Patents
Literature
514 results about "Pitch bearing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
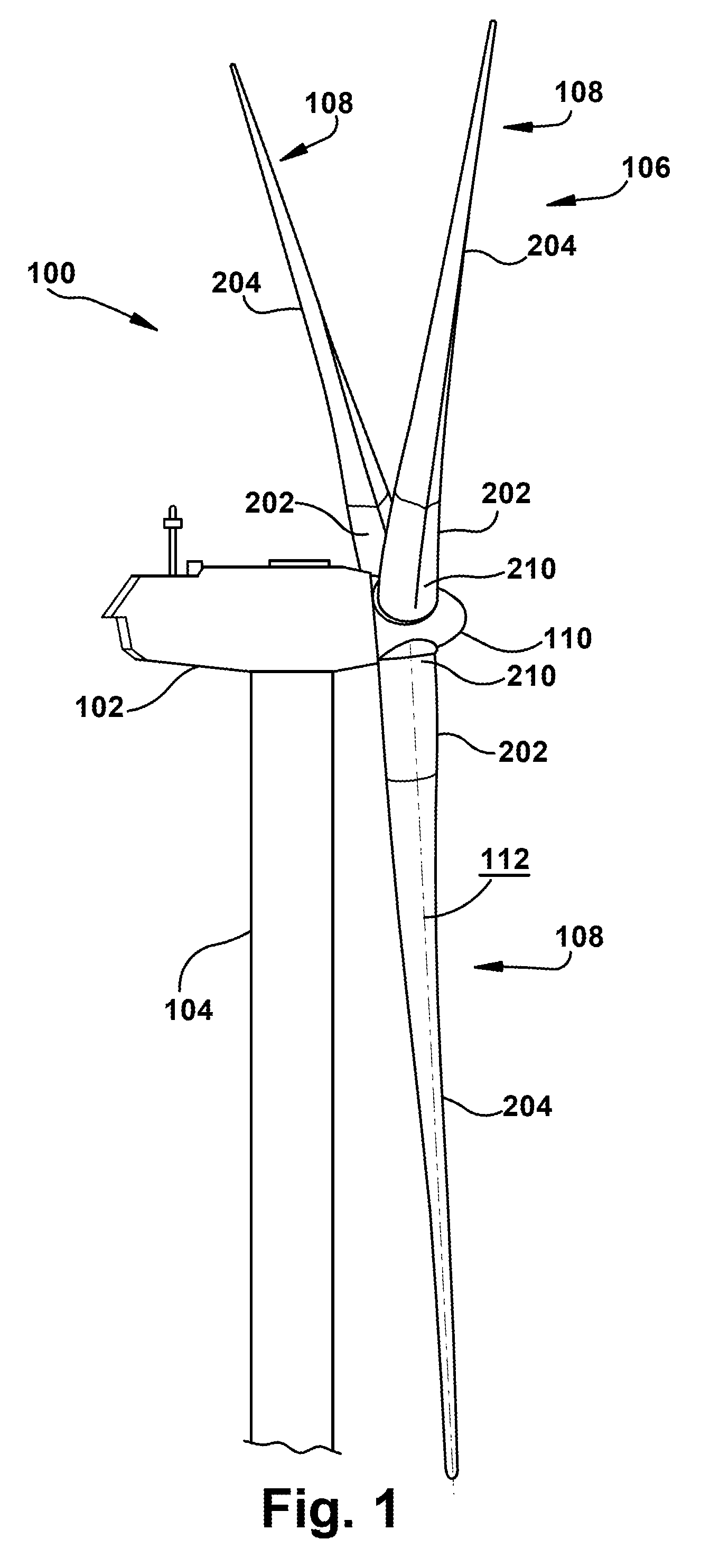
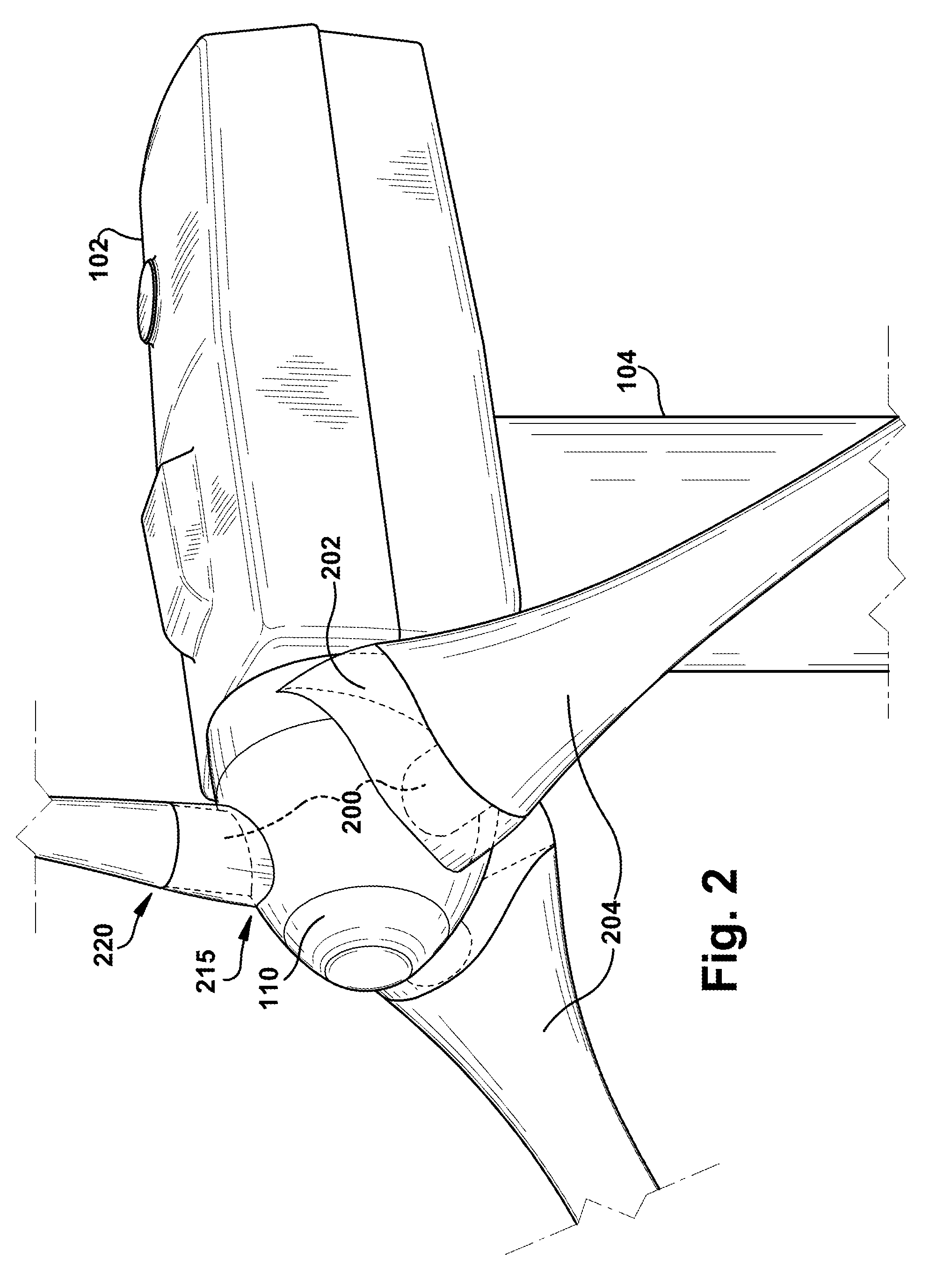
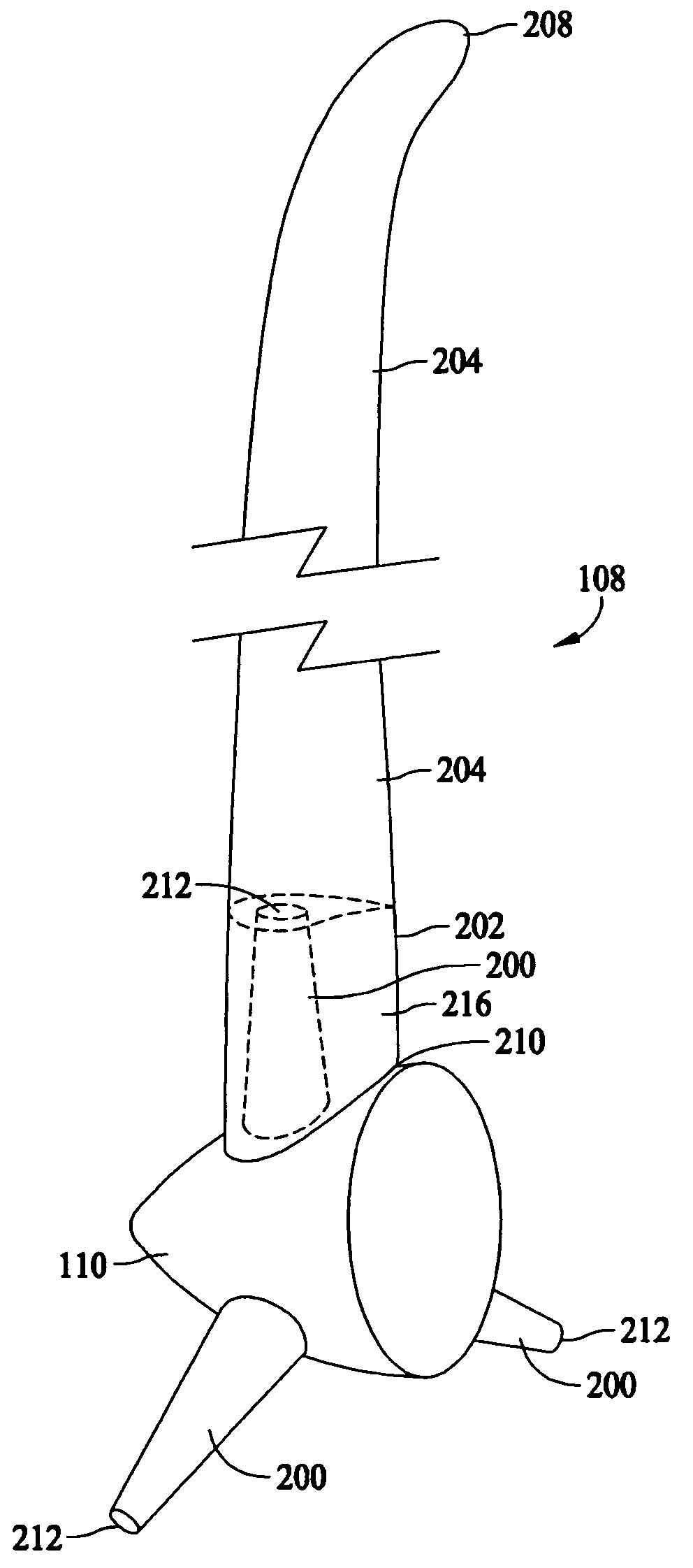
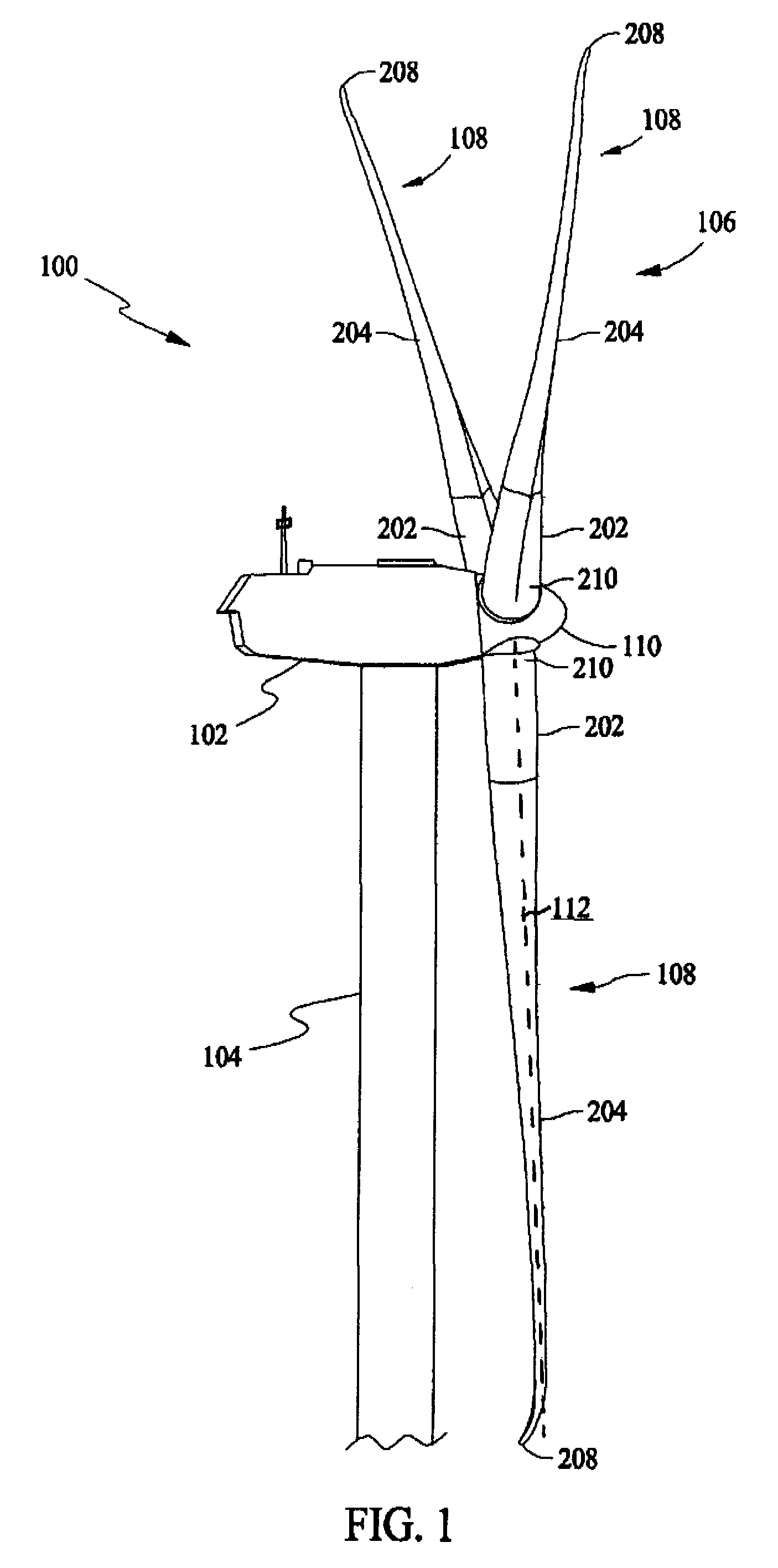
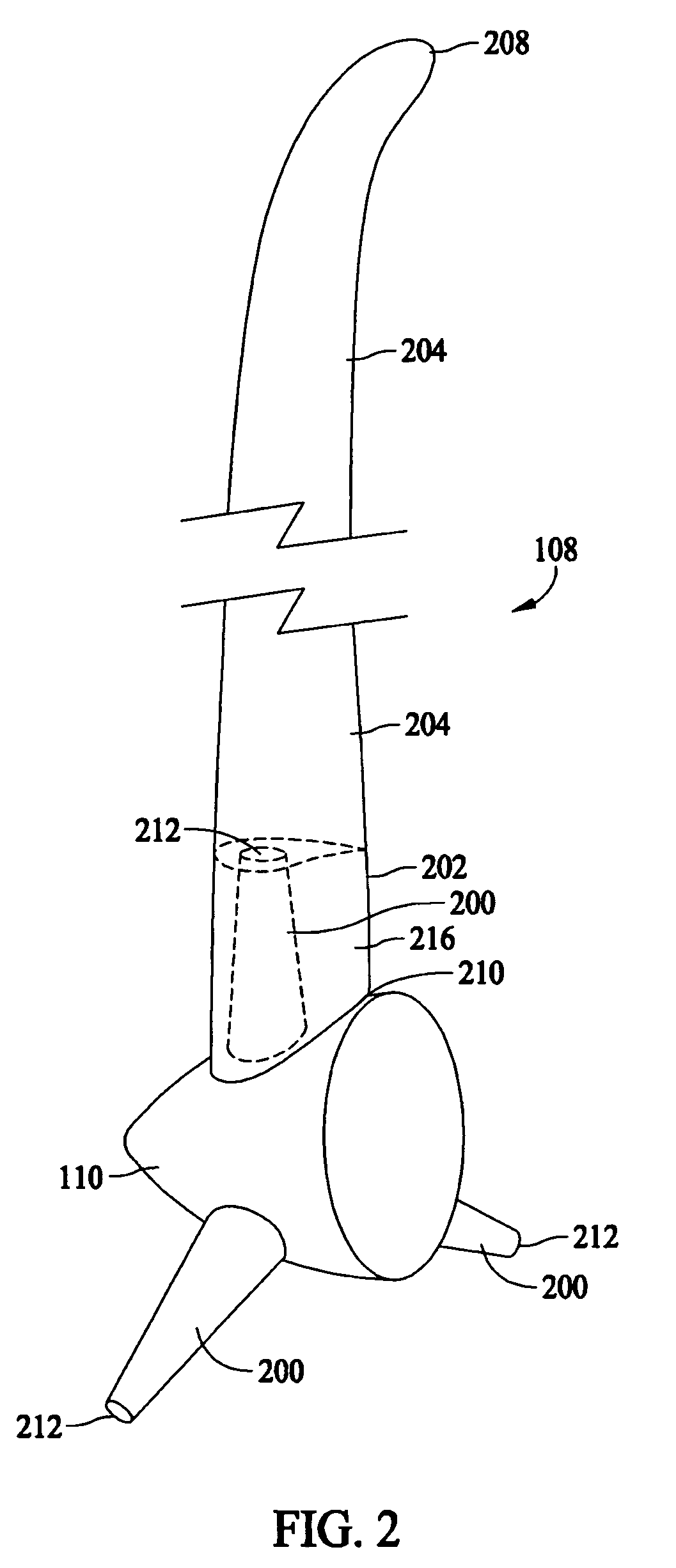
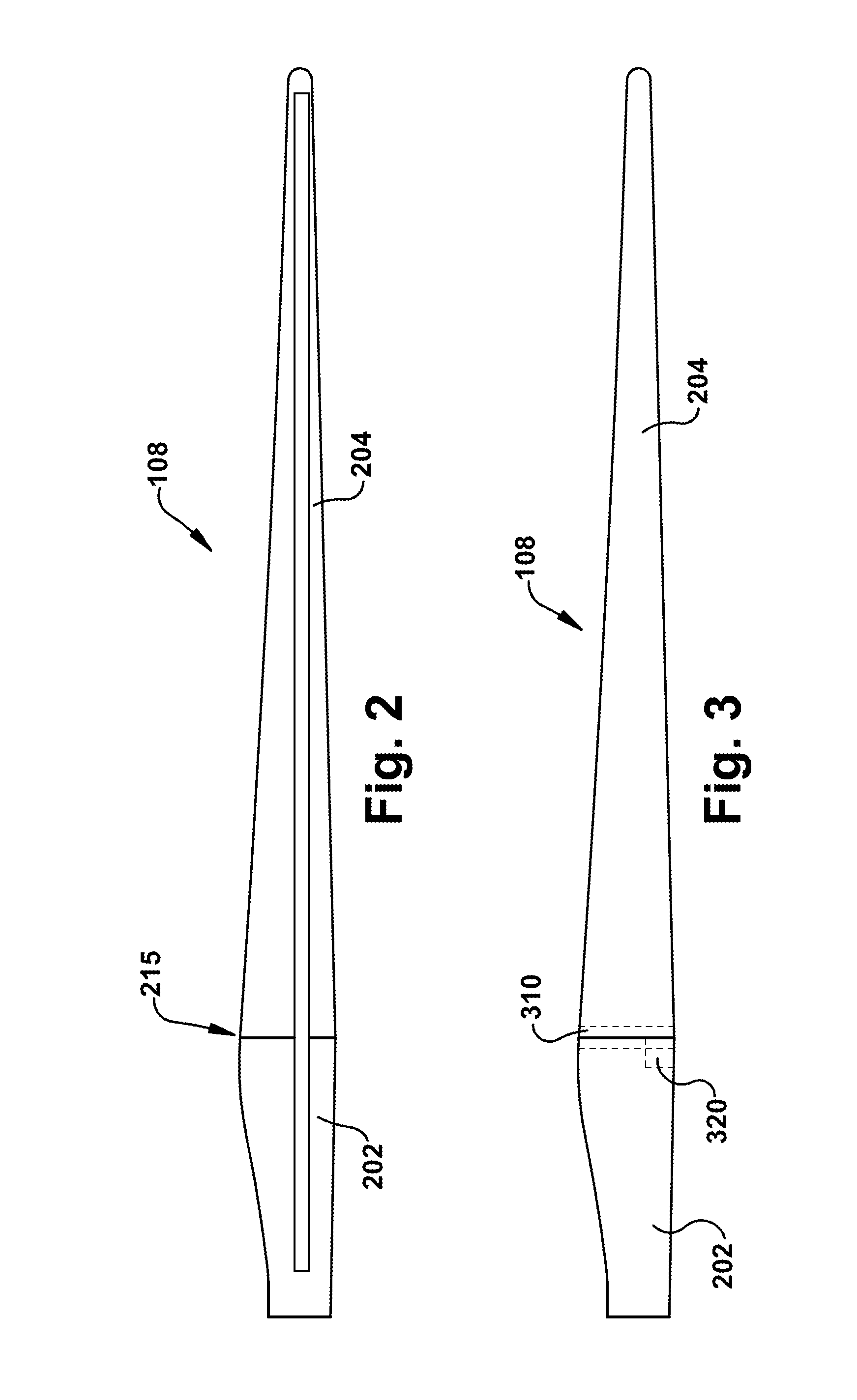
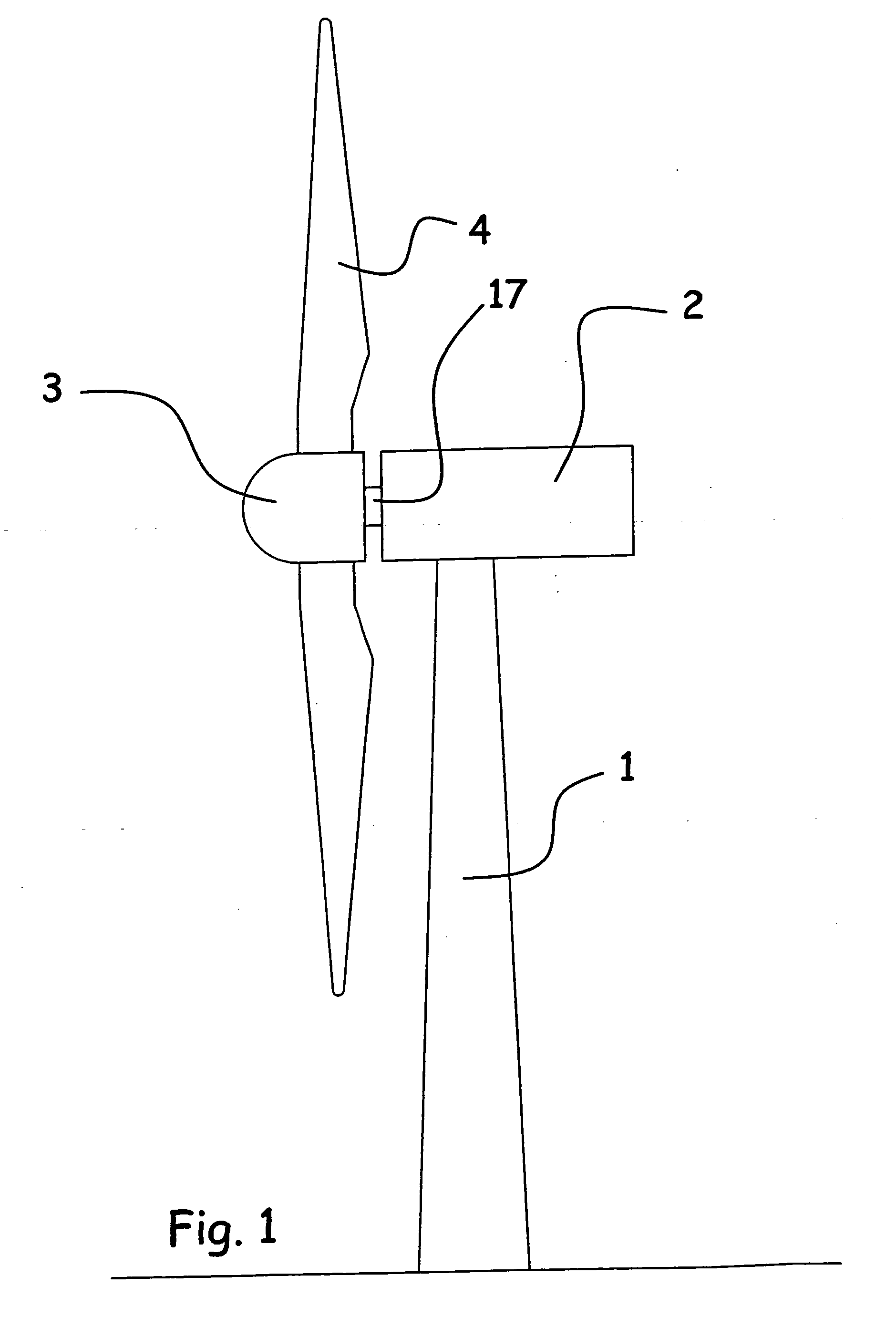
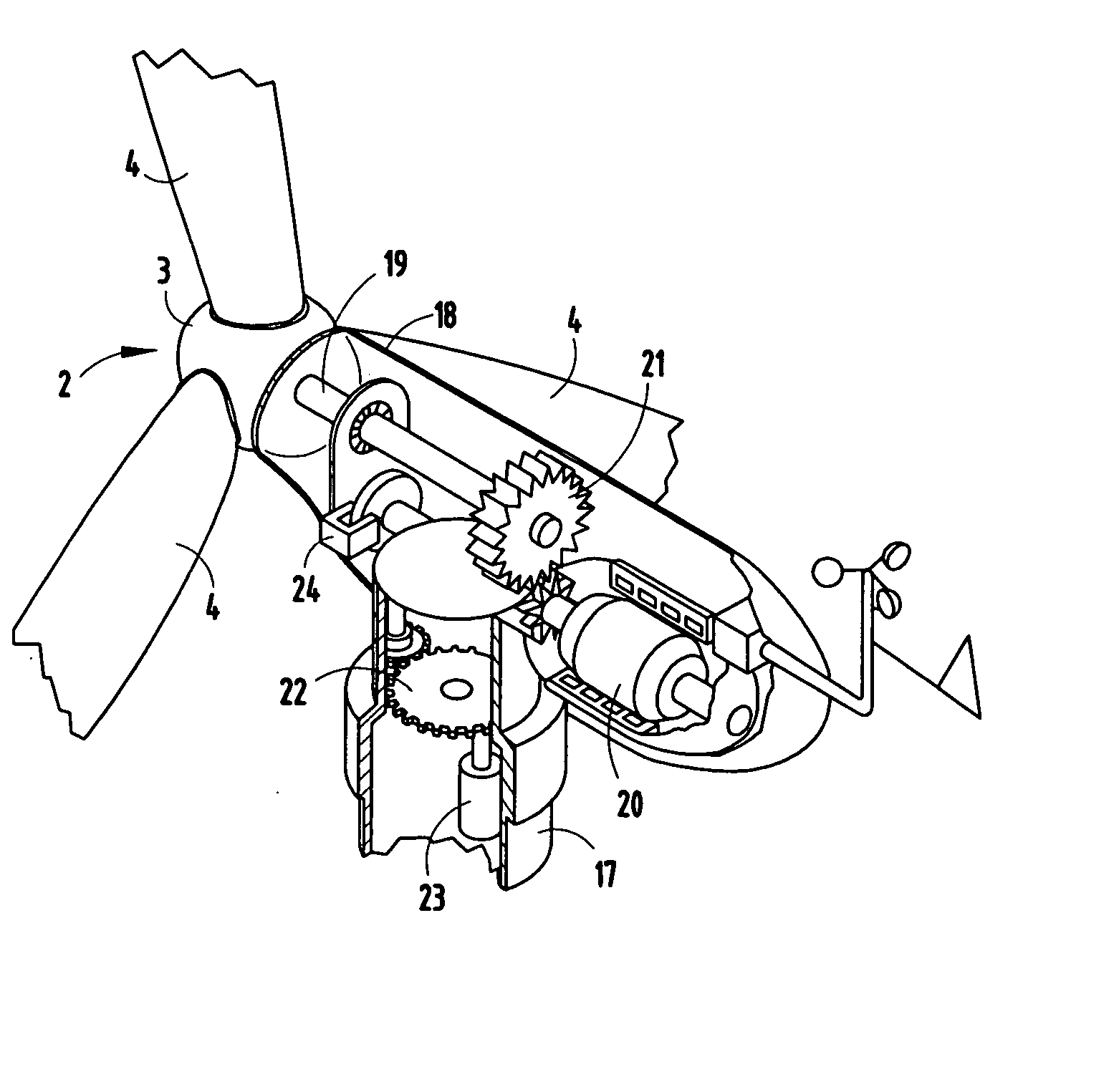
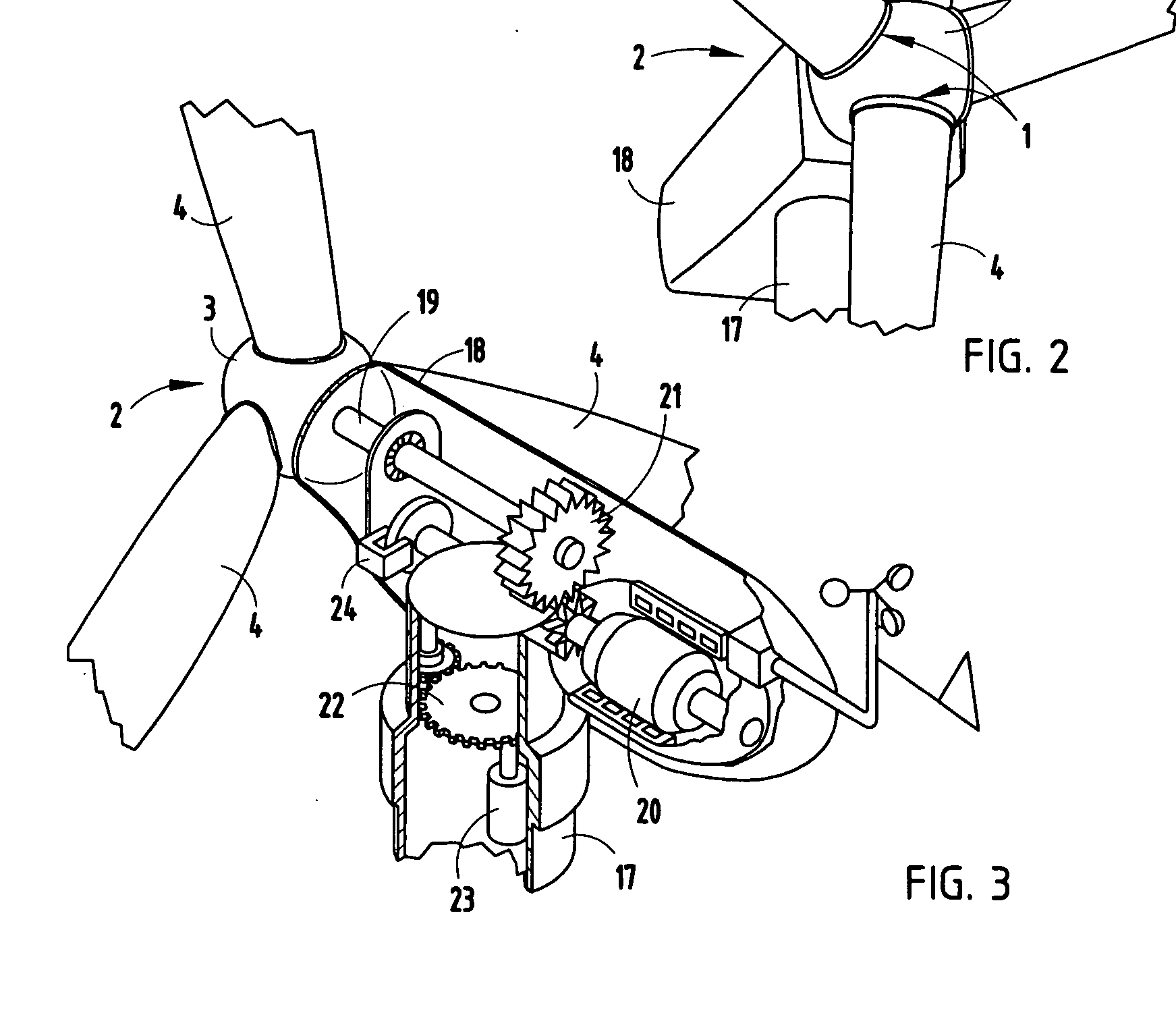
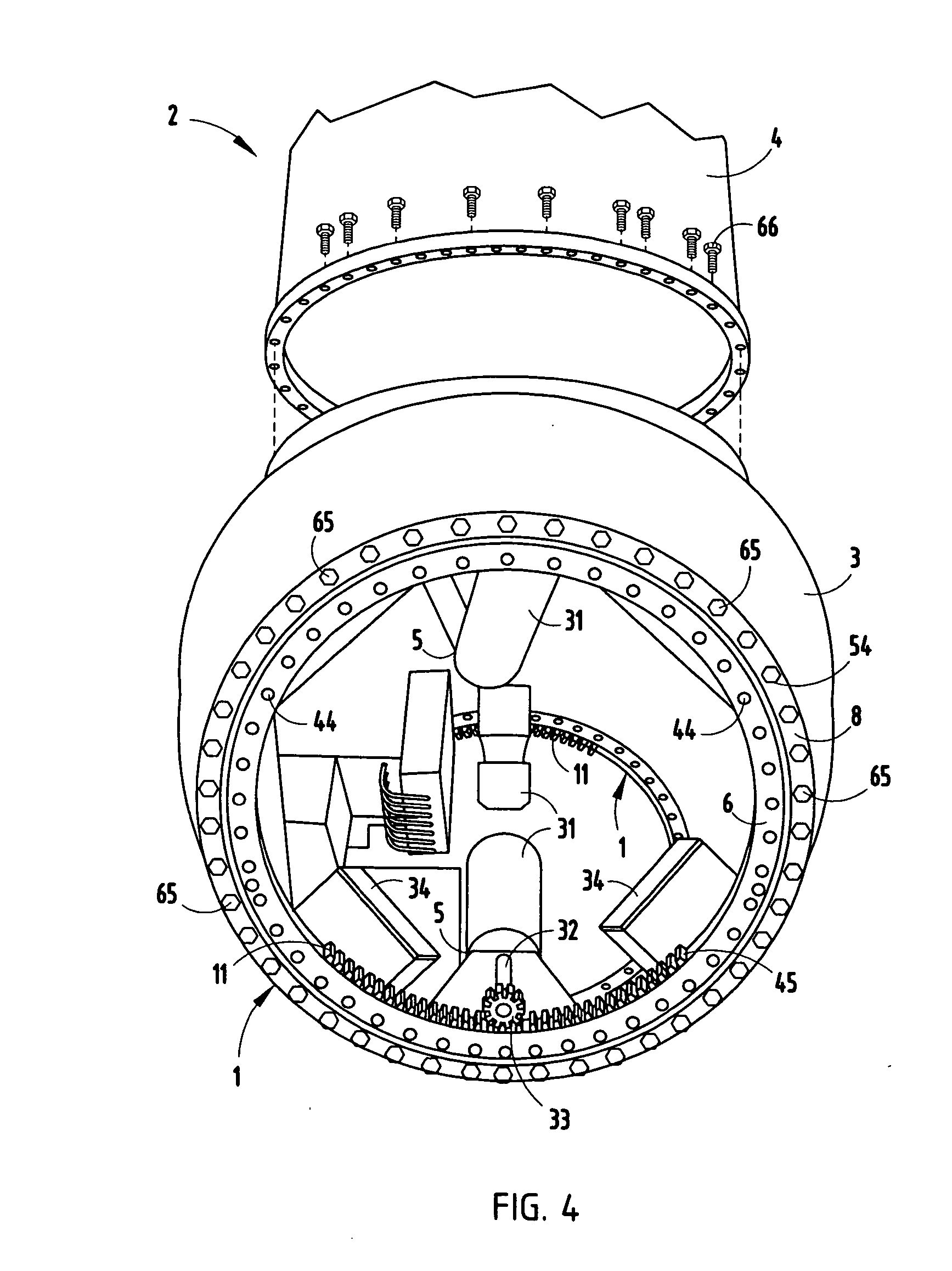
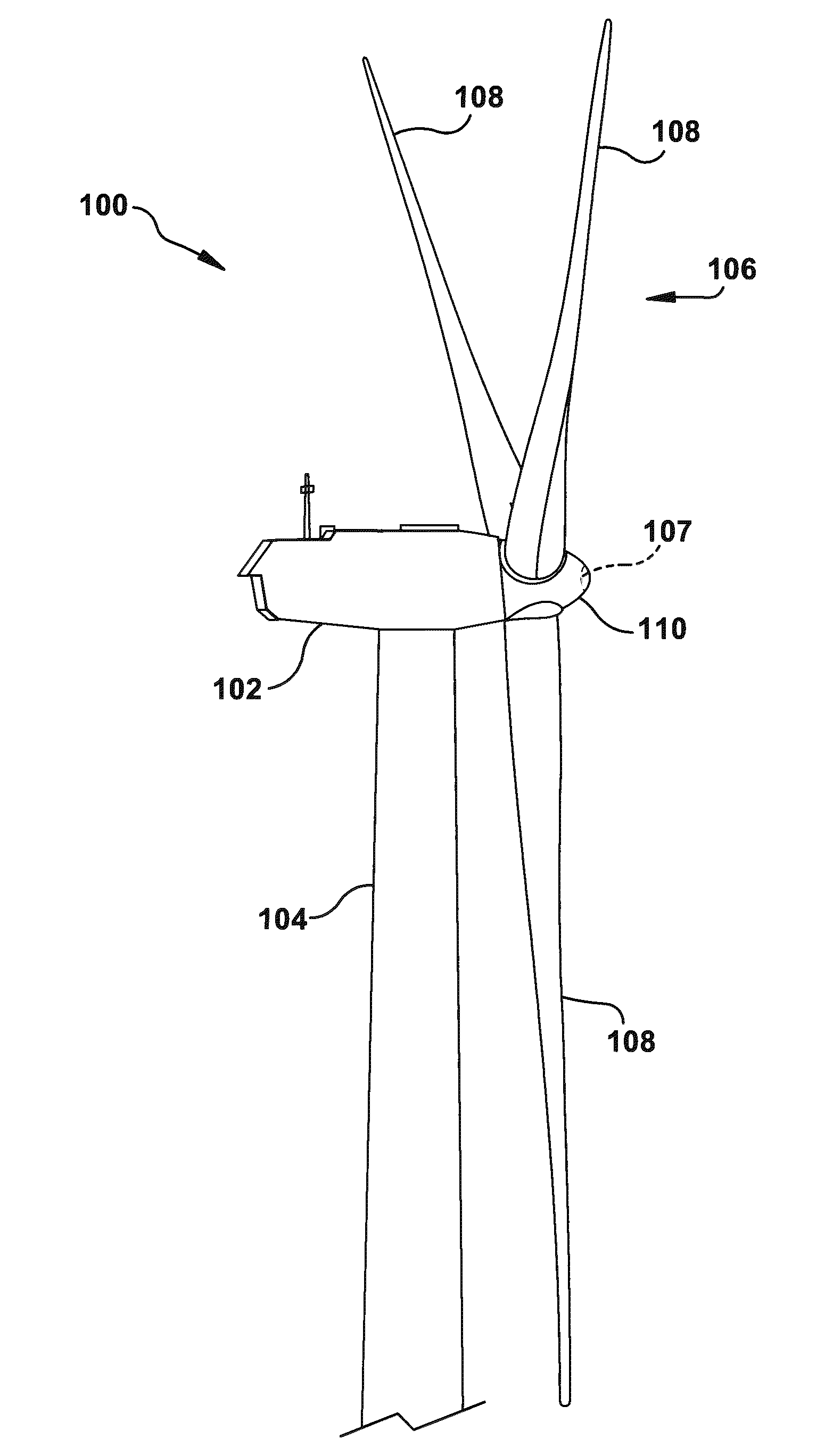
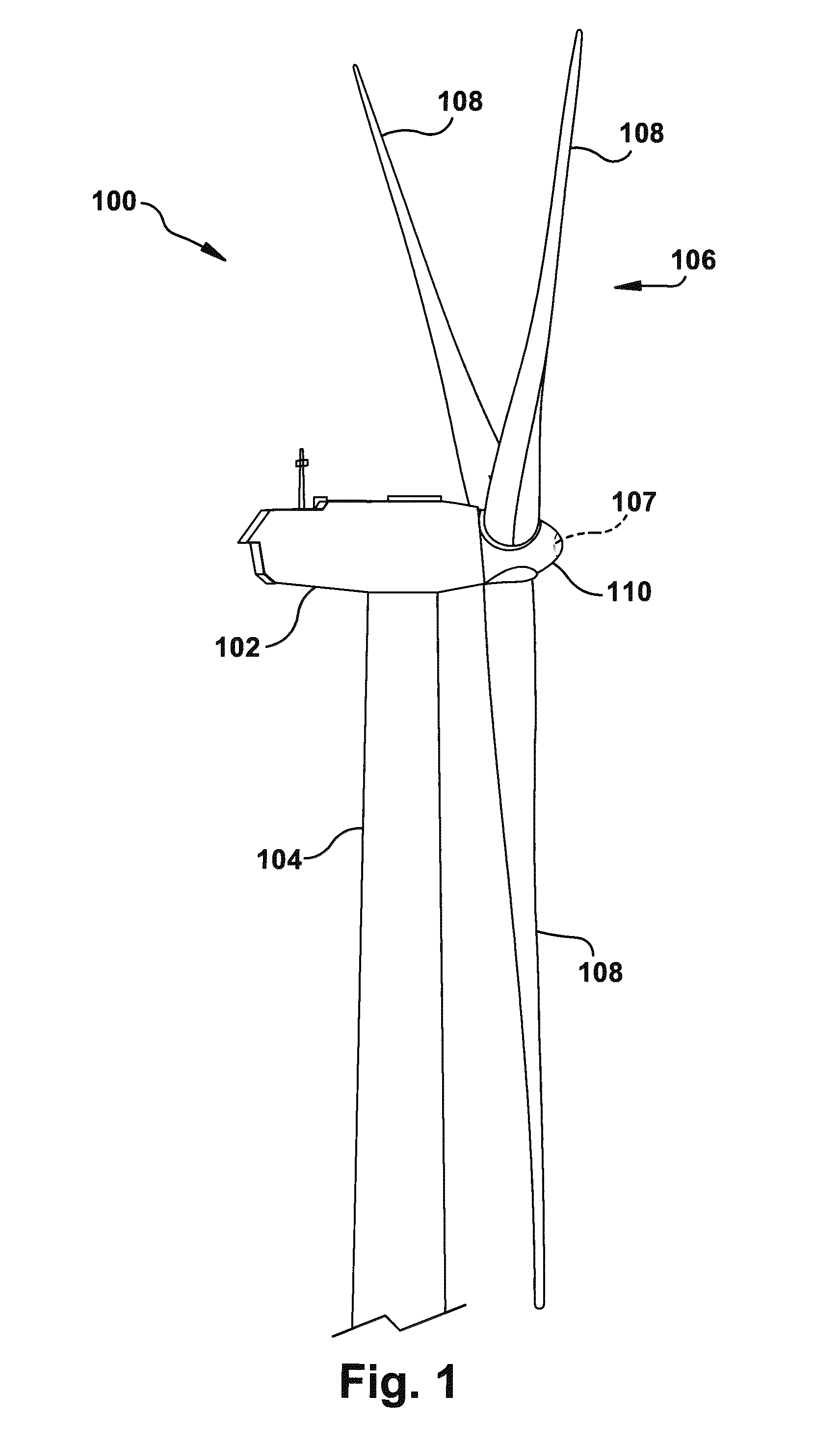
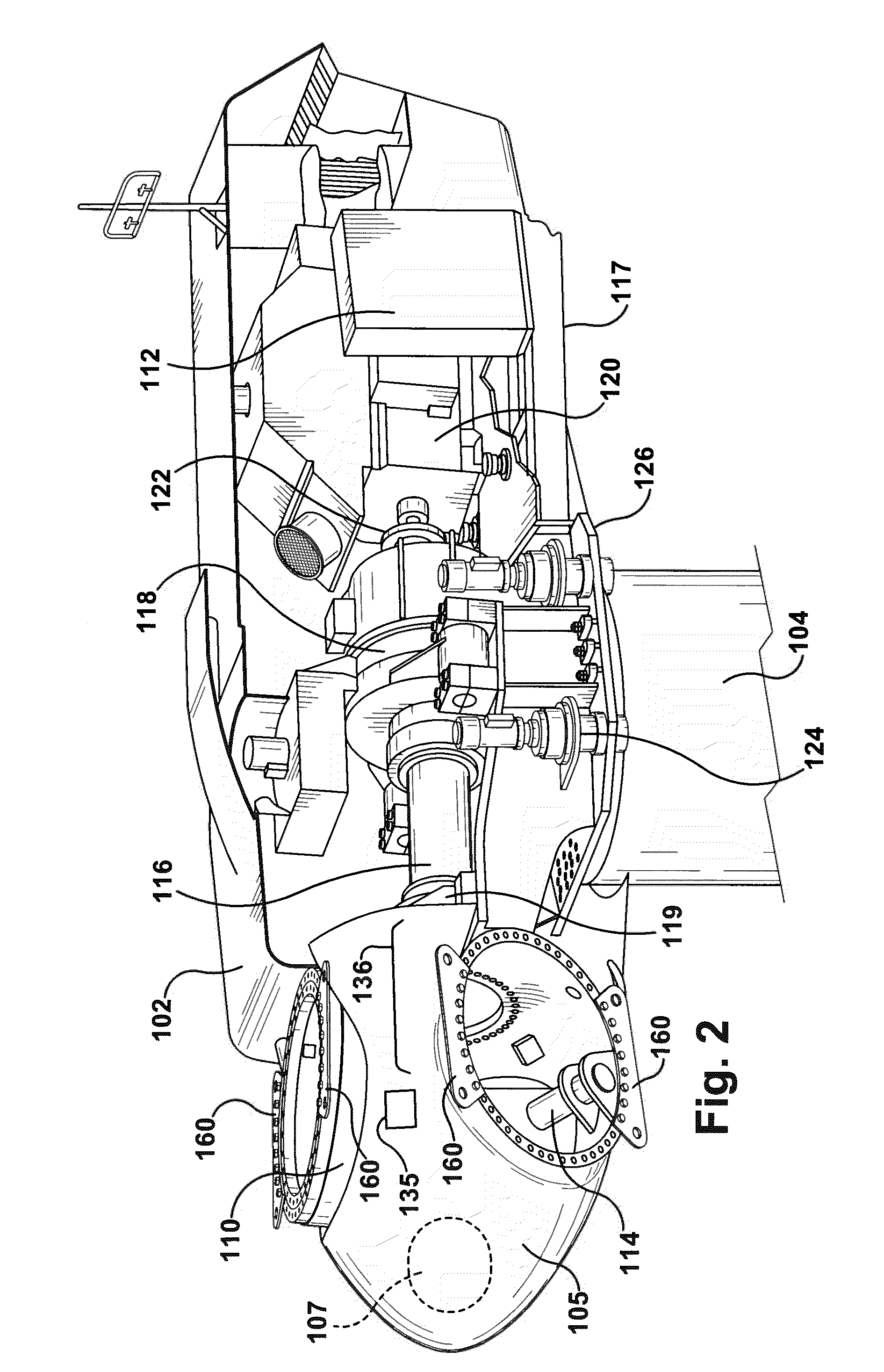
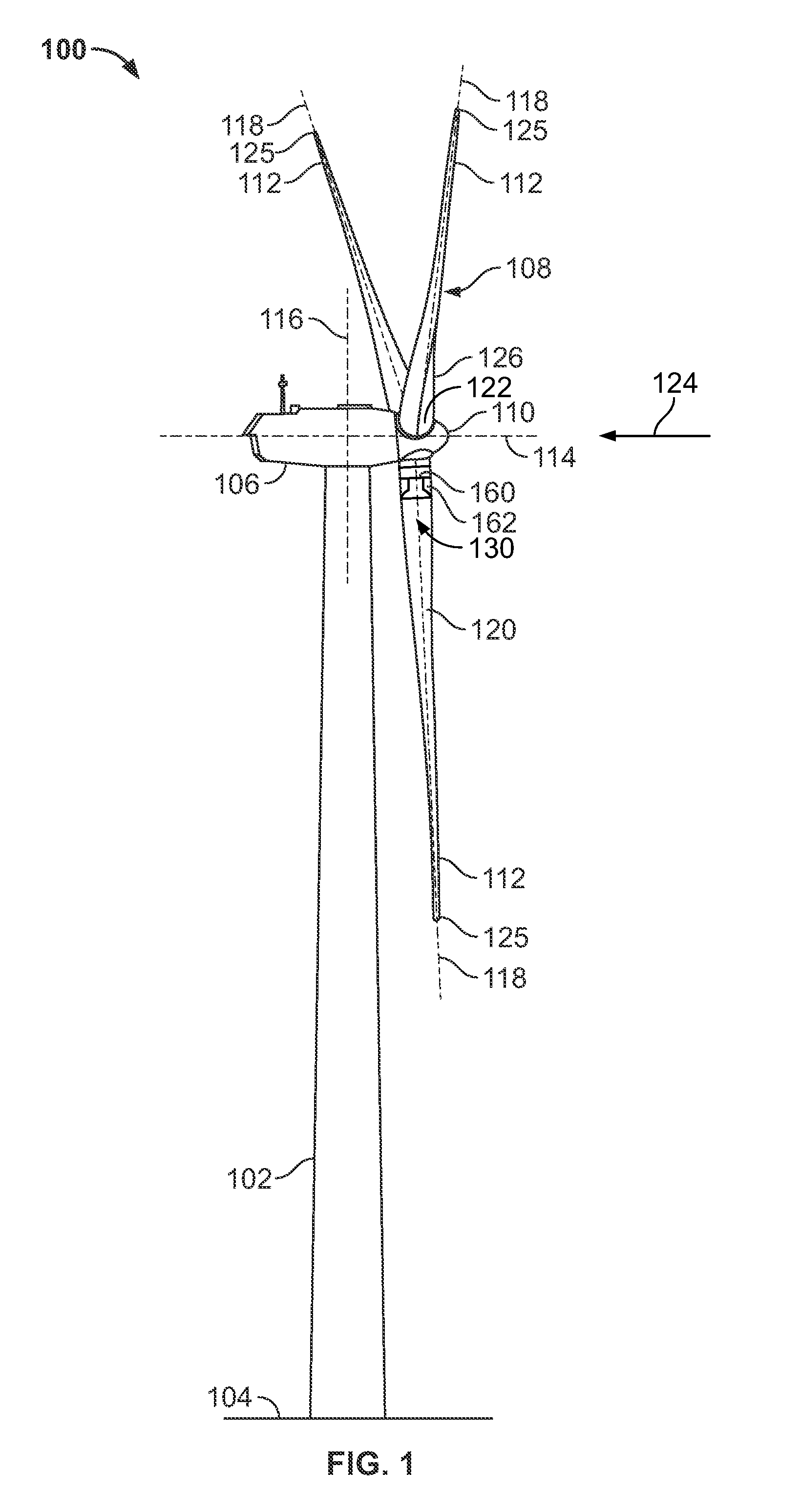
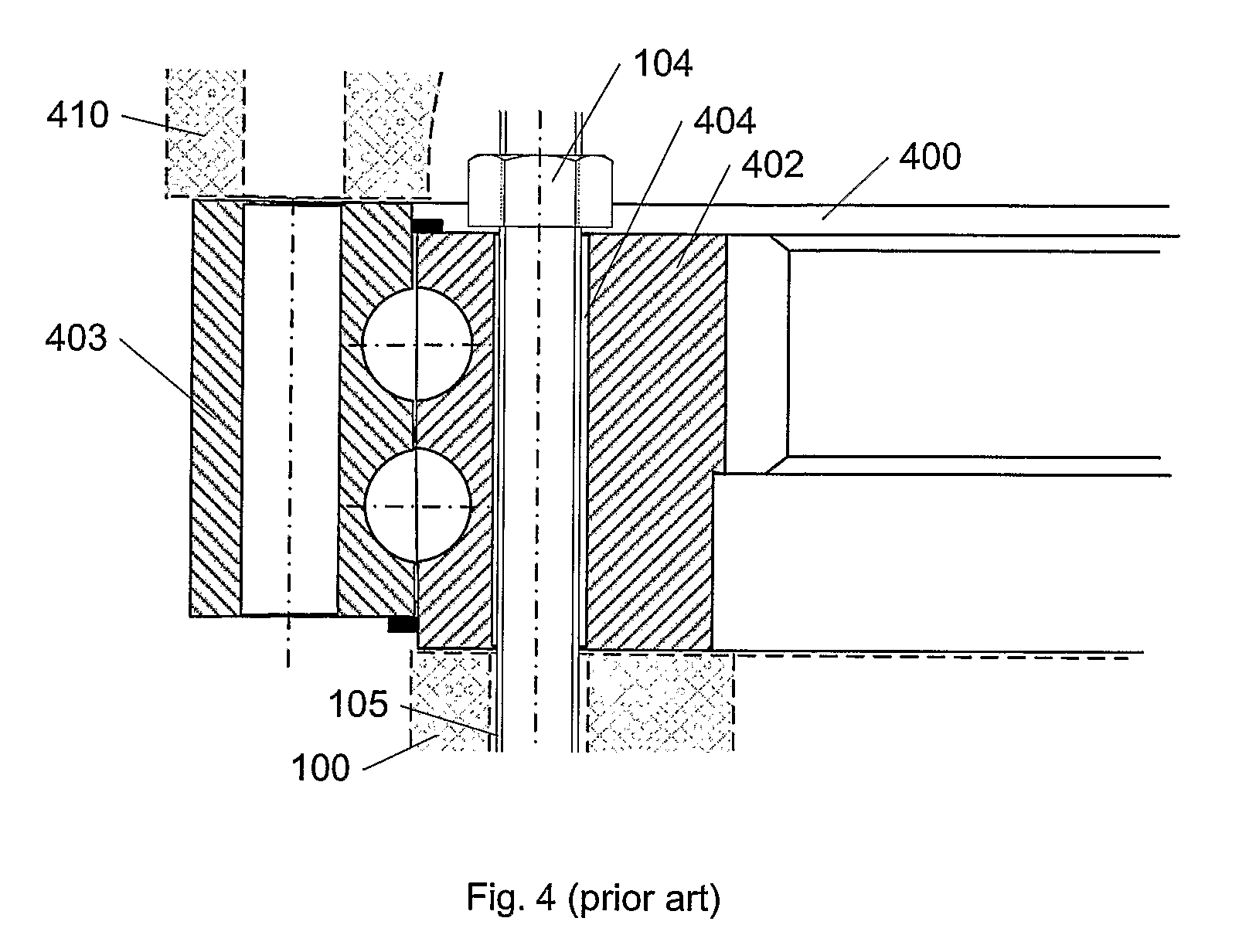
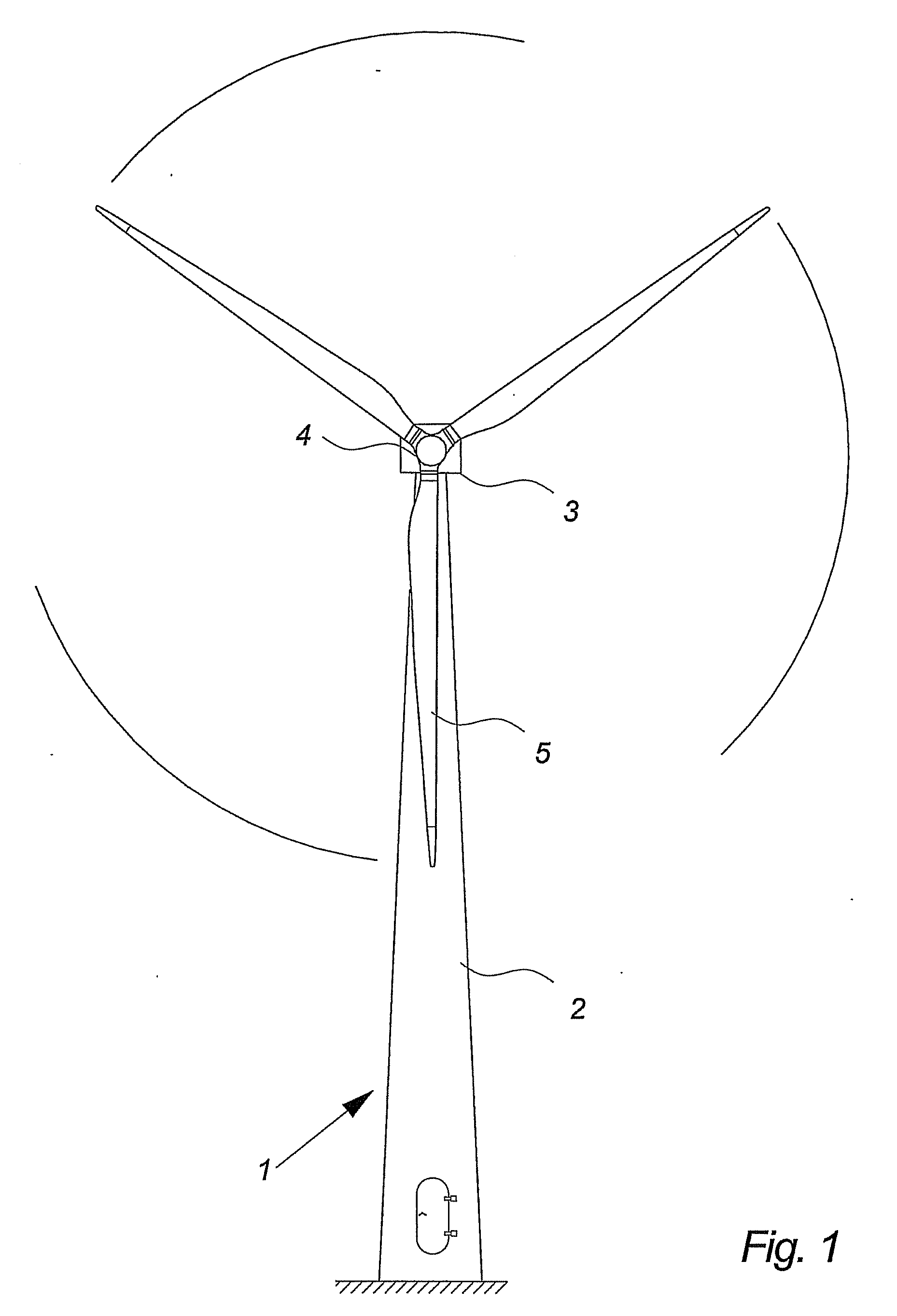
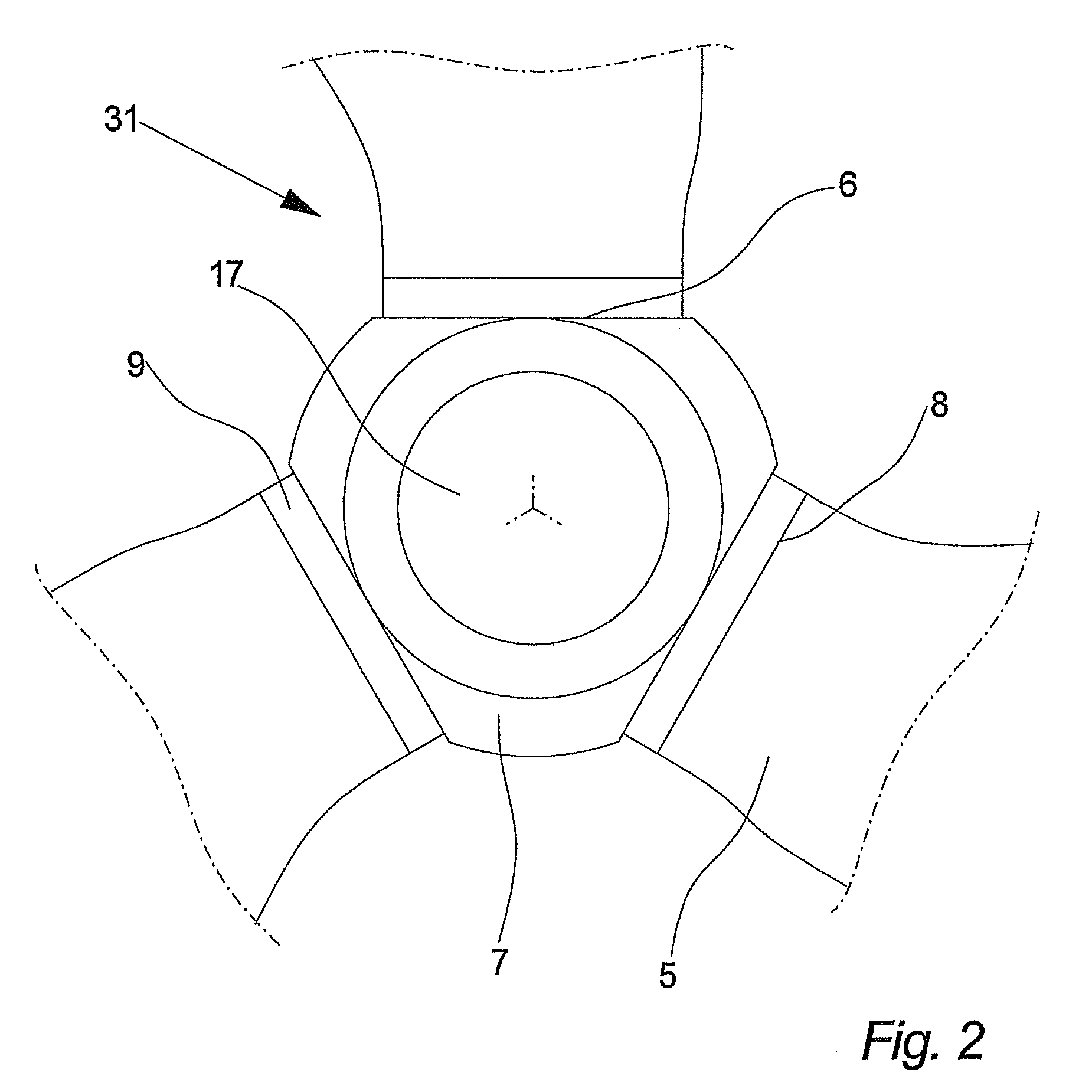
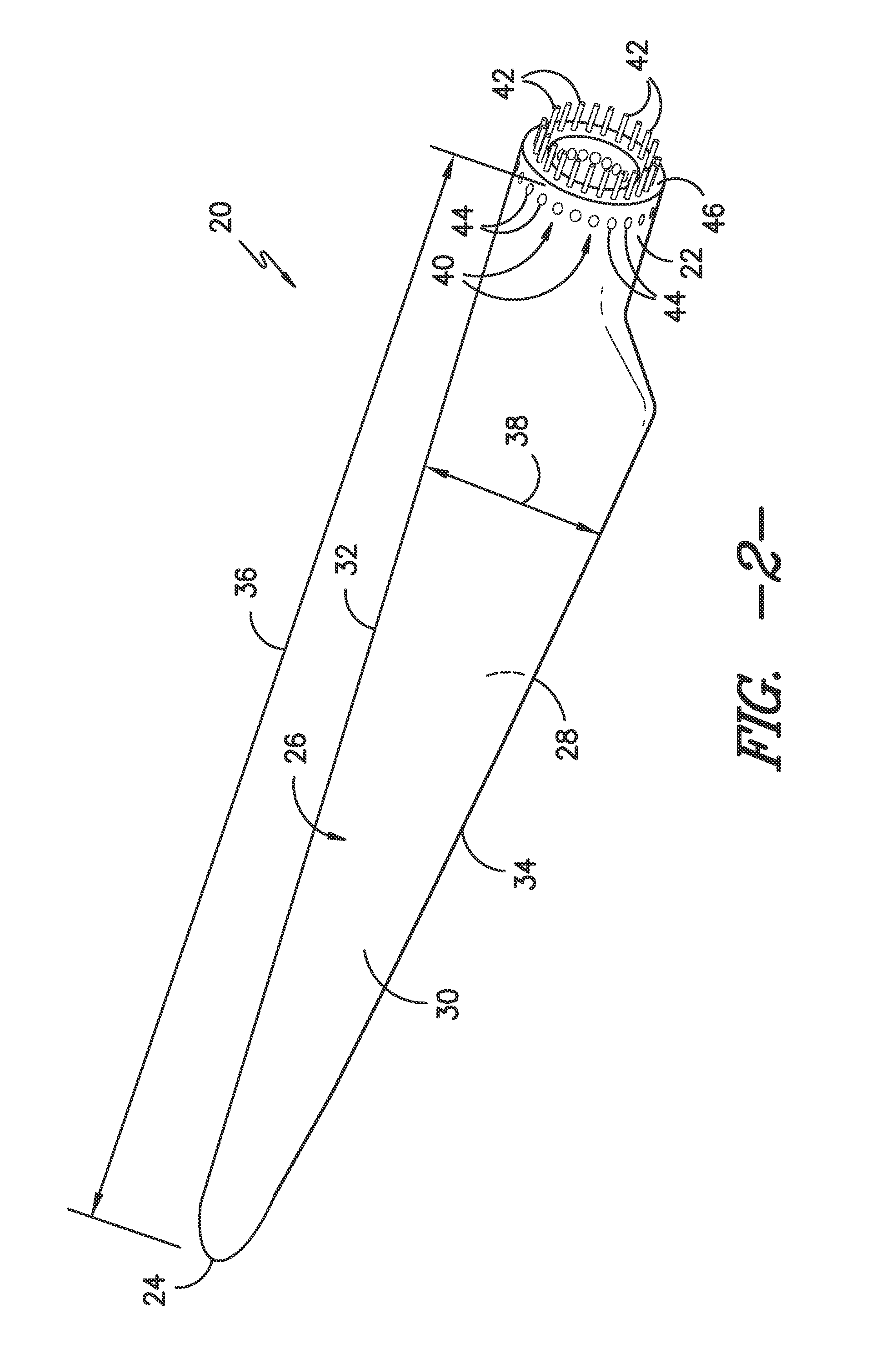
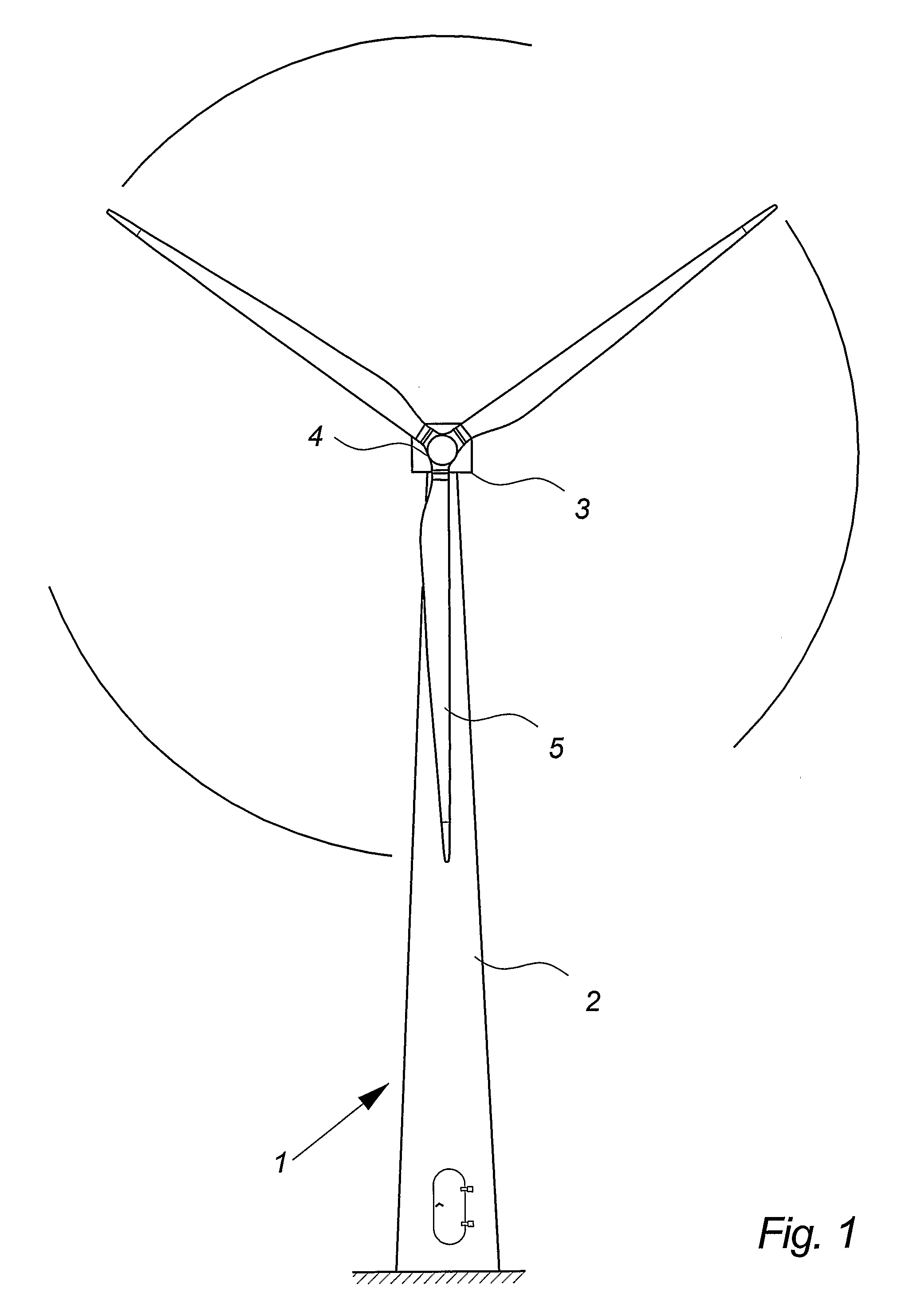
The pitch bearing, also named blade bearing, is a component of modern wind turbines which connect the rotor hub and the rotor blade. The bearing allows the required oscillation to control the loads and power of the wind turbine. The pitch system brings the blade to the desired position by adapting the aerodynamic angle of attack. The pitch system is also used for emergency breaks of the turbine system.
Wind turbine ring/shroud drive system
InactiveUS6951443B1Easy to adaptEliminate structureWind motor controlPump componentsNacelleGear drive
A wind turbine capable of driving multiple electric generators having a ring or shroud structure for reducing blade root bending moments, hub loads, blade fastener loads and pitch bearing loads. The shroud may further incorporate a ring gear for driving an electric generator. In one embodiment, the electric generator may be cantilevered from the nacelle such that the gear on the generator drive shaft is contacted by the ring gear of the shroud. The shroud also provides protection for the gearing and aids in preventing gear lubricant contamination.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-section wind turbine rotor blades and wind turbines incorporating same
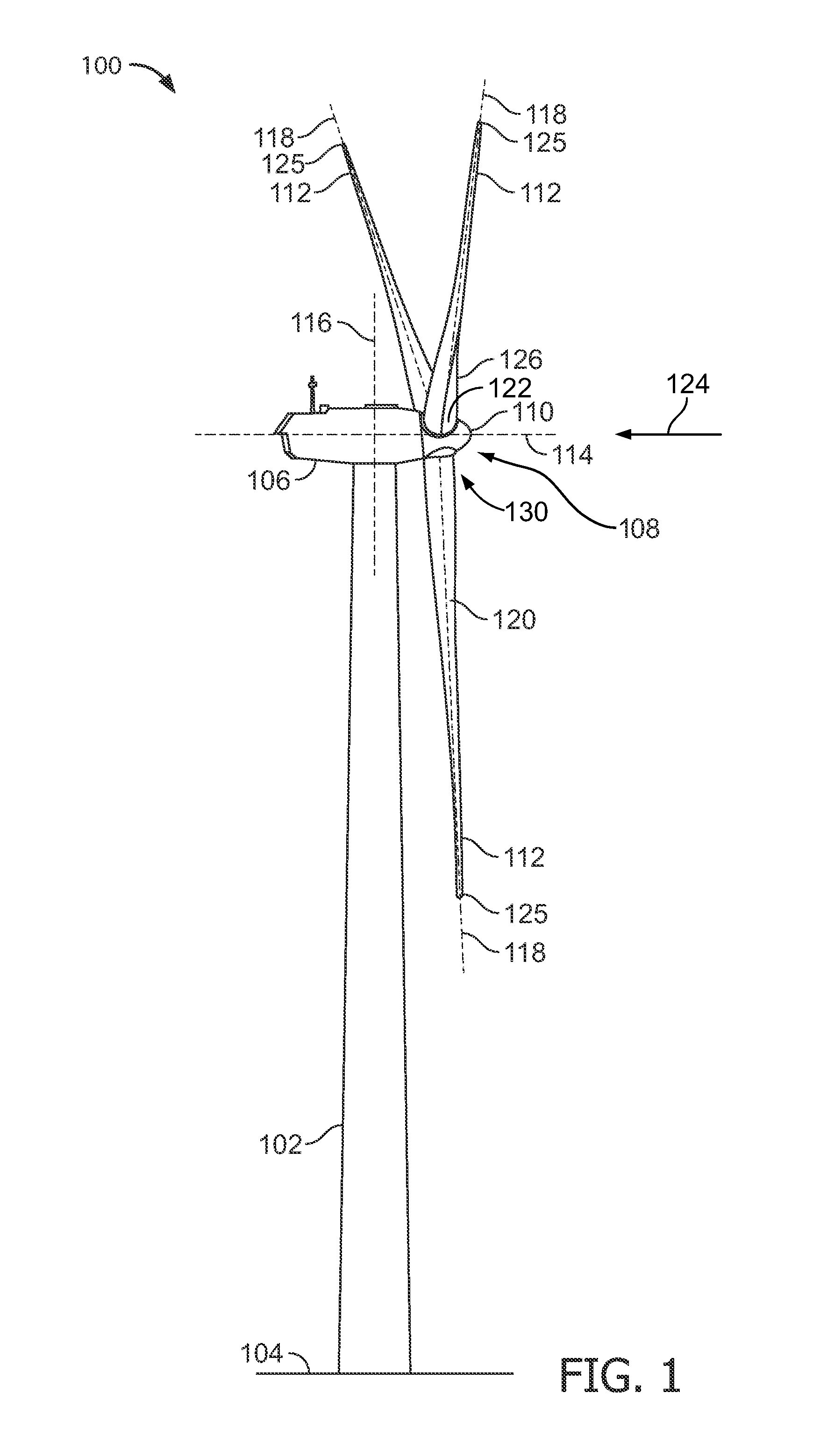
A multi-section blade for a wind turbine comprising a hub extender connected to a hub of the wind turbine is provided. The blade includes at least one pitchable outboard section. The hub extender can have a pitch bearing located near the interface between the hub and hub extender, or the hub extender and outboard blade section. The hub extender can be configured to pitch or not pitch with the outboard blade sections. An aerodynamic fairing is configured to mount over the hub extender and is configured to not pitch with the outboard blade sections.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
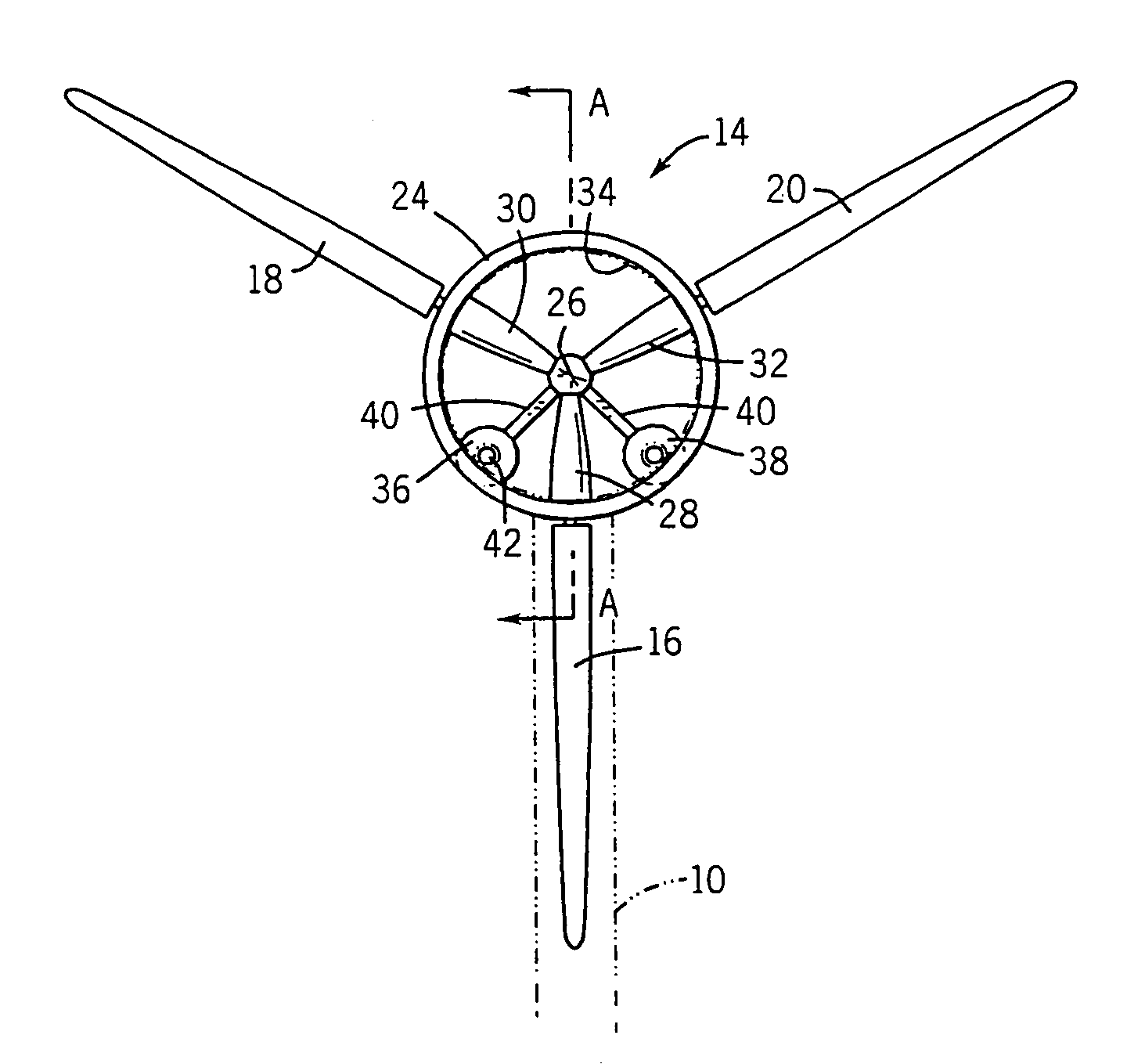
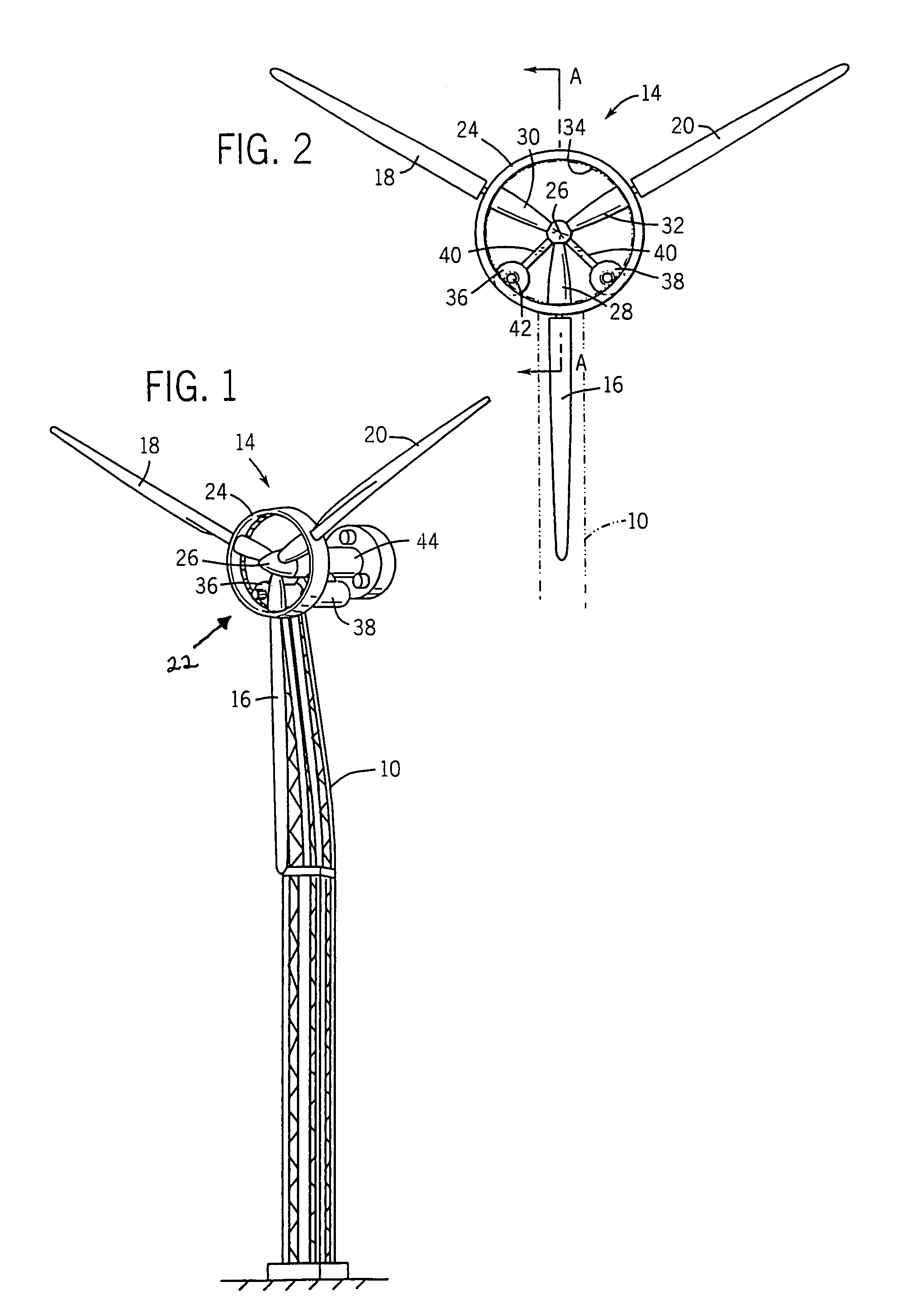
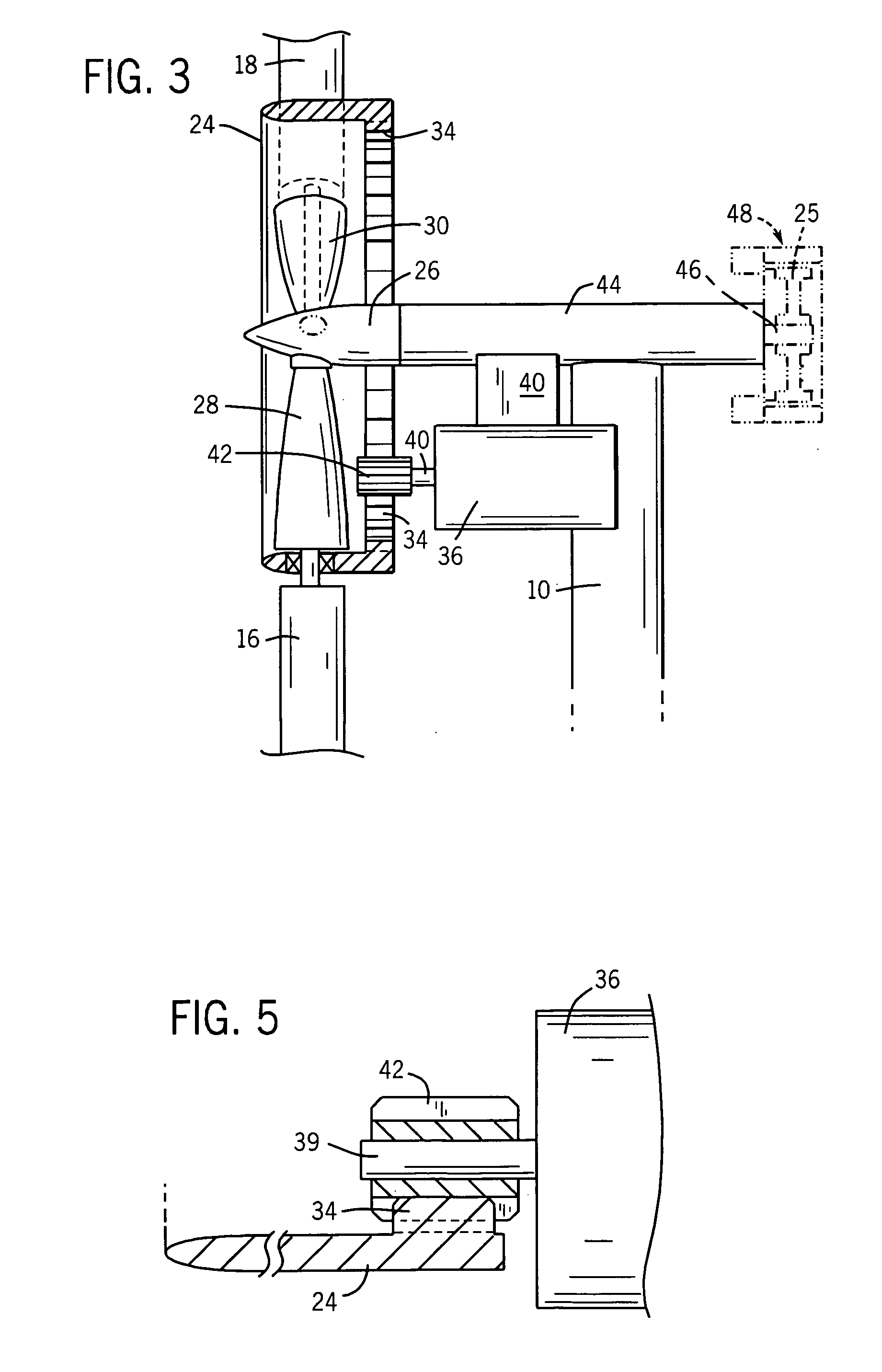
Wind turbine pitch bearing and method
InactiveUS7331761B2Reduce manufacturing costEasy to useRotary bearingsPropellersTurbine bladeWind force
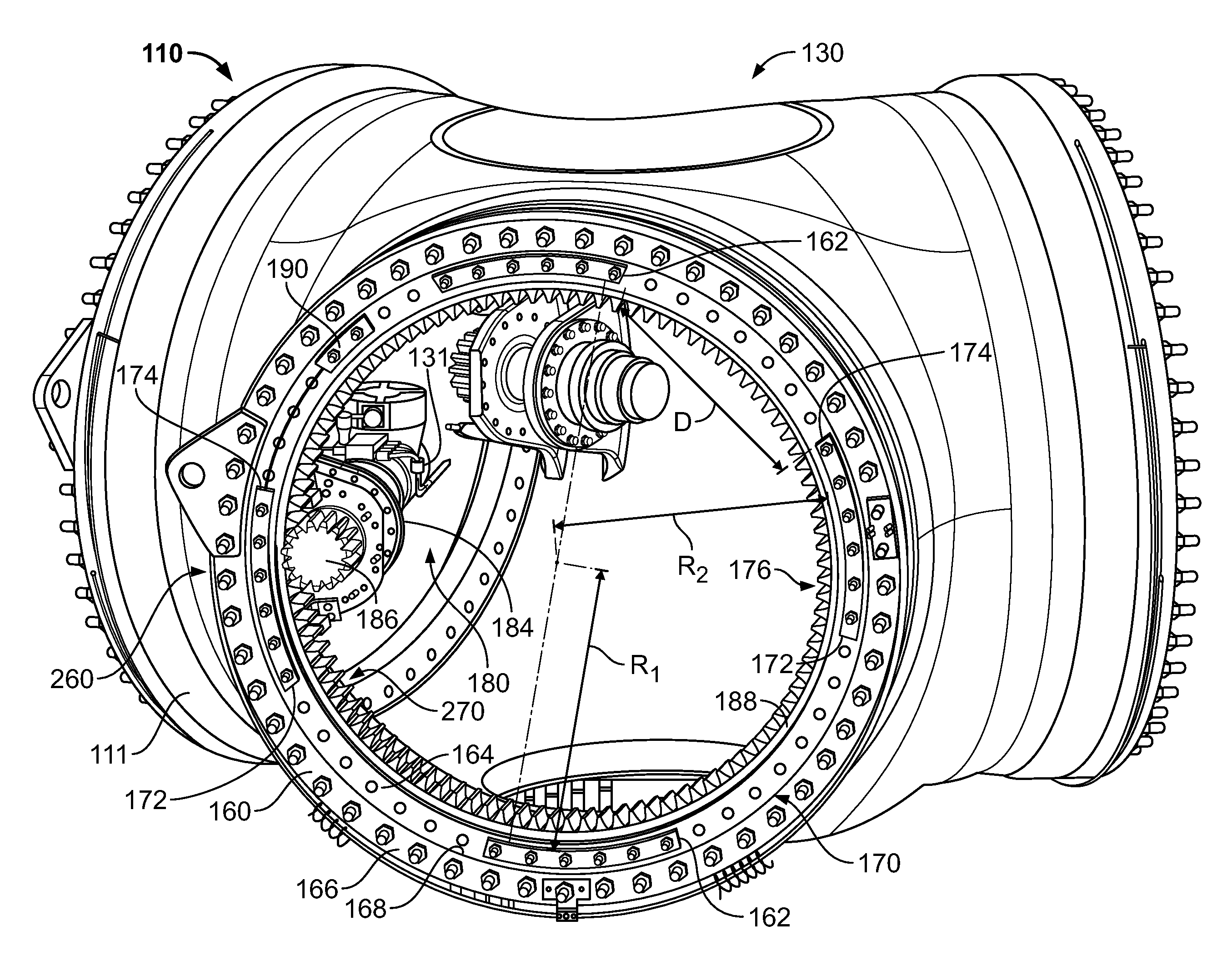
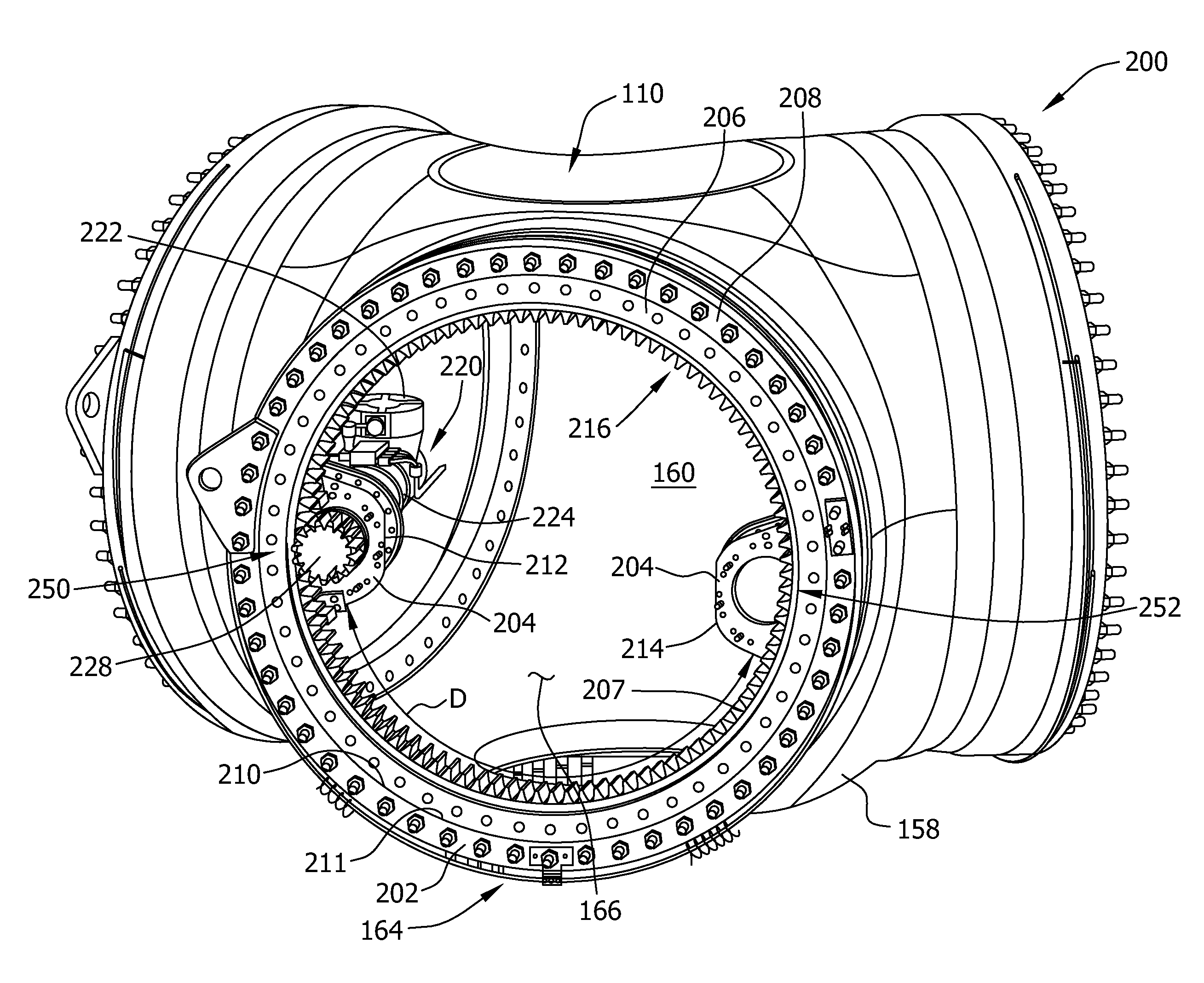
A pitch bearing and related method for wind electric turbines has an annularly-shaped first bearing ring connected with an associated wind turbine blade, and includes a first raceway groove. An annularly-shaped second bearing ring is connected with the rotor portion of the wind turbine, and includes a second raceway groove aligned with the first raceway groove. Rolling elements are positioned in the first and second raceway grooves to rotatably interconnect the two bearing rings. A gear segment is formed on one of the bearing rings, and is configured to engage a pitch drive portion of the wind turbine to pivot the blade axially between different pitch angles. The gear segment has an arcuate measure of less than 200 degrees to facilitate economical manufacture.
Owner:KAYDON CORP
Wind Turbine Pitch Bearing, and Use Hereof
ActiveUS20080213095A1Excessive distortionWithout reducing bearing durability and functionalityPropellersRoller bearingsTurbine bladeBlade pitch
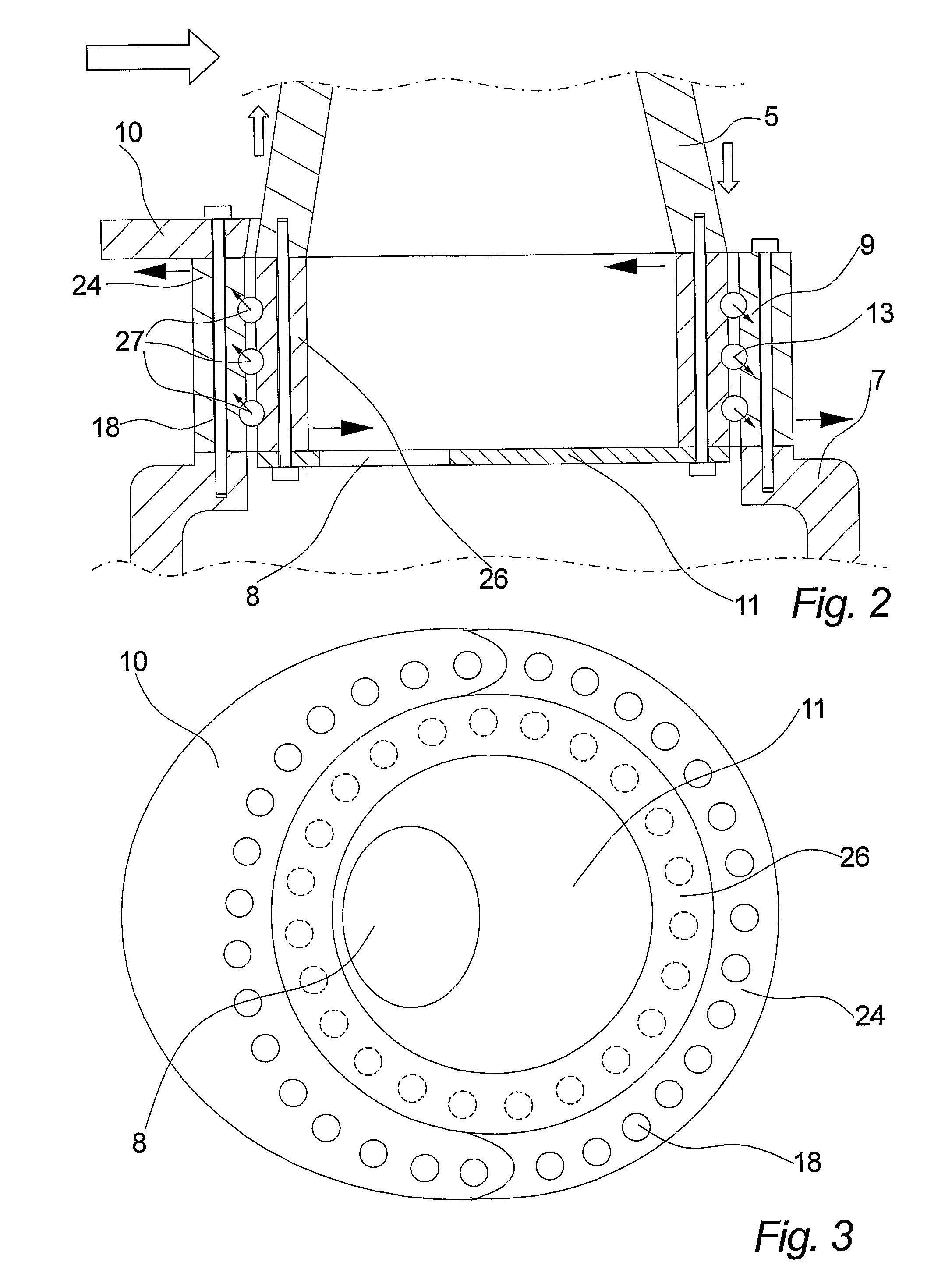
The invention relates to a wind turbine including at least two pitch controlled wind turbine blades. Each blade has pitch bearings including two or more bearing rings, and pitch controlling means for pitching the blades by means of the bearings. The blades are mounted on a hubs via the pitch bearings and the pitch bearings include separate flexibility enhancing means for controlling loads in the bearings.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Lightning protection of a pitch-controlled wind turbine blade
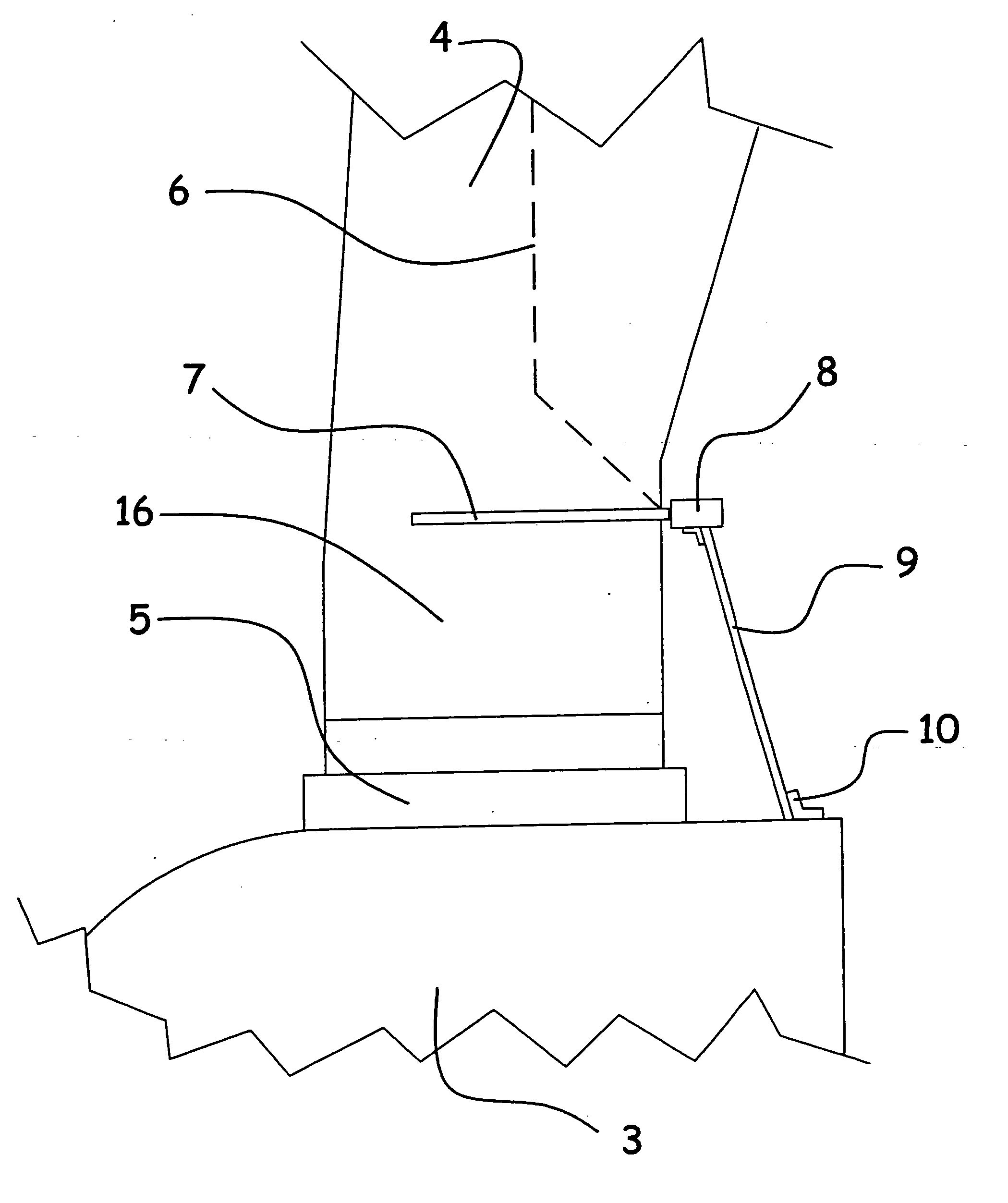
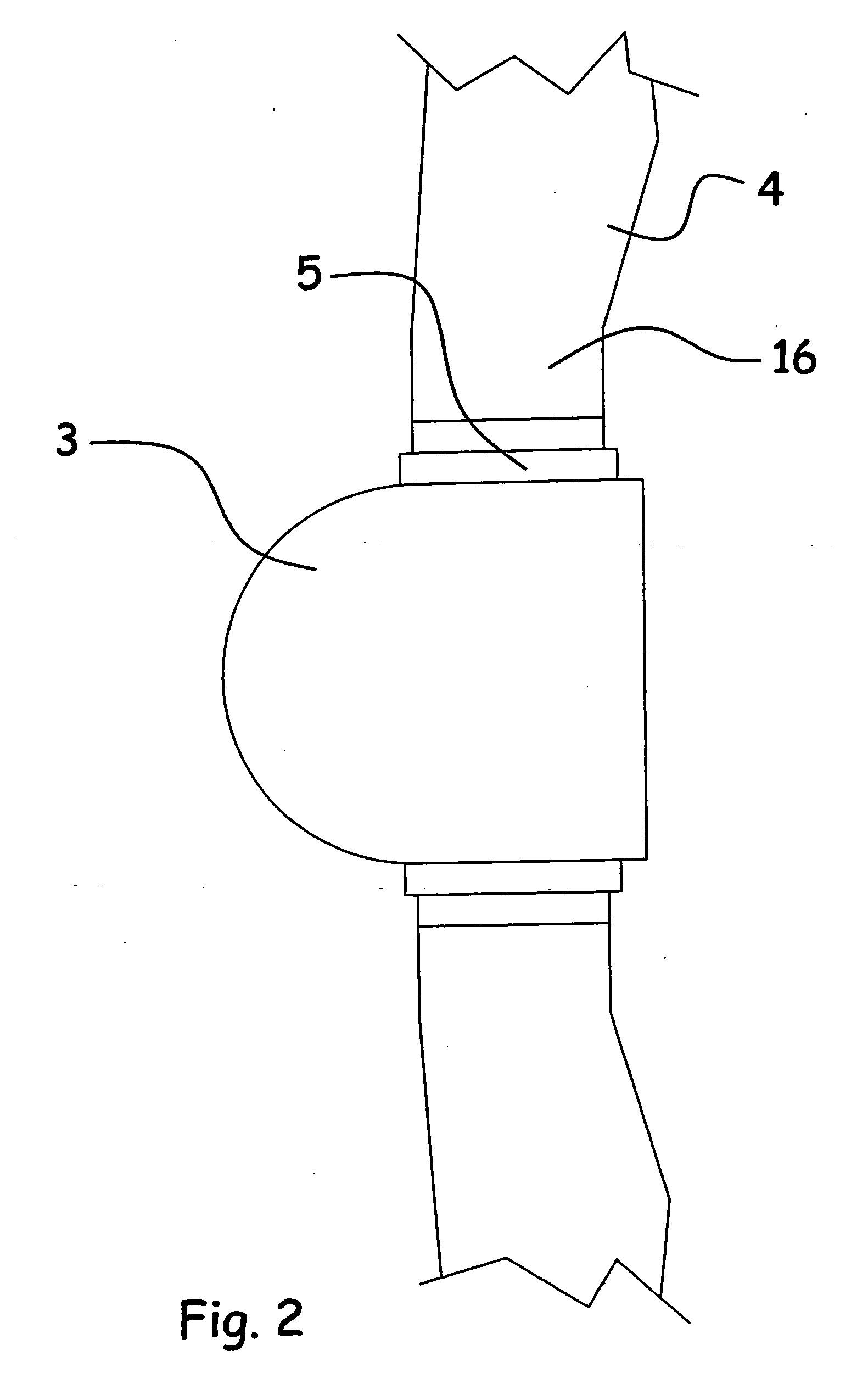
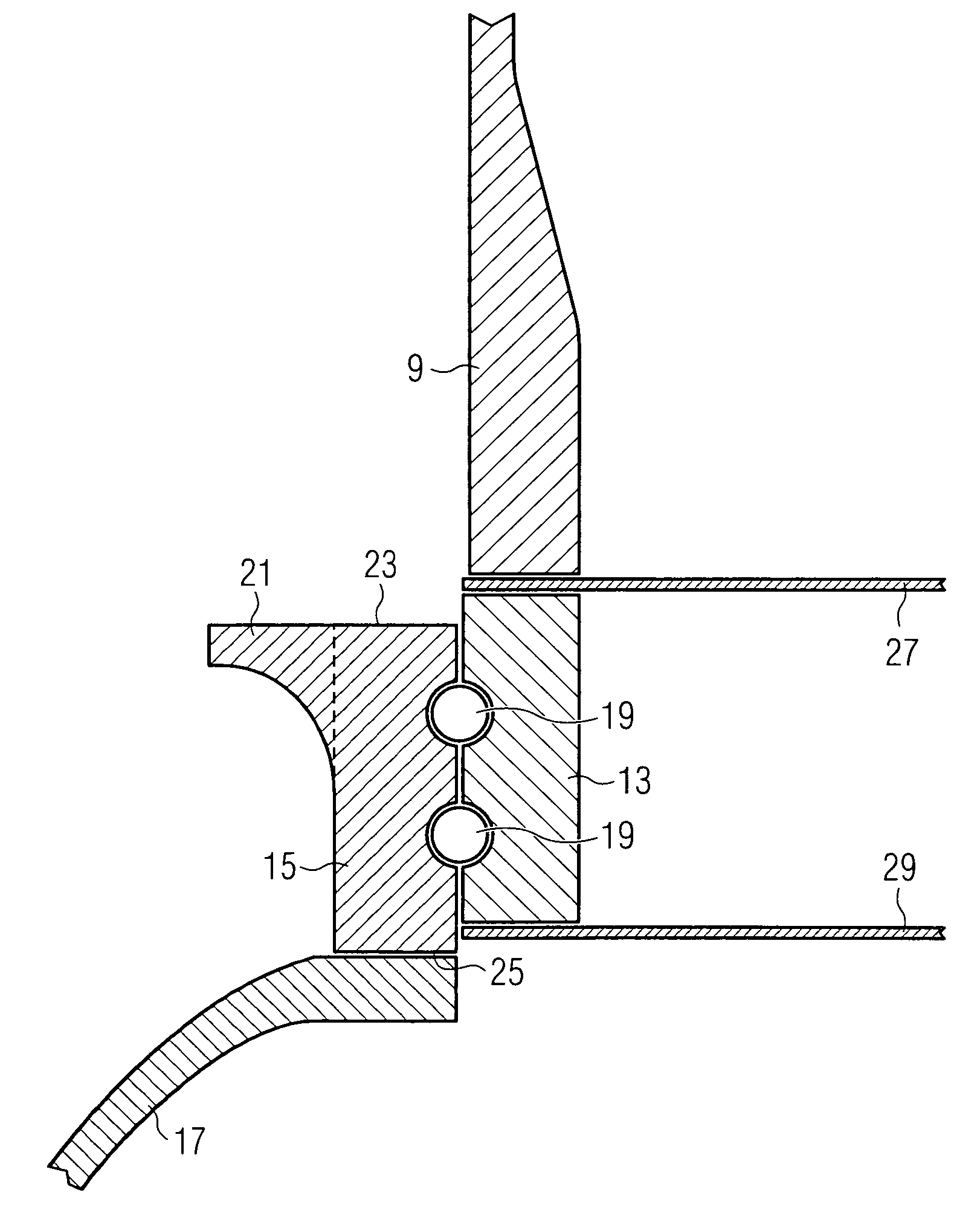
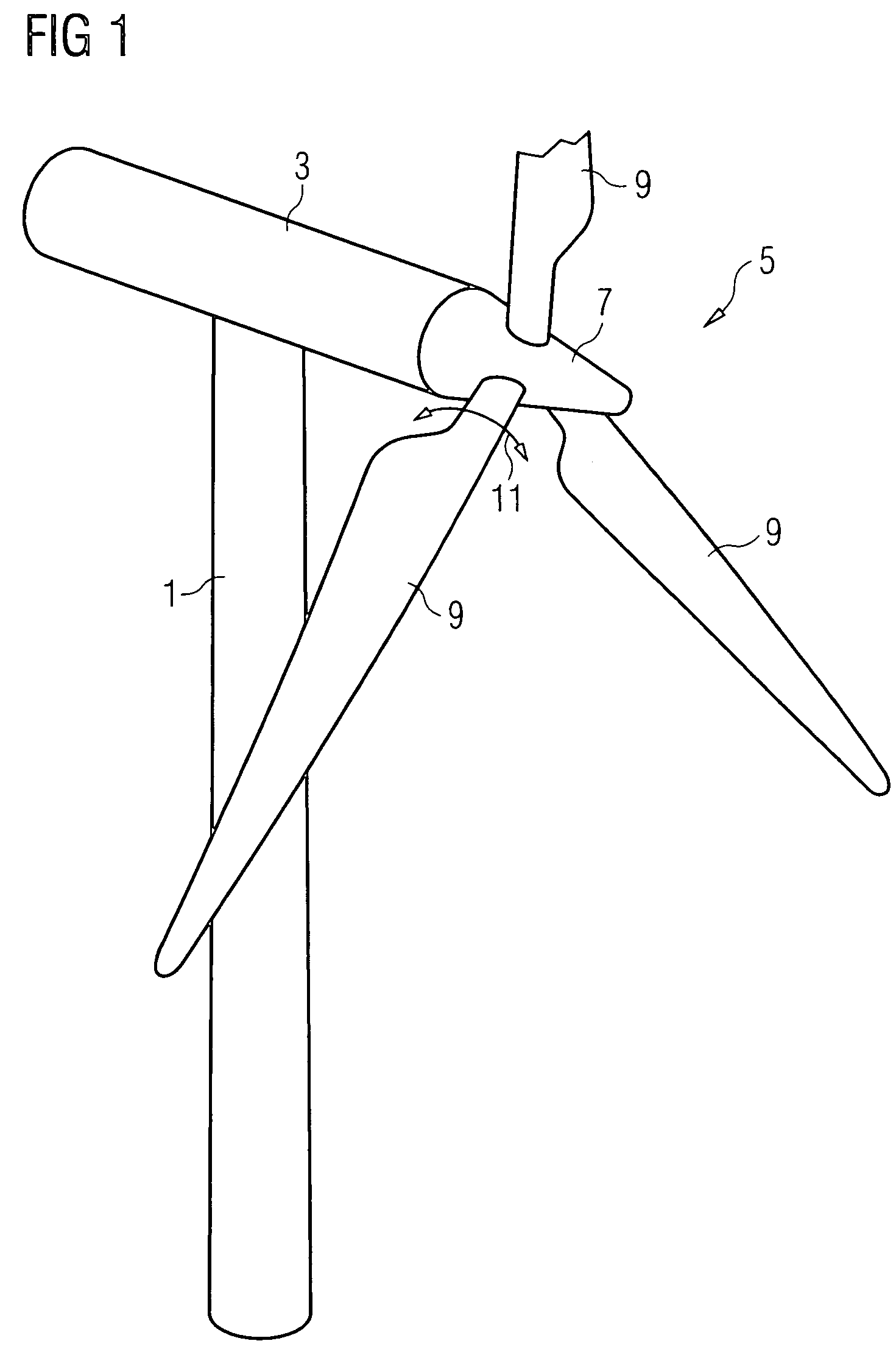
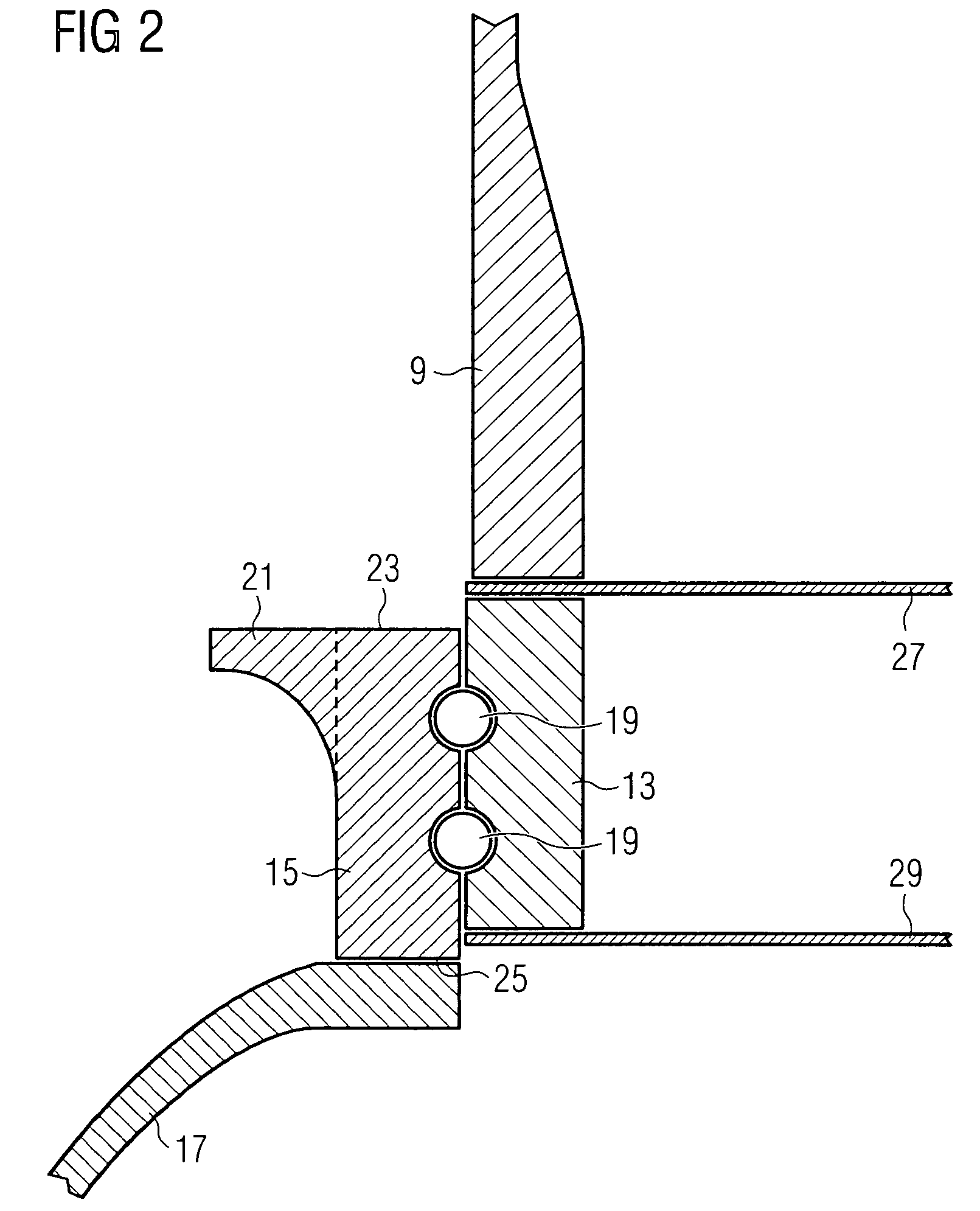
ActiveUS7390169B2Current protectionReduce resistancePropellersPump componentsTurbine bladeBlade pitch
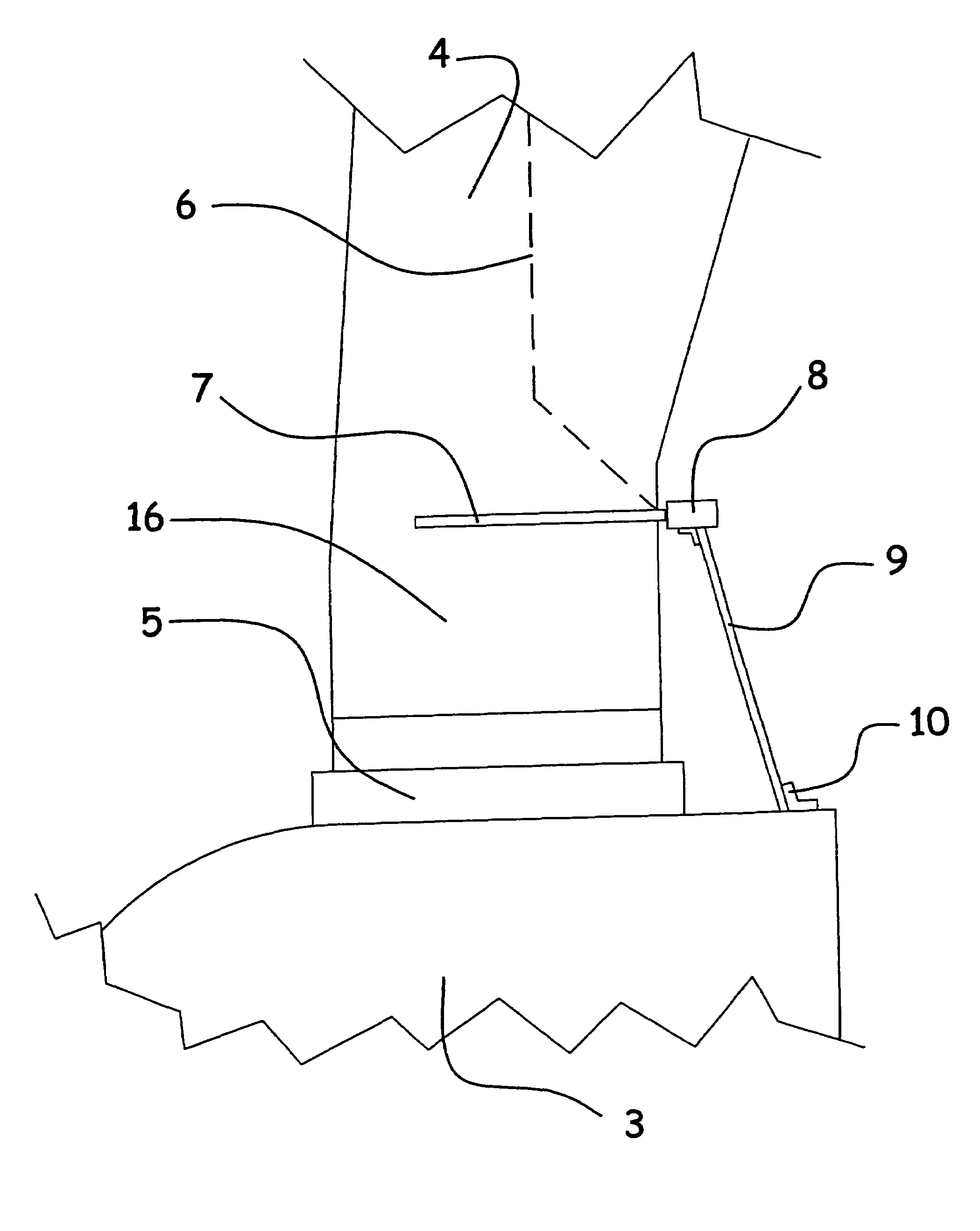
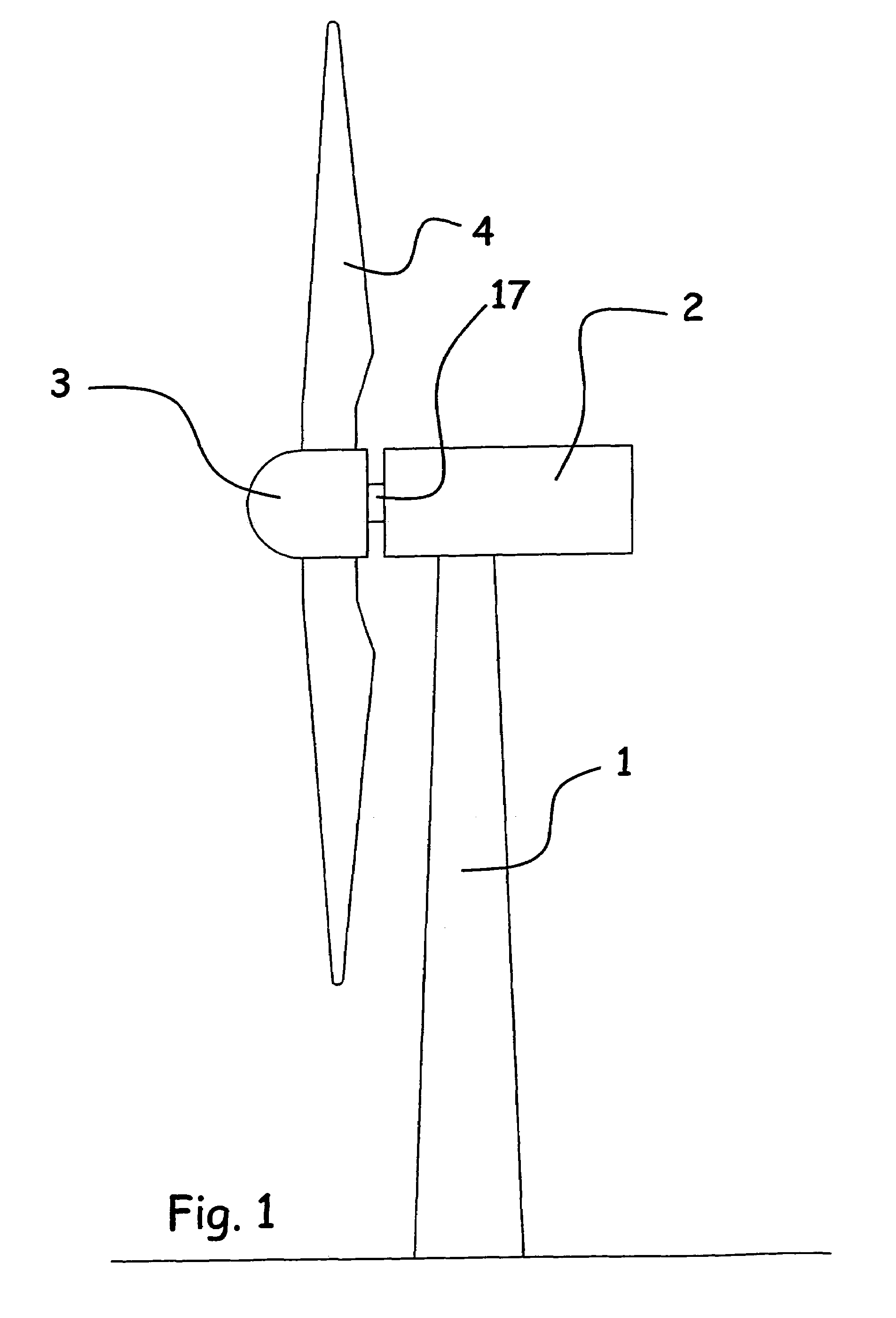
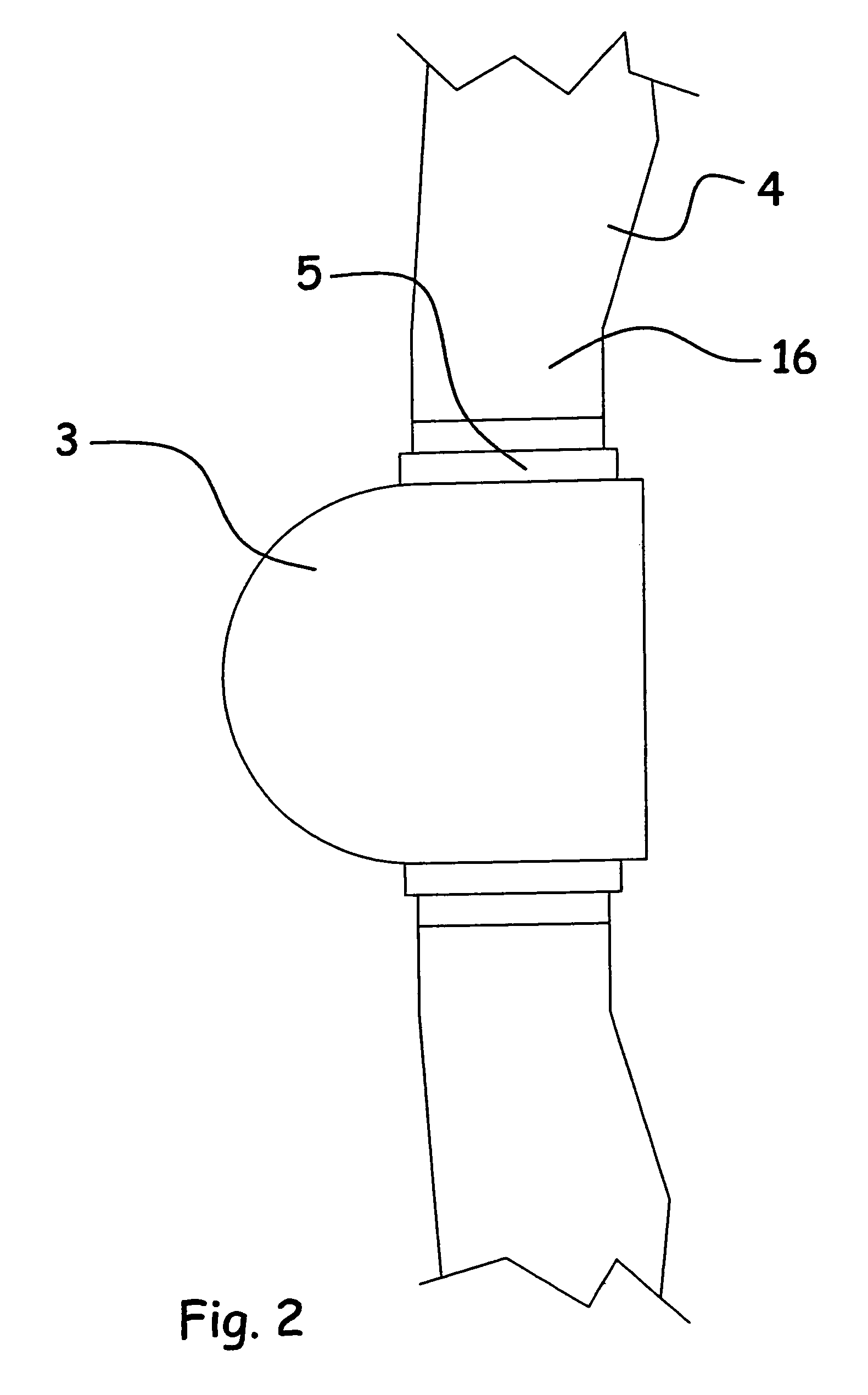
A wind turbine rotor including a rotor hub (3) and a plurality of blades (4), and where each blade root (16) is connected to said rotor hub through a pitch bearing (5) in such a manner that the pitch angle of the blade is adjustable by a turning of the blade about its longitudinal axis relative to the rotor hub. The blade is provided with at least one electrically conducting lightening down-conductor (6) extending in the longitudinal direction of the blade to the blade root and being electrically isolated from the pitch bearing (5). A spark gap (15) is provided between the lightning down-conductor and the rotor hub, said spark gap (15) being adapted to conduct a lightning current passing through the lightning down-conductor. A sliding contact connection (7, 12) is provided parallel to the spark gap (15) between the lightning down-conductor (6) and the rotor hub (3), said sliding contact connection ensuring electrical contact between said lightening down-conductor (6) and said rotor hub (3) irrespective of the pitch angle of the blade. The invention also relates to a wind turbine including such a rotor.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
Multi-section wind turbine rotor blades and wind turbines incorporating same
A multi-section blade for a wind turbine comprising at least one non-pitchable section and at least one pitchable section is provided. The non-pitchable section is configured to be fixed to a hub of the wind turbine. The pitchable section is configured to be rotated about a pitch axis which is substantially parallel to the span of the multi-section blade. A pitch bearing and a pitch motor are located within the blade and near the non-pitchable section and pitchable section interface.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Lightning protection of a pitch-controlied wind turbine blade
A wind turbine rotor including a rotor hub (3) and a plurality of blades (4), and where each blade root (16) is connected to said rotor hub through a pitch bearing (5) in such a manner that the pitch angle of the blade is adjustable by a turning of the blade about its longitudinal axis relative to the rotor hub. The blade is provided with at least one electrically conducting lightening down-conductor (6) extending in the longitudinal direction of the blade to the blade root and being electrically isolated from the pitch bearing (5). A spark gap (15) is provided between the lightning down-conductor and the rotor hub, said spark gap (15) being adapted to conduct a lightning current passing through the lightning down-conductor. A sliding contact connection (7, 12) is provided parallel to the spark gap (15) between the lightning down-conductor (6) and the rotor hub (3), said sliding contact connection ensuring electrical contact between said lightening down-conductor (6) and said rotor hub (3) irrespective of the pitch angle of the blade. The invention also relates to a wind turbine including such a rotor.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
Wind turbine pitch bearing and method
InactiveUS20070104577A1Easy and economical to makeReduce manufacturing costRotary bearingsPropellersTurbine bladeWind force
A pitch bearing and related method for wind electric turbines has an annularly-shaped first bearing ring connected with an associated wind turbine blade, and includes a first raceway groove. An annularly-shaped second bearing ring is connected with the rotor portion of the wind turbine, and includes a second raceway groove aligned with the first raceway groove. Rolling elements are positioned in the first and second raceway grooves to rotatably interconnect the two bearing rings. A gear segment is formed on one of the bearing rings, and is configured to engage a pitch drive portion of the wind turbine to pivot the blade axially between different pitch angles. The gear segment has an arcuate measure of less than 200 degrees to facilitate economical manufacture.
Owner:KAYDON CORP
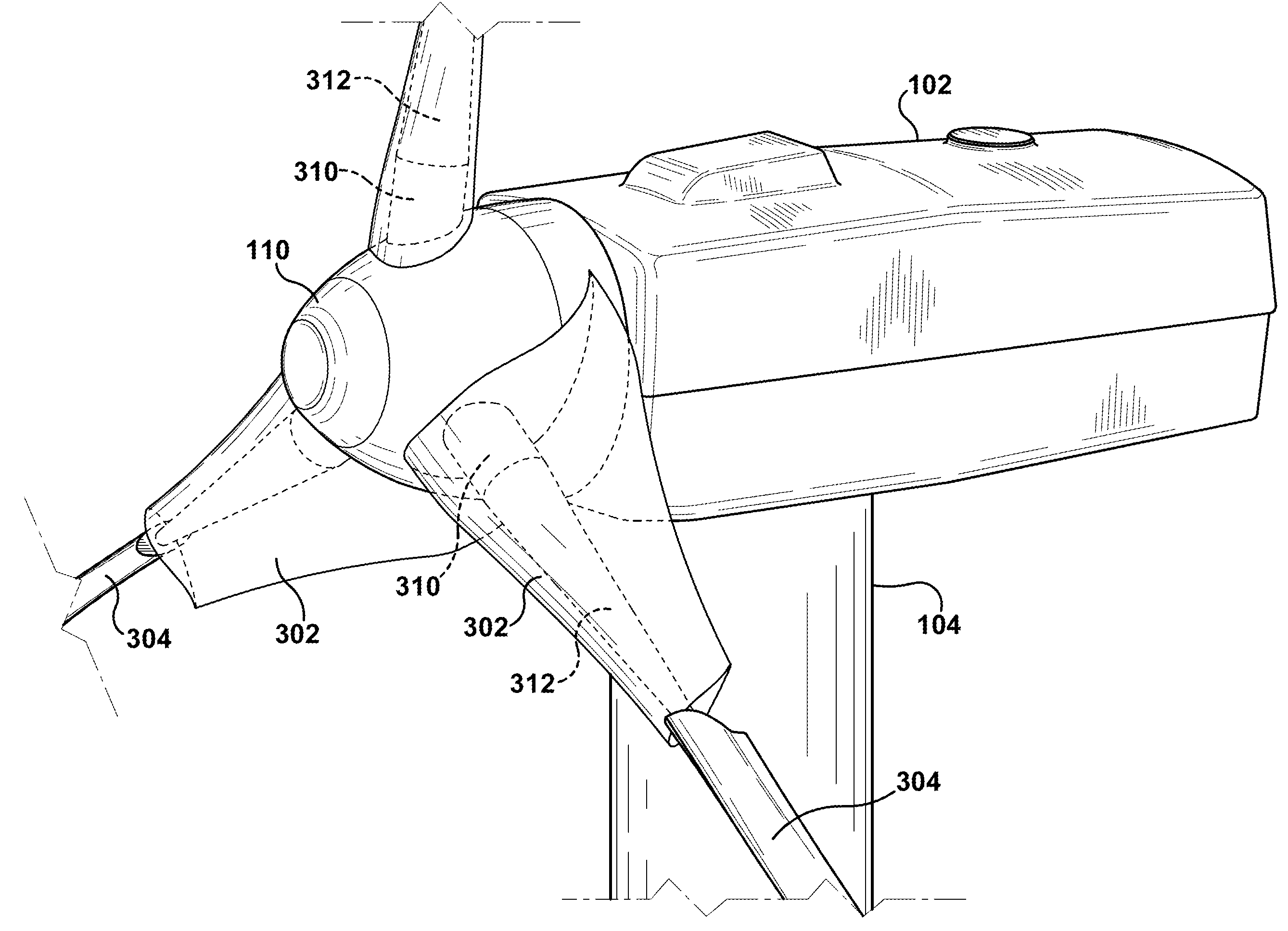
Multi-piece wind turbine rotor blades and wind turbines incorporating same
InactiveUS20060067827A1Increase power generationAdd dimensionPropellersPump componentsCowlingTurbine rotor
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
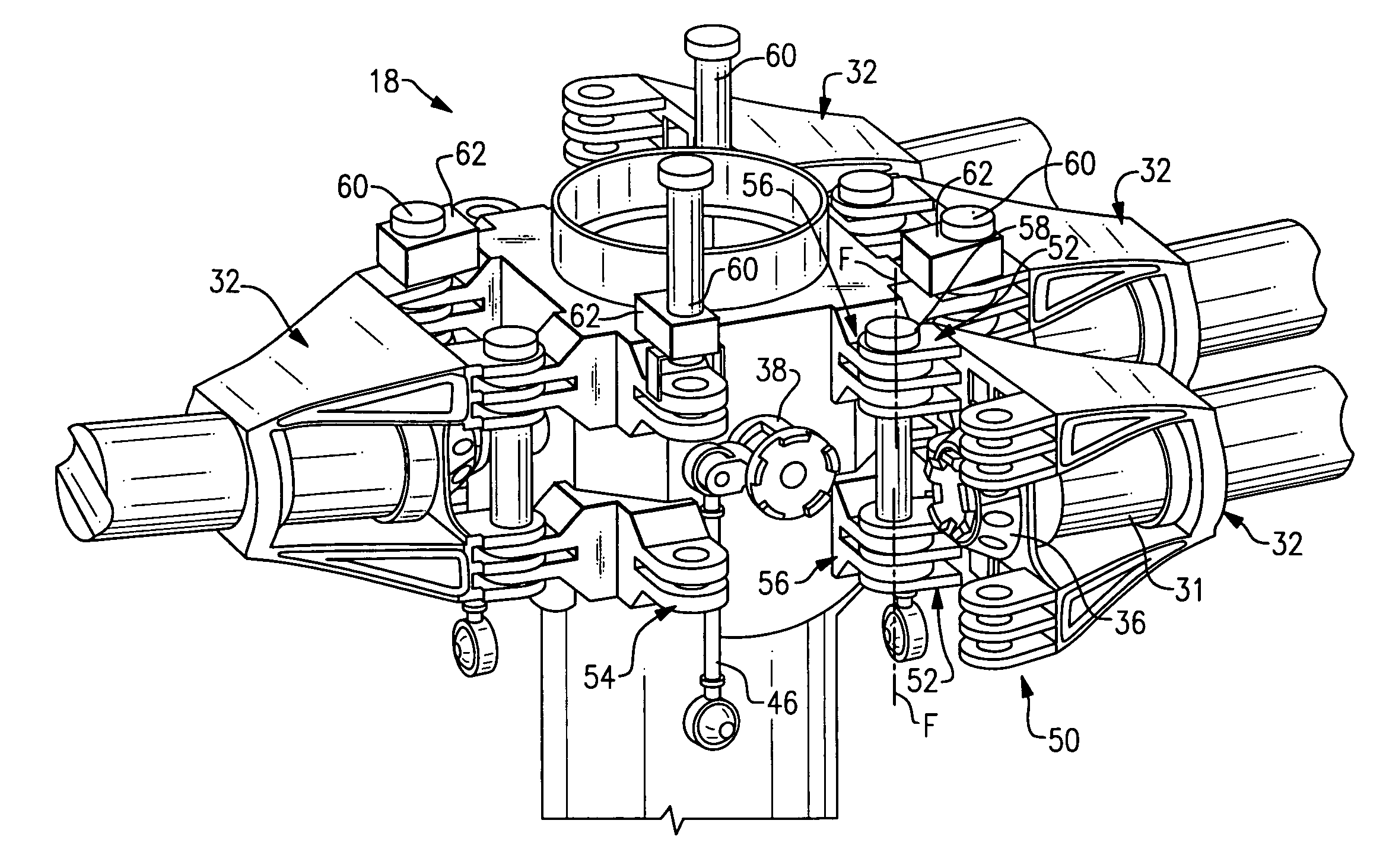
Rotor blade folding system
ActiveUS7530790B2More assembledPitch lock systems are minimized or eliminatedPropellersPump componentsClassical mechanicsStructural engineering
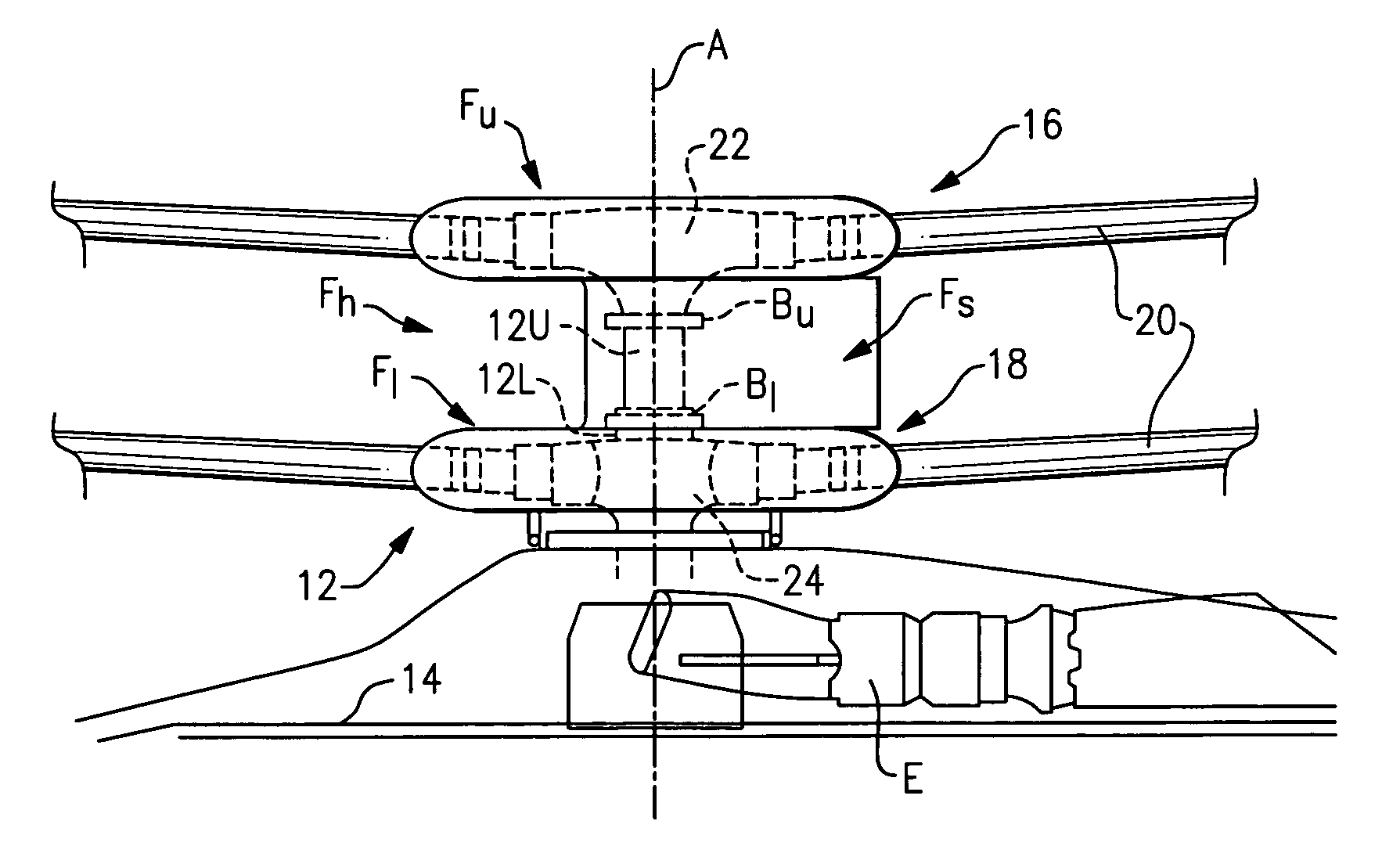
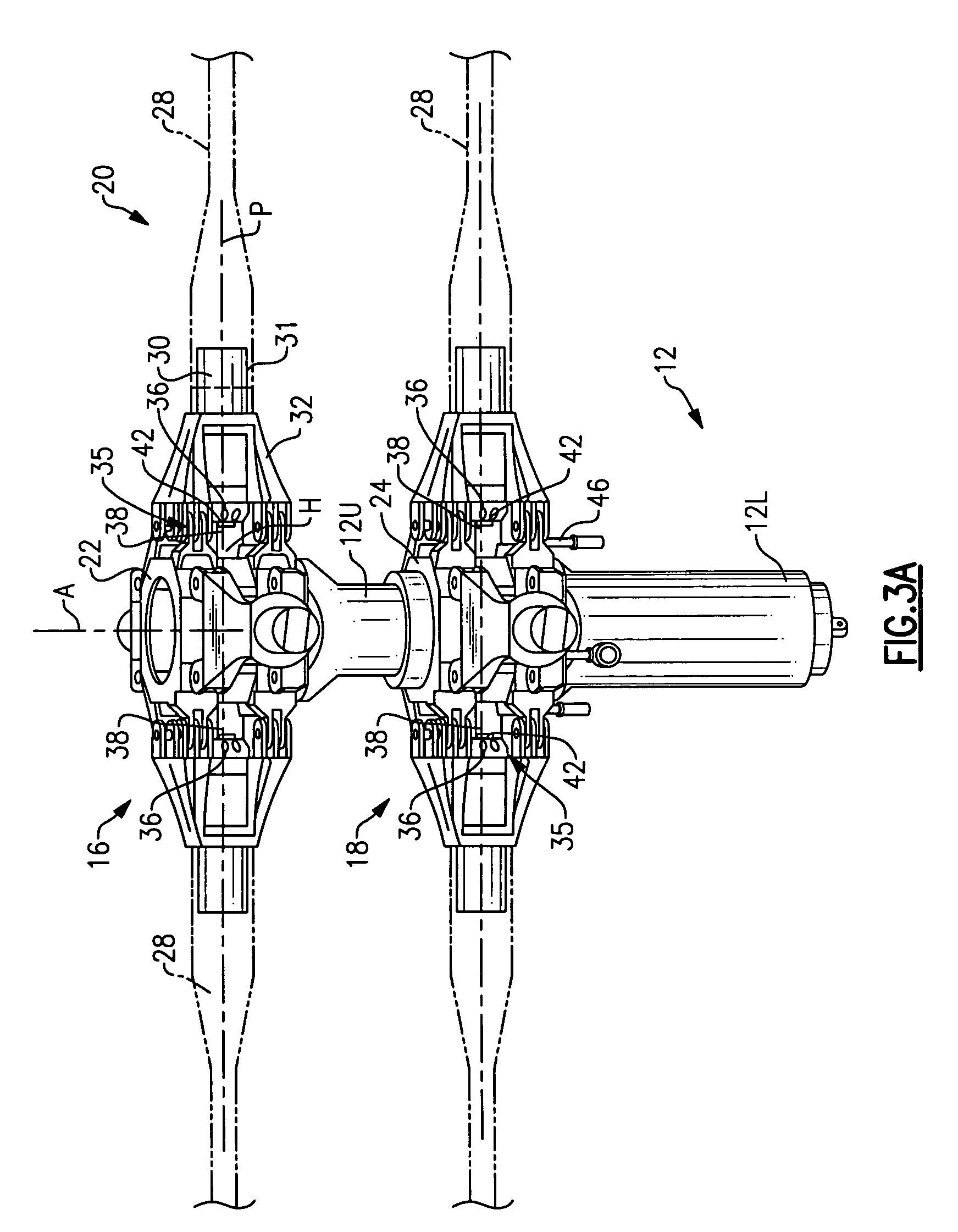
A rotor blade folding system includes a bearing housing which supports a bearing and rotor blade spindle which folds relative the rotor hub assembly about a fold axis. The rotor blade folding system essentially collapses the rotor hub to facilitate compatibility with a fairing system. By rotating the entire pitch bearing assembly, pitch lock systems are also minimized as the pitch lock system need only react a blade-feathering moment.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
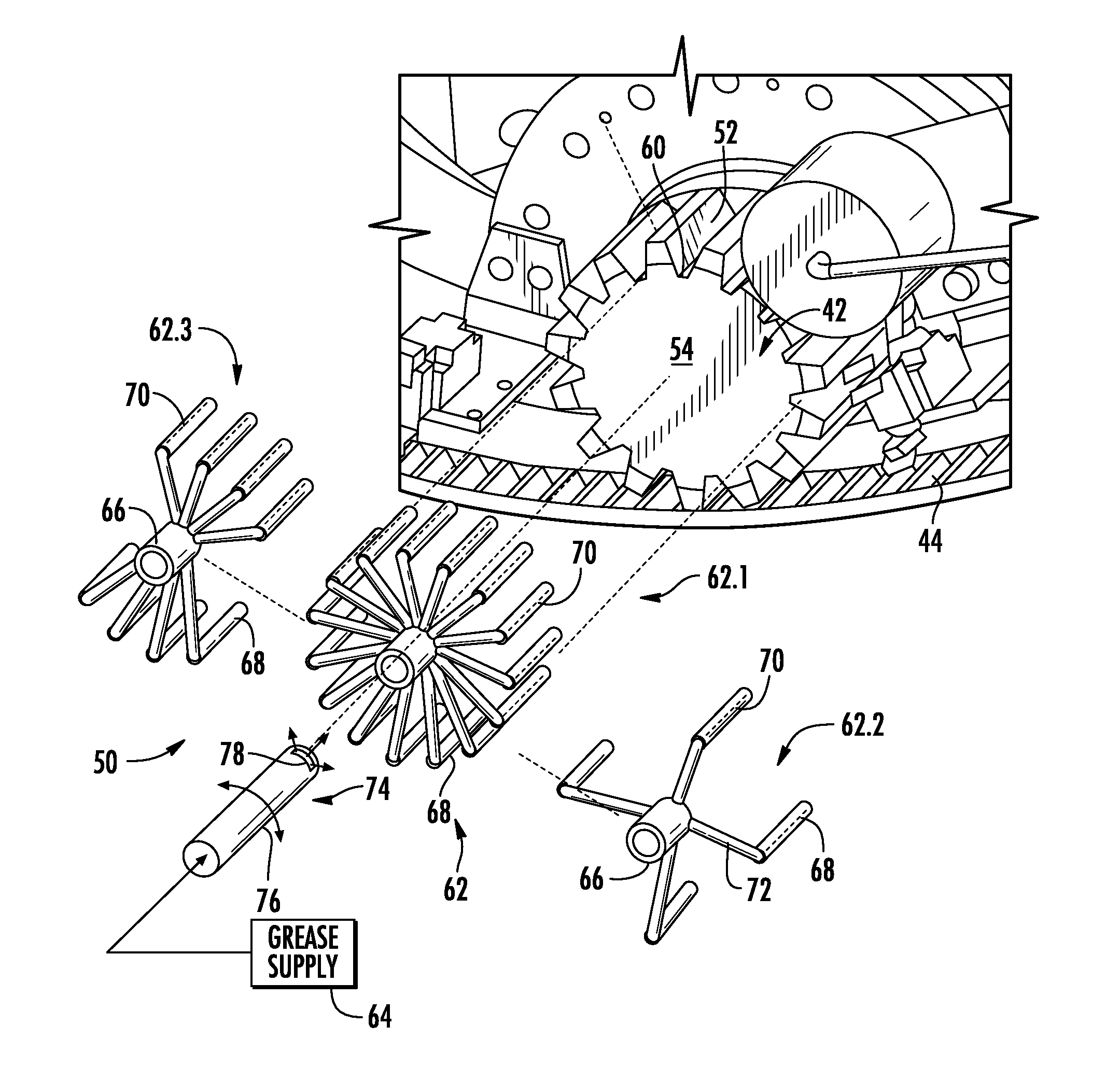
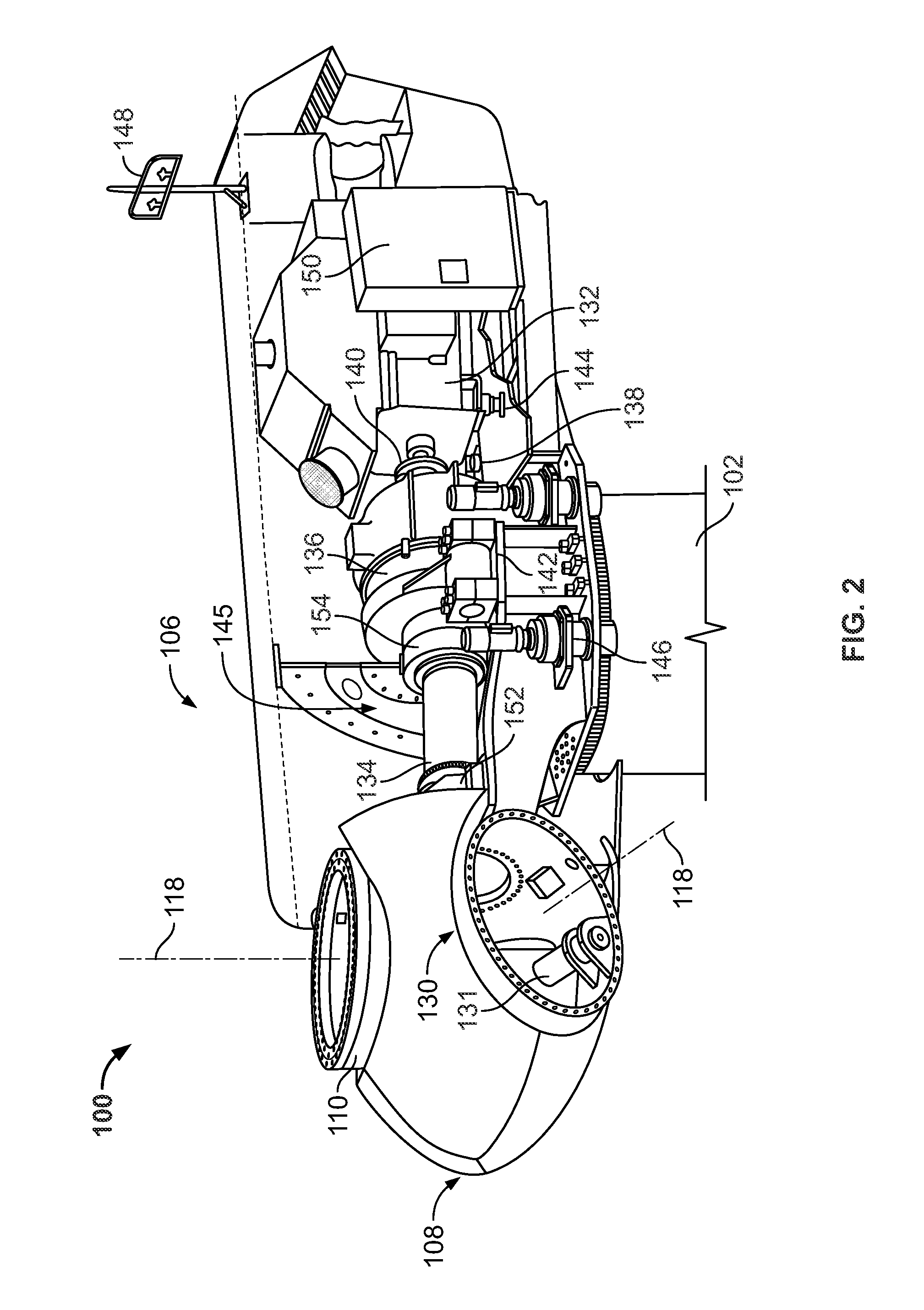
System and method for lubricating gears in a wind turbine
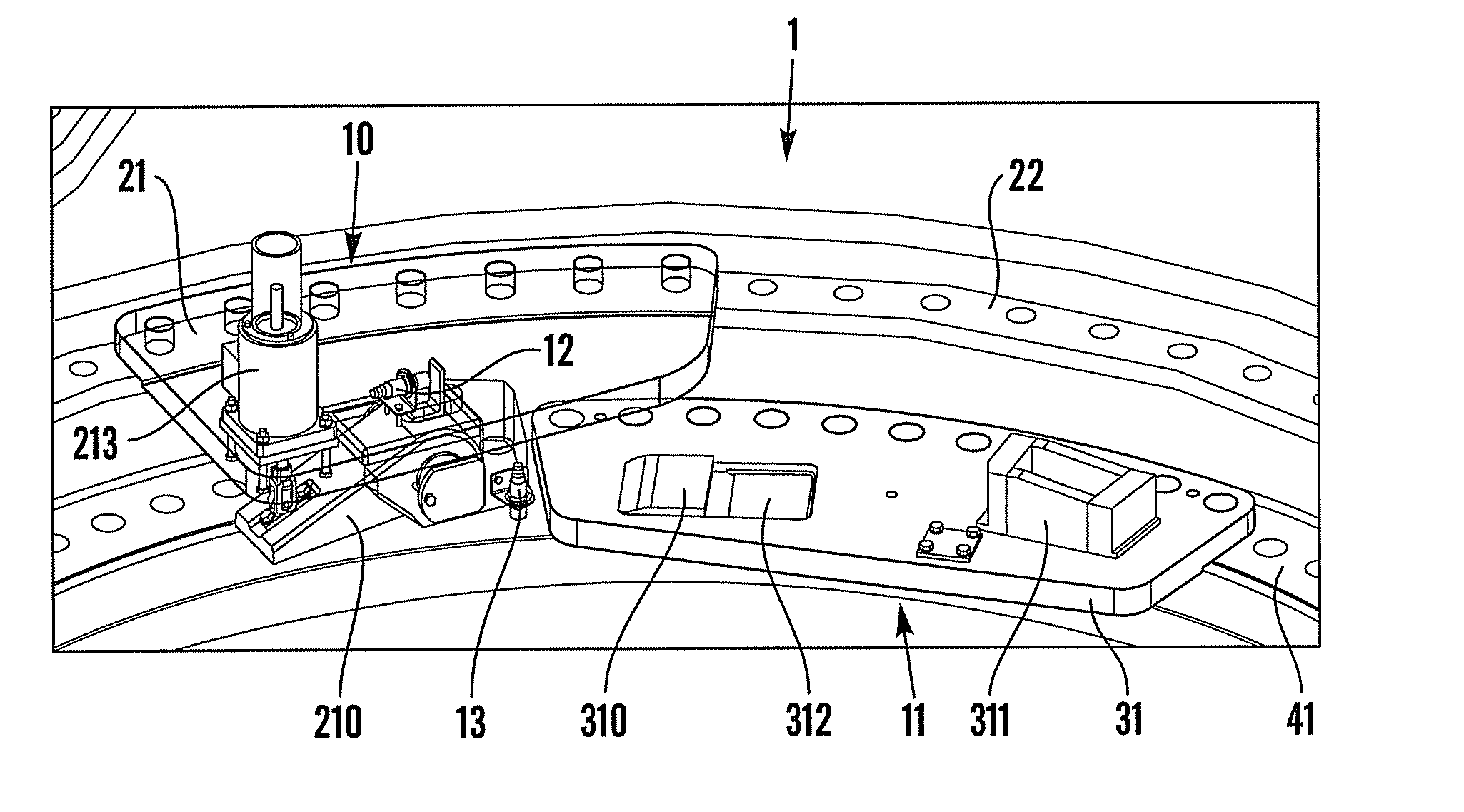
A system and method for lubricating gears in a wind turbine blade pitch drive are provided, wherein the pitch drive comprises a drive pinion gear with gear teeth that engage a pitch bearing gear coupled to a respective wind turbine blade. A grease distributor is configured to mount onto and rotate with the pinion gear, and is configured to deliver grease from an external grease supply to at least one valley defined between adjacent teeth of the pinion gear in a contact area of the pinion gear with the bearing gear without the distributor contacting inter-engaging teeth of the bearing gear.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Spinner-less hub access and lifting system for a wind turbine
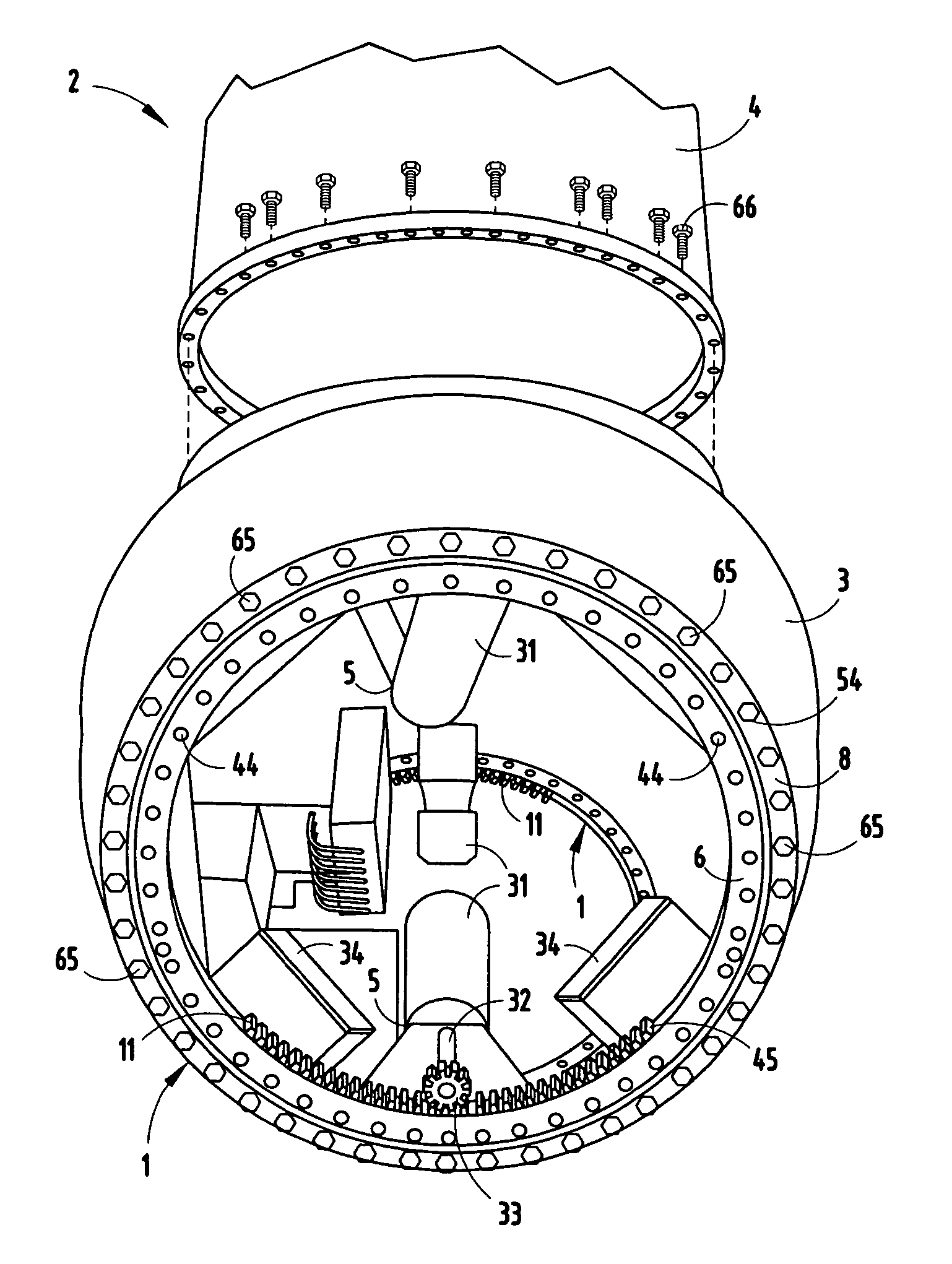
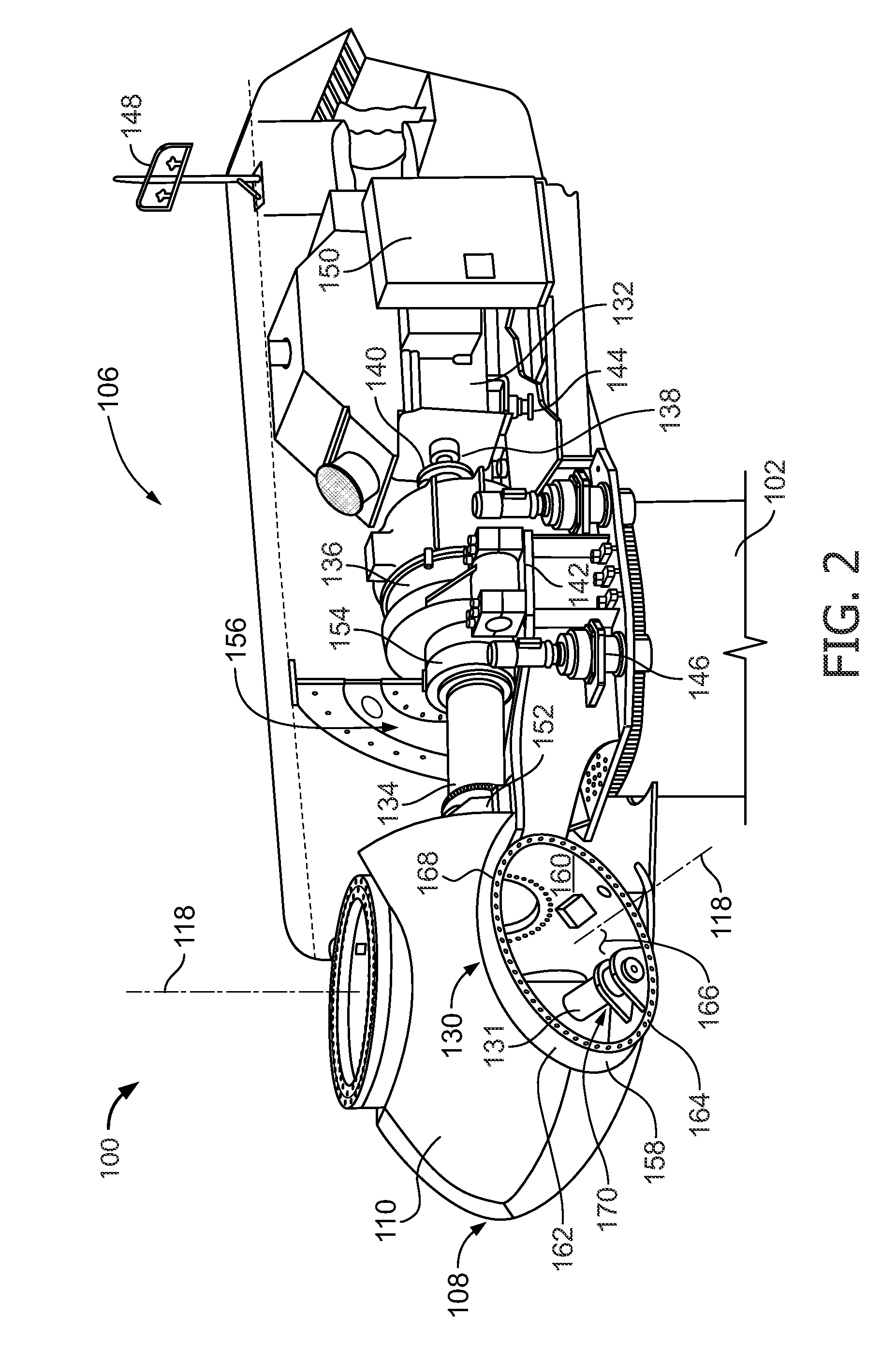
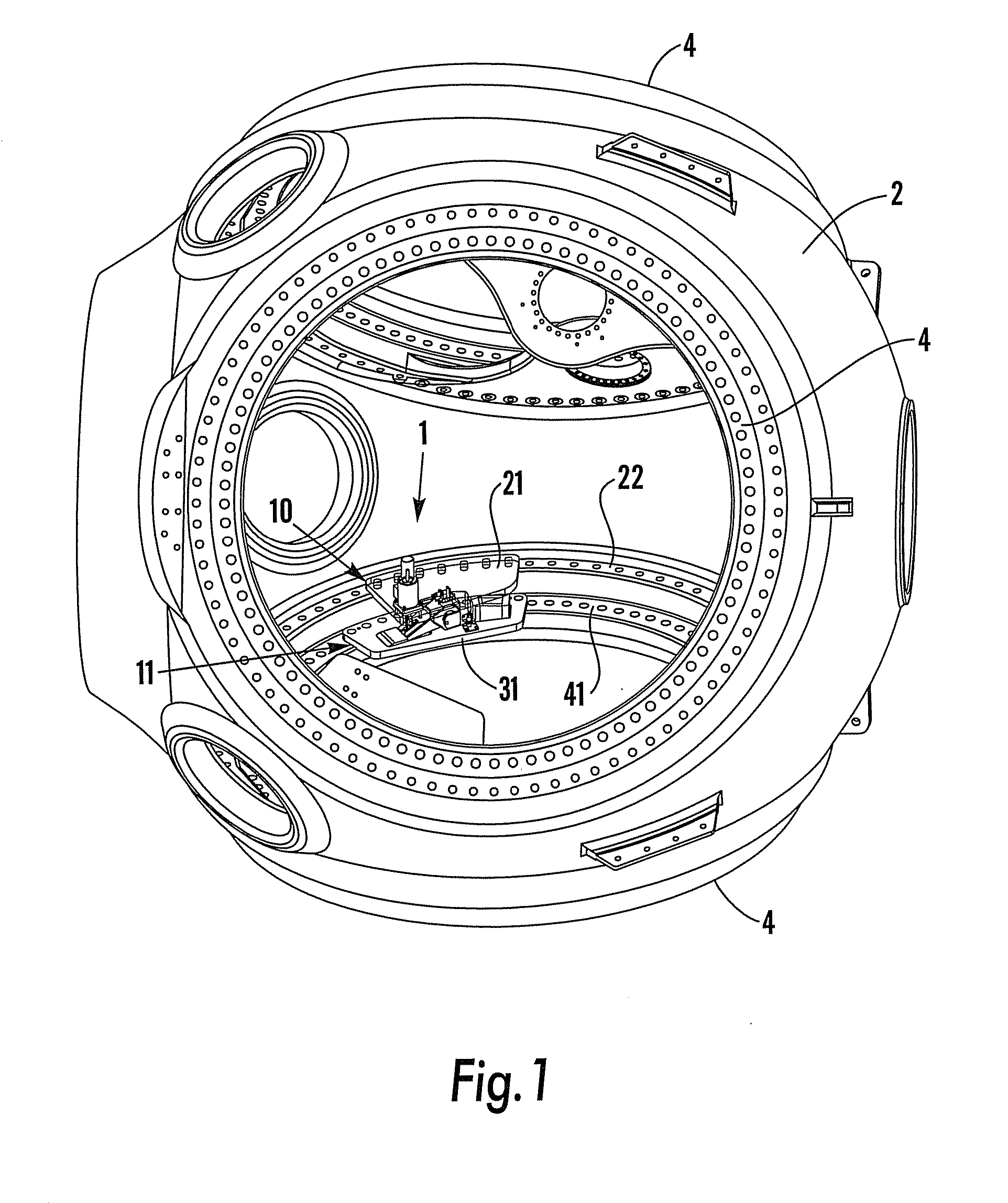
A simple and safe means is provided to gain entry into the rotor hub of a wind turbine for maintenance operations within the hub. A ladder-like structure is mounted onto the rotor hub using the same bolts attaching a fixed outer race of the pitch bearing for the rotor blades. The ladder-like structure has integral with it a protective cage to the front, forming a basket. Structural elements for grasping are provided to a worker over the full path traversed from the nacelle to the entry hatch of the hub. An expanded area between rungs may be provided to facilitate entry by a service worker into the safety cage area. Lifting ears made also be formed with tubular sections integrated into the ladder-like structure.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
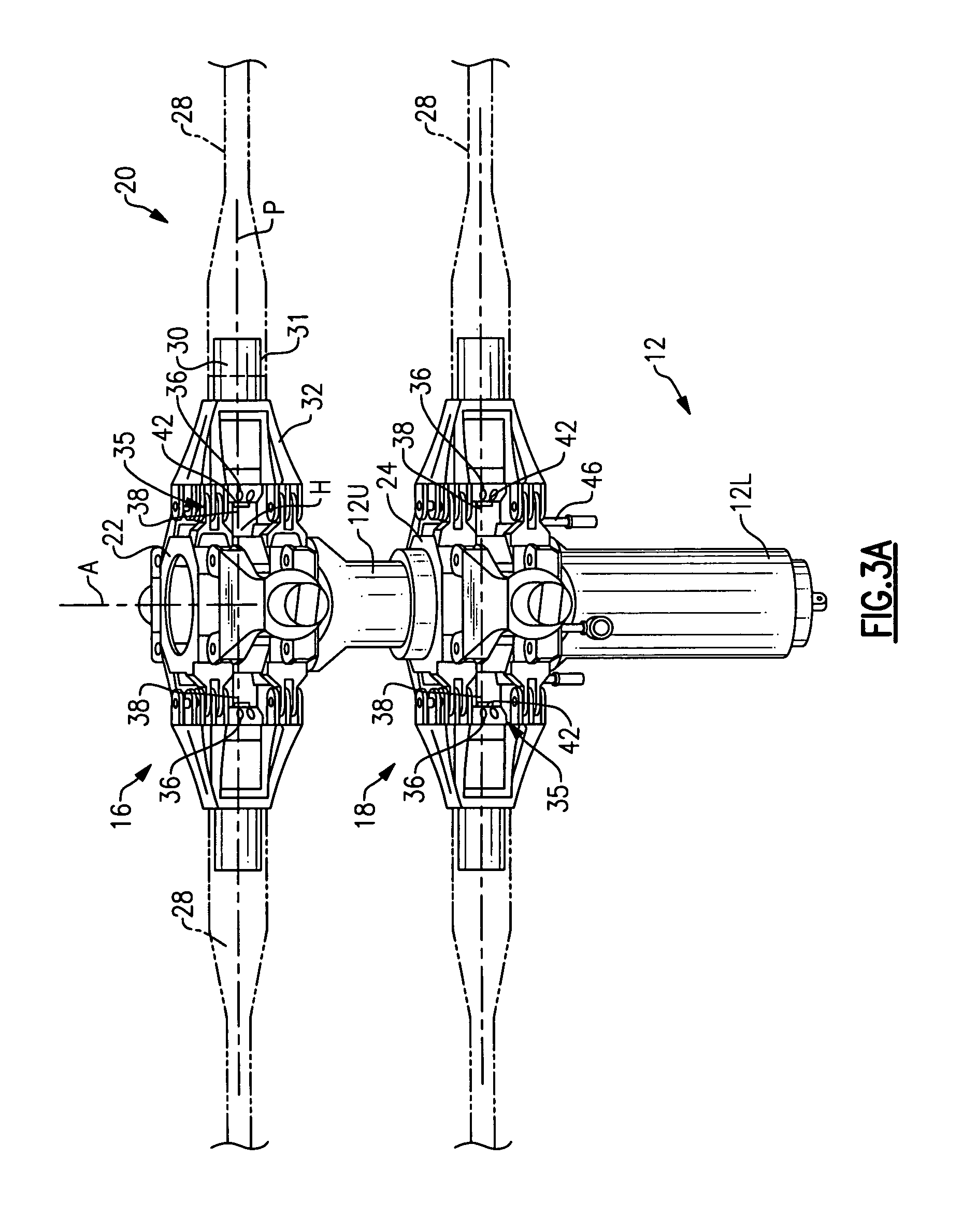
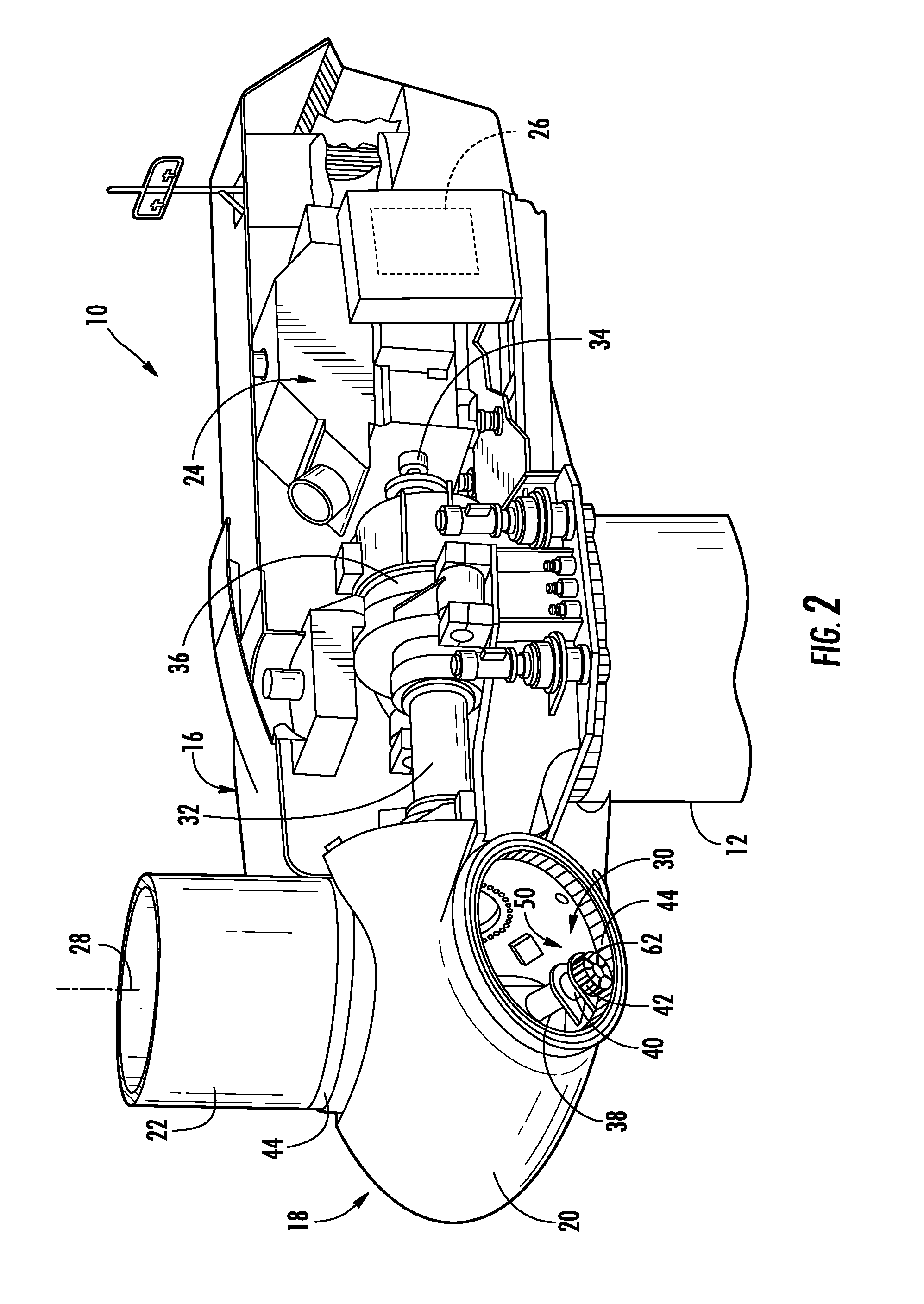
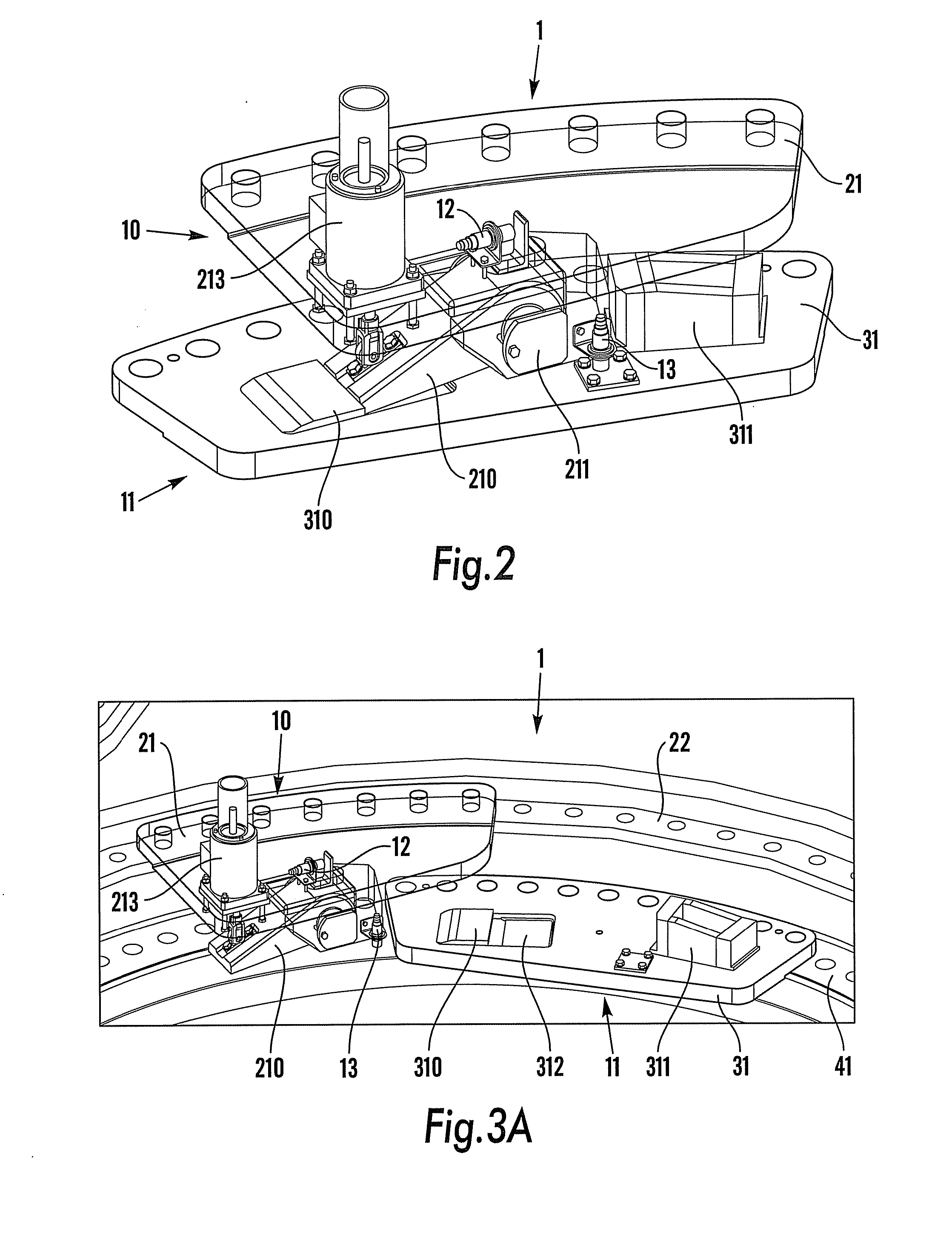
Systems and methods for assembling a pitch assembly for use in a wind turbine
A method of assembling a pitch assembly for use in a wind turbine. The method includes coupling a pitch bearing to a hub of the wind turbine, wherein the pitch bearing includes a plurality of bearing teeth. A pitch drive system is coupled to the pitch bearing such that the pitch drive system contacts a first set of bearing teeth. A plurality of bearing segments is coupled to the pitch bearing to cause the pitch drive system to selectively contact a second set of bearing teeth.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wind turbine blade and hub assembly
ActiveUS20100290912A1Wind power extractionEasy extractionPropellersRotary propellersTurbine bladeWind force
This invention relates to a wind turbine blade with at least two connection members such as bushings and / or threaded bars in the root of the blade for attaching the blade to a hub. The connection members are placed along the blade surface and at least some of the connection members are non-parallel and hence oriented in different directions. Hereby is obtained that the root section of the blade can be shortened and the maximum chord of the wind turbine blade can be moved closer to the hub, whereby the part of the blade exploiting the wind is increased and the power output similarly increased.The present invention further relates to a pitch bearing and a hub comprising a bearing ring with two or more holes for positioning fastening members for attaching a wind turbine blade to the bearing. Here, correspondingly, at least two of the holes are oriented in different angles so that the fastening members positioned in the holes are non-parallel and extend in different directions.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
Wind Turbine, a Hub for a Wind Turbine and Use Hereof
ActiveUS20080199315A1More strainImproved pitch jointPropellersPump componentsTurbine bladeBlade pitch
The invention relates to a wind turbine including at least two blade units. Each blade unit has a pitch controlled wind turbine blade and at least one pitch bearing including at least one outer ring, at least one centre ring and at least one inner ring. The wind turbine further includes a hub comprising a mount area for each of the blade units (31). The mount area comprises at least two concentric load transferring surfaces for attaching the blade unit, via the at least one pitch bearing.The invention further relates a hub and a use hereof.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Rotor blade folding system
ActiveUS20090097973A1More assembledPitch lock systems are minimized or eliminatedPropellersPump componentsEngineeringCowling
A rotor blade folding system includes a bearing housing which supports a bearing and rotor blade spindle which folds relative the rotor hub assembly about a fold axis. The rotor blade folding system essentially collapses the rotor hub to facilitate compatibility with a fairing system. By rotating the entire pitch bearing assembly, pitch lock systems are also minimized as the pitch lock system need only react a blade-feathering moment.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Data modeling based wearing monitoring and early-warning method for variable pitch bearing of wind turbine
The invention relates to a data modeling based wearing monitoring and early-warning method for a variable pitch bearing of a wind turbine. The method includes the following steps: (1) data collection;(2) data pre-processing; (3) sample marking; (4) feature construction; (5) model construction; (6) algorithm verification; (7) model deployment. The method of the invention is high in effectiveness and accuracy, realizes a wearing monitoring and early-warning function for a variable pitch bearing of a wind turbine through modeling and predication by means of common sensor data, such as wind speed, power, rotational speed, pitch angle and pitch motor current, recorded by an SCADA system of the wind turbine, and has the characteristics of low cost, high efficiency, strong interpretation and thelike.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WINDEY
Pitch bearing assembly with stiffener
A pitch bearing assembly for a wind turbine may include an outer race and an inner race rotatable relative to the outer race. The inner race may define an inner circumference and may include a plurality of gear teeth around the inner circumference. The inner race may also include a circumferential flange extending at least partially around the inner circumference. In addition, the pitch bearing assembly may include a stiffener coupled to the circumferential flange.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
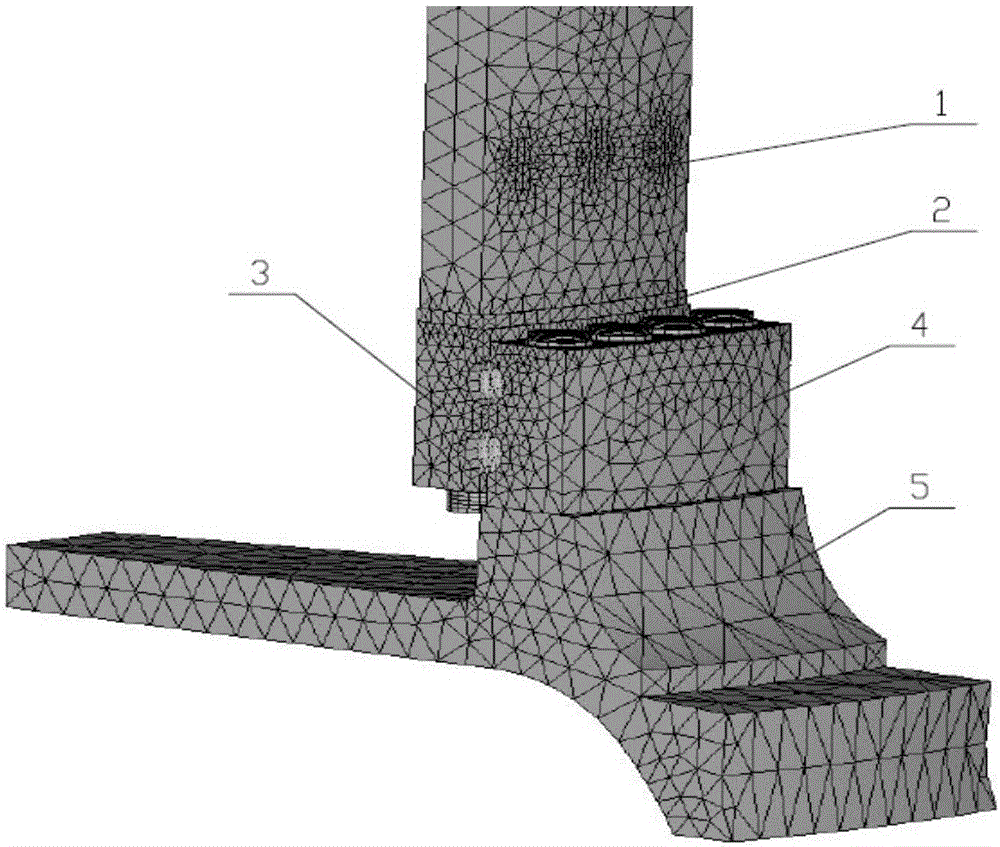
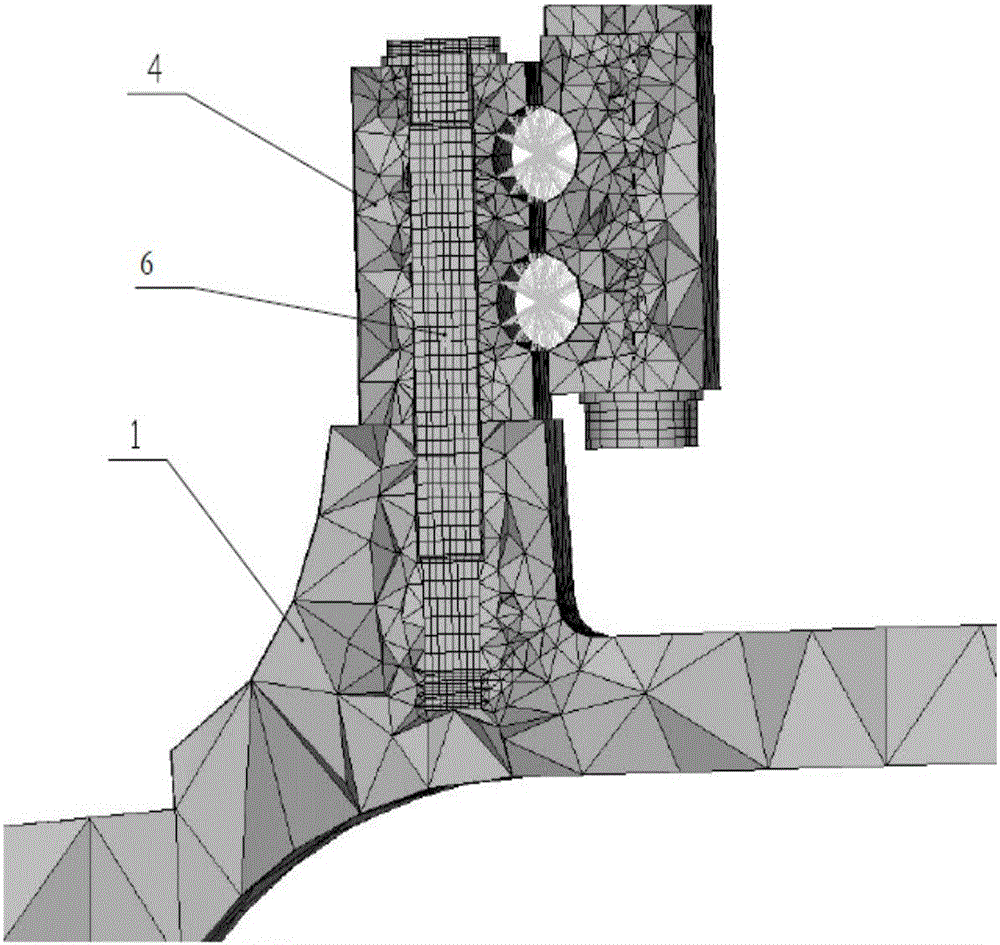
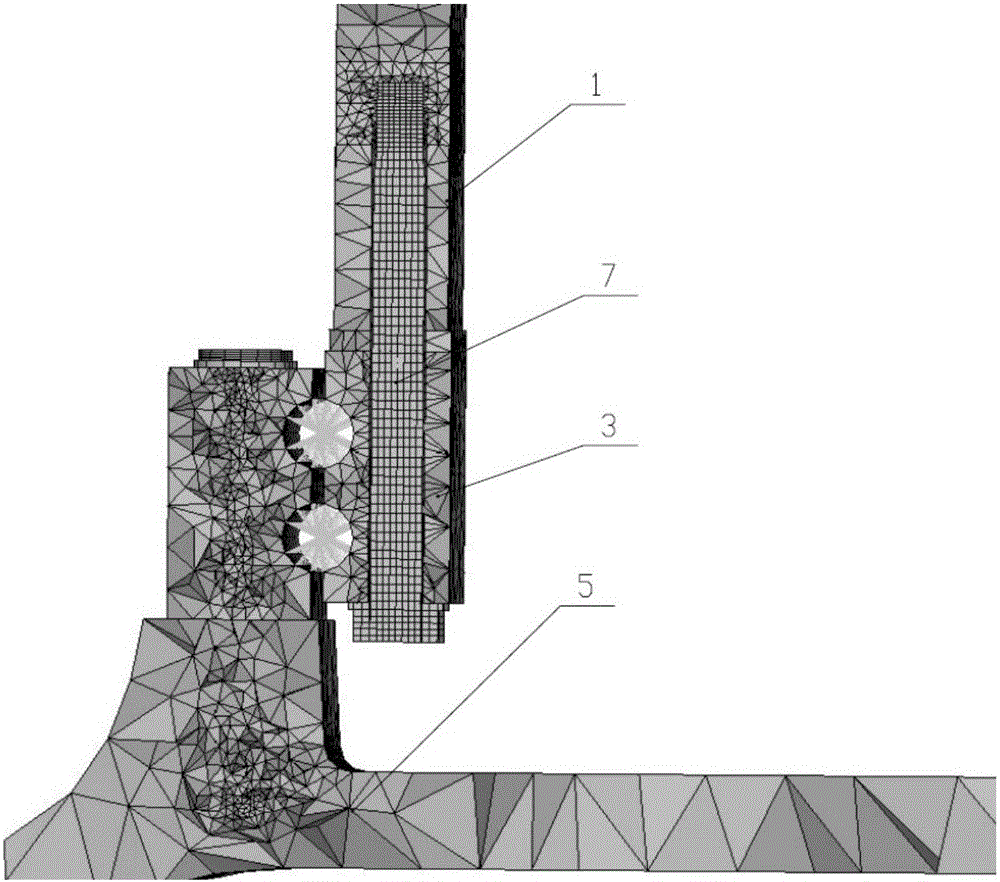
Method for checking strength performances of variable-pitch bearing and hub connecting bolt and variable-pitch bearing and vane connecting bolt of fan
InactiveCN105160067AIntensity is accurateImprove reliabilitySpecial data processing applicationsElement modelEngineering
The invention relates to a method for checking strength performances of a variable-pitch bearing and hub connecting bolt and a variable-pitch bearing and vane connecting bolt of a fan. By utilizing three-dimensional cartographic software, three-dimensional geometrical models of devices in a load transmission path of the variable-pitch bearing and hub connecting bolt and the variable-pitch bearing and vane connecting bolt of the fan are subjected to grid division and assembly separately, and a finite element model is established through finite element software to realize that the load transmission path is complete and consistent with the reality. The devices in the load transmission path at least include a hub, a vane root part, a vane flange, a variable-pitch bearing inner ring, a variable-pitch bearing outer ring, the variable-pitch bearing and hub connecting bolt and the variable-pitch bearing and vane connecting bolt. The method realizes the complete load transmission path, is capable of accurately calculating the limit strength and fatigue strength of the variable-pitch bearing and hub connecting bolt and the variable-pitch bearing and vane connecting bolt of the fan, and improves the operational reliability of a wind power unit.
Owner:XUJI GRP +2
Systems and methods for assembling a pitch assembly for use in a wind turbine
A method of assembling a wind turbine. The method includes coupling a pitch bearing to a hub that includes a wall. The pitch bearing includes a plurality of sets of pitch bearing teeth. At least one blade is coupled to the pitch bearing such that the blade is rotatable about a pitch axis. A plurality of pitch gearbox brackets are coupled to the hub wall. A pitch drive system is selectively coupled to one of the plurality of pitch gearbox brackets, wherein a predetermined set of pitch bearing teeth are in contact with the pitch drive system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Blade pitch lock device
InactiveUS20110044813A1Improve securityImprove reliabilityPropellersWind motor controlPower stationTurbine blade
A locking device for locking a turbine blade of a wind power plant at a predetermined pitch angle, which wind power plant includes a rotor hub and at least one turbine blade where the blade root of the at least one turbine blade is connected to the rotor hub through a pitch bearing so that the pitch angle of the at least one turbine blade is adjustable by turning of the at least one turbine blade about its longitudinal axis relative to the rotor hub and wherein the device for locking the turbine blade includes a mechanical snap-in mechanism which in a locked position prevents the at least one turbine blade from turning about its longitudinal axis thus fixating the at least one turbine blade in the predetermined pitch angle.
Owner:GE WIND ENERGY NORWAY
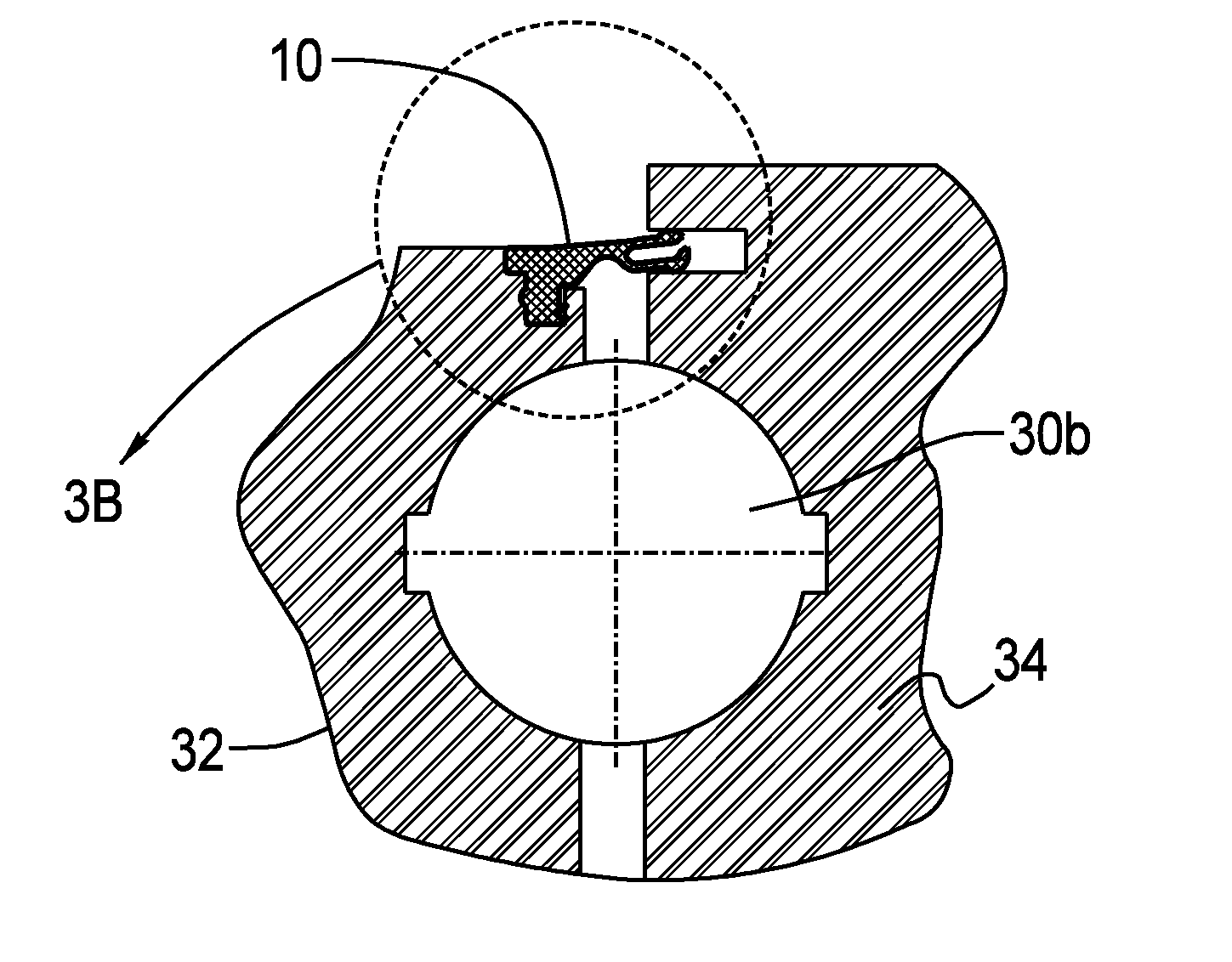
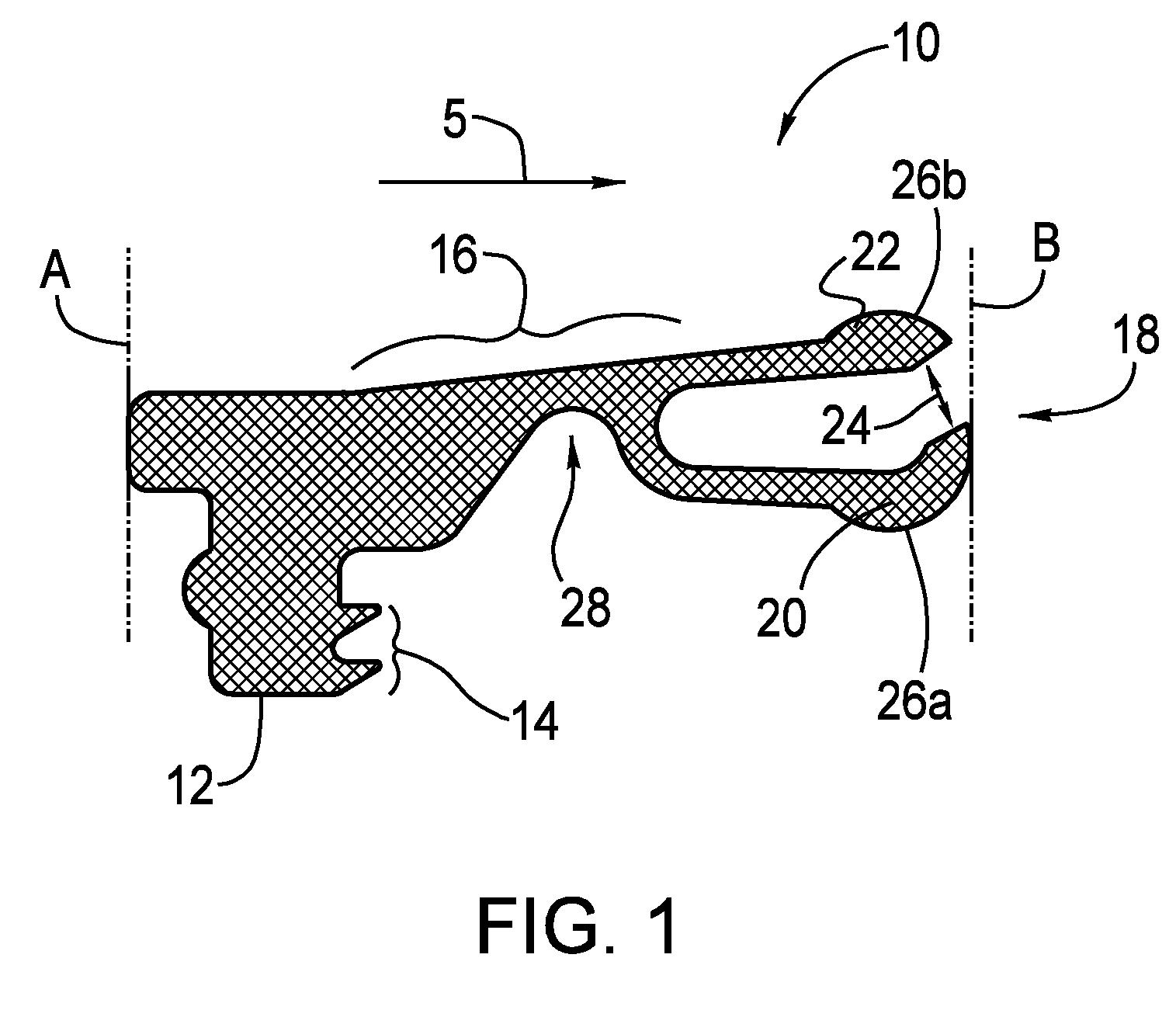
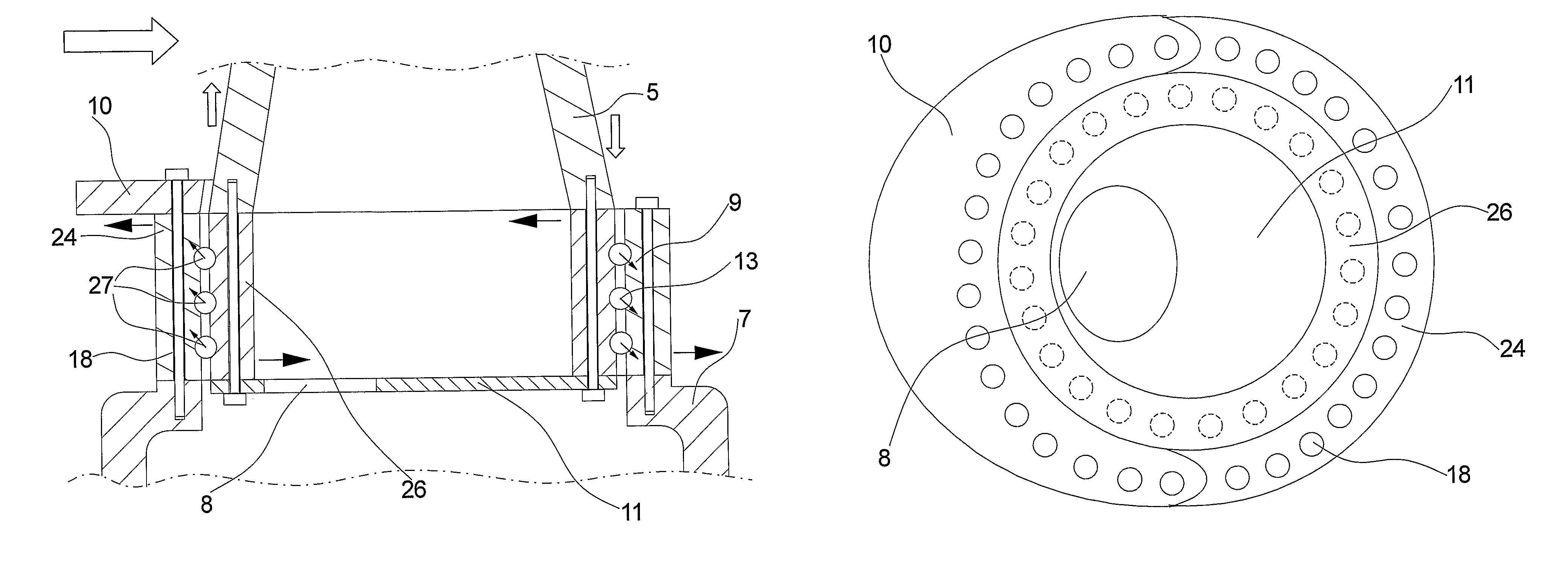
Seal for bearings to accommodate large deformations
A seal for a bearing has a first and a second circumference, and an anchor portion proximate to the first circumference. A span portion extends from the anchor portion towards the second circumference, and a lip extends from the span portion towards the second circumference. The lip protrudes from the span portion transversely to the span direction. A bearing and seal assembly includes a first ring and a second ring in rotatable engagement with the first ring. The first ring defines a groove and the second ring defines a contact surface. The seal is mounted in the groove, the span portion extending from the anchor portion towards the second ring, and the lip extending from the span portion towards the second ring, engaging the contact surface. The bearing and seal assembly may be used as a pitch bearing and / or a yaw bearing in a wind turbine.
Owner:ROLLER BEARING OF AMERICA
Pitch bearing for wind turbine rotor blades
A pitch bearing for a wind turbine rotor comprises a rotor hub and at least one rotor blade, the pitch bearing comprising a cylindrical inner bearing ring connectable to a rotor blade of the wind turbine rotor, a cylindrical outer bearing ring connectable to the rotor hub of the wind turbine rotor and an annular reinforcement section for reinforcing the outer bearing ring. The annular reinforcement section adjoins the cylindrical outer bearing ring at its radial outer surface.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Root end assembly configuration for a wind turbine rotor blade and associated forming methods
ActiveUS20130216394A1Increase stiffnessIncrease in design loadPropellersRotary propellersClassical mechanicsControl theory
An assembly configuration between a wind turbine rotor blade and a rotor hub includes a rotor hub having one or more pitch bearings, with each pitch bearing having an outer diameter race and an inner diameter race. Rotor blades are affixed to the respective pitch bearing rings, with the rotor blades having a root end with an outer diameter. An adaptor is configured between the root end and the pitch bearing, with the adaptor affixed to the inner diameter race and the root end affixed to the adaptor. The adaptor defines a mounting surface for the root end radially inward of the pitch bearing such that the root end outer diameter is less than the diameter of the inner diameter race.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Pitch of Blades on a Wind Power Plant
The present invention relates to a blade for a wind power plant with an assembly face for mounting in a circular pitch bearing, whose pitch axis is angled relative to the longitudinal axis of the blade, and wherein the blade comprises a root part with an approximately elliptic cross-section, in which root part the assembly face is arranged. The invention further relates to a wind power plant in general having a pitch-adjustable blade mounted in a pitch bearing such that the distance between the outermost part of the blade and the tower is increased when the leading edge of the blade is pitched up in the wind. This is accomplished in that the longitudinal axis of the blade is angled in a particular way compared to its pitch axis. The invention also relates to a meth controlling a wind power plant, including to increase the rotor area and / or increasing the distance between the outermost part of at least one blade and the tower by regulating, during operation, the pitch of a blade about a pitch axis which is angled relative to the longitudinal axis of the blade.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
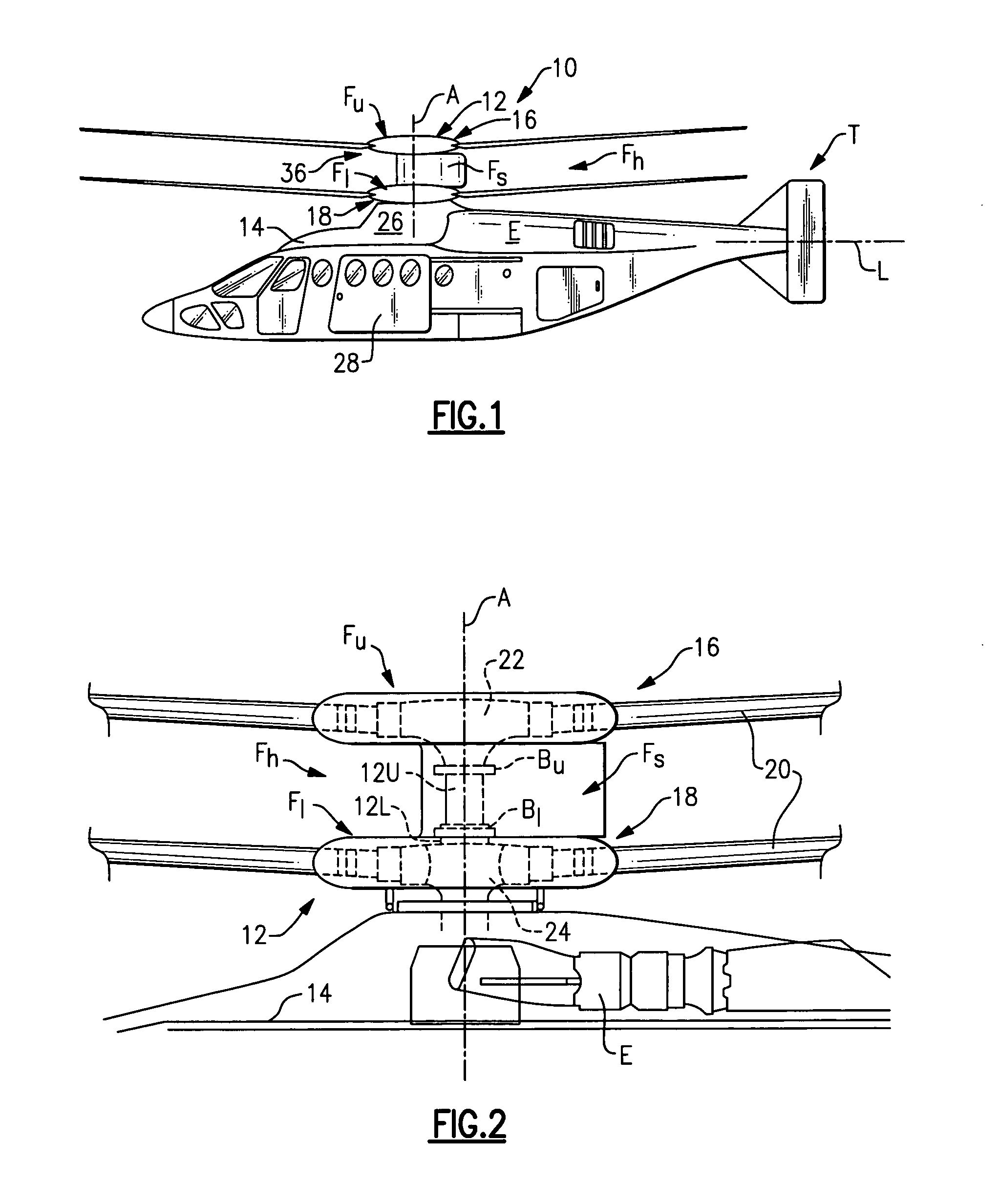
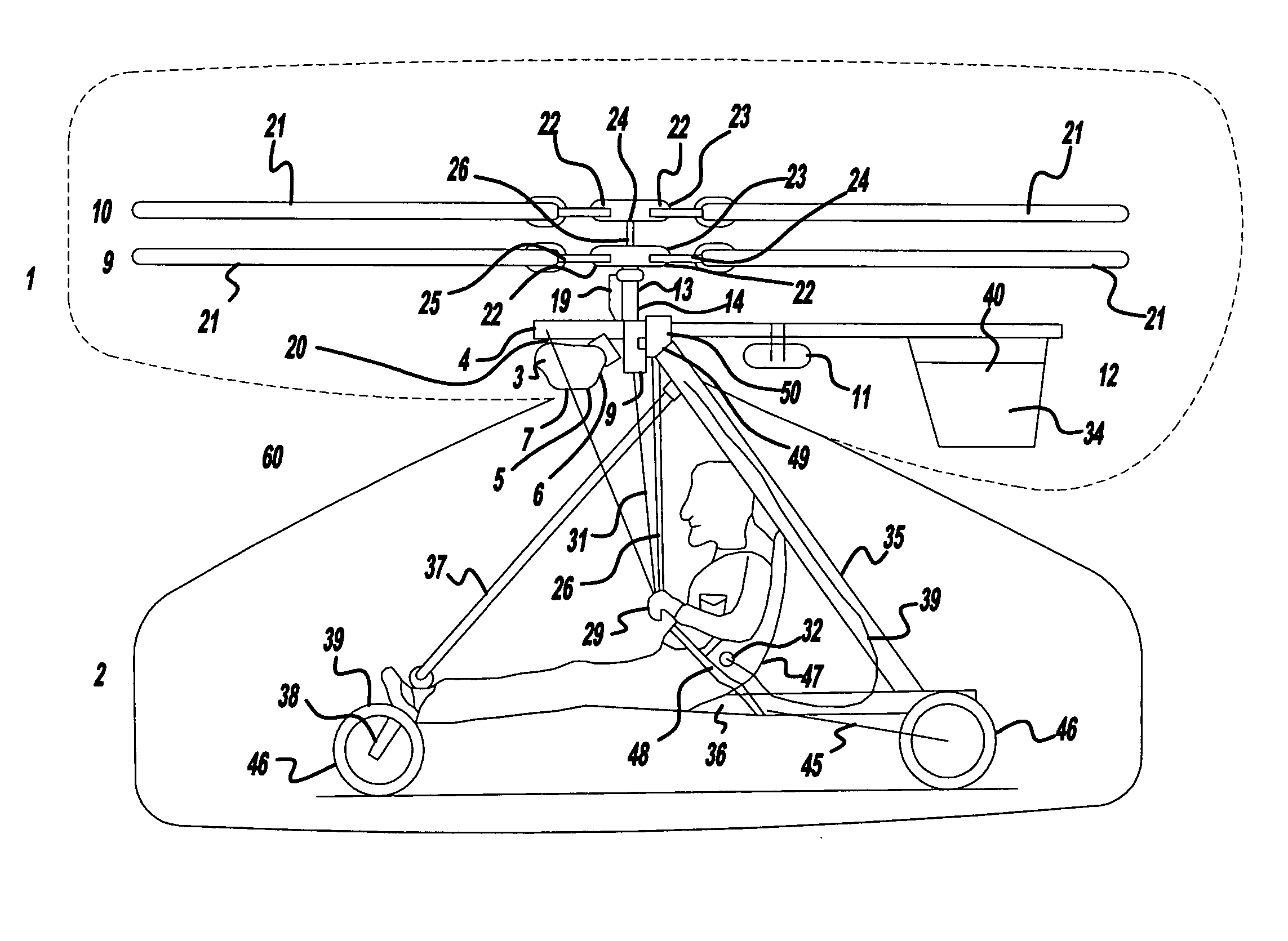
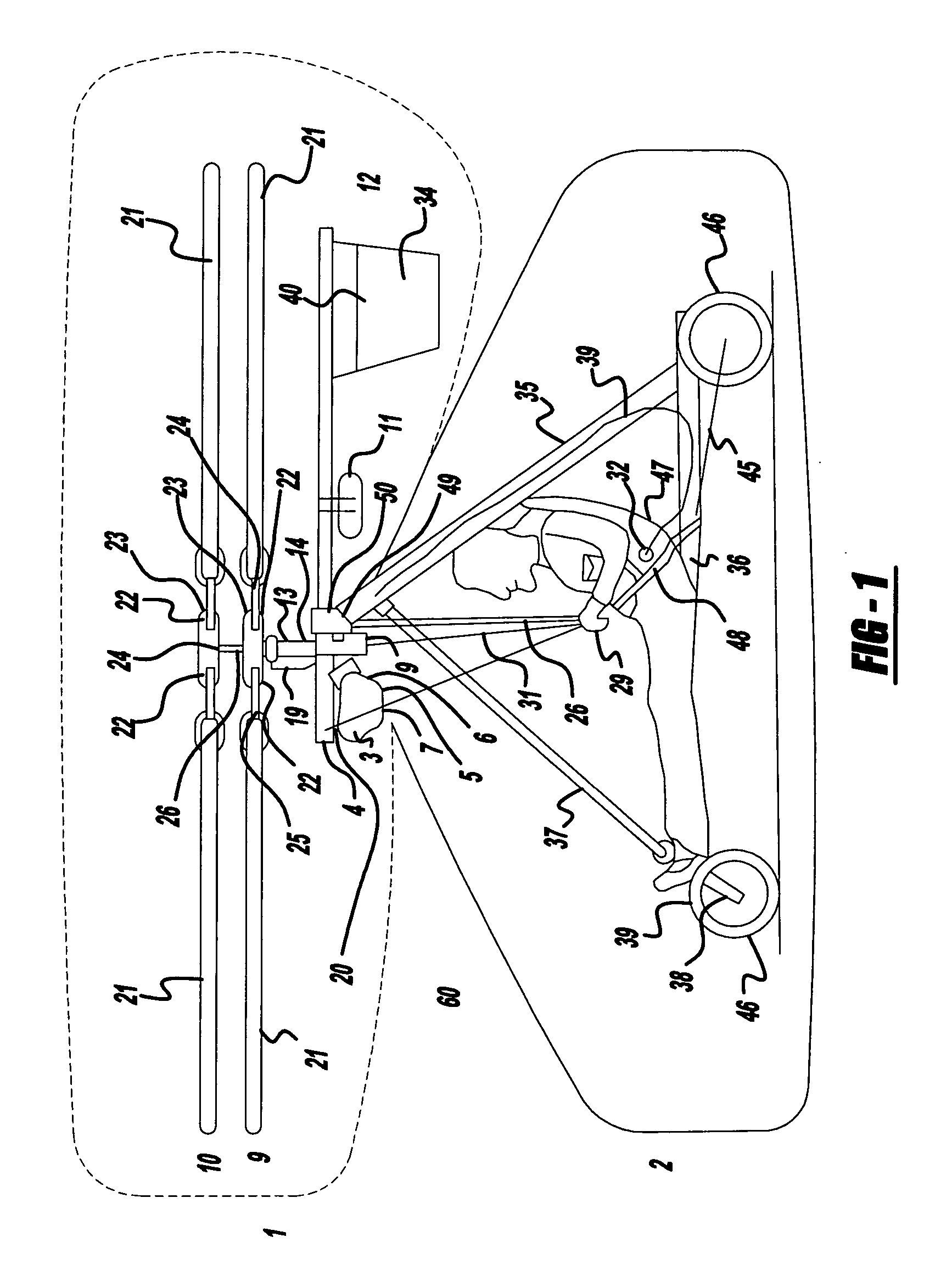
Lightweight helicopter
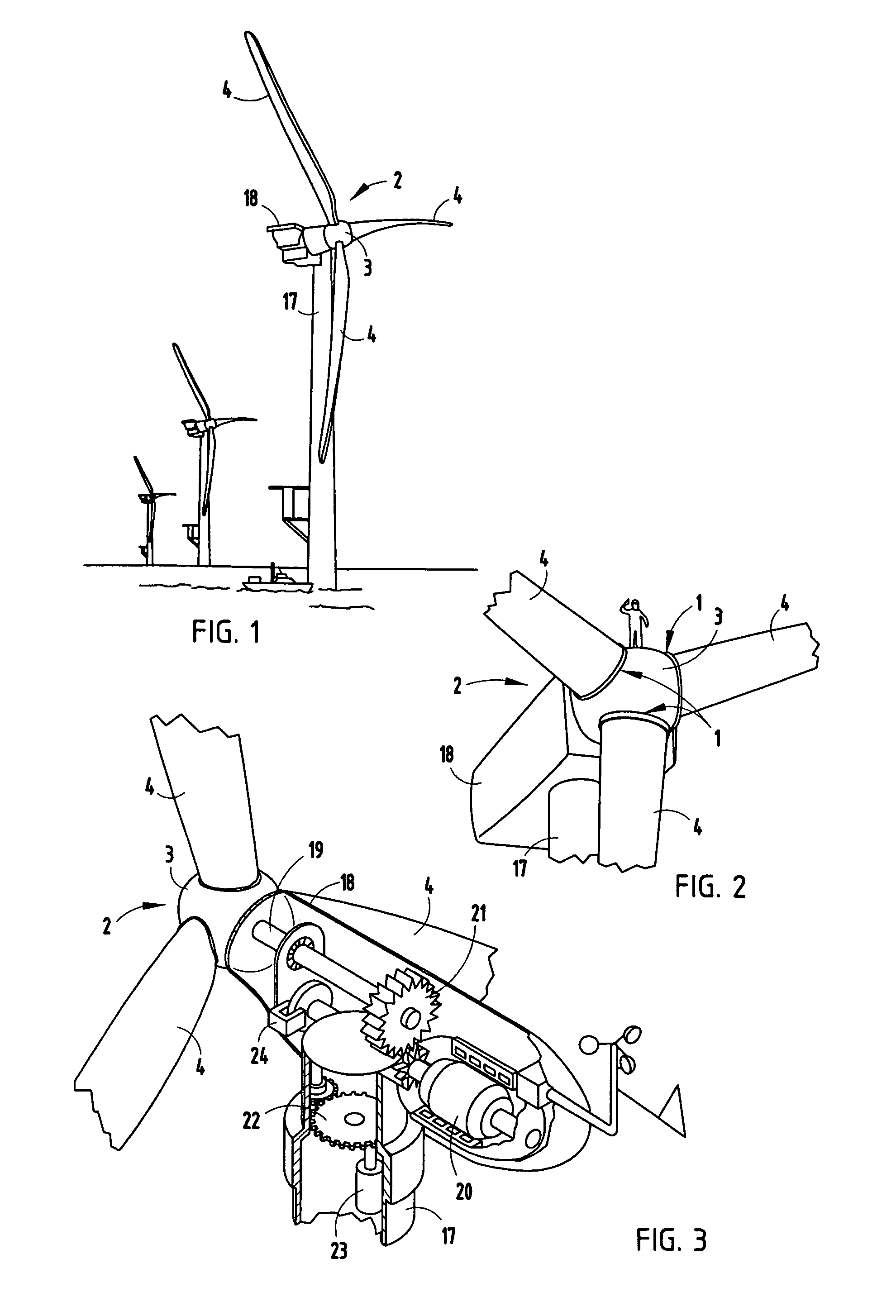
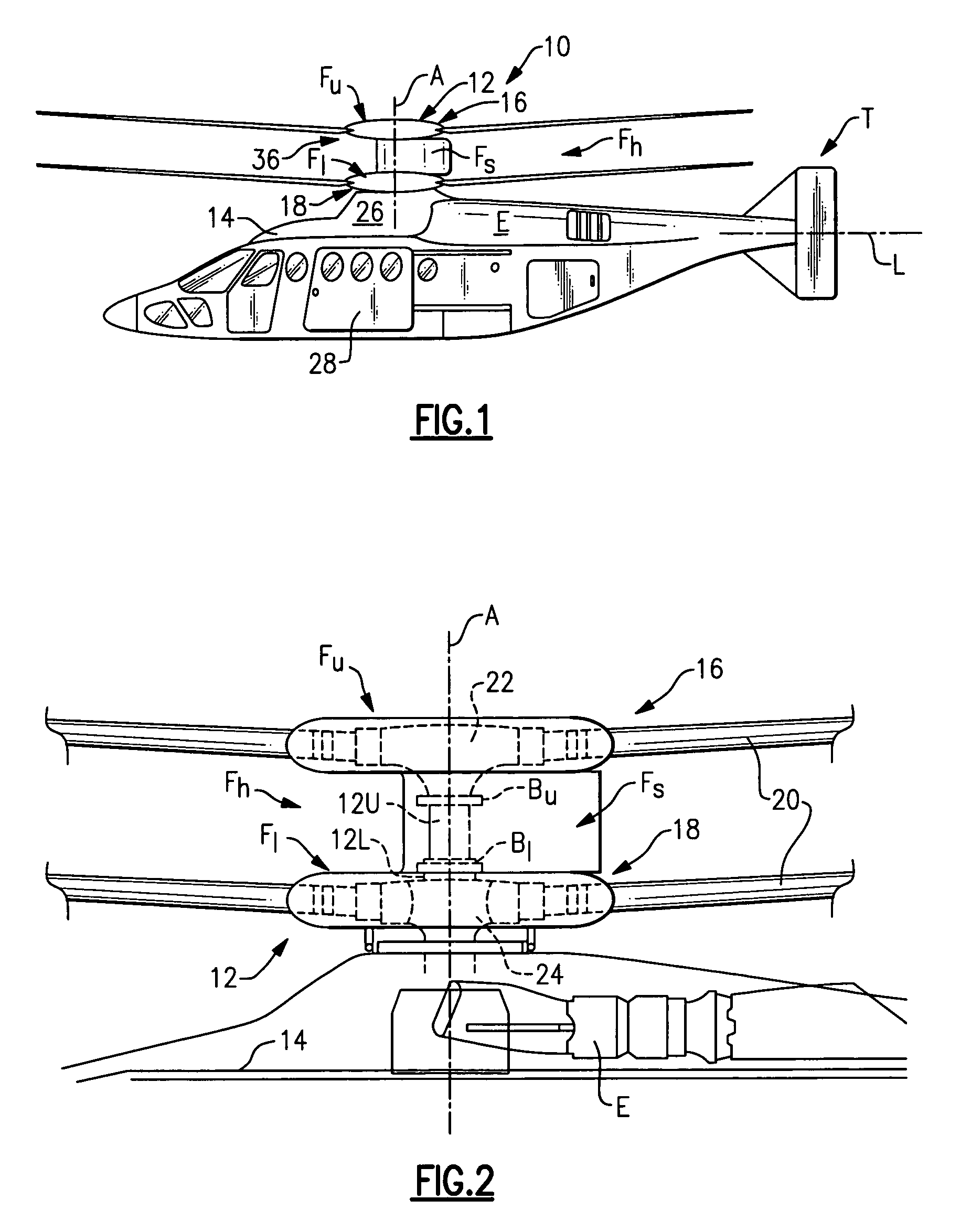
The present invention relates to a lightweight helicopter with features of coaxial, contra-rotating rotors and weight shift control. It has a rotary wing unit attached to a tricycle assembly through a hang bolt. The rotary wing unit has an engine mounted below a keel post, which drives a pair of contra-rotating coaxial rotors through a primary gearbox and a secondary gear box. The keel post is attached to a triangular control frame, the base of which forms the control bar. The keel post also supports a fuel tank connected to the engine and a tail plane having one or more articulated vertical flaps actuated by cables. The secondary gearbox is provided with a free-wheeling clutch, a pinion gear and bevel gears for transmitting the rotary movement of the engine to the counter rotating coaxial vertical shafts each carrying two rotor blades of airfoil cross section fixed by pitch bearing on teetering plates and teetering hinges to form horizontal rotors. The tricycle assembly has a pilot seat and landing gear as well as controls for operation of the engine, rotors, tail plane and landing gear. The directional control of the helicopter is achieved through the weight shift principle by manipulating the control bar, thereby causing a tilt of the contra-rotating rotors, which cause a corresponding tilt in the aerodynamic thrust of the rotors, propelling the helicopter in the required direction.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
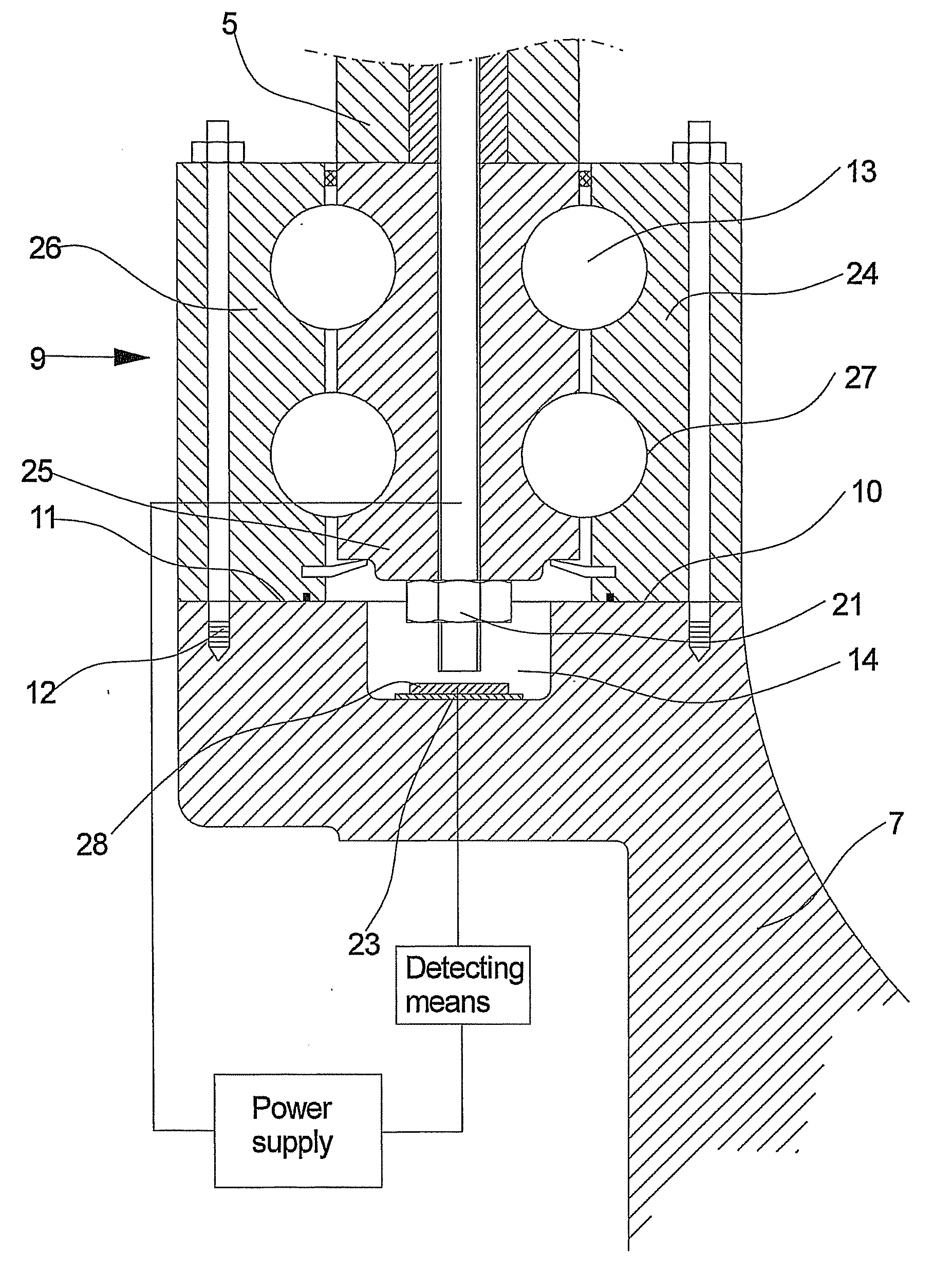
System and method for detecting pitch bearing damage in a wind turbine
The present disclosure is directed to a system and method for detecting damage of a pitch bearing of a wind turbine. The pitch bearing is part of a pitch drive system having a plurality of pitch drive motors. The method includes measuring at least one electrical signal of the pitch drive system. The method also includes processing the electrical signal(s) of the pitch drive system and comparing the electrical signals of the pitch drive system with a baseline threshold. Thus, the method also includes determining whether damage is present in the pitch bearing based, at least in part, on the comparison, wherein the electrical signal(s) exceeding the baseline threshold is indicative of damage in the pitch bearing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
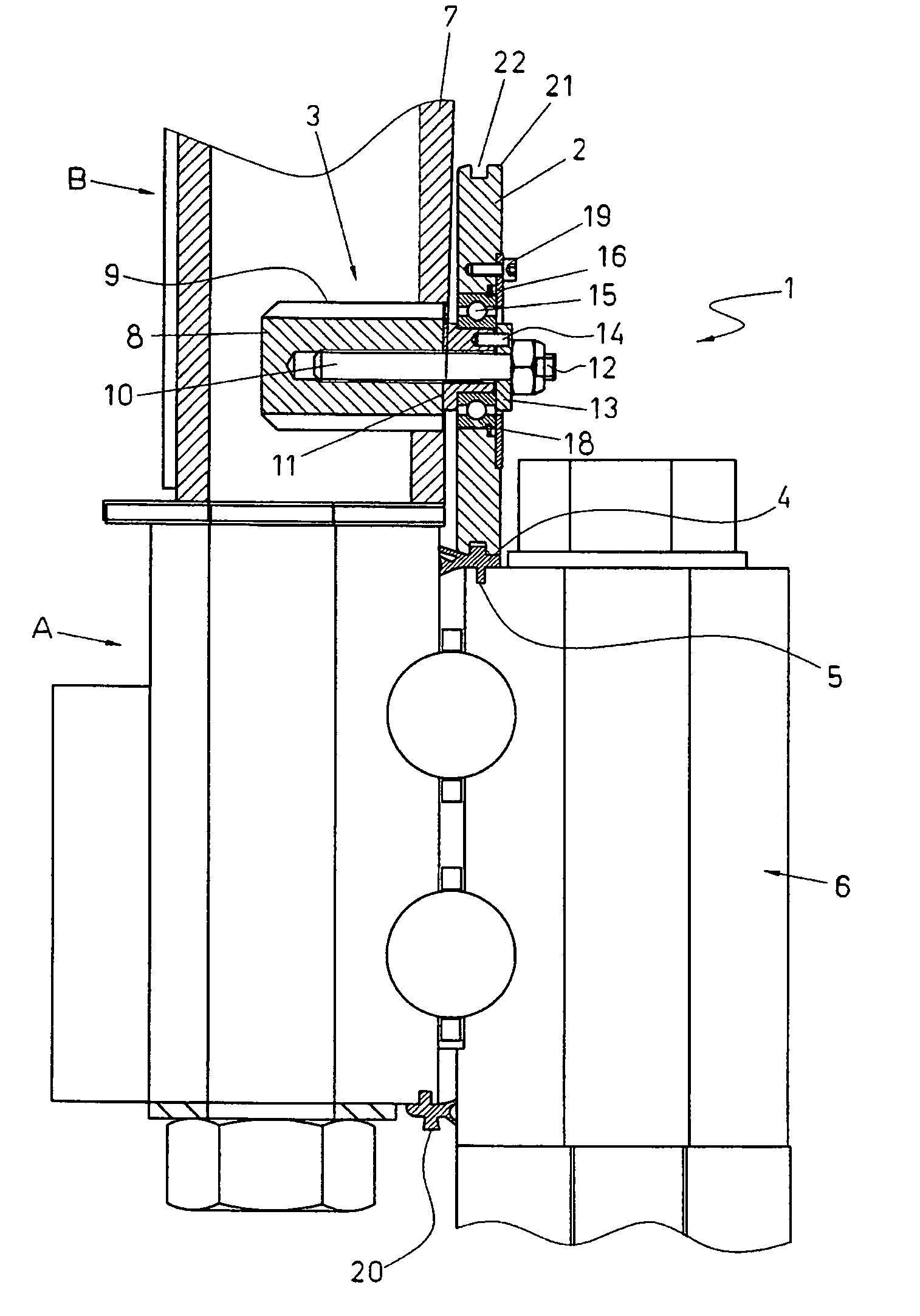
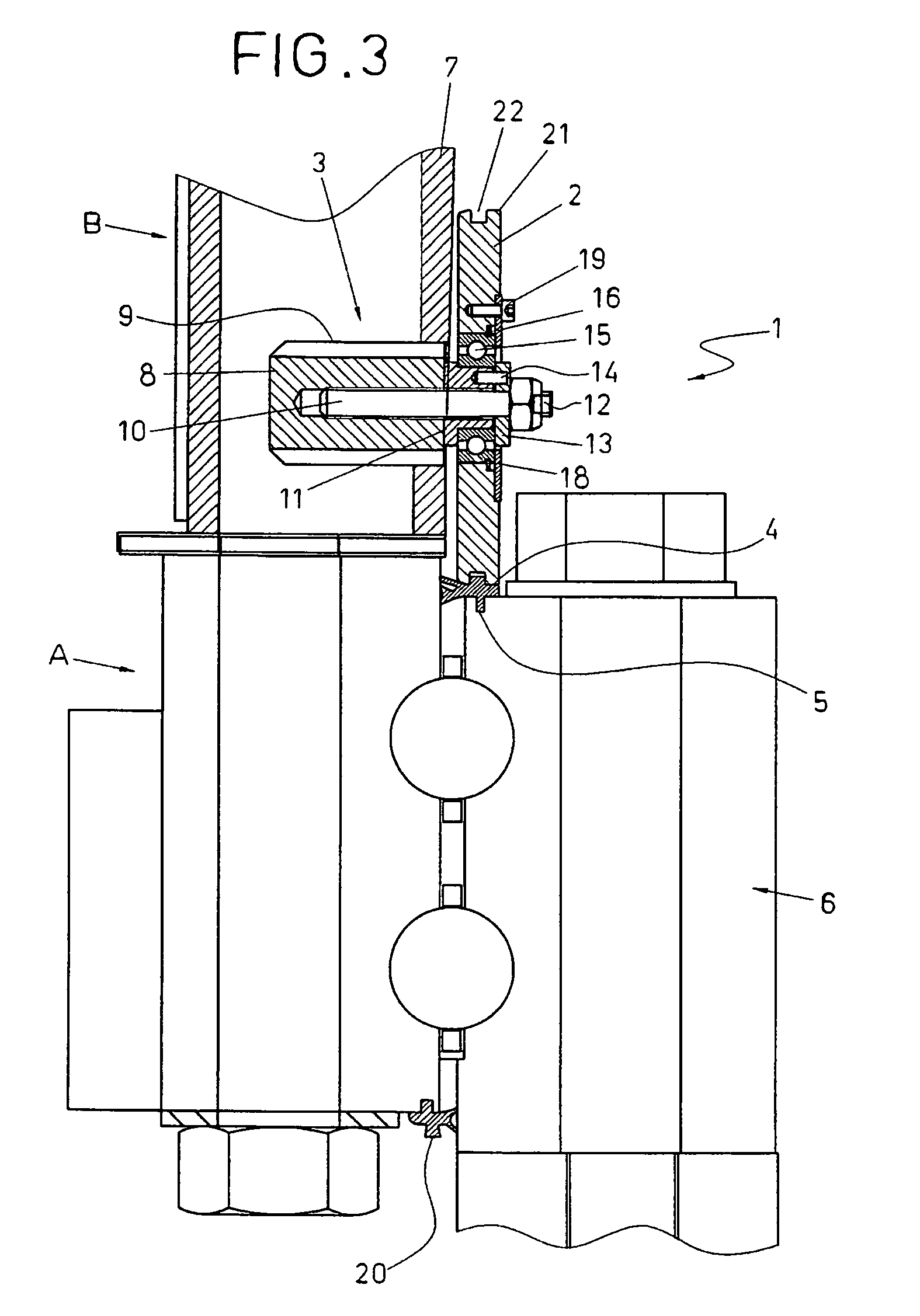
Device for fitting a seal
ActiveUS20080104821A1Easy to operateEasy functionalityPiston ringsFinal product manufactureEngineeringPitch bearing
The device comprises at least one pressing member and an attachment member for attaching it to a wind turbine part, for example, a blade root, which may have a relative movement with regard to a first part, for example, a bearing in a pitch blade mechanism, the first part having a seat into which the joint is to be fitted. Upon relative rotation between the first parts, the pressing member presses the seal into the seat. A method for fitting the seal into the seat is also provided. Operations of maintenance or partial or complete replacement of the seal can be carried out in situ on the wind turbine and also on pitch bearing manufacturing easily and effectively.
Owner:GE RENEWABLE TECH WIND BV +1
Wind turbine pitch bearing, and use hereof
ActiveUS8047792B2Without reducing bearing durability and functionalityCost and weightRotary bearingsPropellersTurbine bladeBlade pitch
The invention relates to a wind turbine including at least two pitch controlled wind turbine blades. Each blade has pitch bearings including two or more bearing rings, and pitch controlling means for pitching the blades by means of the bearings. The blades are mounted on a hub via the pitch bearings and the pitch bearings include separate flexibility enhancing means for controlling loads in the bearings.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com