Peak-current-mode Buck circuit sub-harmonic oscillation elimination method based on slope compensation method
A technology of peak current mode and sub-harmonic oscillation, applied in the direction of output power conversion device, DC power input conversion to DC power output, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of current steady-state oscillation and damage to system stability, etc., to achieve The effect of eliminating subharmonic oscillation and improving stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
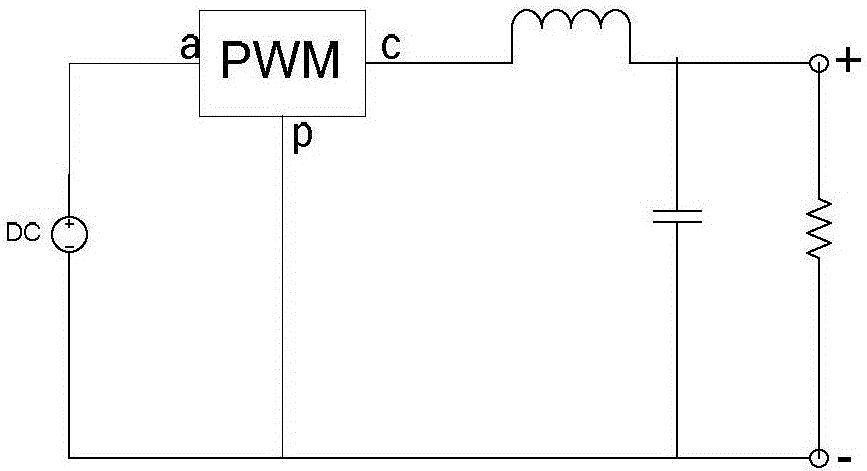
[0022] Specific embodiment one: In the peak current mode Buck circuit subharmonic oscillation elimination method based on the slope compensation method described in this embodiment, the reference voltage signal is input to the same input terminal of the PWM comparator, and the reverse direction of the PWM comparator of the Buck circuit The input terminal inputs a current feedback signal, and the reverse input terminal of the PWM comparator also inputs a voltage signal with a positive slope for compensating the slope of the current feedback signal.
specific Embodiment approach 2
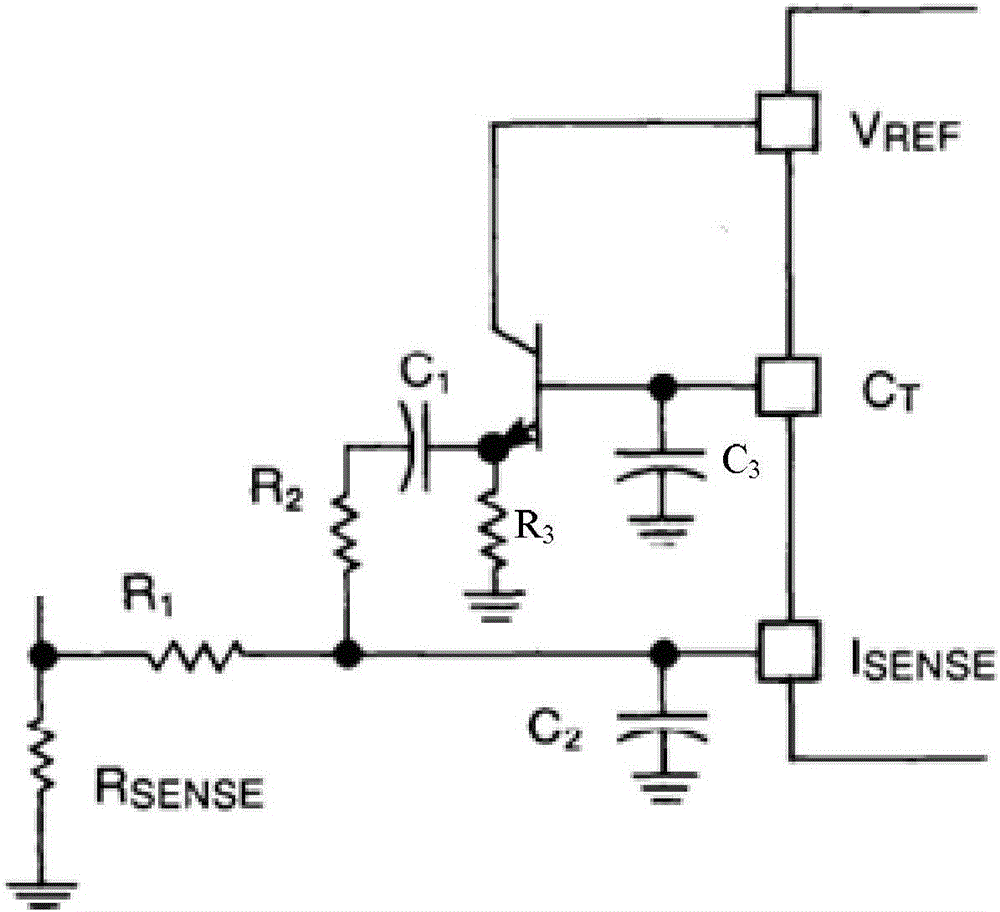
[0023] Specific implementation mode two: combination Figure 1 to Figure 6 This embodiment is described in detail. This embodiment is a further description of the peak current mode Buck circuit subharmonic oscillation elimination method based on the slope compensation method described in the first embodiment. In this embodiment, the voltage signal with a positive slope is as follows device generated, the device includes:
[0024] Resistance R SENSE , resistance R 1 , resistance R 2 , resistance R 3 , electrolytic capacitor C 1 , electrolytic capacitor C 2 and electrolytic capacitor C 3 and triode;
[0025] Resistance R SENSE One end of the ground, resistor R SENSE The other end of the resistor R 1 Connected to one end of the resistor R SENSE and resistor R 1 The common terminal of the positive slope voltage signal is connected to the negative input terminal of the PWM comparator, and the resistor R 1 The other end of the resistor R 2 One end of the electrolytic c...
specific Embodiment approach 3
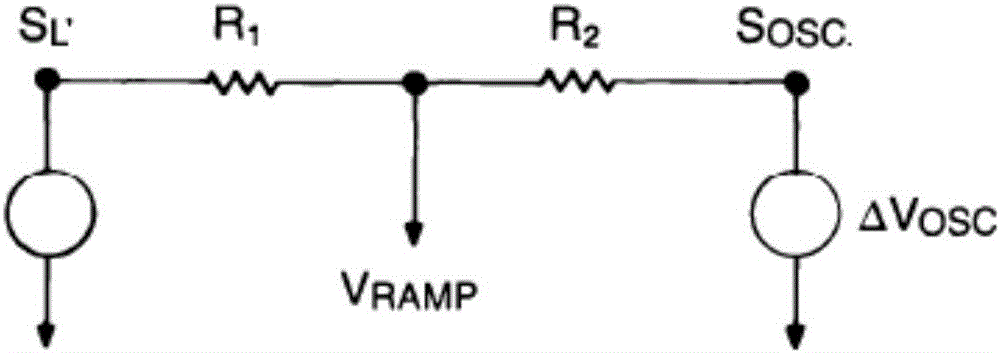
[0042] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment is a further description of the peak current mode Buck circuit sub-harmonic oscillation elimination method based on the slope compensation method described in specific embodiment two. In this embodiment, the resistor R 2 The resistance R2 is:
[0043]
[0044] R1 is the resistor R 1 ΔVosc is the voltage differential at osc point, VS(L) is the voltage at SL point, and M is the slope compensation coefficient.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com