Scooter for the disabled
A technology of scooter and support mechanism, which is applied in the direction of motor vehicles, bicycles, transportation and packaging, etc. It can solve the problems of leg muscle atrophy, provide exercise function, and cannot be used for users, and achieve safe and stable operation, simple operation, and design ingenious effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The objects and functions of the present invention and methods for achieving the objects and functions will be clarified by referring to the exemplary embodiments. However, the present invention is not limited to the exemplary embodiments disclosed below; it can be implemented in various forms. The essence of the description is only to help those skilled in the relevant art comprehensively understand the specific details of the present invention.
[0022] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings. In the drawings, the same reference numerals represent the same or similar components, or the same or similar steps.
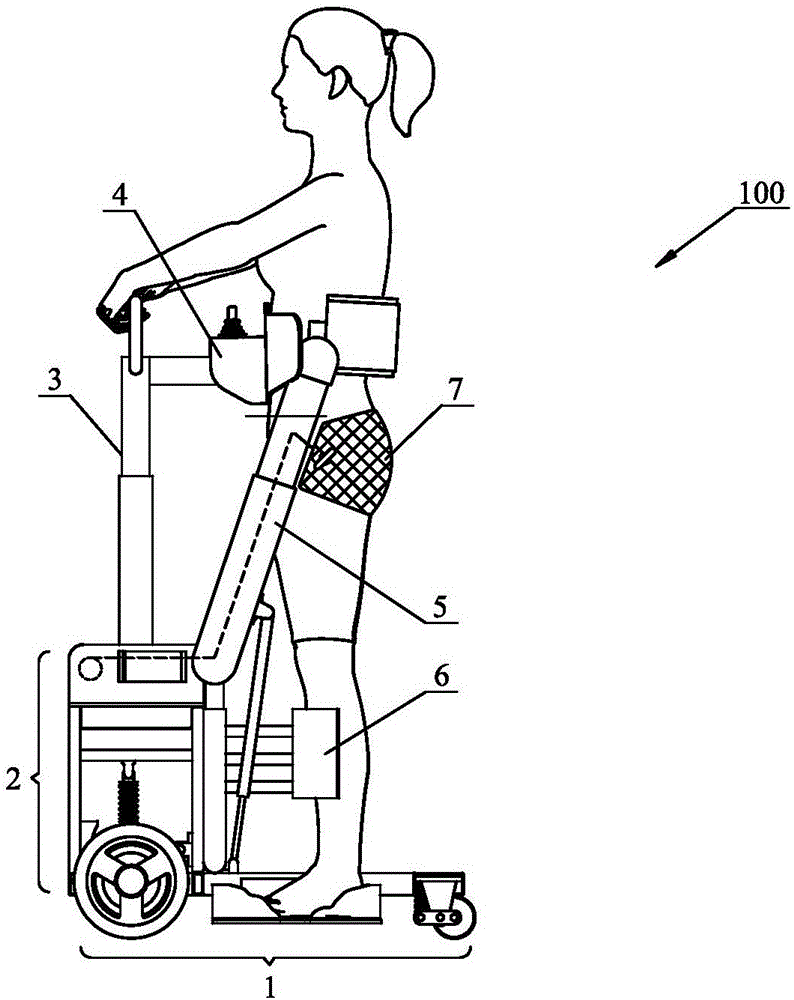
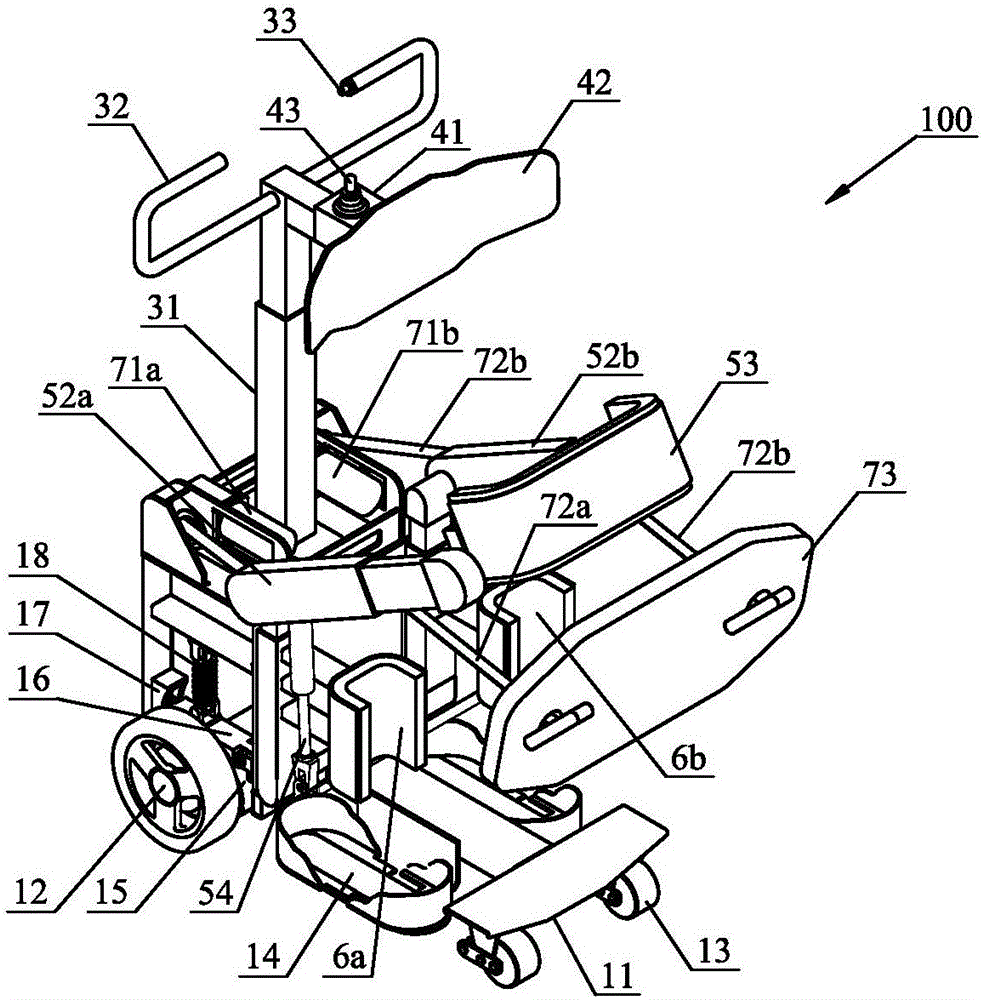
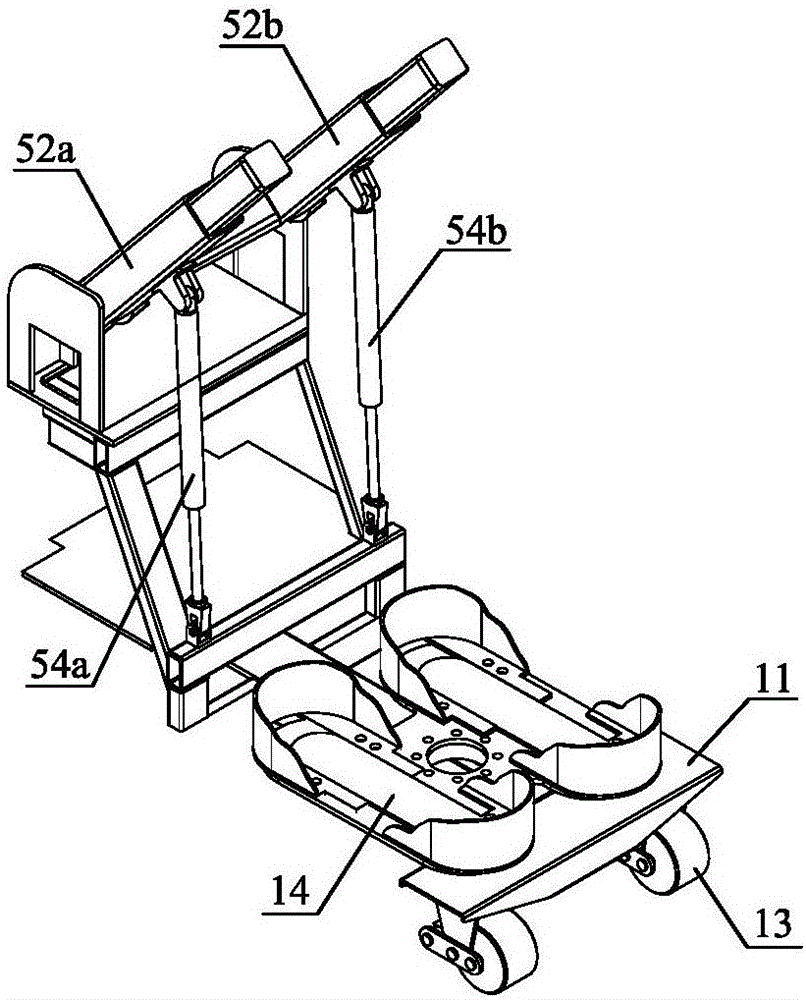
[0023] figure 1 with figure 2 A schematic diagram and a three-dimensional structure diagram of a walking vehicle 100 for disabled persons according to the present invention are shown respectively during driving. The scooter 100 of the present invention comprises: a chassis walking mecha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com