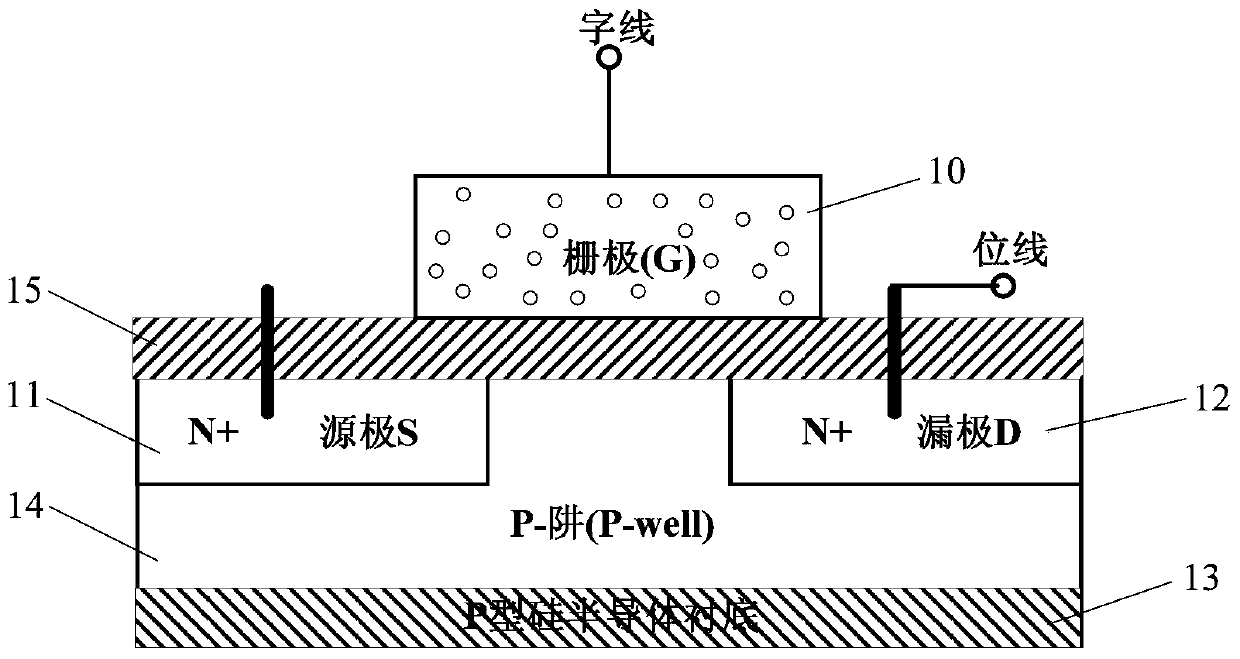
A Replacement Method for Dead Pixel Units in Non-Volatile Memory
A storage unit, non-volatile technology, applied in static memory, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as data reading errors, reducing the service life of non-volatile memory, storage unit threshold voltage drift, etc., to avoid working performance effect of influence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
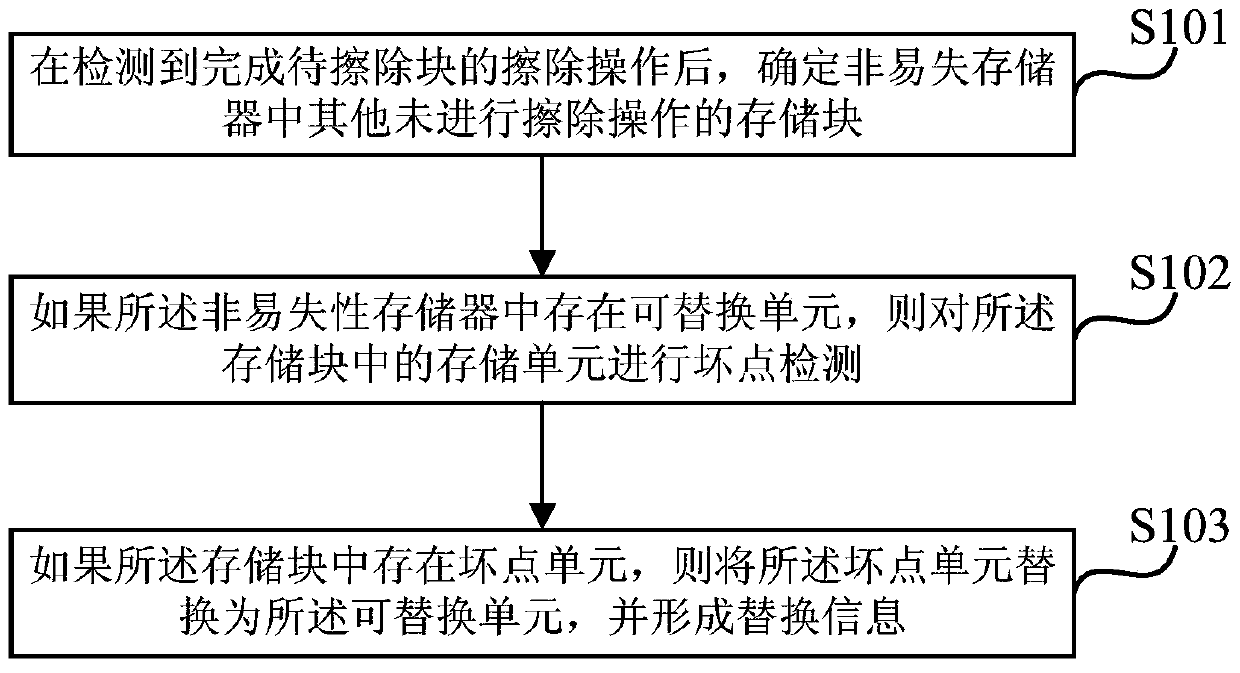
[0041] figure 2 A schematic flow chart of a method for replacing dead cells in a non-volatile memory provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention, as shown in figure 2 As shown, the method for replacing a bad pixel unit in a non-volatile memory provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention specifically includes the following operations:
[0042] It should be noted that, since the programming operation is performed in units of storage pages, and after the programming operation of the current programming page is completed, the programming operation will be performed on the next page to be programmed, and the setting between two adjacent programming operations The time interval is short. If after each programming operation, detection and replacement of bad pixel cells are performed on other memory pages that have not been programmed, and then the programming operation is started on the next page to be programmed, the gap between two adjacent programming operations wil...
Embodiment 2
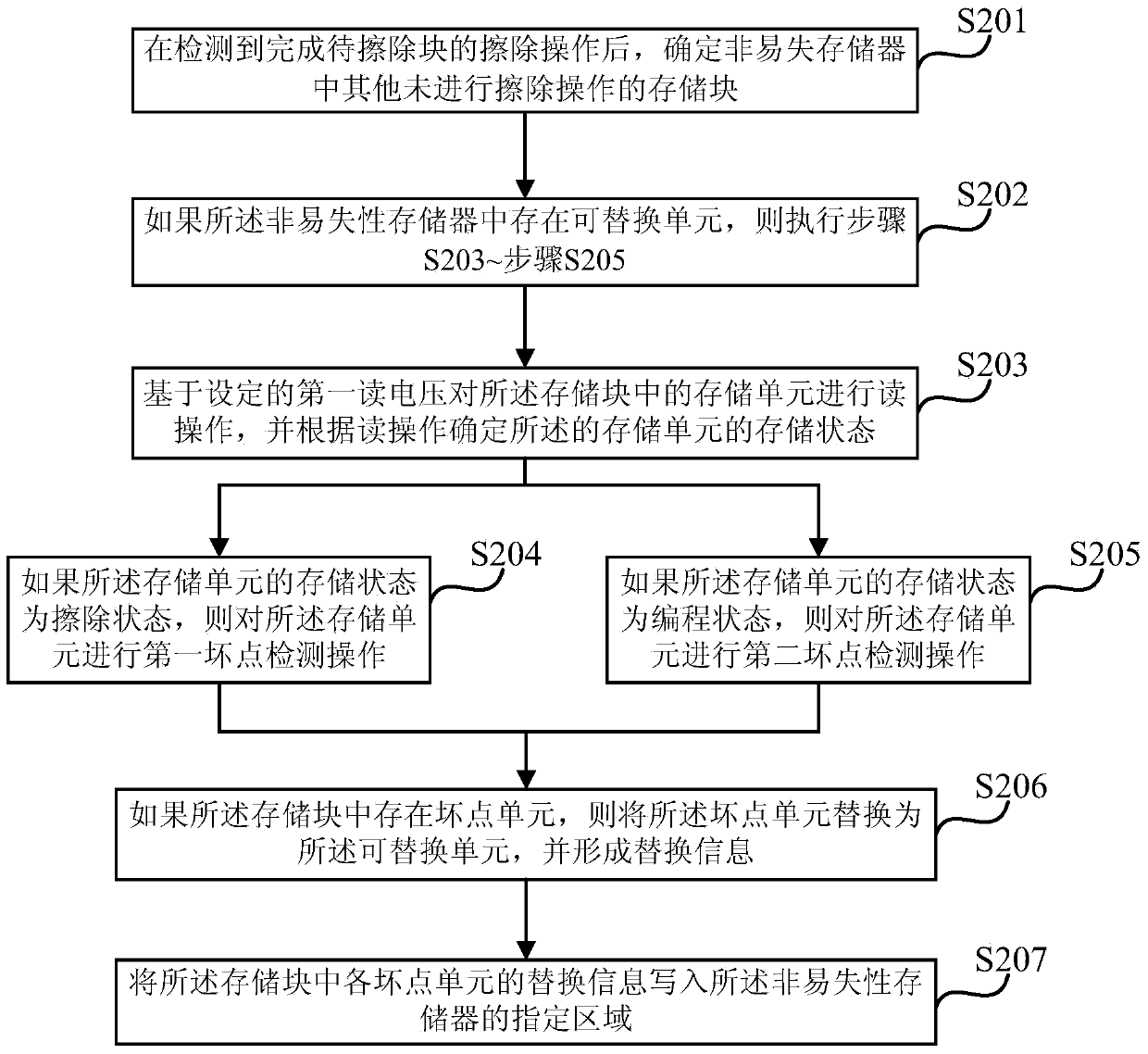
[0054] Figure 3a It is a schematic flow chart of a method for replacing dead cells in a non-volatile memory provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention. Embodiment 2 of the present invention is optimized on the basis of the above embodiments. In this embodiment, the specific optimization of "performing dead point detection on the memory cells in the memory block" is: based on the set first read voltage, the Perform a read operation on the storage unit in the storage block, and determine the storage state of the storage unit according to the read operation; if the storage state of the storage unit is an erased state, then perform the first dead point detection on the storage unit Operation: if the storage state of the storage unit is a programming state, perform a second dead point detection operation on the storage unit.
[0055] Further, in the second embodiment of the present invention, after the formation of the replacement information, an optimization is added: wri...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Figure 4 It is a schematic flowchart of a method for replacing dead cells in a non-volatile memory provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Embodiment 3 of the present invention is optimized on the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments. In this embodiment, if there is a replaceable unit in the non-volatile memory, perform a dead point on the storage unit in the storage block. Before the detection, the optimization also includes: detecting the enabling flag bit of the redundant unit in the free area of the non-volatile memory; determining whether there is a redundant unit whose enabling flag bit is 0, and if there is, determining the There is a replaceable unit in the non-volatile memory; if not, it is determined that there is no replaceable unit in the non-volatile memory.
[0089] On the basis of the above optimization, the replacement of the bad pixel unit with the replaceable unit, and forming replacement information, is specifically optimized as fol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com