RAID model, data reading and writing and reconstruction method thereof
A technology for data reading and writing, data writing, applied in electrical digital data processing, data processing input/output process, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as matching failure to adapt, write amplification, and inability to efficiently cooperate with I/O. , to achieve high I/O efficiency and improve performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
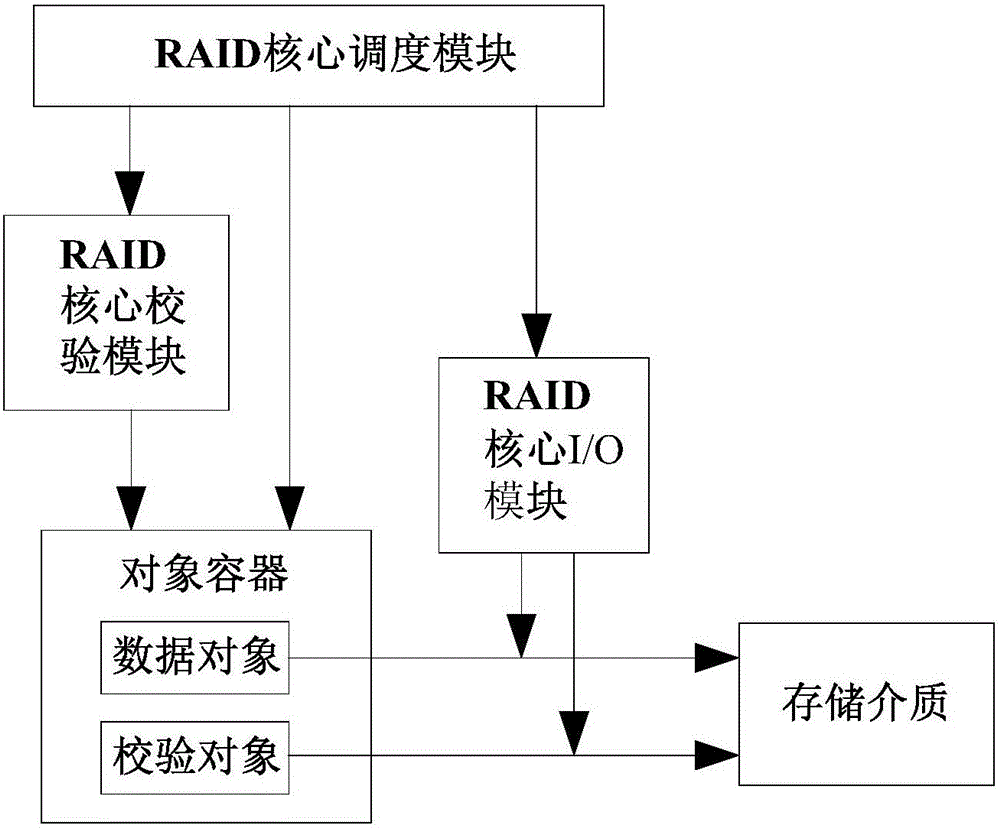
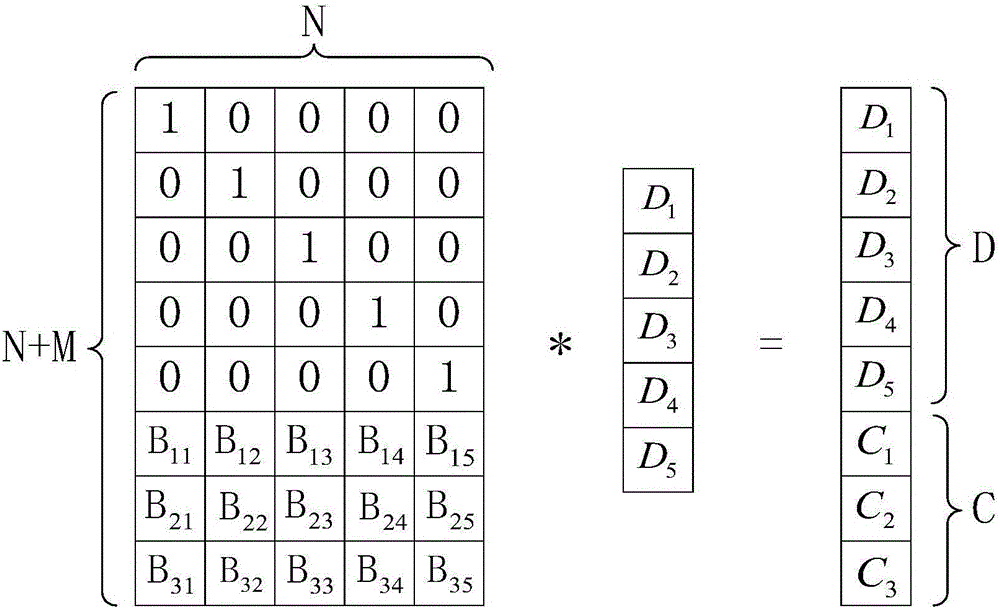
[0052] The present invention provides a RAID model of a novel storage mode, such as figure 1 As shown, the RAID model includes: a RAID core check module, which adopts an Erasure code check algorithm based on Vandermonde matrix RS encoding; the Erasurecode check algorithm supports N data blocks to generate M check data, and the RAID core schedules module, which is used to uniformly schedule all the data read and write operations of the RAID model; the RAID core scheduling module selects N correct data blocks through a scheduling algorithm, and calculates corresponding M school data blocks through the RAID core verification module and, the RAID core I / O module, which is used to perform RAID data read and write operations; the RAID core scheduling module schedules the RAID core I / O module to write the N correct data blocks and corresponding After the M verification data are successfully written, the RAID core scheduling module sends a notification that N correct data blocks are s...
Embodiment approach 2
[0059] On the basis of Embodiment 1, the present invention provides a data reading and writing method of a RAID model, comprising steps: the RAID core scheduling module uniformly schedules the write operations of all data of the RAID model, such as image 3 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0060] S10, the RAID core scheduling module creates object containers to accommodate all data; the RAID core scheduling module marks the object containers one by one;
[0061] S11, the RAID core scheduling provides a data writing interface for additional writing, and the user writes the data block into the data object through the data writing interface; the RAID core scheduling module schedules the RAID core verification module to perform verification calculation on the data block in the data object, The corresponding test data is obtained and stored in the test object;
[0062] S12, the RAID core scheduling module schedules the RAID core I / O module, and writes the data block ...
Embodiment approach 3
[0073] On the basis of Embodiment 2, the present invention provides a method for rebuilding a RAID model, such as Figure 5 shown, including the following steps:
[0074] S30, during the data writing process, define the data blocks and check data written into the storage medium as valid data; mark the storage space occupied by the valid data as allocated space, and mark other storage spaces as unallocated space, then, All data in the unallocated space and valid data in the allocated space are marked as invalid data after being actively deleted by the user;
[0075] S31, during the data writing process, the RAID core scheduling module establishes a query table of the corresponding relationship between the object container and the storage space of the storage medium;
[0076] S32, during data reconstruction, the RAID core scheduling module queries and judges all valid data to determine whether it is lost; if valid data is lost, then determine which object containers the lost va...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com