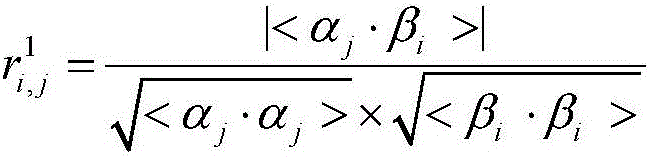Representativeness-based optimal sampling method
An optimized and representative technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problem of inability to update and evaluate the increment and difference of new sensor information.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
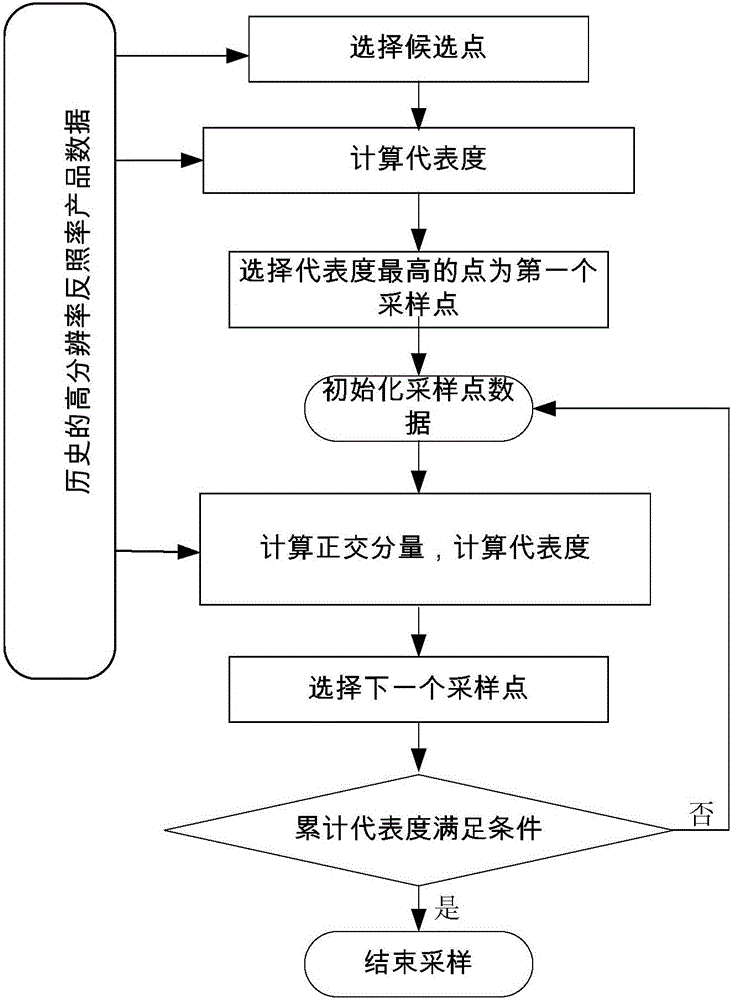
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, a representative optimal sampling method is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0035] S1. Select candidate points. With the help of the historical long-term series of HJ albedo product data as prior knowledge, when selecting points, it is necessary to consider the uniformity of the point to be selected and the surrounding area first, and first select the point that is more consistent with the surrounding surface. Higher points are used as candidate points;
[0036] S2. Calculate the degree of representativeness of the candidate points, and select the point with the highest degree of representativeness from the candidate points as the first sampling point;
[0037] S3. Initialize the sampling point data, calculate the orthogonal component, and calculate the degree of representativeness;
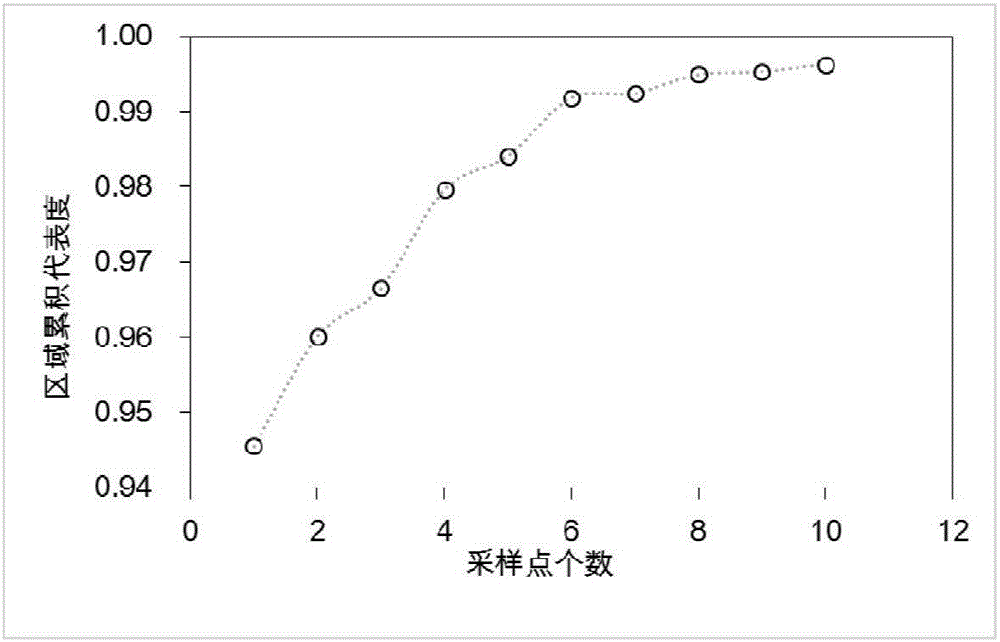
[0038] S4. Select the next sampling point, and calculate whether the cumulative representativeness meets the conditions. If the cumul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com