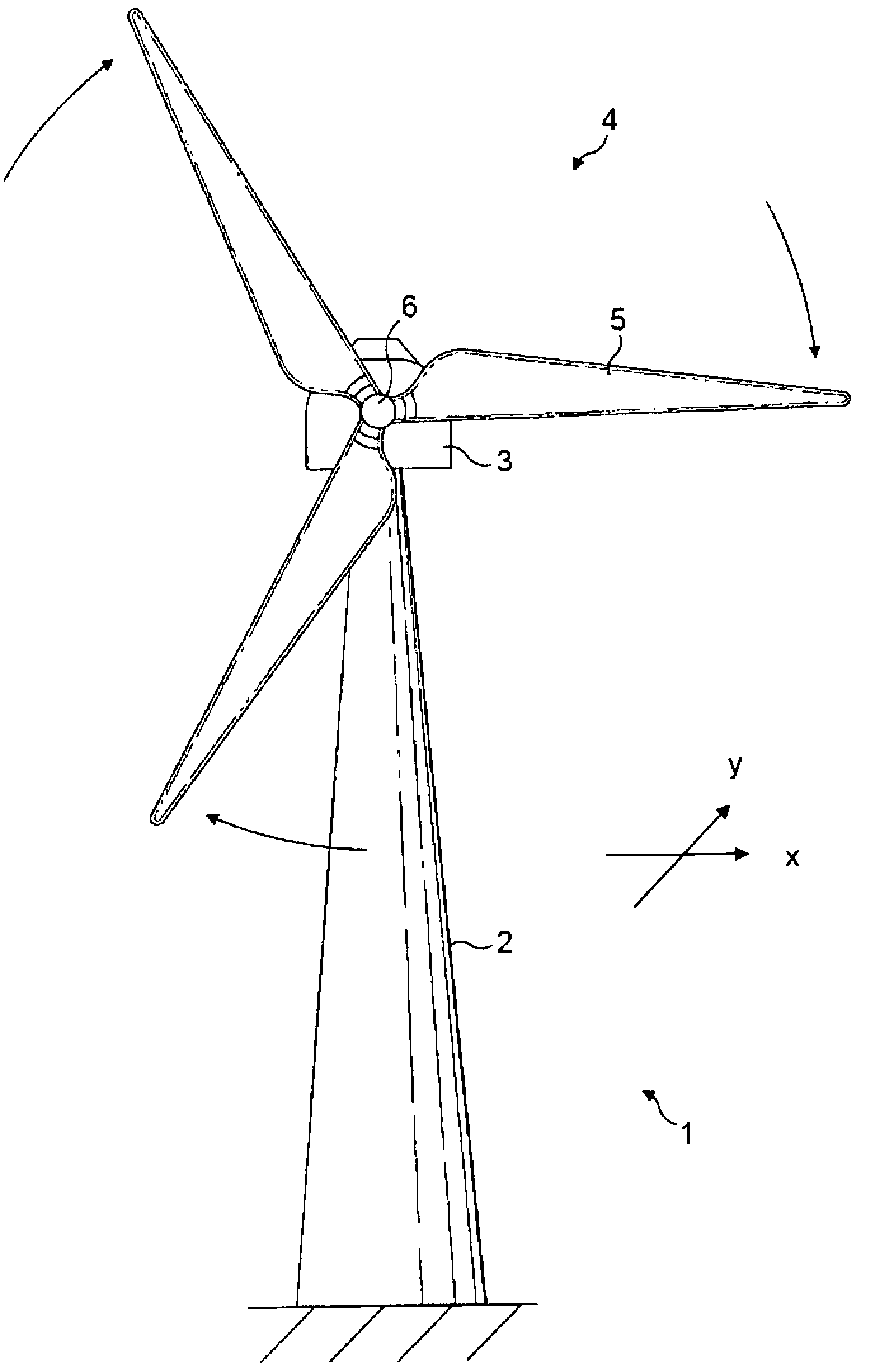
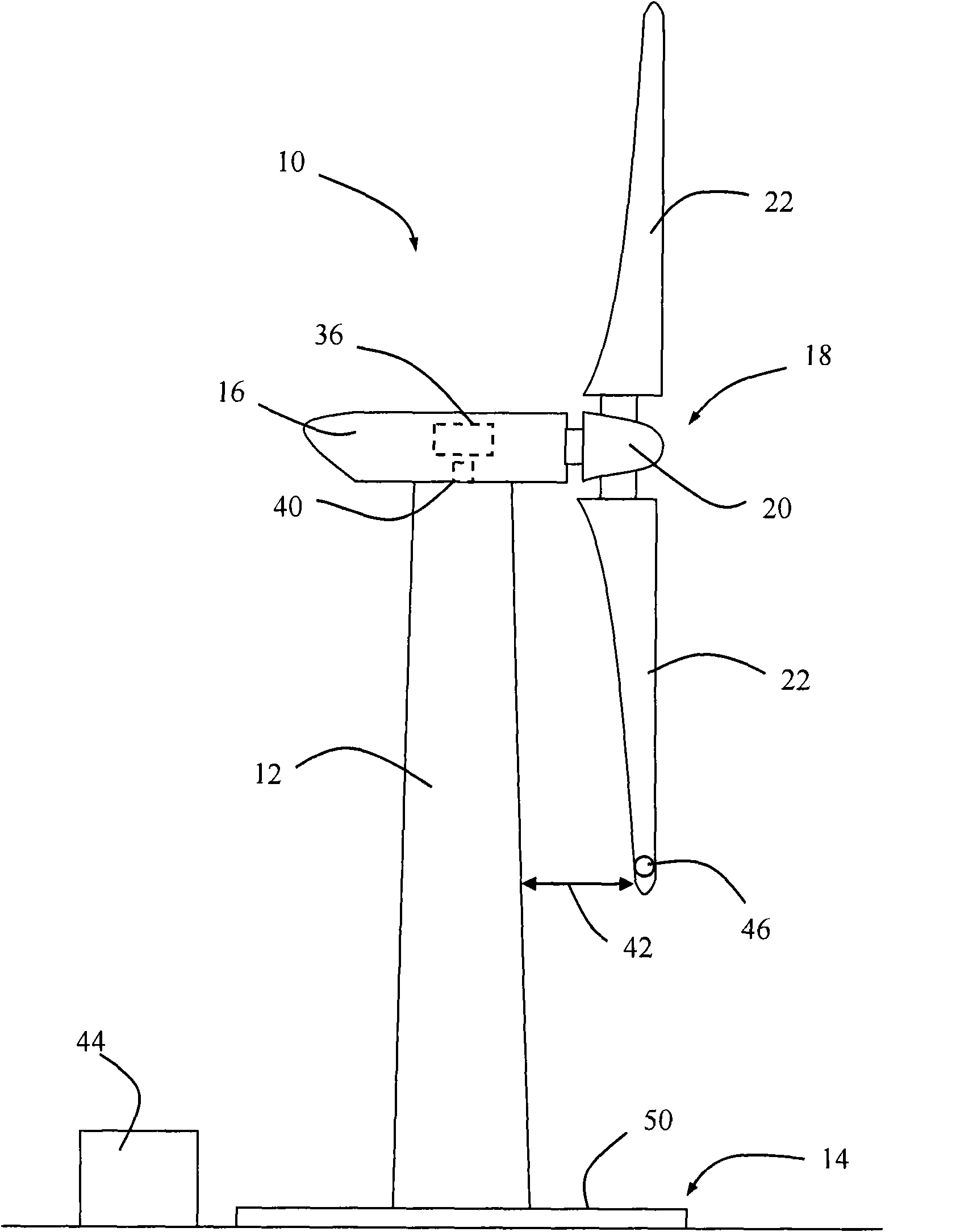
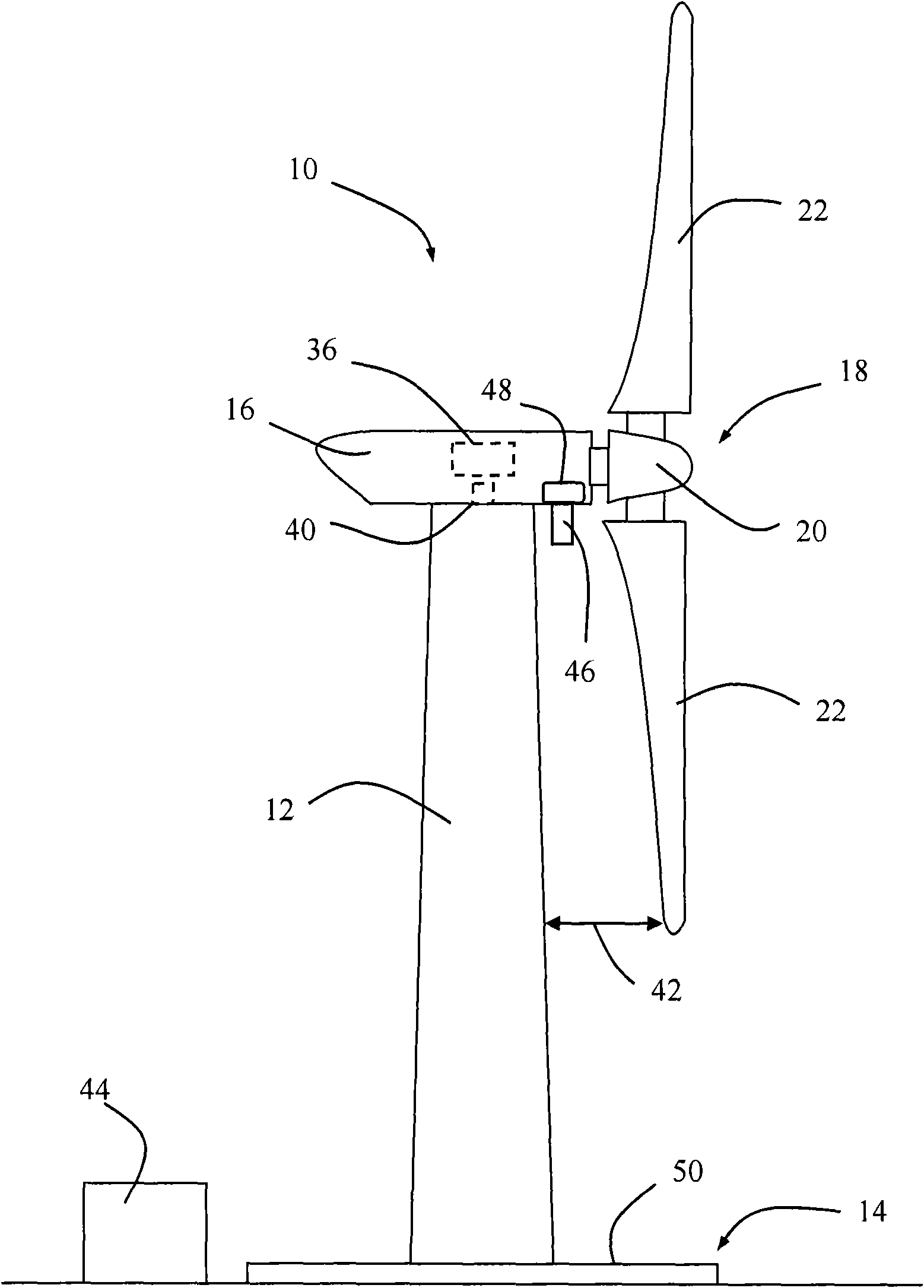
A wind turbine with a sensor that measures the out-of-plane deflection of the blades and a controller that uses the signal from the sensor to determine the risk of a tower strike. The controller takes any necessary action to prevent a tower strike when it determines that the risk of a strike is high. The sensor can include strain gages or accelerometers mounted on the blades or it can include a fixed sensor mounted on the side of the tower to measure tower clearance as the blade passes by. The control action taken can include pitching blades, yawing the nacelle, or stopping the turbine. The controller is preferably a fuzzy logic controller.
Owner:BOSCHE JOHN VANDEN
Wind turbine blade deflection control system
A wind turbine with a sensor that measures the out-of-plane deflection of the blades and a controller that uses the signal from the sensor to determine the risk of a tower strike. The controller takes any necessary action to prevent a tower strike when it determines that the risk of a strike is high. The sensor can include strain gages or accelerometers mounted on the blades or it can include a fixed sensor mounted on the side of the tower to measure tower clearance as the blade passes by. The control action taken can include pitching blades, yawing the nacelle, or stopping the turbine. The controller is preferably a fuzzy logic controller.
Owner:BOSCHE JOHN VANDEN
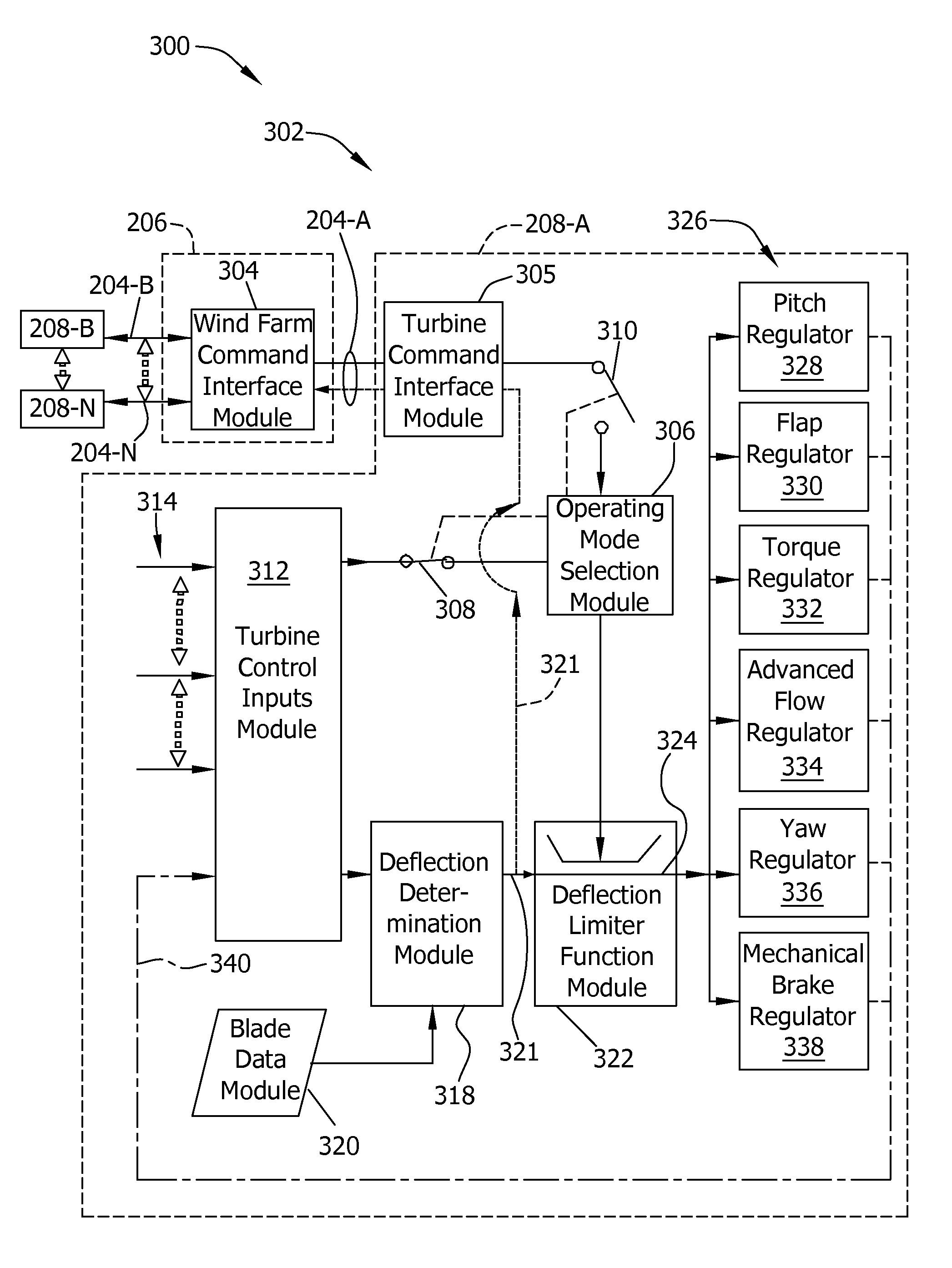
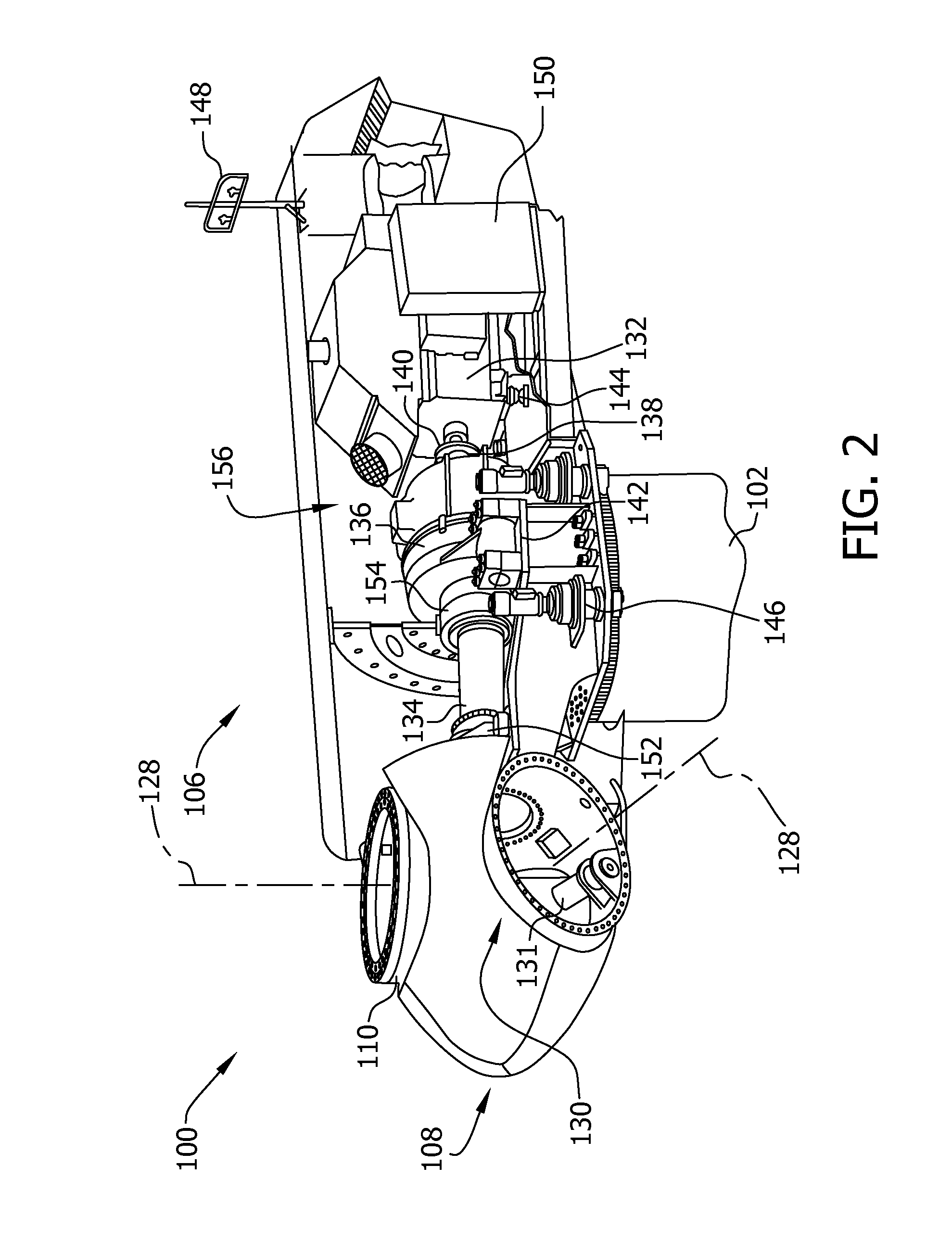
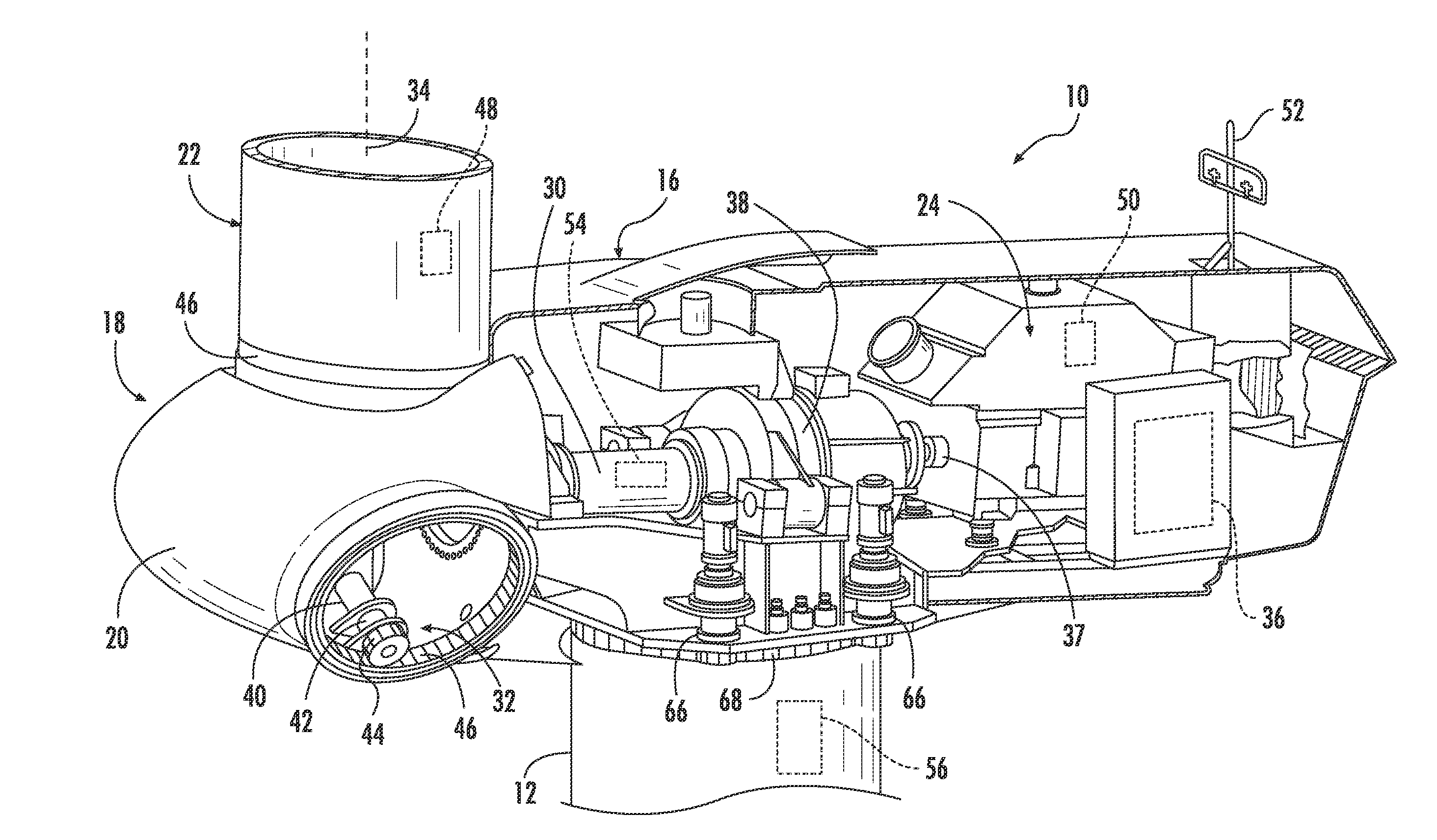
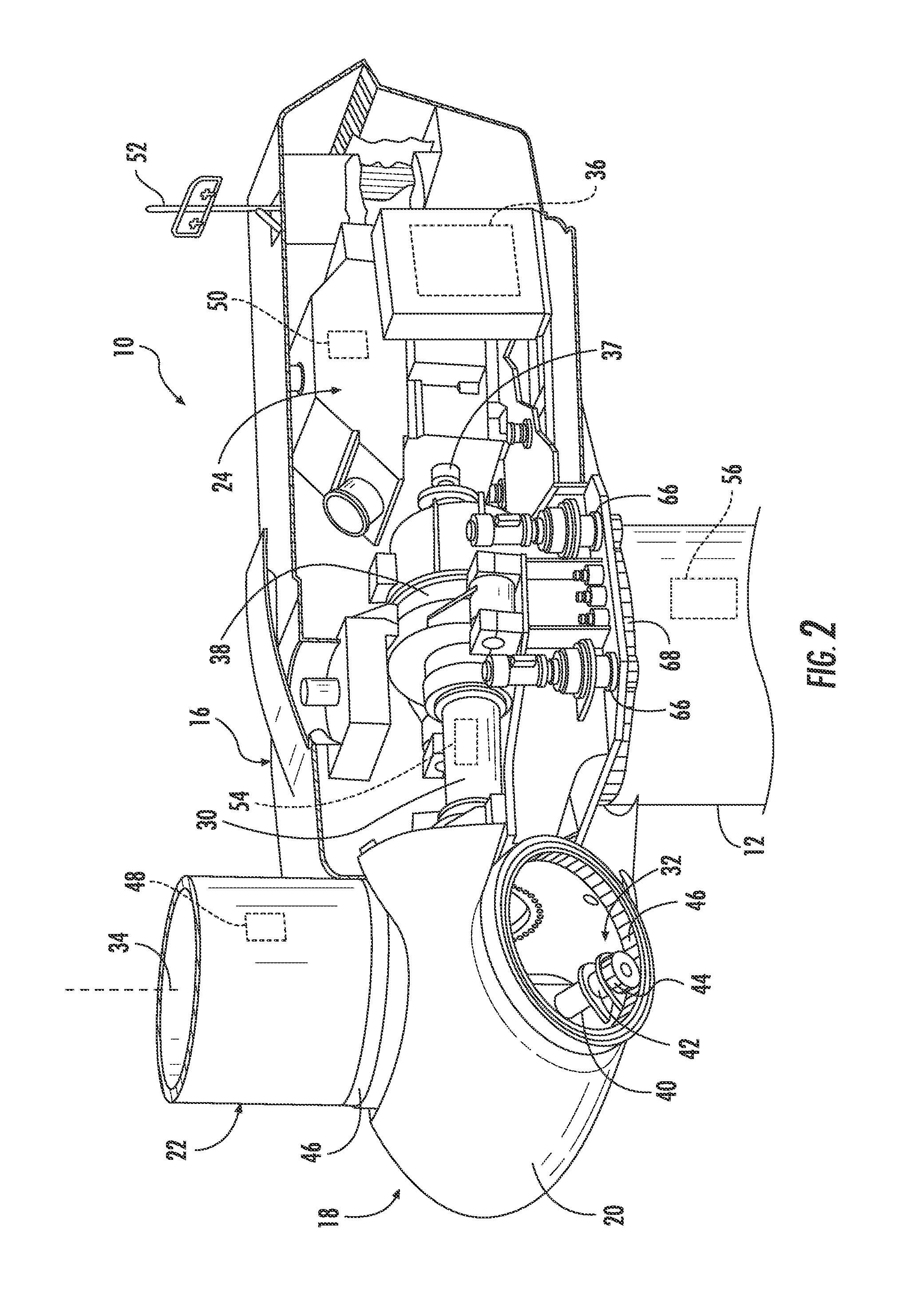
System and method for monitoring and controlling wind turbine blade deflection
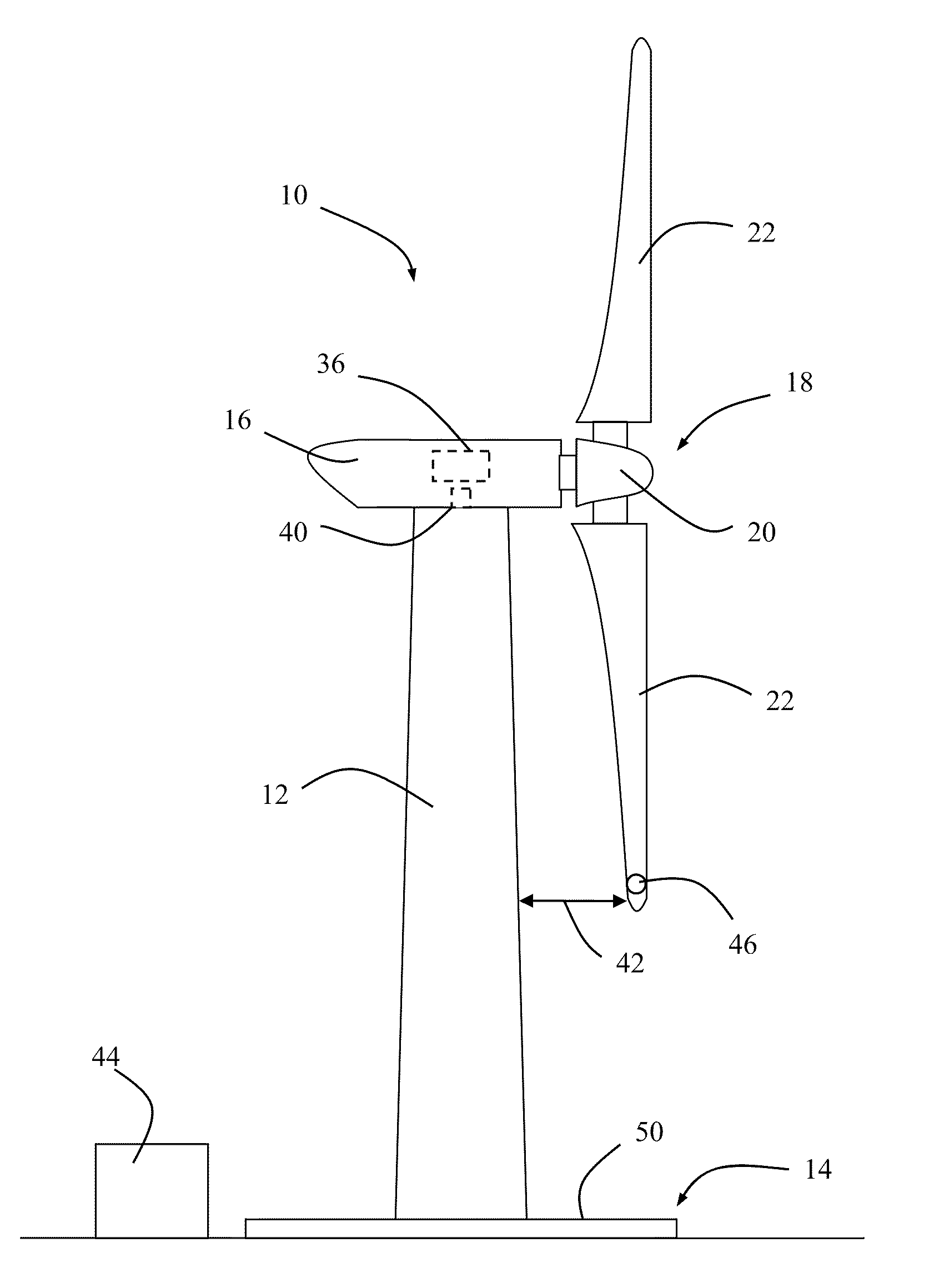
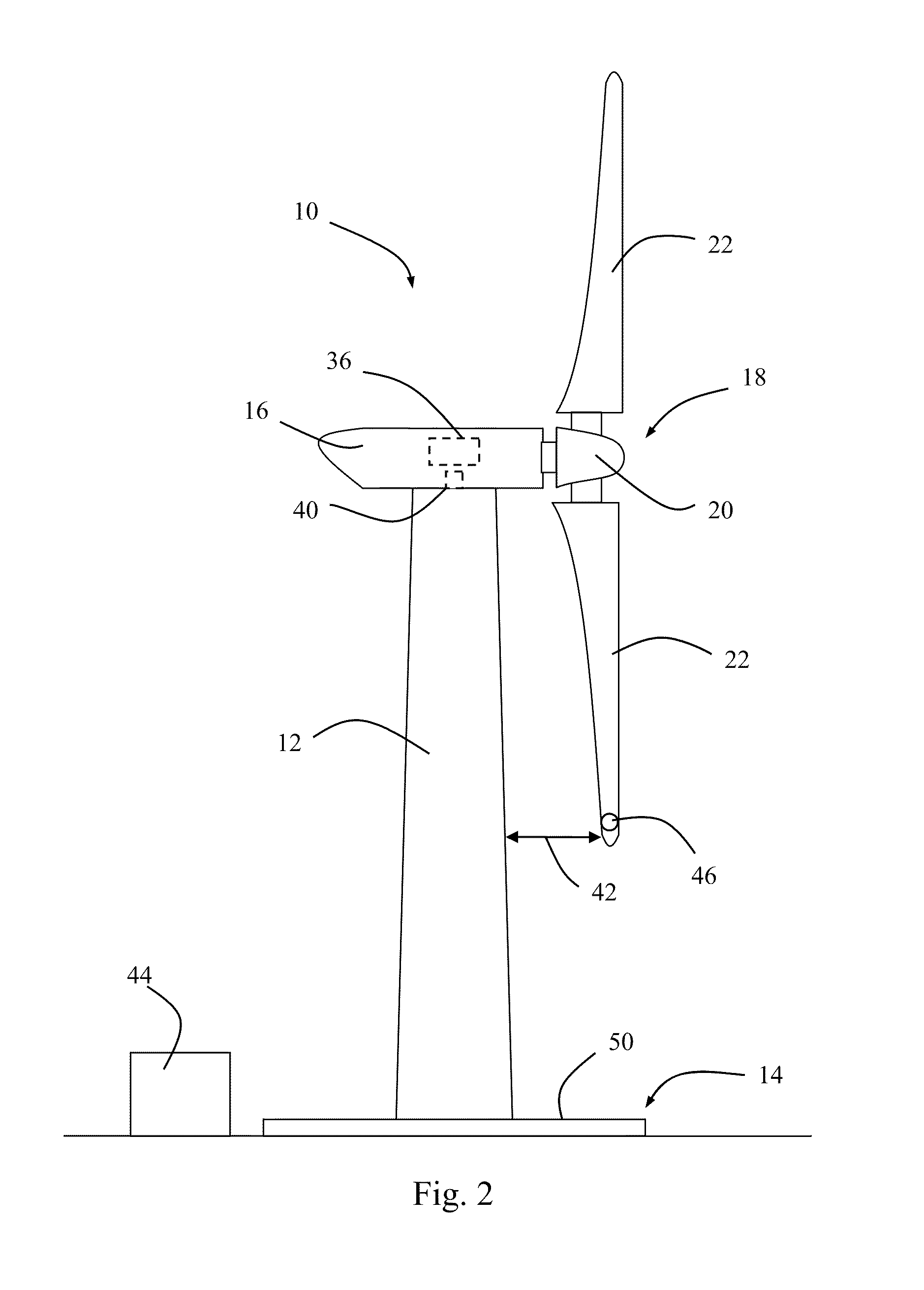
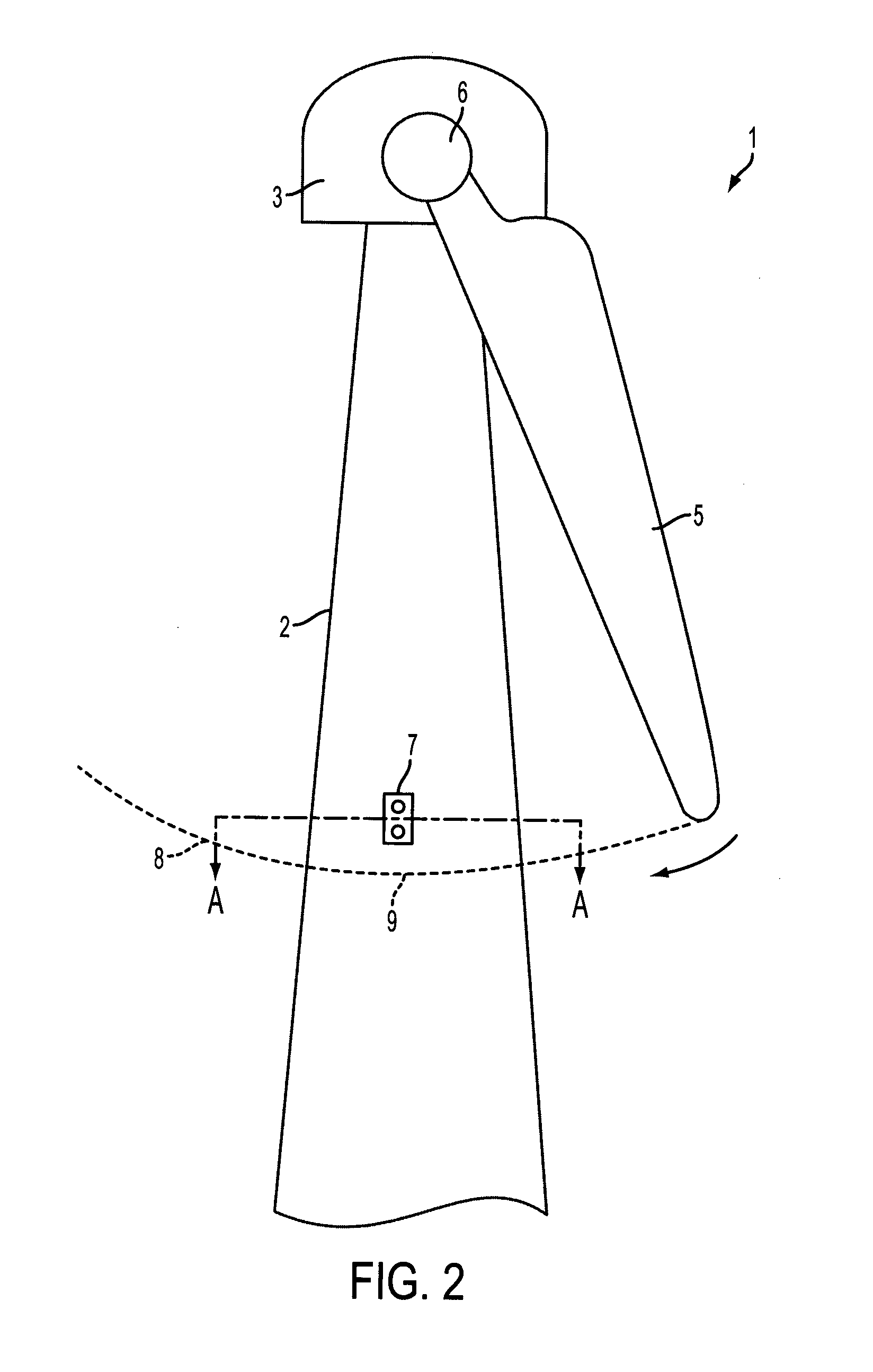
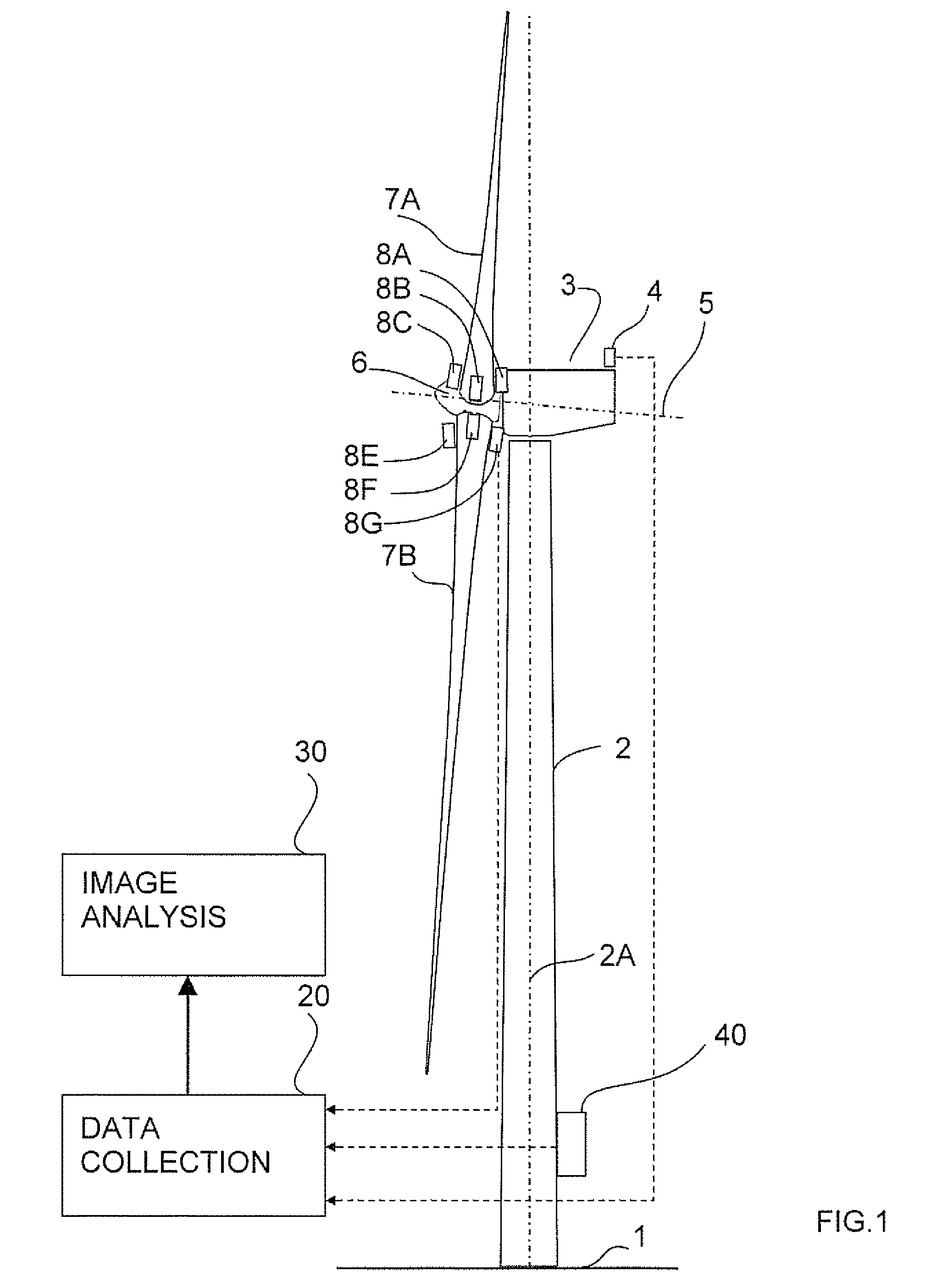
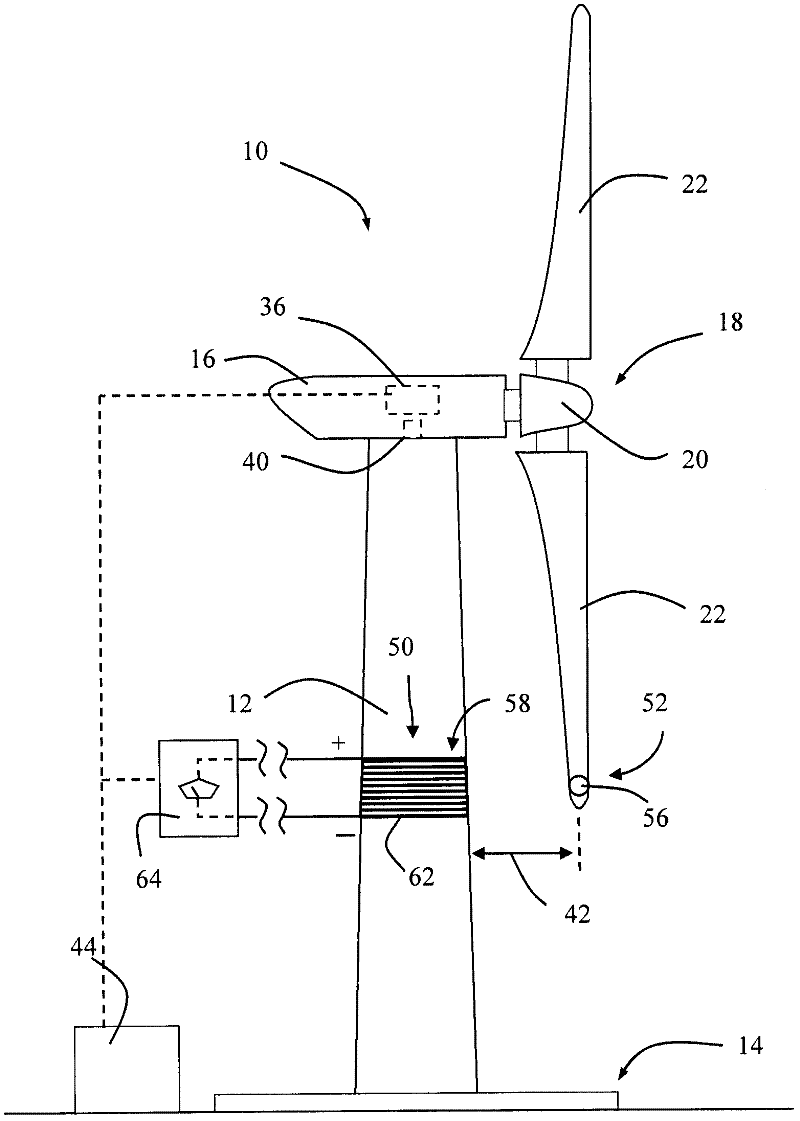
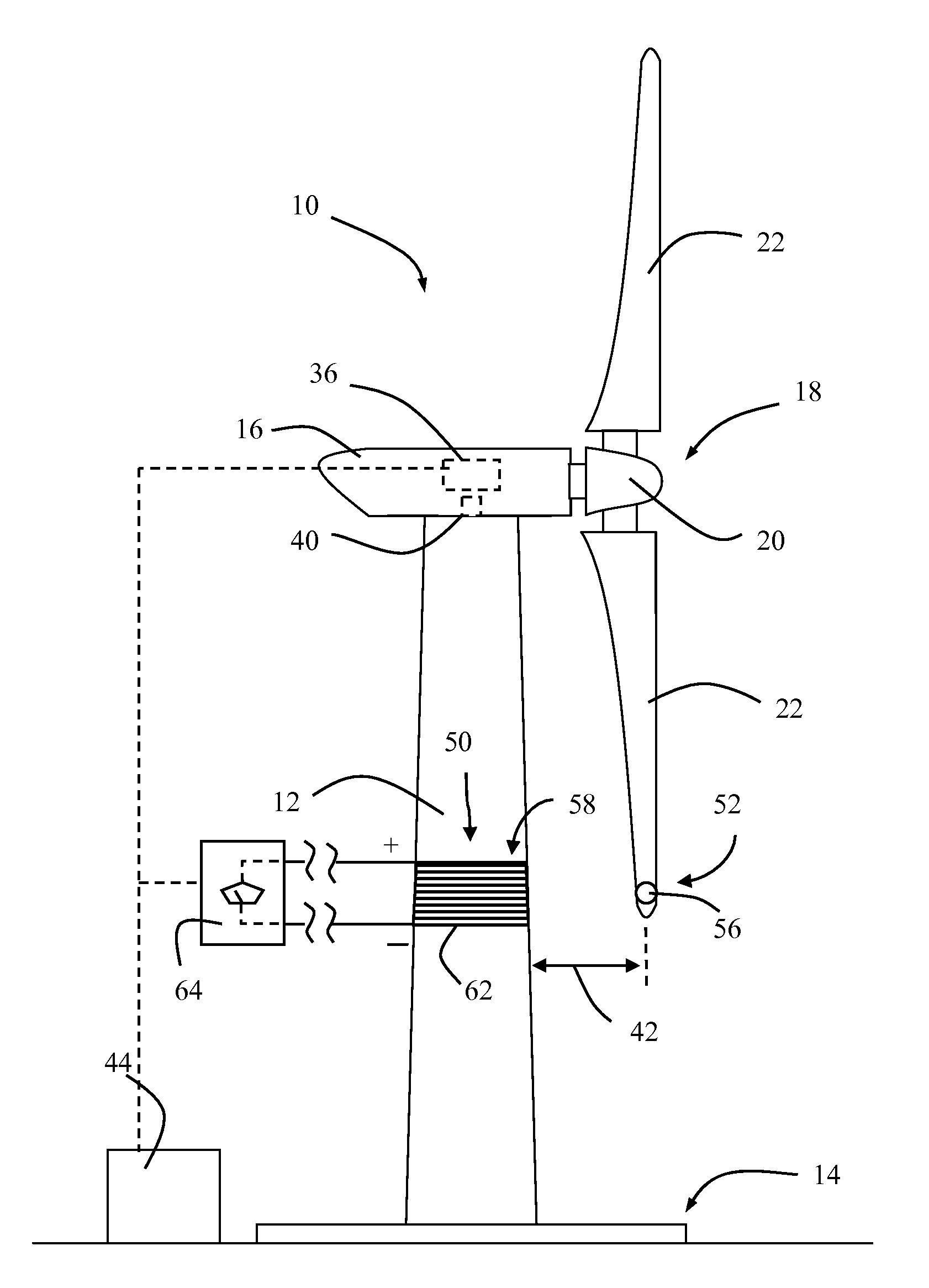
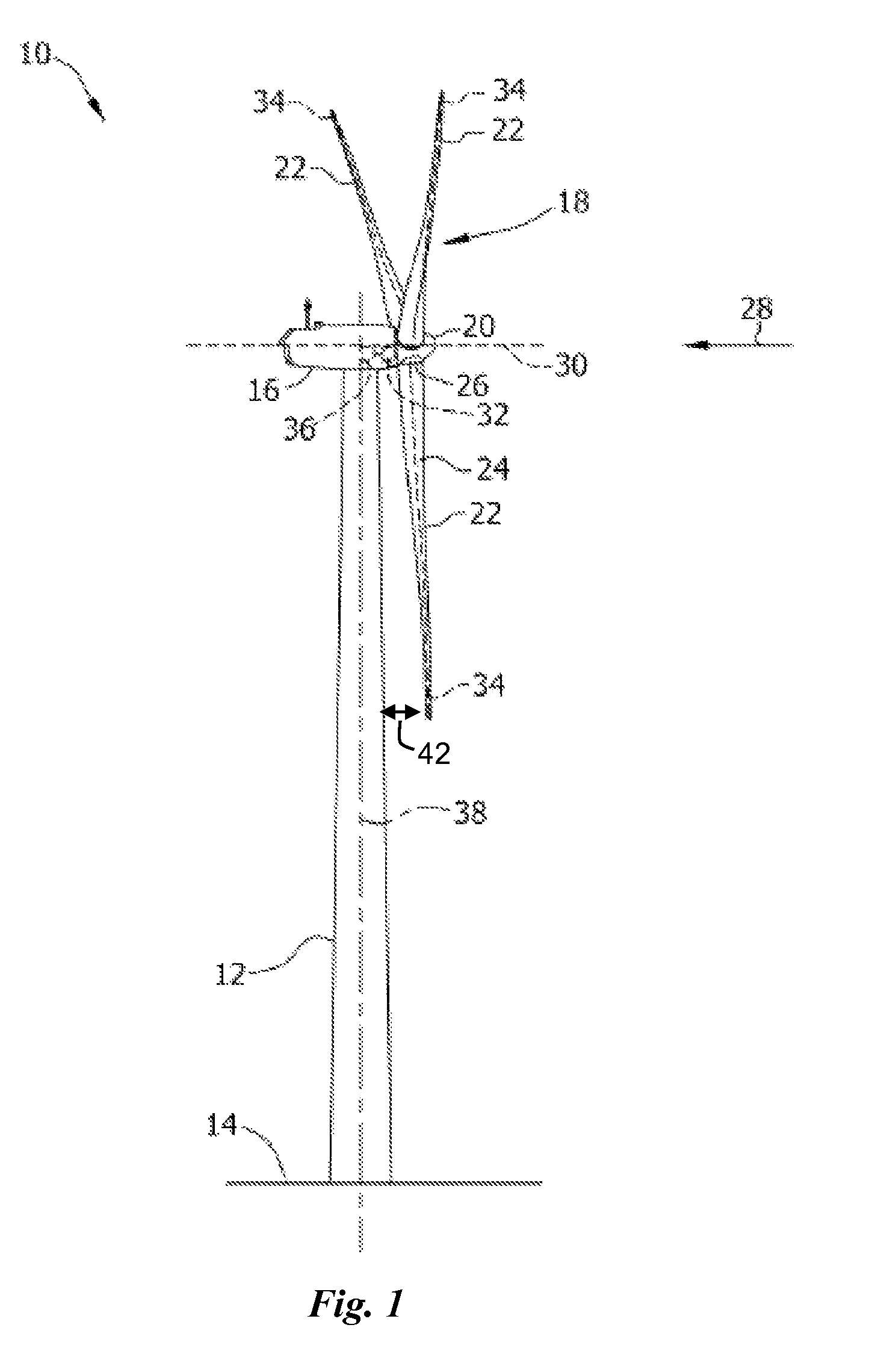
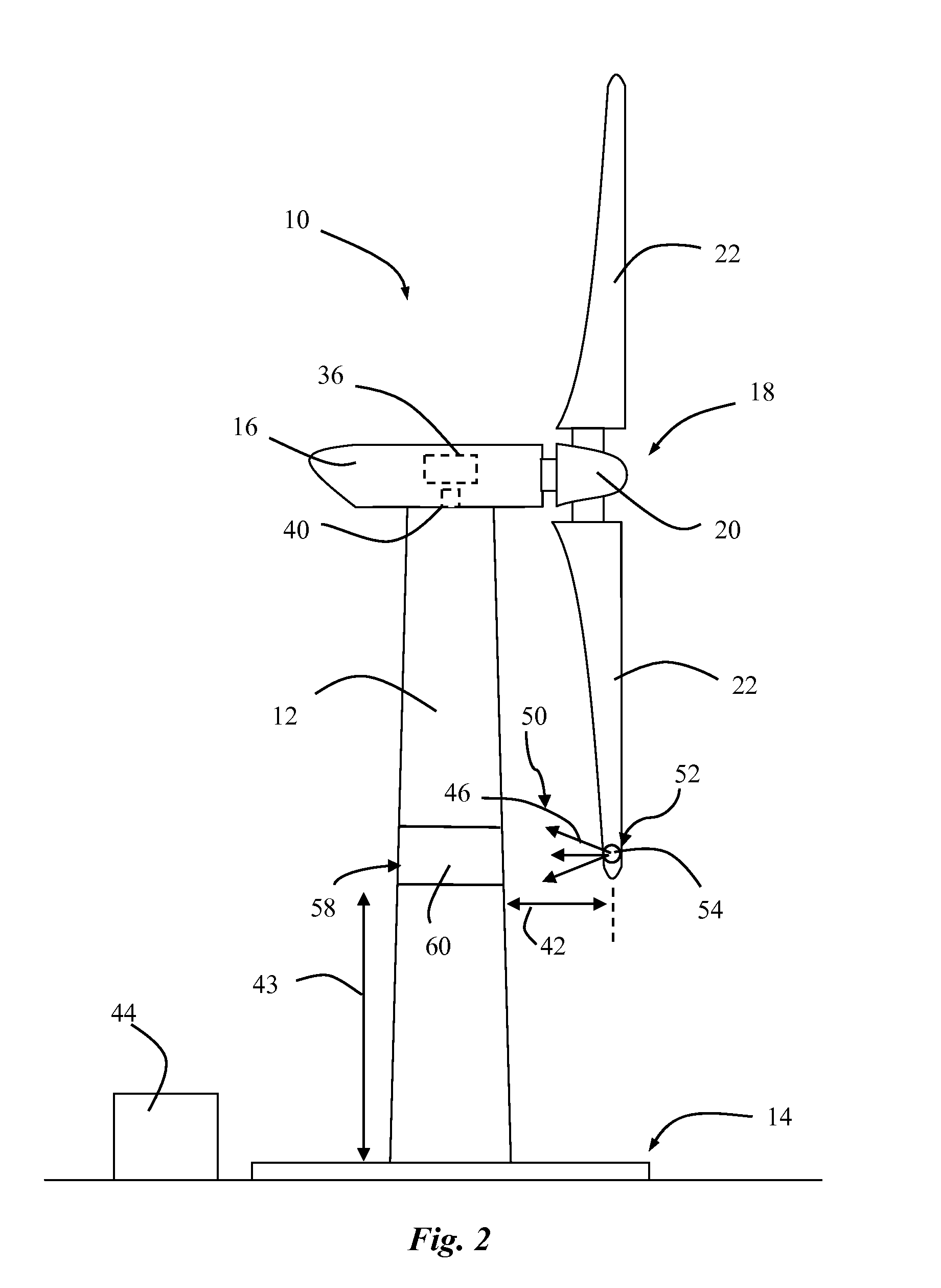
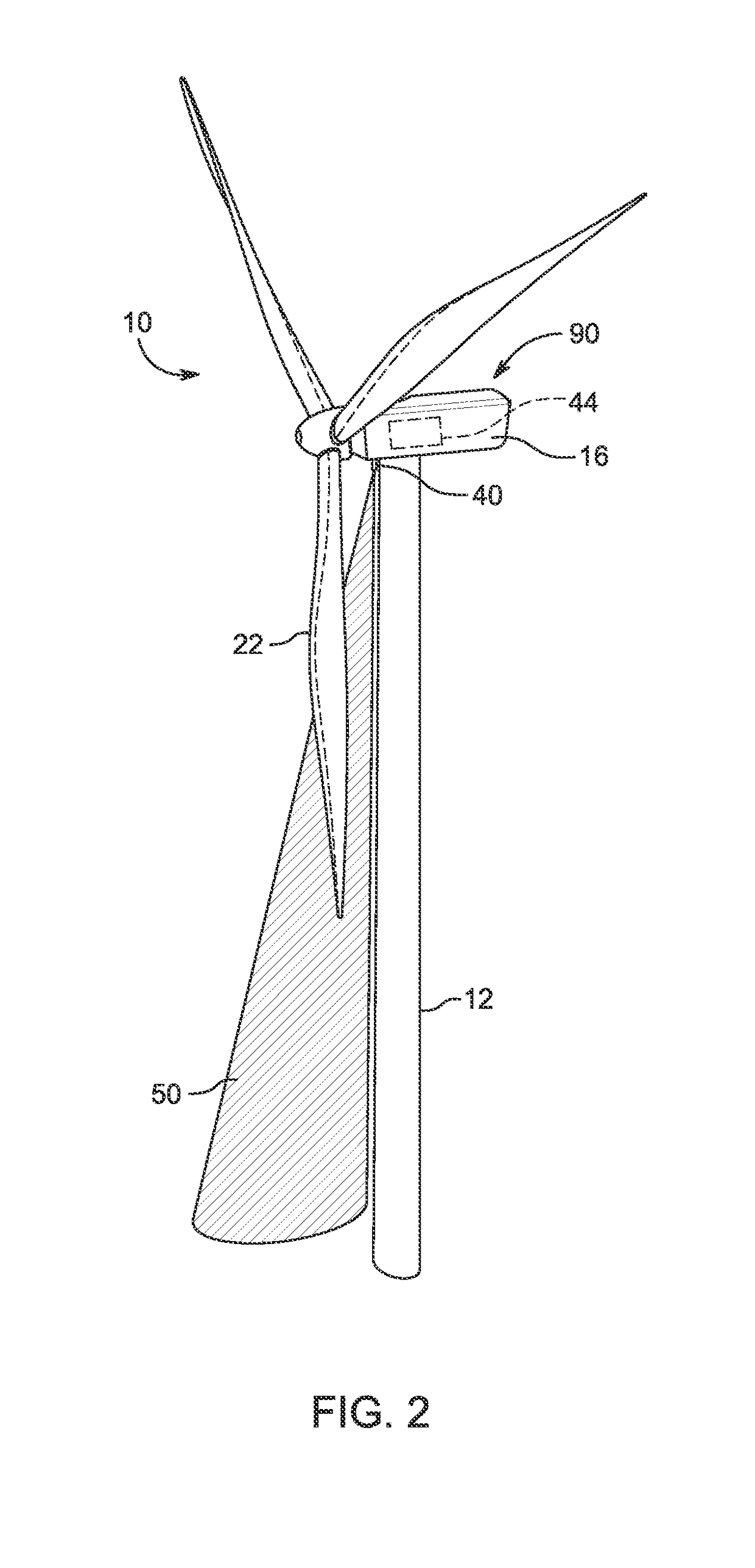
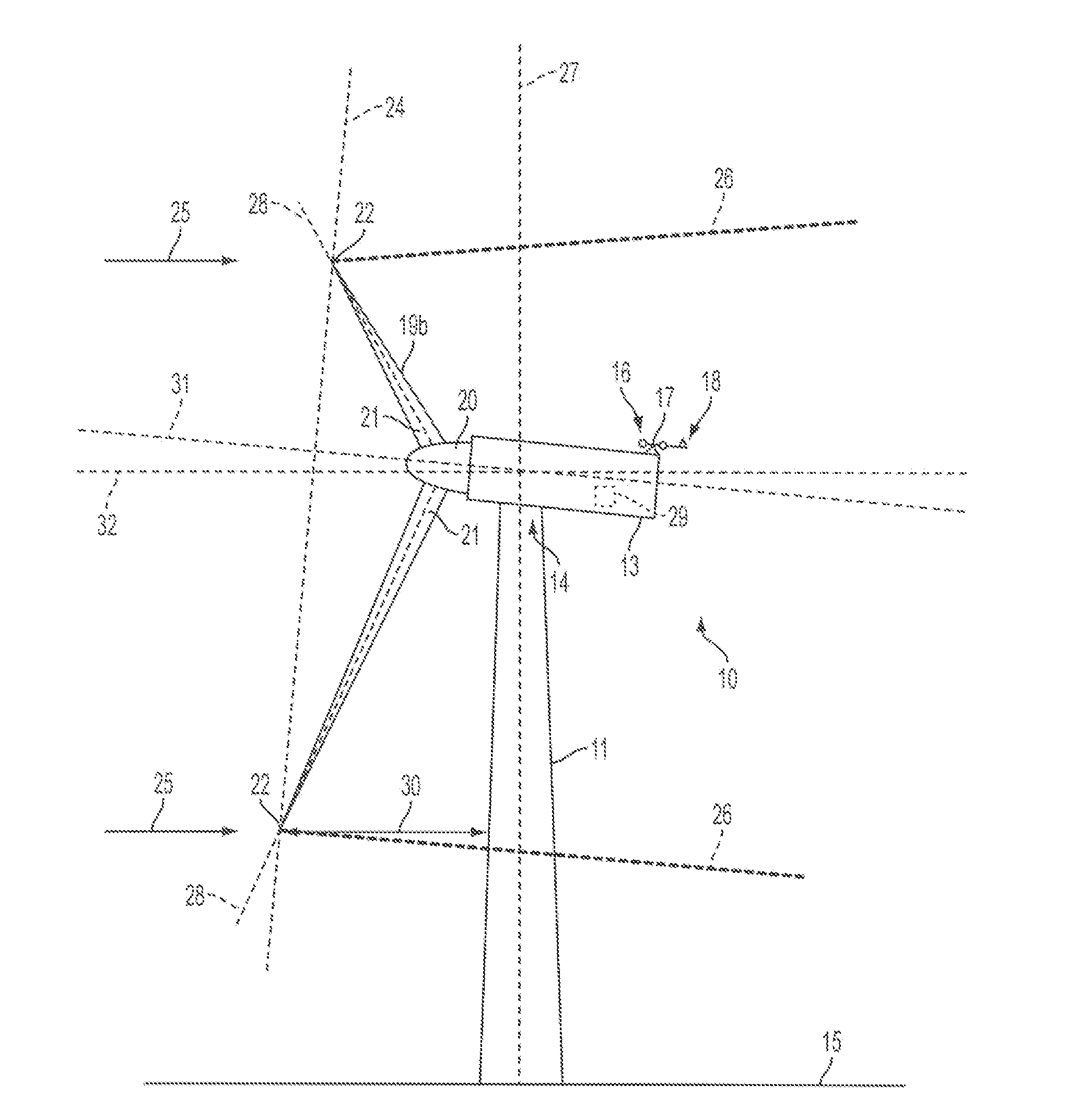
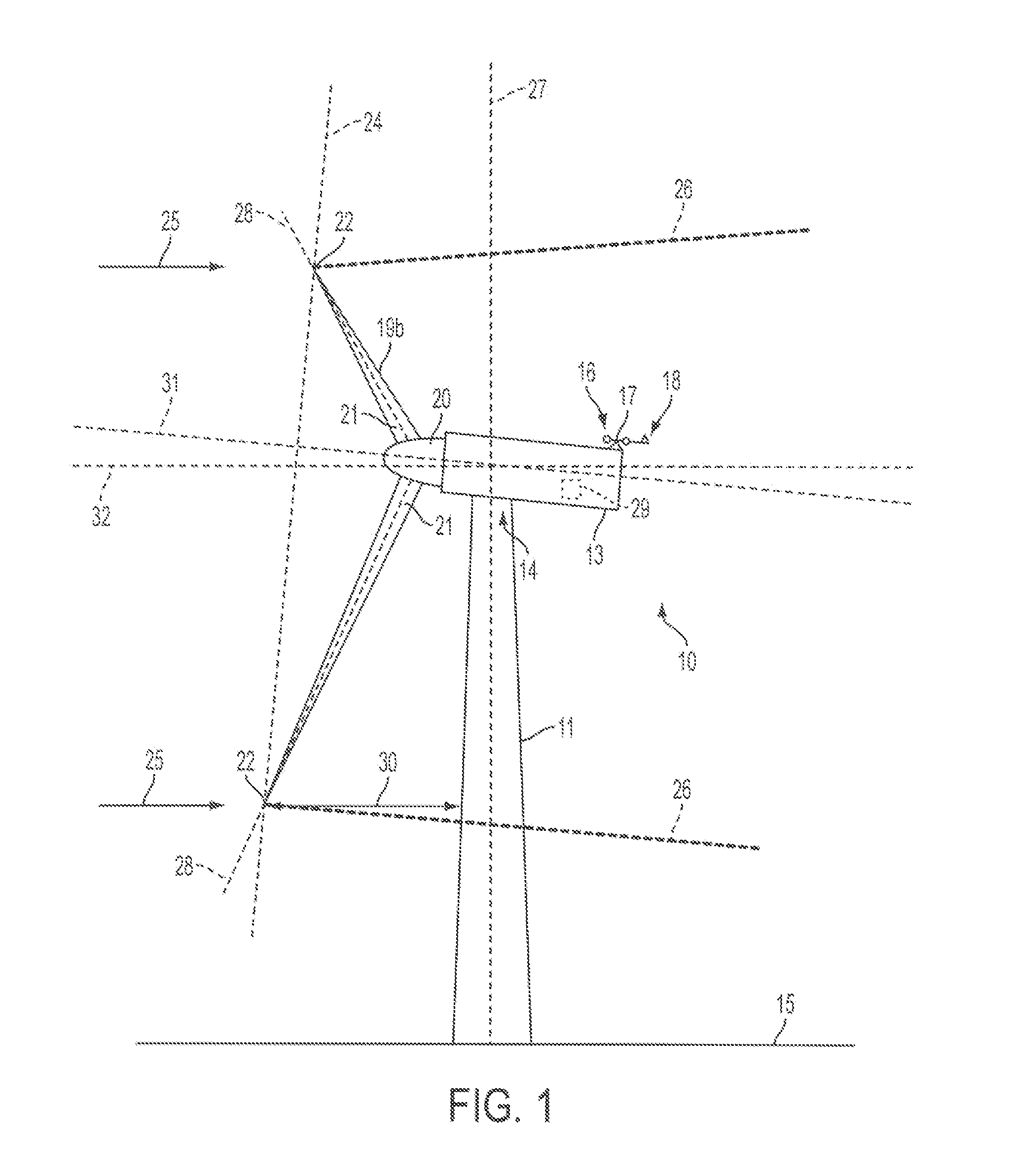
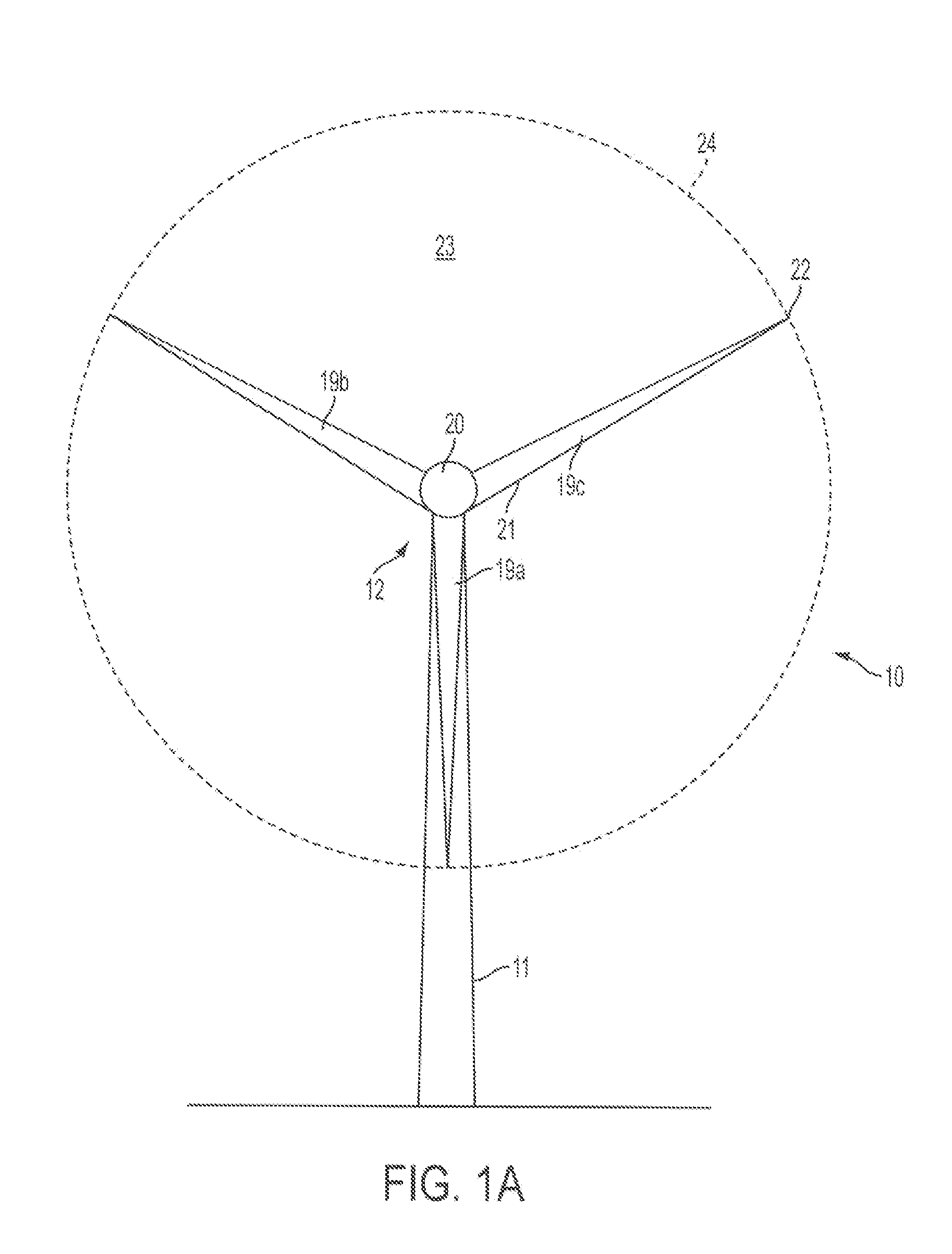
A system is disclosed for monitoring and controlling the deflection of turbine blades of a wind turbine. The system includes a passive position detecting apparatus and a controller. The passive position detecting apparatus may be configured to acquire and transmit data relating directly to a position of at least one of the turbine blades. The controller may be configured to receive the data from the passive position detecting apparatus and compare such data to a known position reference to determine turbine blade deflection.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cyclic Pitch Control System for Wind Turbine Blades
InactiveUS20130045098A1Enhance tower shadow effectLess powerAvoid excessive blade deflectionPropellersLoop controlControl system
In a wind turbine, an open loop control algorithm for incrementally or positively adjusting the pitch angles of individual rotor blades may be used to increase spacing between the base of the turbine tower and an approaching blade tip. As each rotating blade passes in front of the tower base, a minimum clearance distance may be assured to avoid blade tip strikes of the base. In accordance with at least one embodiment of the control algorithm, as each blade approaches the tower base, it may be feathered to reduce its power loading, and to facilitate increased clearance beyond the normal unloading or feathering produced by the so-called tower shadow effect. To offset resultant loss of torque, the remaining blades may be correspondingly pitched toward power, i.e. into the wind, to balance and / or smooth out the overall rotor torque curve, and thus to avoid torque ripples.
Owner:CLIPPER WINDPOWER INC
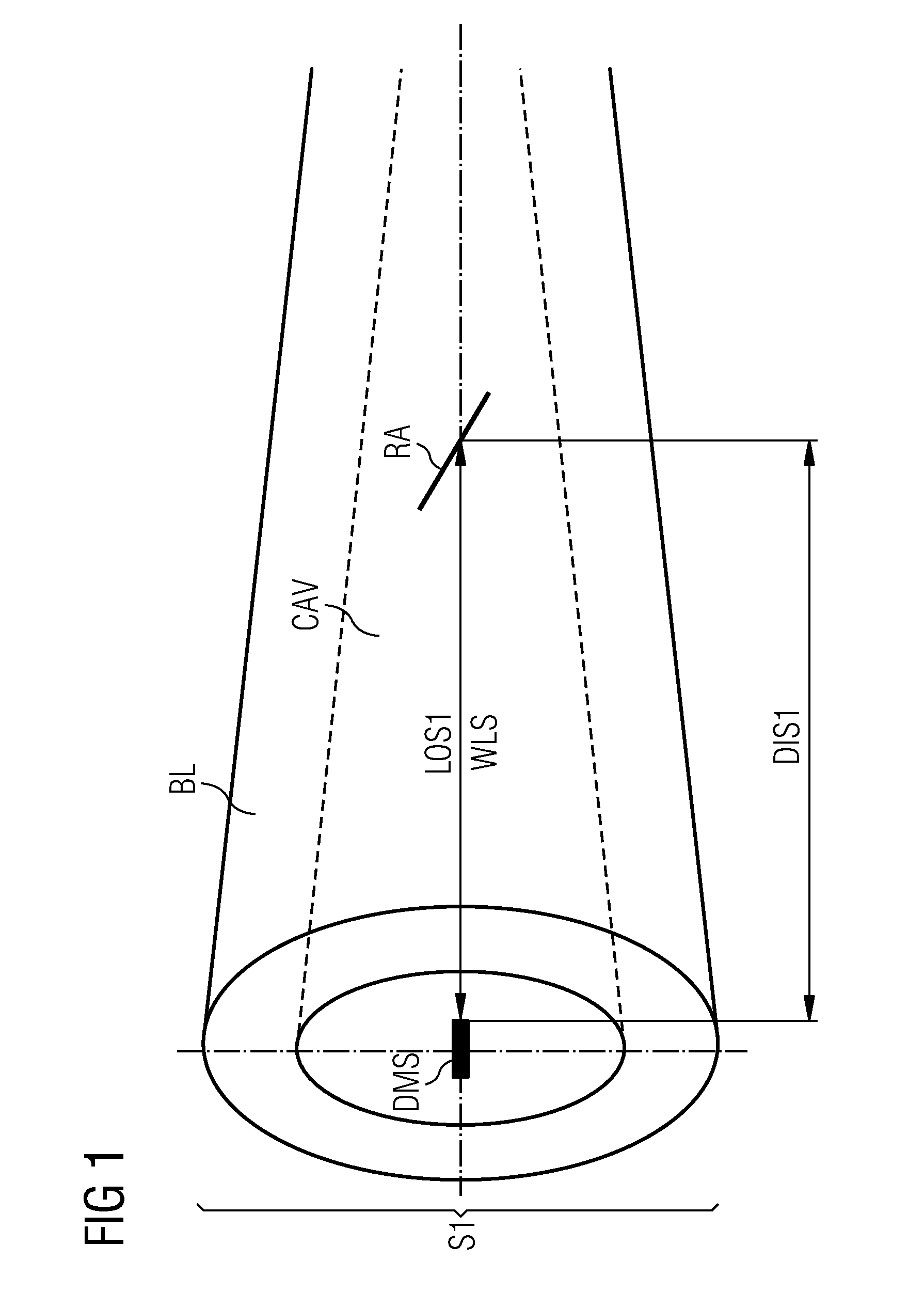
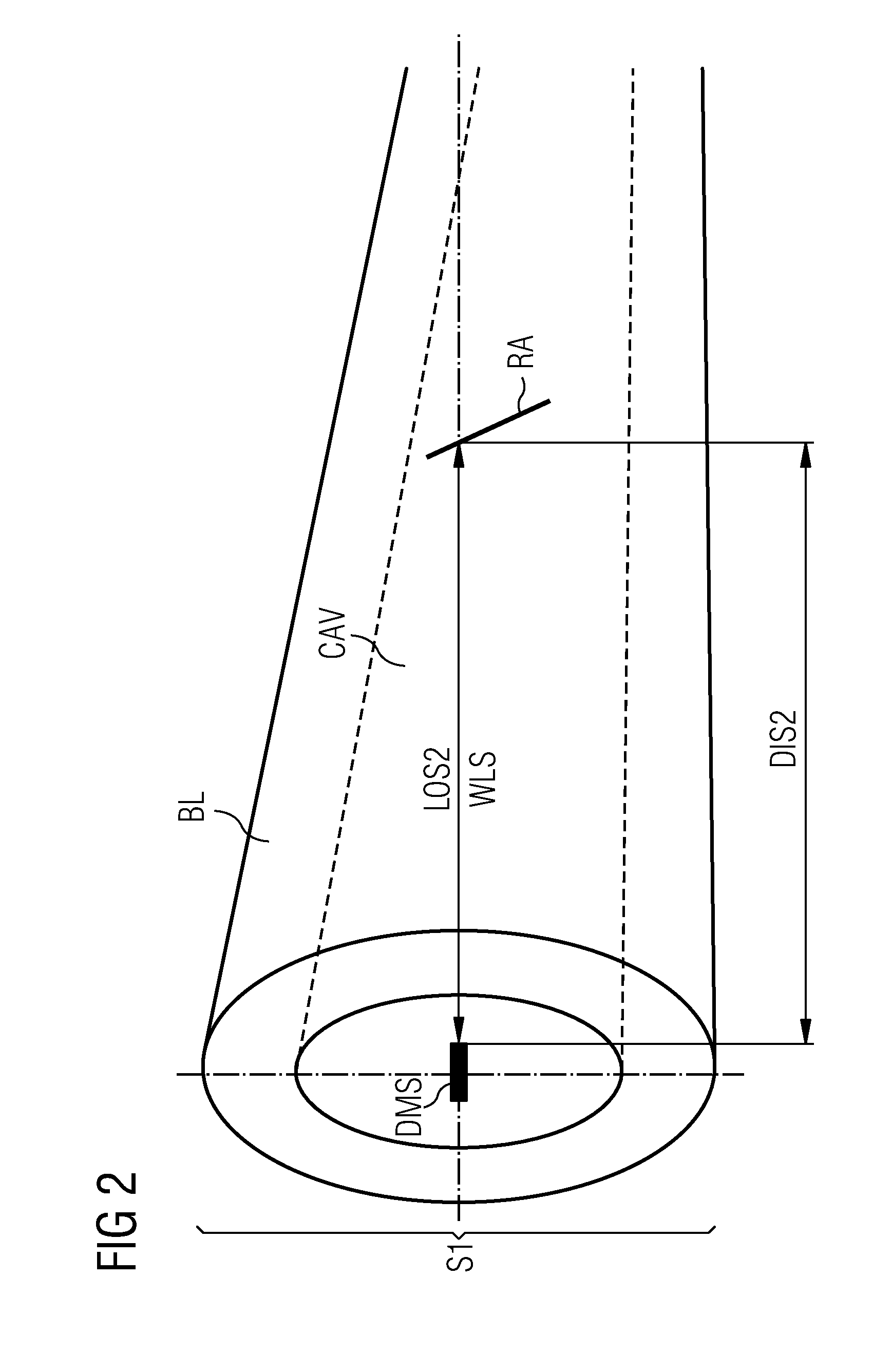
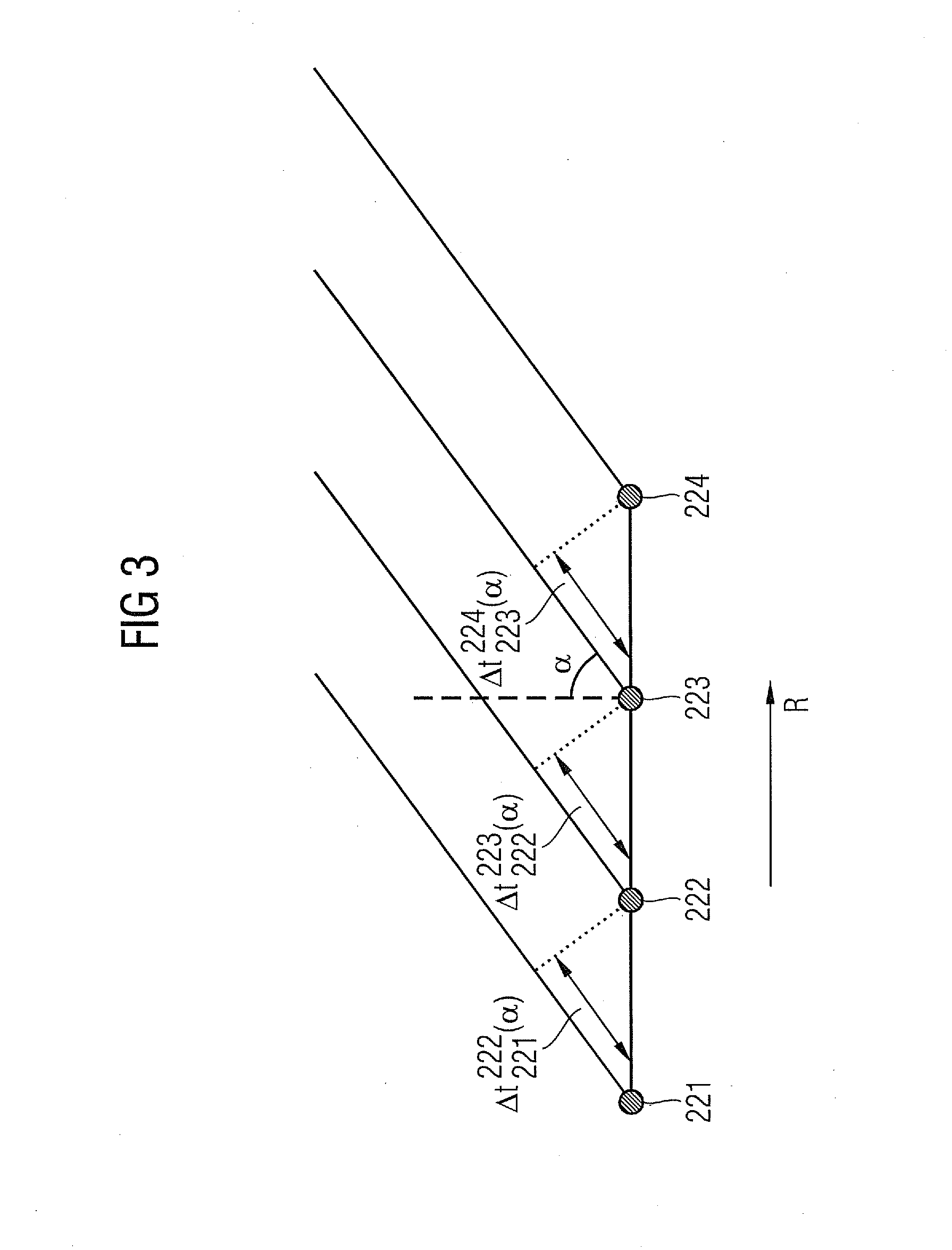
Method and arrangement to measure the deflection of a wind turbine blade
InactiveUS20100253569A1Improve securityReduce stability overheadAvoid excessive blade deflectionOptical rangefindersTurbine bladeEngineering
A method and arrangement to measure the deflection of a blade of a wind-turbine are provided. The blade comprises a cavity inside the blade. A reflector, which is located inside the cavity of the blade, is coupled by a wireless signal with a distance-measurement-device. The distance-measurement-device uses the wireless signal to measure the distance between the distance-measurement-device and the reflector. A line of sight is established and maintained between the distance-measurement-device and the reflector even when the blade is deflected. The reflector is inclined relative to the line of sight in a way, that a lateral movement of the reflector relative to the line of sight results in a change of the distance between the distance-measurement-device and the reflector, while the lateral movement is caused by an deflection of the blade. The distance-measurement-device is designed to measure the change of the distance, which is used to determine the deflection of the blade.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
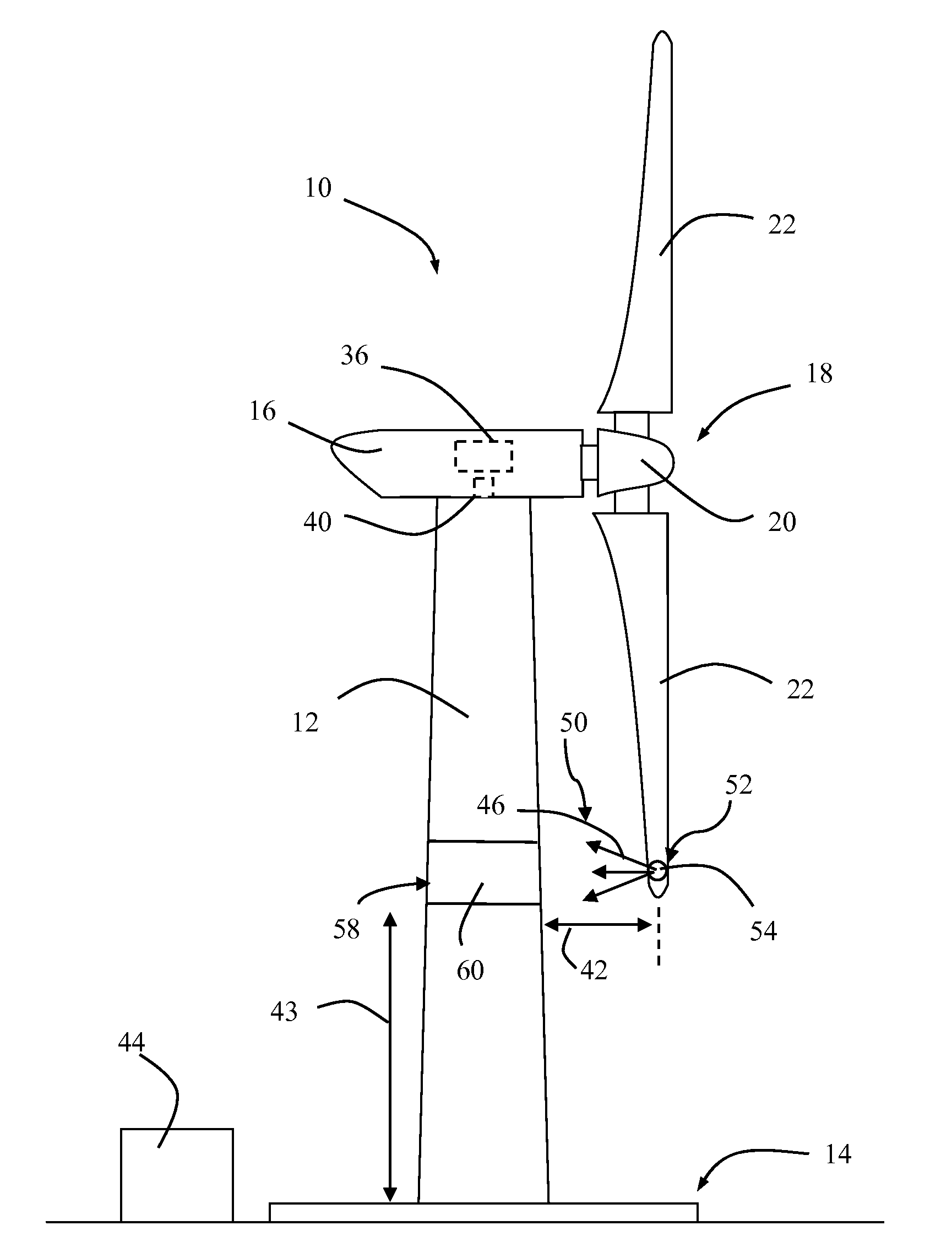
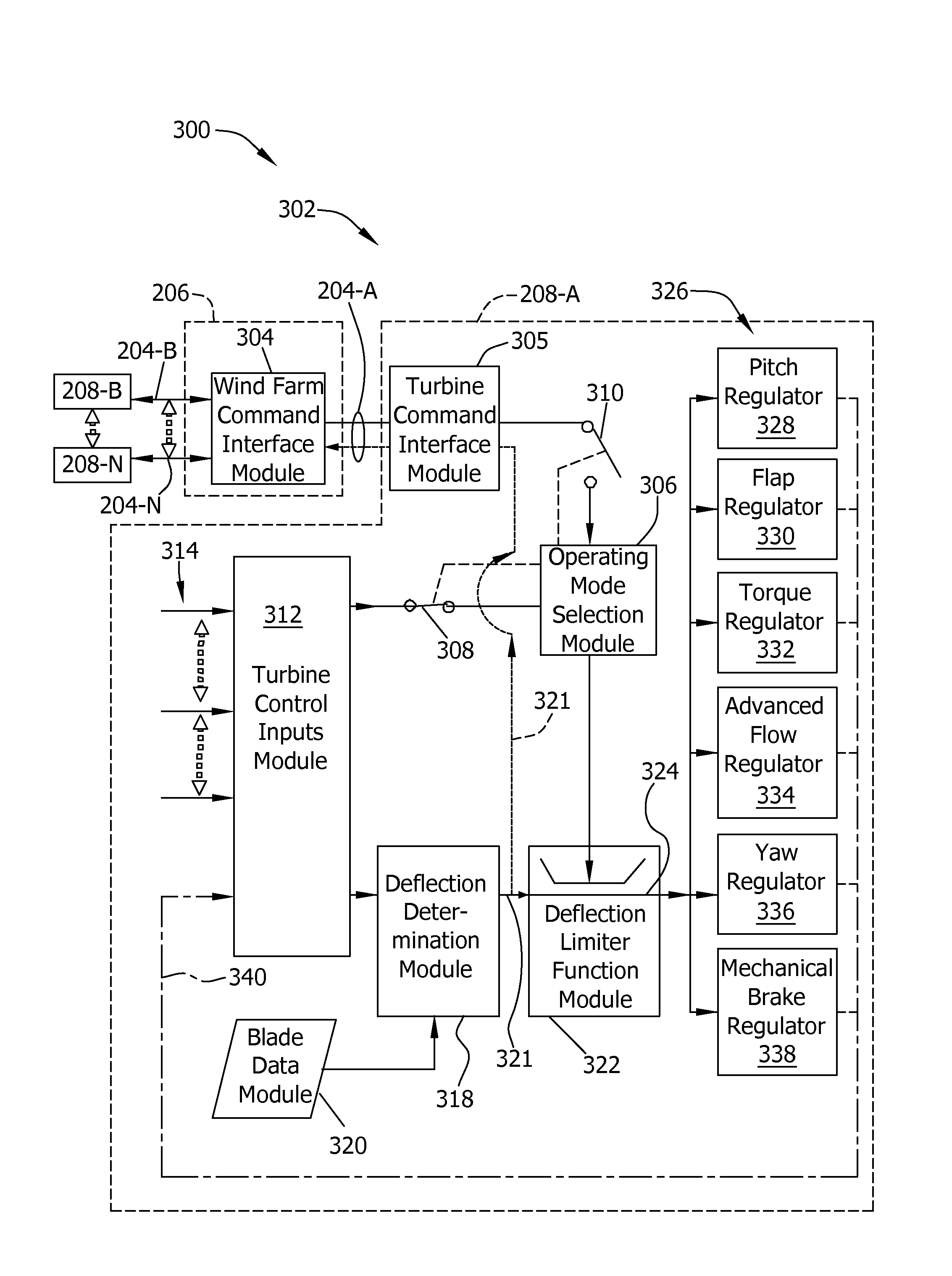
Wind turbine farm and method of controlling at least one wind turbine
A method of controlling a wind turbine that includes at least one rotor shaft and at least one blade operatively coupled to the rotor shaft includes measuring a first wind turbine operational condition that is representative of a blade deflection value and generating a first operational condition signal based on that first wind turbine operational condition. The wind turbine also includes a drive train including at least one rotor shaft and an electric generator. The method also includes measuring at least one second wind turbine operational condition and generating at least one second operational condition signal. The method further includes changing the blade deflection value by changing the second operational condition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System for detecting proximity between a wind turbine blade and a tower wall
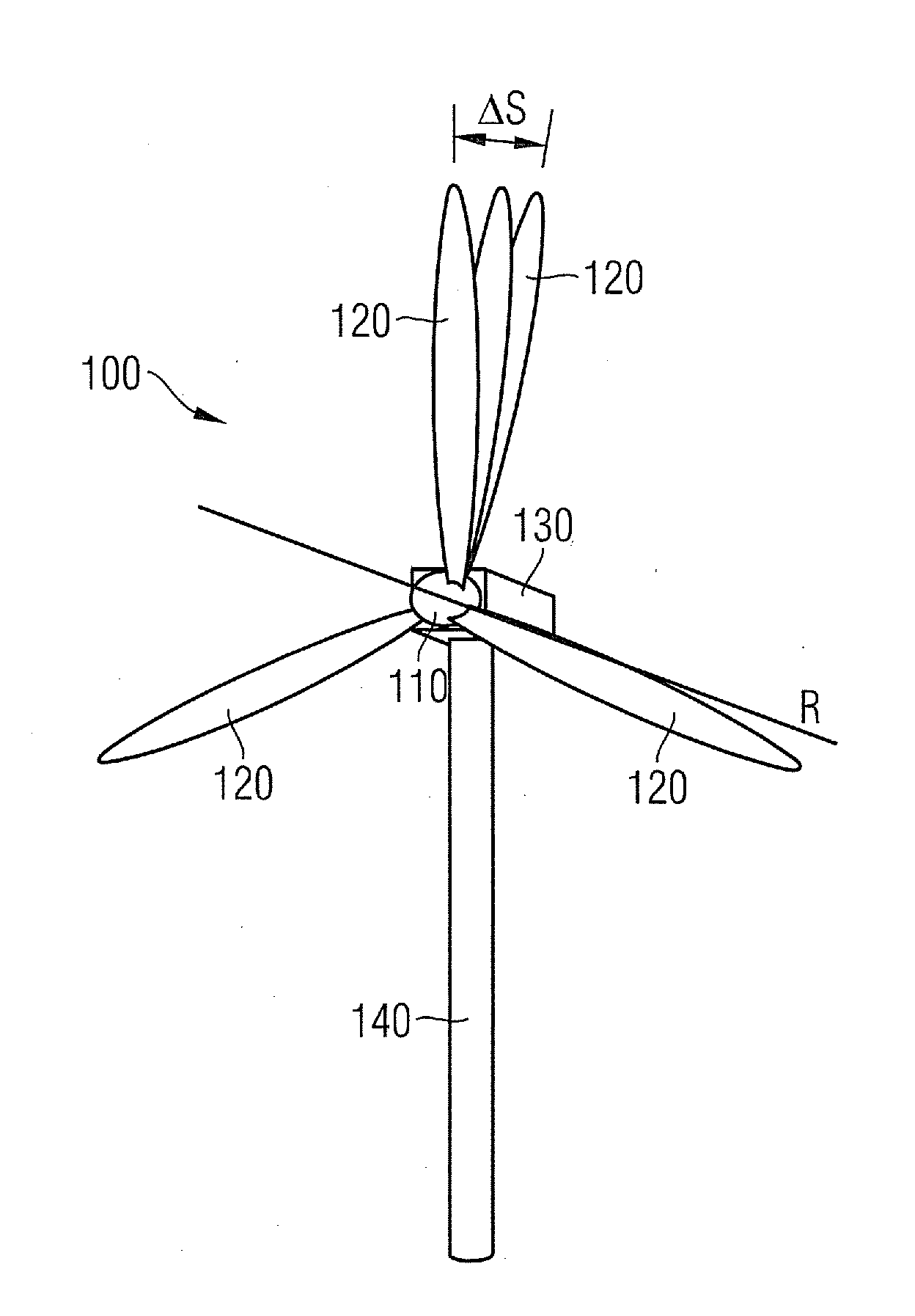
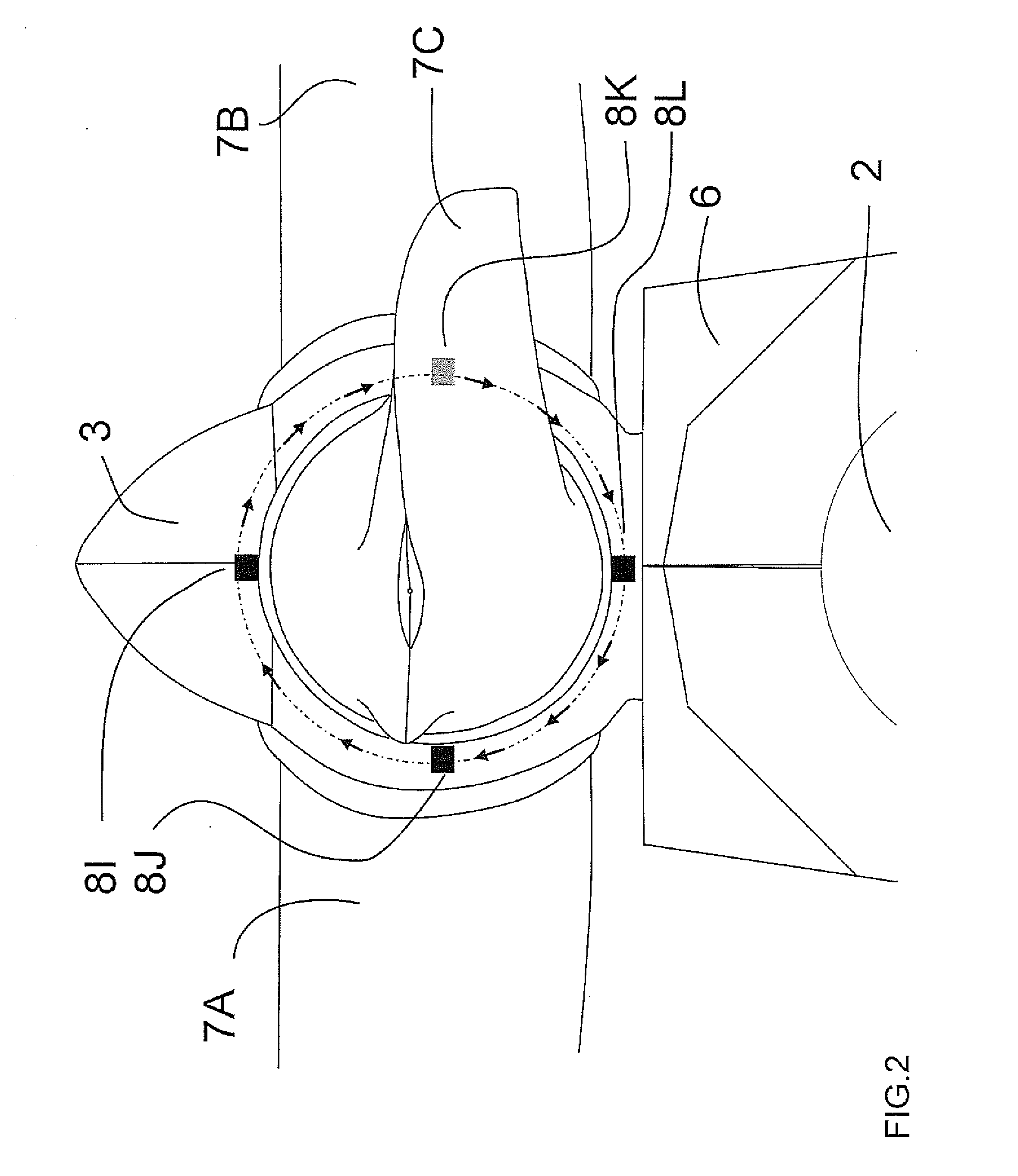
A sensor system monitors deflection of turbine blades of a wind turbine. The system includes a first component configured on the turbine blades. A second component is configured on the tower at a height so as to detect the presence of the first component as the blades rotate past the tower. The second component generates a corresponding measurable parameter or value that is indicative of distance between the blades and tower. The second component is disposed substantially completely around the circumference of the tower so as to detect the first components at any rotational position of the turbine nacelle relative to the tower.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for reducing rotor blade deflections, loads, and/or peak rotational speed
A method for reducing at least one of loads, deflections of rotor blades, or peak rotational speed of a wind turbine includes storing recent historical pitch related data, wind related data, or both. The stored recent historical data is analyzed to determine at least one of whether rapid pitching is occurring or whether wind speed decreases are occurring. A minimum pitch, a pitch rate limit, or both are imposed on pitch angle controls of the rotor blades conditioned upon results of the analysis.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for reducing rotor blade deflections, loads, and/or peak rotational speed
A method for reducing at least one of loads, deflections of rotor blades, or peak rotational speed of a wind turbine includes storing recent historical pitch related data, wind related data, or both. The stored recent historical data is analyzed to determine at least one of whether rapid pitching is occurring or whether wind speed decreases are occurring. A minimum pitch, a pitch rate limit, or both are imposed on pitch angle controls of the rotor blades conditioned upon results of the analysis.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Wind turbine blade vibration detection and radar calibration
ActiveUS20150159632A1Reduces manufacturing and maintenance costEasy to replacePropellersWind motor controlTurbine bladeTower
A wind turbine (1) is provided, having a wind turbine tower (2) and at least one rotatable blade (5), and further comprising a system for measuring rotor blade vibration of said wind turbine. The system comprises at least one Doppler radar unit (7) operatively configured to emit and receive radar signals, the radar unit being mounted on the wind turbine tower at a position above the lowest position of the at least one blade, the radar unit being positioned so as to measure reflections of an emitted radar signal from the turbine blade. A processing unit is configured to receive measurement data from the radar unit and to determine, by analysis of Doppler shift in received radar signals relative to transmitted signals due to movement of the blade towards or away from the turbine tower, the velocity of the blade in the direction towards or away from the turbine tower. Using a radar unit to measure blade velocity allows a determination to be made of the vibrations occurring in the blade without needing an internal sensor in the blade. This reduces manufacturing and maintenance costs of the blades since sensors in the blades will not need to be replaced, and sensors positioned on the tower are easier to replace in the field.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Detection of Deformation of a Wind Turbine Blade
InactiveUS20110150647A1Early detectionLow costPropellersPump componentsTurbine bladeRadiotransmitter
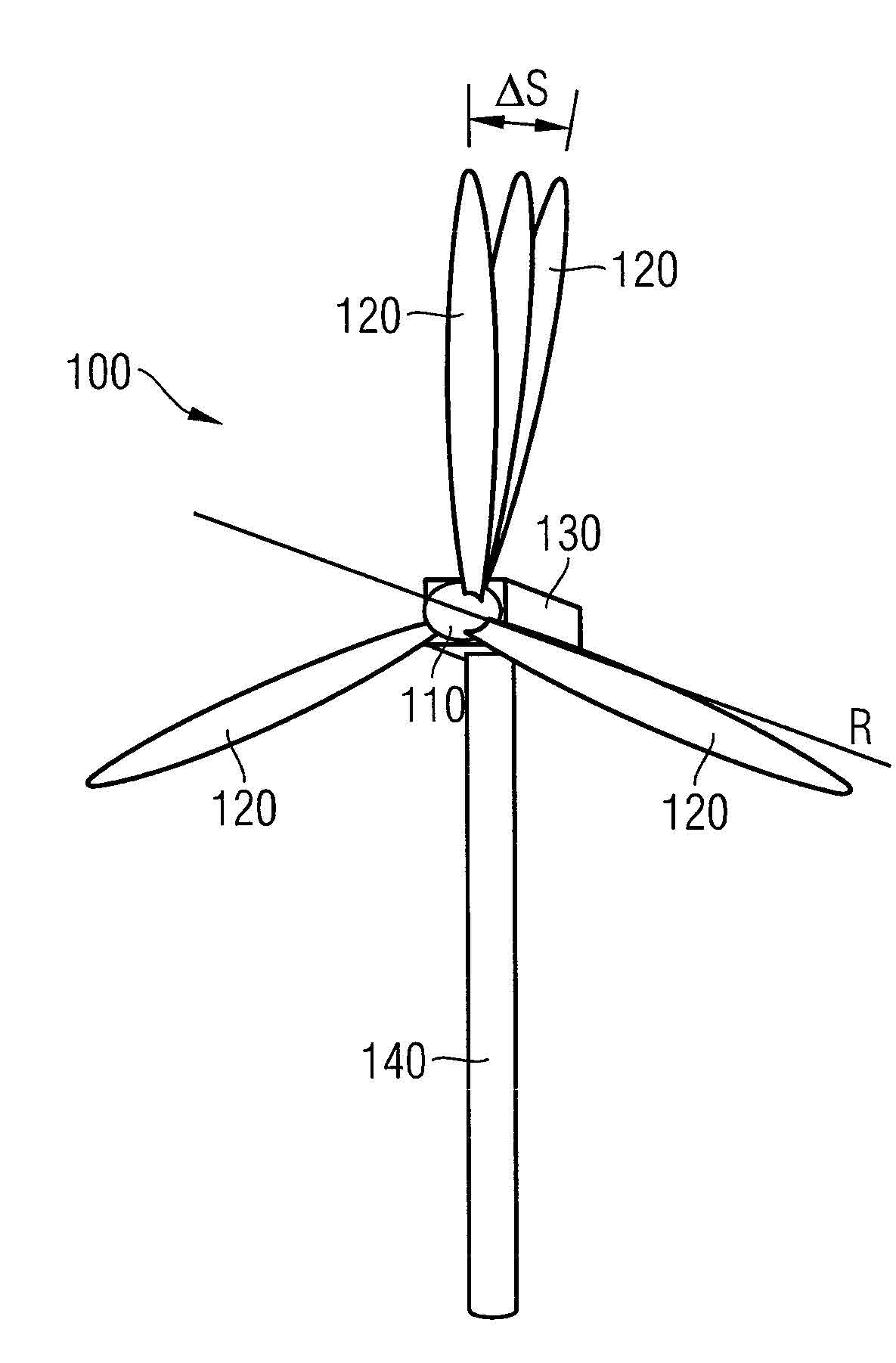
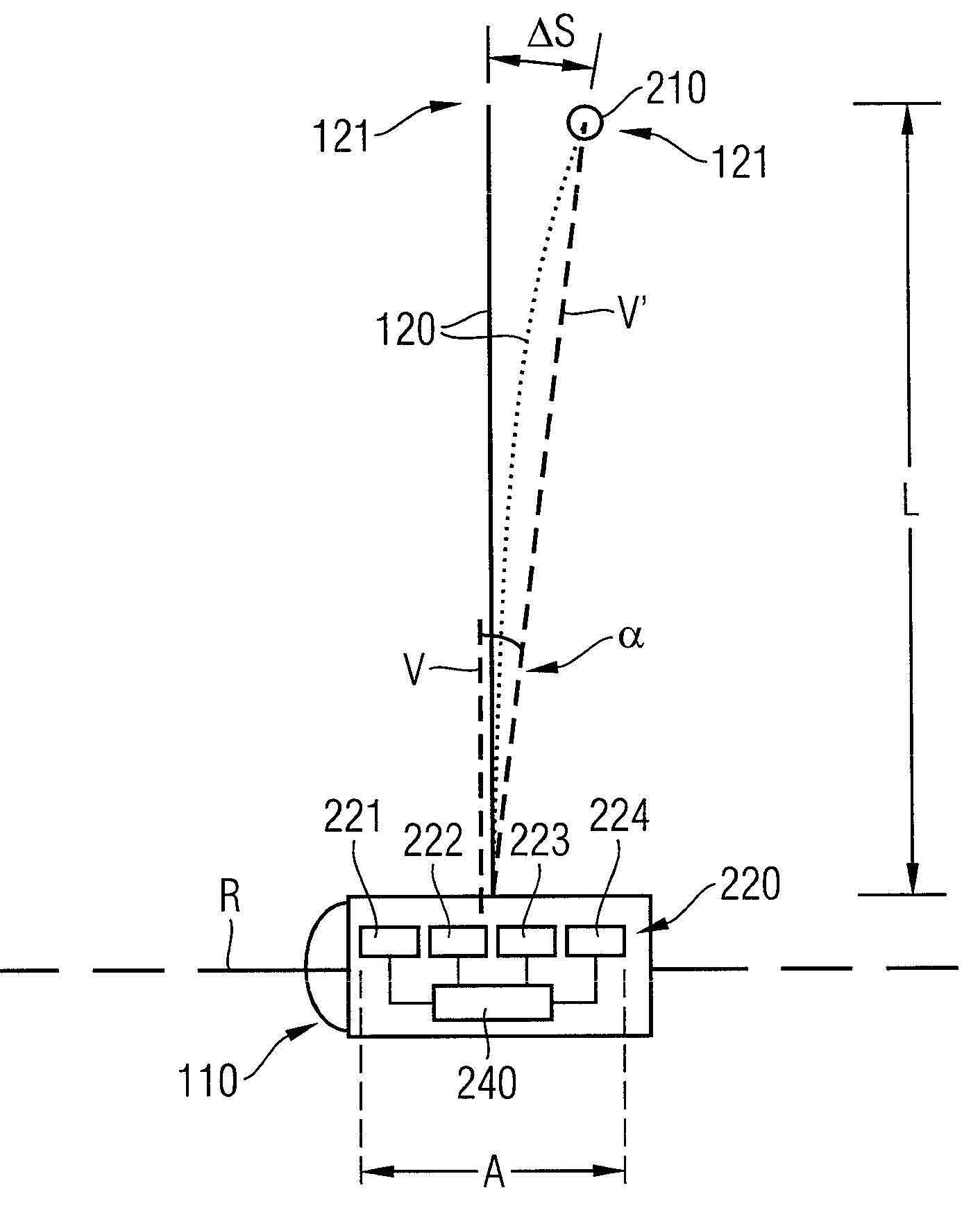
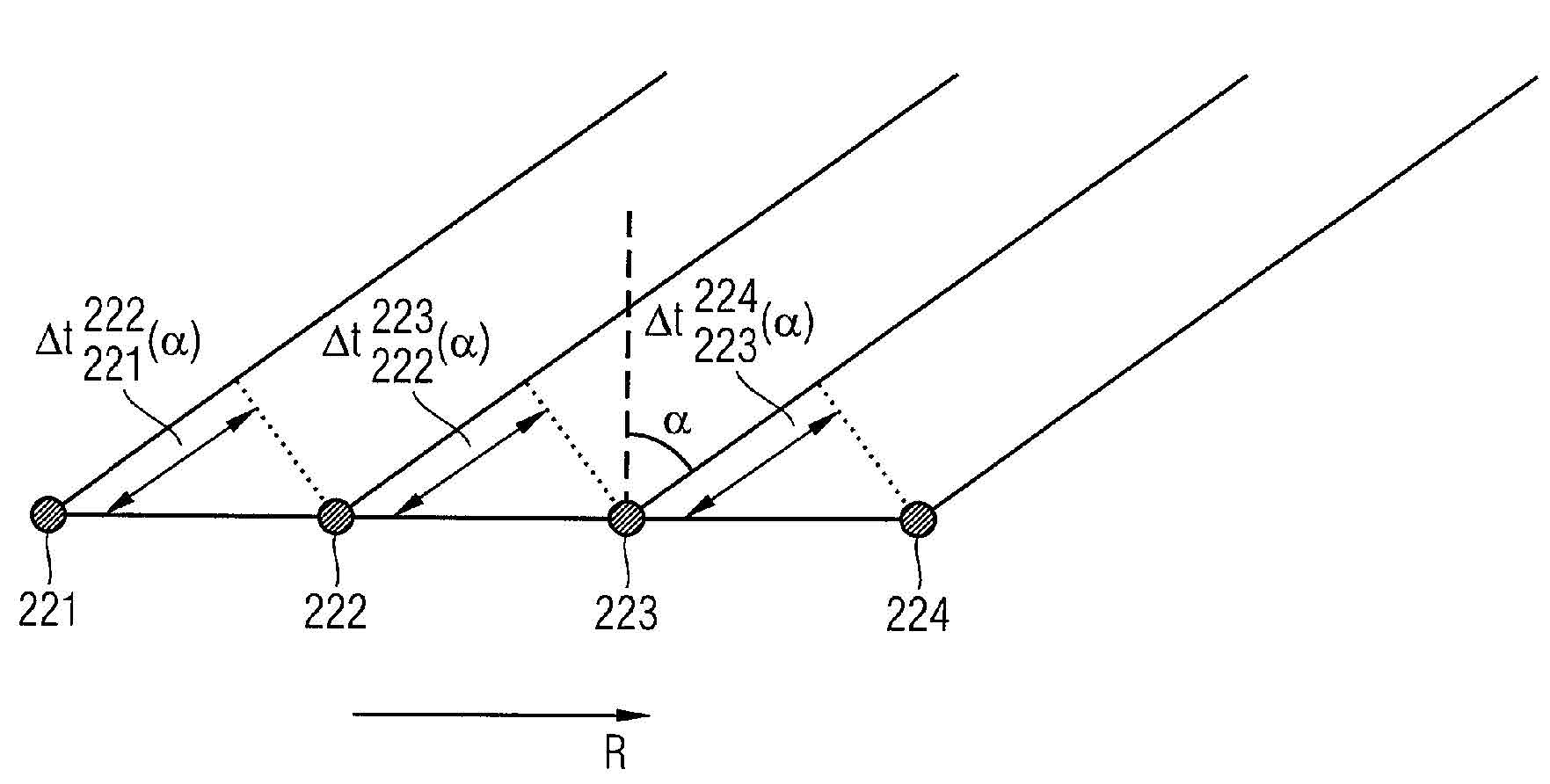
An arrangement for detecting bending deflection of a wind turbine blade is provided. The arrangement for the wind turbine includes a radio transmitter and a linear antenna array assigned to the radio transmitter. The radio transmitter is mounted on the blade tip and emits a signal. The antenna array is mounted on the rotor of the wind turbine in a co-rotating manner and receives the signal. On the basis of the transit times of the signal from the rotor to the individual antennas of the array, the position of the radio transmitter relative to the array is determined. In the event of blade deflection, for example when a high wind load is present, the relative position changes which is detected by the arrangement.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
System and method for monitoring and controlling wind turbine blade deflection
ActiveUS20160146189A1Increase probabilityReduce probabilityPropellersWind motor controlTurbine bladeTime segment
A system and method for monitoring and controlling the deflection of rotor blades of a wind turbine so as to prevent tower strikes is disclosed. The method includes operating the wind turbine at standard pitch angle settings. Another step includes monitoring a loading condition of the wind turbine over a predetermined time period. A further step includes tracking a number of wind condition deviations of a certain magnitude occurring during a predetermined time period. The method also include altering one or more of the standard pitch settings of the rotor blades in response to the number of wind condition deviations exceeding a wind deviation threshold and / or the loading condition exceeding a loading threshold as an exceedance indicates an increased probability of rotor blade deflection. The method further includes performing one or more additional corrective actions so as to reduce the probability of a rotor blade tower strike.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for Detecting Deflection of the Blades of a Wind Turbine
InactiveUS20150252789A1Quick checkEasy to detectImage enhancementAvoid excessive blade deflectionNacelleExternal data
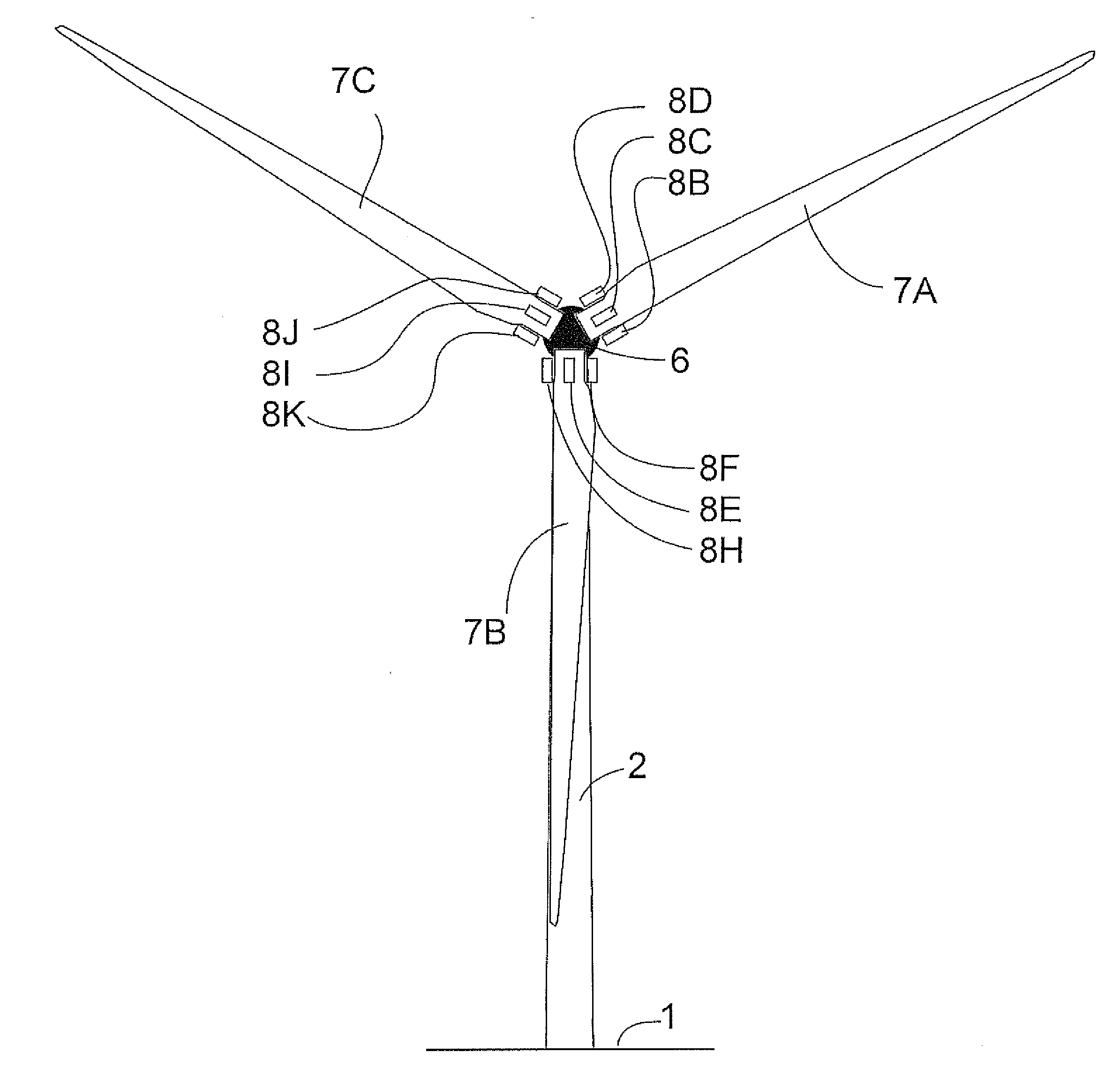
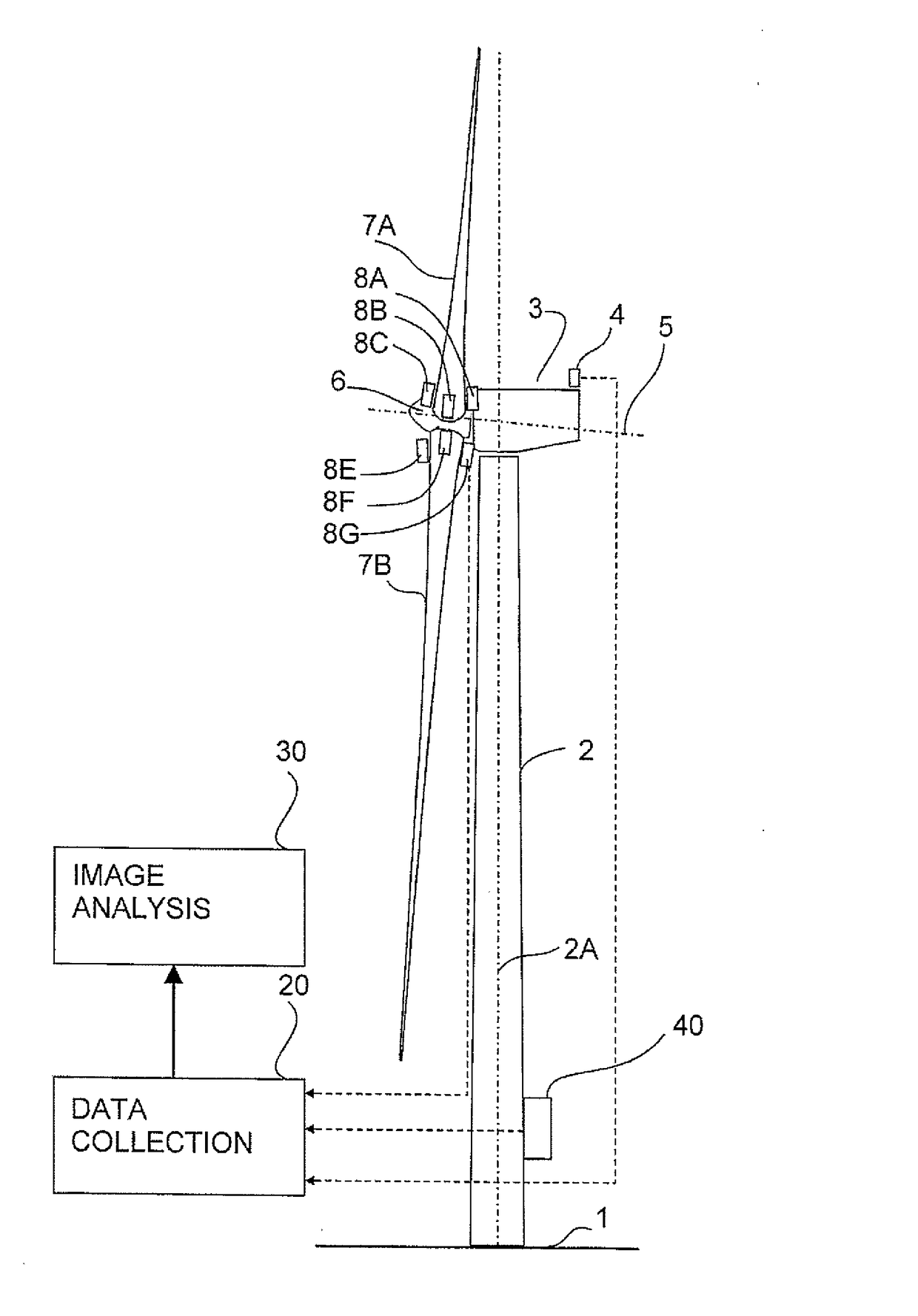
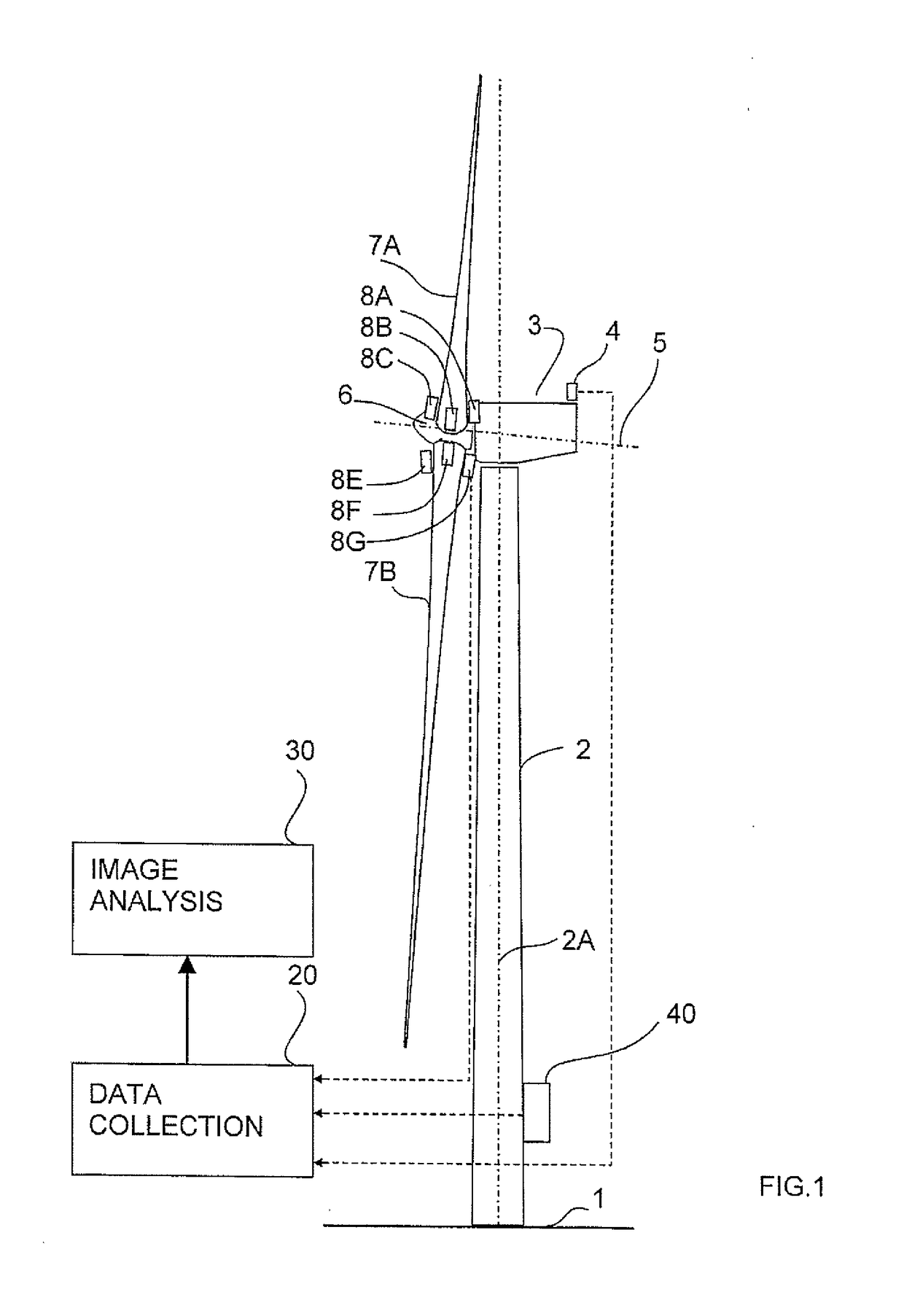
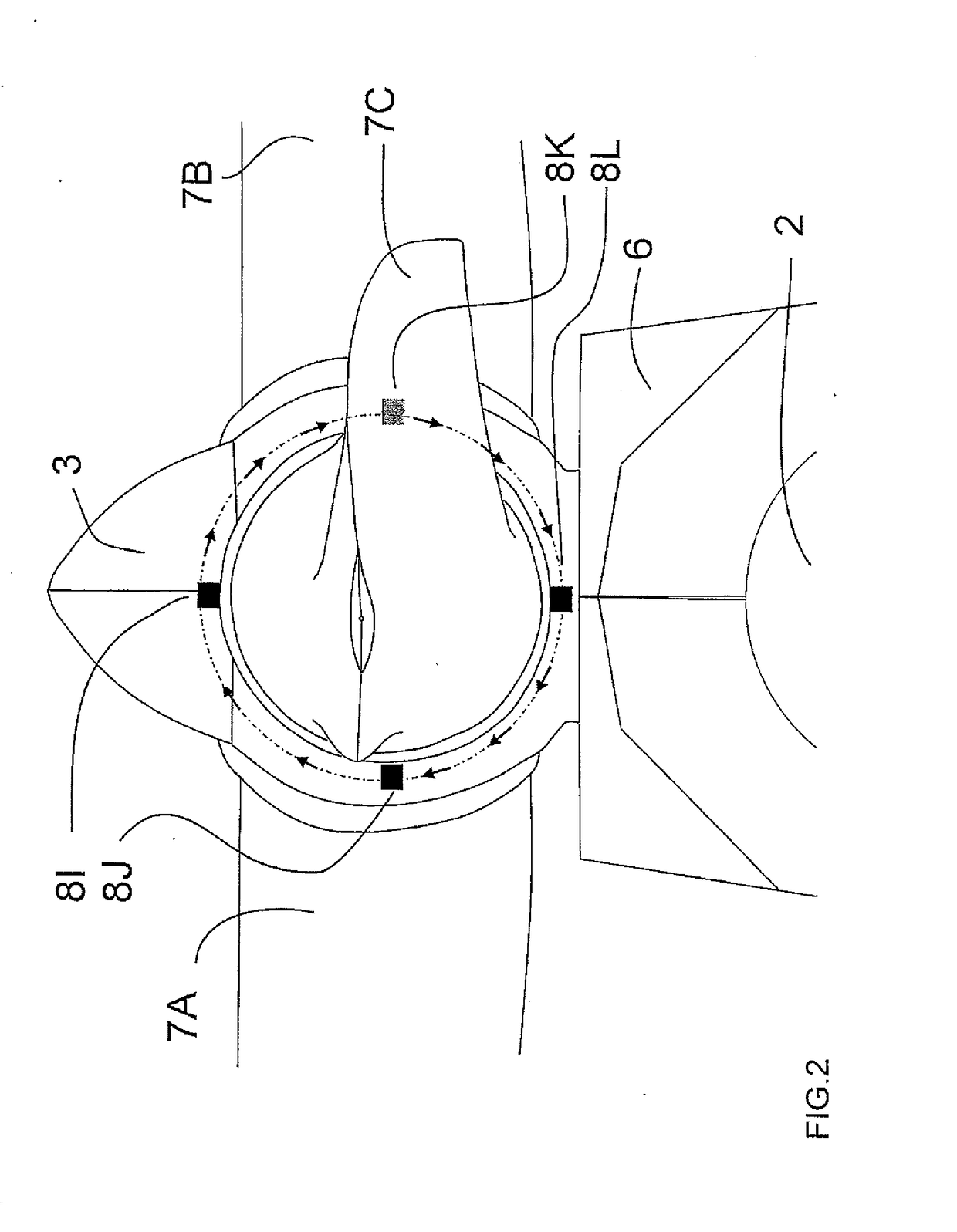
An amount of the deflection of the blades of a rotor of a wind turbine of the type including a tower and a nacelle mounted to the top of the tower, the rotor being rotatably connected to the nacelle for rotating about a rotor axis and having a plurality of equally spaced blades includes positioning video cameras on the rotor at a root of a respective one of the blades so as to provide a line of sight of the camera along the respective one of the blades to the tip to obtain a video image of the rotor and tip and carrying out an analysis of the images of the tip to determine a position of the tip and hence the deflection of the tip time synchronized analyzed potentially with external data providing load, capacity, power produced or environmental data.
Owner:BUNGE STEFFEN
System for detecting proximity between a wind turbine blade and a tower wall
The invention provides a system for detecting proximity between a wind turbine blade and a tower wall. A sensor system monitors deflection of turbine blades of a wind turbine. The system includes a first component configured on the turbine blades. A second component is configured on the tower at a height so as to detect the presence of the first component as the blades rotate past the tower. The second component generates a corresponding measurable parameter or value that is indicative of distance between the blades and tower. The second component is disposed substantially completely around the circumference of the tower so as to detect the first components at any rotational position of the turbine nacelle relative to the tower.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC RENOVABLES ESPANA SL
Systems and methods for controlling tower clearance in a wind turbine
A wind turbine control system includes a detecting unit for adjusting a reference nodding moment of a wind turbine rotor based on at least one of an aerodynamic thrust on the wind turbine rotor and a speed of wind; a compensating unit for determining a physical nodding moment of the wind turbine rotor, comparing the physical nodding moment with the reference nodding moment, and using the comparison to compute a pitch angle command for at least one wind turbine blade; and a driving unit for changing a pitch of the at least one blade based on the pitch angle command to control the physical nodding moment of the wind turbine rotor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
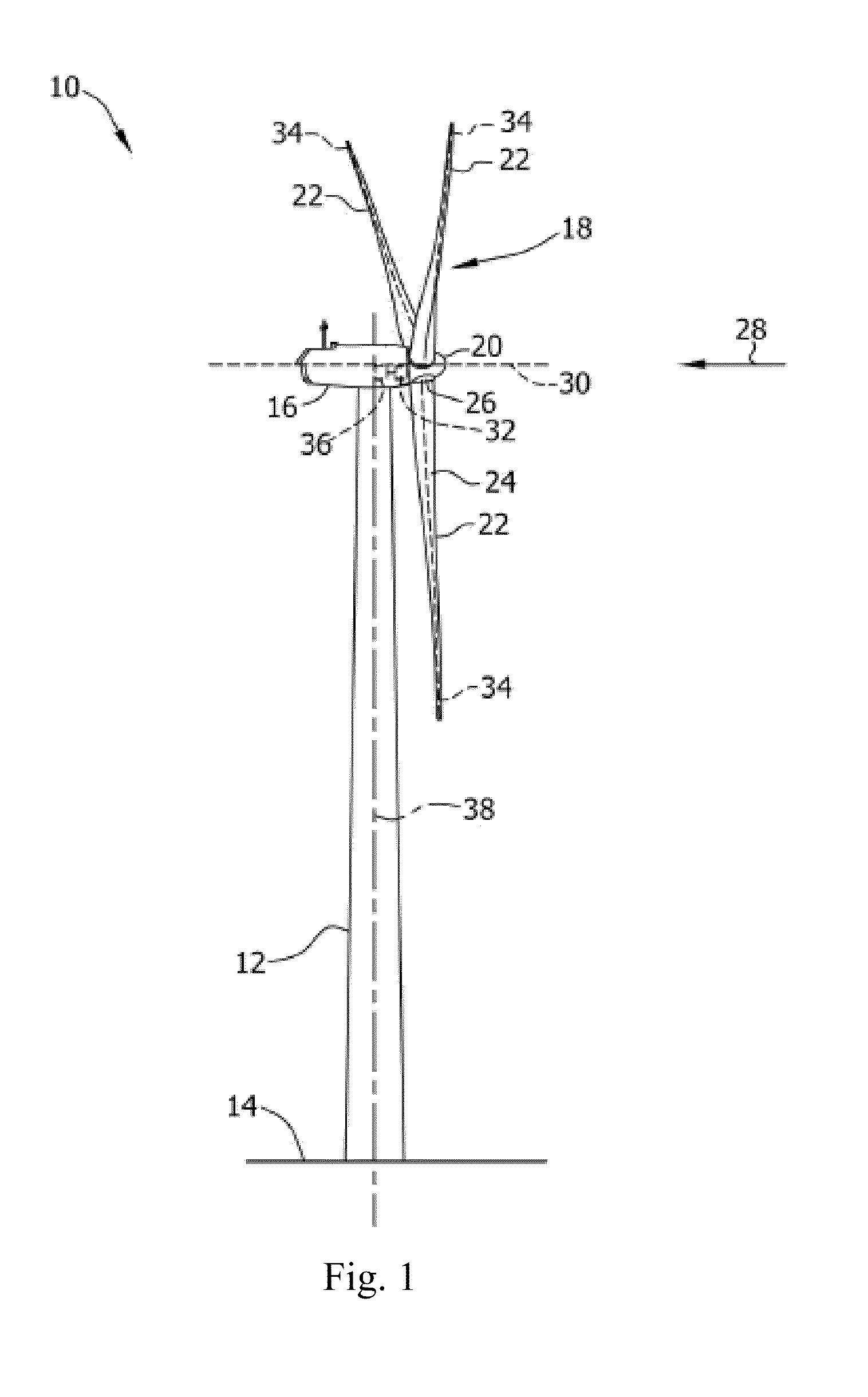
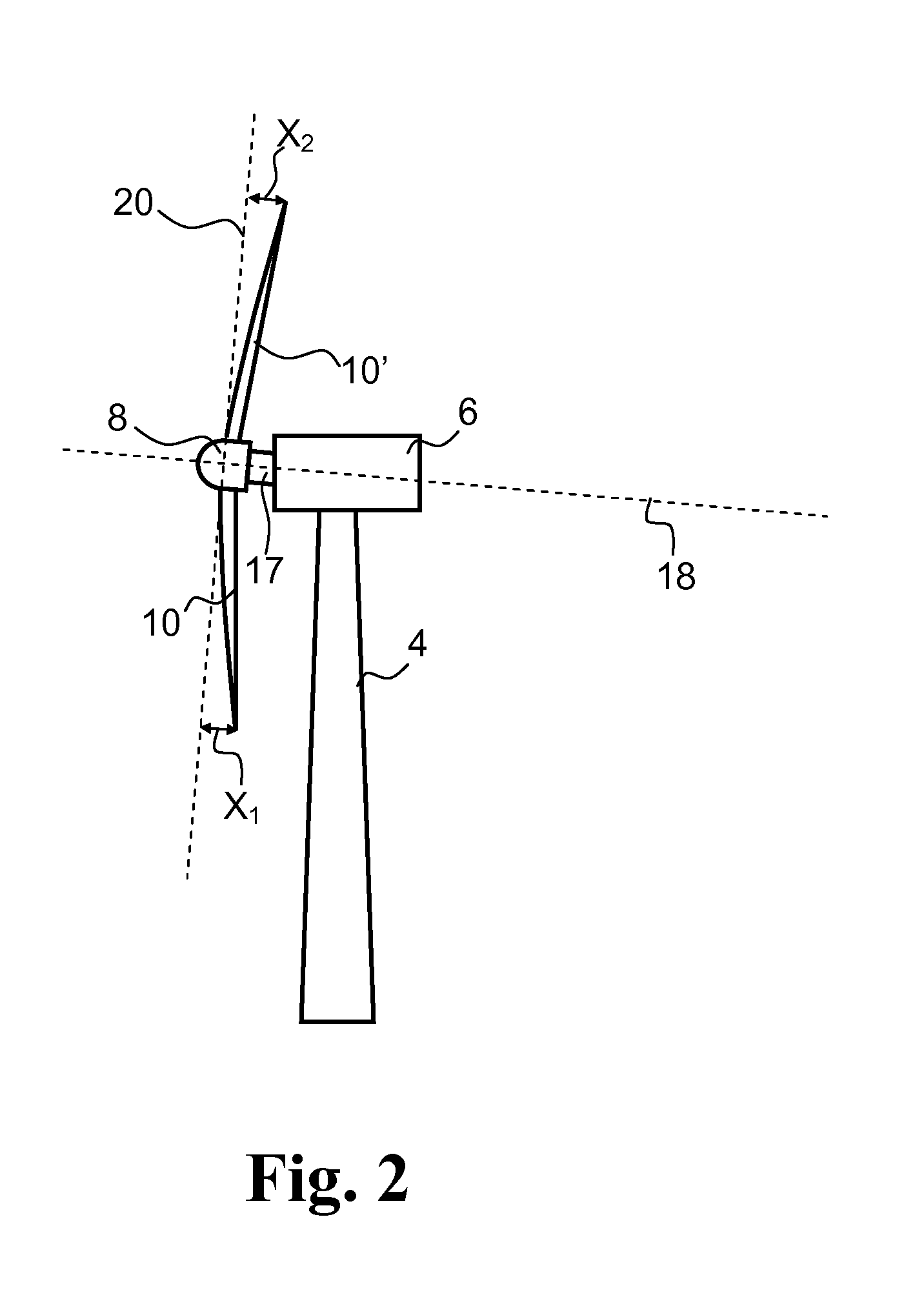
Pitch of Blades on a Wind Power Plant
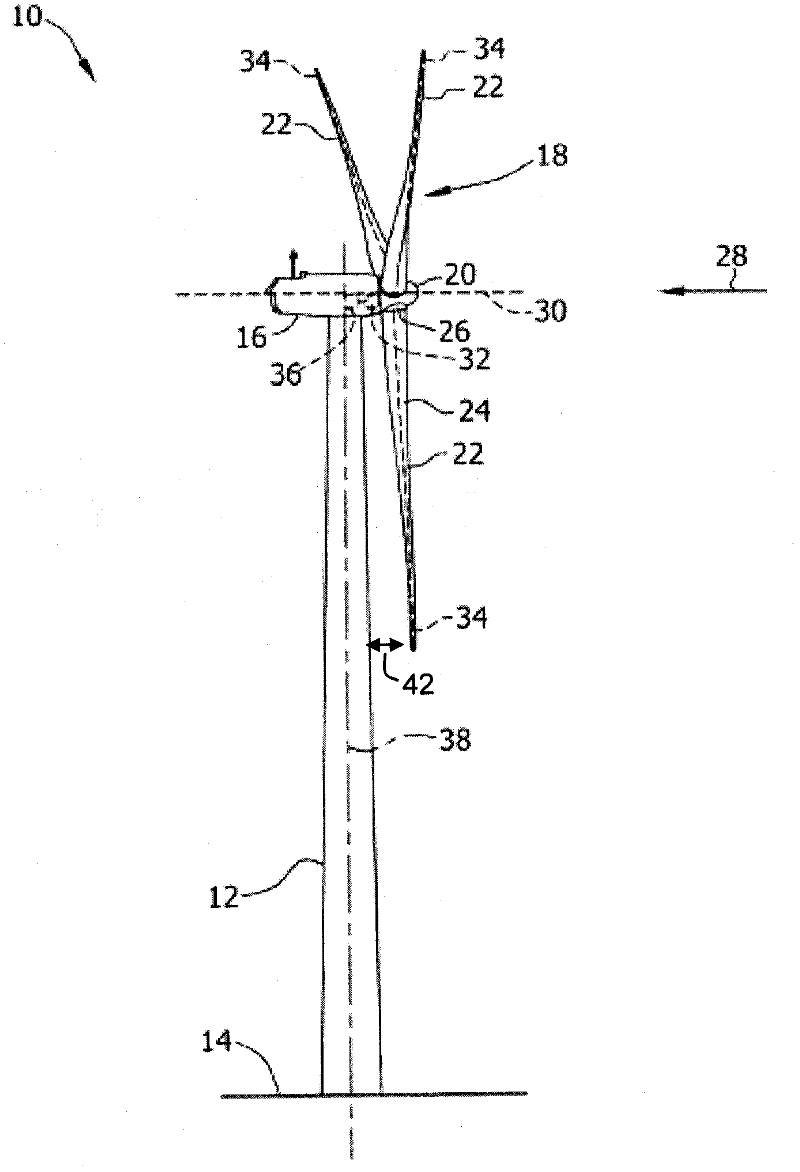
The present invention relates to a blade for a wind power plant with an assembly face for mounting in a circular pitch bearing, whose pitch axis is angled relative to the longitudinal axis of the blade, and wherein the blade comprises a root part with an approximately elliptic cross-section, in which root part the assembly face is arranged. The invention further relates to a wind power plant in general having a pitch-adjustable blade mounted in a pitch bearing such that the distance between the outermost part of the blade and the tower is increased when the leading edge of the blade is pitched up in the wind. This is accomplished in that the longitudinal axis of the blade is angled in a particular way compared to its pitch axis. The invention also relates to a meth controlling a wind power plant, including to increase the rotor area and / or increasing the distance between the outermost part of at least one blade and the tower by regulating, during operation, the pitch of a blade about a pitch axis which is angled relative to the longitudinal axis of the blade.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
System for detecting proximity between a wind turbine blade and a tower wall
A sensor system monitors deflection of turbine blades of a wind turbine. The system includes a first component configured on the turbine blades. A second component is configured on the tower at a height so as to detect the presence of the first component as the blades rotate past the tower. The second component generates a corresponding measurable parameter or value that is indicative of distance between the blades and tower. The second component is disposed substantially completely around the circumference of the tower so as to detect the first components at any rotational position of the turbine nacelle relative to the tower.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Individual pitch control system with controller policy and pitch control method
InactiveCN106224161AReduce fatigue loadExtended service lifeAvoid excessive blade deflectionWind motor controlElectricityElectric machine
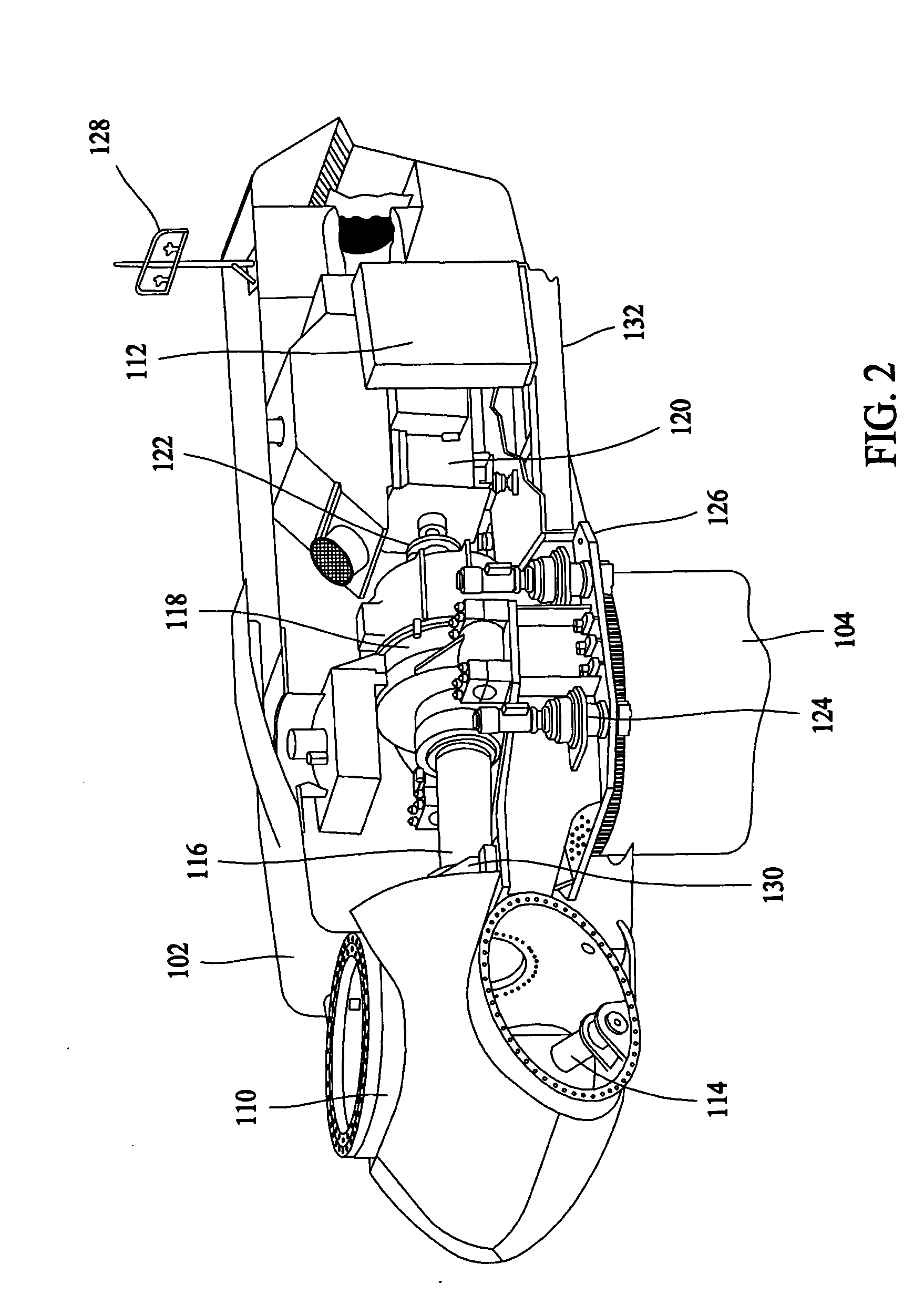
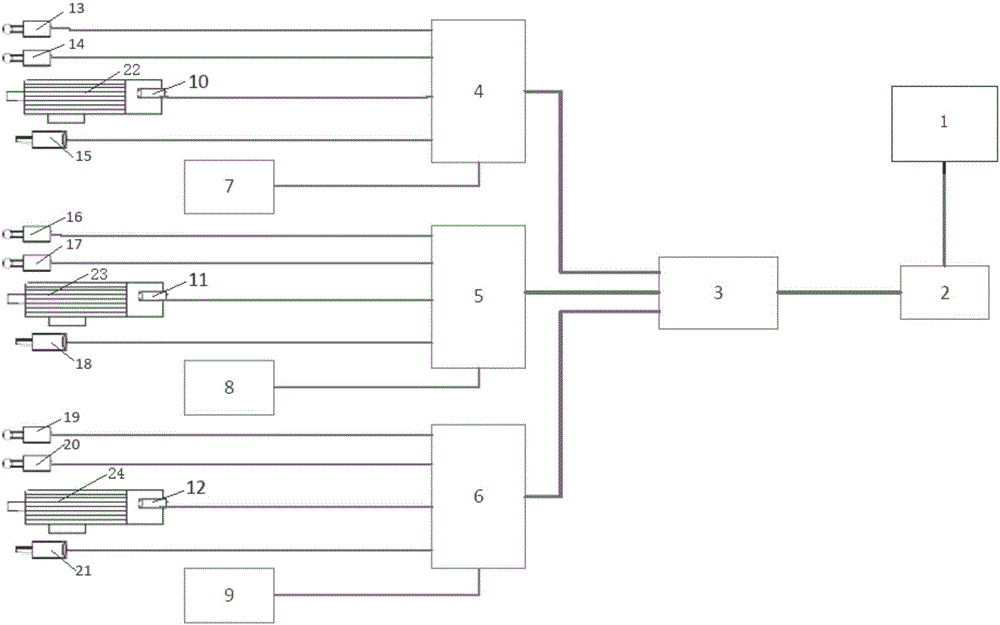
The invention discloses an individual pitch control system with a controller policy and a pitch control method, and belongs to the technical field of wind power industry. The individual pitch control system comprises a wind driven generator unit main control controller, a variable pitch controller, three sets of servo drives corresponding to blades, a spare power supply, a pitch control motor, an encoder and a limiting switch; the variable pitch controller is respectively communicated with the wind driven generator unit main control controller and the three servo drives; each servo drive is respectively connected with the pitch control motor, the motor encoder, the spare power supply and the limiting switch; the motor encoder is mounted at the tail end of the pitch control motor; and the angle encoder is engaged and linked with blade bearing inner teeth through measuring gears. The individual pitch control system can realize individual pitch control function through the variable pitch controller, realizes safety protection for fault diagnosis, state monitoring, lightning protection and battery management, can properly reduce the fatigue load of fan blades, prolongs the unit service life, is simple and reliable in control, has no need to additionally provide excessive hardware, is lower in cost, and is higher in safety.
Owner:CHINA CREATIVE WIND ENERGY +3
Method of controlling a wind turbine and related system
ActiveUS20140140844A1Avoid excessive wearReduce and eliminate numberPropellersPump componentsTurbine bladeTower
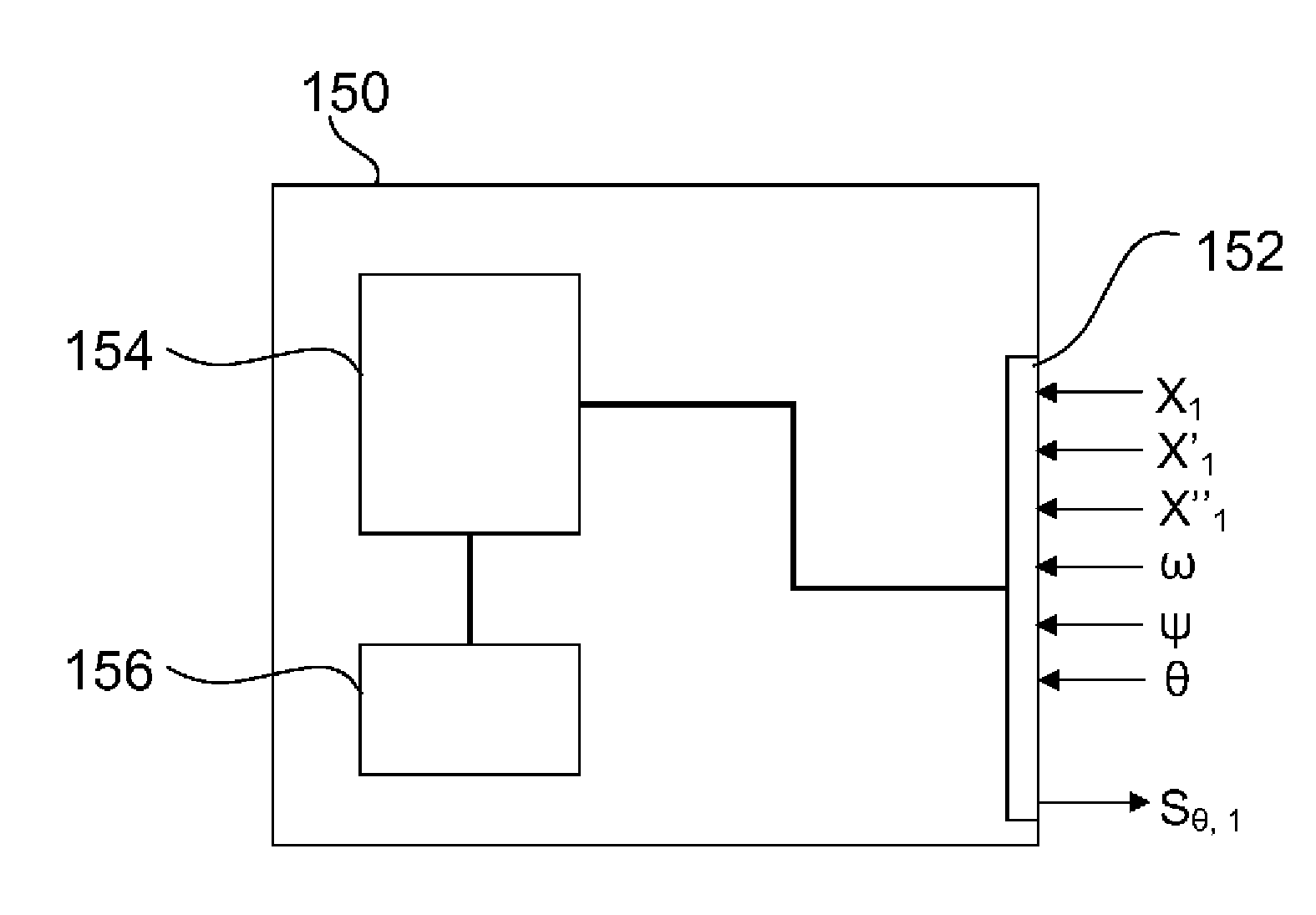
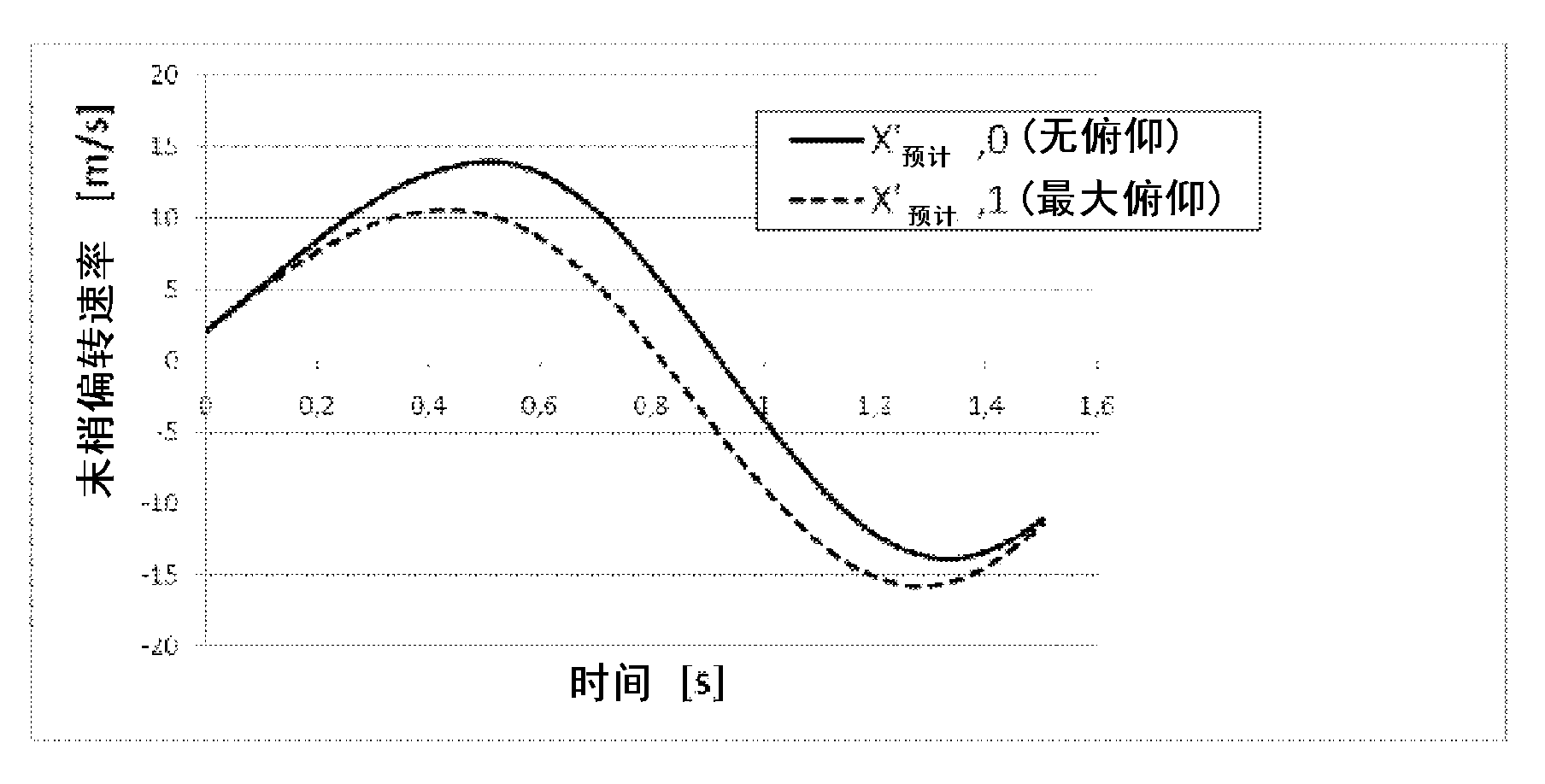
The present invention relates to a method for controlling a wind turbine comprising a pitch of one or more blades and collecting first data indicative of a dynamic condition of the first wind turbine blade and a rotor, the first data comprising rotor data and first deflection data, the rotor data indicative of the azimuth position and rotational velocity of the rotor in a rotor plane perpendicular to the rotor axis, and the first deflection data indicative of the position, speed and acceleration of one or more parts of the first wind turbine blade. The method comprises calculating an expected tower clearance distance at a later time of tower passage for the first blade based on the first data including acceleration of one or more parts of the first blade, and performing measures to prevent tower collision, if the expected tower clearance distance fulfills a collision risk criterion.
Owner:LM WIND POWER AS
A system and method for identifying the likelihood of a tower strike in a wind turbine
ActiveCN103261680AAccurate identificationSmall safety marginAvoid excessive blade deflectionWind motor controlWind forceEngineering
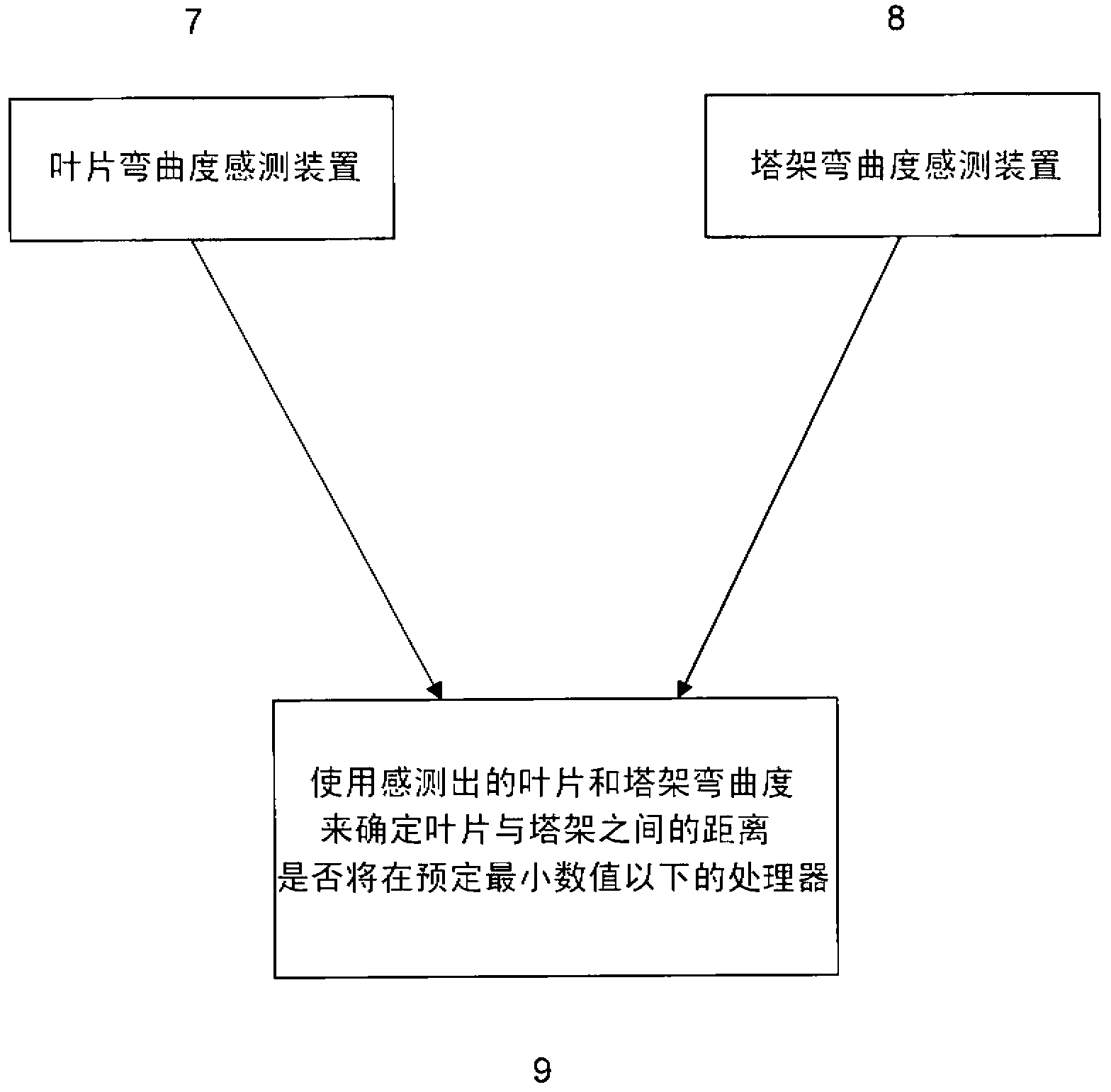
A system for identifying the likelihood of a wind turbine rotor blade striking a wind turbine tower comprises a device for sensing bending of a wind turbine rotor blade and a device for sensing bending of a wind turbine tower. In a preferred embodiment Long Period Grating (LPG) sensors are used to measure bending of the tower. Preferably a plurality of LPG sensors is provided along the length of the blade. In one embodiment at least one of the LPG sensors comprises two sensing elements arranged to sense in perpendicular directions. In another embodiment a plurality of LPG sensors are provided each on different sides of the wind turbine tower. A processor uses the sensed blade and tower bending to determine whether the distance between the blade and the tower will be below a predetermined minimum value. If the distance is determined to be below the predetermined minimum value a controller may be used to adjust a wind turbine variable to reduce loading on the blade and thereby reduce the likelihood of a tower strike.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
System and method for monitoring blade deflection of wind turbines
ActiveUS20180171984A1Programme controlAvoid excessive blade deflectionLocation detectionTurbine blade
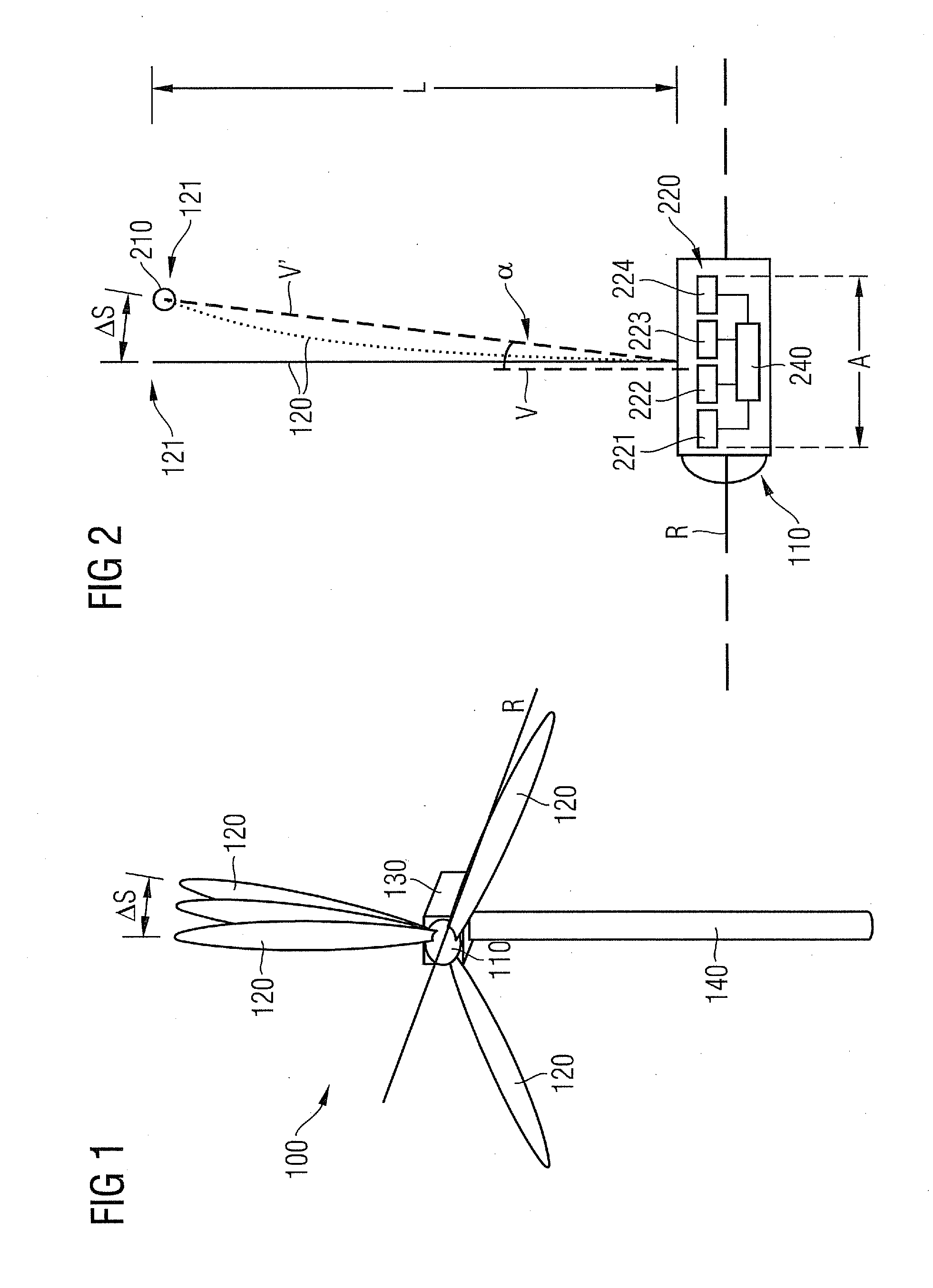
Described is a system for monitoring deflection of turbine blades of a wind turbine comprising a tower. The system comprises a position detecting apparatus mounted to the wind turbine comprising a plurality of position detection components each collecting data regarding a field of detection through which a segment of the turbine blades passes, wherein the position detection components are monitoring distinct fields of detection to collect distances of a plurality of segments of each one of the turbine blades travelling through the fields of detection. The system further comprises a deflection controller configured to receive the collected distances and to determine deflection of the turbine blades accordingly. An associated method comprises collecting distances of a plurality of distinct segments of the turbine blades when the turbine blades travel within a plurality of fields of detections, and processing the collected distances to determine clearance between the turbine blades and the tower.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE +1
Method for Replacing the Blades of a Wind Turbine to Maintain Safe Operation
ActiveUS20180003159A1Quick checkEasy to detectAvoid excessive blade deflectionImage enhancementNacelleExternal data
An amount of the deflection of the blades of a rotor of a wind turbine of the type including a tower and a nacelle mounted to the top of the tower, the rotor being rotatably connected to the nacelle for rotating about a rotor axis and having a plurality of equally spaced blades includes positioning video cameras on the rotor at a root of a respective one of the blades so as to provide a line of sight of the camera along the respective one of the blades to the tip to obtain a video image of the rotor and tip and carrying out an analysis of the images of the tip to determine a position of the tip and hence the deflection of the tip time synchronized analyzed optionally with external data providing load, capacity, power produced or environmental data.
Owner:BUNGE STEFFEN
Wind turbines
An upwind wind turbine comprising a tower and a rotor is described. The wind turbine additionally includes a pressure-sensing device supported by the tower at a location within the wake of the rotor. The pressure-sensing device is configured to sense air pressure and provide a signal indicative of the sensed air pressure to a wind turbine controller for use in controlling the rotor of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Method for operation of a wind energy installation
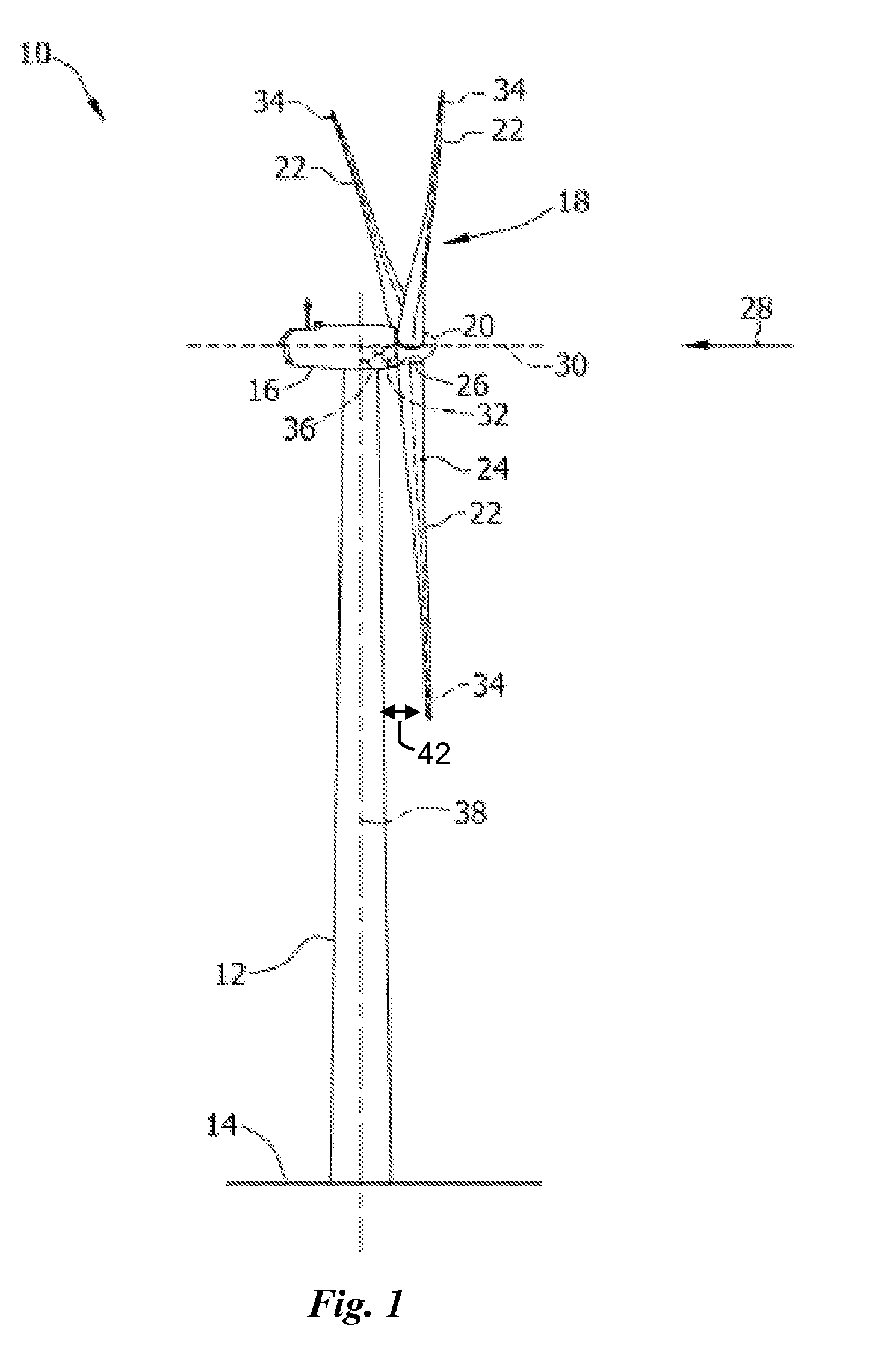
InactiveUS7638894B2Reduce wind loadsAvoid excessive blade deflectionPropellersMeasurement deviceMechanical energy
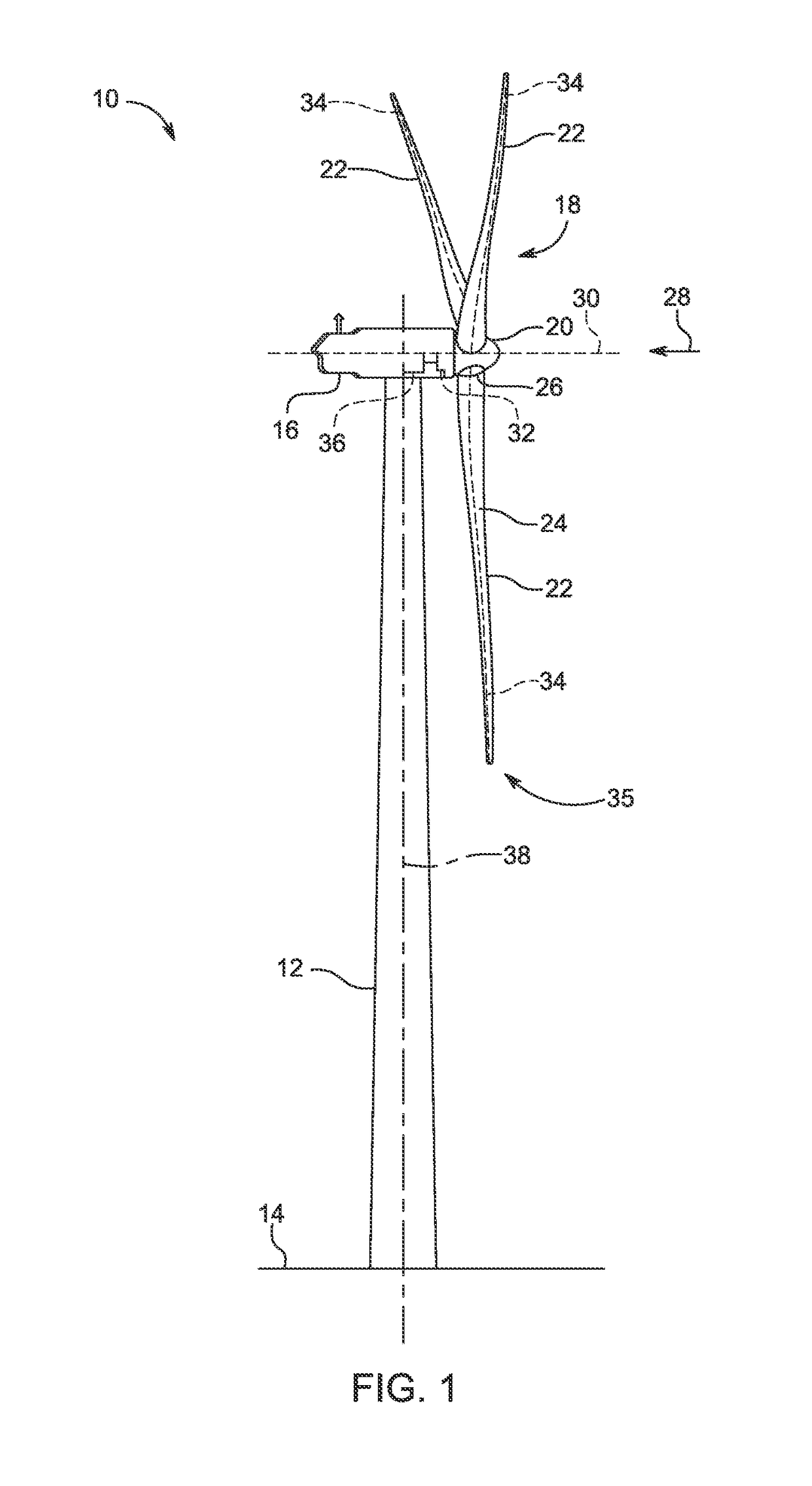
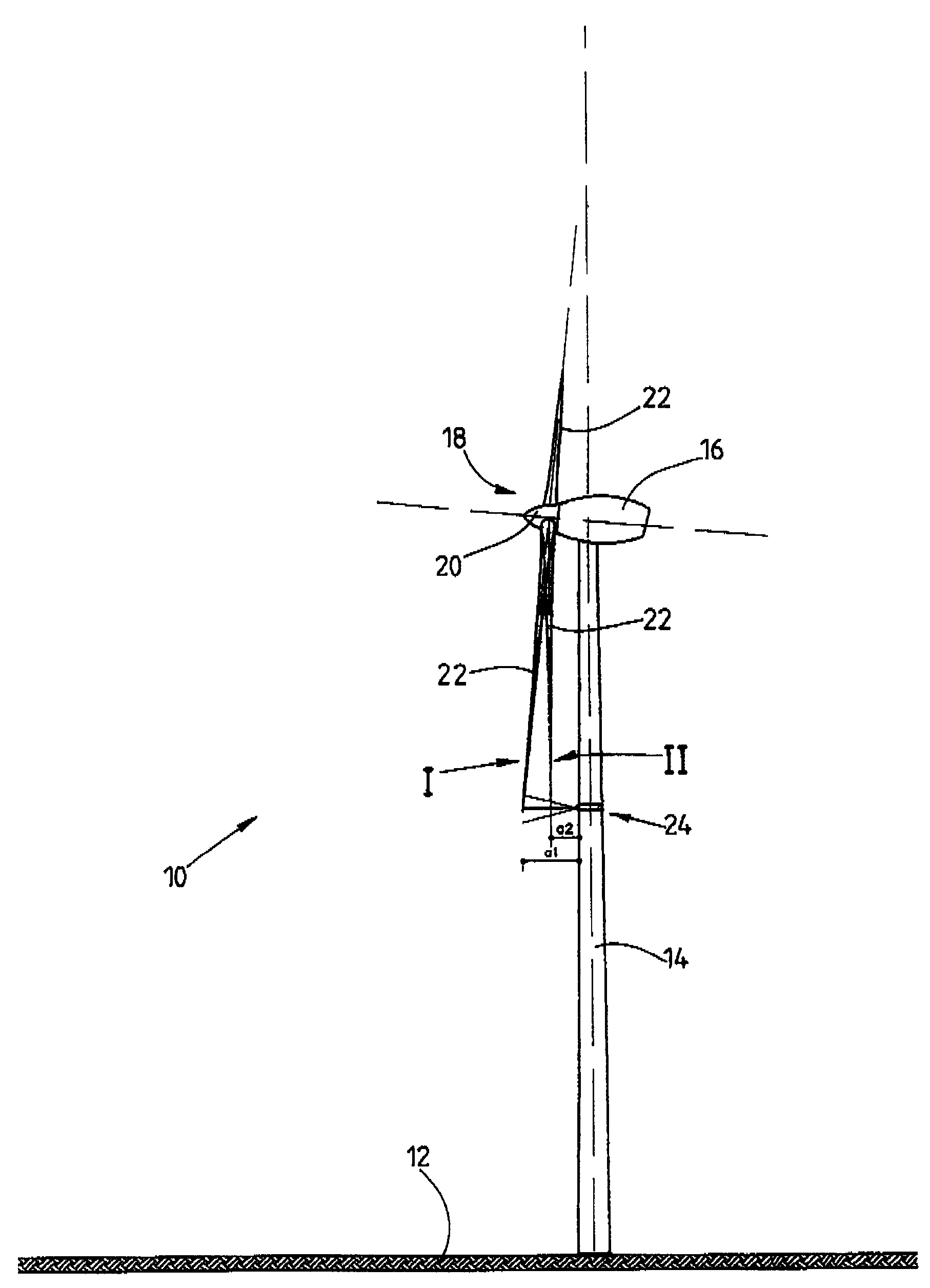
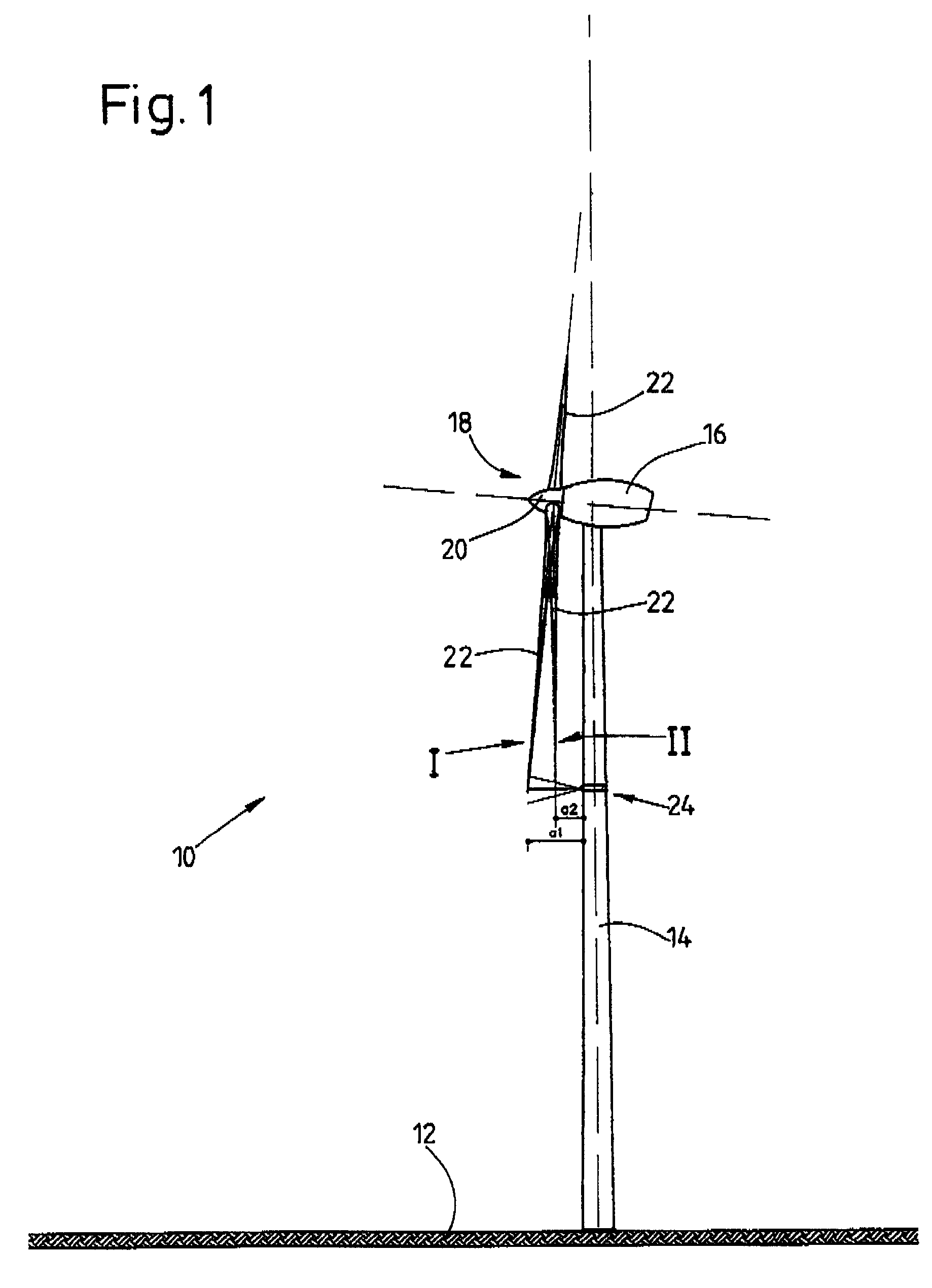
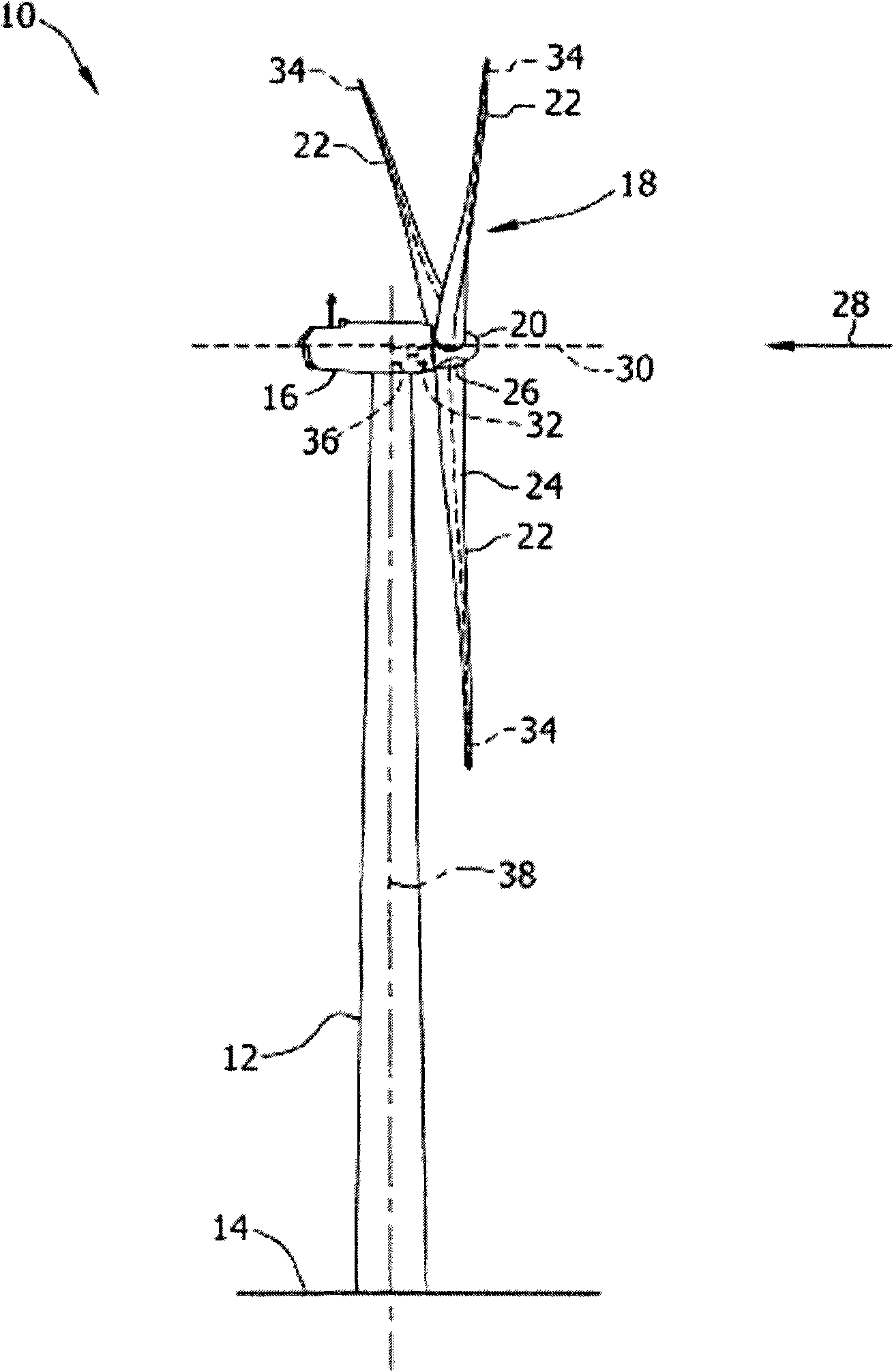
A wind energy installation (10) and a method for operation of a wind energy installation (10), with the wind energy installation (10) having a rotor (18) which can be driven by wind, having at least one rotor blade (22), a generator for conversion of the mechanical energy of the rotor (18) to electrical energy, as well as a tower (14) on which the rotor (18) is arranged. At least one measurement variable is measured, preferably more than once, by means of a suitable measurement device during. operation of the wind energy installation (10), which measurement variable is a measure of the bending of the rotor blade (22) in the tower direction as a result of a given wind load, and is thus a measure of the risk of the rotor blade (22) colliding with the tower (14) of the wind energy installation (10) as it passes the tower, with at least one operating parameter of the wind energy installation (10) being adjusted as a function of this measurement variable for determination of the rotor blade bending.
Owner:DAUBNER & STOMMEL BAU WERK PLANUNG
Detection of deformation of a wind turbine blade
InactiveCN102102639AReduce rigiditySavings potentialAvoid excessive blade deflectionWind motor controlTurbine bladePropagation time
An arrangement for detecting bending deflection of a wind turbine blade is provided. The arrangement for the wind turbine includes a radio transmitter and a linear antenna array assigned to the radio transmitter. The radio transmitter is mounted on the blade tip and emits a signal. The antenna array is mounted on the rotor of the wind turbine in a co-rotating manner and receives the signal. On the basis of the transit times of the signal from the rotor to the individual antennas of the array, the position of the radio transmitter relative to the array is determined. In the event of blade deflection, for example when a high wind load is present, the relative position changes which is detected by the arrangement.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method of controlling a wind turbine and related system
ActiveCN103890383AReduce the numberDegree of reductionAvoid excessive blade deflectionWind motor controlTurbine bladeClassical mechanics
The present invention relates to a method for controlling a wind turbine,in particular a method for controlling pitch of one or more blades of a wind turbine and related system. The method comprises collecting first data indicative of a dynamic condition of the first wind turbine blade and the rotor, the first data comprising rotor data and first deflection data, the rotor data being indicative of the azimuth position and rotational velocity of the rotor in a rotor plane perpendicular to the rotor axis, and the first deflection data being indicative of the position, speed and acceleration of one or more parts of the first wind turbine blade.; Further, the method comprises calculating an expected tower clearance distance at a later time of tower passage for the first wind turbine blade based on the first data including acceleration of one or more parts of the first wind turbine blade, and performing measures to prevent tower collision, if the expected tower clearance distance fulfills a collision risk criterion.
Owner:LM WP PATENT HLDG
System and method for monitoring and controlling wind turbine blade deflection
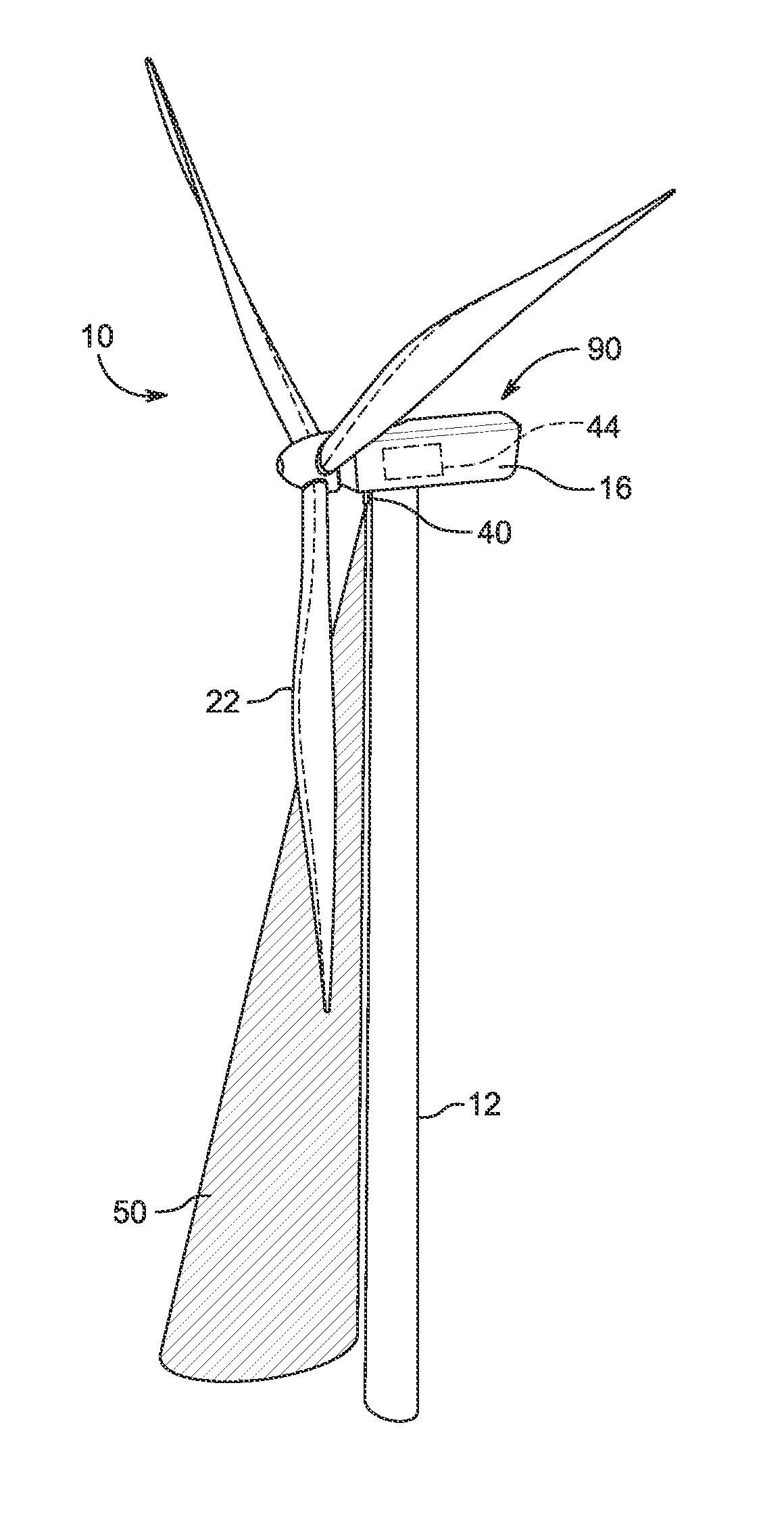
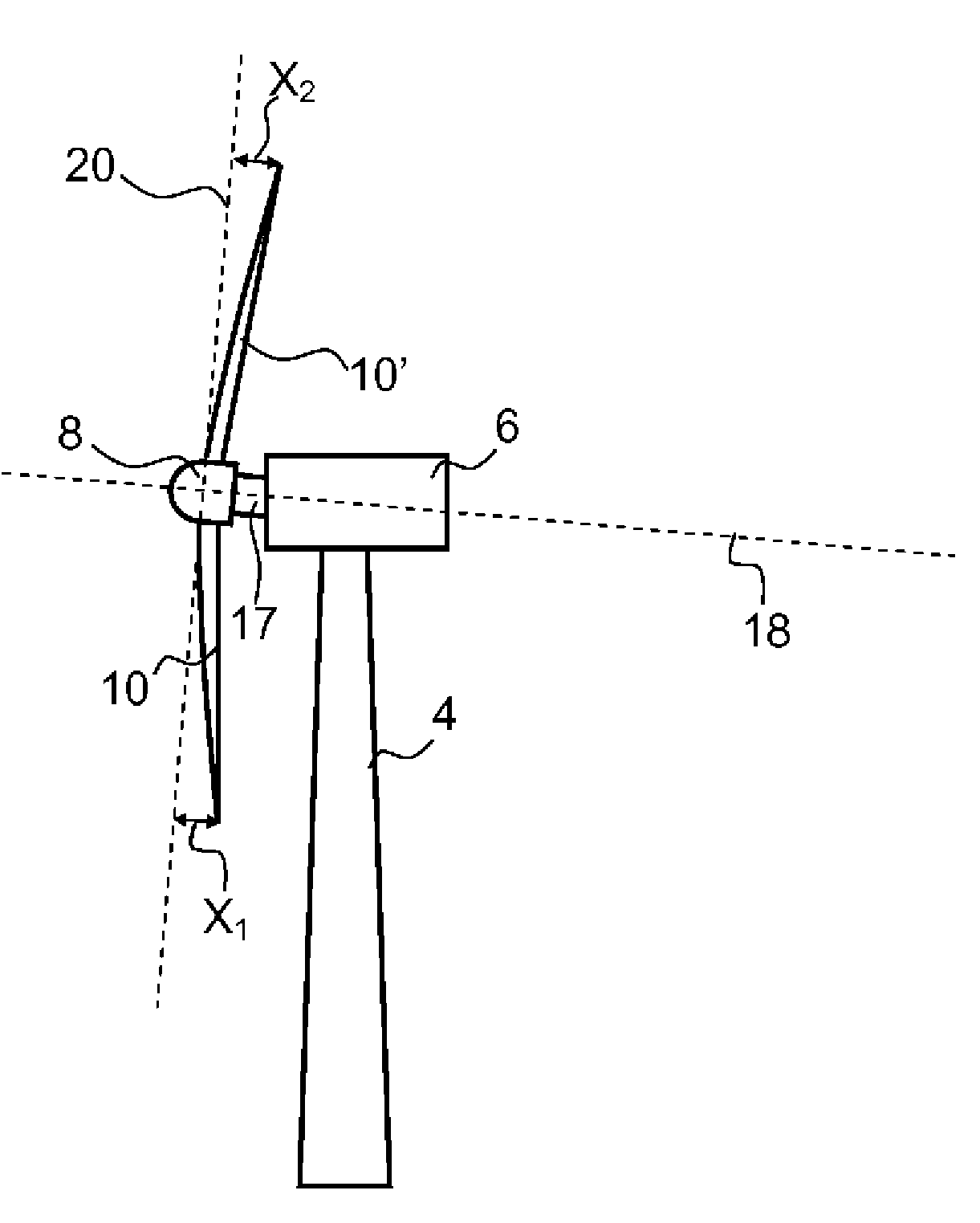
The present application relates to a system and a method for monitoring and controlling wind turbine blade deflection. A system is disclosed for monitoring and controlling the deflection of turbine blades (22) of a wind turbine (10). The system includes a passive position detecting apparatus (46) and a controller (36). The passive position detecting apparatus (46) may be configured to acquire and transmit data relating directly to a position of at least one of the turbine blades (22). The controller (36) may be configured to receive the data from the passive position detecting apparatus (46) and compare such data to a known position reference to determine turbine blade deflection.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wind turbine farm and method of controlling at least one wind turbine
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Wind turbine, tower and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20110135493A1Increased static clearanceReduce the overall diameterFinal product manufactureWind motor supports/mountsCircular coneEngineering
A wind turbine, tower and method for making same are provided. The wind turbine includes a rotor having one or more blades and a rotor radius distance approximately equal to the distance measured from a centerline of the rotor to a tip of one of the blades. The tower has one or more tower sections, including a first tower section having a generally cylindrical or frusto-conical shape. The first tower section has at least one first diameter. A reduced diameter tower section is connected to the first tower section, and has a waist portion with at least one second diameter that is smaller than the first diameter. At least a portion of the reduced diameter tower section having the second diameter is located about one rotor radius distance from the centerline of the rotor, and the reduced diameter section provides increased static clearance to the tip of the blades.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wind turbine and control method for controlling the same
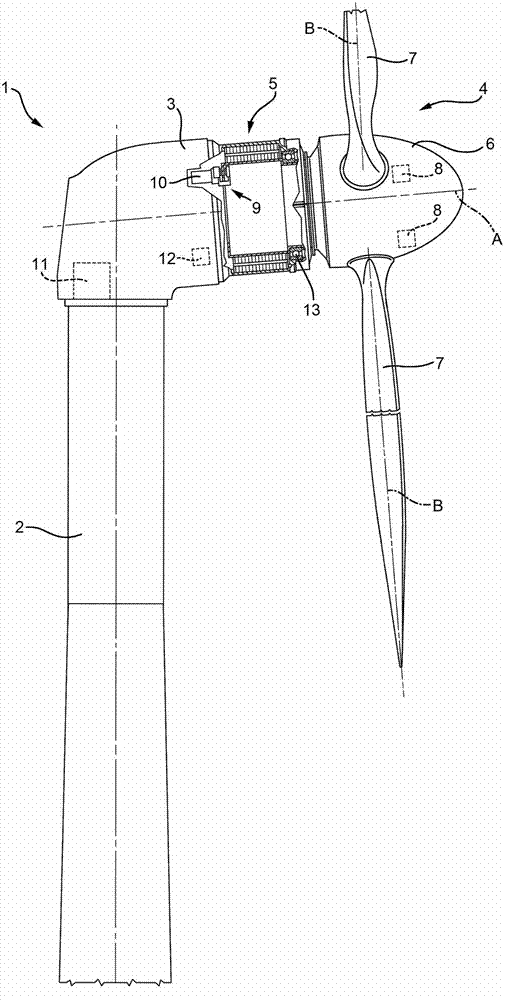
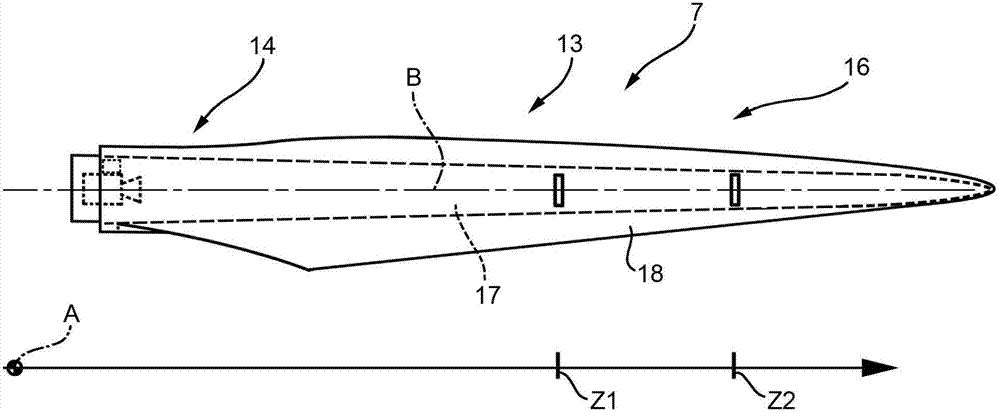
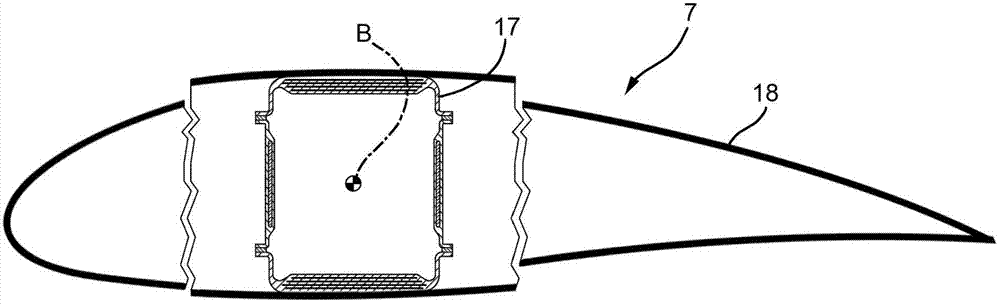
InactiveCN102808722AEasy to controlAvoid excessive blade deflectionWind motor controlElectric machineControl signal
The invention relates to a wind turbine and a control method for controlling the same. The wind turbine (1) is provided with a rotor (4) rotatable about a rotor axis (A) and having a plurality of blades (7) rotatably fitted to a hub (6) about a blade axis (B) and a plurality of pitch actuators (8) for adjusting the pitch angles of the blades (7); a brake (9) controlled by a brake actuator (10) for arresting the rotor (4); a rotating electric machine (5) connected to the rotor (4); an inverter (11) for controlling the rotating electric machine (5); and a control system (22) configured to emit control signals for selectively controlling at least one of pitch actuators (8); the brake actuator (10); and the inverter (11) as a function of the deformations retrieved by means of a plurality of image reflection measuring devices (24) configured for detecting the deformations of each blade (7).
Owner:WILIC SARL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com