Nonnegative adaptive filter
An adaptive filter and non-negative technology, applied in the direction of adaptive network, impedance network, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of slow convergence speed and poor robustness, achieve strong robustness, and improve the resistance to impulse noise interference Ability, the effect of speeding up the convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
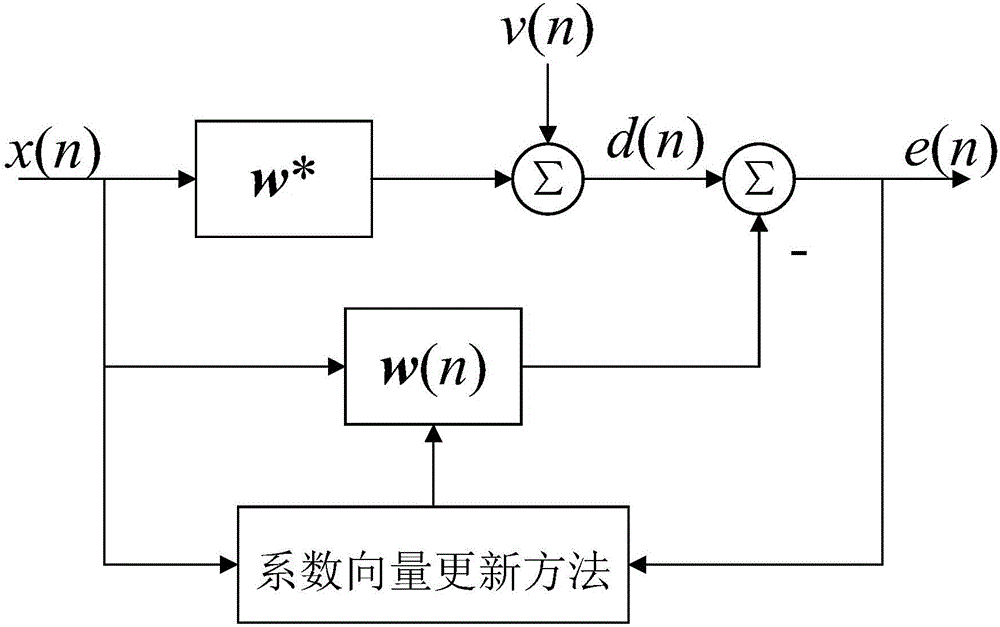
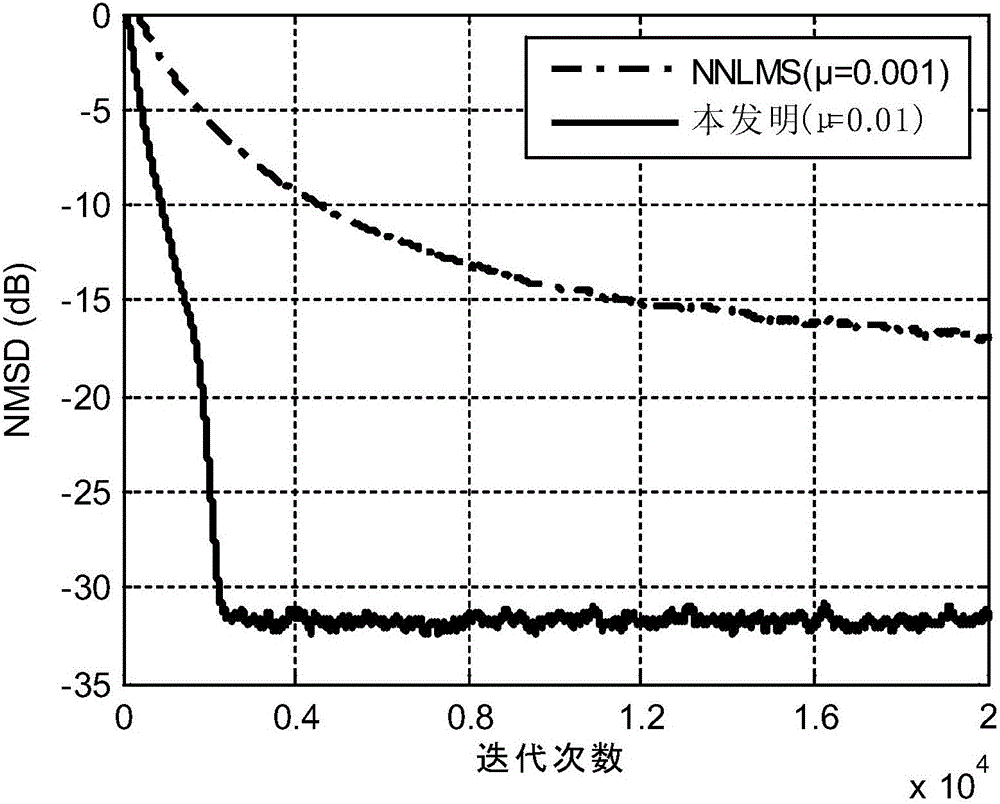
[0021] In this embodiment, a computer experiment method is used to verify the performance of the non-negative adaptive filter. In the experiment, the non-negative adaptive filter disclosed by the present invention is used to identify the unknown sparse system in the environment of impulse noise interference, and its performance is compared with that of the NNLMS adaptive filter. Such as figure 1 As shown, the identification of the unknown sparse system by the non-negative adaptive filter disclosed in the present invention includes the following steps:
[0022] 1) Calculate the error signal e(n) through the input signal x(n) and the expected signal d(n) at time n, that is, e(n)=d(n)-w T (n)x(n), where x(n)=[x(n),x(n-1),…,x(n-M+1)] T is an input vector composed of the first M samples of the input signal {x(n), x(n-1),...,x(n-M+1)}, w(n)=[w 1 (n),w 2 (n),...,w M (n)] T is a coefficient vector formed by M tap coefficients of the non-negative adaptive filter, and T represents...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com