Starch-based modified composite material for 3D printing
A composite material, 3D printing technology, applied in the field of 3D printing, can solve problems such as affecting printing efficiency and printing accuracy, affecting the quality of printed products, poor fluidity of powder materials, etc., to improve printing efficiency, low cost, and easy bonding. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
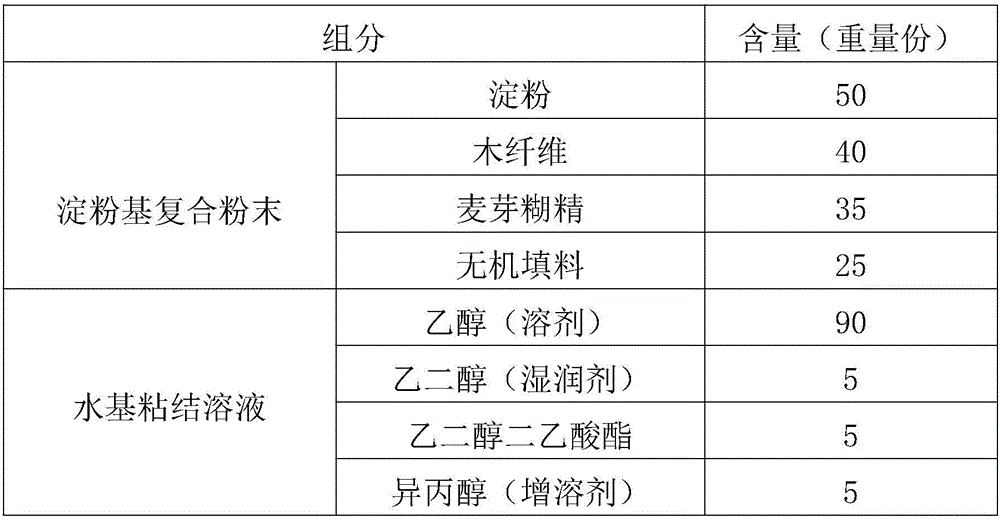
[0026] A modified material is disclosed in Example 1, and its formula is shown in Table 1.
[0027] Formulation table in table 1 embodiment 1
[0028]
[0029] In Example 1, the preparation method of the above-mentioned modified starch: mix water, modifier, and starch evenly, adjust the pH to an alkaline environment with sodium hydroxide, react at 45° C. for 10 h, and collect the starch solid after the reaction is completed; Then add alcohol and catalyst to the solid, reflux at 60-90° C. for 45 hours, collect the solid after the reaction, and then dry to obtain the modified starch, which is ready for use.
[0030] The above-mentioned modified starch is passed through a 200-400 mesh sieve, the above-mentioned wood fiber is crushed and passed through a 200-mesh sieve, and the above-mentioned wood fiber is soaked in a mixed solution of lithium chloride and dimethylformamide for 40 minutes at a temperature of 30-40°C. dry.
[0031] Specifically, the modifier mentioned above m...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The material formulation in Example 2 is shown in Table 2.
[0038] Formulation table in table 2 embodiment 2
[0039]
Embodiment 3
[0041] The material formulation in Example 3 is shown in Table 3.
[0042] Formulation table in table 3 embodiment 3
[0043]
[0044] The starch modification method in embodiment 2-3 is the same as embodiment 1, and the selection of other components is also the same as embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com