Connecting structure of middle phalanx and proximal phalanx of prosthetic finger
A technology of connecting structure and proximal knuckles, applied in the field of bionic hands, can solve the problems of bending residual deformation of extension springs, prone to failure, not distinguishing between the distal knuckles of fingers and the proximal knuckles of fingers, etc., so as to eliminate the effect of bending moment. , the effect of improving the performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
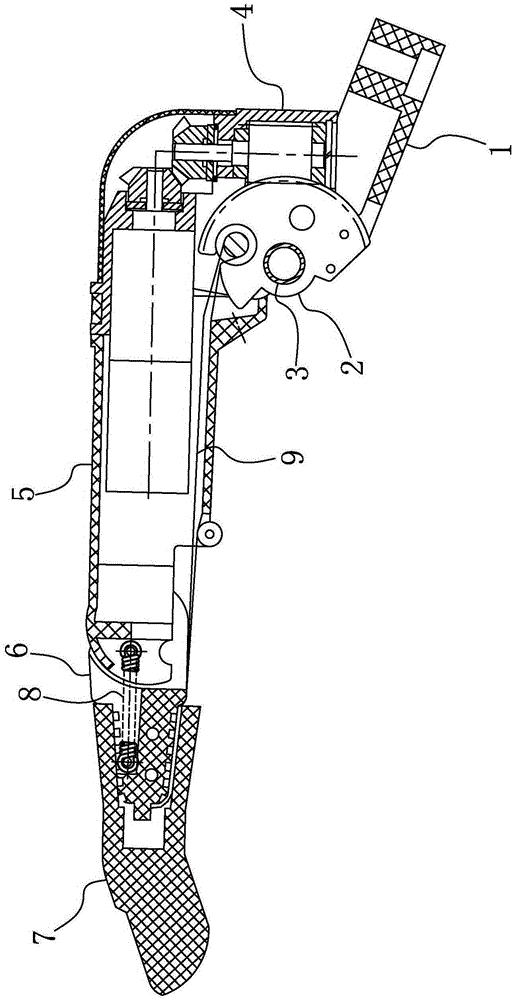
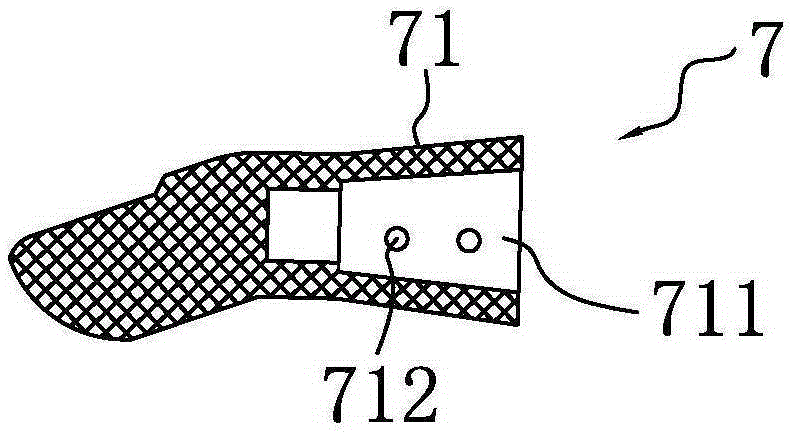
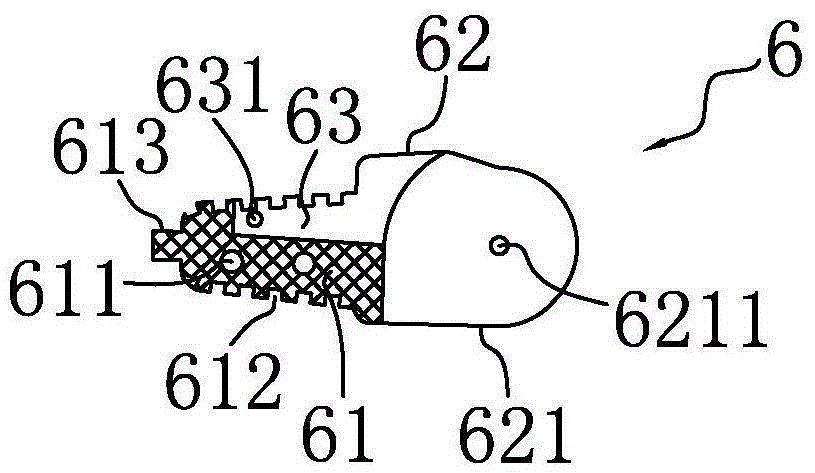
[0037] The structure of the prosthetic hand, the prosthetic finger and the parts thereof according to the embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0038] In order to facilitate an accurate understanding of the description of this embodiment, before proceeding to the description, explain the orientation words mentioned in this embodiment: on the prosthetic finger and specific components, "distal end" refers to the end close to the fingertip, "Proximal end" is opposite to "far end", "proximal end" refers to the end close to the root of the finger (or the base of the finger joint or the palm); "upper", which represents the orientation, refers to the position between the top of the finger and the back of the hand when the finger is straightened. The orientation corresponding to the orientation; the "down" representing the orientation refers to the orientation corresponding to the orientation of the finger a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com