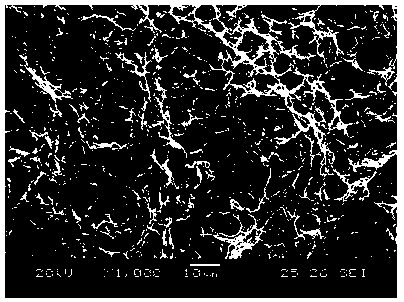
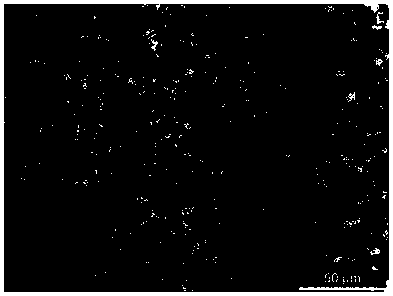
High-strength toughness non-quenched and tempered steel wire rod and its preparation method
A non-quenched and tempered steel, high-strength and toughness technology, applied in the field of high-strength and toughness non-quenched and tempered steel wire rod and its preparation, can solve the problems of low impact toughness, complicated process, increased cost, etc., achieve high impact toughness, reduce banding Segregation, the effect of reducing manufacturing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: The high-strength toughness non-quenched and tempered steel wire rod is prepared by the following method.
[0023] (1) Smelting and continuous casting process: molten steel is smelted and continuously cast into slabs, the composition of which is by weight percentage: C 0.29%, Mn 1.48%, Si 0.55%, P 0.011%, S 0.010%, Cr 0.18%, V 0.05 %, Ti 0.025%, N 0.018%, Al 0.023%, Cu 0.05%, Ni 0.02%, Mo 0.01%, and the rest are iron and unavoidable impurity elements.
[0024] (2) Heating process: heat the billet in a heating furnace, the heating temperature is 1160°C, the residual oxygen content is 0.5%, and the time in the furnace is 100min.
[0025] (3) Rolling process: the steel billet is rolled into wire rod at high speed, the temperature for finishing rolling is 820°C, and the coiling temperature is 800°C.
[0026] (4) Cooling process: the wire rod enters the cooling roller table, and is first cooled to 650°C at a rate of 4°C / s, and then cooled at a rate of 1.5°C / s.
...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2: The high-strength toughness non-quenched and tempered steel wire rod is prepared by the following method.
[0029] (1) Smelting and continuous casting process: molten steel is smelted and continuously cast into steel slabs, its composition by weight percentage is: C 0.27%, Mn 1.35%, Si 0.49%, P 0.008%, S 0.005%, Cr 0.15%, V 0.10 %, Ti 0.030%, N 0.012%, Al 0.050%, Cu 0.05%, Ni 0.02%, Mo 0.03%, and the rest are iron and unavoidable impurity elements.
[0030] (2) Heating process: heat the billet in a heating furnace, the heating temperature is 1140°C, the residual oxygen content is 0.8%, and the time in the furnace is 100min.
[0031] (3) Rolling process: the steel billet is rolled into wire rod at high speed, the temperature for finishing rolling is 810°C, and the coiling temperature is 810°C.
[0032] (4) Cooling process: The wire rod enters the cooling roller table, and is cooled to 600°C at a speed of 5°C / s, and then cooled at a speed of 2.5°C / s.
[0033]...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3: The high-strength toughness non-quenched and tempered steel wire rod is prepared by the following method.
[0035] (1) Smelting and continuous casting process: molten steel is smelted and continuously cast into steel slabs, its composition by weight percentage is: C 0.31%, Mn 1.20%, Si 0.25%, P 0.010%, S 0.015%, Cr 0.10%, V 0.13 %, Ti 0.010%, N 0.010%, Al 0.010%, Cu 0.07%, Ni 0.03%, Mo 0.02%, and the rest are iron and unavoidable impurity elements.
[0036] (2) Heating process: heat the billet in a heating furnace, the heating temperature is 1120°C, the residual oxygen content is 2%, and the time in the furnace is 130min.
[0037] (3) Rolling process: the steel billet is rolled into wire rod at high speed, the temperature for finishing rolling is 800°C, and the coiling temperature is 780°C.
[0038] (4) Cooling process: the wire rod enters the cooling roller table, and is first cooled to 550°C at a speed of 8°C / s, and then cooled at a speed of 3°C / s.
[003...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com