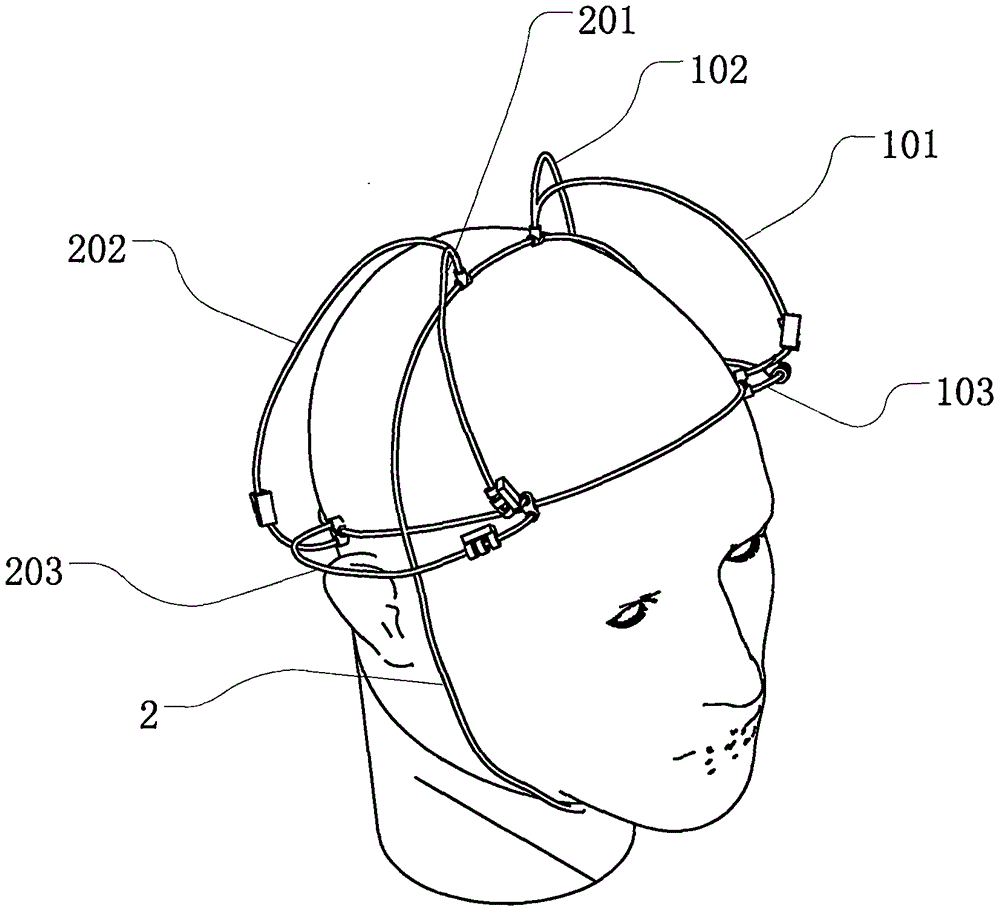
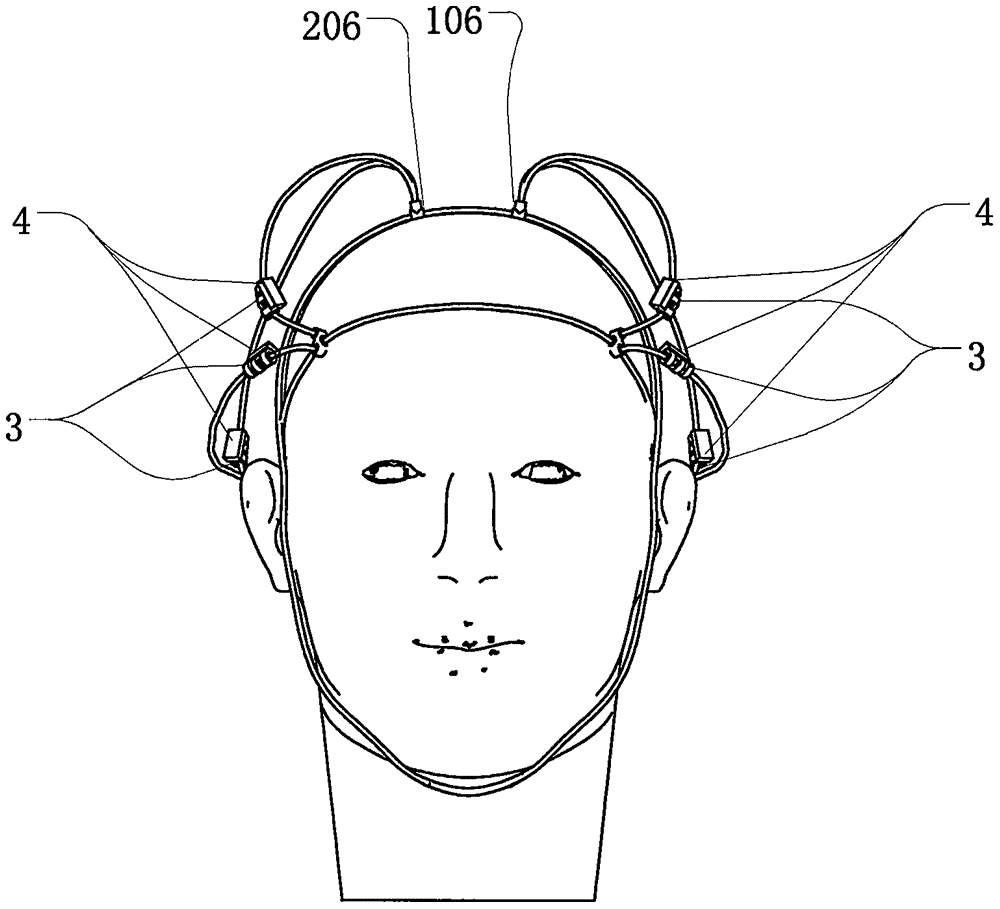
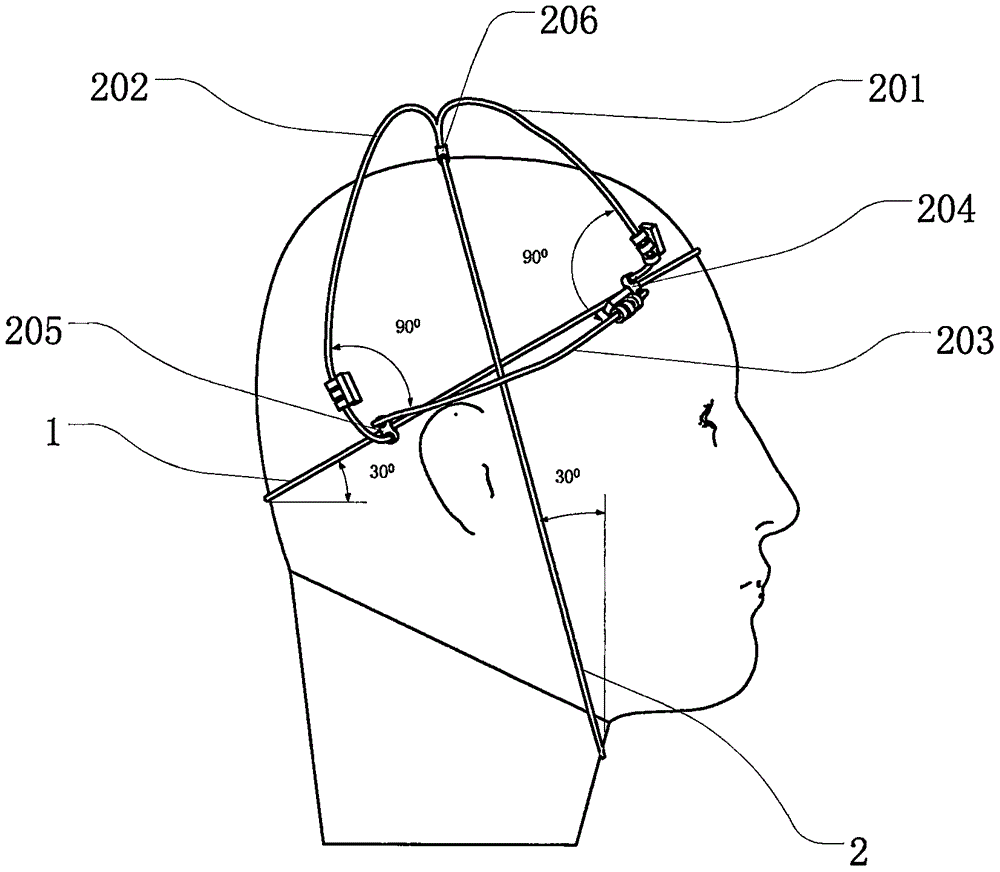
Simulation semicircular canal otolith total head model
A technology of semicircular canal and head model, which is applied in the field of simulating the whole head model of semicircular canal otolith, which can solve the problems of lack of comprehensiveness in otolith simulation and inability to simulate bilateral otolith flow.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] Example 1: Simulated Dix-Hallpike provocation test and Epley repositioning treatment.
[0081] Dix-Hallpike induced test: magnets were used to attract and fix the other simulated otoliths except the simulated otolith of the right posterior semicircular canal ring, so that the simulated otolith of the right posterior semicircular canal ring could slide freely. Place the human head model in the center and simulate the patient's sitting position. The artificial otolith of the right posterior semicircular canal ring is located at the ampullary end at the bottom of the right posterior semicircular canal ring, then rotate the human head model 45° to the right, and then lie back to the deepest position. Suspend the head so that the human head model and the ground are at about 30°. At this time, the simulated otolith moves away from the ampulla end and flows to the lowest point of the right posterior semicircular canal ring under the action of its own gravity, resulting in chara...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Embodiment 2: Simulation Roll test induces test and BBQ reset treatment
[0084] Roll test induction test: magnets were used to attract and fix other artificial otoliths except the artificial otolith of the right horizontal semicircular canal ring. Allow the simulated otoliths of the right horizontal semicircular canal ring to slide freely. Place the human head model in the middle of the simulated patient's sitting position, and the artificial otolith of the right horizontal semicircular canal ring is located on the bottom foot of the horizontal semicircular canal ring, then lie the human head model down to simulate the patient's supine position, and raise the head and the horizontal plane at an angle of about 30° At this time, turn the human head model 90° to the right to simulate the right turn of the patient's head. At this time, the artificial otolith flows to the lowest point of the right horizontal semicircular canal ring under the action of its own gravity, causi...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Example 3: Simulated side-lying induction test and semont repositioning treatment
[0087] Side-lying induction test: magnets were used to attract and immobilize other artificial otoliths except the artificial otolith of the right posterior semicircular canal ring. The simulated otolith of the right posterior canal ring was allowed to slide freely. Place the human head model in the middle of the simulated patient's sitting position, and the artificial otolith of the right posterior semicircular canal ring is located at the bottom ampullary end, then rotate the human head model 45° to the left, and then lay the human head model to the right to simulate the right side of the patient In the supine position, the simulated otolith of the right posterior semicircular canal ring moves away from the ampulla under the action of its own gravity and slides to the lowest point of the right posterior semicircular canal ring, resulting in characteristic nystagmus. The left posterior...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com