Patents
Literature
152 results about "Coaxial rotors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
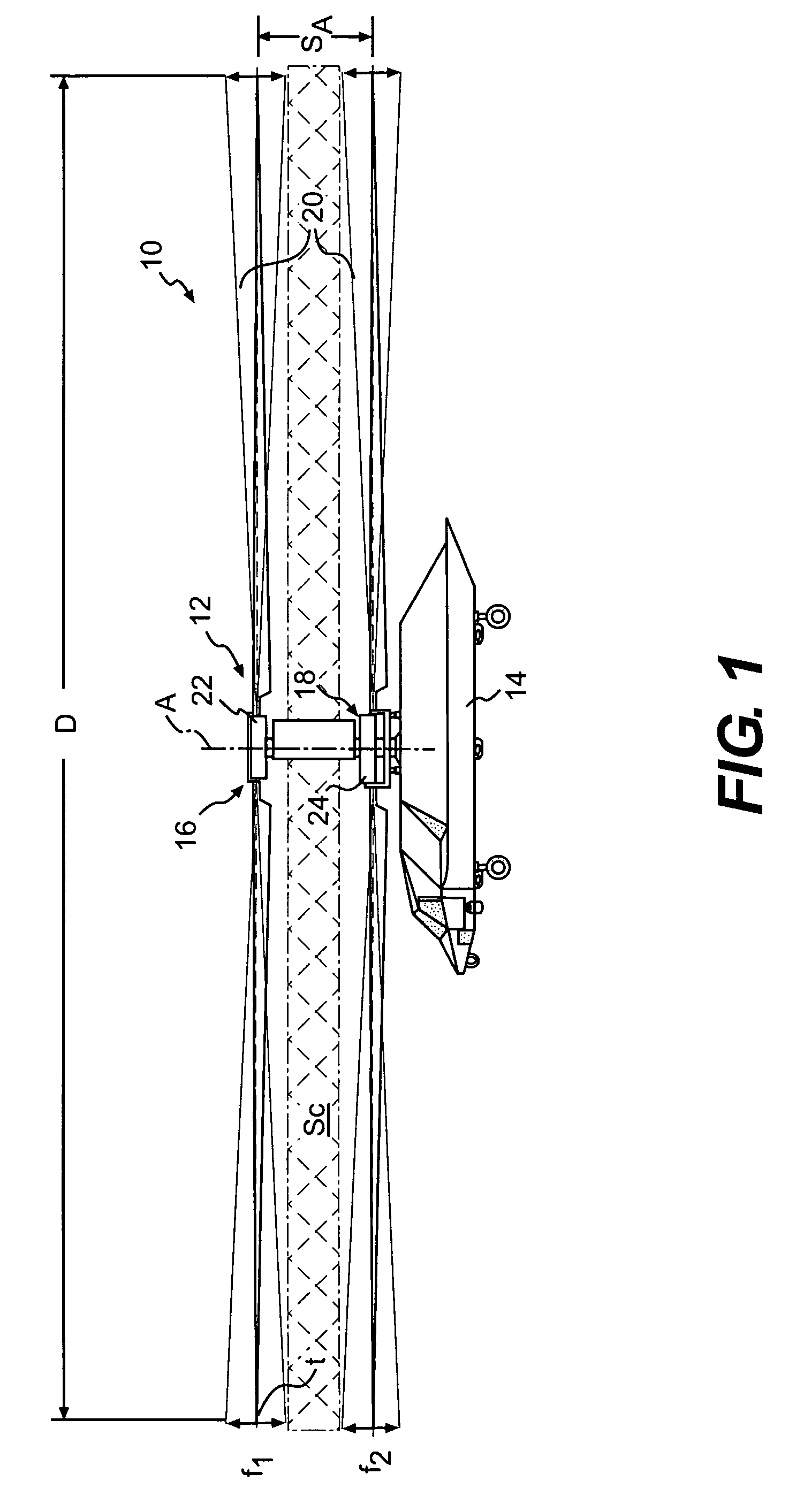
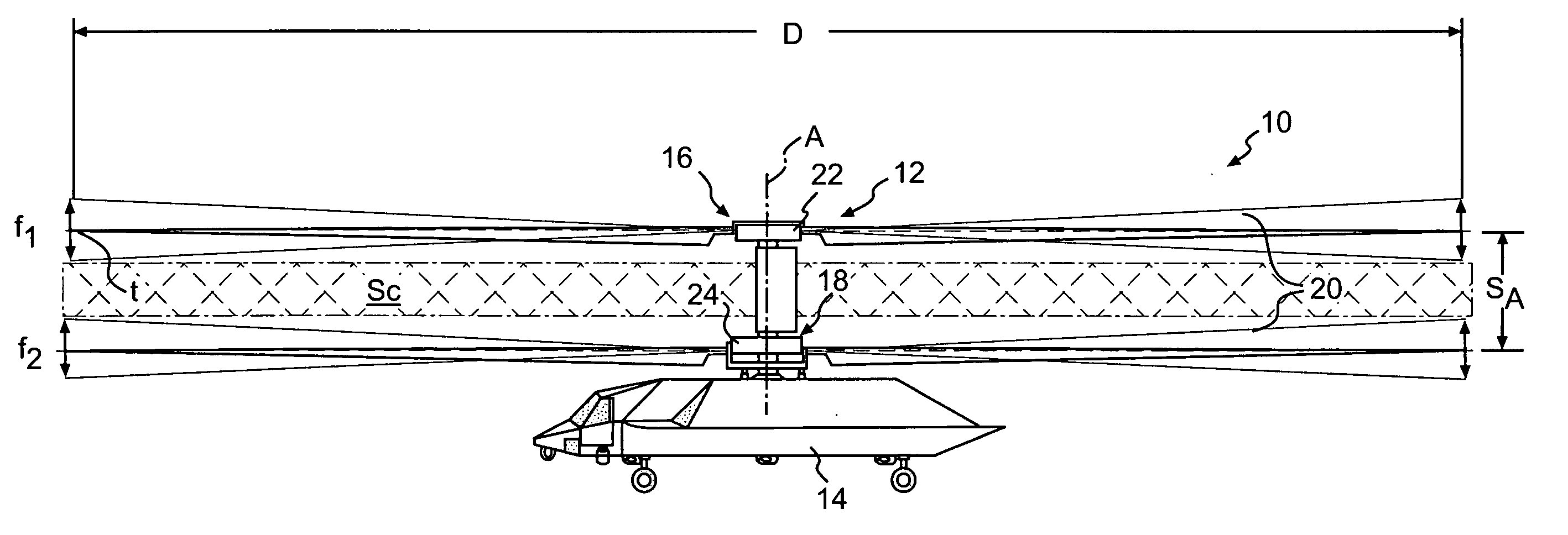
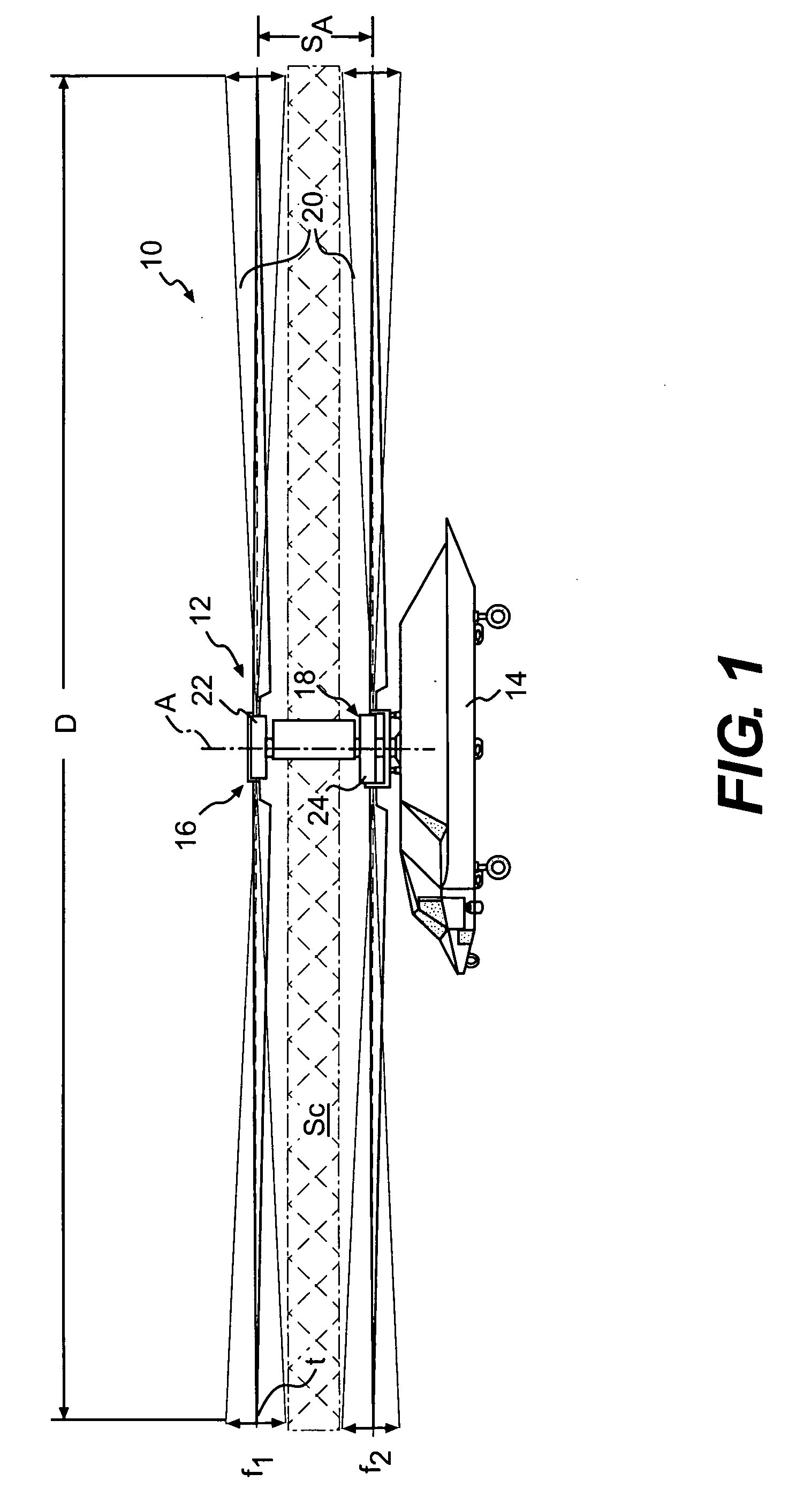
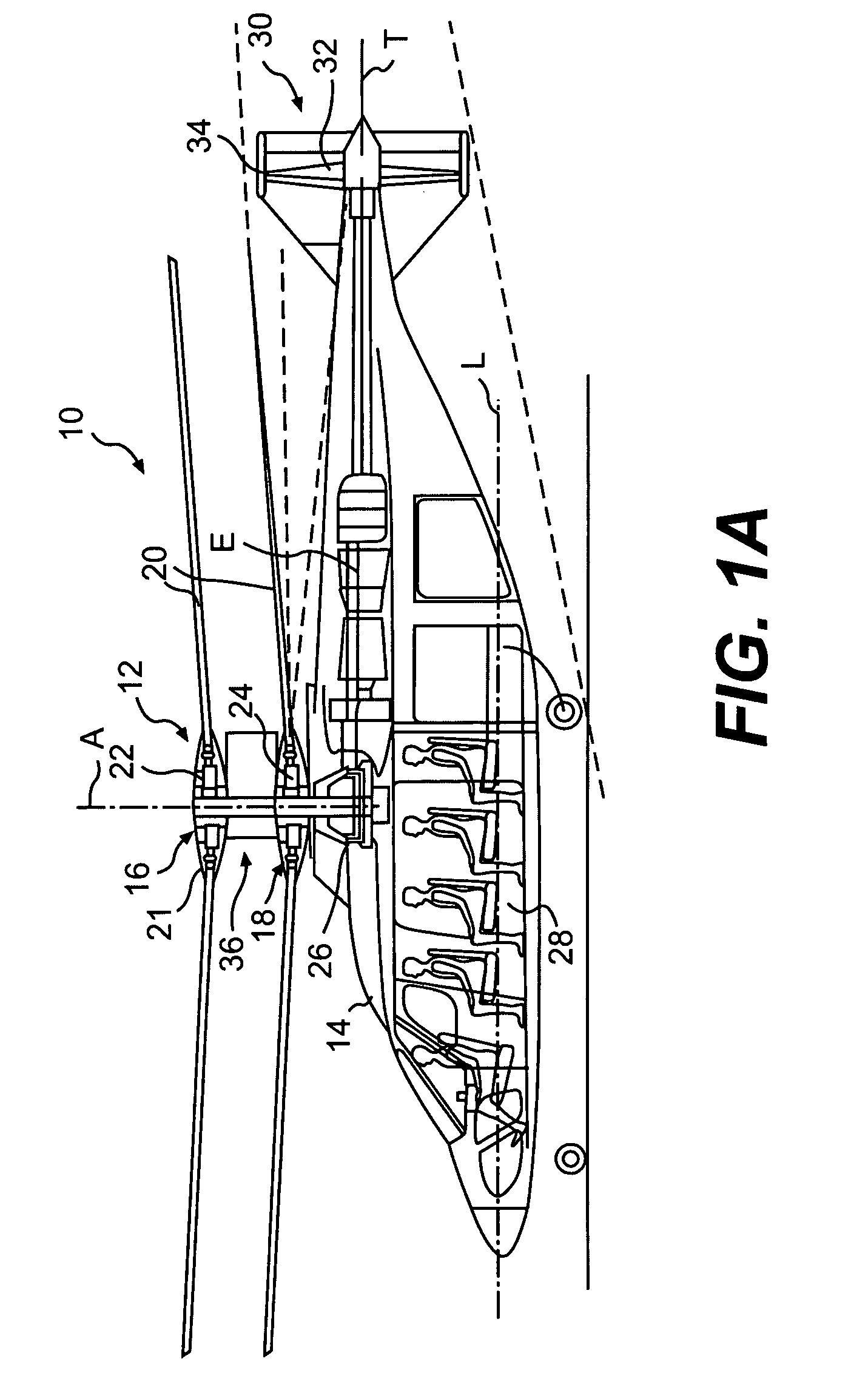
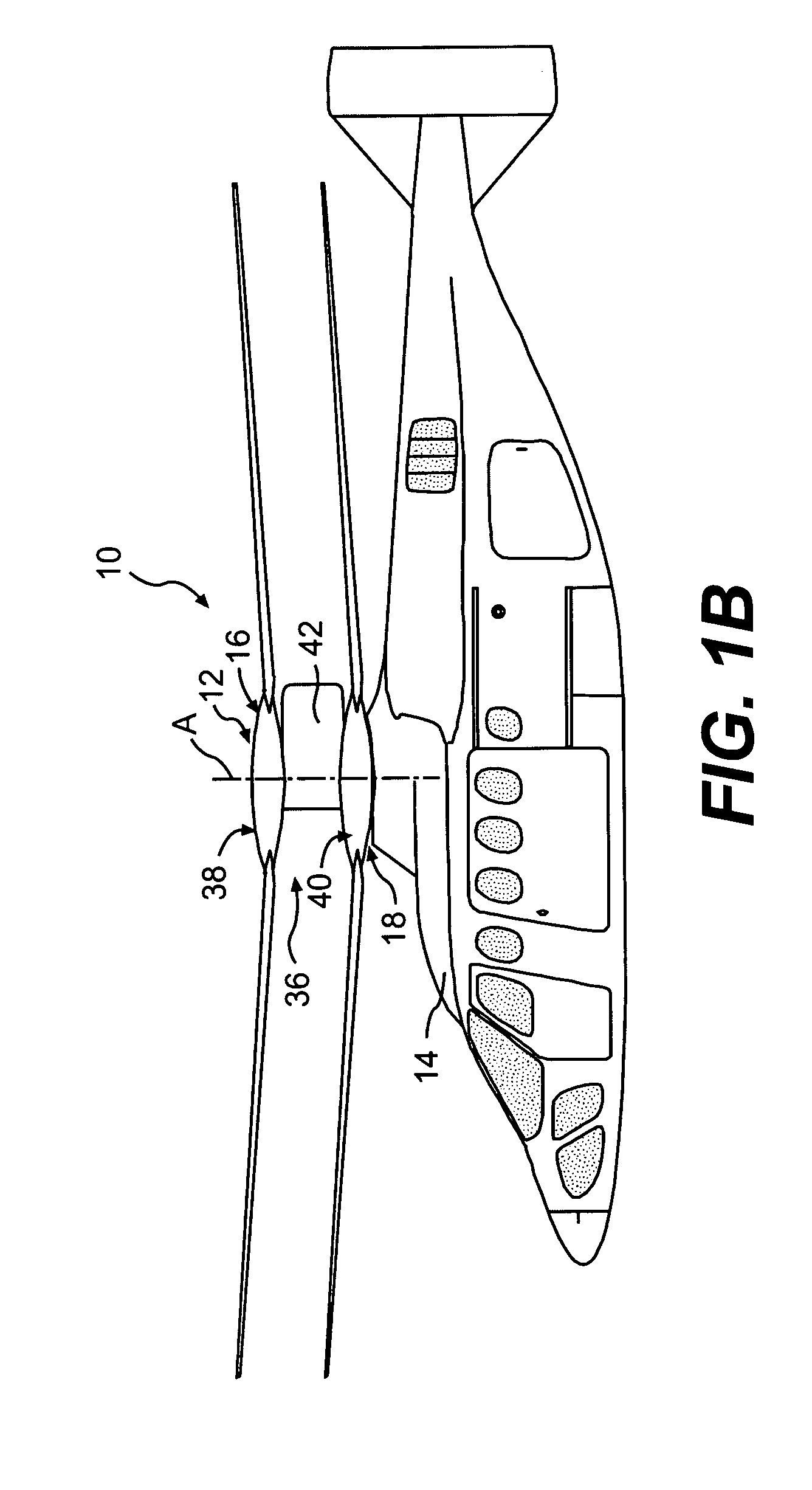
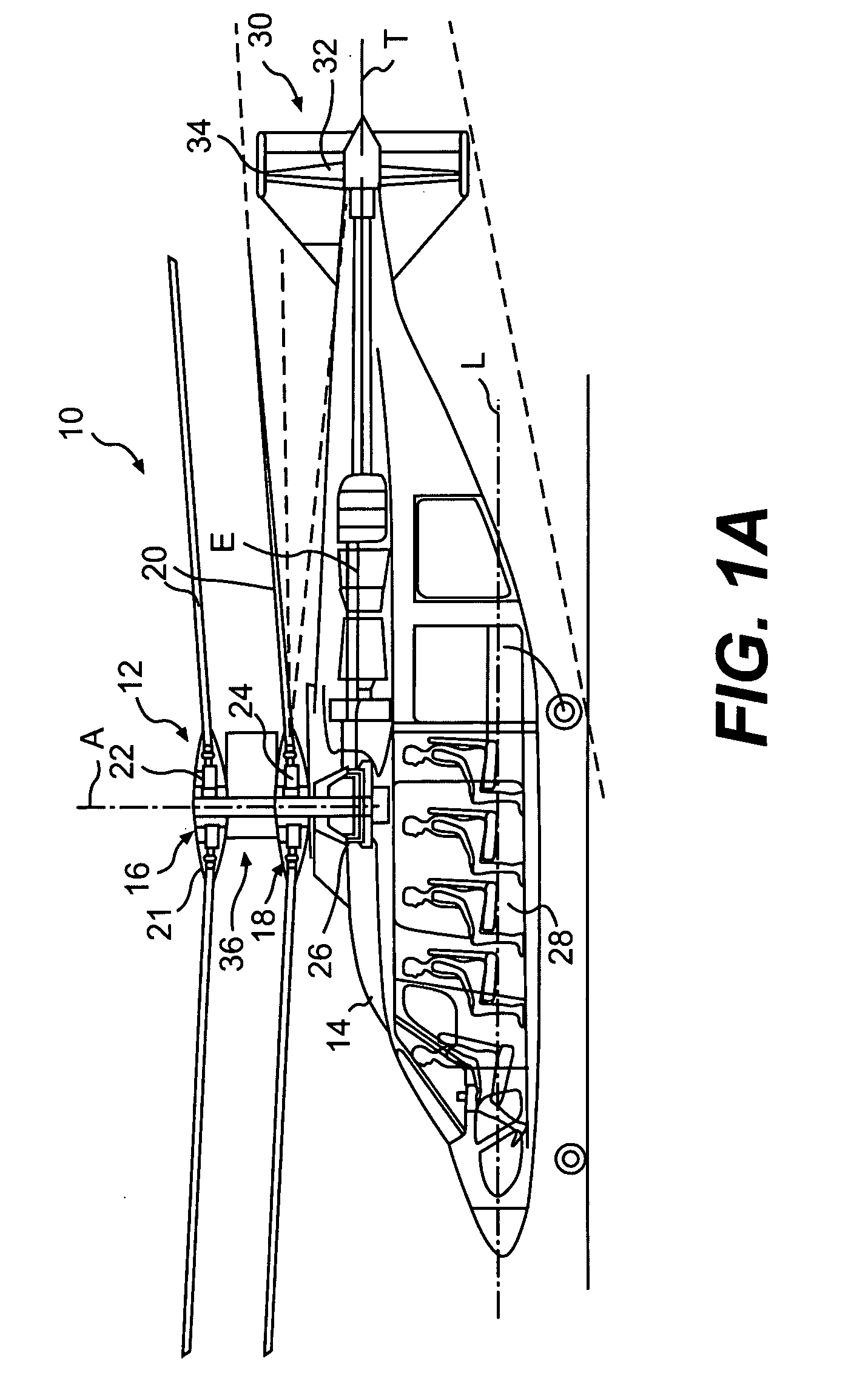
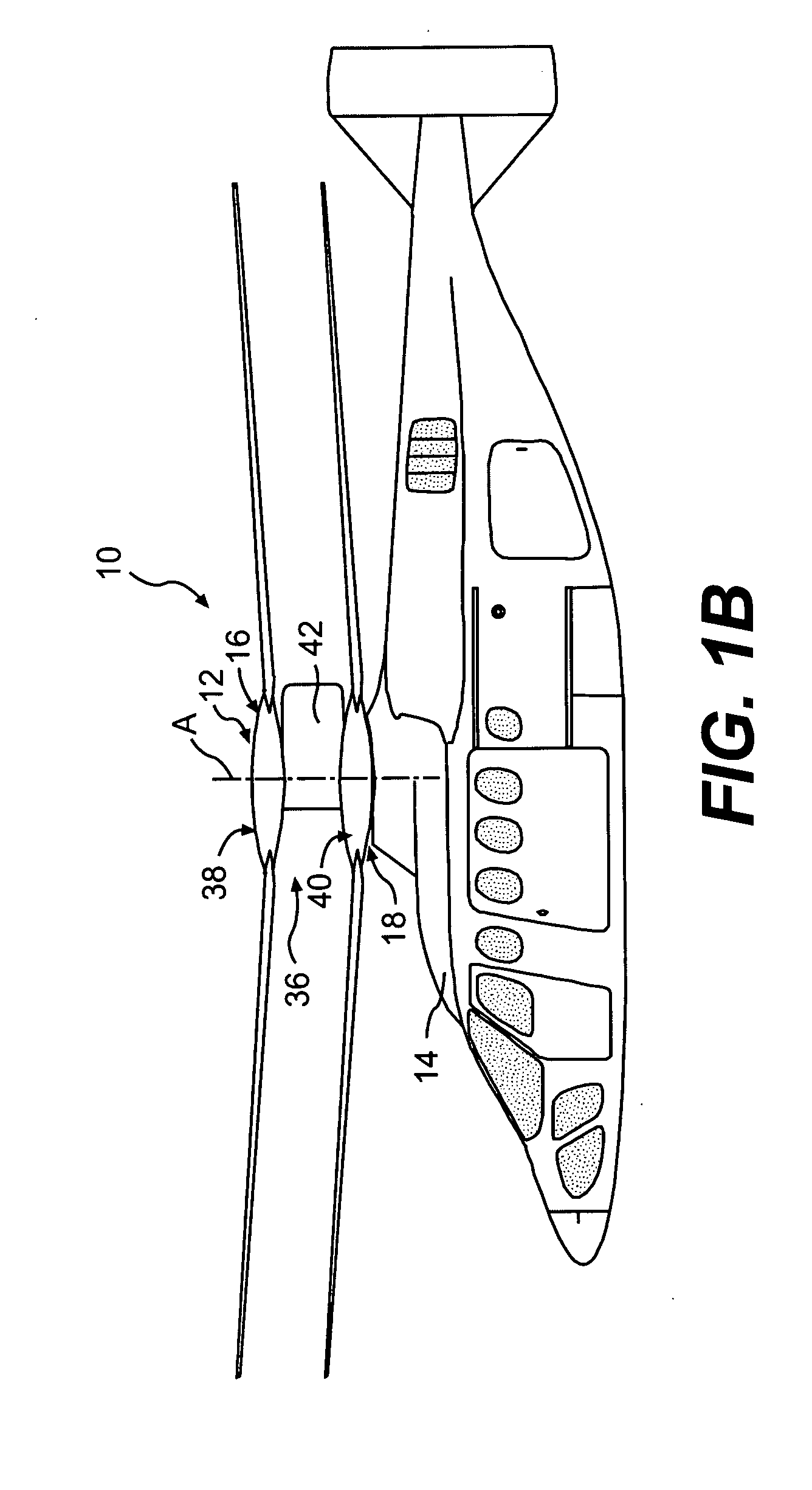
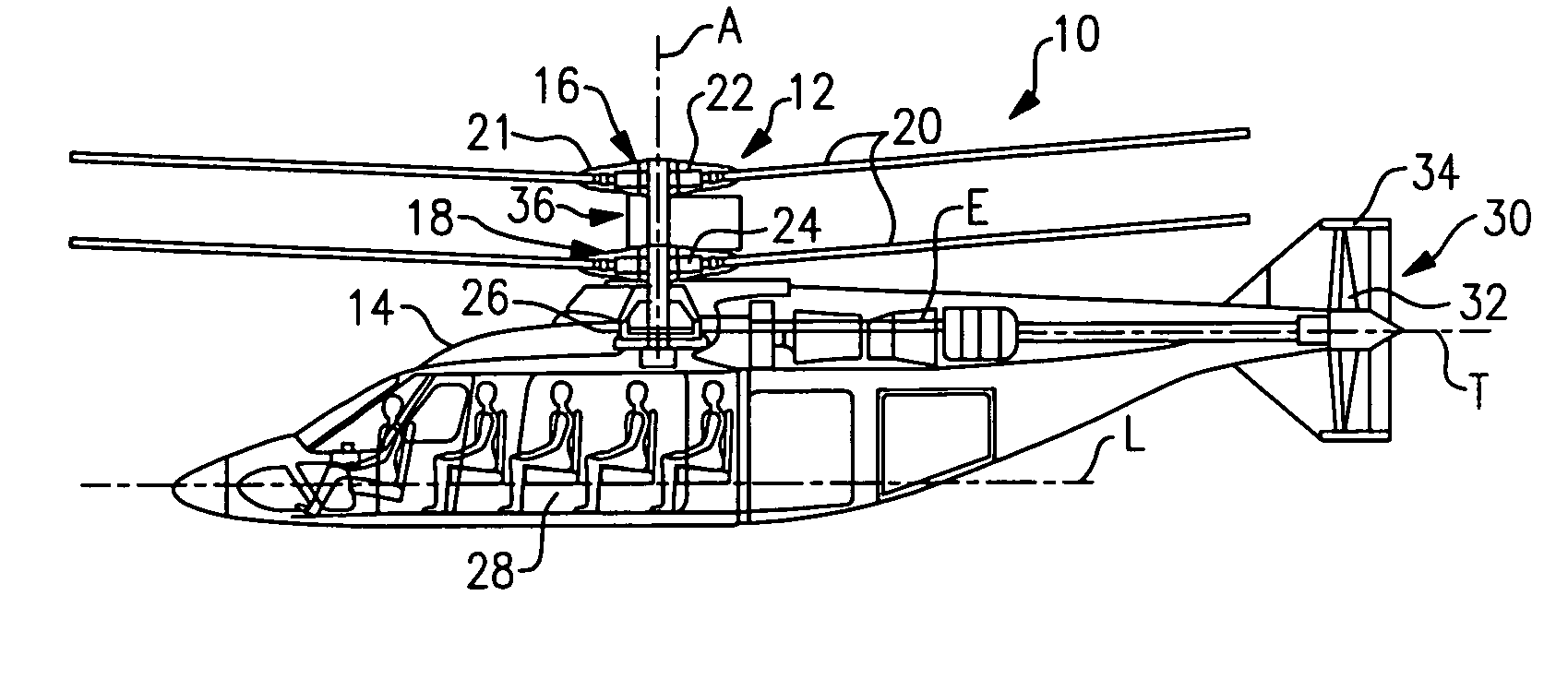
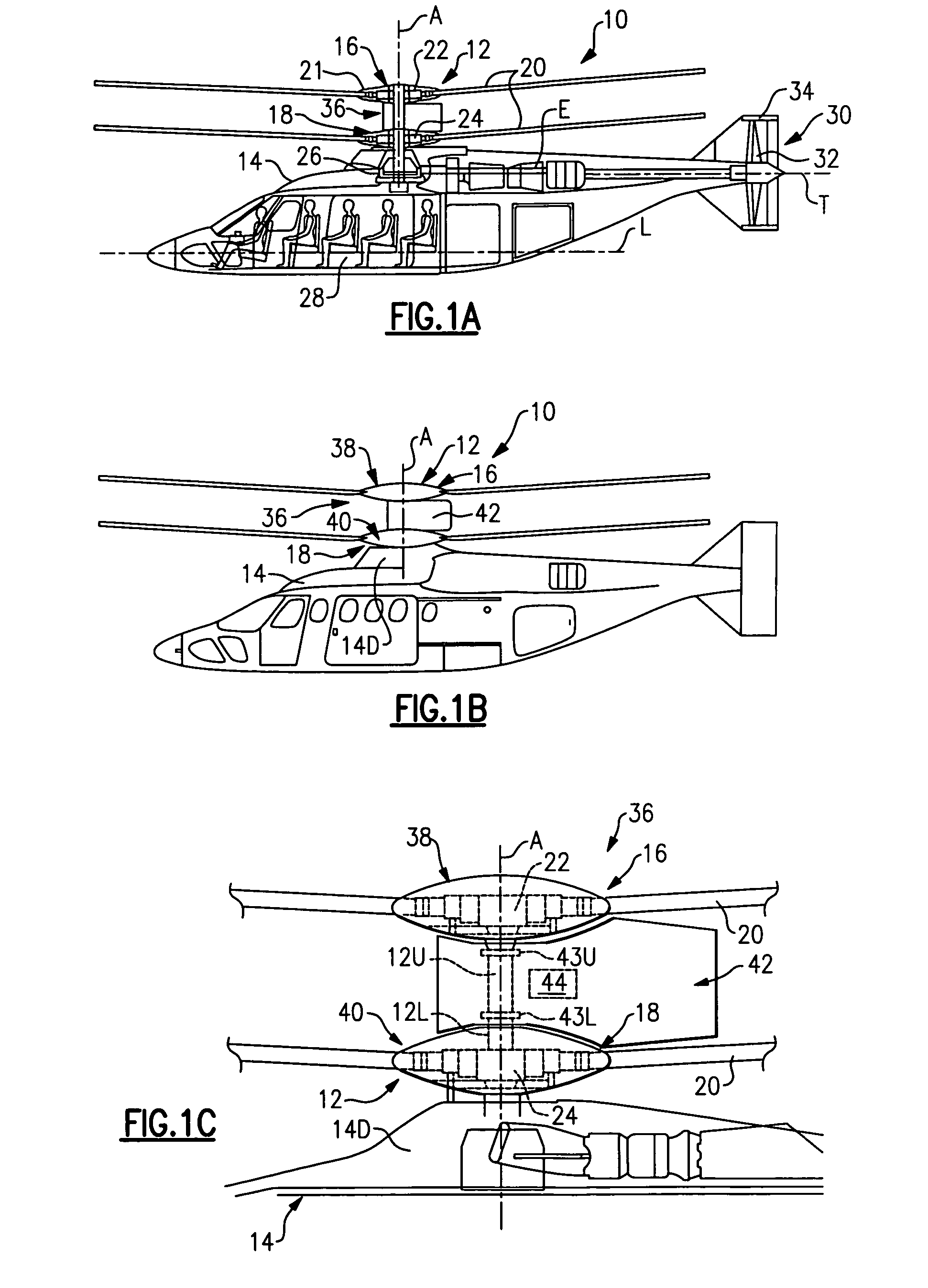
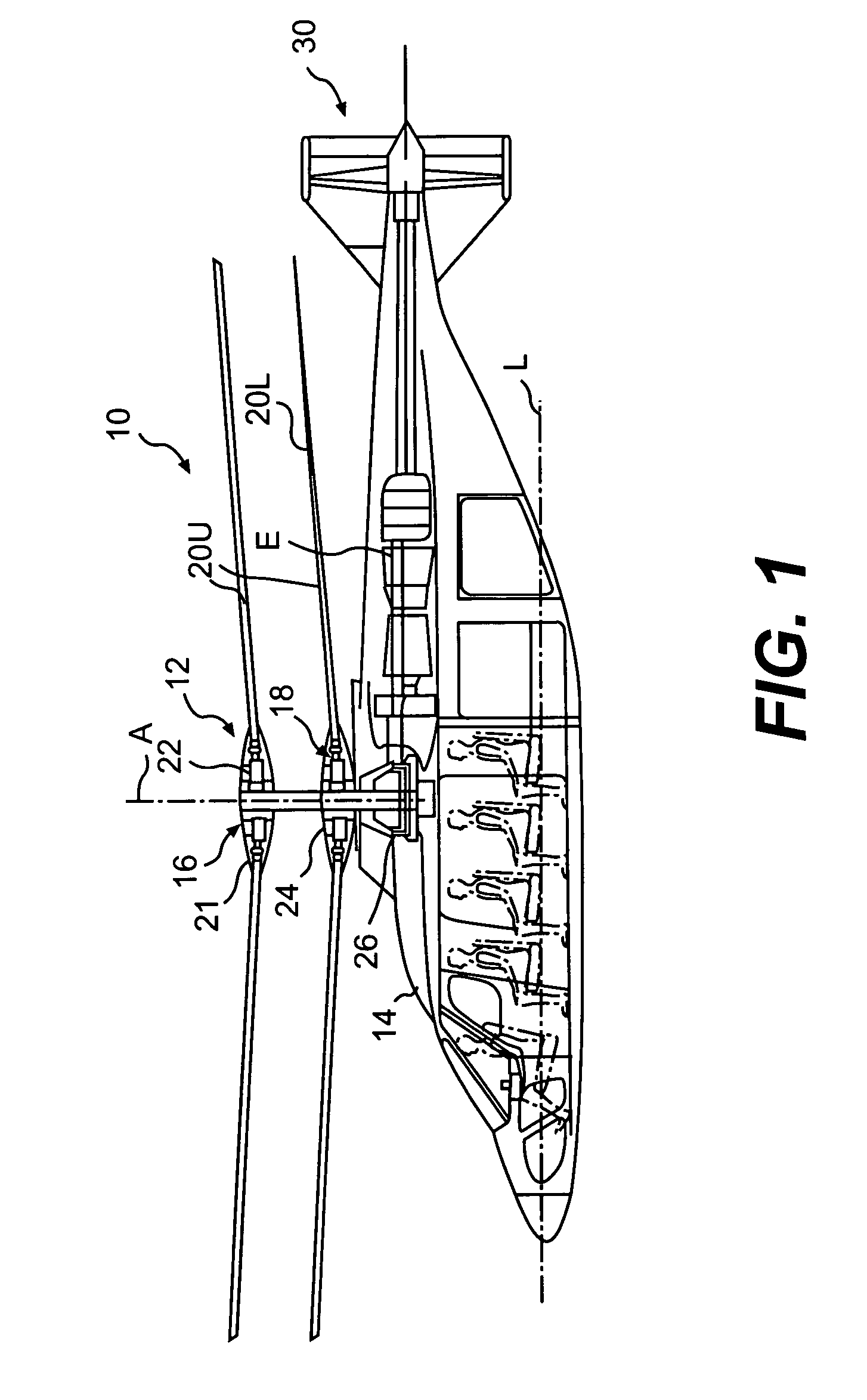
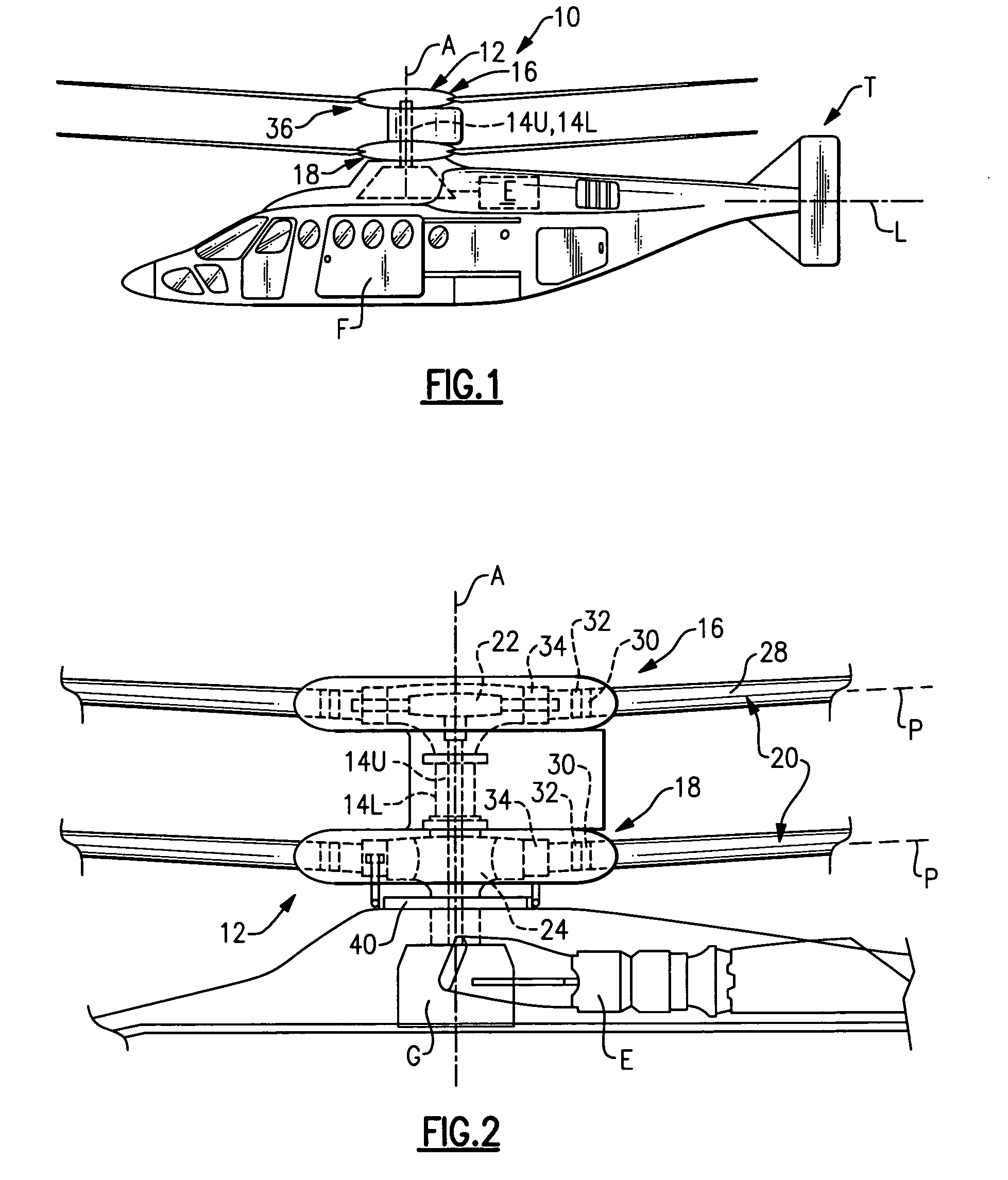
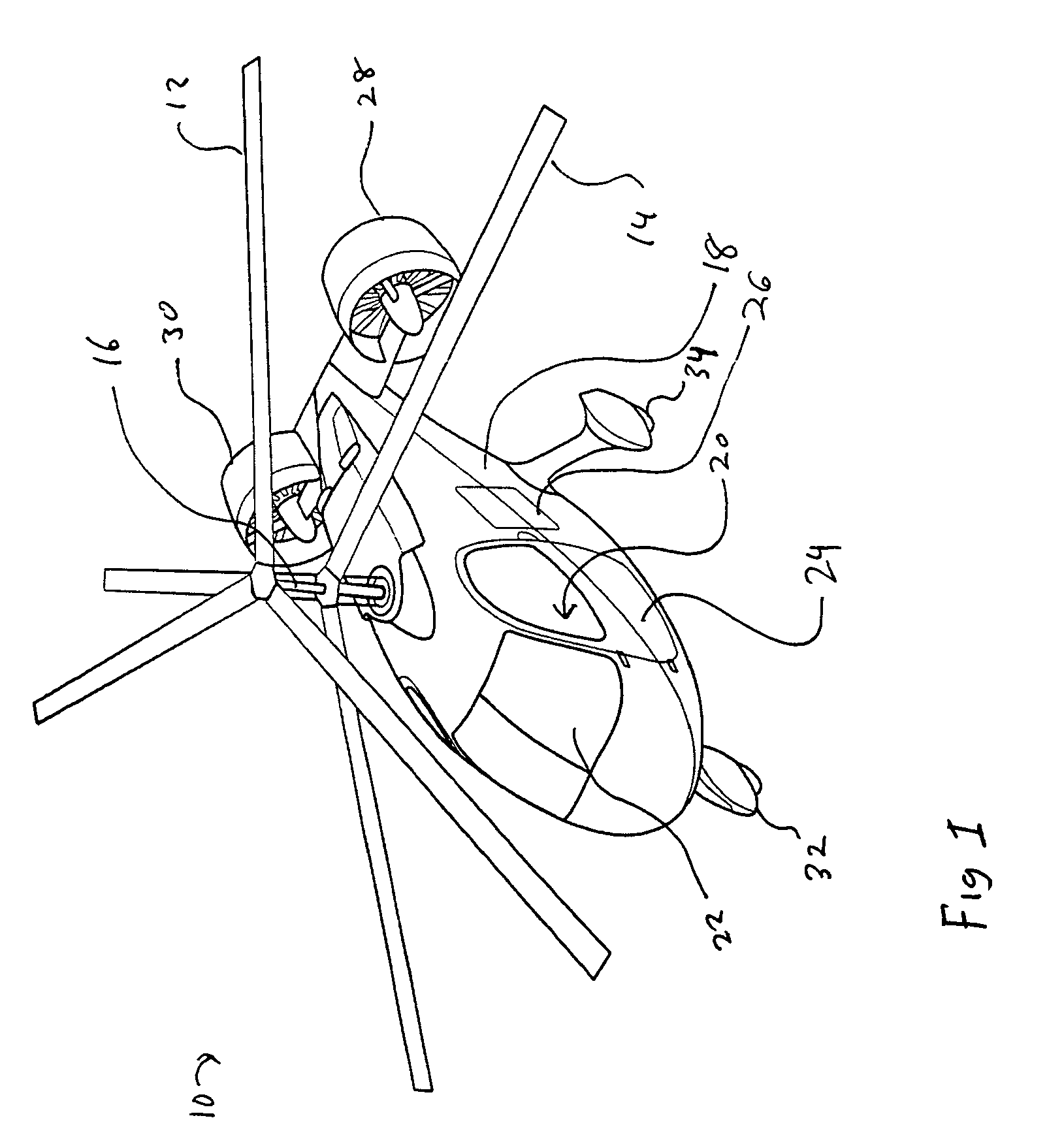
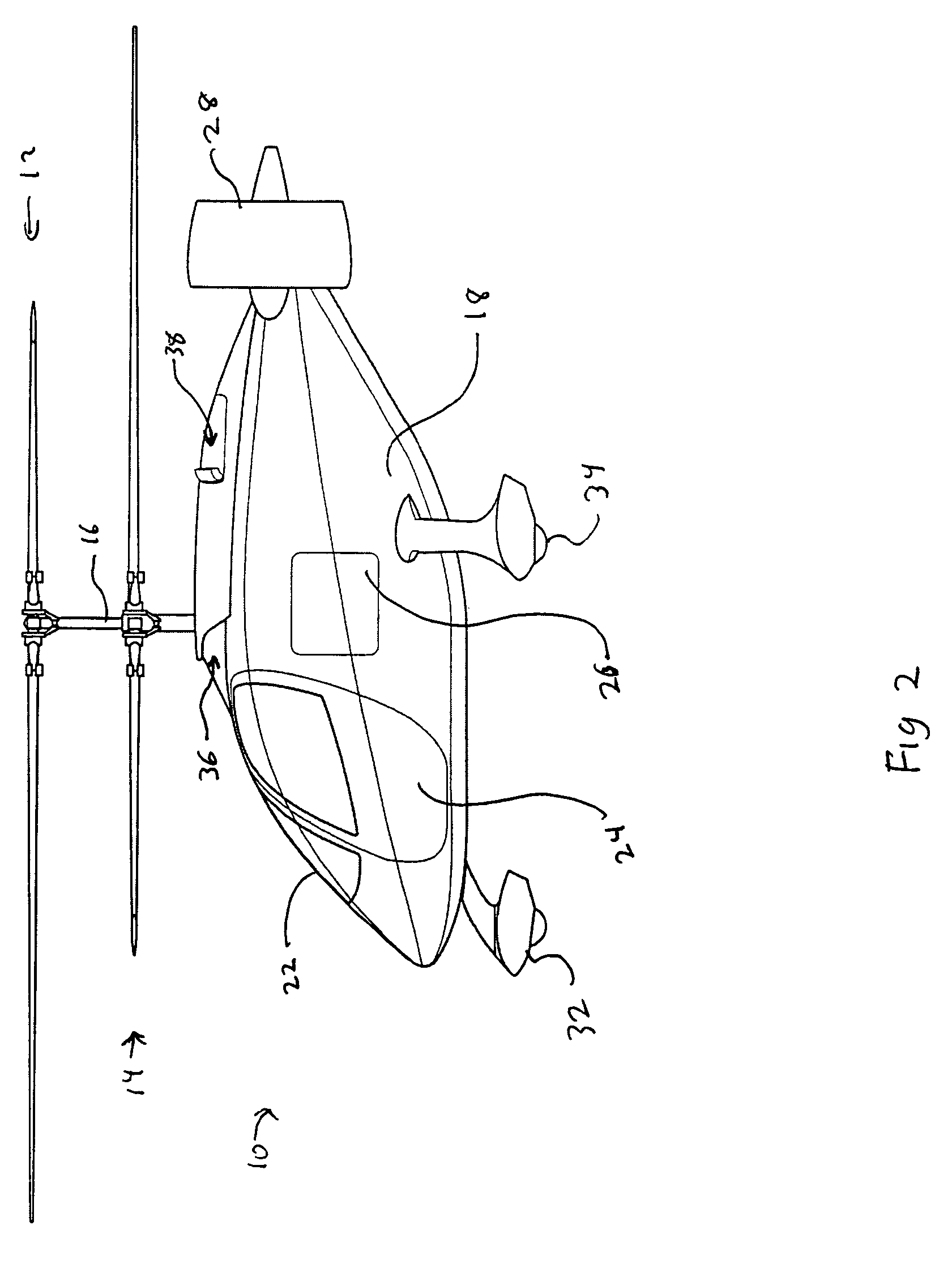
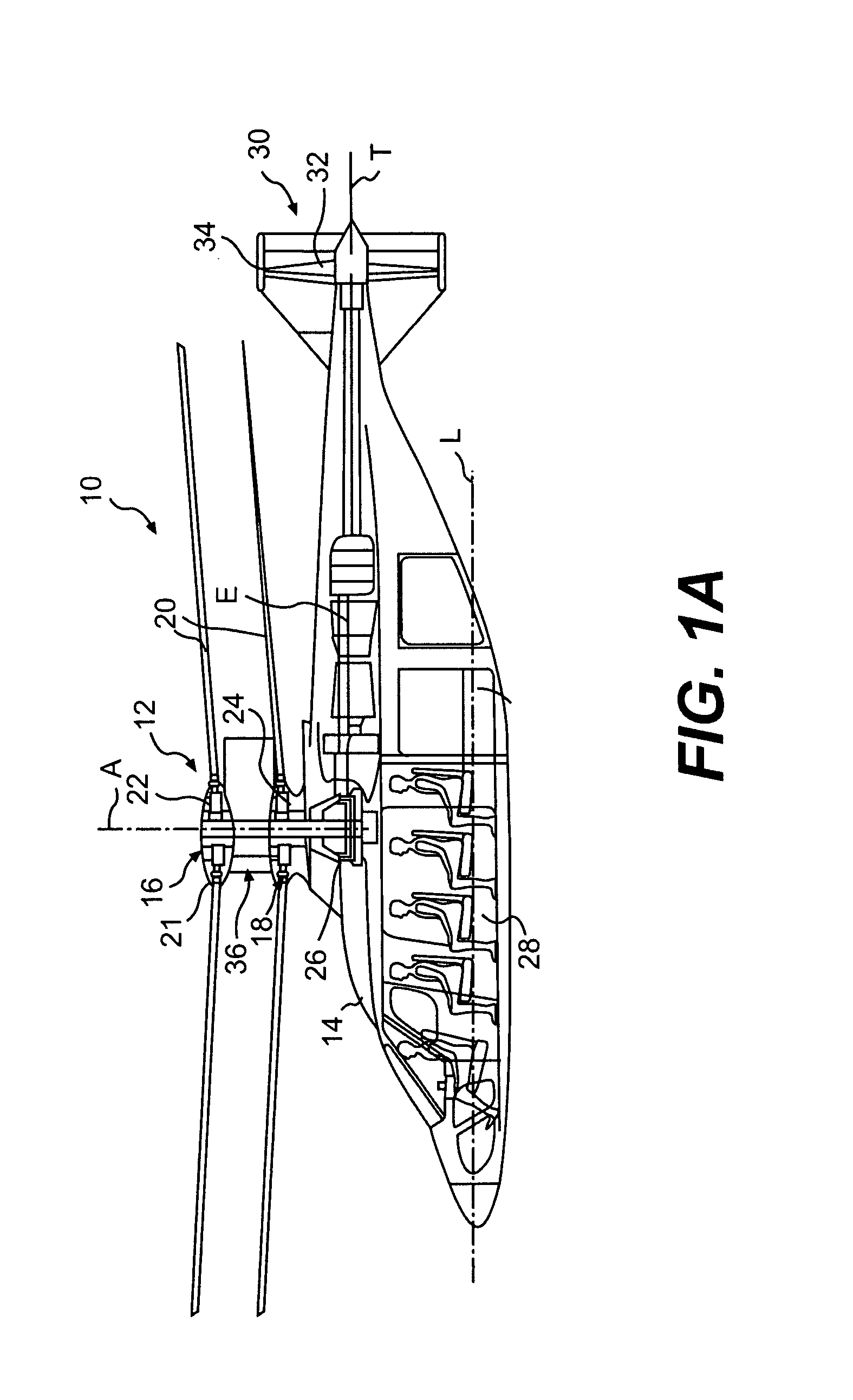
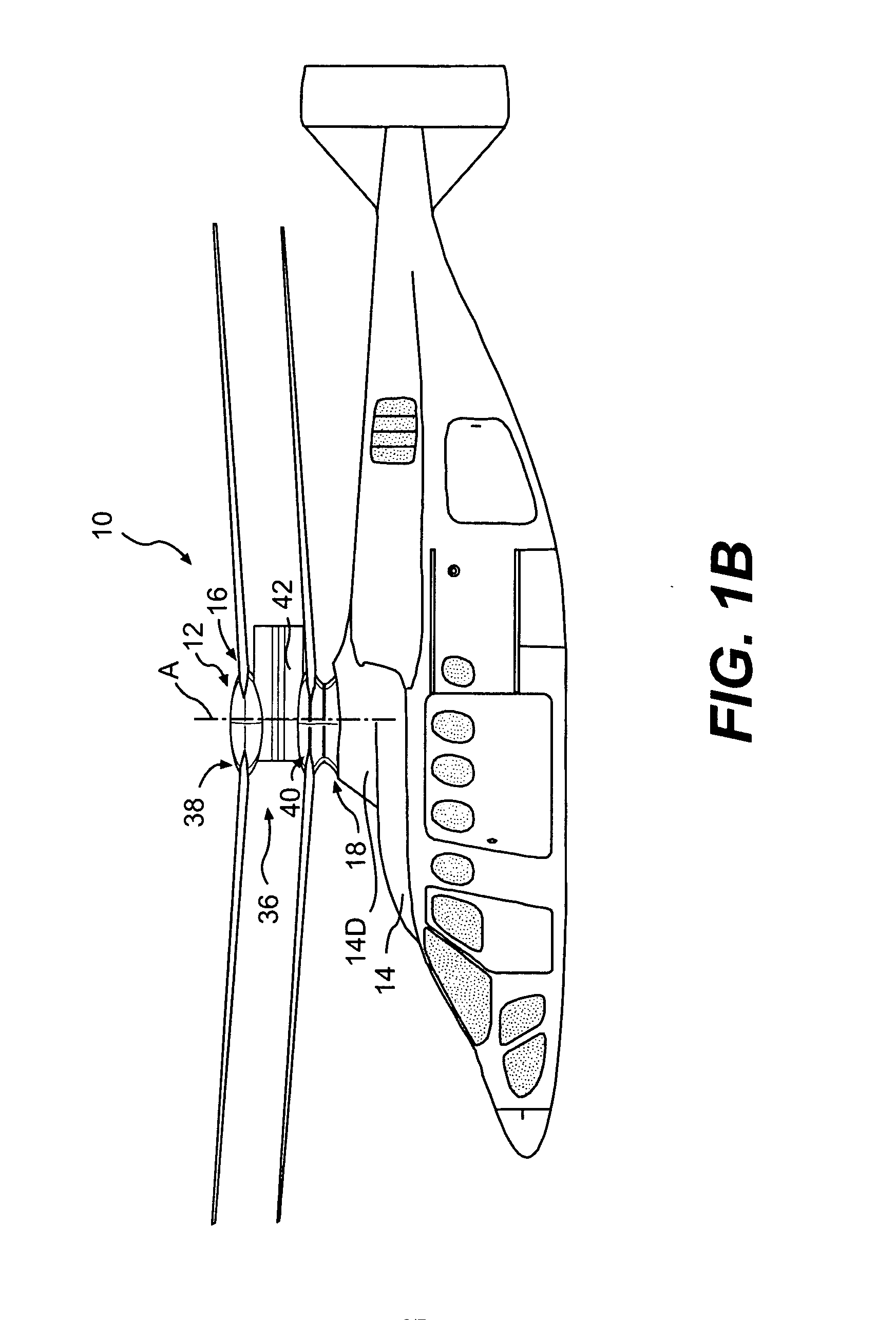
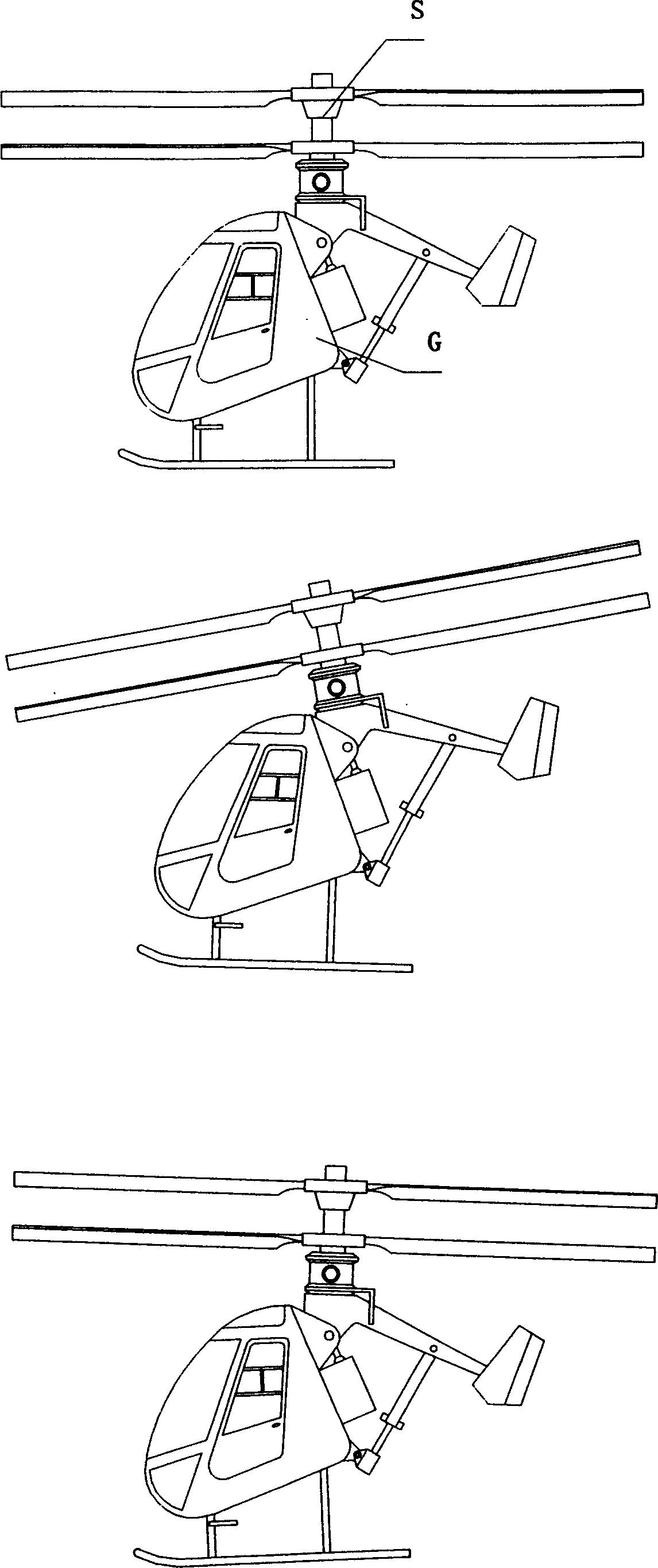
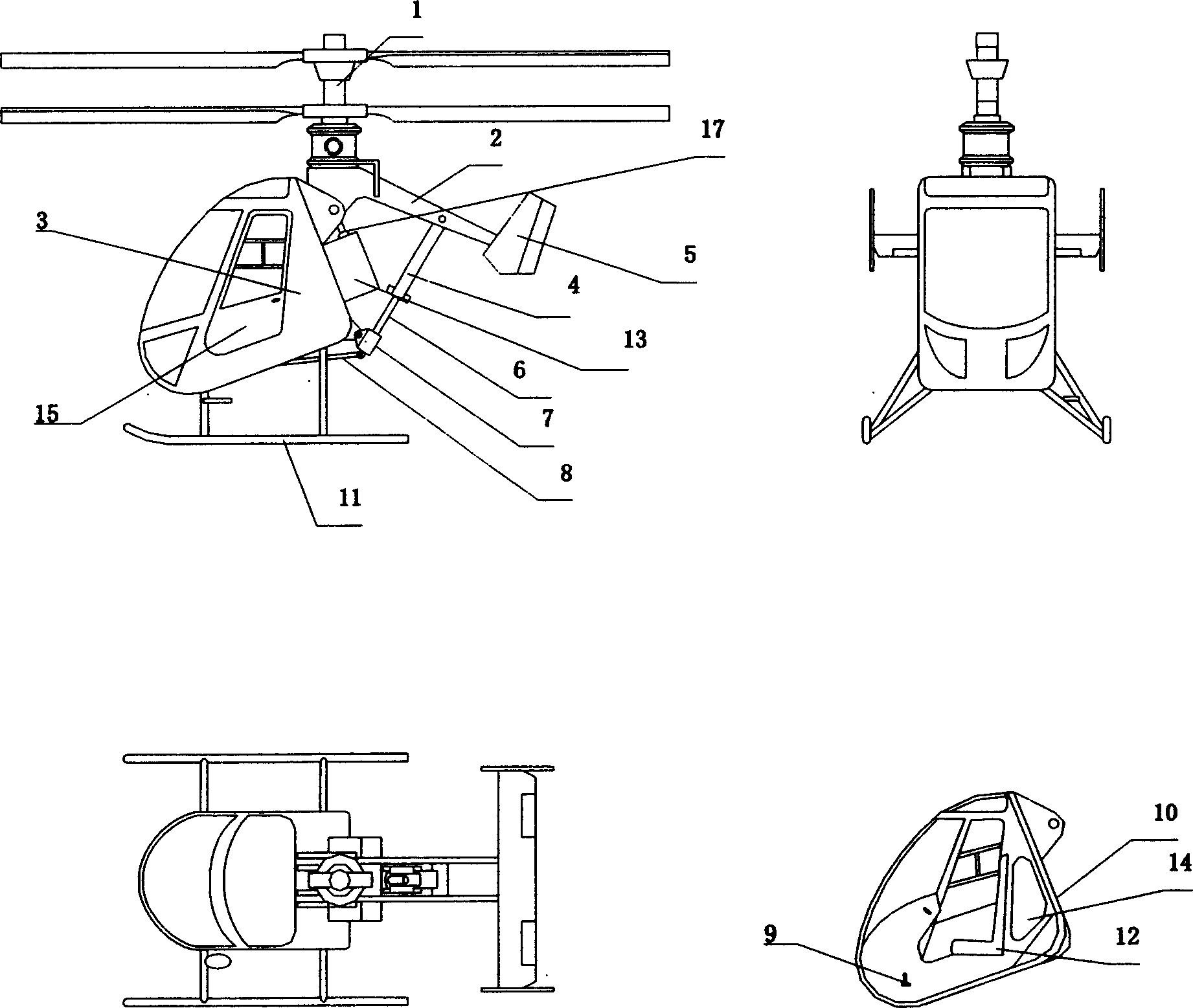
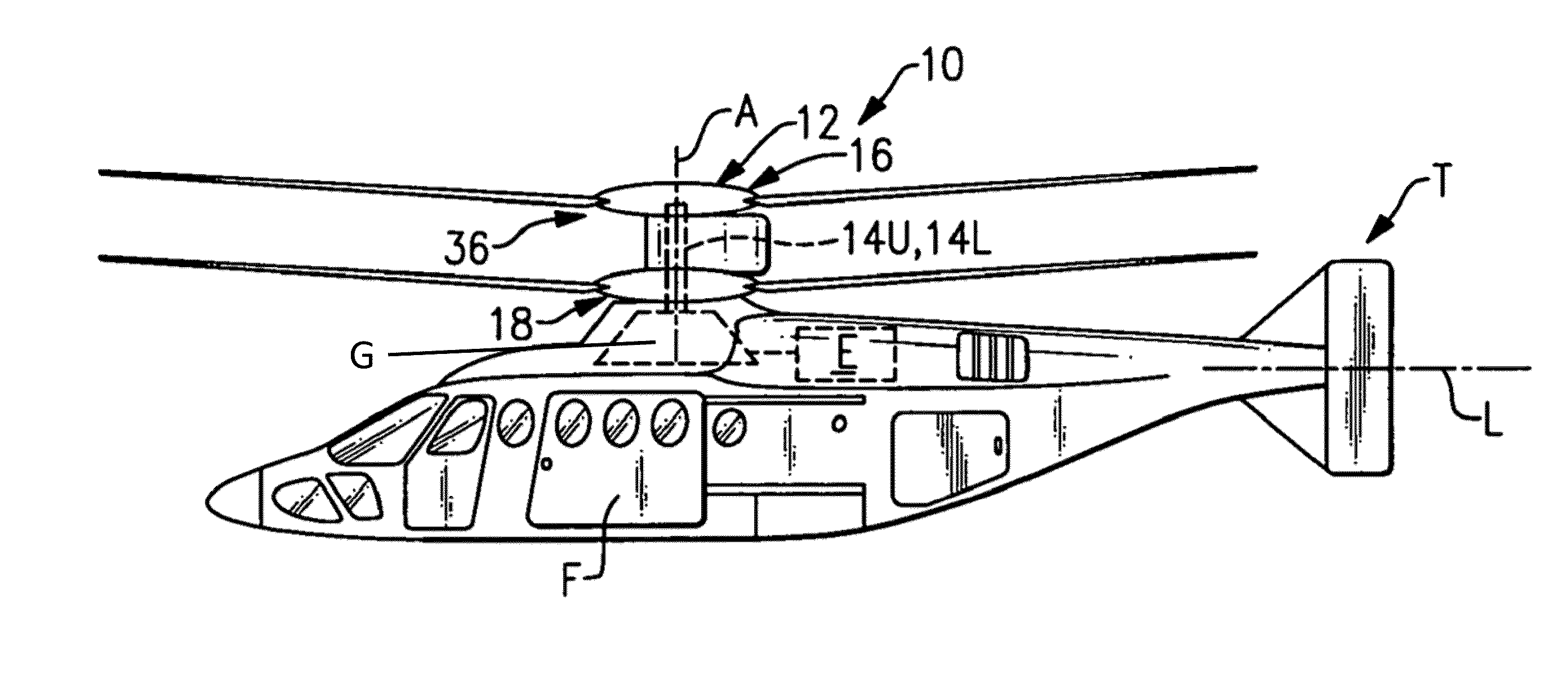
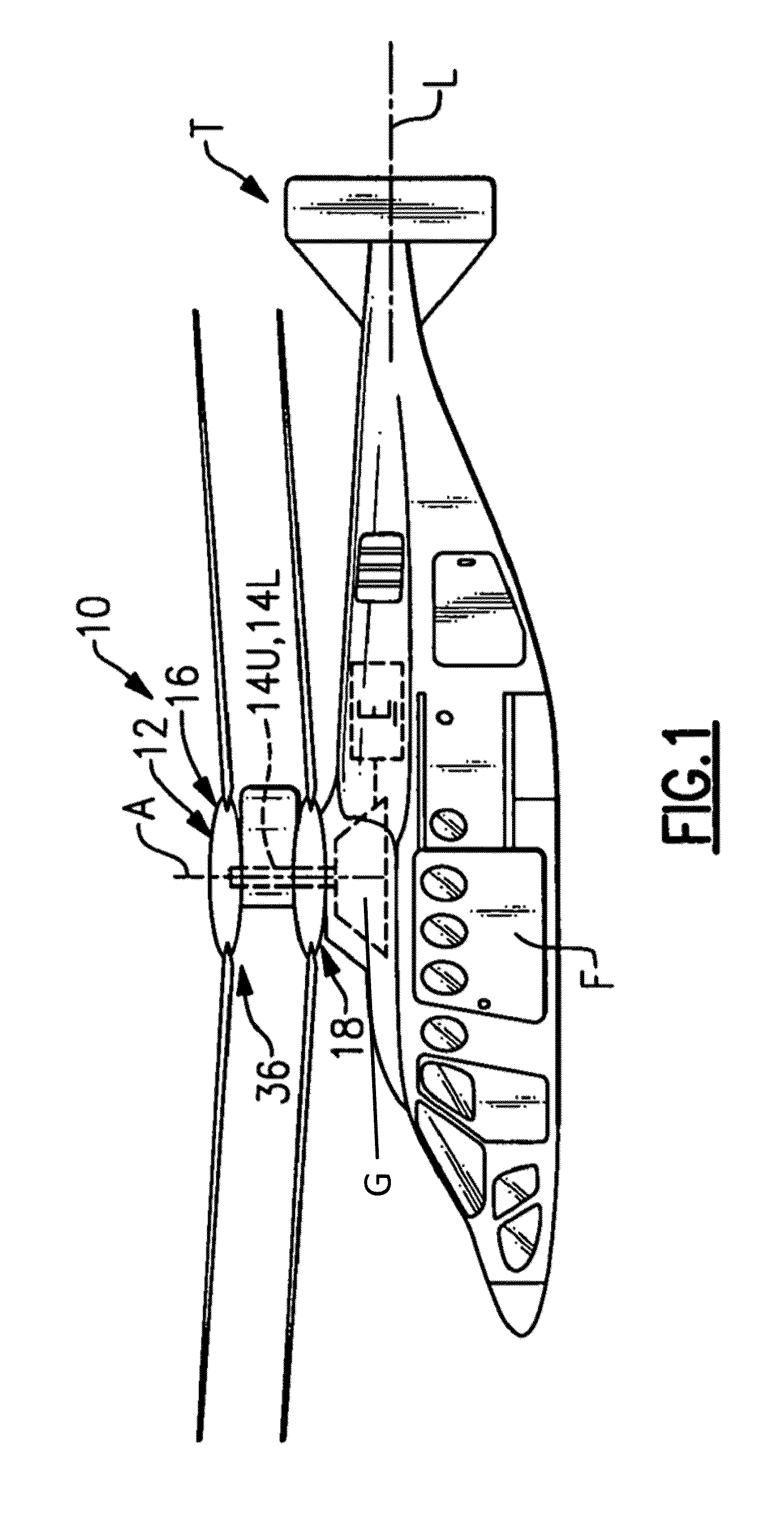
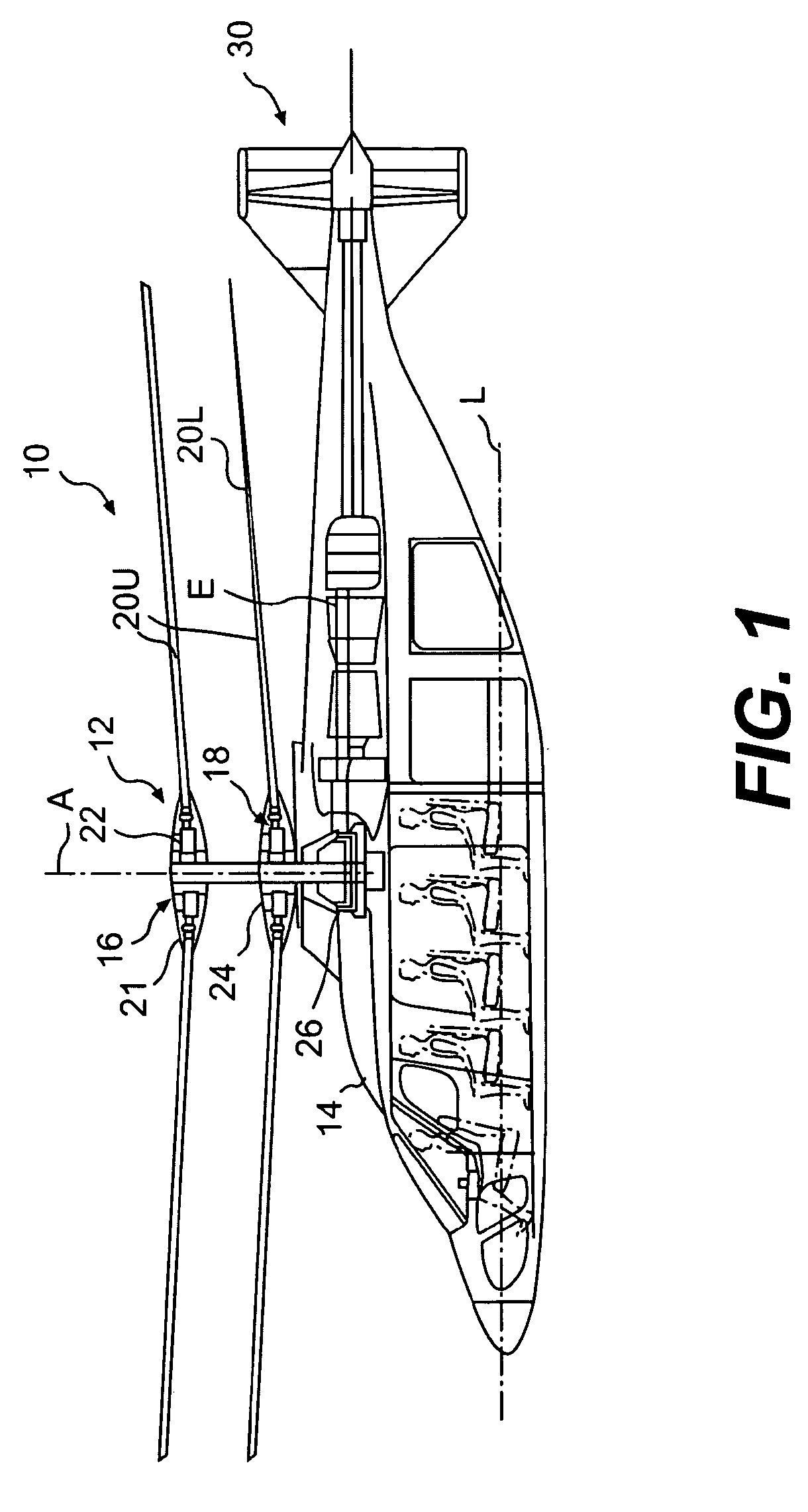
Coaxial rotors or "coax rotors" are a pair of helicopter rotors mounted one above the other on concentric shafts, with the same axis of rotation, but turning in opposite directions (contra-rotating). This tiltrotor configuration is a feature of helicopters produced by the Russia Kamov helicopter design bureau.
Coaxial helicopter
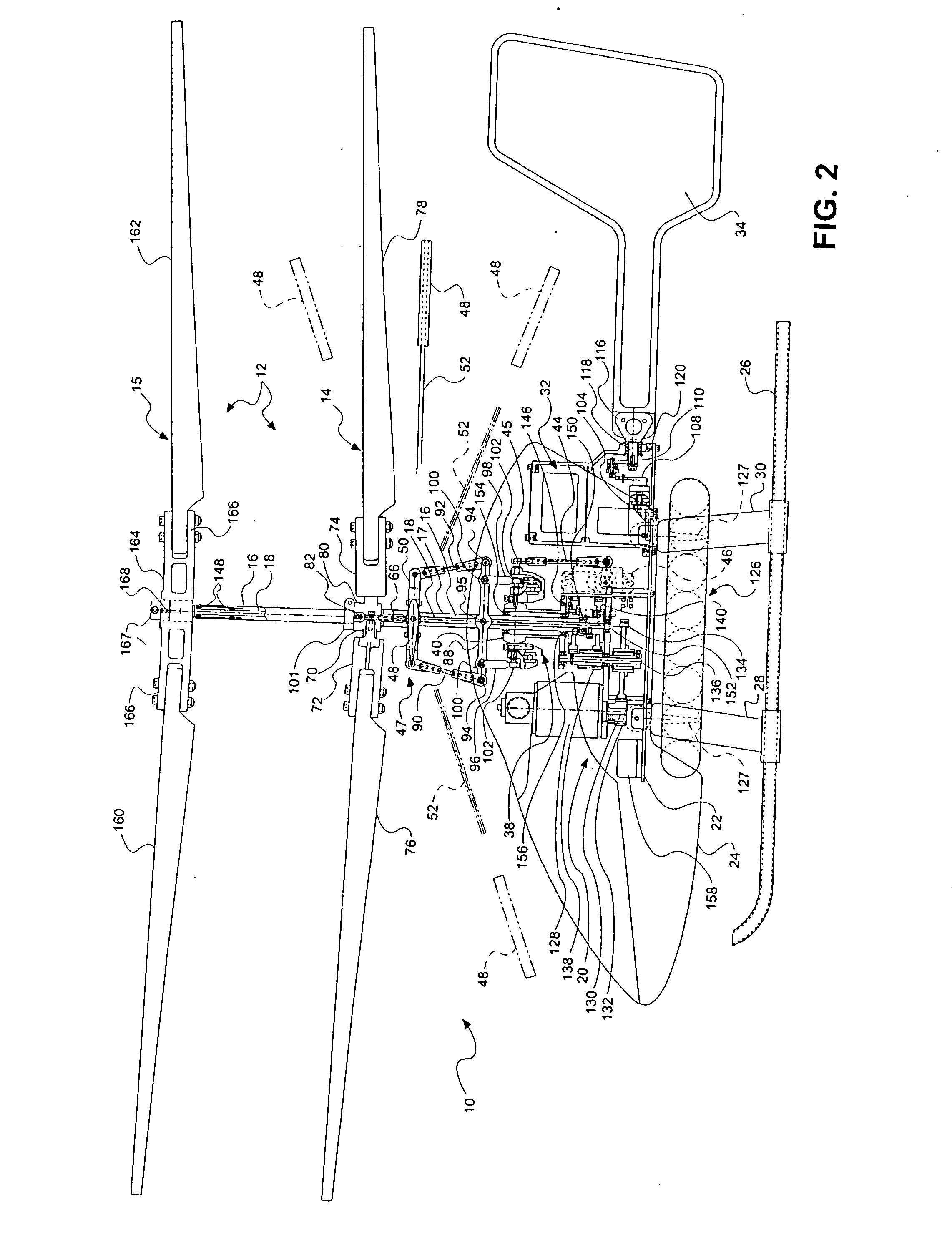
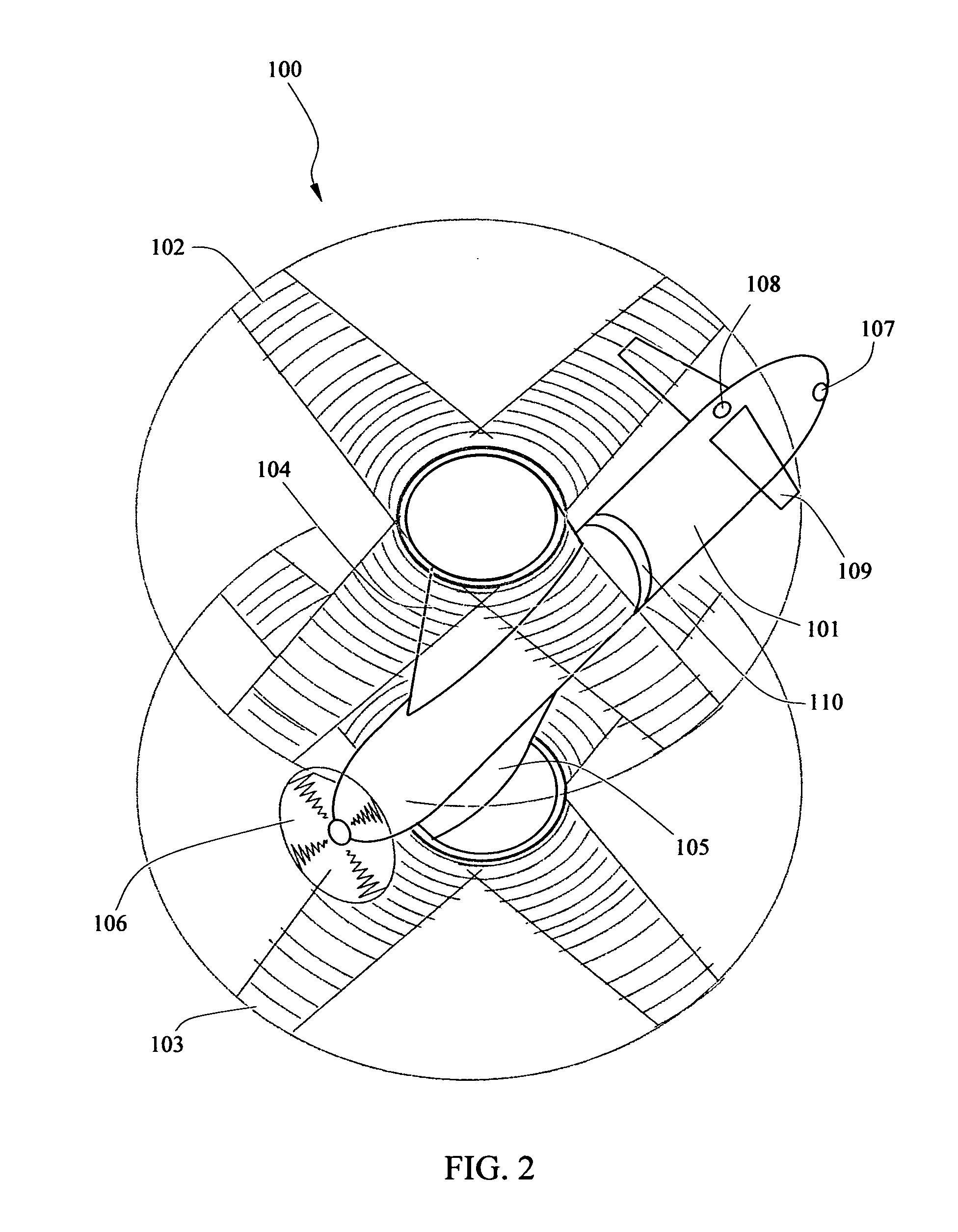
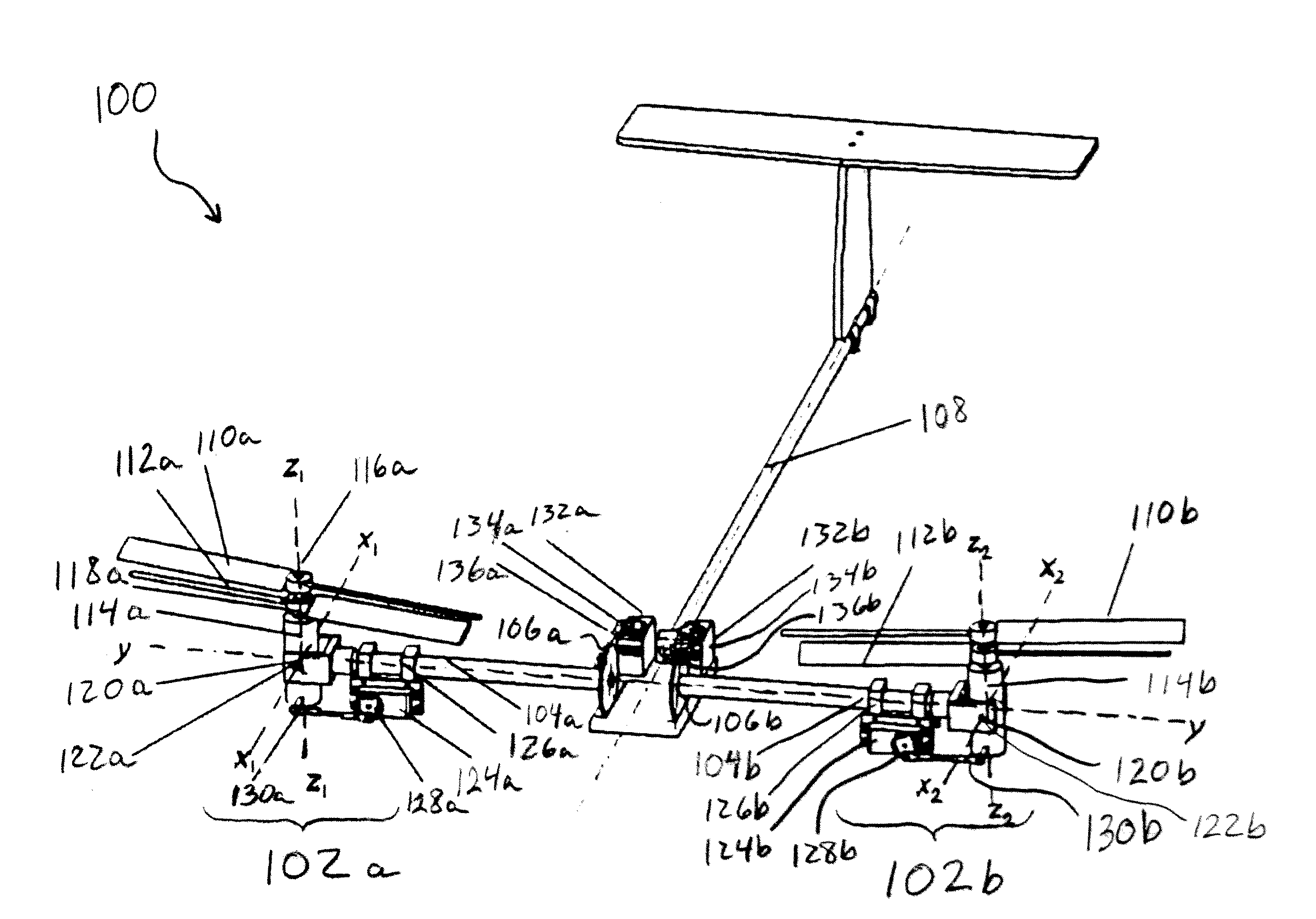
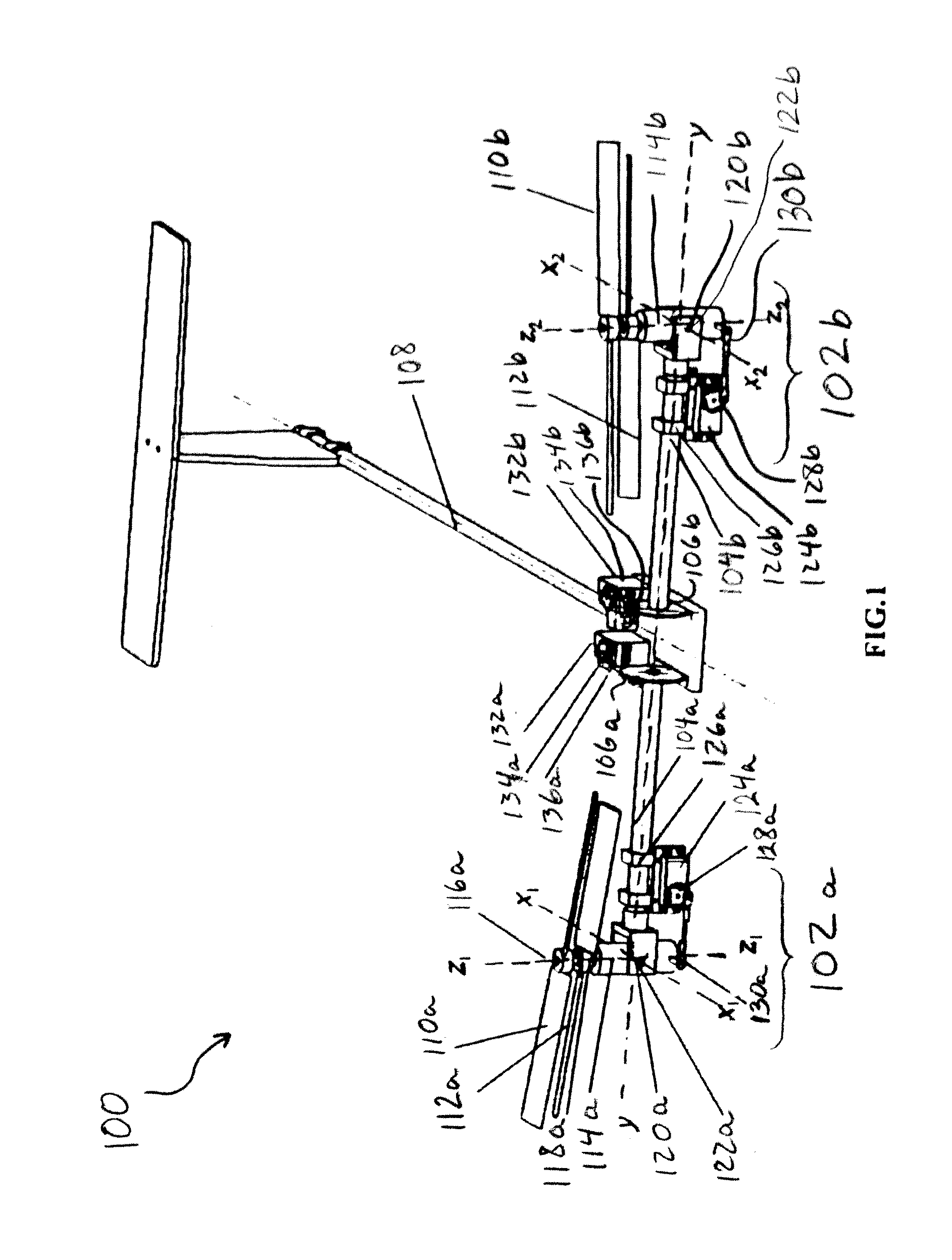
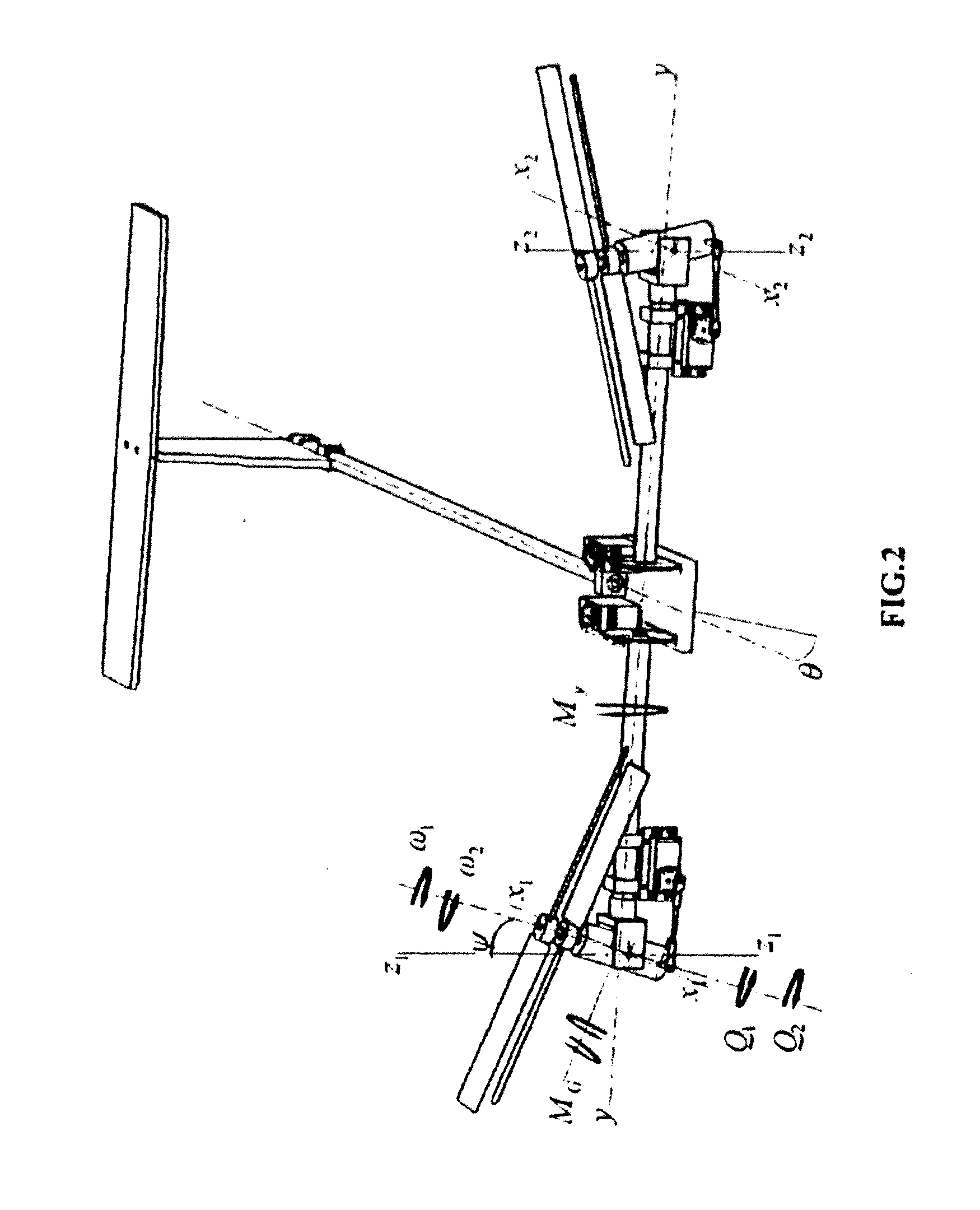
A coaxial helicopter, comprising a first rotor carried by a first shaft and a second rotor carried by a second shaft; wherein one of the first and second rotors has cyclic pitch control and the other rotor does not have cyclic pitch control, at least pitch and roll control being implemented by cyclic blade pitch control of only one rotor of the coaxial rotor set. Provisions for yaw control can include differential collective control of the first and second rotors, providing yaw paddles and / or a tail rotor, ducted fan, or an air jet configured for yawing the coaxial helicopter.
Owner:AEROTWIN MOTORS
Helicopter vibration control system and rotary force generator for canceling vibrations
ActiveUS20060083617A1Reduce periodic vibrationInertia force compensationPropellersVibration controlControl system
A helicopter rotating hub mounted vibration control system for a helicopter rotary wing hub having a periodic vibration while rotating at a helicopter operational rotation frequency. The helicopter rotating hub mounted vibration control system includes an annular ring rotary housing attachable to the helicopter rotary wing hub and rotating with the helicopter rotary wing hub at the helicopter operational rotation frequency. The annular ring housing is centered about the rotary wing hub axis of rotation and has an electronics housing cavity subsystem and preferably an adjacent coaxial rotor housing cavity subsystem. The rotor housing cavity subsystem contains a first coaxial frameless AC ring motor having a first rotor with a first imbalance mass and a second coaxial frameless AC ring motor having a second rotor with a second imbalance mass. The electronics housing cavity subsystem contains an electronics control system which receives sensor outputs and electrically controls and drives the first coaxial frameless AC ring motor and the second coaxial frameless AC ring motor such that the first imbalance mass and the second imbalance mass are directly driven at a vibration canceling rotation frequency greater than the helicopter operational rotation frequency wherein the helicopter rotary wing hub periodic vibration is reduced.
Owner:LORD CORP
Coaxial rotorcraft control system
A control system for a coaxial rotorcraft comprises a coaxial rotor set, further comprising an upper rotor actuated by a first drive shaft and a lower rotor actuated by a second drive shaft, the lower rotor having a direction of rotation counter to a direction of rotation of the upper rotor. A collective blade pitch control is configured to: collectively control pitch of only one of the upper rotor and the lower rotor and not another of the upper rotor and the lower rotor; and create an unbalanced torque force which acts on the rotorcraft and which enables a yaw attitude control input through said collective blade pitch control.
Owner:AIRSCOOTER CORP
Coaxial rotor aircraft
ActiveUS20090159740A1Easy to flySimplified Control RequirementsDepending on number of propellersRotocraftCruise speedHorizontal and vertical
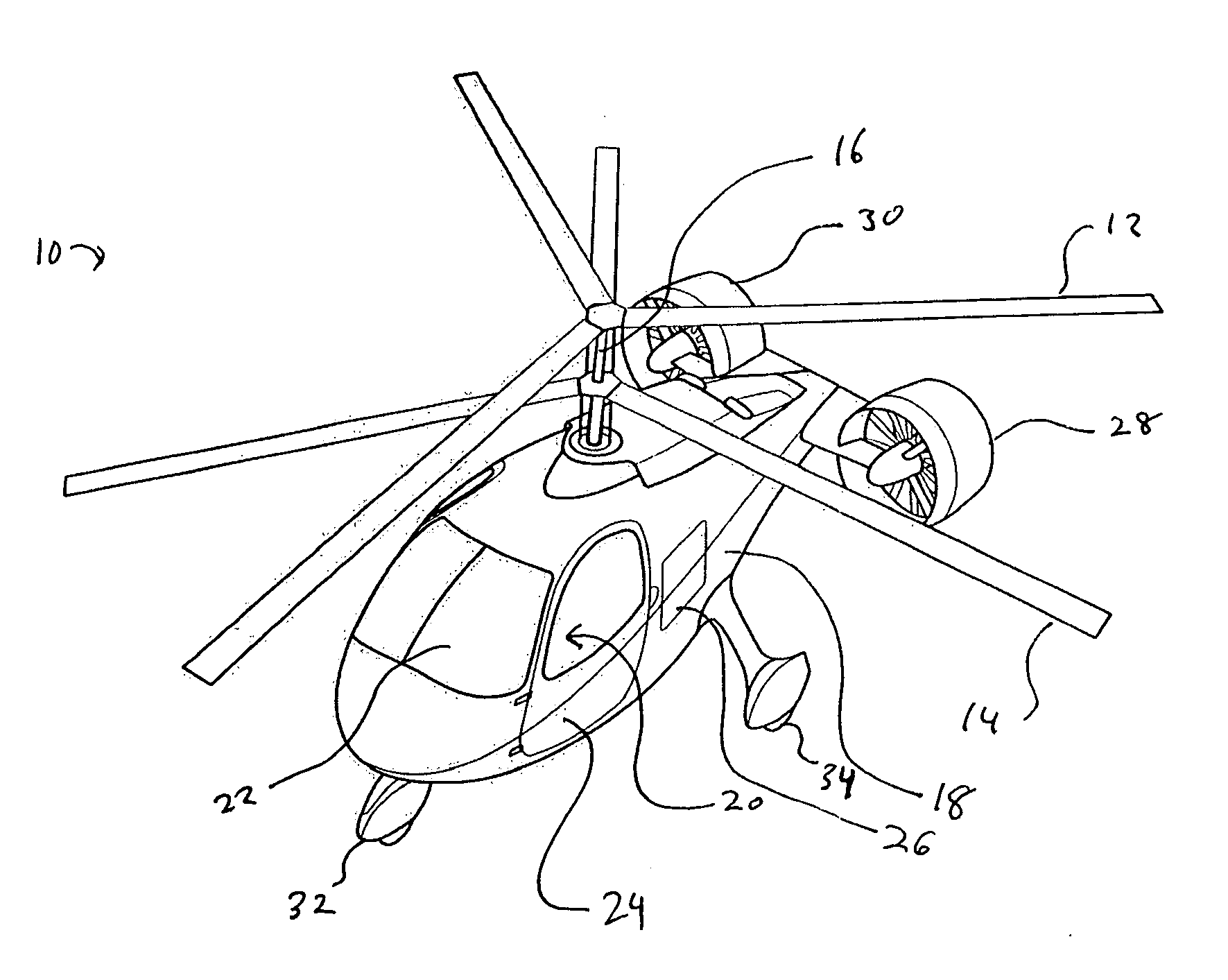
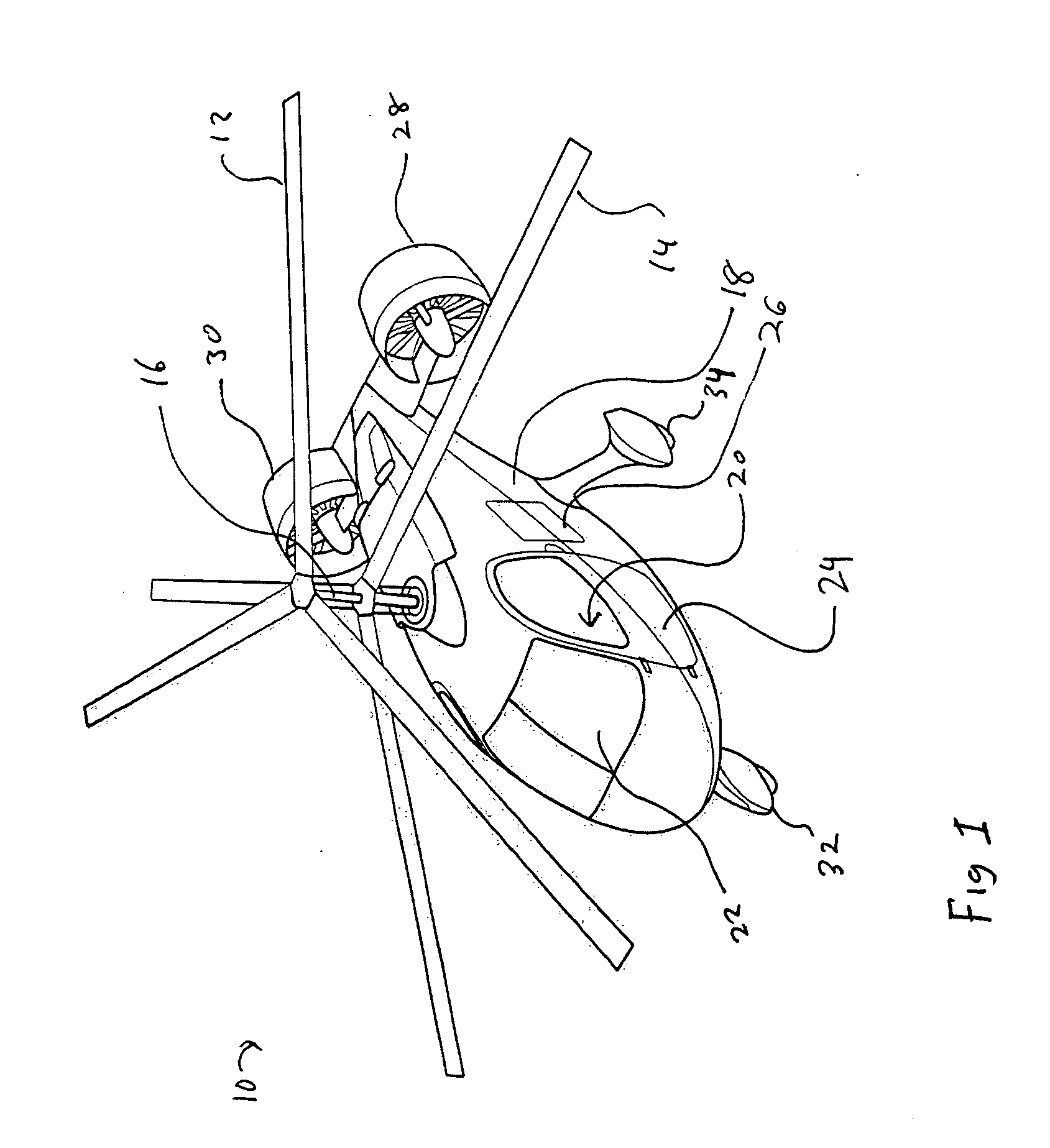
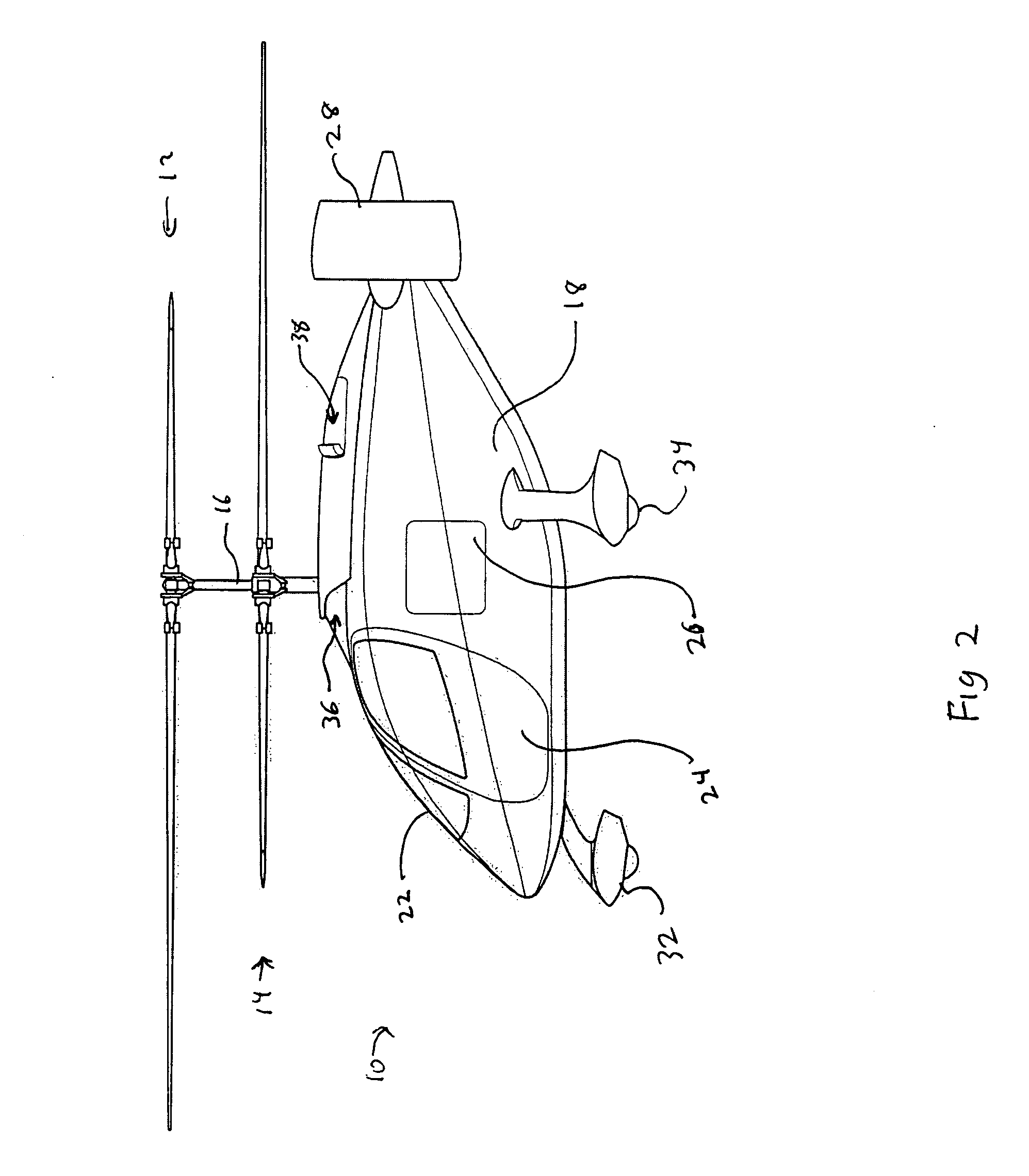
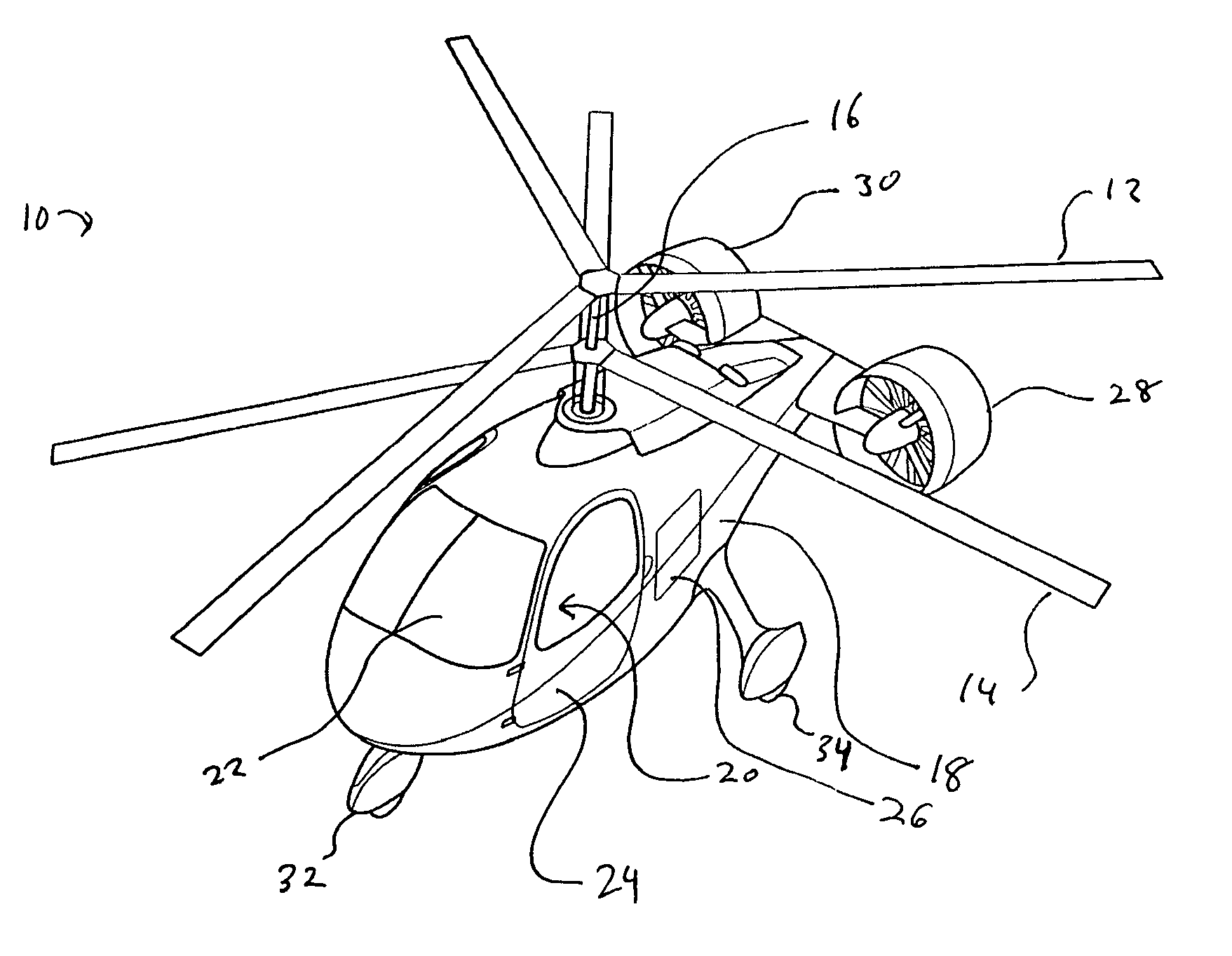
A dual, coaxial rotor helicopter is provided that is relatively easy to fly. Thrust is provided by two ducted fans that are mounted at the rear of the aircraft and spaced apart laterally. Differential thrust generated by the fans provides yaw control for the aircraft, and forward thrust is provided by the fans working in combination. The coaxial rotors are preferably utilized primarily for lift, and not for forward thrust, which simplifies the control requirements. The coaxial rotor with ducted fan configuration also results in lower vibratory loads being imposed on the helicopter, thereby increasing its speed capability. The fan ducts serve to protect the fans, augment the fan thrust at low airspeeds, increase the efficiency of the fans at cruise speeds, and provide horizontal and vertical stabilizing surfaces to ensure aircraft flight stability.
Owner:AVX AIRCRAFT
Ultralight coaxial rotor aircraft
InactiveUS20070262197A1Improve directabilityImprove controllabilityActuated personallyMicrolight aircraftsGear wheelFuel tank
An ultralight coaxial dual rotor helicopter having a substantially L shaped frame. Attached to the back of the frame is a vertical shaft engine, and a pair of yaw paddles for controlling yaw of the craft. The drive shaft connects to a belt drive at the top of the frame, which transmits the engine power to a transmission and coaxial drive gear for driving the rotors. Crank actuators are provided for tilting the rotor axis to control the pitch and roll of the craft. A pilot seat and ballast tank are attached to the front of the frame. The ballast tank may be filled with a volume of water to balance the craft for the weight of the pilot. The fuel tank is located behind the pilot seat on the centerline of the helicopter, such that as fuel is used and the weight of fuel in the tank changes, the balance of the craft will not be affected.
Owner:AEROTWIN MOTORS
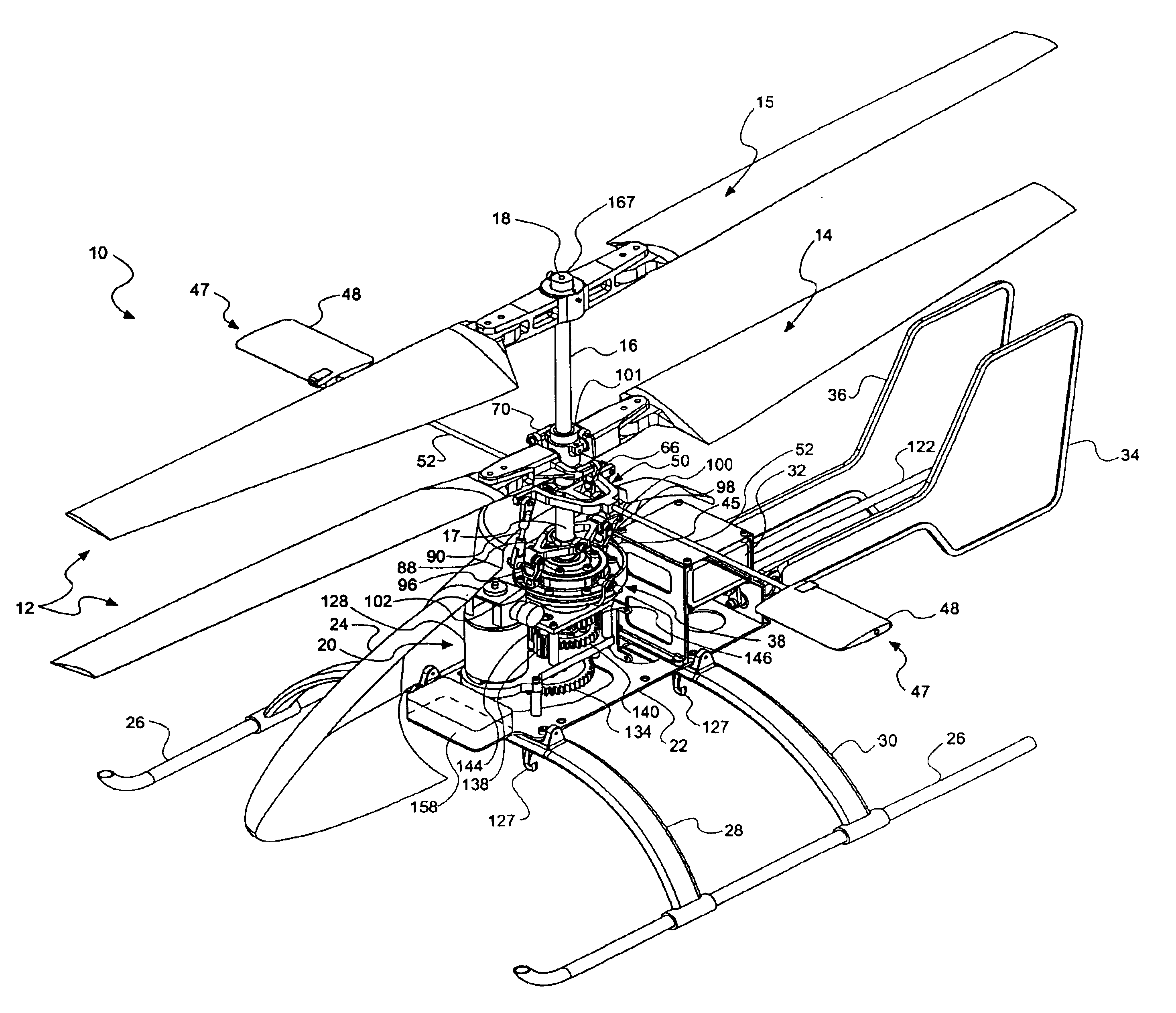
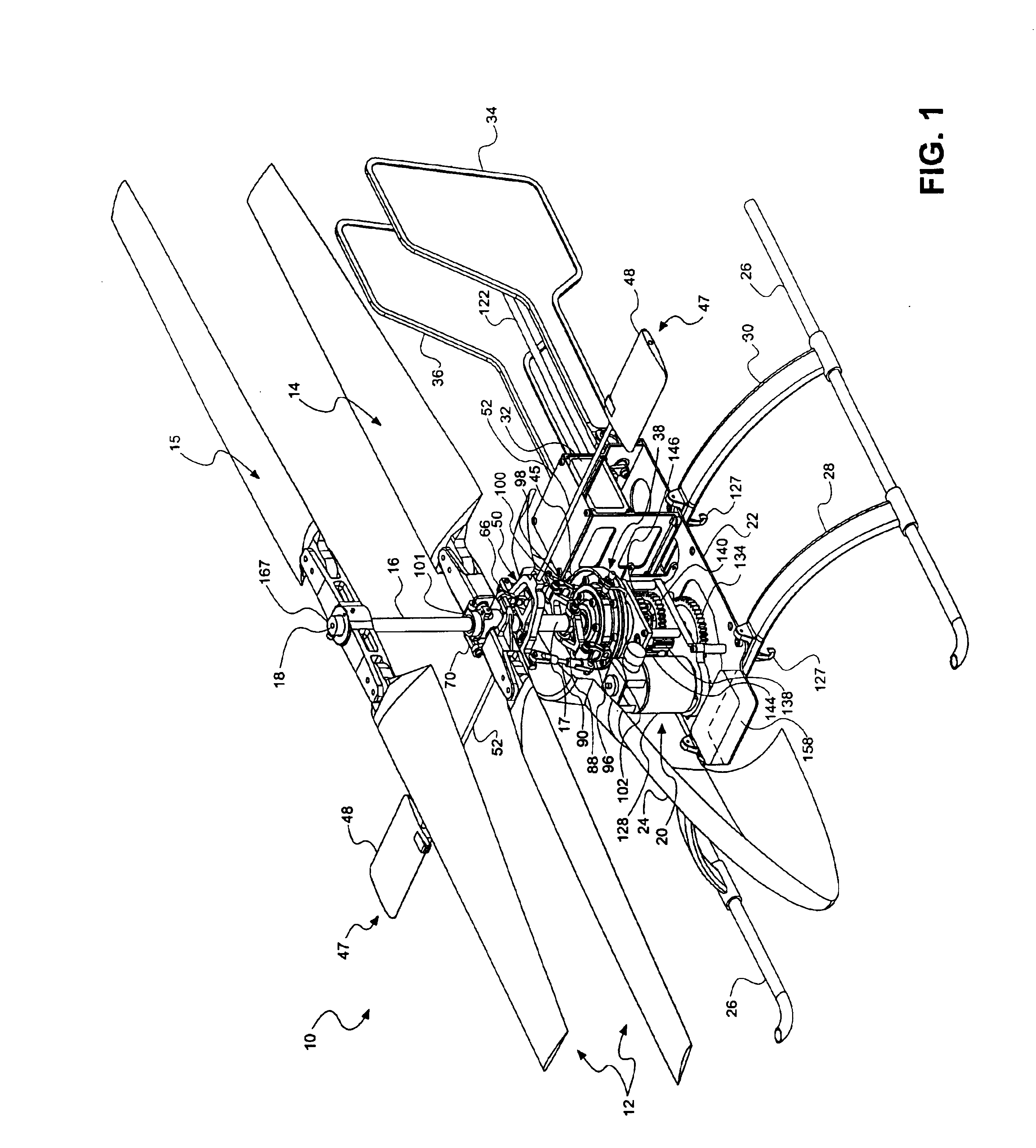
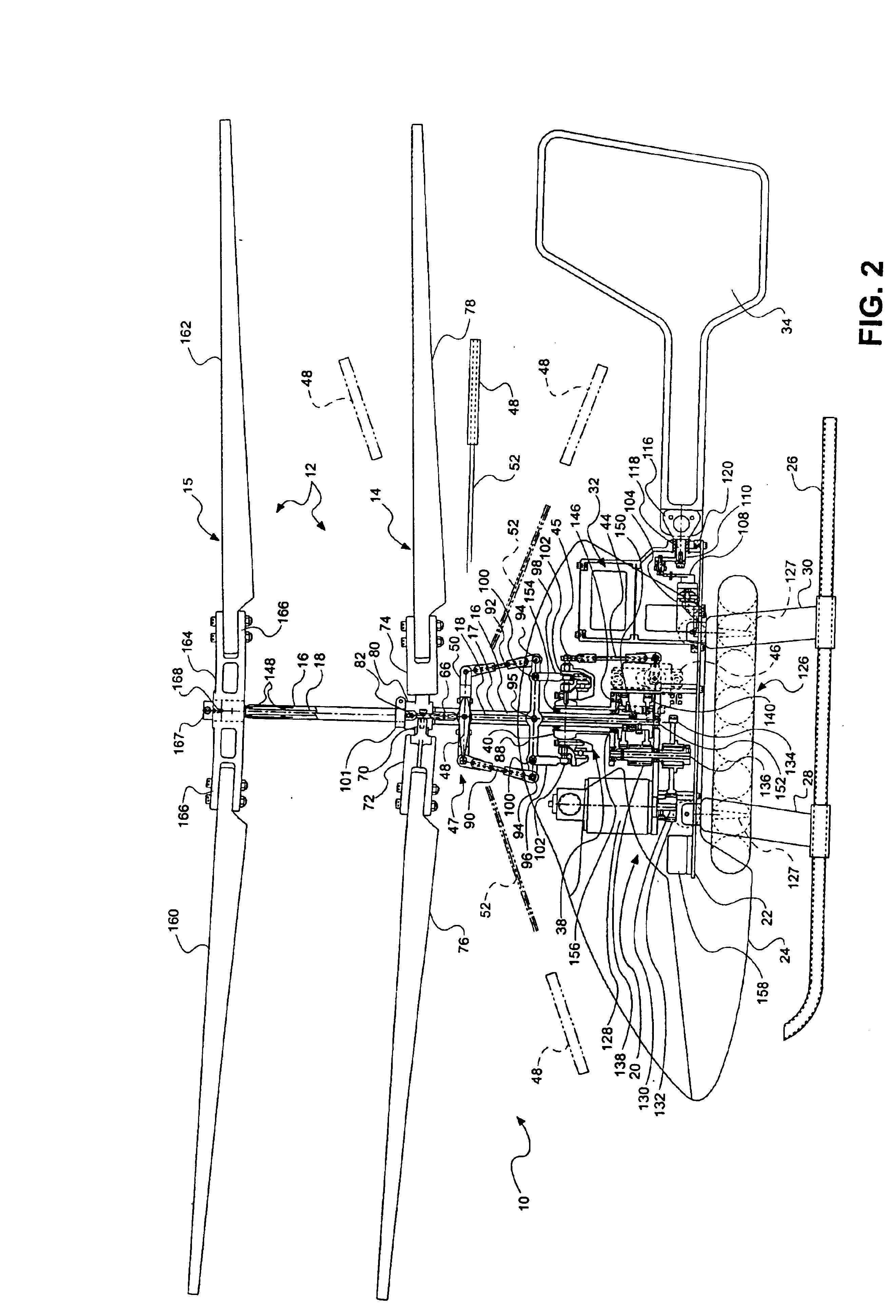
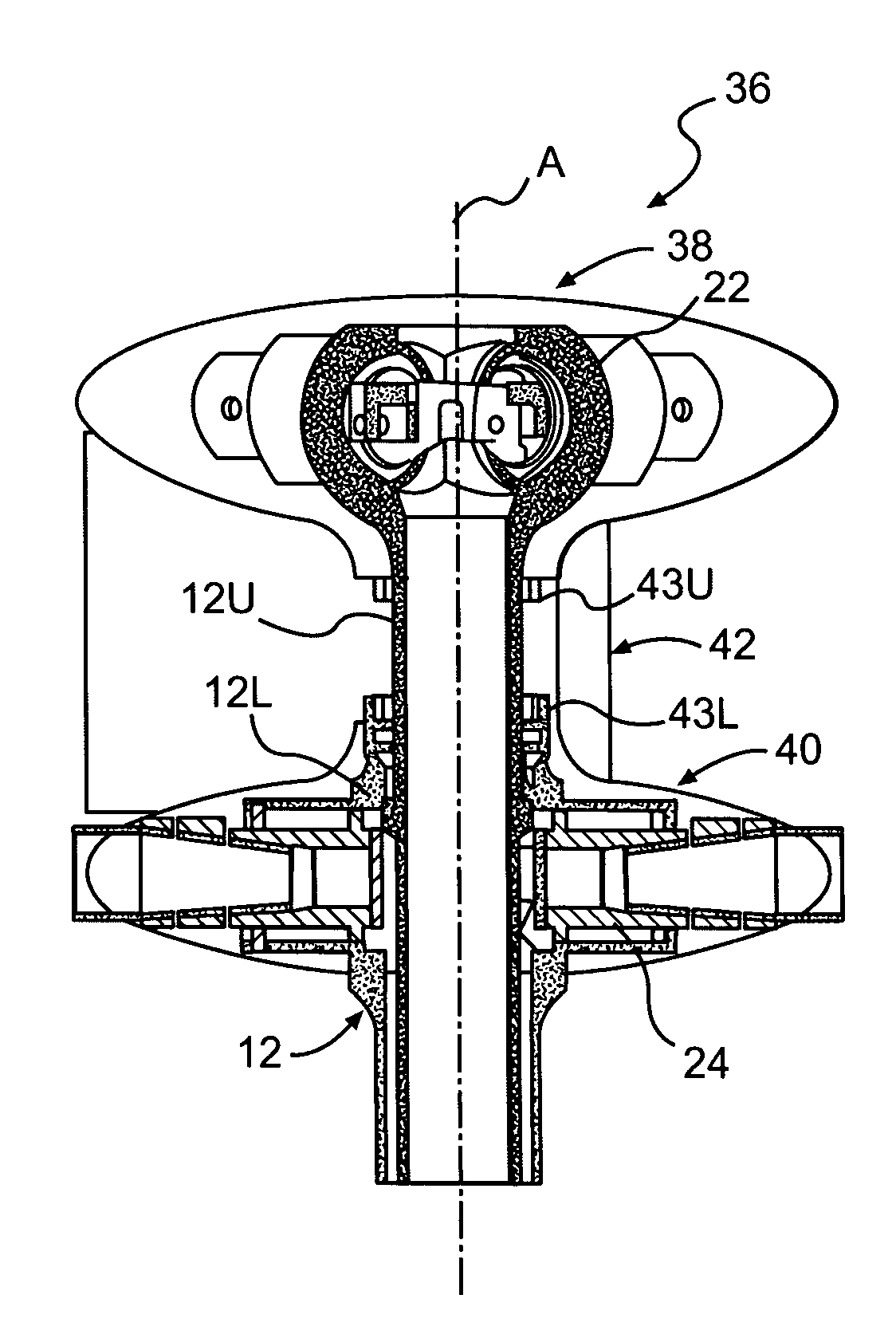
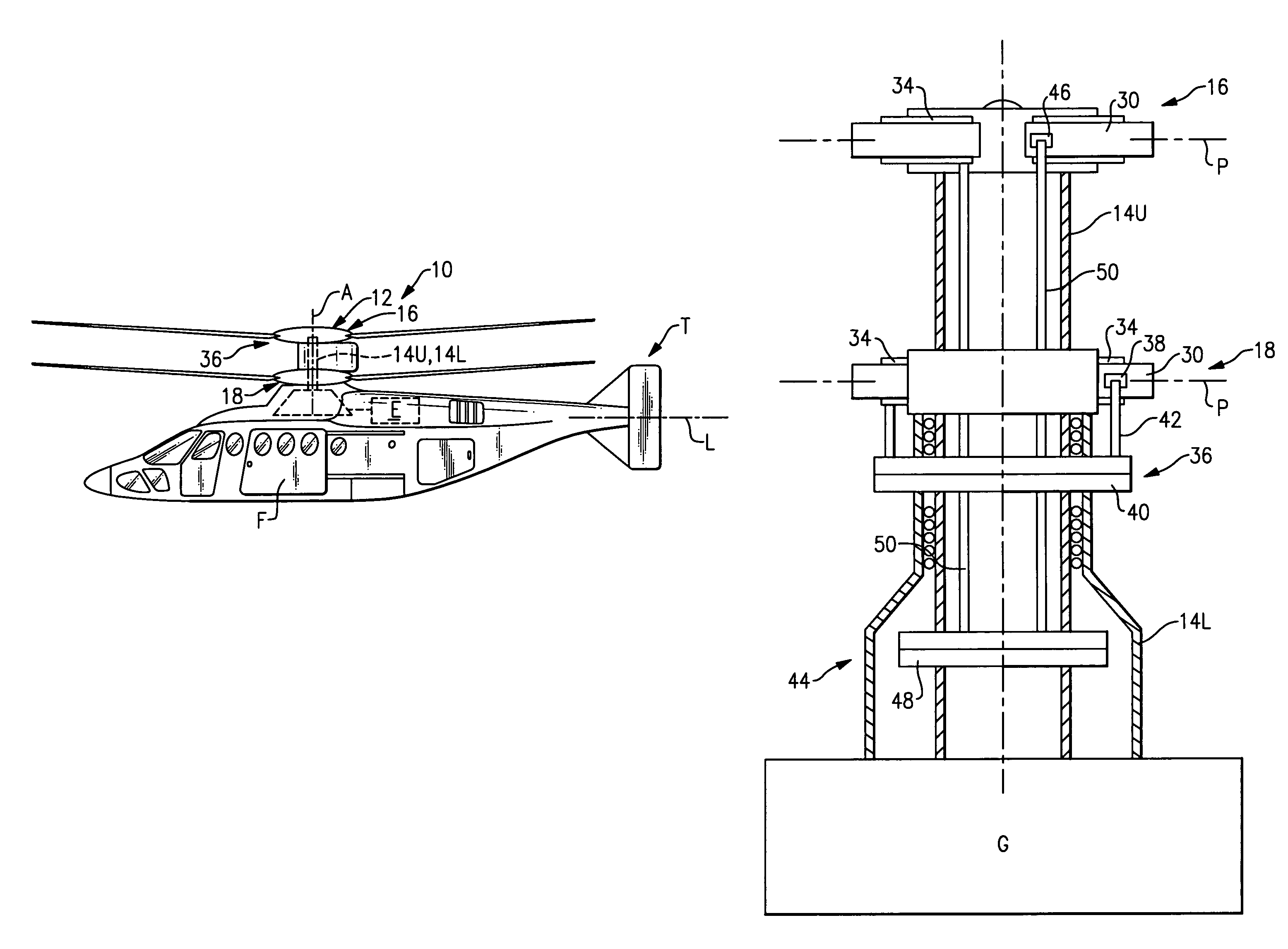
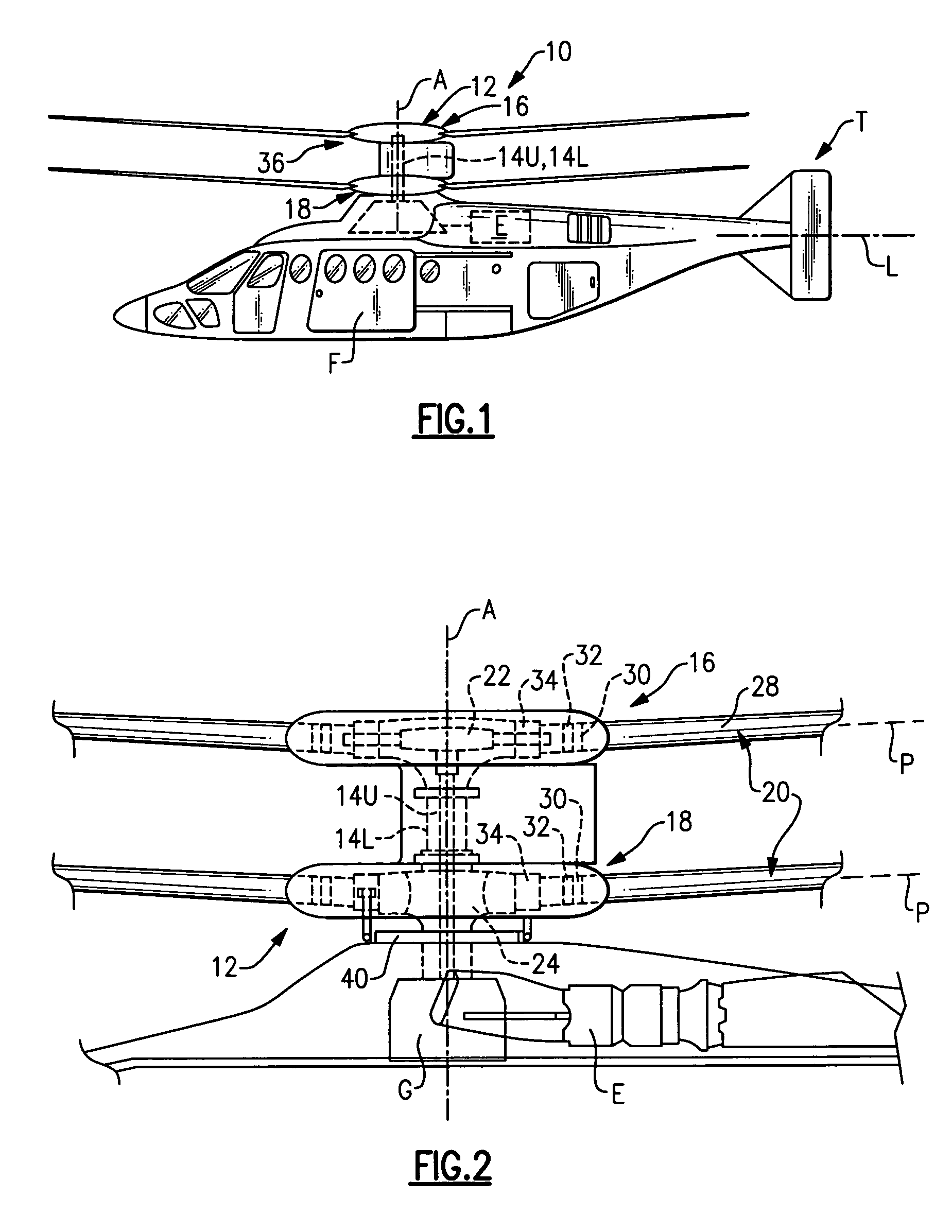
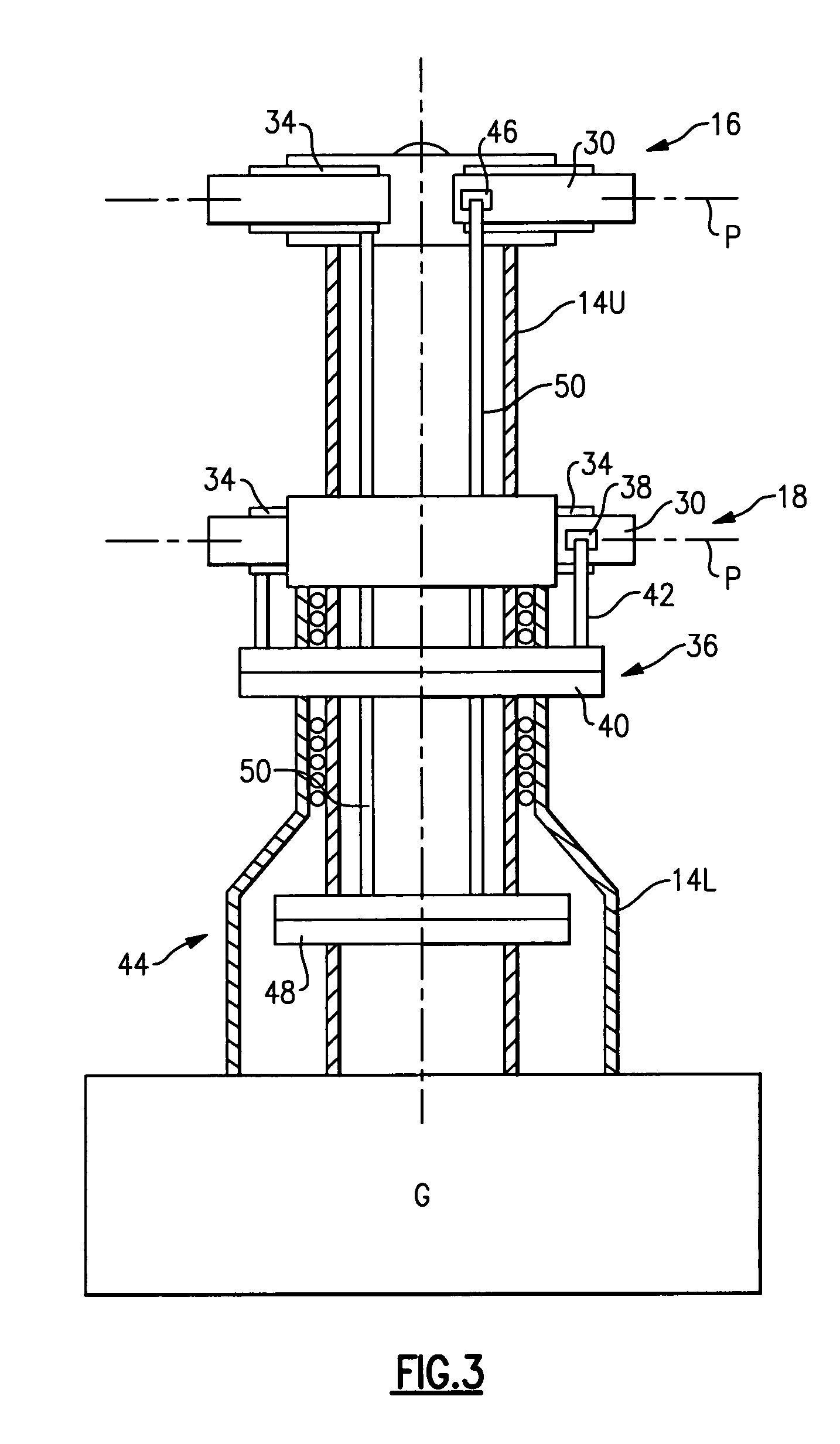
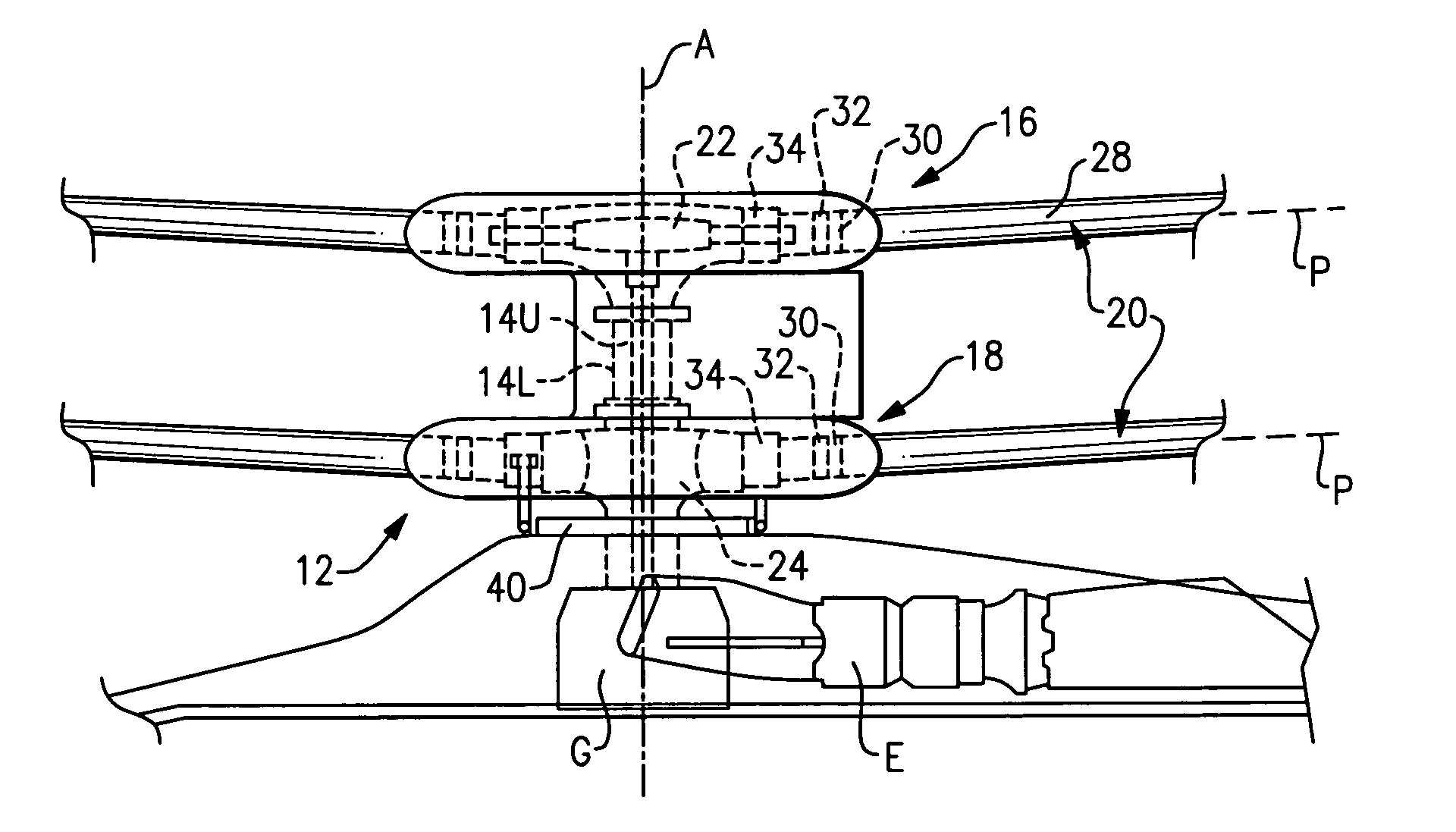
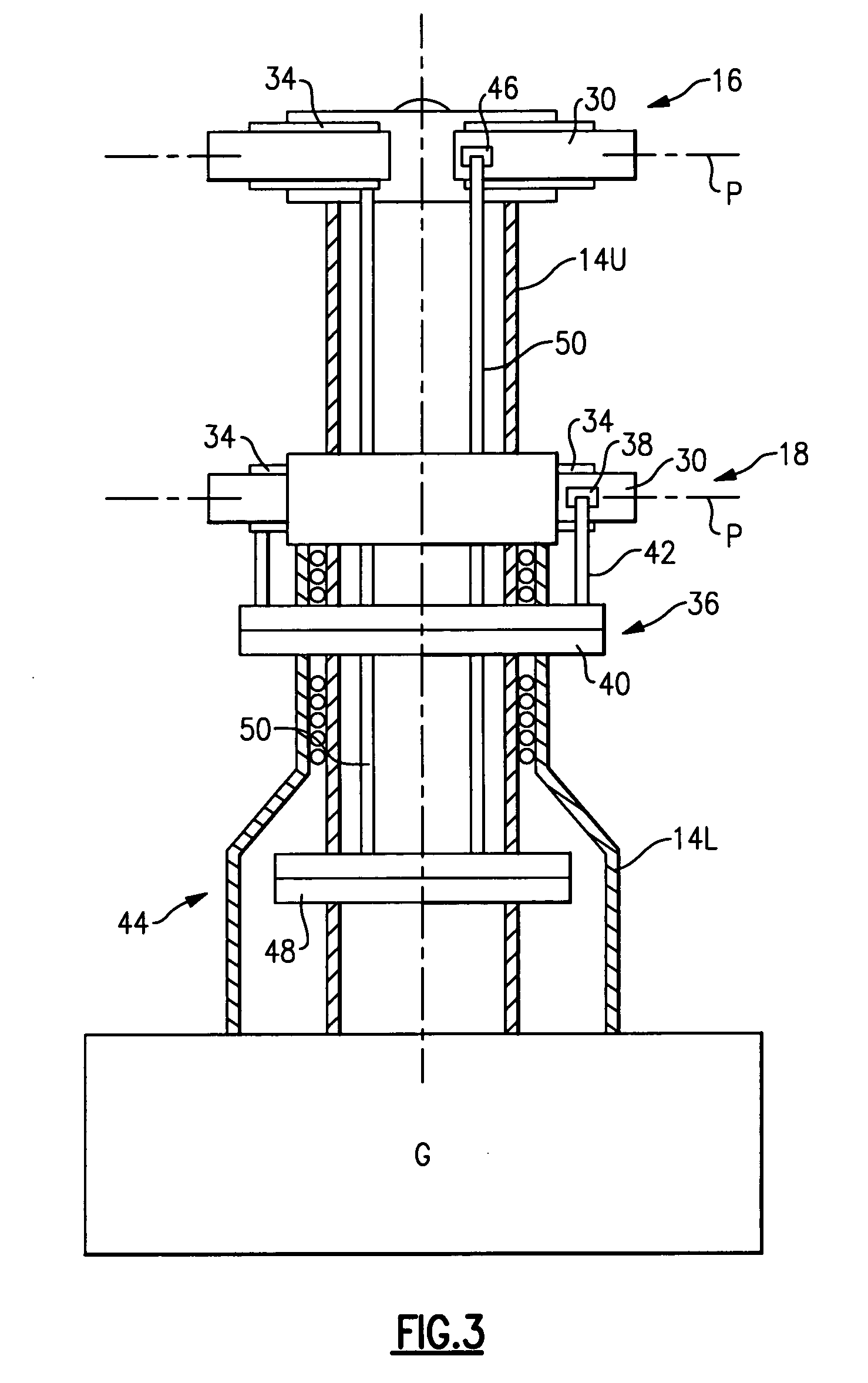
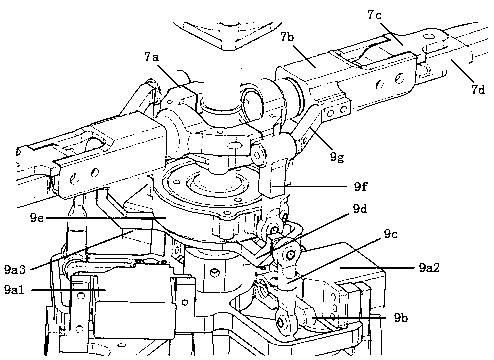
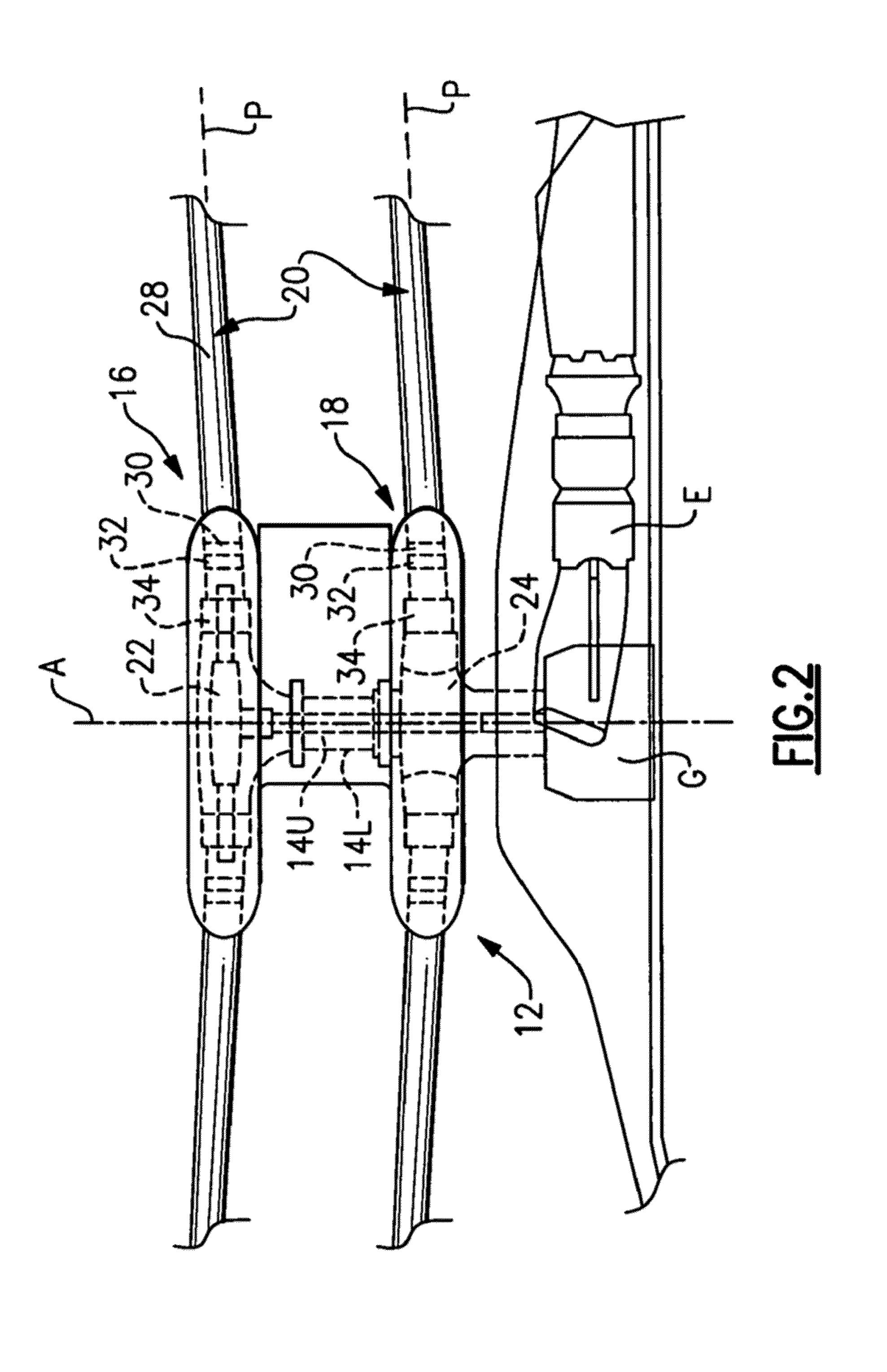
Compact co-axial rotor system for a rotary wing aircraft and a control system thereof
ActiveUS7083142B2Easy to separateReduce the overall heightPropellersPump componentsTip positionControl system
A dual, counter rotating, coaxial rotor system provides an upper and lower rotor system, with a reduced axial rotor separation distance along a common axis by way of rotor tip position sensing and rotor position controls to avoid tip contact.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Compact co-axial rotor system for a rotary wing aircraft and a control system therefor
ActiveUS20050236518A1Easy to separateReduce the overall heightPropellersPump componentsTip positionControl system
A dual, counter rotating, coaxial rotor system provides an upper and lower rotor system, with a reduced axial rotor separation distance along a common axis by means of rotor tip position sensing and rotor position controls to avoid tip contact.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
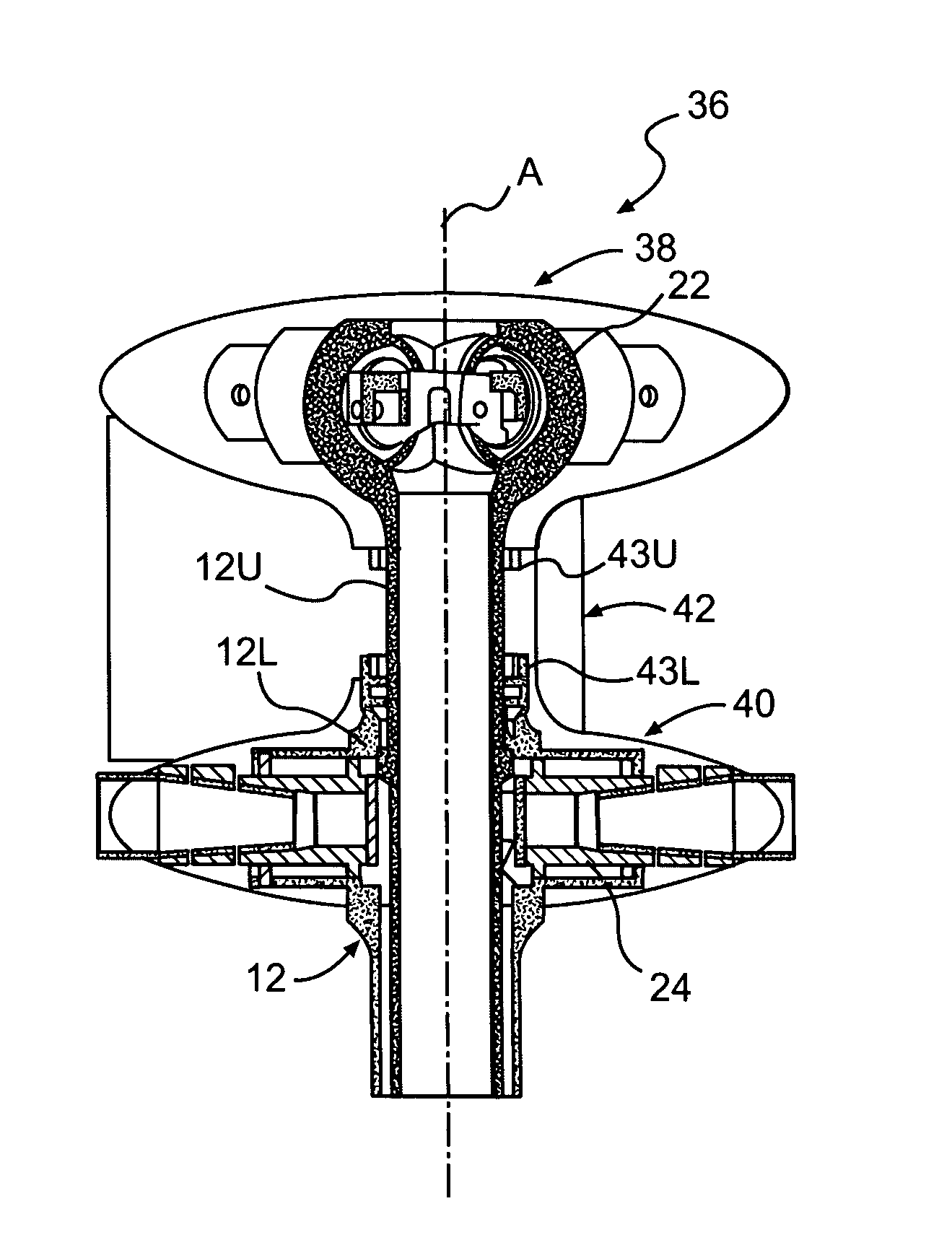
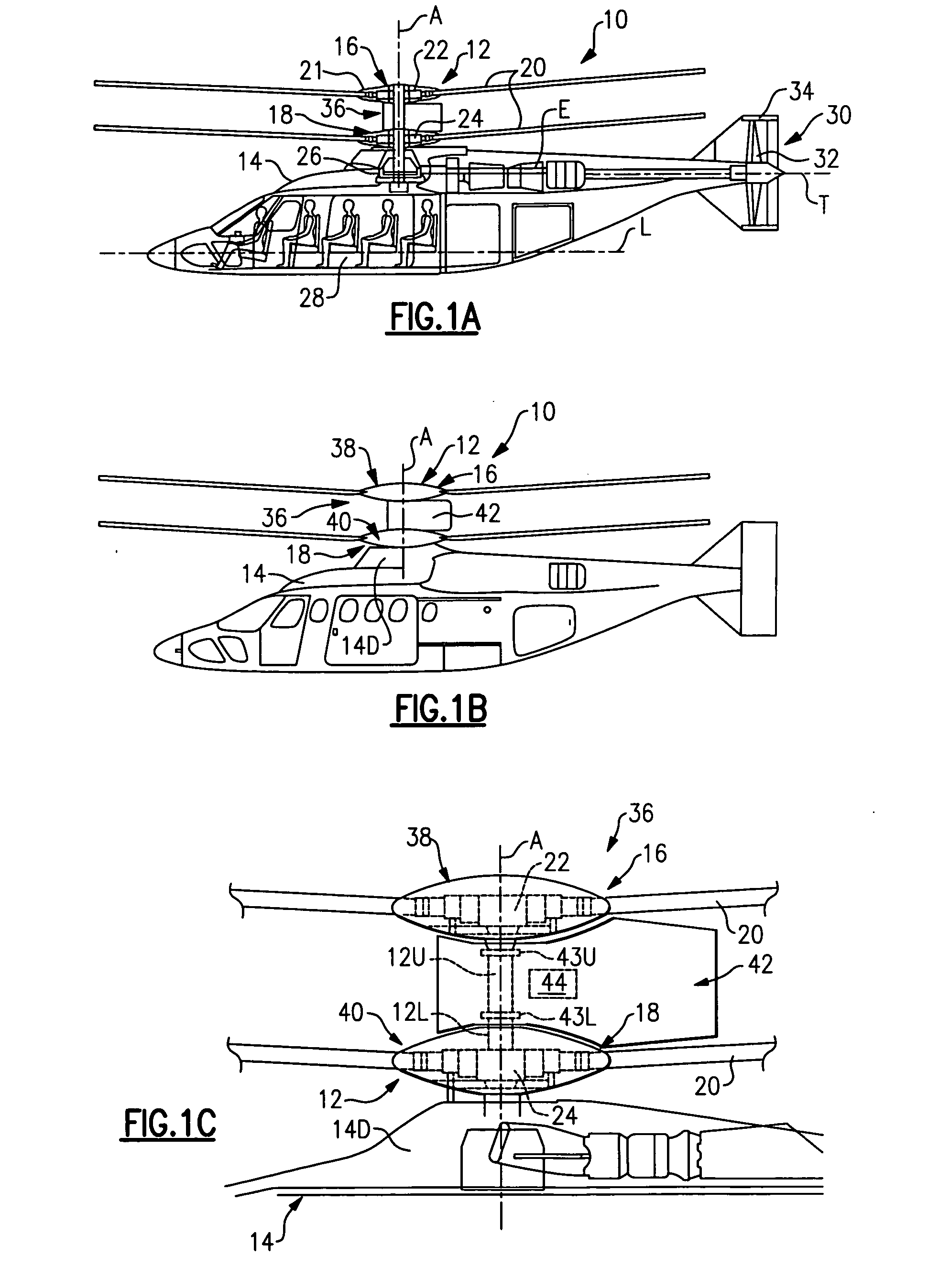
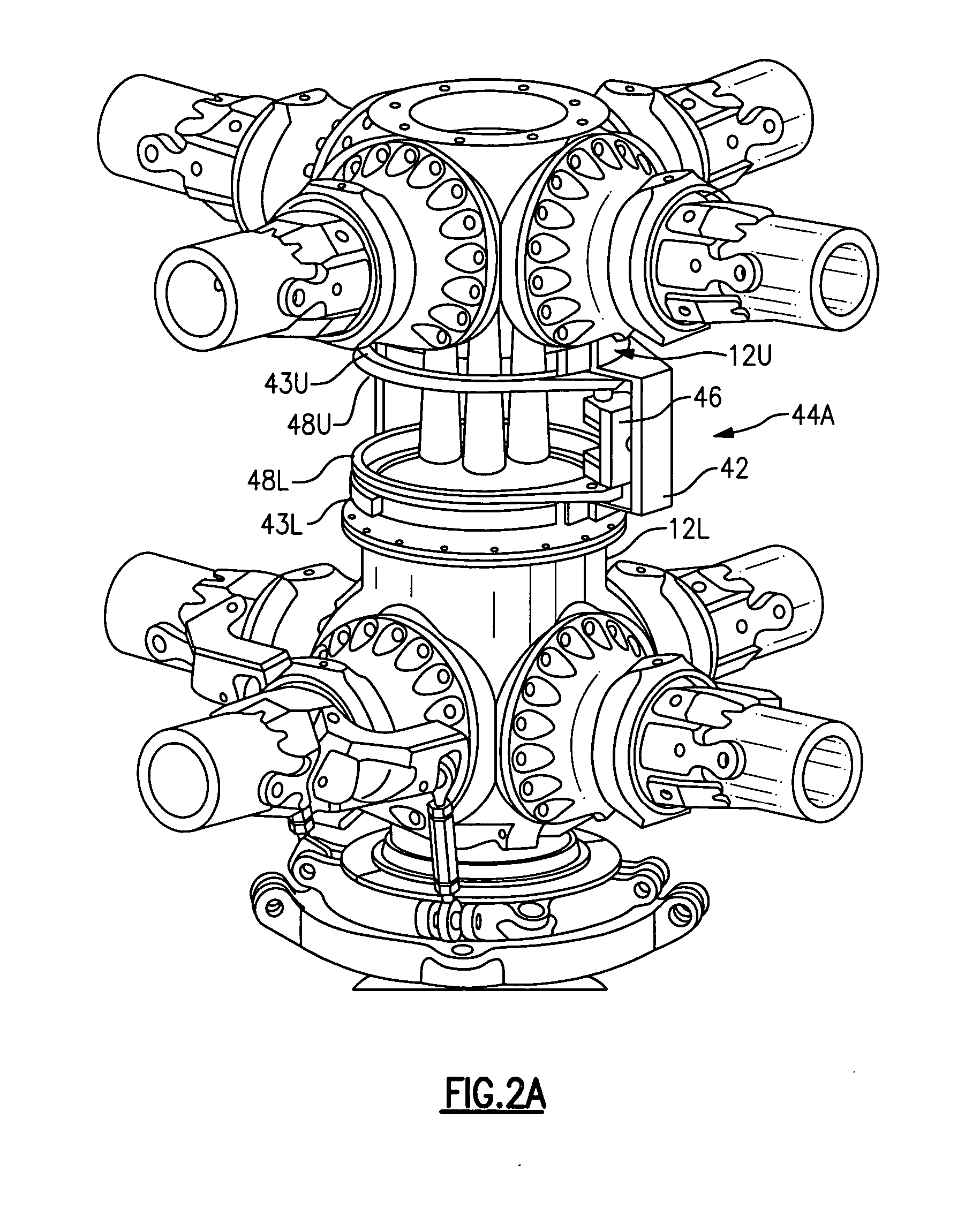
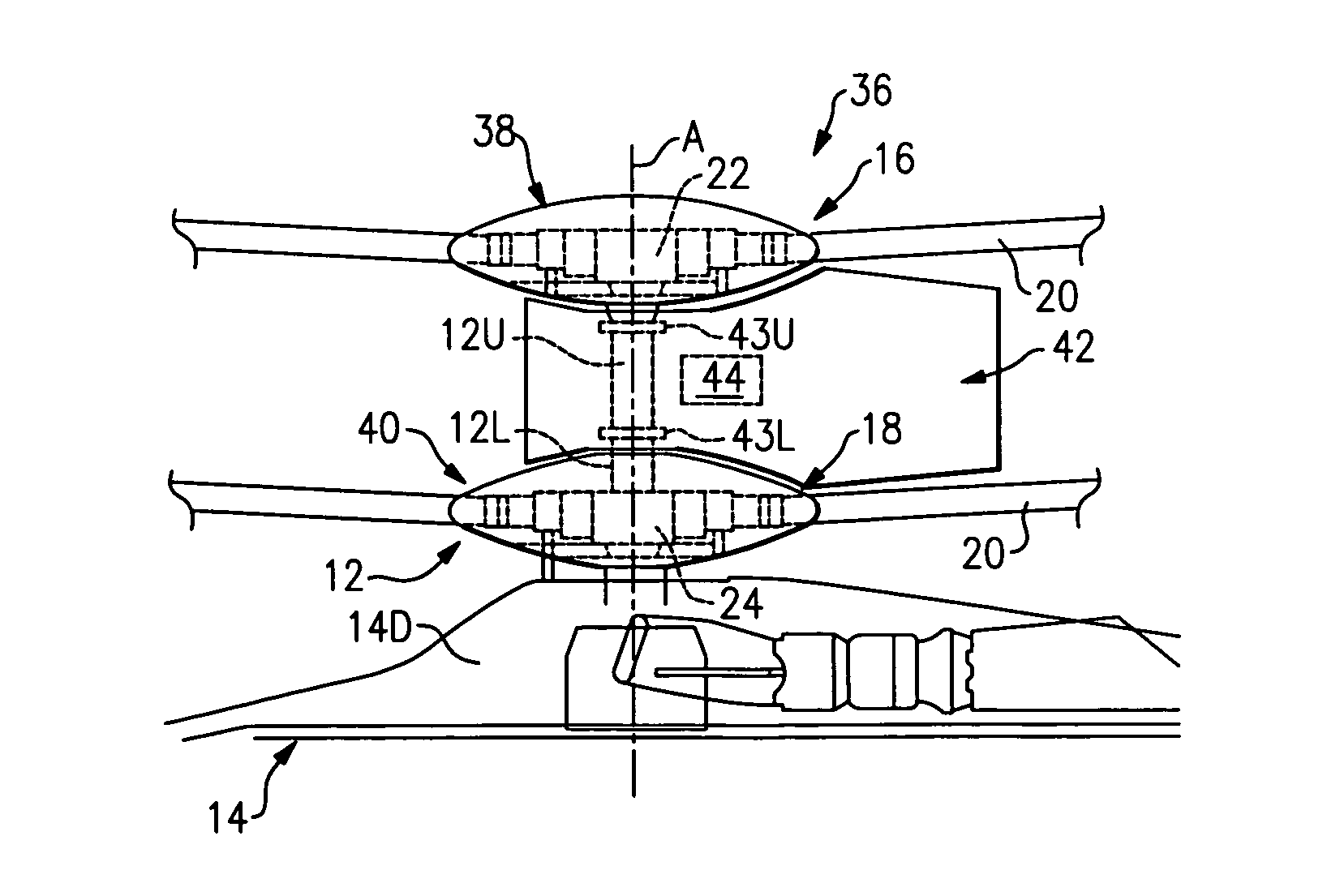
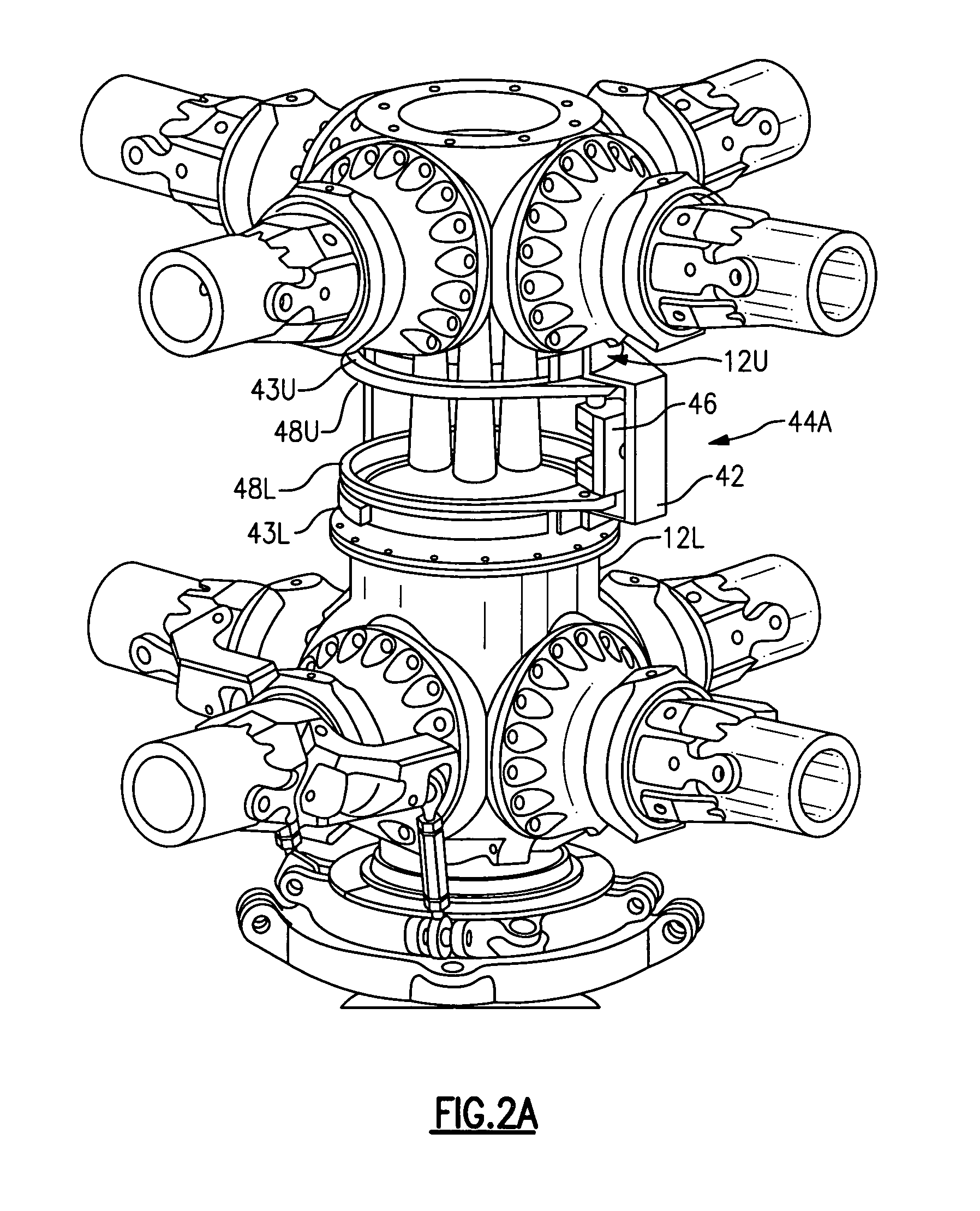
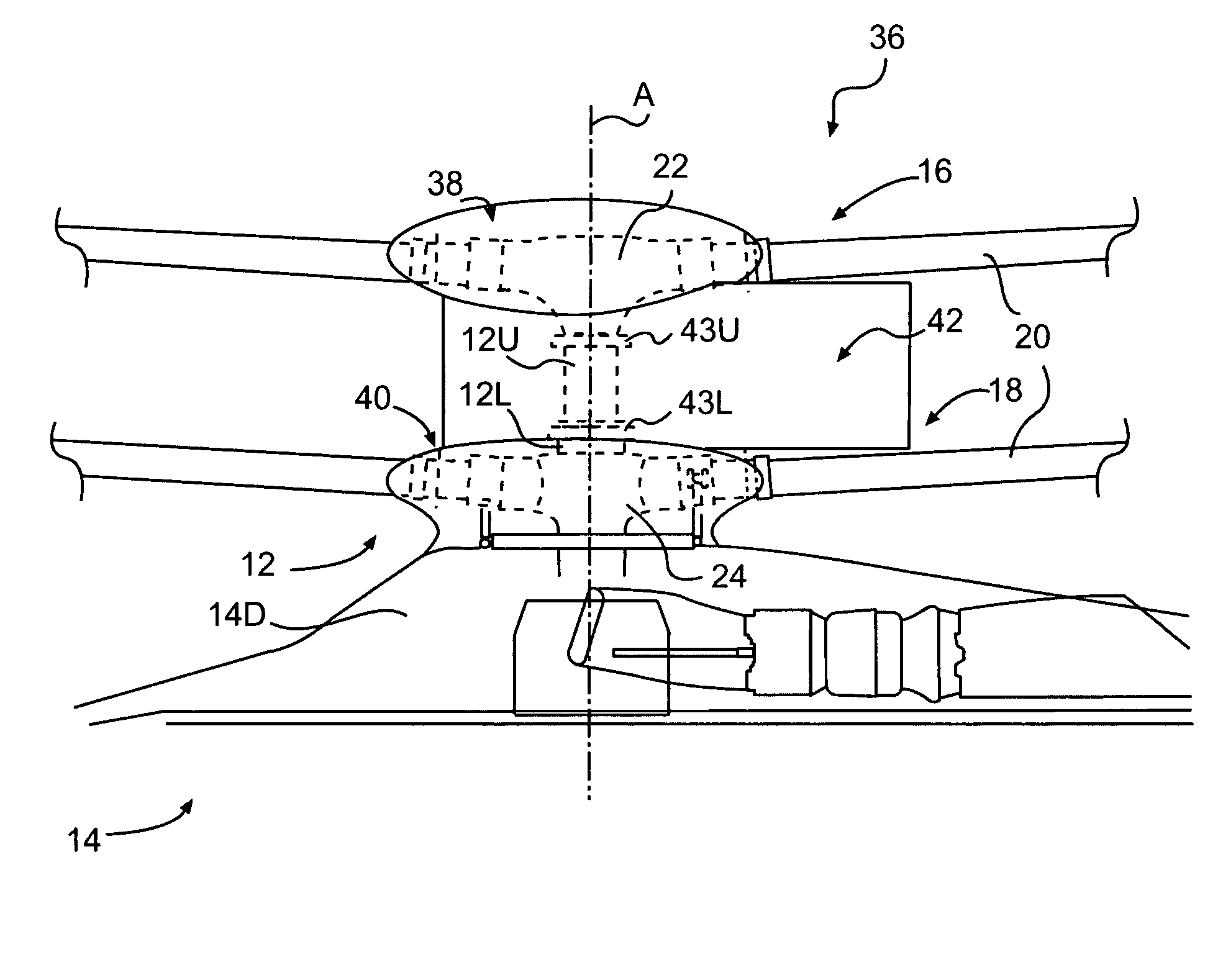
Rotor hub fairing system for a counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system
ActiveUS7229251B2Reduce the overall drag on the rotor systemMinimizing excessive separationPropellersPump componentsCowlingAerodynamics
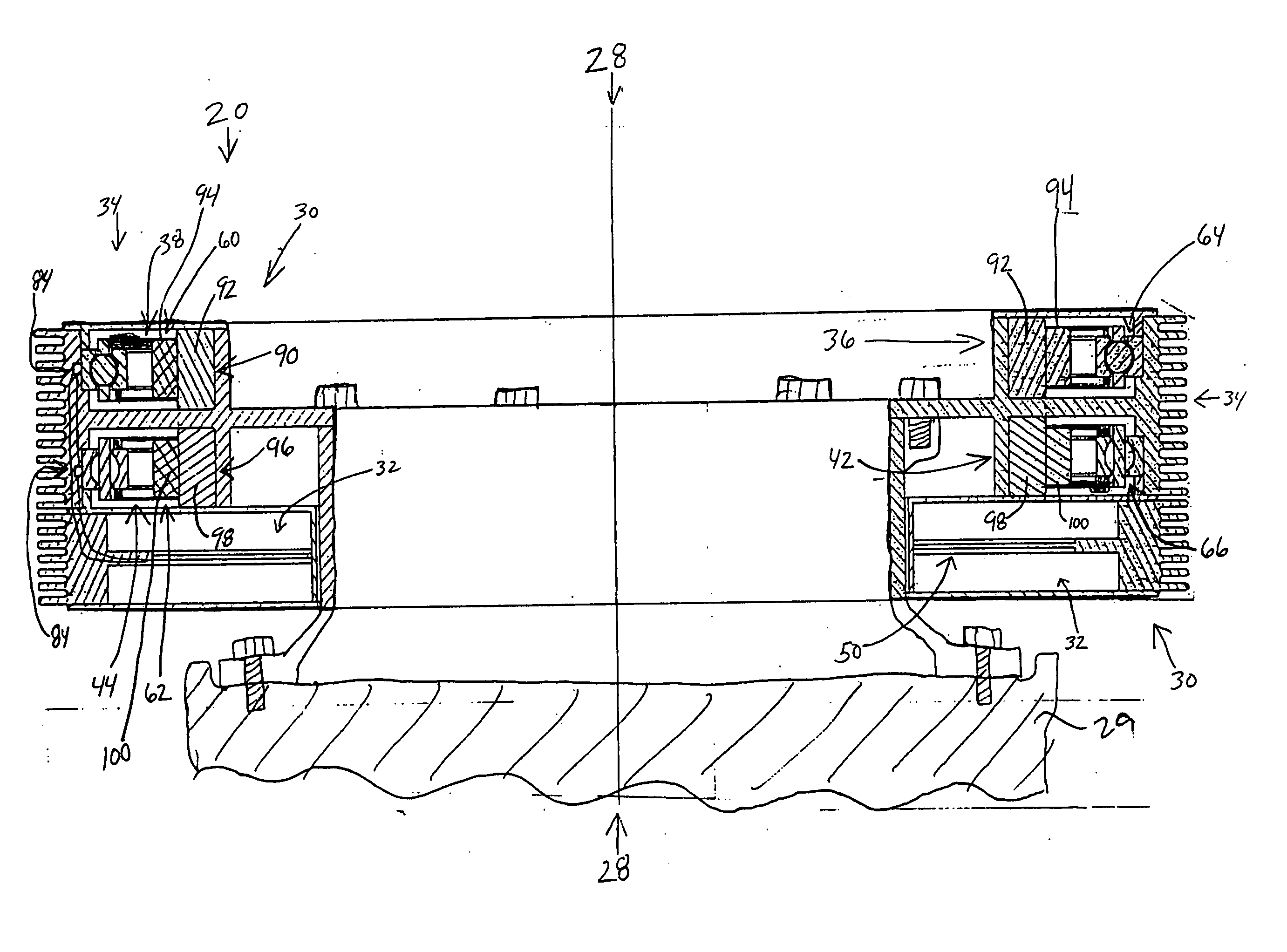
A rotor hub fairing system includes an upper hub fairing, a lower hub fairing and a shaft fairing therebetween. The rotor hub fairing system is sized and configured to reduce the overall drag on a dual, counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system. Preferably, the rotor hub fairing is fully integrated. The shaft fairing preferably includes a minimal thickness at the midsection to reduce drag with an increasing thickness adjacent the upper and lower hub fairings to reduce the flow separation on the hub fairing surfaces without overly excessive drag. Other aerodynamic structures, such as a horizontal splitter and / or a plurality of turning vanes may be mounted to the shaft fairing to facilitate flow around the upper and lower hub fairings to reduce flow separation and drag.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Rotor hub fairing system for a counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system
A rotor hub fairing system includes an upper hub fairing, a lower hub fairing and a shaft fairing therebetween. The rotor hub fairing system is sized and configured to reduce the overall drag on a dual, counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system. Preferably, the rotor hub fairing is fully integrated. The shaft fairing preferably includes a minimal thickness at the midsection to reduce drag with an increasing thickness adjacent the upper and lower hub fairings to reduce the flow separation on the hub fairing surfaces without overly excessive drag. Other aerodynamic structures, such as a horizontal splitter and / or a plurality of turning vanes may be mounted to the shaft fairing to facilitate flow around the upper and lower hub fairings to reduce flow separation and drag.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
De-rotation system for a counter-rotating, coaxial rotor hub shaft fairing
A rotor hub fairing system includes an upper hub fairing, a lower hub fairing and a shaft fairing therebetween. The rotor hub fairing system is attached to the counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system through a bearing arrangement such that the shaft fairing may be positioned at an azimuthal position about the main rotor axis of rotation relative the airframe by a de-rotation system. The de-rotation system controls the position of the shaft fairing about the axis of rotation such that the shaft fairing is prevented from rotating freely in unison with either shaft as may otherwise result during some flight regimes.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Coaxial rotor/wing aircraft
InactiveUS20140312177A1Efficient and safe transitionFast shippingRotocraftRotational axisFlight vehicle
A system and method which enable efficient, rapid and safe transition between rotary-wing and fixed-wing flight mode in rotor / wings aircrafts is disclosed. The aircraft comprises of two rotor / wings on the same axis of rotation, one above the fuselage and the other one under the fuselage. During rotary-wing mode, the rotor / wings rotate coaxially and provide vertical lift. During transition between rotary-wing and fixed-wing modes, the synchronised operation of the two rotor / wings maintains lateral symmetry of lift on the aircraft. The reaction of the rotor / wings on the fuselage is also canceled. During fixed-wing flight mode, the two rotor / wings are stopped and locked in a biplane configuration, both providing lift as fixed wings. The rotor / wings may be further reconfigured for higher subsonic or supersonic speed. Tandem and multiple rotor / wings aircrafts with increased cargo capacity, speed and range, comprise of multiple of these coaxial rotor / wings.
Owner:GAONJUR RAJESH
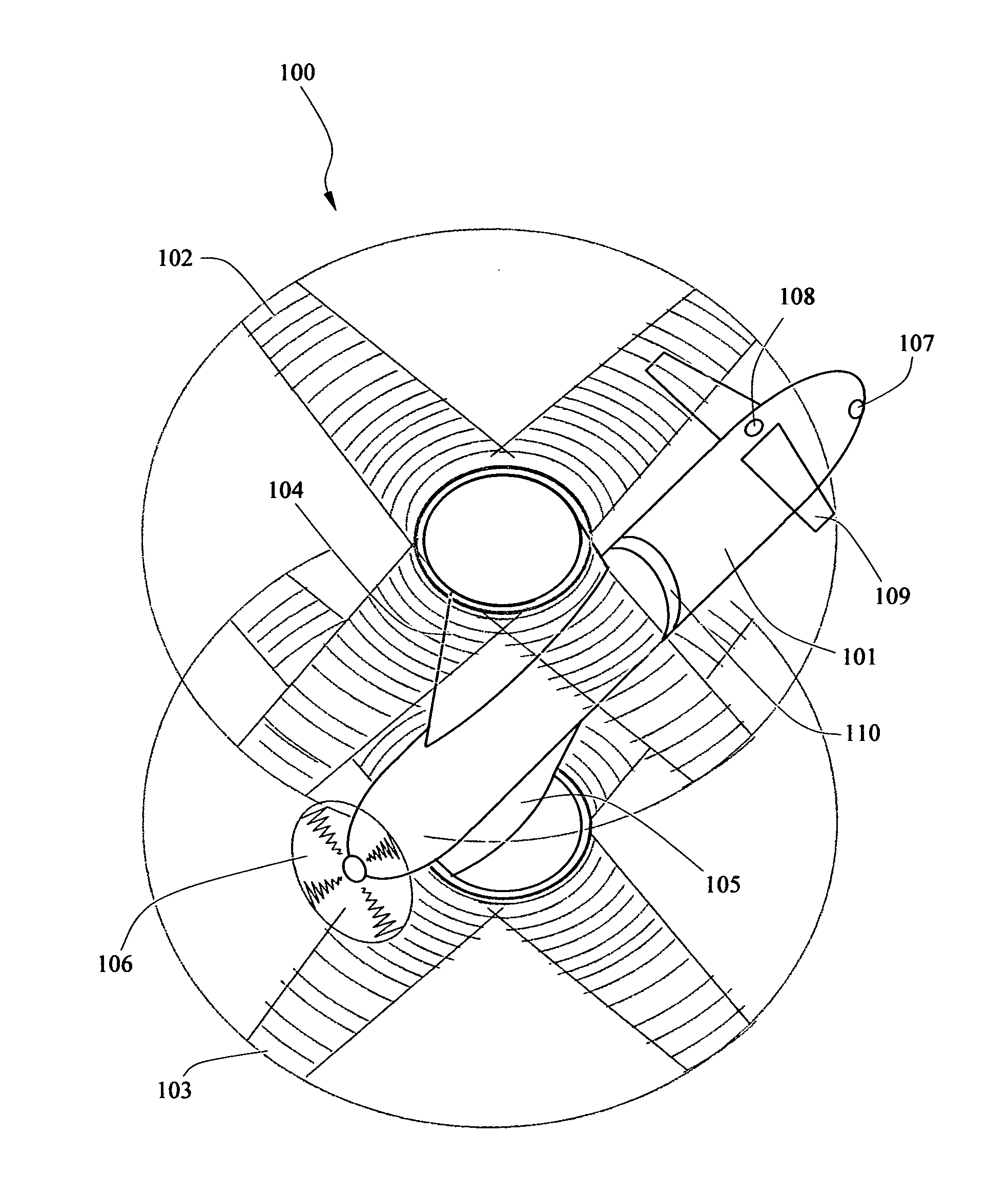
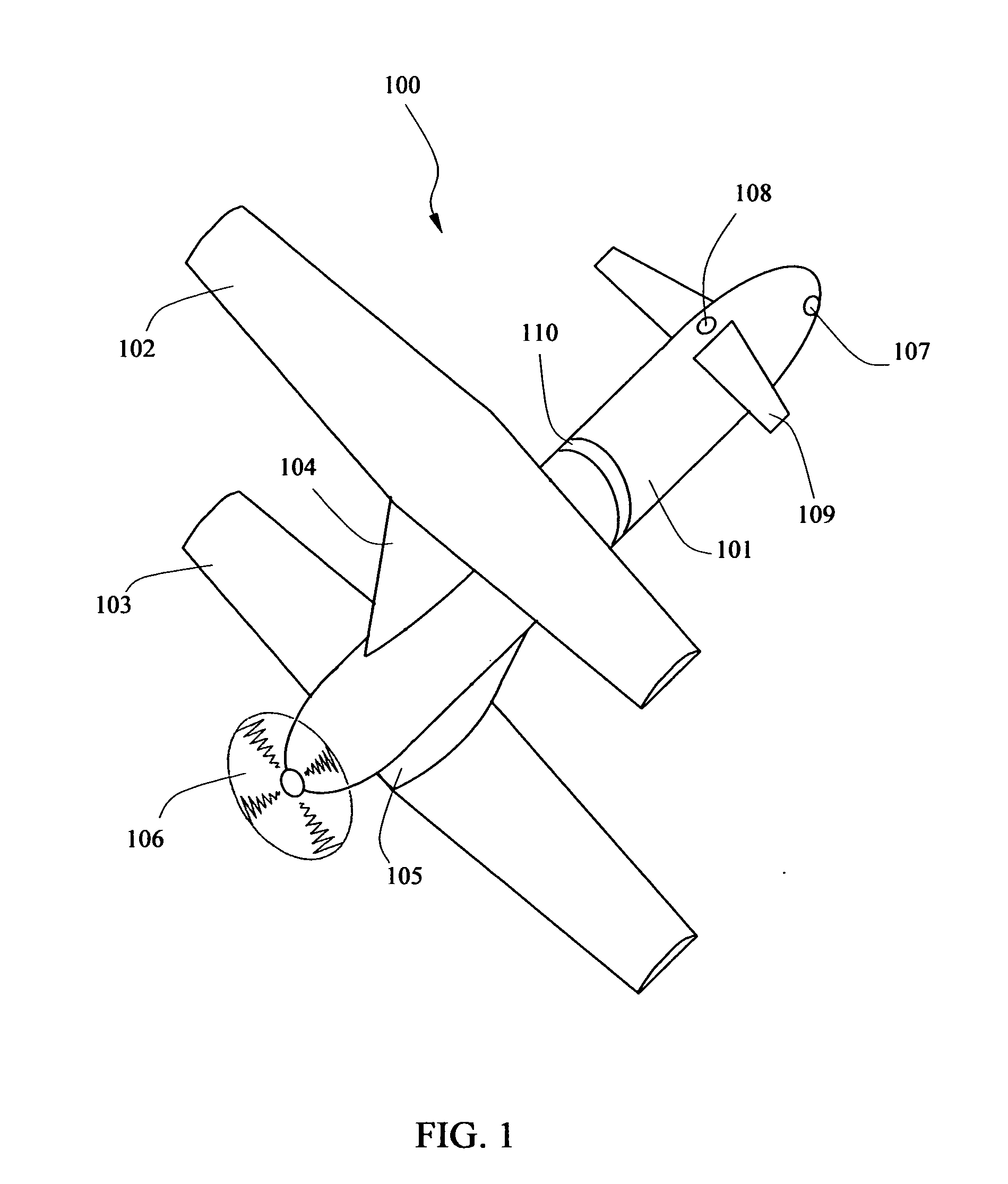
High-speed aircraft with vertical lift and self-revolving ability
InactiveUS20100001120A1Improve securityAdjustable angleAircraft stabilisationFuselagesPropellerFixed wing
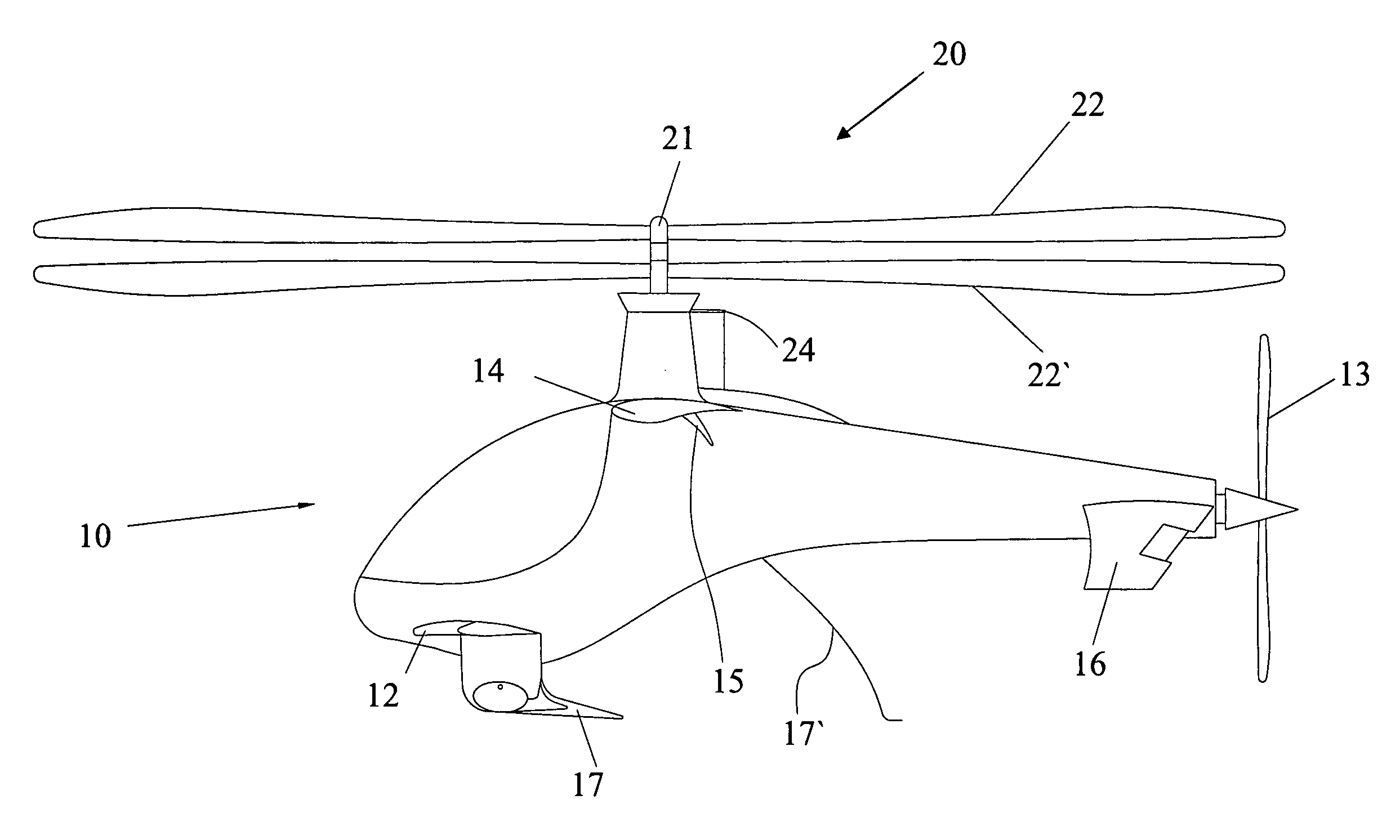
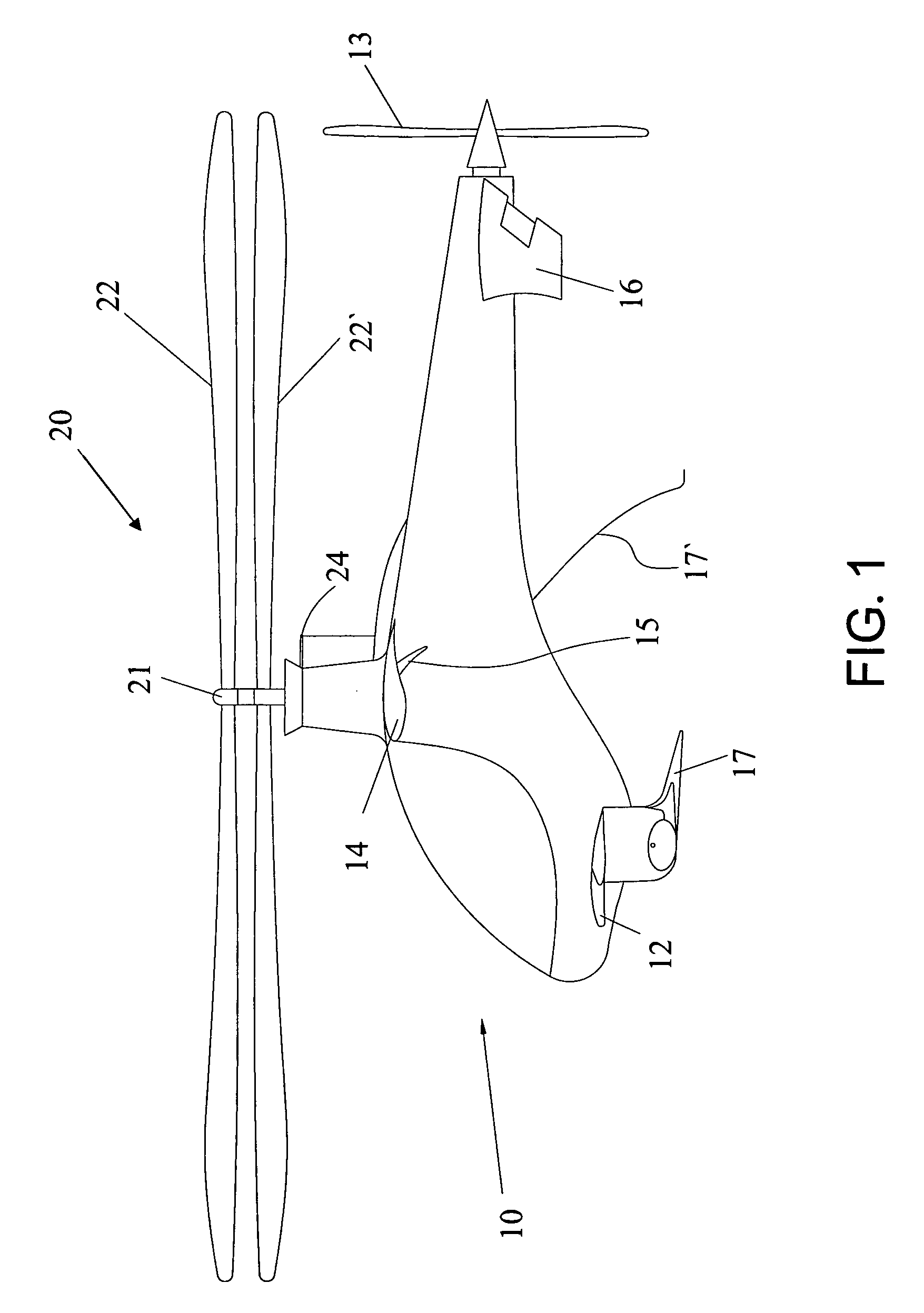
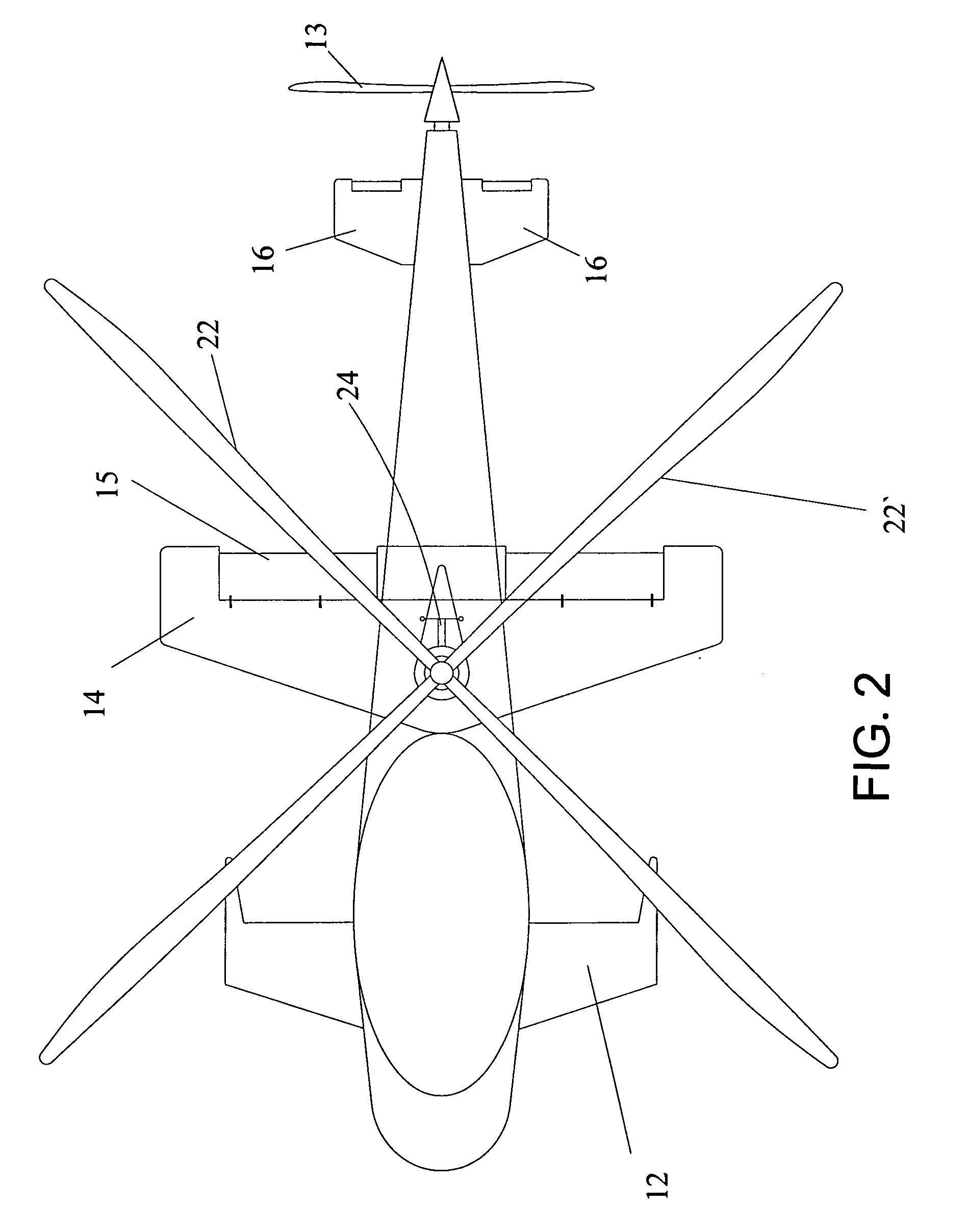
An aircraft includes a fuselage; a cockpit formed in the fuselage; a coaxial rotor assembly mounted to the top of fuselage, containing an upper rotor and a lower rotor, drivable by a first motor inside the fuselage; wherein, the aircraft also comprises: a couple of fixed wings mounted to the opposite sides of the aircraft respectively; and a rear propeller mounted to the tail end of fuselage, driven by a second motor inside the fuselage. The aircraft of the invention has the advantages of helicopter and autogyro, such as high-safety and high-speed.
Owner:SUN WEI HONG
Dual higher harmonic control (HHC) for a counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system
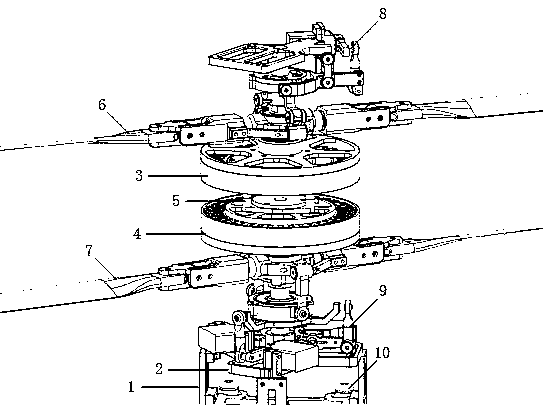
A dual, counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system provides individual control of an upper rotor system and a lower rotor system. The lower rotor control system and the upper rotor control system provide six controls or “knobs” to minimize or theoretically eliminate airframe vibration. In a dual, counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system, application of a HHC system to the two rotor systems individually but located on the common axis, will yield essentially complete vibration reduction because the 6 controls will suppress the 6 loads.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
De-rotation system for a counter-rotating, coaxial rotor hub shaft fairing
A rotor hub fairing system includes an upper hub fairing, a lower hub fairing and a shaft fairing therebetween. The rotor hub fairing system is attached to the counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system through a bearing arrangement such that the shaft fairing may be positioned at an azimuthal position about the main rotor axis of rotation relative the airframe by a de-rotation system. The de-rotation system controls the position of the shaft fairing about the axis of rotation such that the shaft fairing is prevented from rotating freely in unison with either shaft as may otherwise result during some flight regimes.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
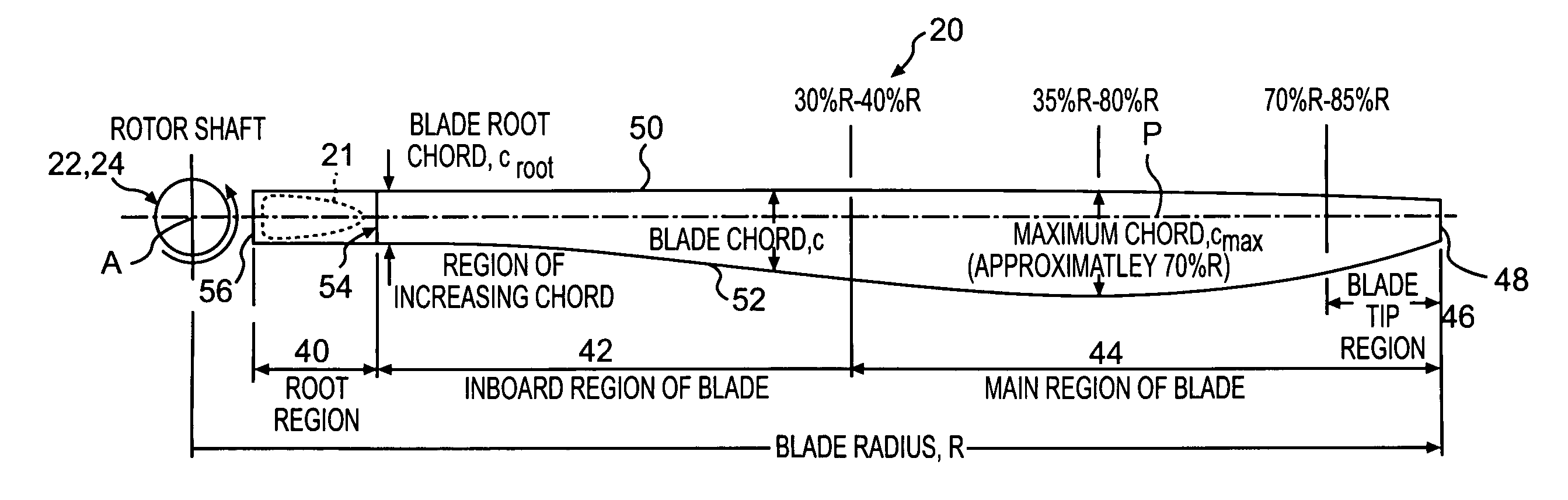
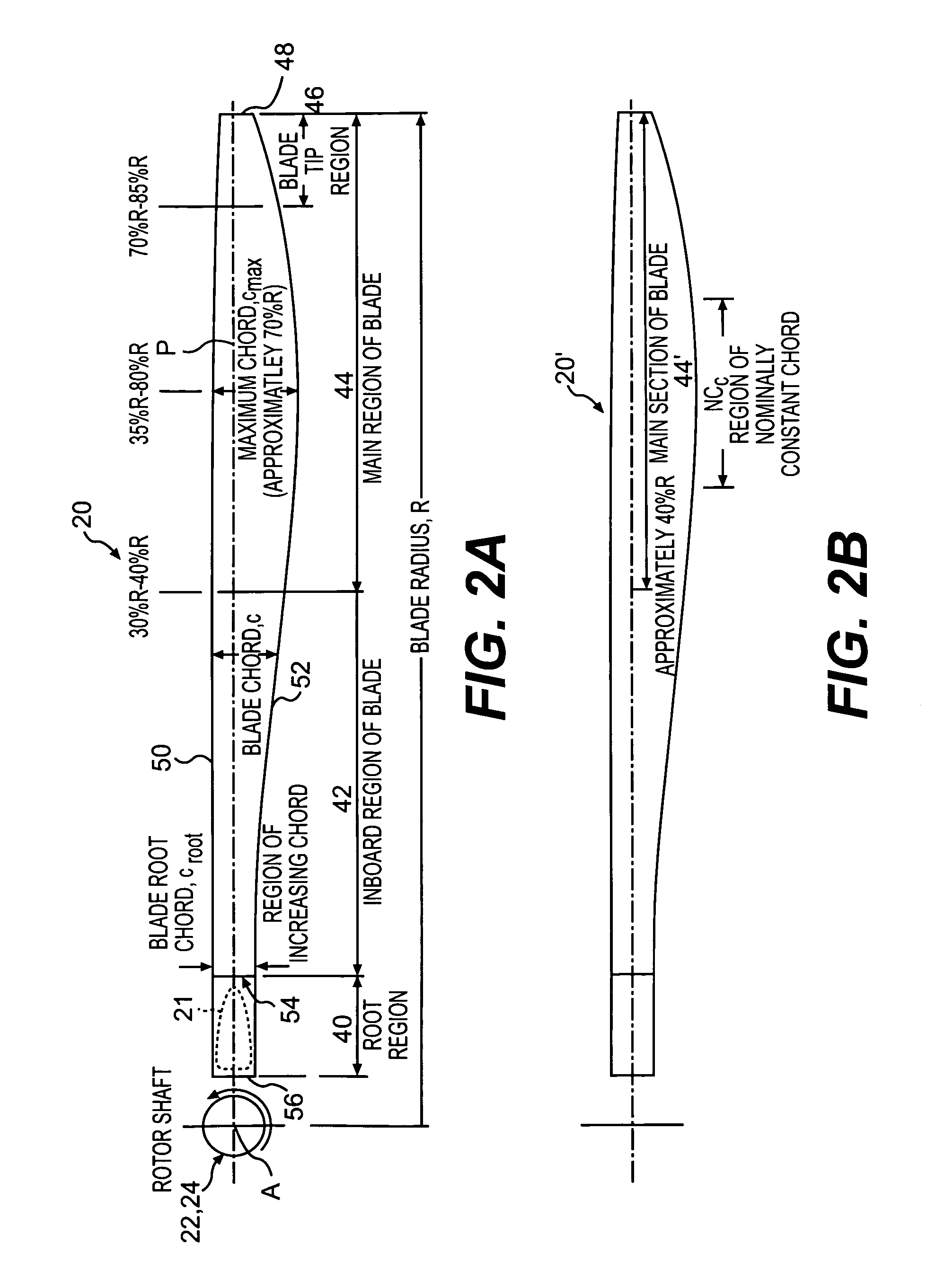
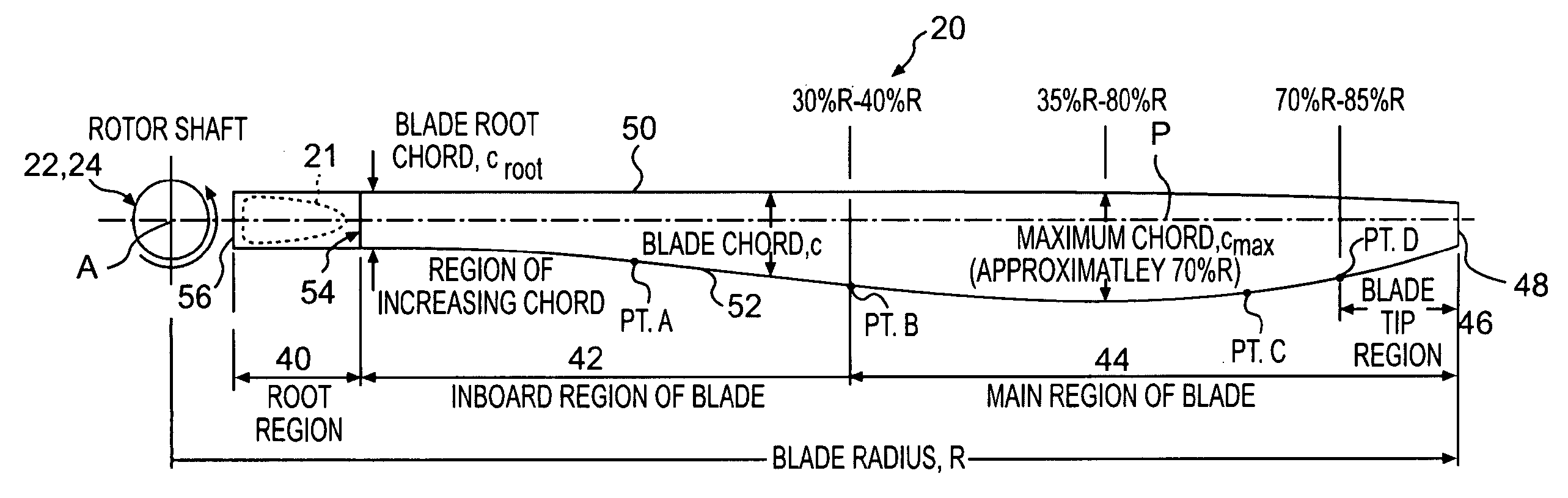
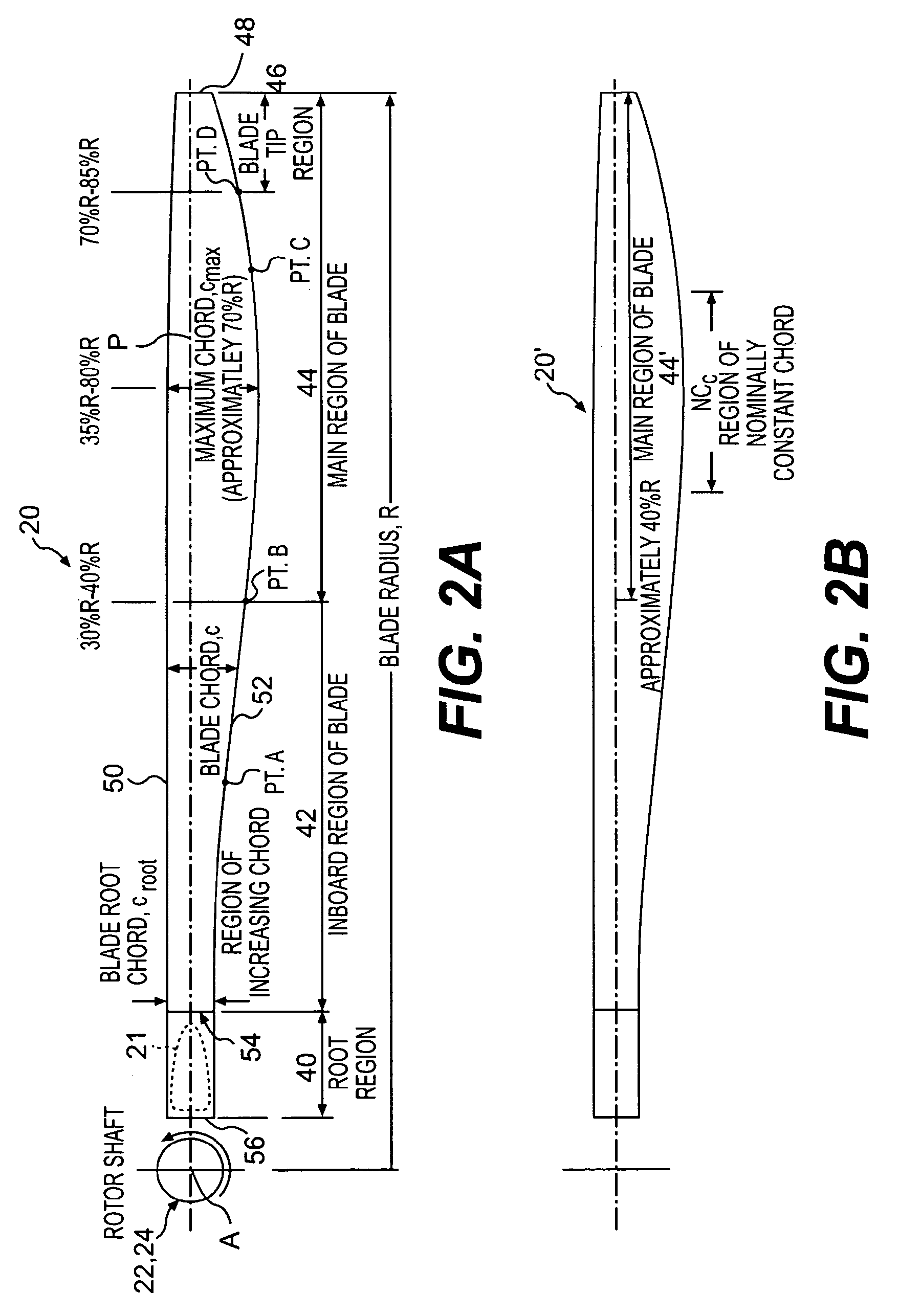
Rotor blade twist distribution for a high speed rotary-wing aircraft
ActiveUS20070110582A1Optimizing rotor performanceImprove flight efficiencyPropellersPump componentsFigure of meritRotary wing
Main rotor blades of the dual, counter-rotating, rigid coaxial rotor system exhibit a unique unconventional combination of positive and negative twist gradients in which the rotor system rotor Figure of Merit (hover efficiency) is improved by providing a dissimilar twist distribution between the lower rotor blade and the upper rotor blades. This improvement is specifically a result of reduced profile drag of the lower rotor system, achieved by driving the effective operating condition of the lower rotor blades to be similar to the upper rotor blade such that the tip drag losses of the lower main rotor have been reduced considerably using a mathematically vigorous approach. While minimal induced power consumption resulted due to the dissimilar lower main rotor twist, a significant profile power benefit is realized, resulting in the improved hover efficiency with essentially no reduction in rotor forward flight performance.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Dual higher harmonic control (HHC) for a counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system
ActiveUS20100003133A1Minimize and theoretically eliminate airframe vibrationEliminate vibrationPropellersPump componentsHarmonicControl system
A dual, counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system provides individual control of an upper rotor system and a lower rotor system. The lower rotor control system and the upper rotor control system provide six controls or “knobs” to minimize or theoretically eliminate airframe vibration. In a dual, counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system, application of a HHC system to the two rotor systems individually but located on the common axis, will yield essentially complete vibration reduction because the 6 controls will suppress the 6 loads.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
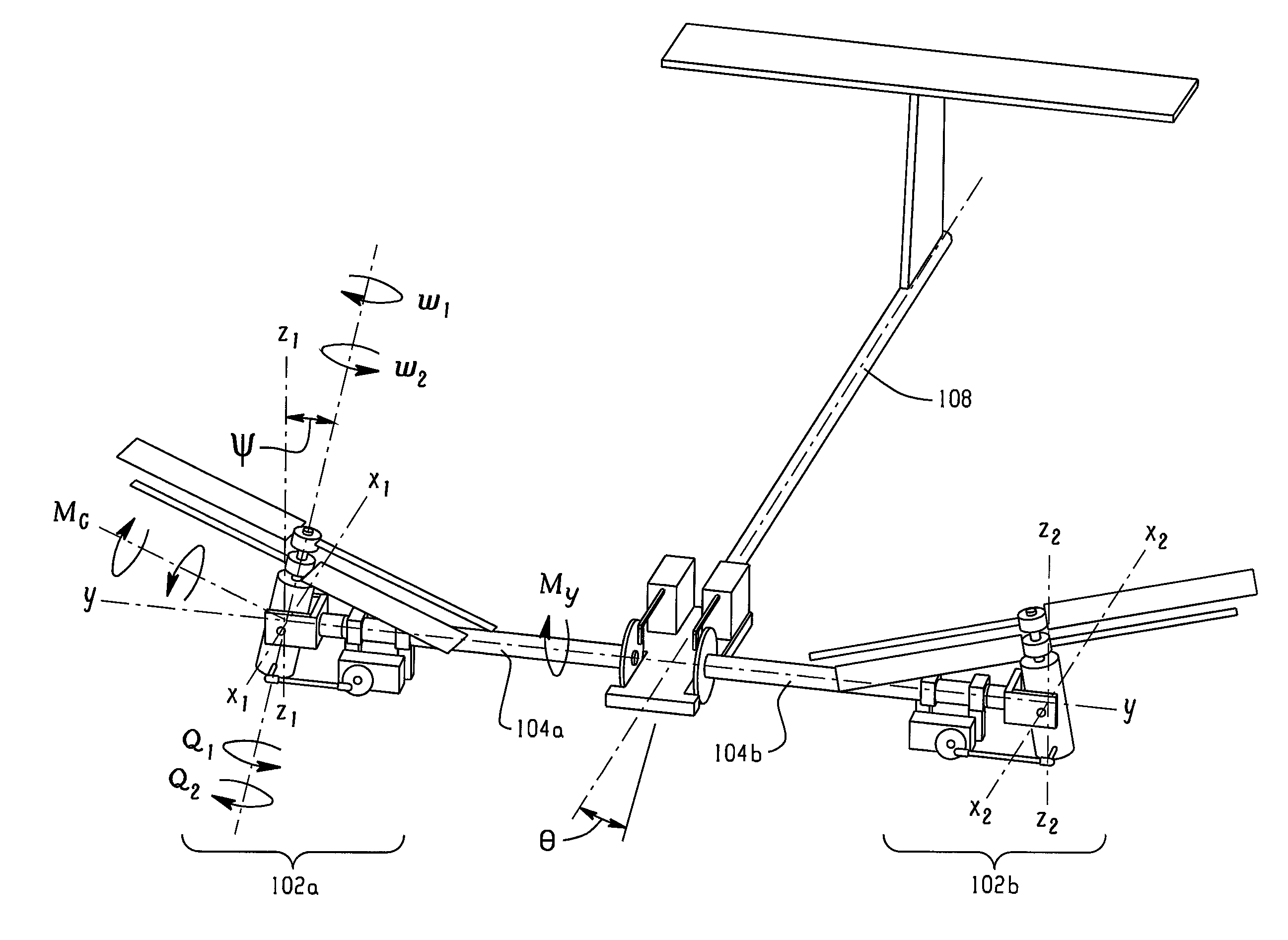
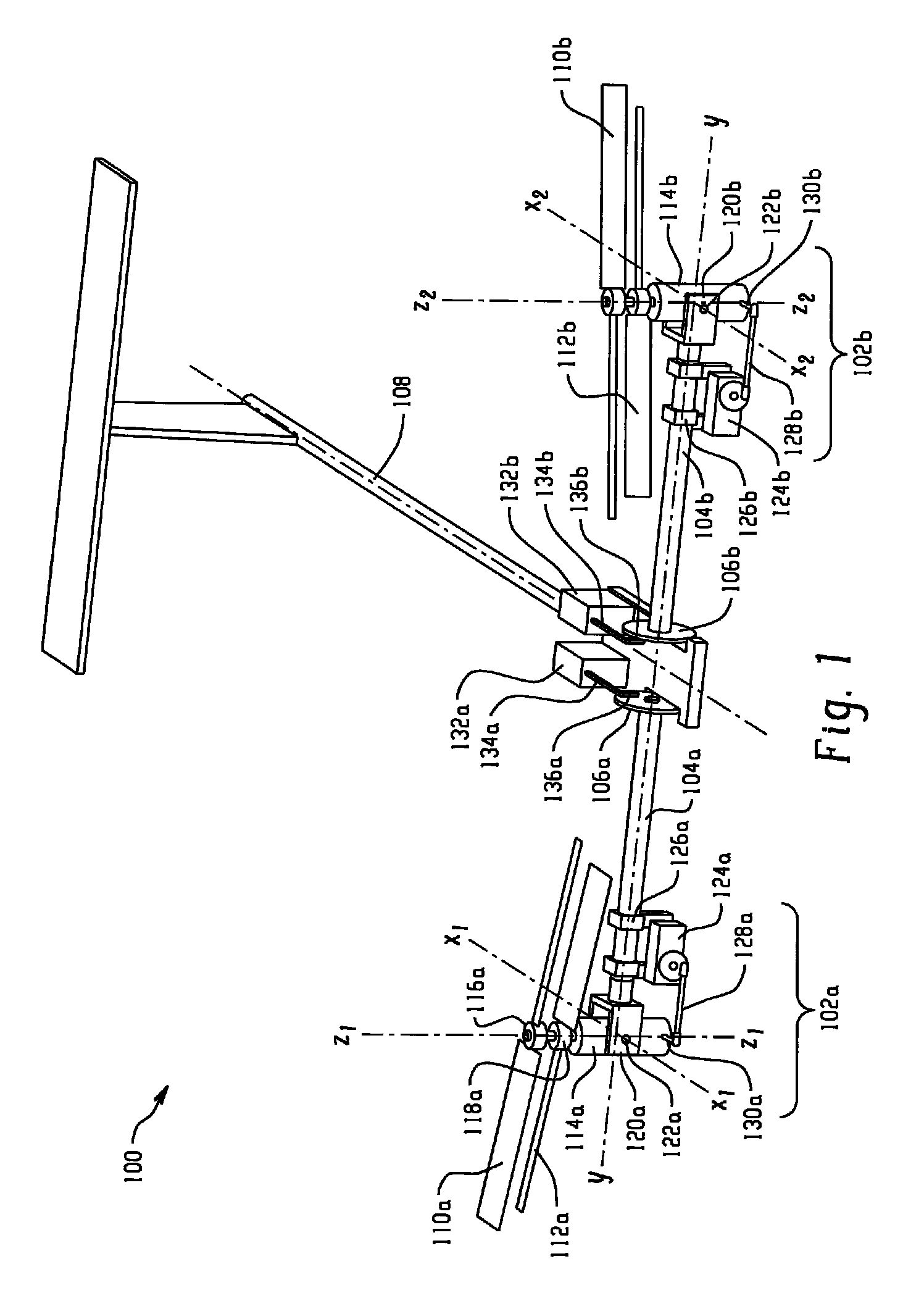
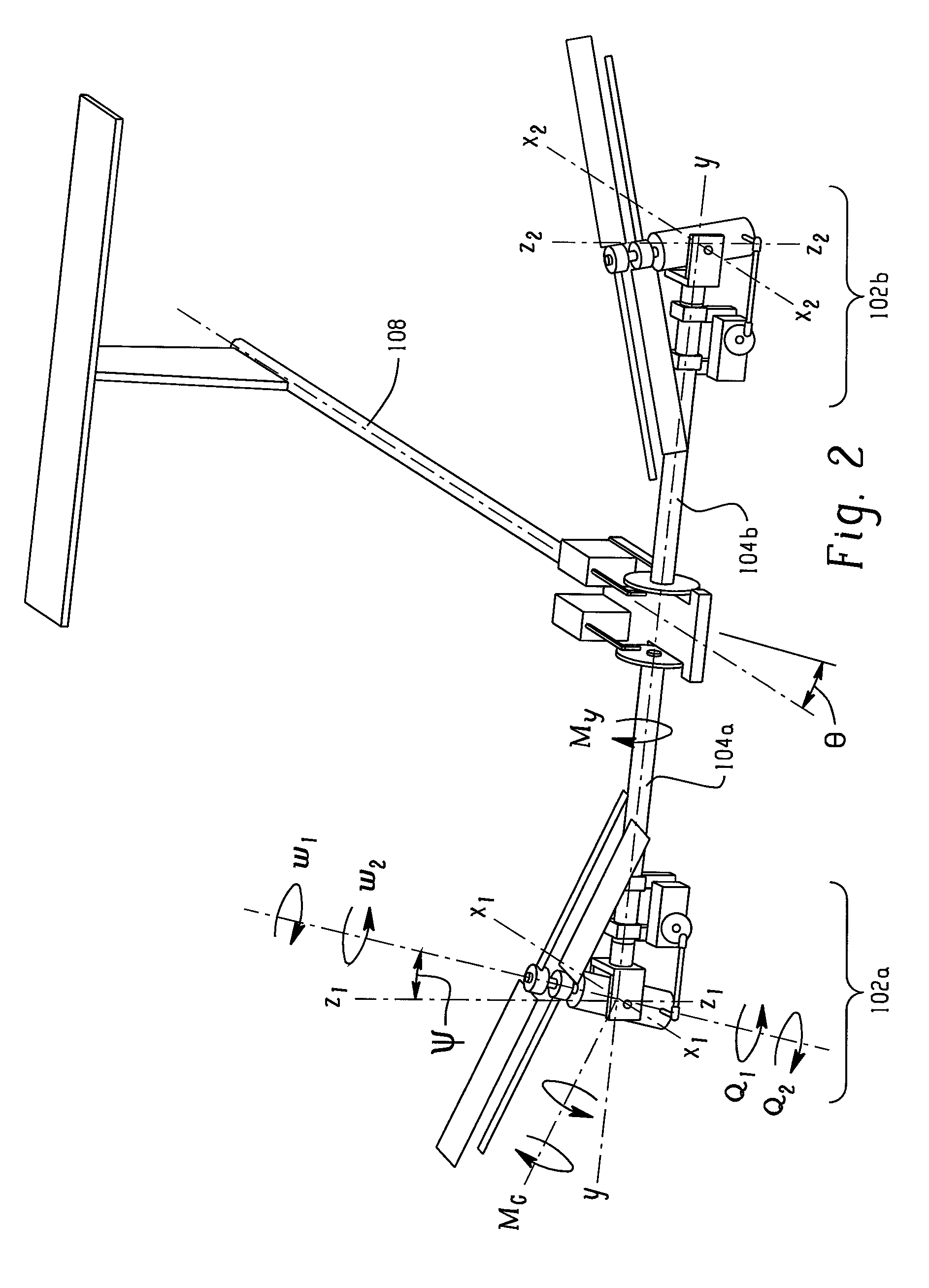
Sided performance coaxial vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) UAV and pitch stability technique using oblique active tilting (OAT)
InactiveUS20130105620A1Increasing thrust and power capabilityReduce total powerModel aircraftPropellersRotational axisGyroscopic moment
A system for increasing the thrust and power capabilities of a side by side vertical takeoff and landing vehicle and to optimize the coaxial rotor performance. The system including a first coaxial rotor spaced from an aircraft body and a second coaxial rotor spaced from the aircraft body and opposite the first coaxial rotor. The first coaxial rotor having a first top propeller aligned with a first bottom propeller along a first rotational axis. The second coaxial rotor having a second top propeller aligned with a second bottom propeller along a second rotational axis. A gyroscopic moment to maintain pitch stability is controlled by modulating the first and second top propellers having a different angular speed or different torque from the first and second bottom propellers and tilting the first and second coaxial rotors towards the central axis with a common tilt angle and a common tilt rate.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH II DESIGN & DEV BUREAU
Coaxial rotor aircraft
A dual, coaxial rotor helicopter is provided that is relatively easy to fly. Thrust is provided by two ducted fans that are mounted at the rear of the aircraft and spaced apart laterally. Differential thrust generated by the fans provides yaw control for the aircraft, and forward thrust is provided by the fans working in combination. The coaxial rotors are preferably utilized primarily for lift, and not for forward thrust, which simplifies the control requirements. The coaxial rotor with ducted fan configuration also results in lower vibratory loads being imposed on the helicopter, thereby increasing its speed capability. The fan ducts serve to protect the fans, augment the fan thrust at low airspeeds, increase the efficiency of the fans at cruise speeds, and provide horizontal and vertical stabilizing surfaces to ensure aircraft flight stability.
Owner:AVX AIRCRAFT
Rotor hub fairing system for a counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system
A rotor hub fairing system includes an upper hub fairing, a lower hub fairing and a shaft fairing therebetween. The rotor hub fairing system reduces the total drag on a dual, counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system. Other aerodynamic structures may be mounted to the shaft fairing, hub fairings and airframe to facilitate flow around the upper and lower hub fairings to reduce flow separation and drag.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Sided performance coaxial vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) UAV and pitch stability technique using oblique active tilting (OAT)
InactiveUS8931729B2Increasing thrust and power capabilityReduce total powerModel aircraftPropellersRotational axisPower capability
A system for increasing the thrust and power capabilities of a side-by-side vertical takeoff and landing vehicle to optimize the coaxial rotor performance. The system includes a first coaxial rotor spaced from an aircraft body and a second coaxial rotor spaced from the aircraft body and opposite the first coaxial rotor. The first coaxial rotor has a first top propeller aligned with a first bottom propeller along a first rotational axis. The second coaxial rotor having a second top propeller aligned with a second bottom propeller along a second rotational axis. A gyroscopic moment to maintain pitch stability is controlled by modulating the first and second top propellers, which have a different angular speed or different torque from the first and second bottom propellers, and tilting the first and second coaxial rotors towards the central axis with a common tilt angle and a common tilt rate.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH II DESIGN & DEV BUREAU
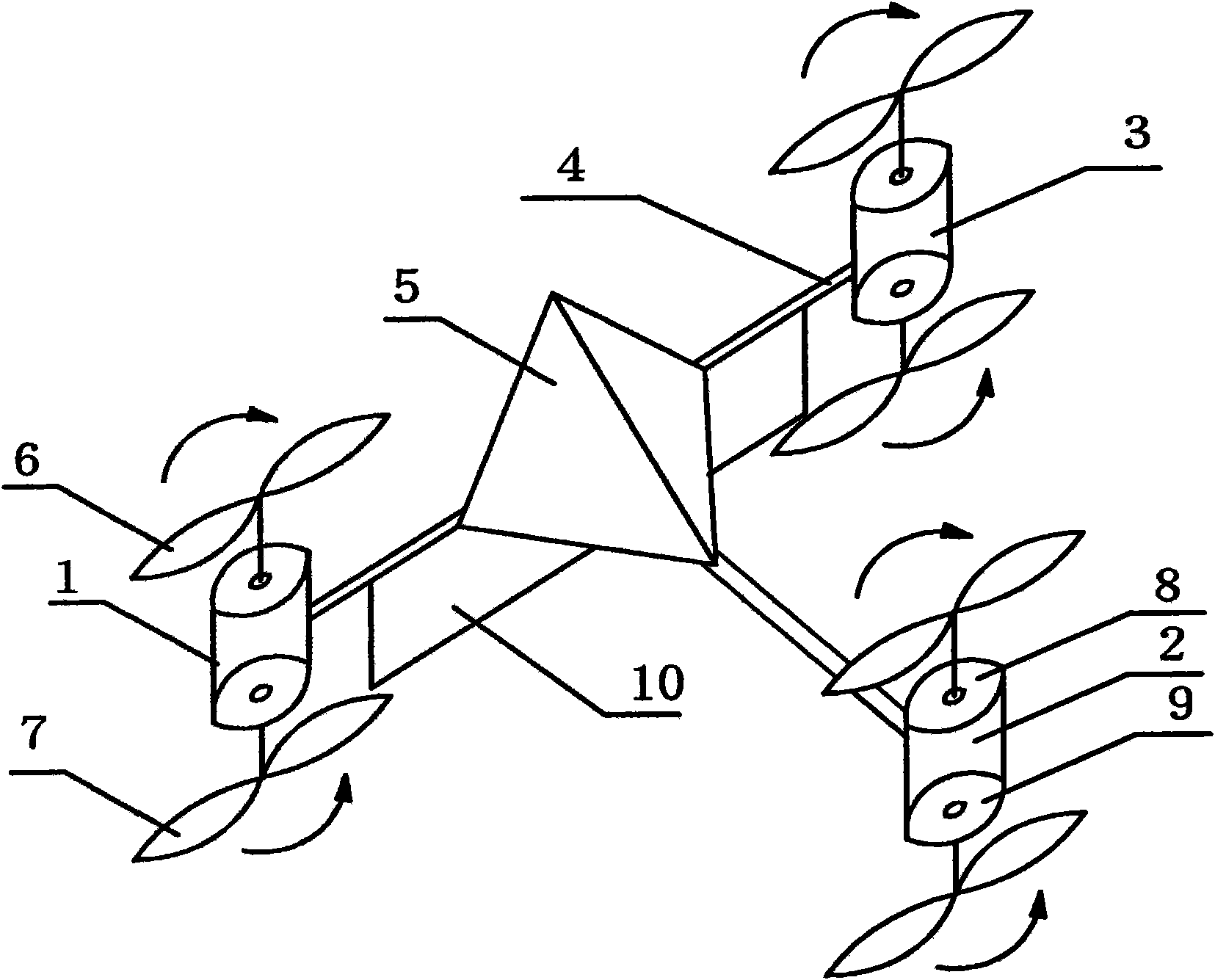
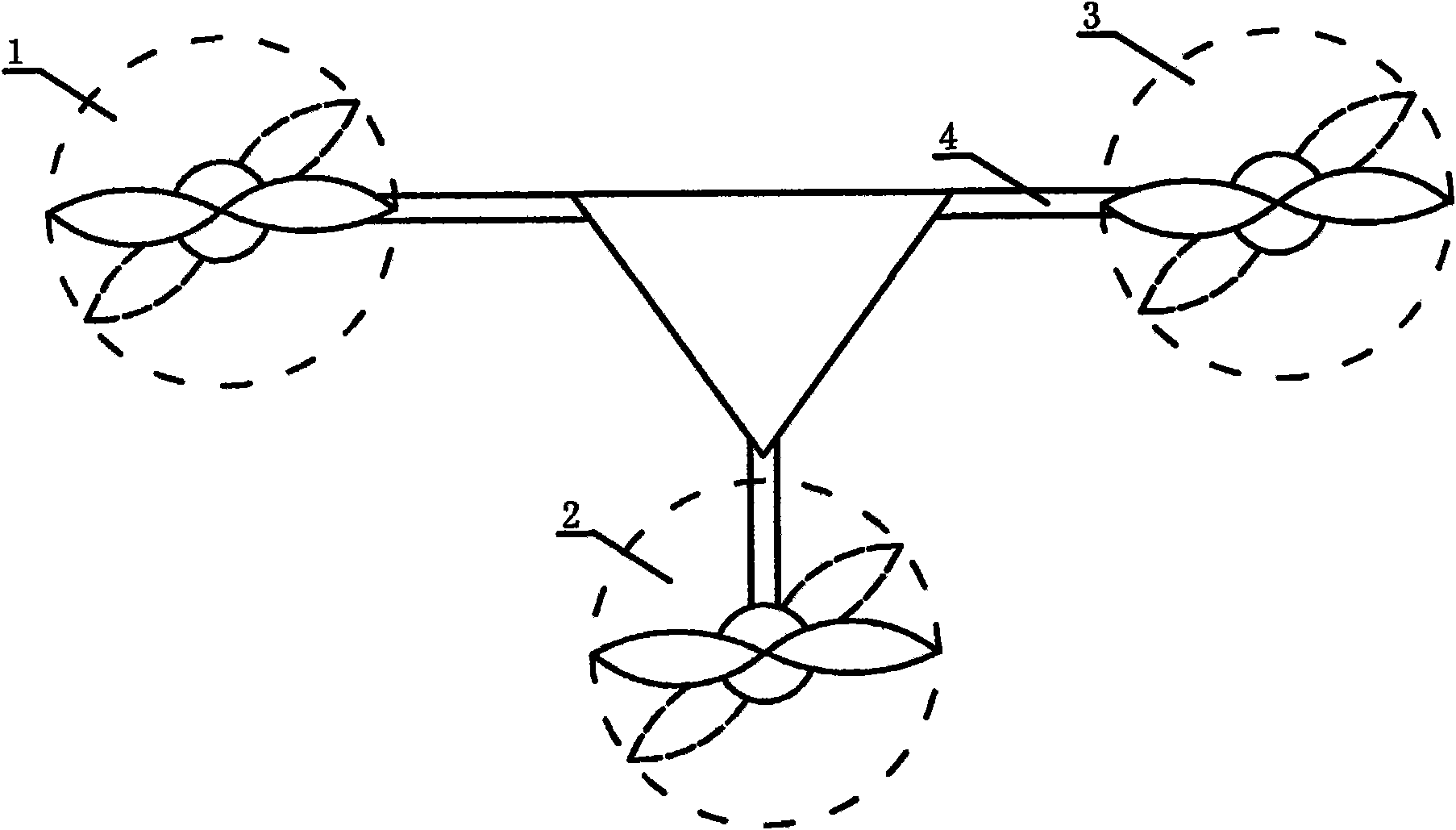
Flight-mode-variable unmanned aircraft with multiple sets of coaxial rotors
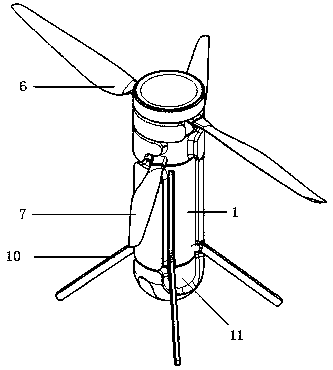
The invention relates to a flight-mode-variable unmanned aircraft with multiple sets of coaxial rotors. The structure of the unmanned aircraft is that the airframe is a framework structure which is provided with multiple sets of the coaxial rotors, wherein each set of the coaxial rotors consist of an upper motor and a lower motor which are arranged back to back with the same axis and are connected with an upper rotor and a lower rotor respectively, the rotation directions of the upper rotor and the lower rotor are opposite to each other, blades of the rotors are symmetrical with each other positively and negatively and are arranged coaxially with lift force, the torsional moment of each set of the coaxial rotor is balanced automatically, and an on-board avionics flight control box is arranged at the gravity center of the airframe. The unmanned aircraft overcomes the defects that the prior device has a complex structure, poor stability, complicated use and operation, and high cost no matter for manufacturing or use. The flight-mode-variable unmanned aircraft has good maneuverability and stability, is easy to control the flight mode switch and the relative flight speed, and solves the problems of transportation and use. The flight-mode-variable unmanned aircraft has the advantages of simple structure, low manufacturing and using cost, and easy operation.
Owner:徐锦法
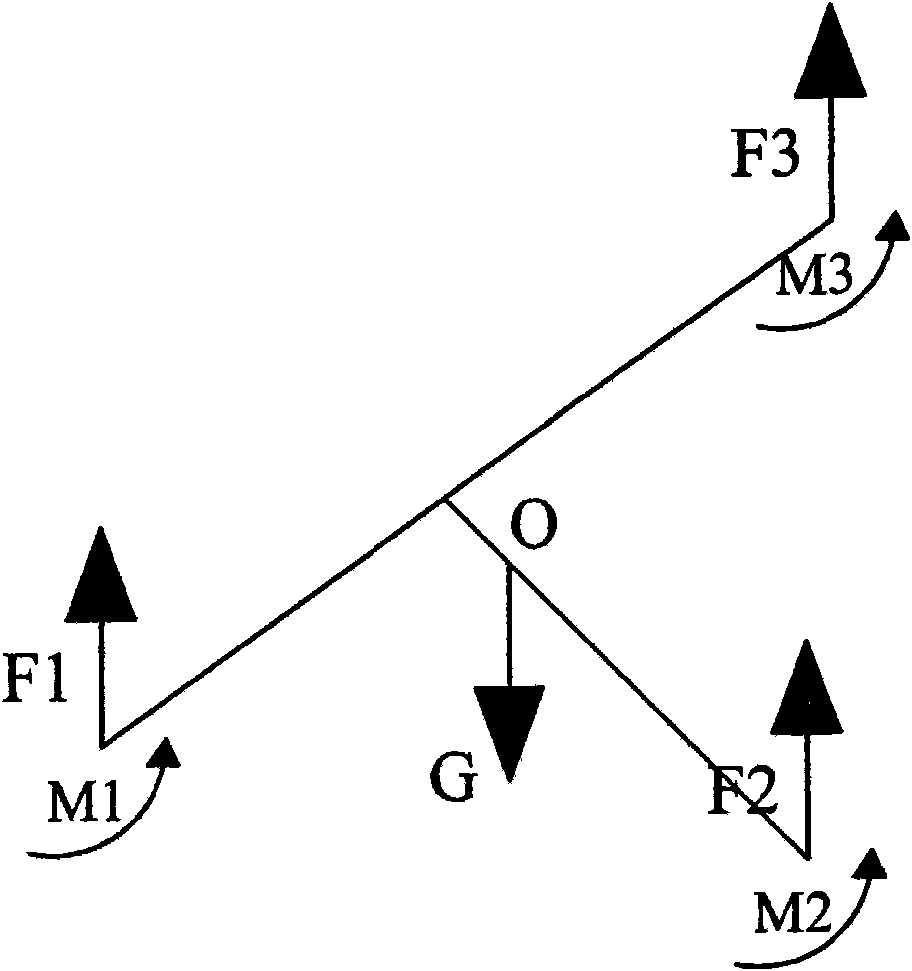
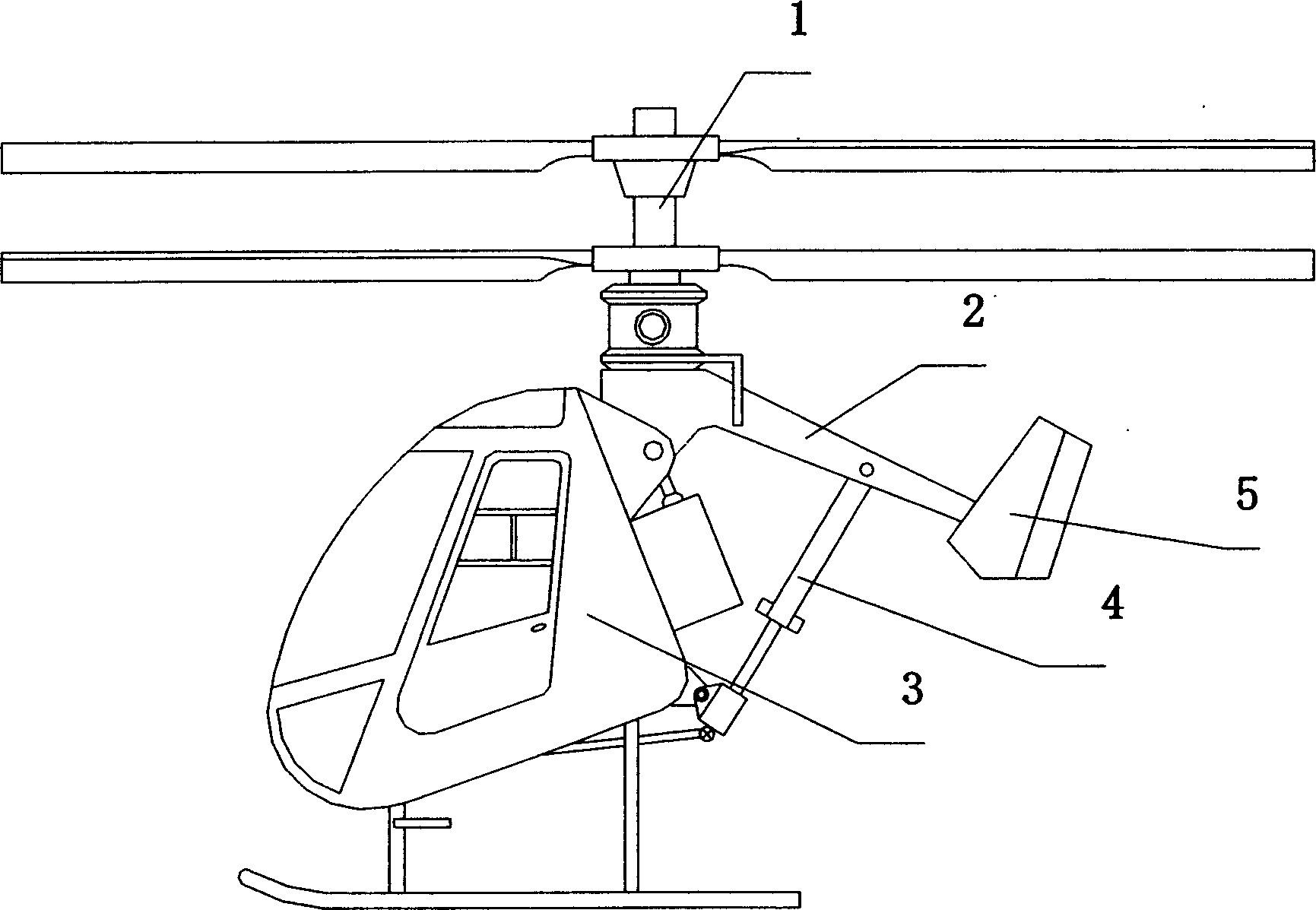
Rotor shaft controllable tilting coaxial rotor wing helicopter
InactiveCN1857965AExtended range of movementImprove efficiencyRotocraftThrottle controlFlight direction
The coaxial rotor wing helicopter with controllable inclined rotor shaft has fixed rotor elevation, rotor shaft fixed before the tailboom, hinge device connecting tailboom to the fuselage and flight attitude regulator of adjustable length connecting the tailboom to the fuselage. Regulating the length of the flight attitude regulator can regulate the position of the rotor shaft extension line relatively to the helicopter gravity center, and when the rotor shaft extension line coincides with the gravity center, the helicopter is in vertical lift state. Increasing the length of the flight attitude regulator to make the gravity center in front of the rotor shaft extension line makes the helicopter fly forwards; and decreasing the length of the flight attitude regulator to make the gravity center in back of the rotor shaft extension line makes the helicopter fly backwards. The engine throttle controls the rotation speed of the rotor wing, while vertical tail wing regulates the flying direction.
Owner:胡俊峰
Foldable coaxial double-rotor aircraft and control method thereof
The invention discloses a foldable coaxial double-rotor aircraft and a control method thereof. The foldable coaxial double-rotor aircraft comprises an aircraft body, a rotor system mounting base, an upper rotor action motor, a lower rotor actuation motor, an actuation motor connecting part, a foldable upper rotor part, a foldable lower rotor part, an upper rotor variable-pitch mechanism, a lower rotor variable-pitch mechanism, foldable landing gears and airborne equipment. The foldable coaxial double-rotor aircraft is characterized in that the aircraft body is in a column shape, and the outside surface is provided with a groove along the bus direction towards the interior of the aircraft body; the foldable upper rotor, the foldable lower rotor and the foldable landing gears are respectively folded into the groove along the bus direction of the aircraft body through self root hinges; the upper rotor variable-pitch mechanism and the lower rotor variable-pitch mechanism are used for independently completing the variable-pitch operation. By adopting the foldable coaxial double-rotor layout plan, the foldable coaxial double-rotor aircraft has the advantages that by extending and accommodating the foldable double rotors and the foldable landing gears, the aircraft can complete flight operation in a normal coaxial rotor state under the working condition; under the non-working condition, the size is smaller, and the manufacturing, transportation, carrying and storage are convenient.
Owner:南京韬讯航空科技有限公司
Vibration control of a swashplateless coaxial rotor
A rotary wing aircraft is provided including a dual counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system having an upper rotor system and a lower rotor system rotatable about a common axis. A plurality of blade assemblies is mounted to a portion of either the upper rotor system or the lower rotor system. A plurality of individually controllable actuators is coupled to each of the plurality of blade assemblies. Each of the plurality of actuators is configured to control movement of the coupled blade assembly about a pitch axis. The rotary-wing aircraft additionally includes a sensor system within an airframe. A higher harmonic control (HHC) controller is arranged in communication with the sensor system and the plurality of actuators to individually control the upper rotor system and the lower rotor system to reduce vibration.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
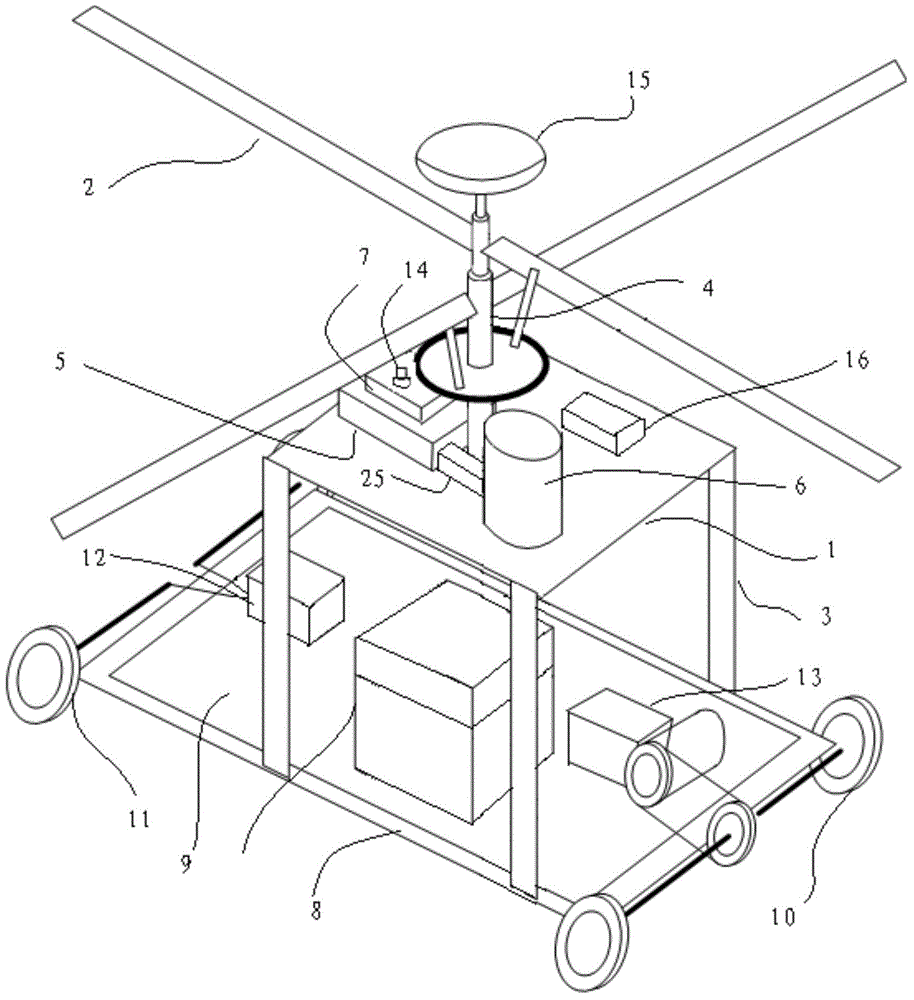
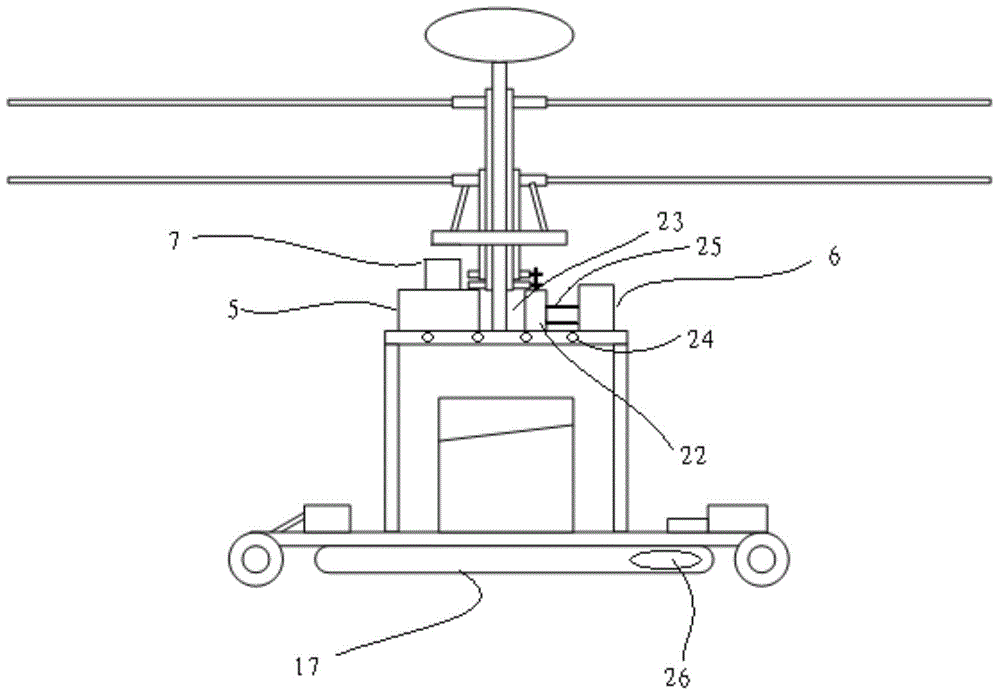
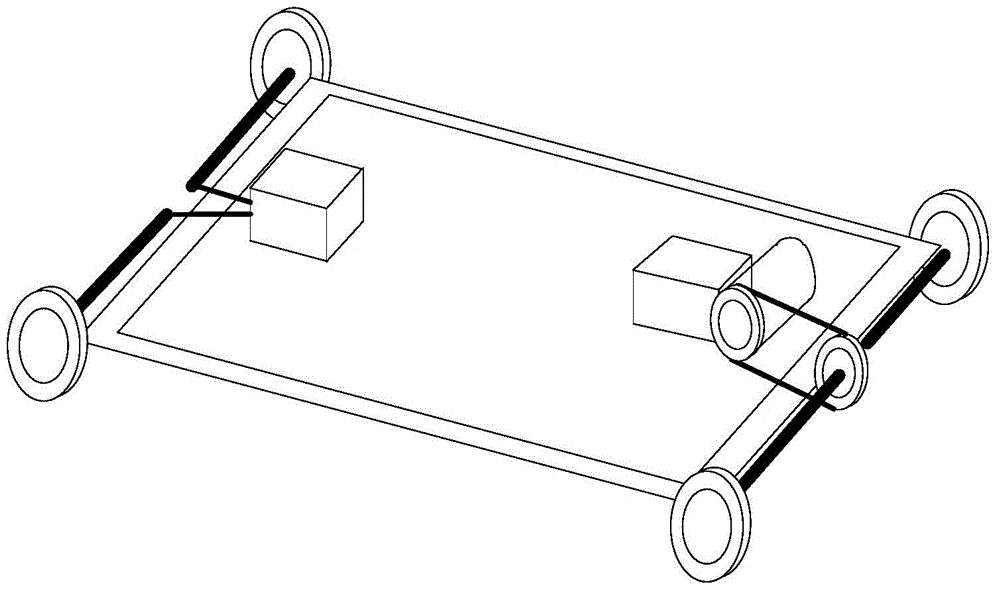
Logistics unmanned rotor wing aircraft capable of walking on ground
ActiveCN104401487AReduce falling speedAvoid the pitfalls of draggingParachutesAircraft landing aidsAviationPulley
The invention belongs to the technical field of aviation, and relates to an unmanned aerial vehicle, in particular to a logistics unmanned rotor wing aircraft capable of walking on the ground. The logistics unmanned rotor wing aircraft comprises an aircraft case and double coaxial rotor wings arranged on the aircraft case, wherein a walking device is arranged at the bottom of the logistics unmanned rotor wing aircraft. Through the adoption of the design that the walking device is arranged on the unmanned rotor wing aircraft, the unmanned rotor wing aircraft has an automatic walking function after landing, and the defect that pulleys have to be additionally arranged at the bottom of a traditional unmanned aerial vehicle for dragging due to inaccurate points of fall after the unmanned aerial vehicle lands is avoided; by mounting a parachute launching device, in the failure of an oil-driven engine of the unmanned rotor wing aircraft, a parachute is launched, and an emergency descent damping device is opened, so that the unmanned rotor wing aircraft slowly lands on the ground, and the damage on objects and crowds of people on the ground is prevented.
Owner:AVIATION IND INFORMATION CENT
Rotor blade twist distribution for a high speed rotary-wing aircraft
ActiveUS7600976B2Increase the areaImprove performancePropellersRotary propellersFriction lossFigure of merit
Main rotor blades of the dual, counter-rotating, rigid coaxial rotor system exhibit a unique unconventional combination of positive and negative twist gradients in which the rotor system rotor Figure of Merit (hover efficiency) is improved by providing a dissimilar twist distribution between the lower rotor blade and the upper rotor blades. This improvement is specifically a result of reduced profile drag of the lower rotor system, achieved by driving the effective operating condition of the lower rotor blades to be similar to the upper rotor blade such that the tip drag losses of the lower main rotor have been reduced considerably using a mathematically vigorous approach. While minimal induced power consumption resulted due to the dissimilar lower main rotor twist, a significant profile power benefit is realized, resulting in the improved hover efficiency with essentially no reduction in rotor forward flight performance.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Electric machine with non-coaxial rotors
A rotary electric machine having plural rotary elements in a non-coaxial arrangement is disclosed. The rotary electric machine includes a housing assembly, at least one stator frame mounted in the housing assembly, at least one stator winding wound on the at least one stator frame, and at least two rotors mounted in the housing assembly having axes of rotation that are non-coaxial, wherein each of the at least two rotors is mechanically decoupled from the other rotors such that each of the at least two rotors rotates independent from one another. The rotary electric machine also includes a control unit, with the control unit including at least one electronic control electrically connected to the at least one stator winding. The control unit is configured to control an exchange of power to or from each of the at least one stator windings.
Owner:CASEY JOHN R
Coaxial double-rotor-wing system of aircraft
The invention relates to a coaxial double-rotor-wing system of an aircraft. The coaxial double-rotor-wing system comprises a speed reducer, a lower rotor wing shaft, a lower rotor wing hub, a lower rotor wing, an upper rotor wing, an upper rotor wing shaft, an upper rotor wing hub, an upper rotor wing and a control link or controlling the upper rotor wing and the lower rotor wing and is characterized in that the upper rotor wing and the lower rotor wing are rigid coaxial rotor wings only provided with an axial hinge, a pull rod direct-connection structure between the upper automatic inclinator and the lower automatic inclinator of the control link is omitted, and the control link further comprises a cyclic pitch control mechanism and a differential cyclic pitch control mechanism. The coaxial double-rotor-wing system has the advantages that lift force compensation of the rotor wings is omitted by utilizing the rigid coaxial rotor wings; further aerodynamic limiting caused by air flow separation and air supersonic turbulent flows is avoided under the situation that the condition of lift force compensation is not met; a retreating propeller pitch is decreased by adding the differential cyclic pitch control mechanism, accordingly the aerodynamic resistance of the retreating positions of rotor wing blades can be reduced, ineffective consumption is reduced, and the flat flight speed is improved based on the same output power.
Owner:DEA GENERAL AVIATION HLDG CO LTD
Multi-purpose airship
InactiveUS7036768B2Reduce maintenance costsIncrease speedAircraft stabilisationNon-rigid airshipsJet enginePropeller
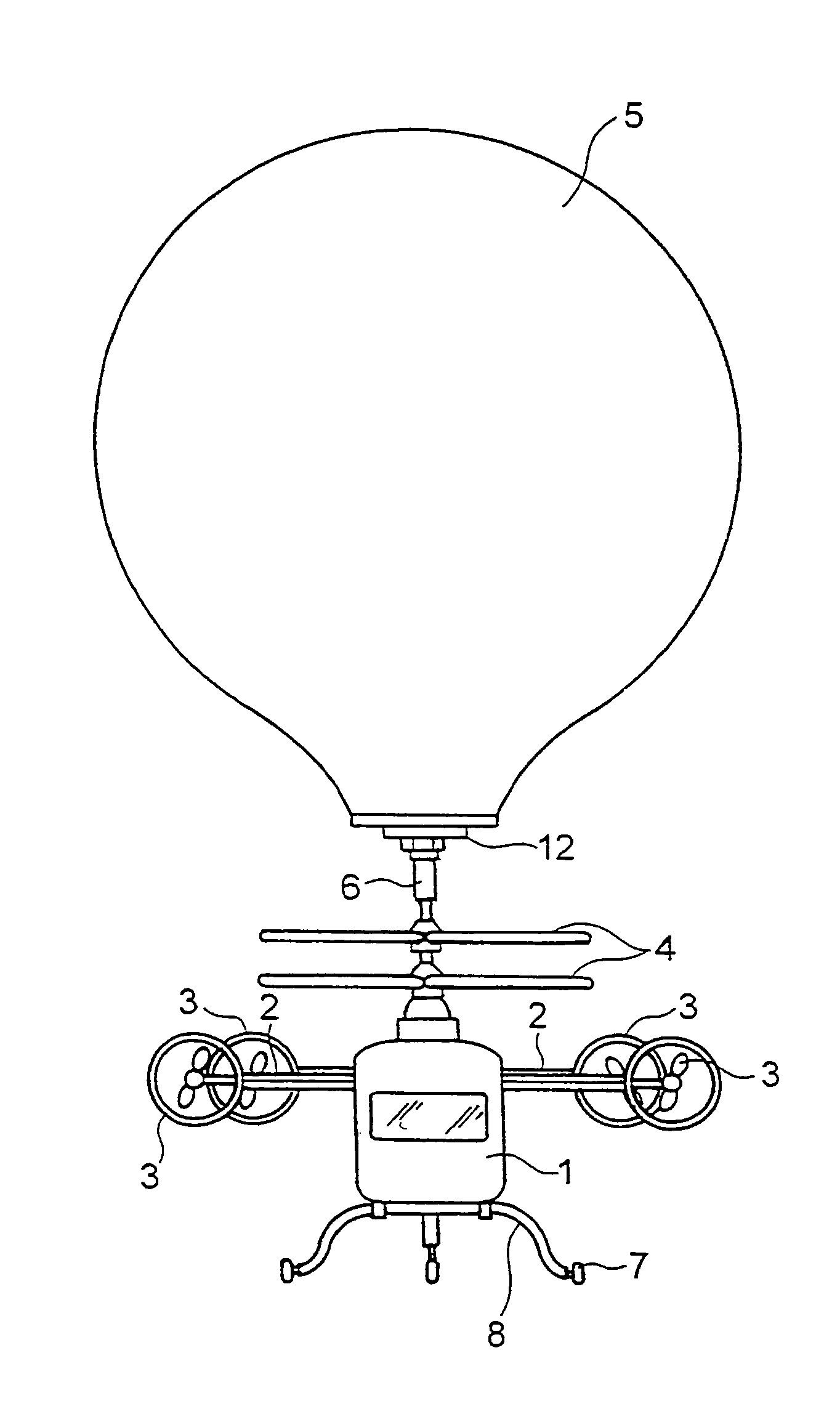
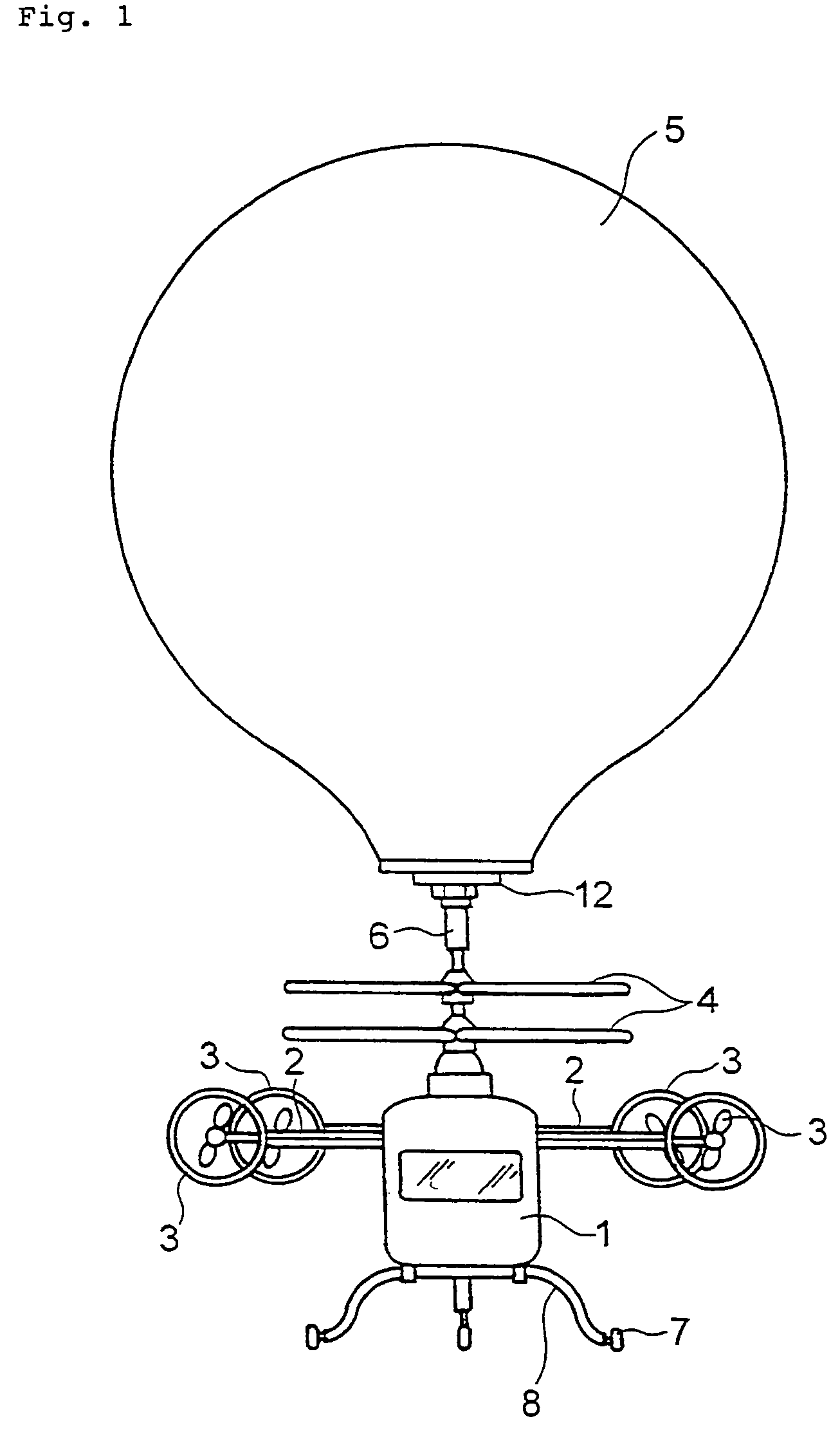
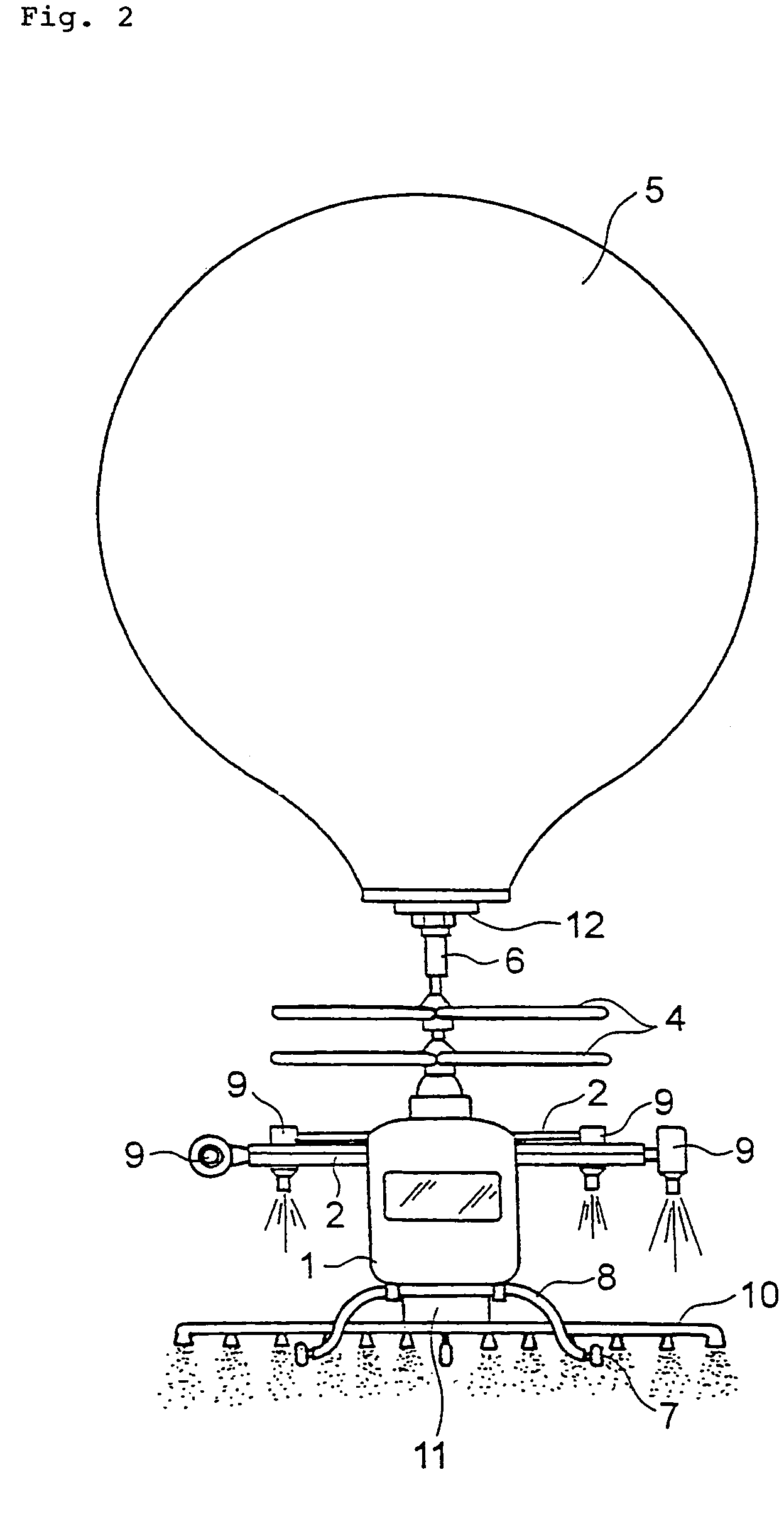
A multi-purpose airship usable for multi-purposes with less maintenance cost is provided. The multi-purpose airship comprises an operator cabin (1) to which a work device of agricultural chemical scattering device (10) or the like is fittable, a rotor (4) fitted to a top of the operator cabin (1) and having rotor blades of plural stages (or coaxial rotors) of which fitting angle (or pitch) is adjustable to generate a lifting force and propulsive force, a balloon (5) detachably fitted to a top of the rotor (4) and filled with gas lighter than air to generate a lifting force, a stabilizing wing (2) elongating horizontally from each side of the operator cabin (1) and a propulsion device (3) comprising a propeller device or jet engine fitted to a distal end of the stabilizing wing (2) to vary a thrust direction between the horizontal direction and the vertical direction.
Owner:BUNDO MUTSURO
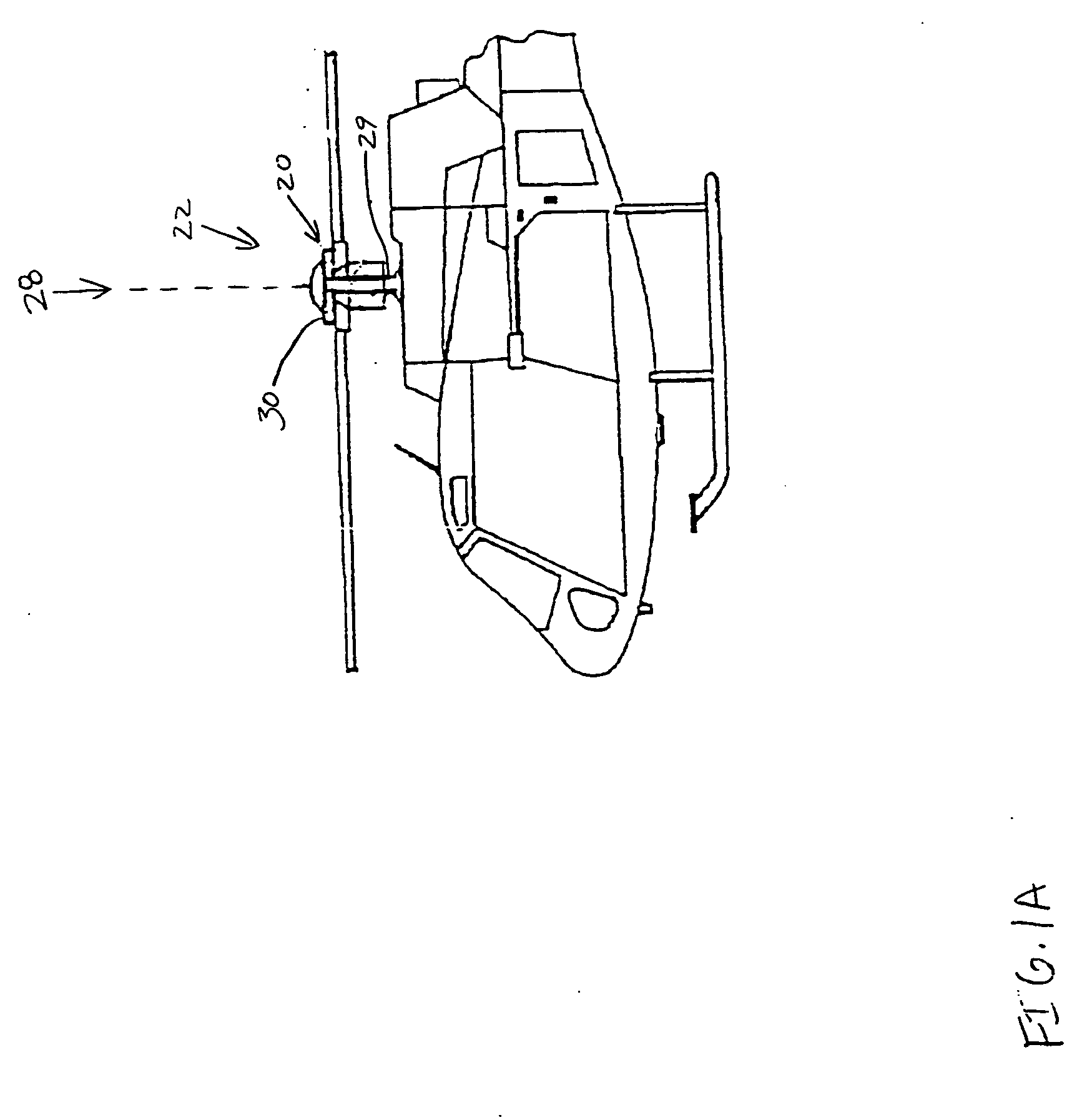
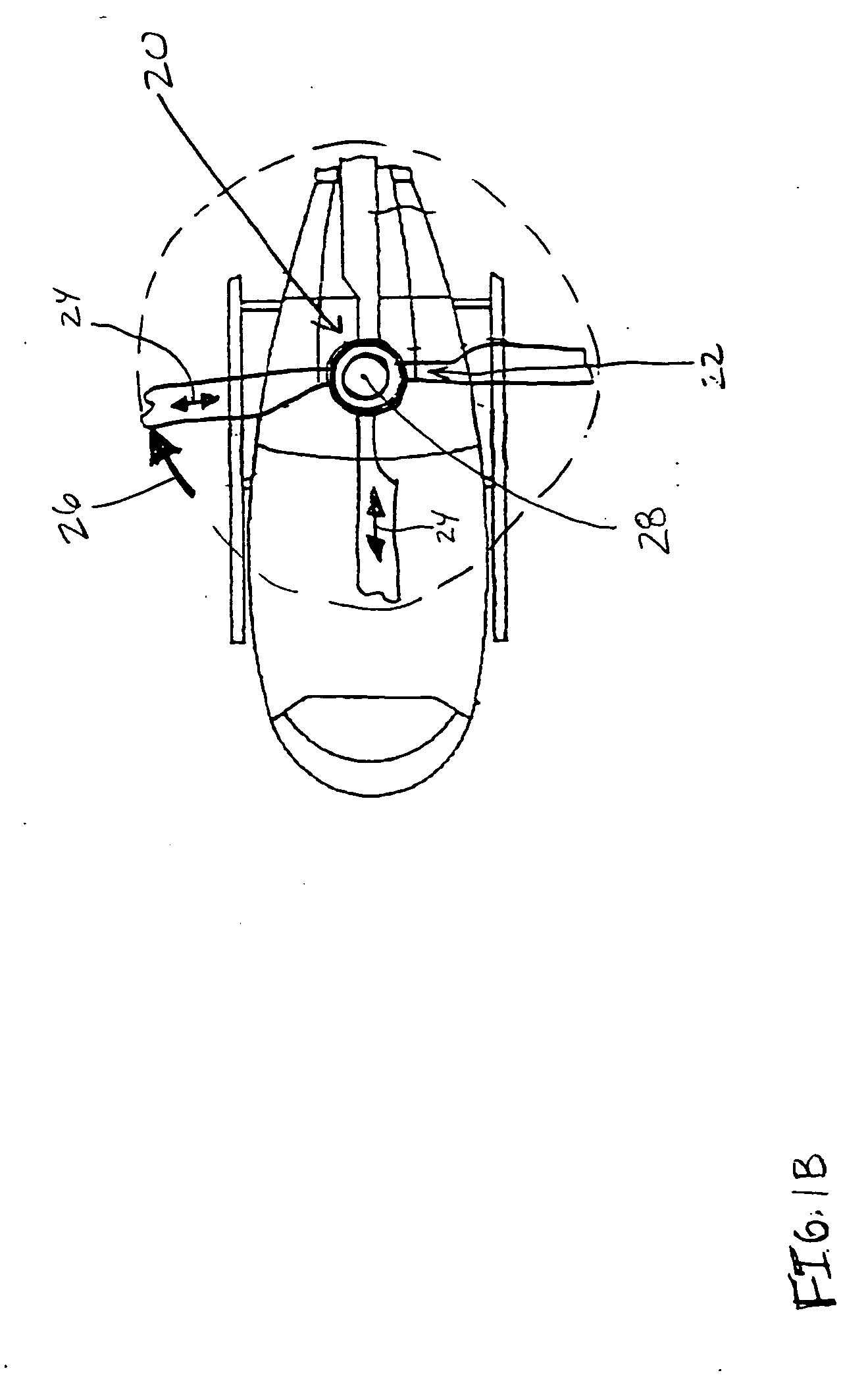
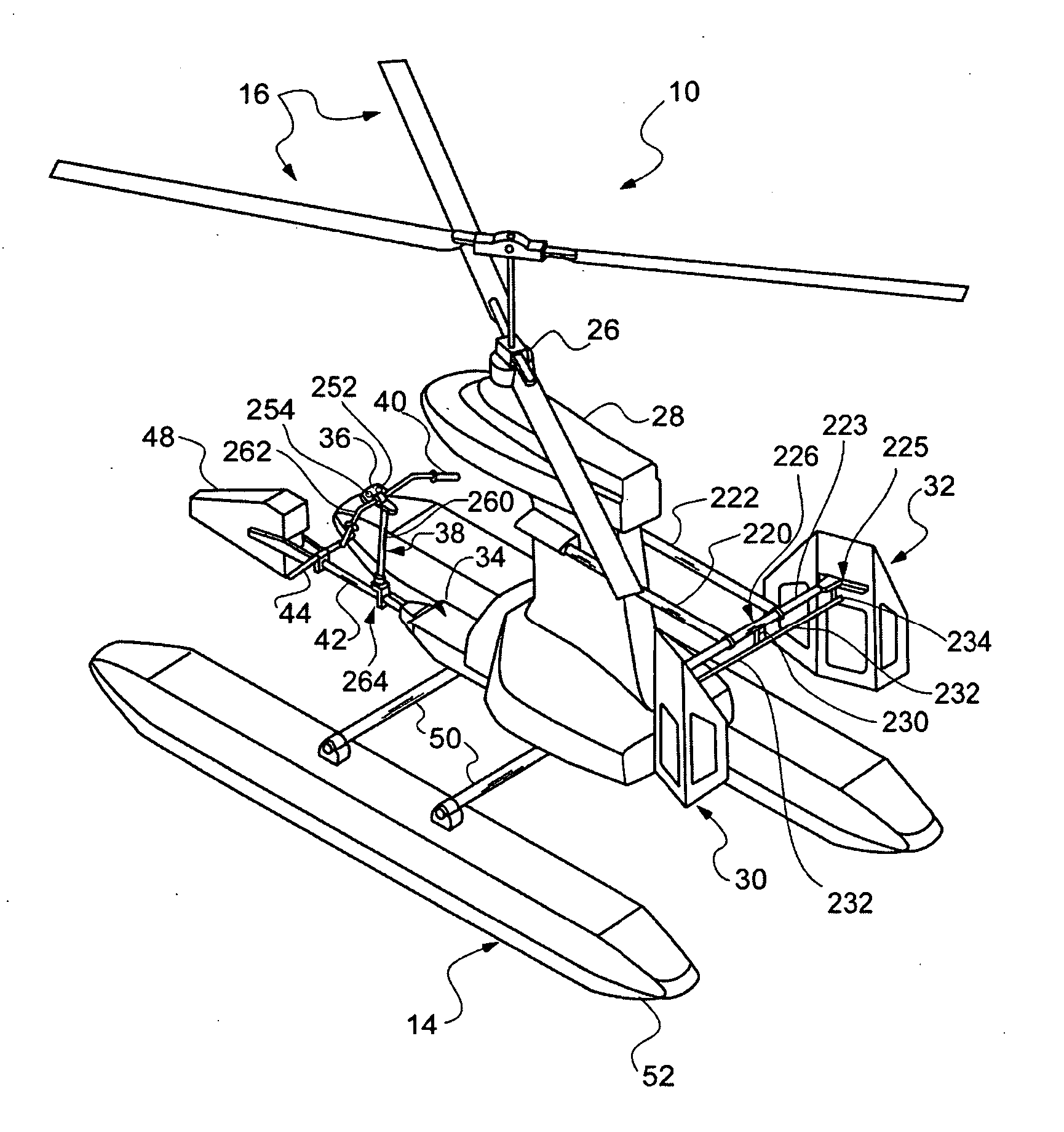
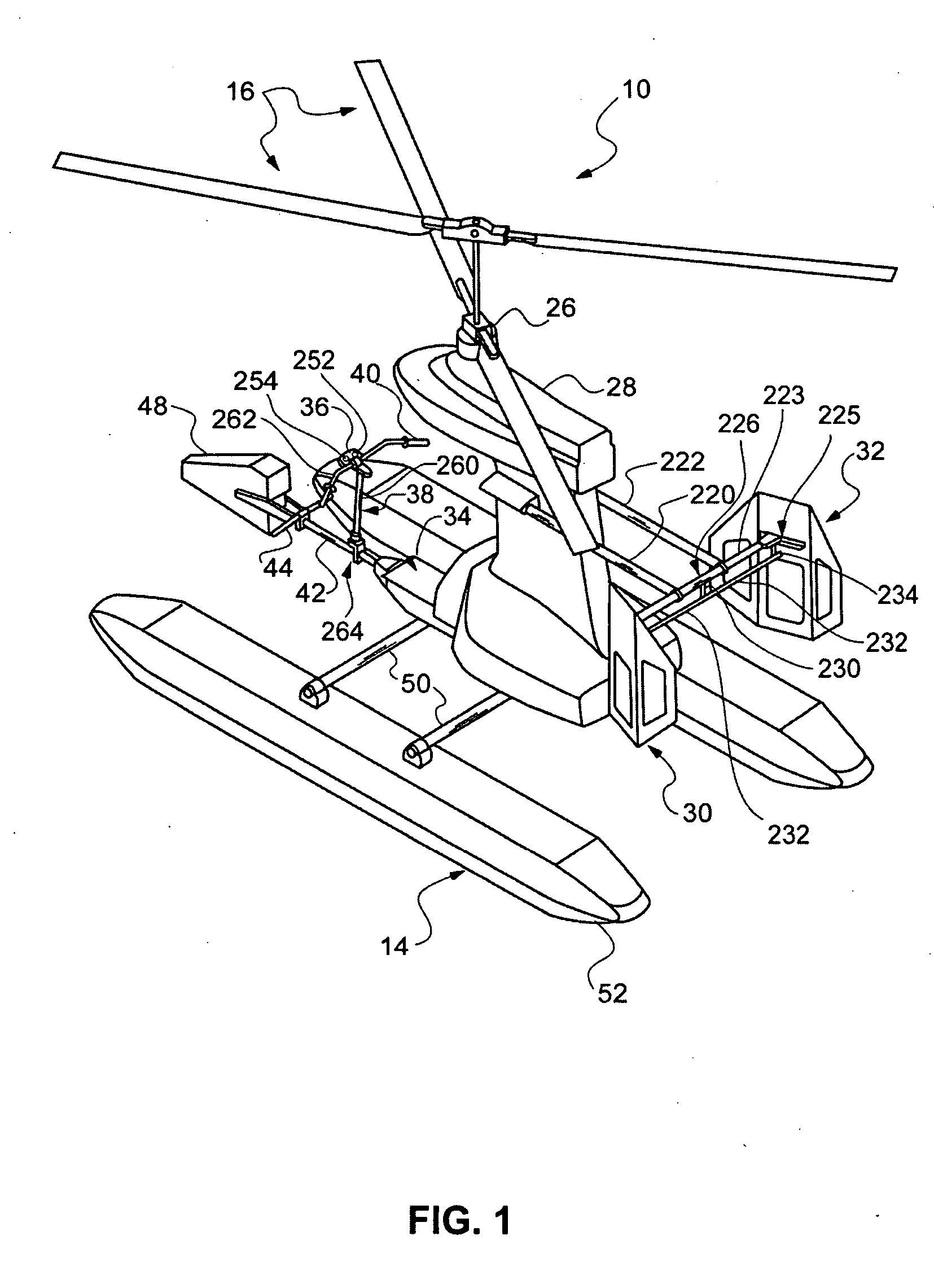
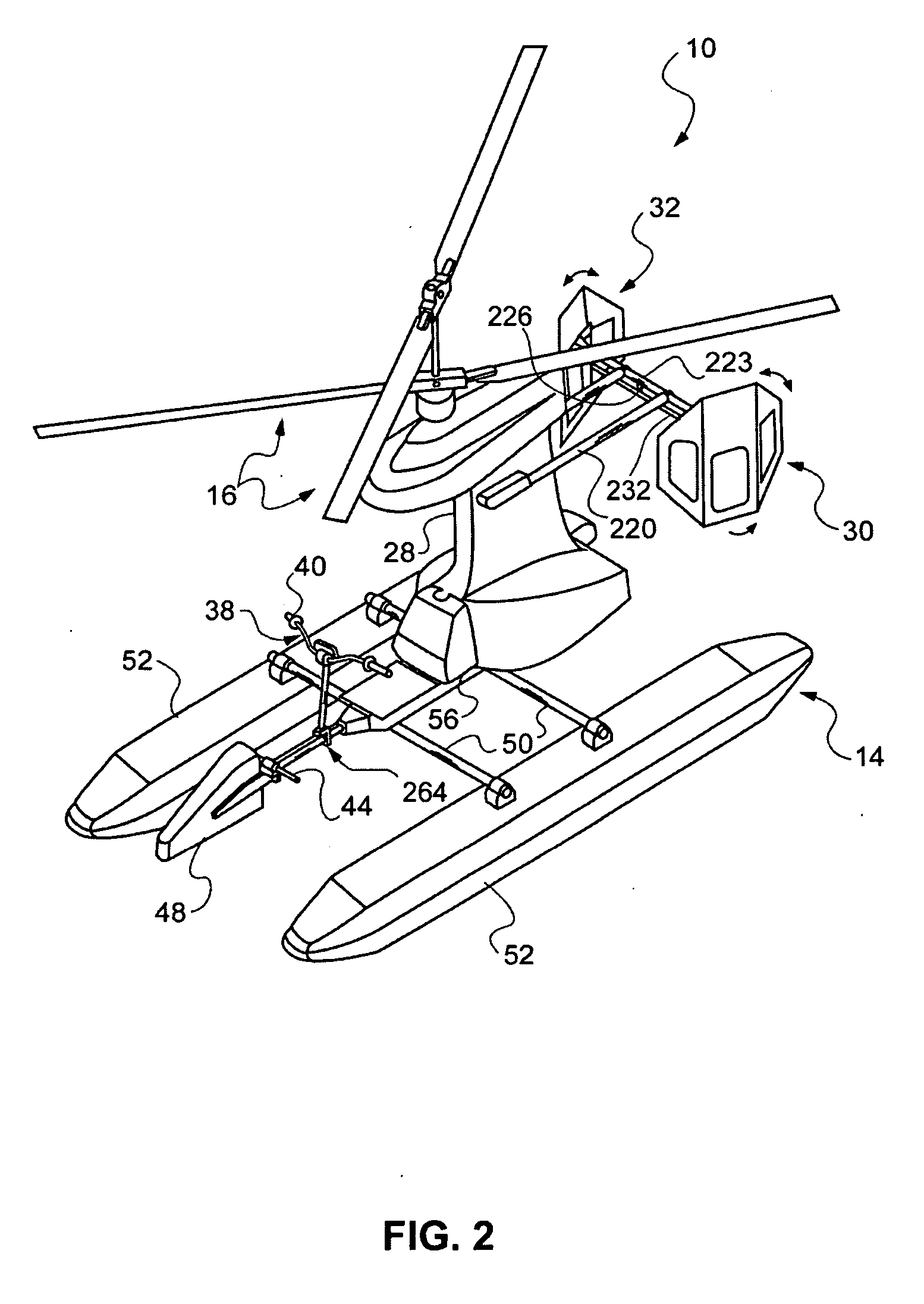
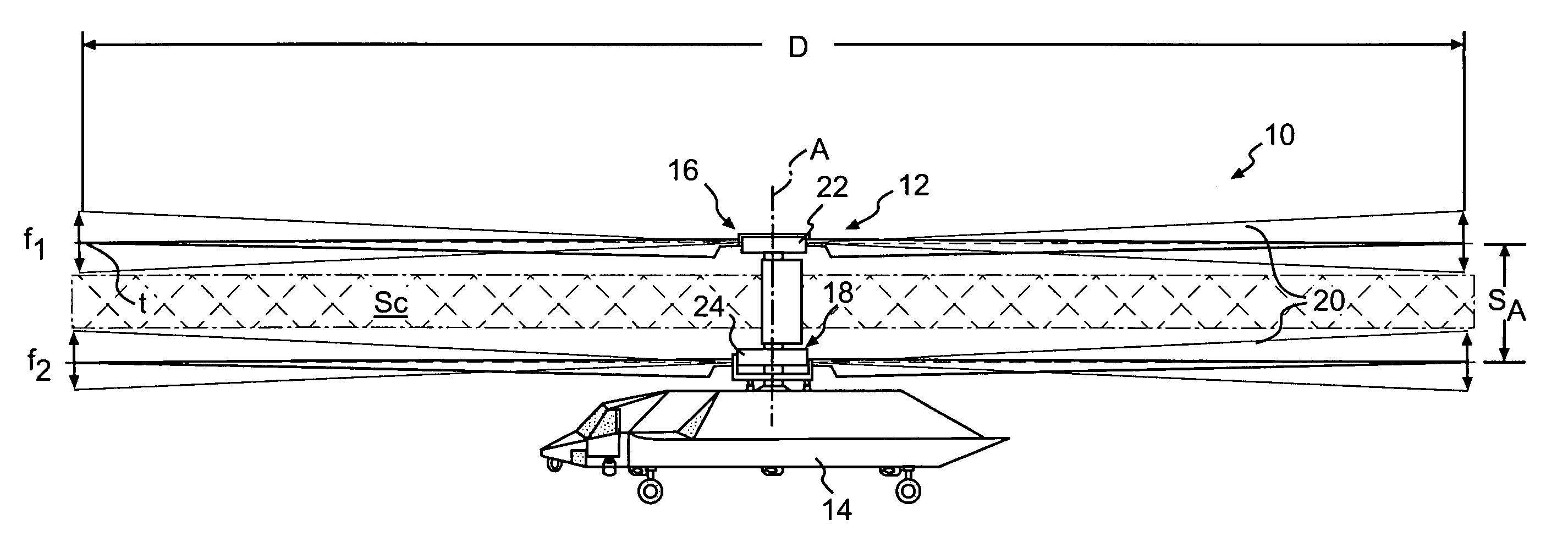
Lightweight helicopter
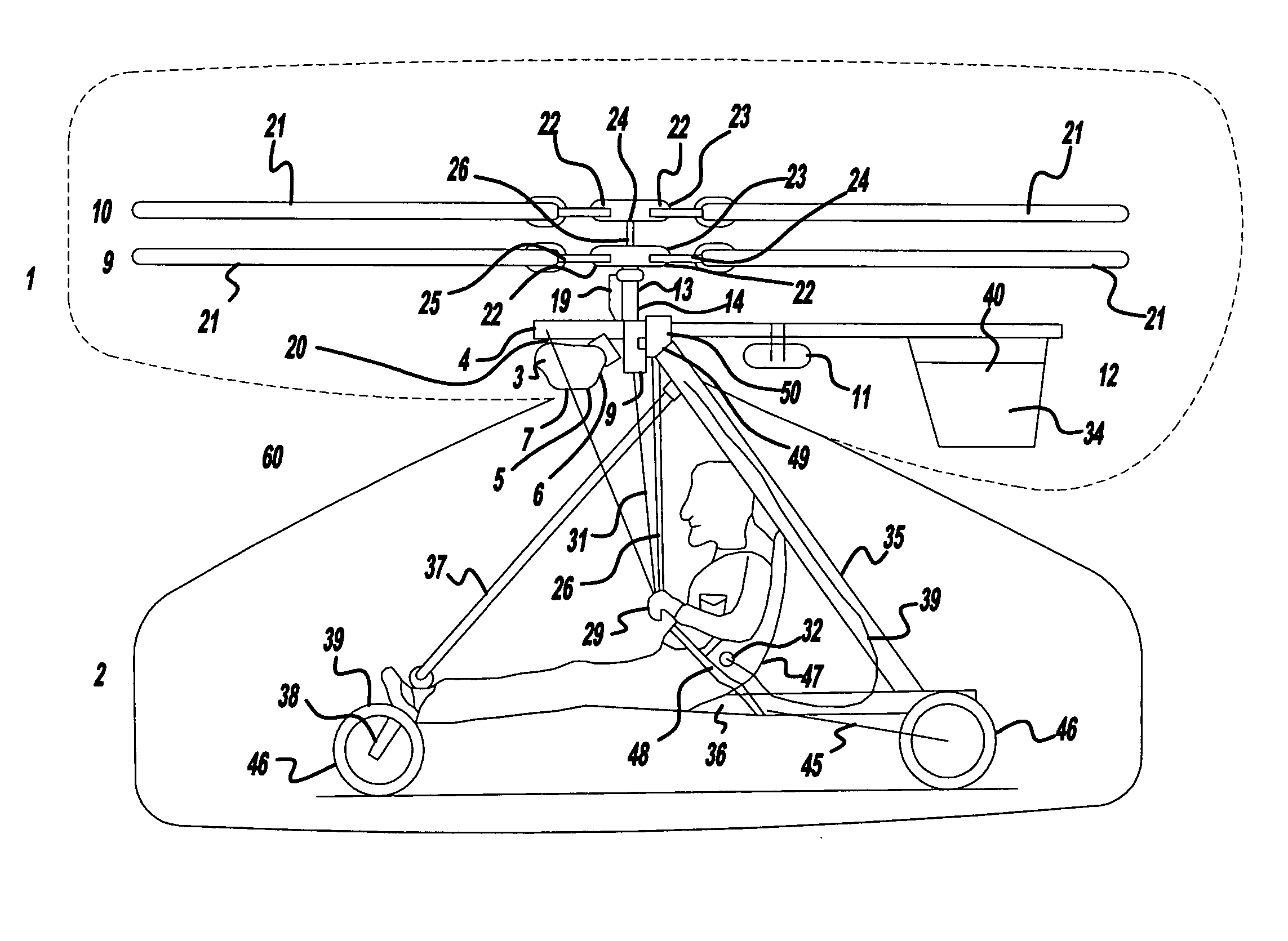
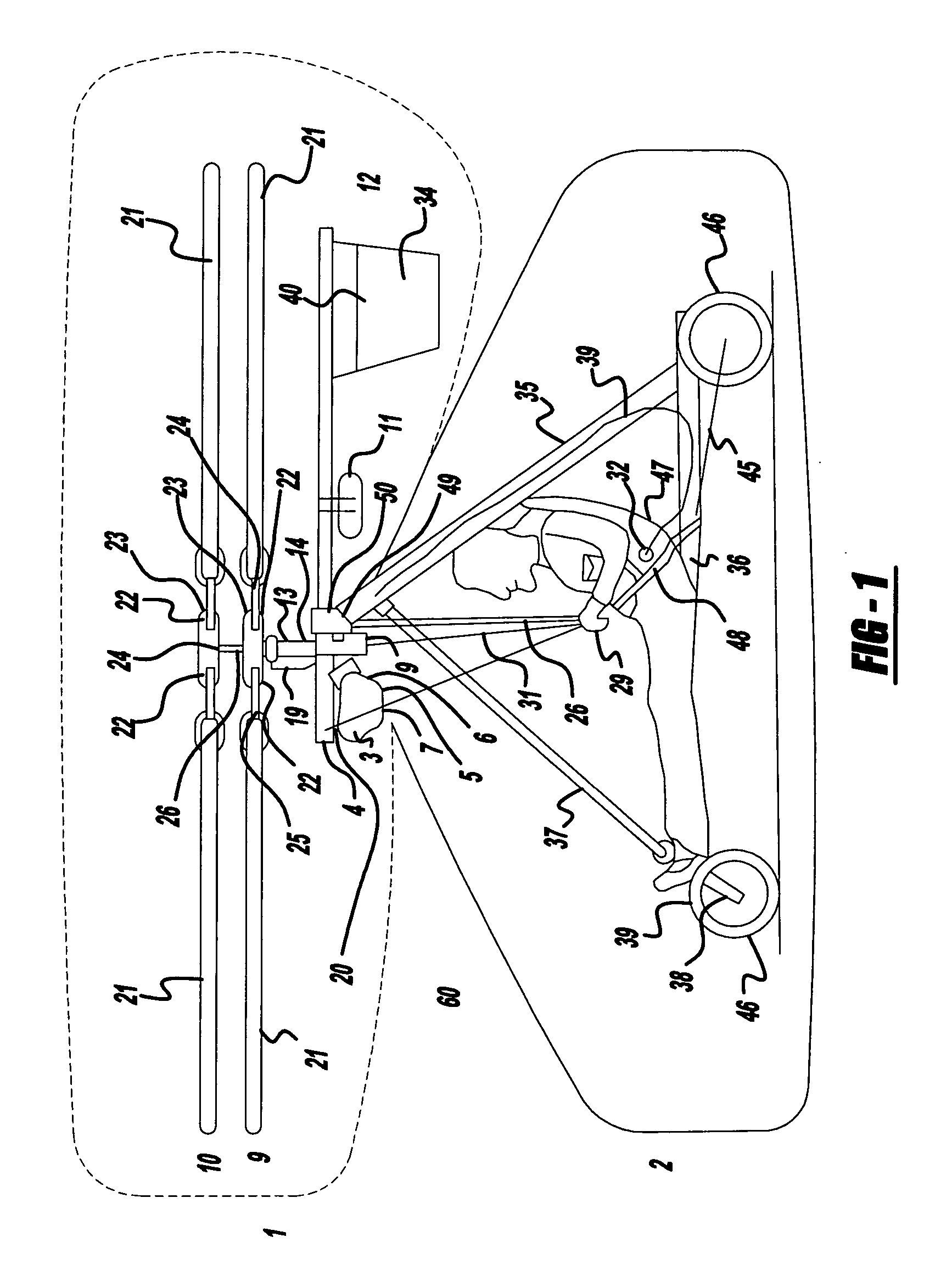
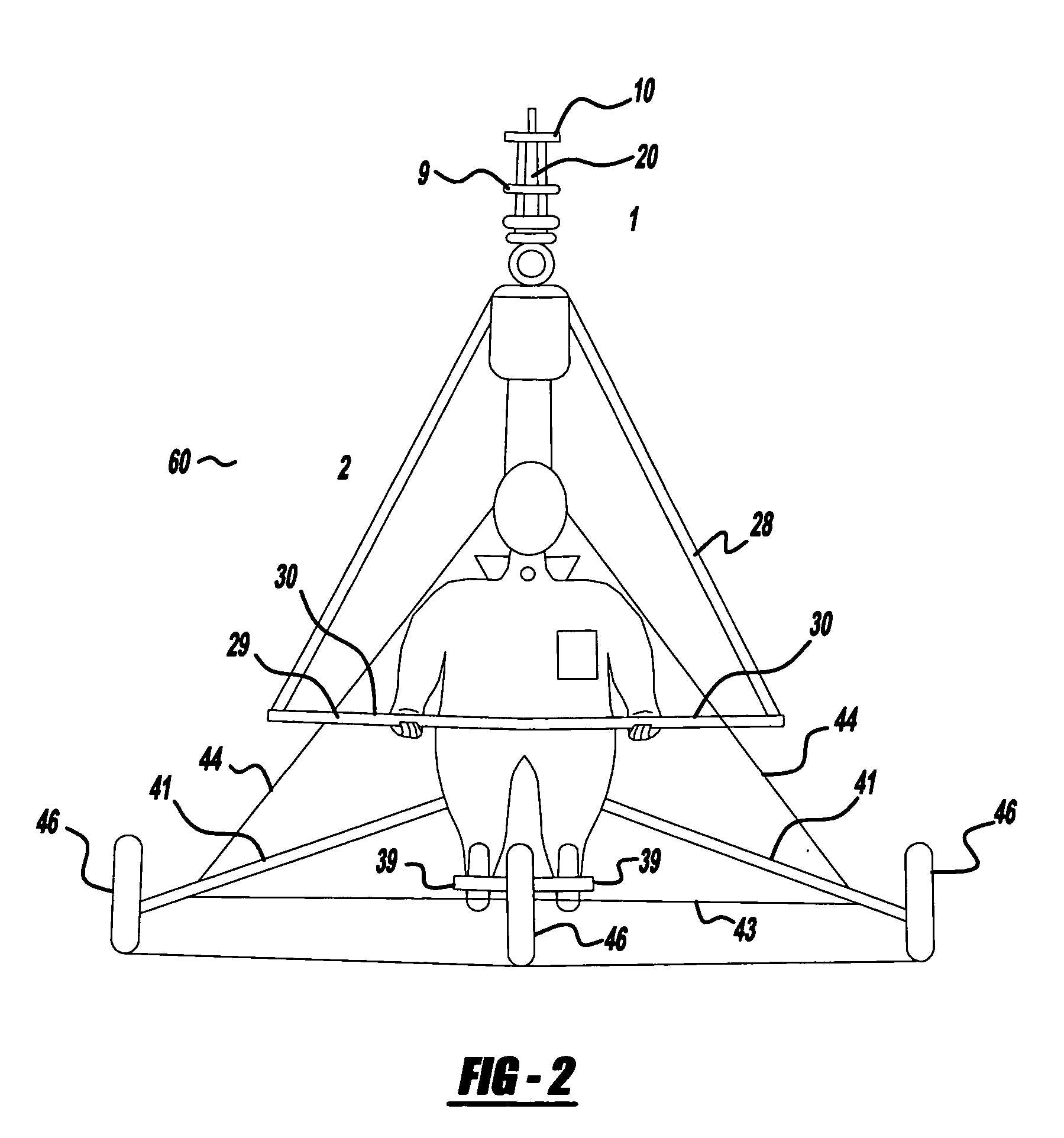
The present invention relates to a lightweight helicopter with features of coaxial, contra-rotating rotors and weight shift control. It has a rotary wing unit attached to a tricycle assembly through a hang bolt. The rotary wing unit has an engine mounted below a keel post, which drives a pair of contra-rotating coaxial rotors through a primary gearbox and a secondary gear box. The keel post is attached to a triangular control frame, the base of which forms the control bar. The keel post also supports a fuel tank connected to the engine and a tail plane having one or more articulated vertical flaps actuated by cables. The secondary gearbox is provided with a free-wheeling clutch, a pinion gear and bevel gears for transmitting the rotary movement of the engine to the counter rotating coaxial vertical shafts each carrying two rotor blades of airfoil cross section fixed by pitch bearing on teetering plates and teetering hinges to form horizontal rotors. The tricycle assembly has a pilot seat and landing gear as well as controls for operation of the engine, rotors, tail plane and landing gear. The directional control of the helicopter is achieved through the weight shift principle by manipulating the control bar, thereby causing a tilt of the contra-rotating rotors, which cause a corresponding tilt in the aerodynamic thrust of the rotors, propelling the helicopter in the required direction.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com