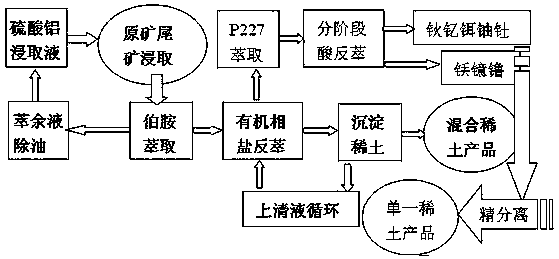
A high-efficiency green extraction method of ion-adsorption rare earths using aluminum sulfate as a leaching agent
An ion-adsorption type and extraction method technology, which is applied in the field of ion-adsorption type rare earth efficient green extraction, can solve the problems of difficult rare earth and aluminum separation, serious emulsification, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding emulsification and three-phase problems and simple extraction and separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1 The leaching effect of different leaching agents on ion adsorption type rare earth
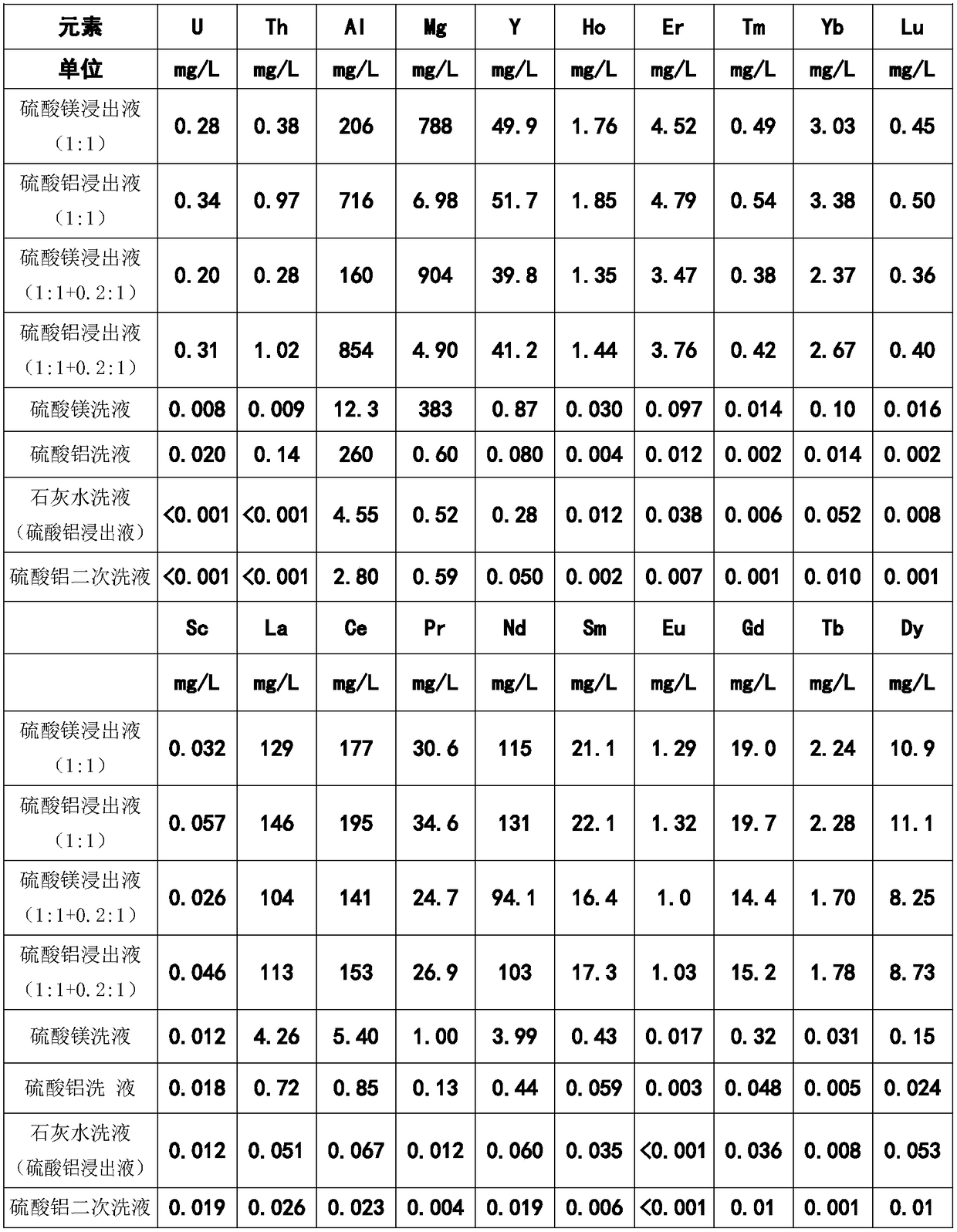
[0021] Ammonium sulfate, ammonium chloride, magnesium sulfate, magnesium chloride, aluminum sulfate and magnesium chloride solutions of the same normal concentration (0.1N) are used respectively for the same ore sample at the same column ratio and leaching liquid-solid ratio (leaching agent solution to ore The weight ratio is 1:1, the ratio of top water to ore weight is 0.2:1), the leaching effluent is collected, and samples are sent to the Analysis and Testing Center of Jiangxi Geology and Mineral Bureau for ICP-MS analysis. The results are listed in Table 1. It can be seen that the leaching effect of sulfate of the same metal ion is better than that of chloride. The leaching effect of sulfate is good, among which the leaching effect of aluminum sulfate is the best, followed by ammonium sulfate and magnesium sulfate is the least. It shows that aluminum sulfate has the highes...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2 The efficiency comparison of extracting rare earths from various leaching solutions with N1923 and back-extracting rare earths with hydrochloric acid
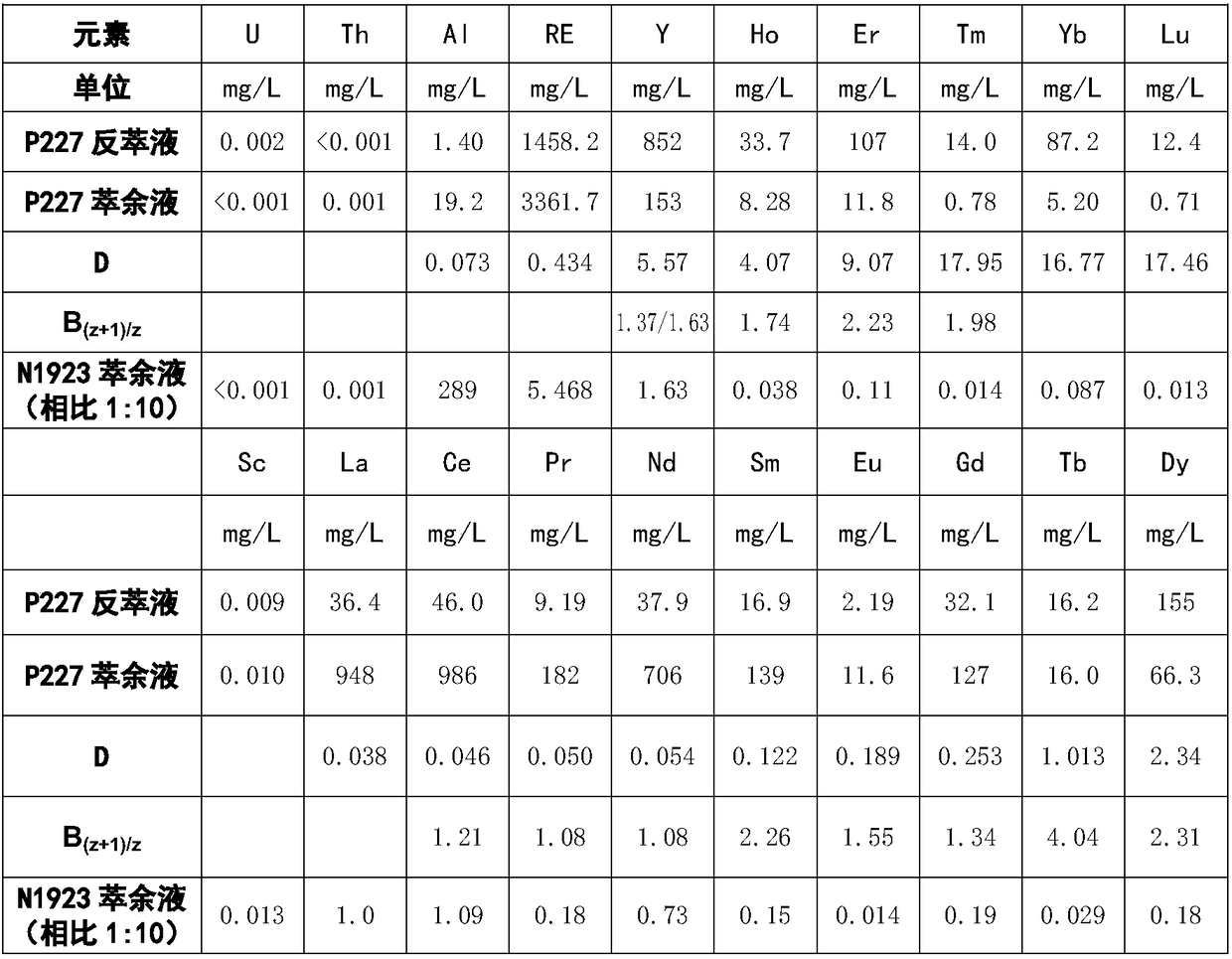
[0023] Use 20% N1923-10% 2-octanol-70% kerosene as the extraction organic phase, after 1MH 2 SO 4 After the solution is protonated, it is used to extract the rare earth in the leaching solution. The ratio is 1:2. The organic phase after the rare earth extraction is back-extracted with hydrochloric acid. The results are also listed in Table 1. The results show that the residual amount of rare earth in the raffinate of primary extraction is low, and the extraction rate is above 99%. However, the residual amount of aluminum is large and the extraction rate is low. In the stripping solution, the concentration of rare earth is high, while the concentration of aluminum is low. A good purification effect has been achieved. The table also lists that the rare earth in the raffinate can be reduced to less than 0.01p...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Example 3 Comparison of Effects of Aluminum Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Solution on Ion Adsorption Type Rare Earth Staged Leaching
[0025] The amount of ore is 2 kg, and the leaching liquid, top replenishment water and washing water are rinsed according to the liquid-solid ratio of 1:1, 0.2:1 and 1:1 respectively, and the effluent is received in stages, and the metal ions in the effluent are respectively measured Concentration, the results are shown in Table 2. For the leaching of aluminum sulfate, follow-up tail protection steps such as lime water + water washing are also added. The results of the analysis of the resulting effluent are also listed in Table 2. It can be seen from the results that the leaching effect of aluminum sulfate is still higher than that of magnesium sulfate, and the content of rare earths in the effluent of subsequent washing is also much lower than that of magnesium sulfate leaching, indicating that aluminum sulfate has a strong ability to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com