Patents
Literature
53 results about "Subharmonic oscillation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
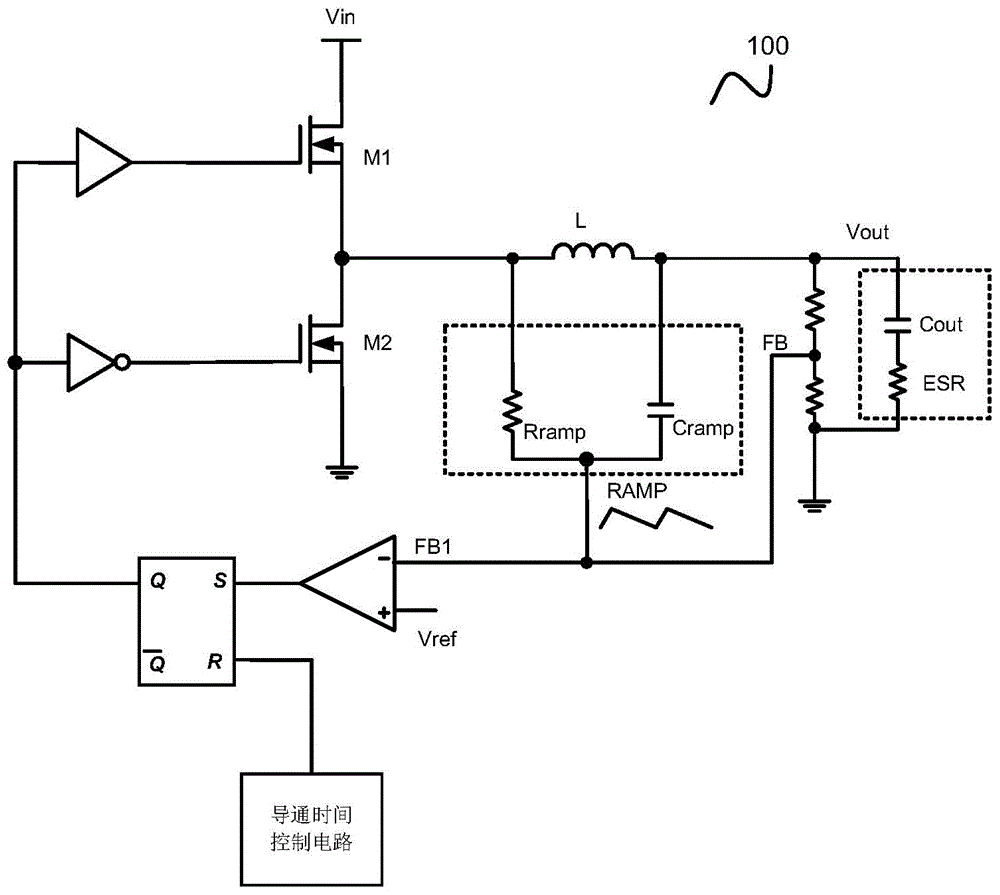
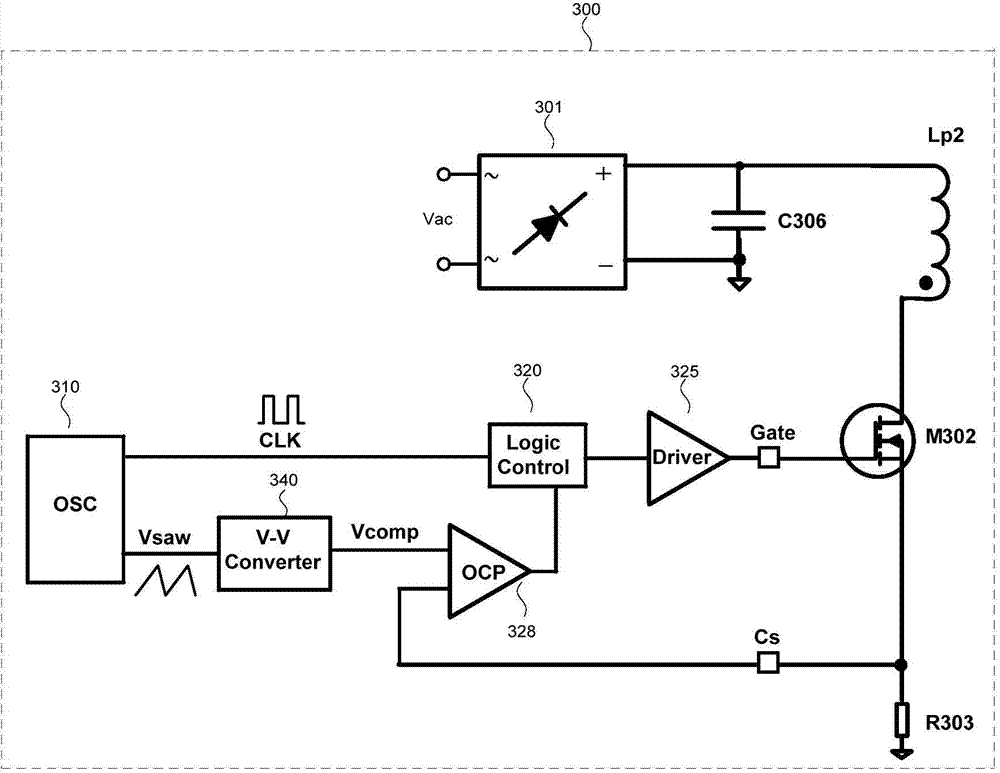
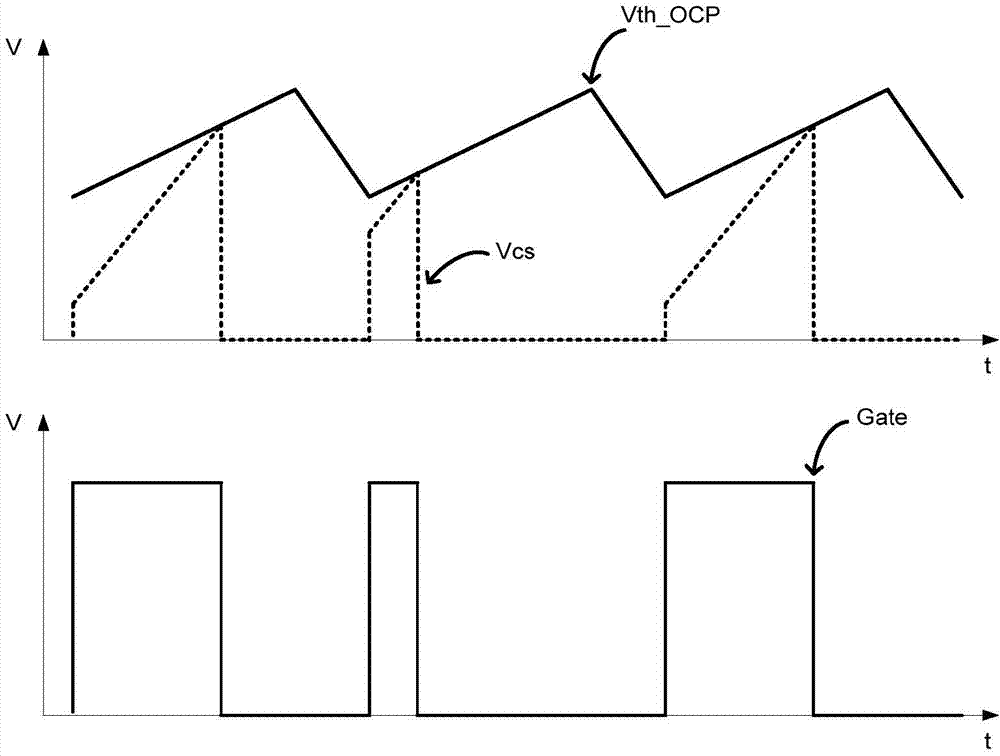
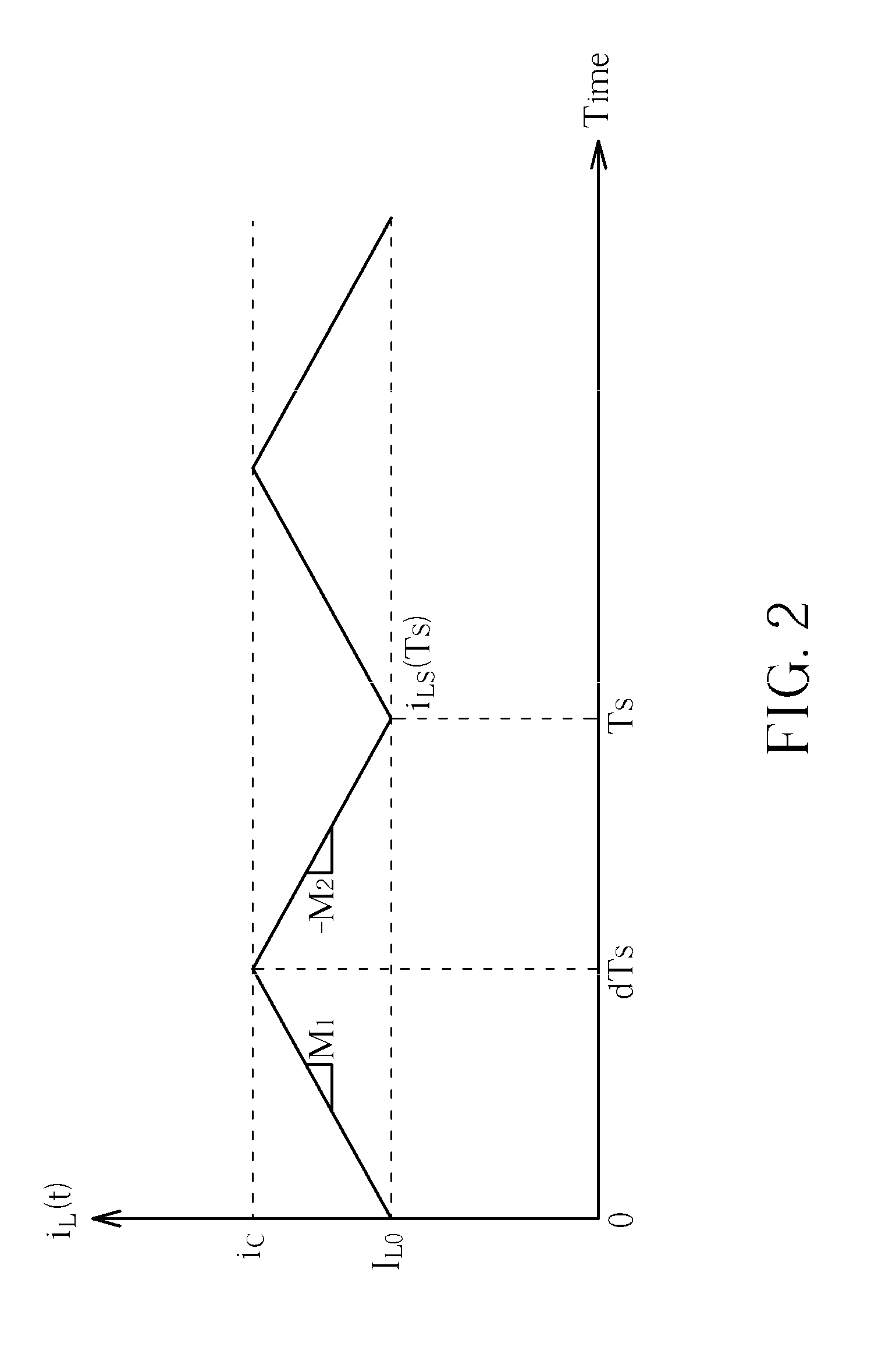
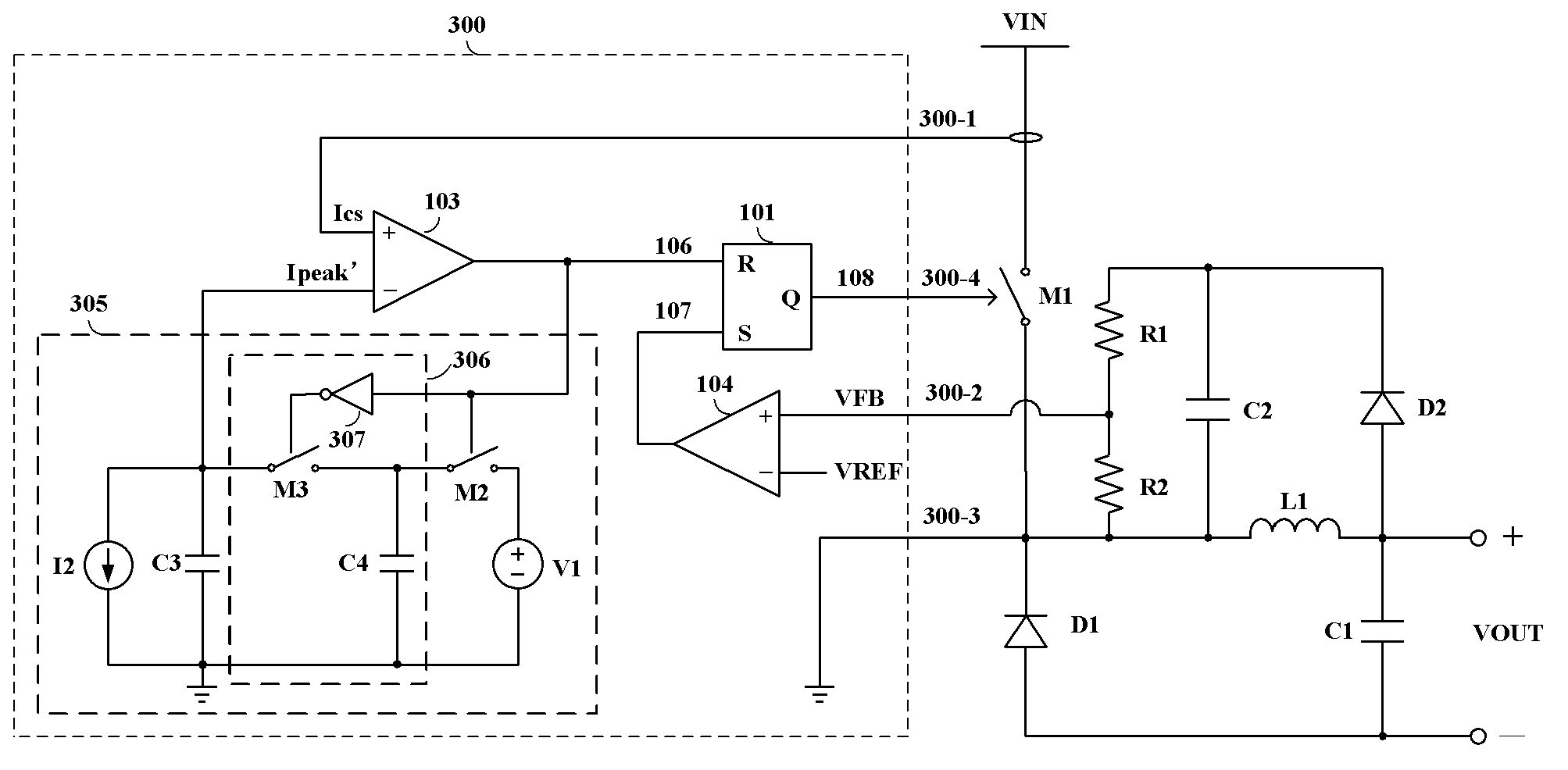
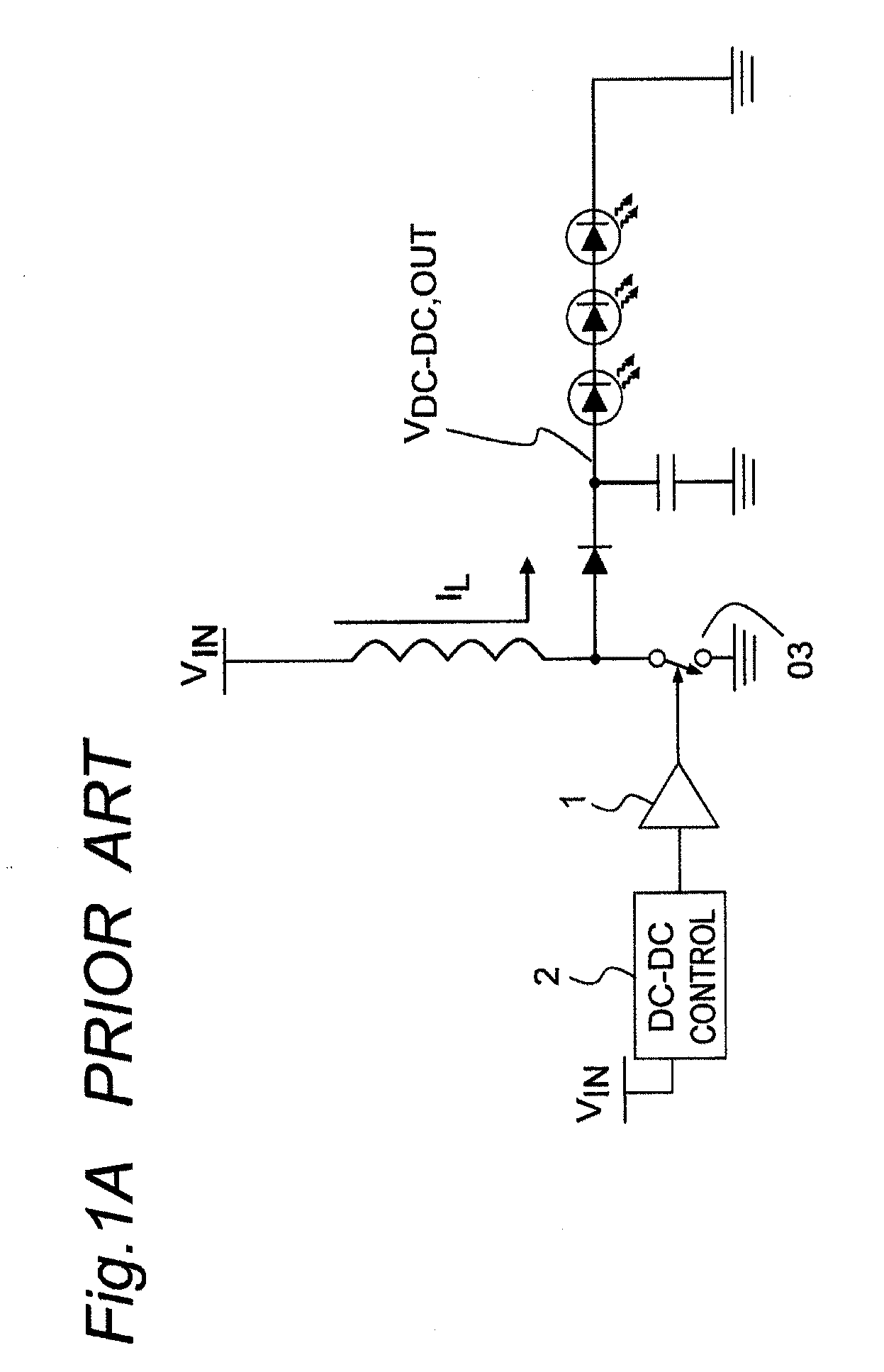
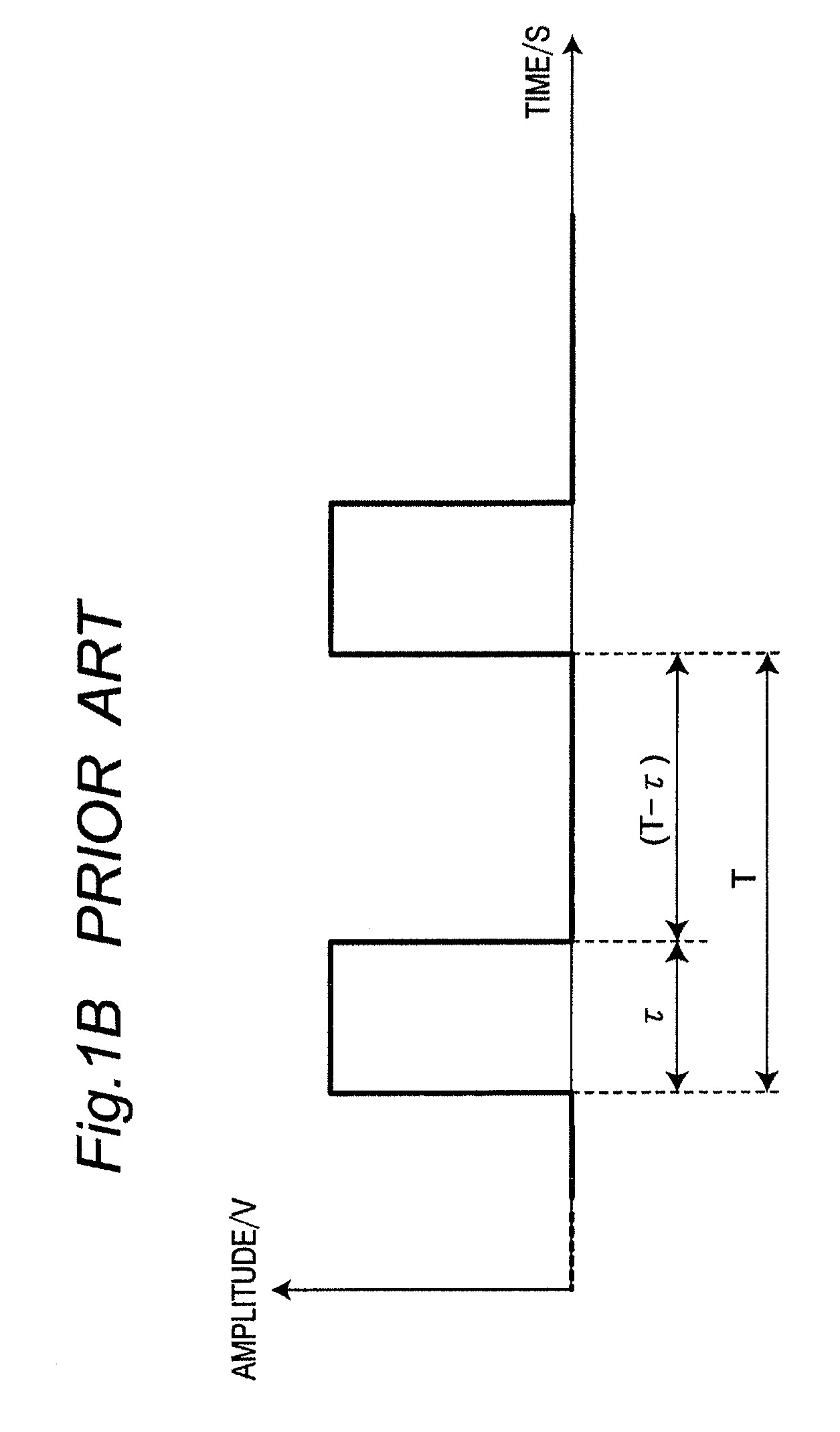
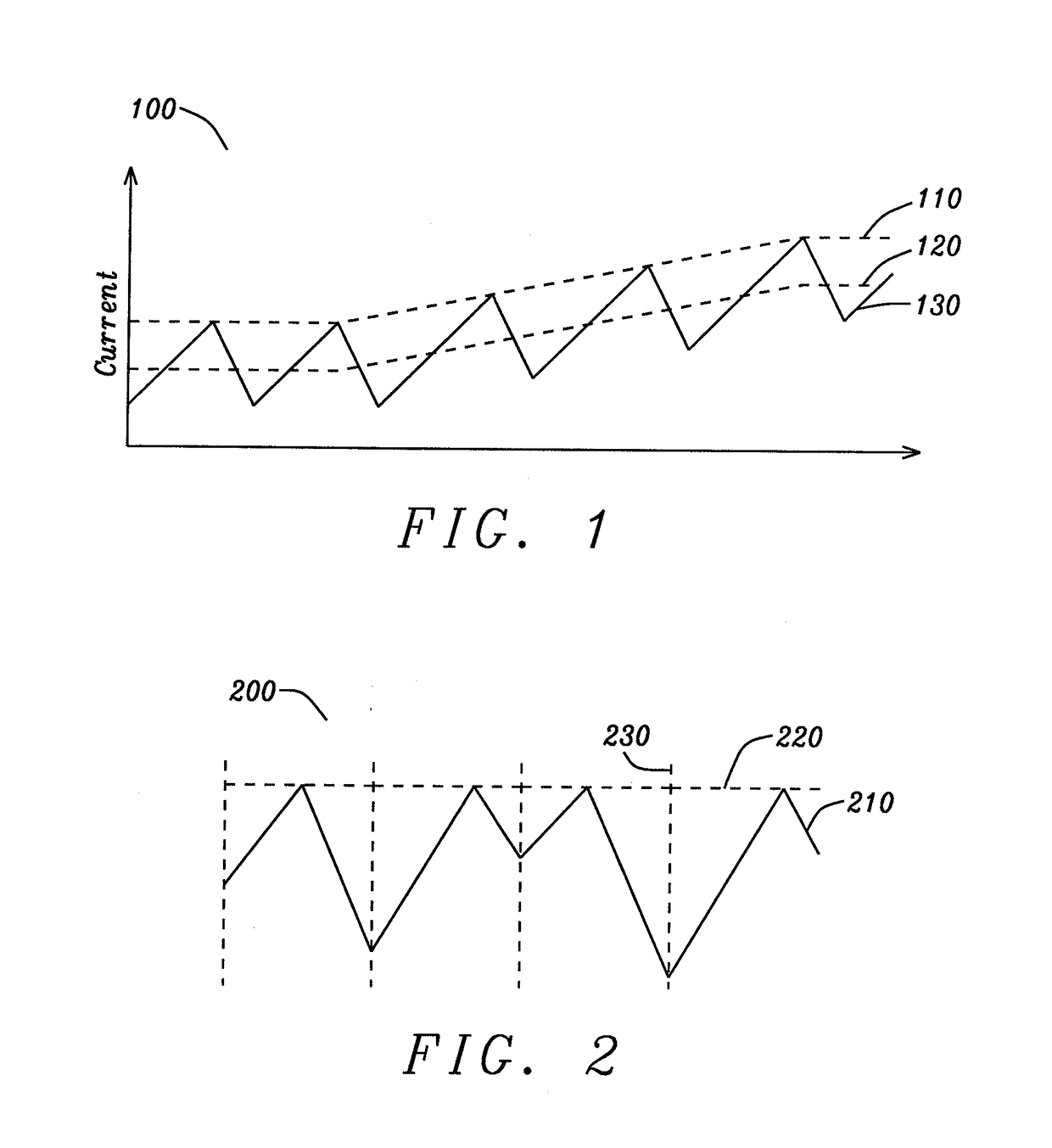
Basically subharmonic oscillation is not a small signal instability, it's a large signal phenomenon in peak current mode control that occurs when the duty cycle is greater than 50%.
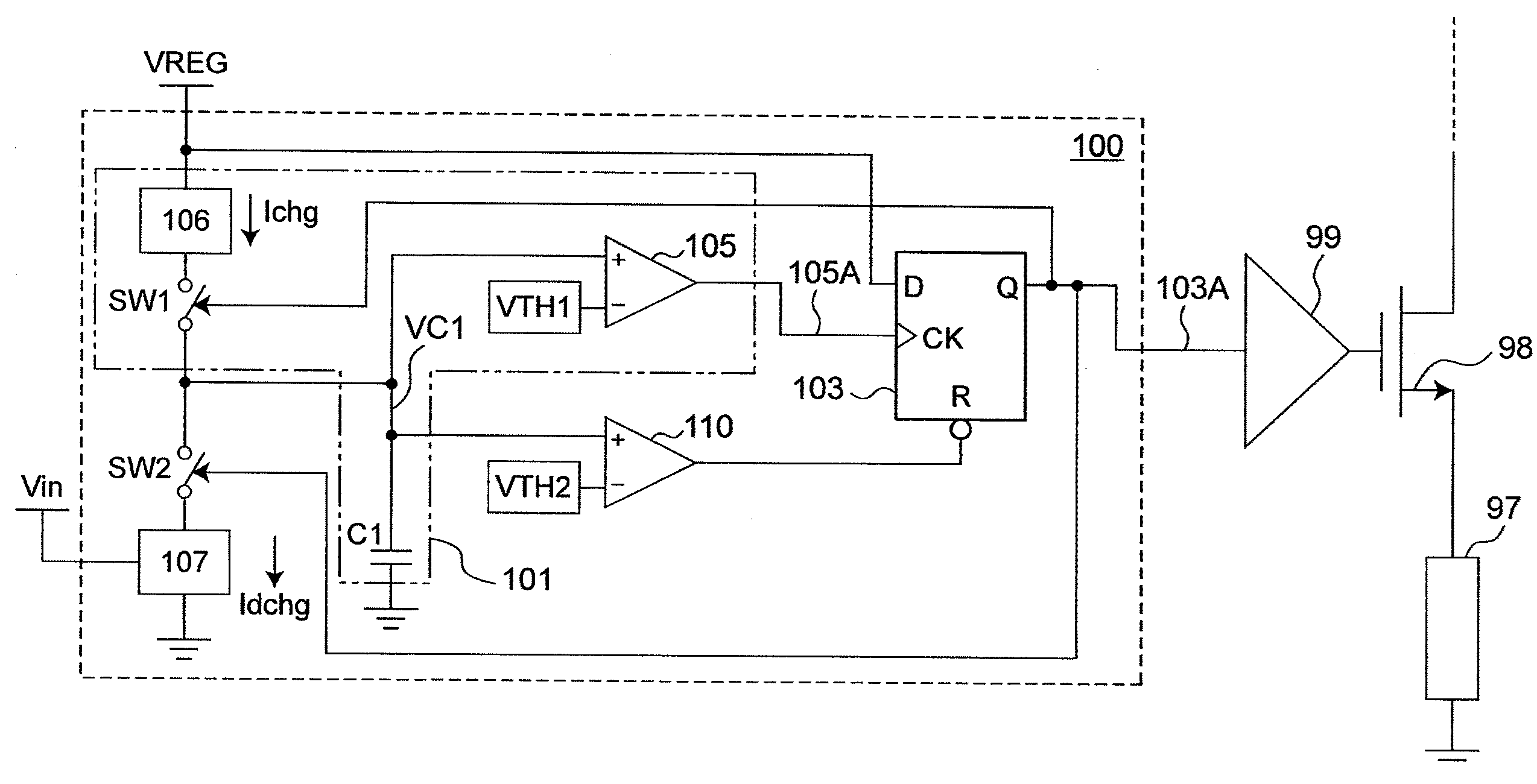
Switch converter and control circuit and method thereof
ActiveCN104022648AAvoid jitterAvoid Subharmonic OscillationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSubharmonic oscillationControl signal
The invention discloses a switch converter with constant connection time control, and a control circuit and method thereof. A compensation control signal is generated according to the input voltage or a control signal, and a compensation signal is adjusted according to the compensation control signal so that the compensation signal can be adjusted to a proper value within a wide input range. Compared with the prior art, jittering and subharmonic oscillation under low input can be avoided, and dynamic response and load adjusting rate under high input are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
Ups frequency converter and line conditioner
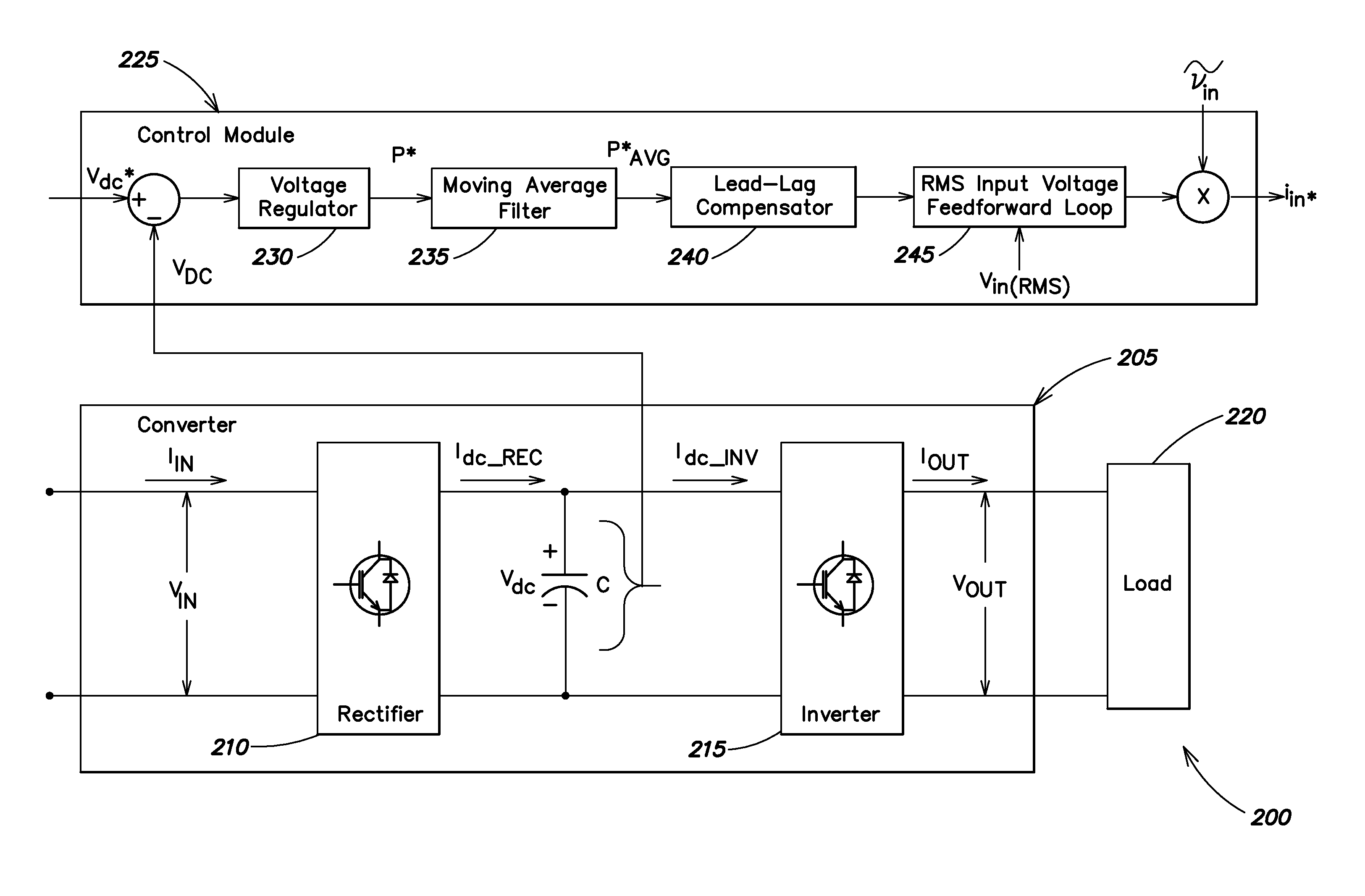
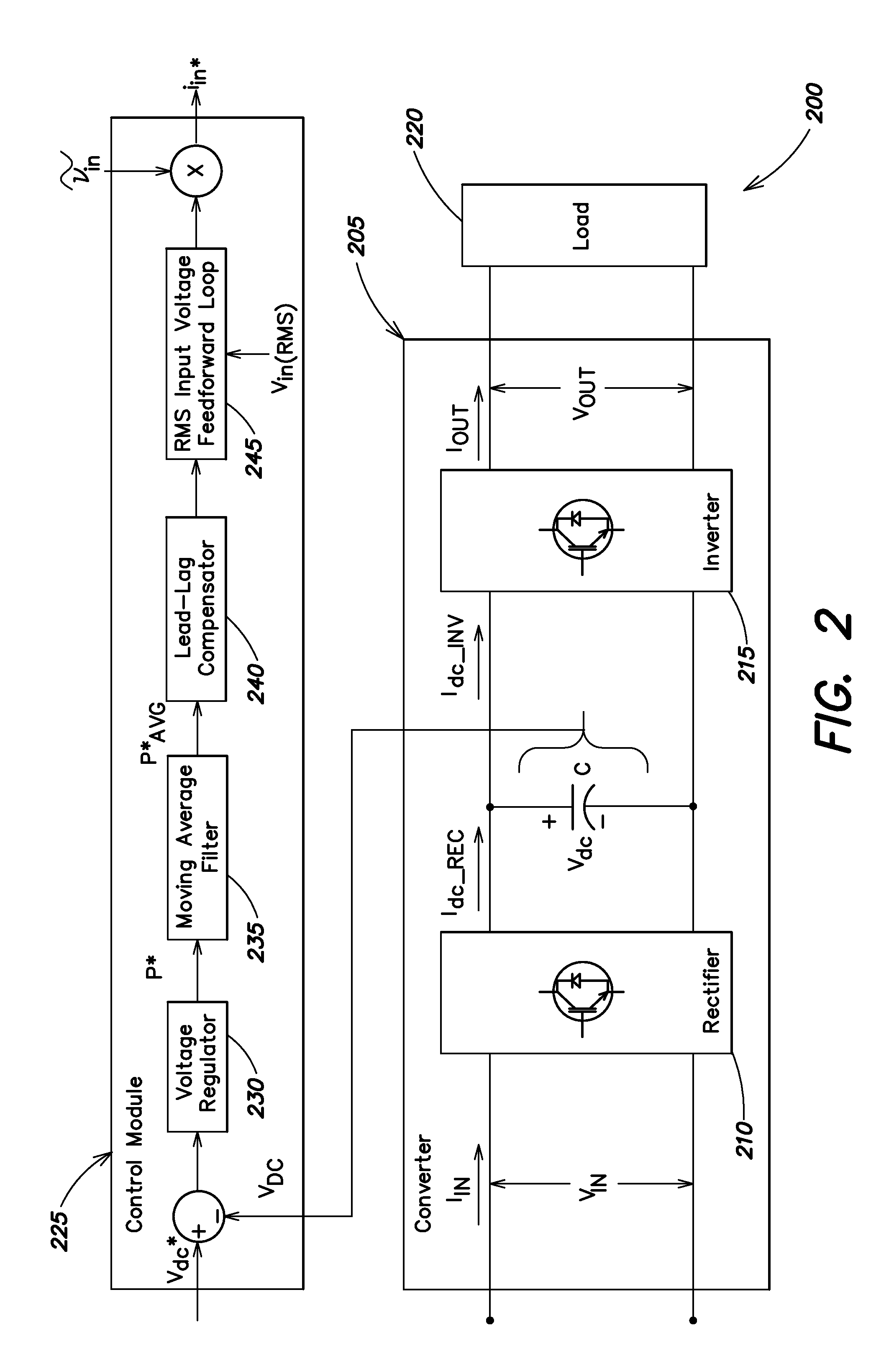
ActiveUS20090237963A1Improve efficiencyImproves converter operationEfficient power electronics conversionDc circuit to reduce harmonics/ripplesSubharmonic oscillationTotal harmonic distortion
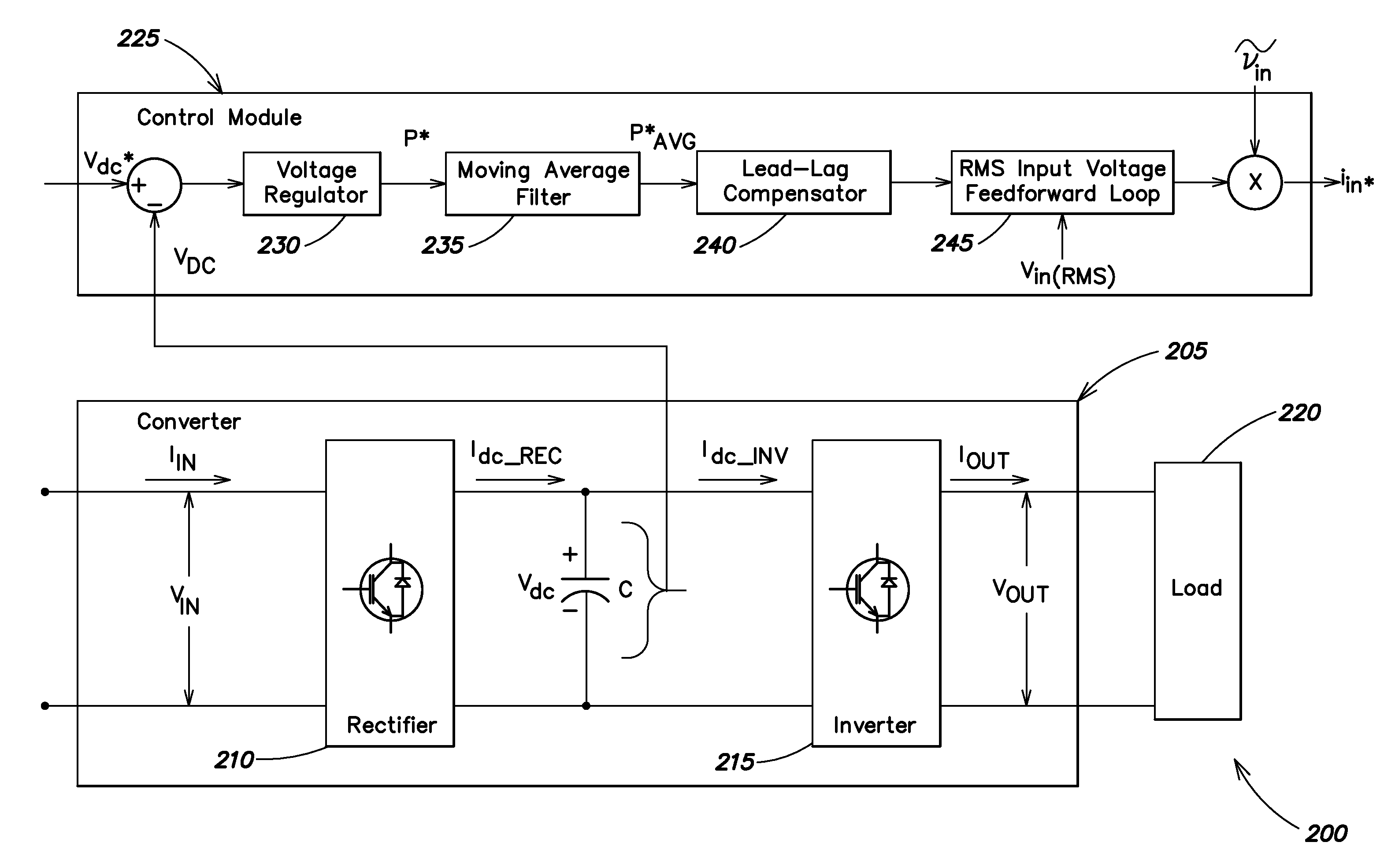
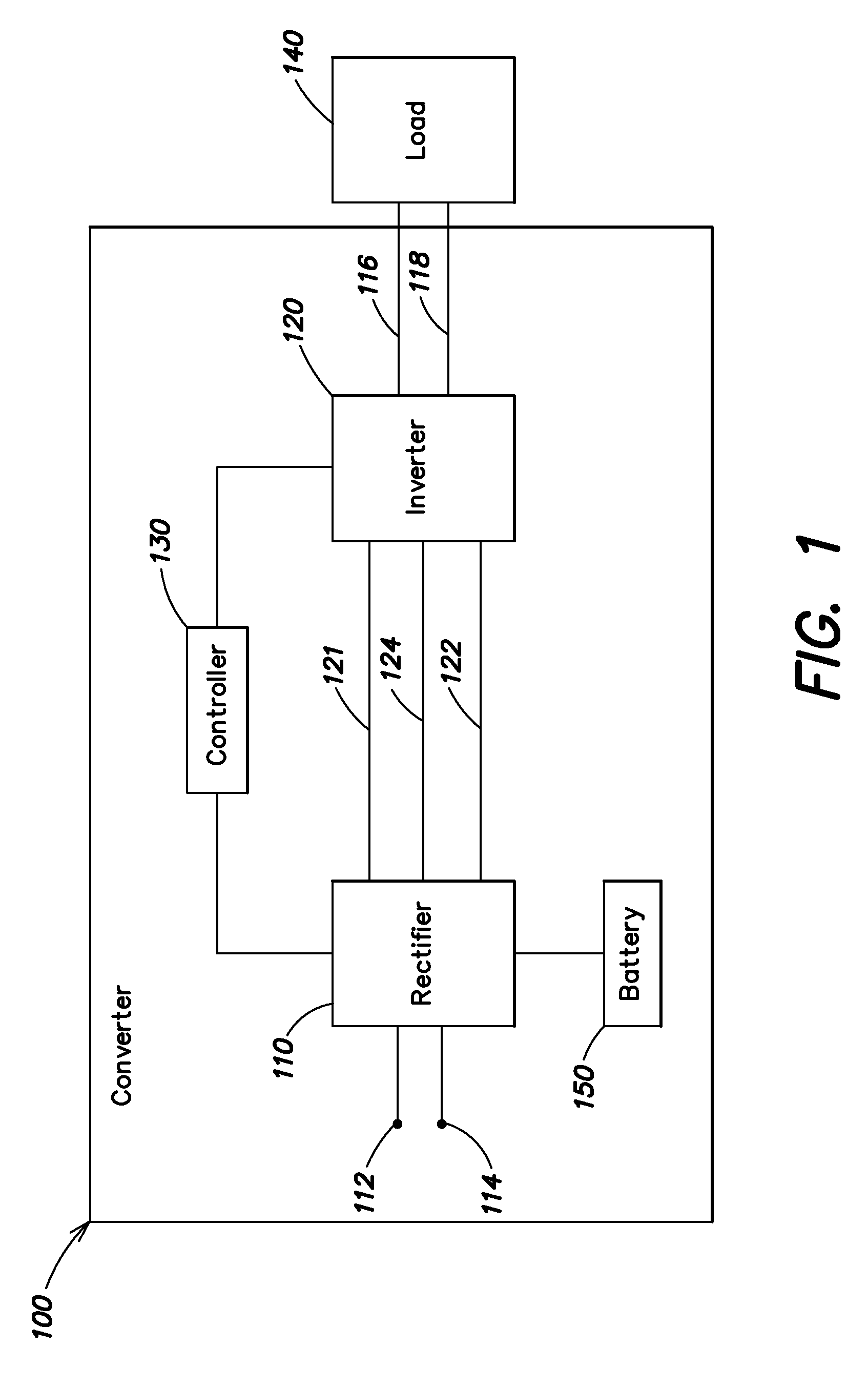
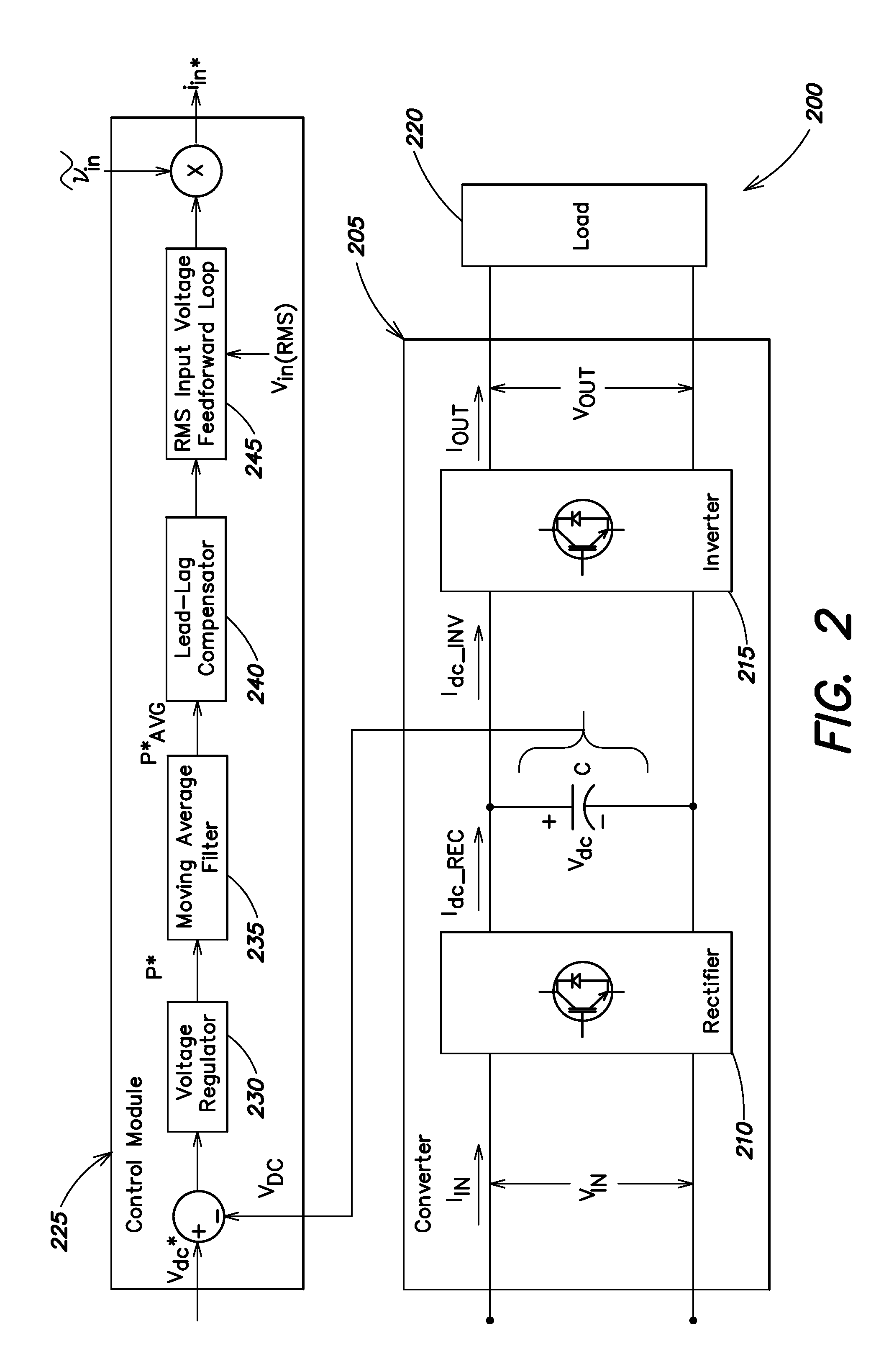
Systems and methods disclosed herein monitor and control input to a converter in one or more of a UPS, a frequency converter, or a line conditioner. Distortion due at least in part to ripple voltage can be removed from a control signal that controls input current to the converter. The systems and methods described herein afford a simple and effective way to reduce or eliminate one or more of subharmonic oscillation and total harmonic distortion from a converter input current during synchronous and asynchronous modes of operation. The converter may include one or more of a rectifier and an inverter.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IT CORP
Control circuit and control method of current mode control type DC-DC converter
ActiveUS20060202669A1Subharmonic oscillation is preventedPrevent output from droppingEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLower limitCurrent mode control
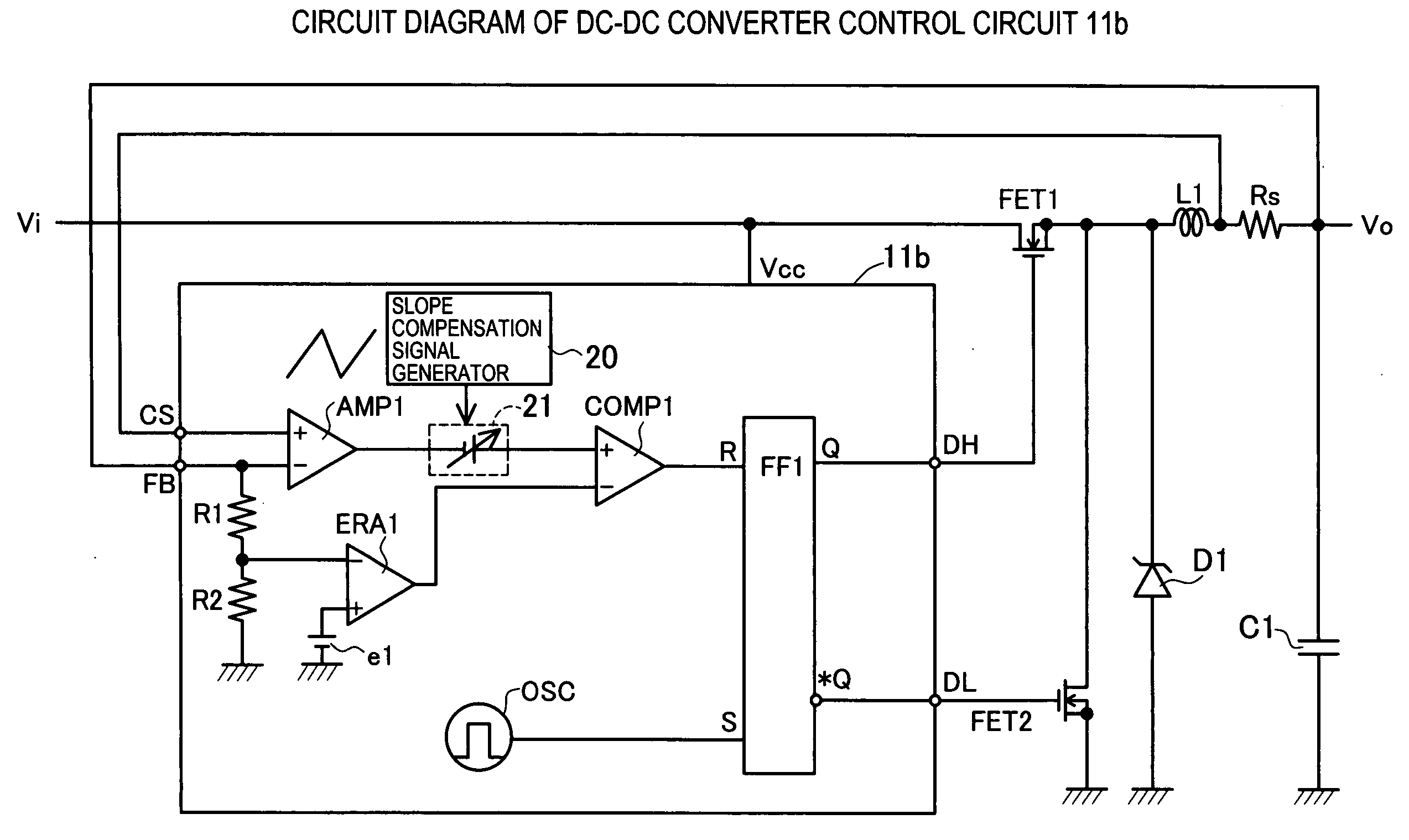
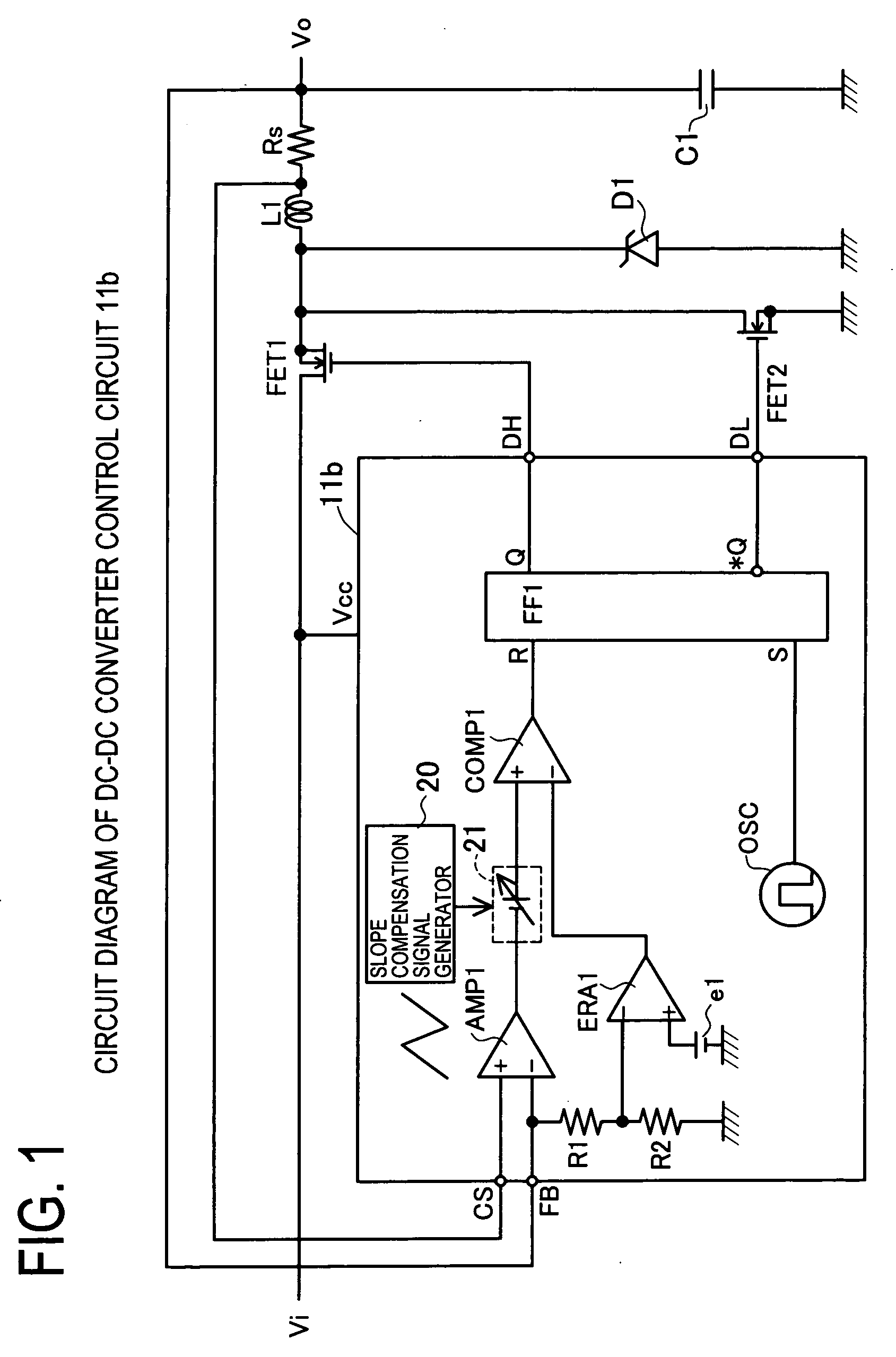
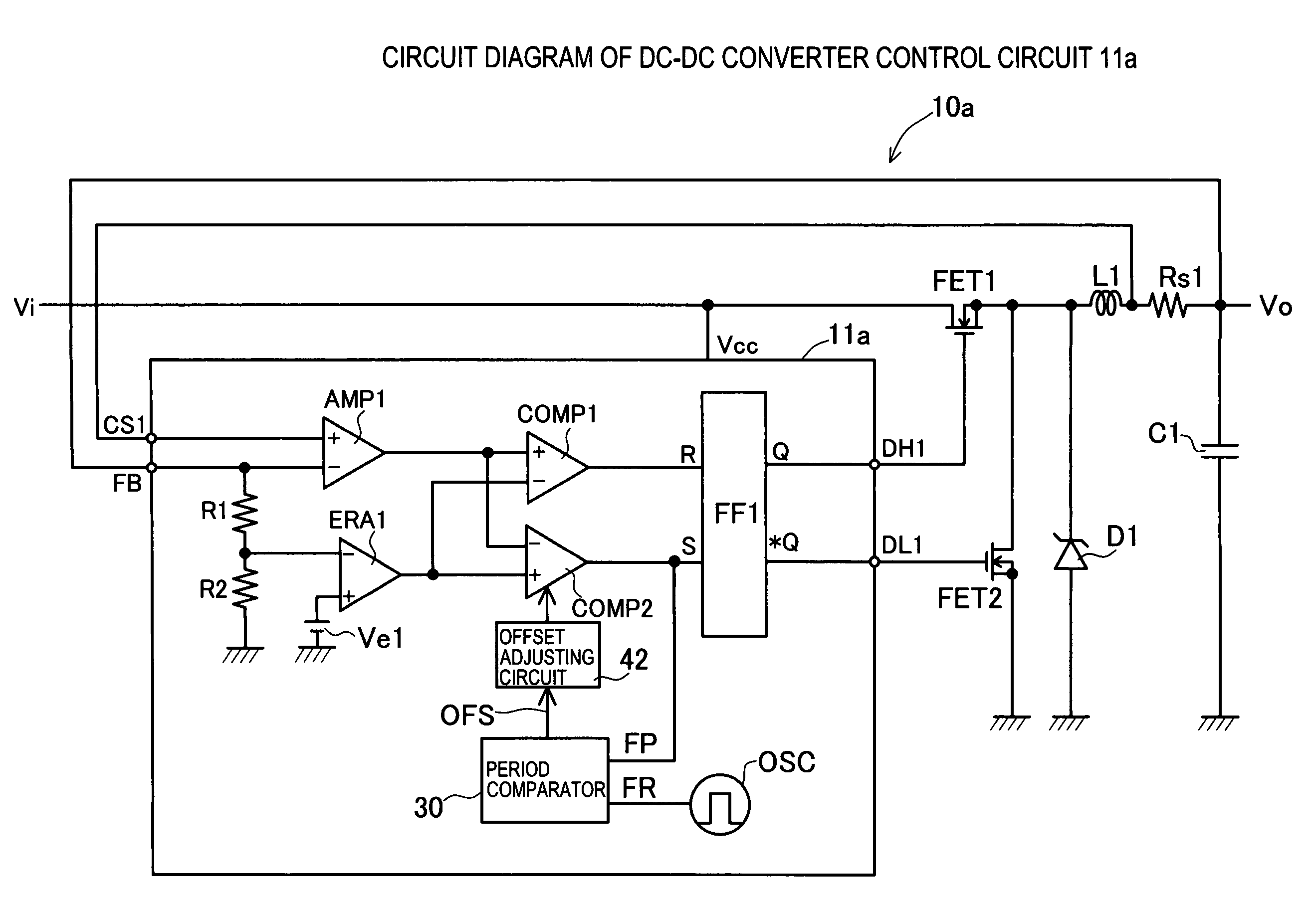
The invention presents a control circuit and a control method of DC-DC converter capable of suppressing subharmonic oscillation of coil current even if the on-duty is over 50%. An error amplified signal V1 is an output voltage of an error amplifier ERA1. An offset voltage unit Ve2 outputs a lower limit set voltage V2 obtained by subtracting offset voltage e2 from error amplified signal V1. A voltage comparator COMP2 compares lower limit set voltage V2 output from offset voltage Ve2, and output voltage signal VIL. When the voltage value of output voltage signal VIL is decreased to lower limit set voltage V2 (region E2), the output of voltage comparator COMP2 changes from low level to high level. As a result, main transistor FET1 is set in conductive state. On the other hand, when the voltage value of output voltage signal VIL reaches an error amplified signal V1 (region E1), main transistor FET1 is set in non-conductive state.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Adaptive slope compensation module and method
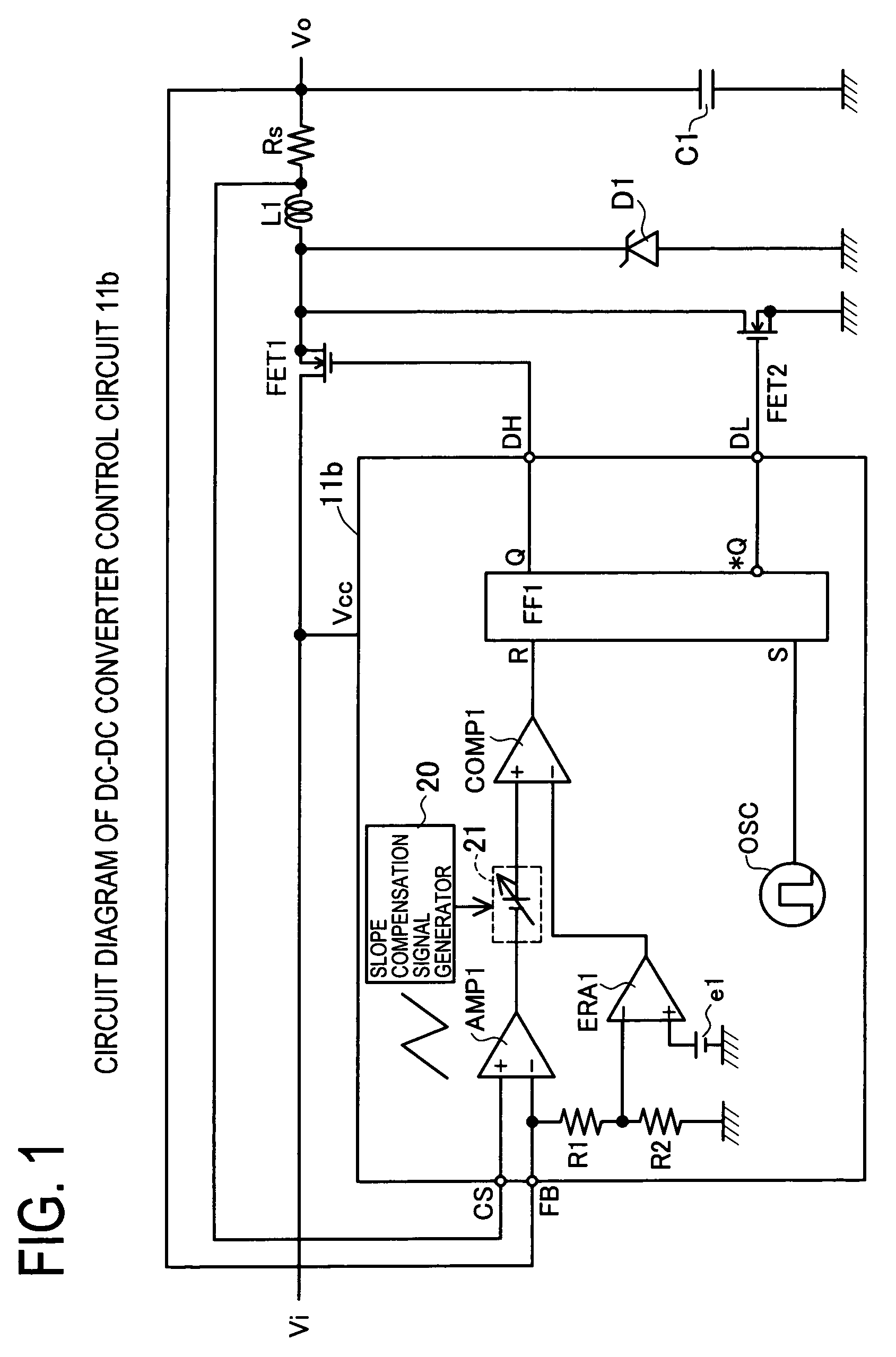
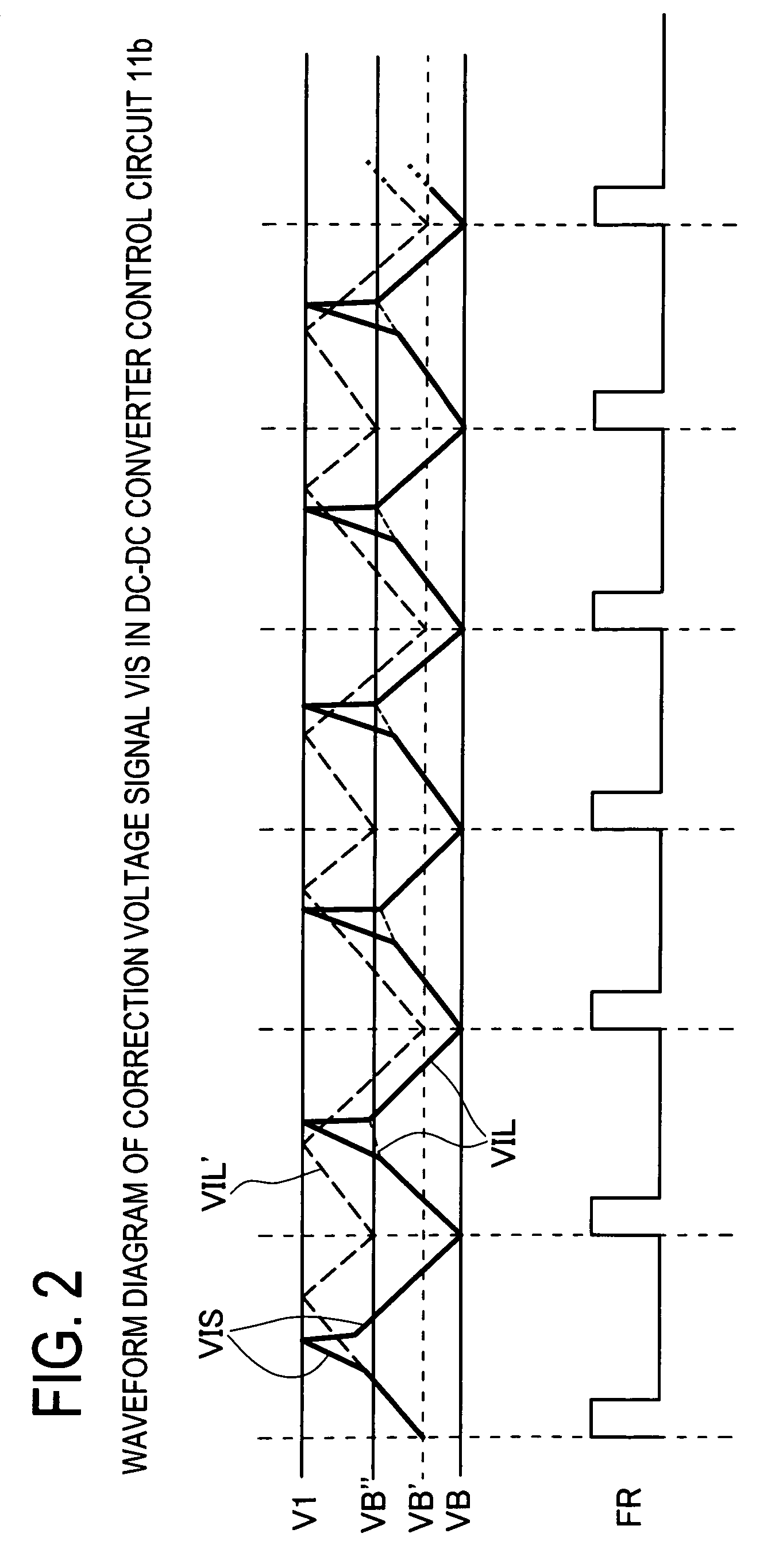
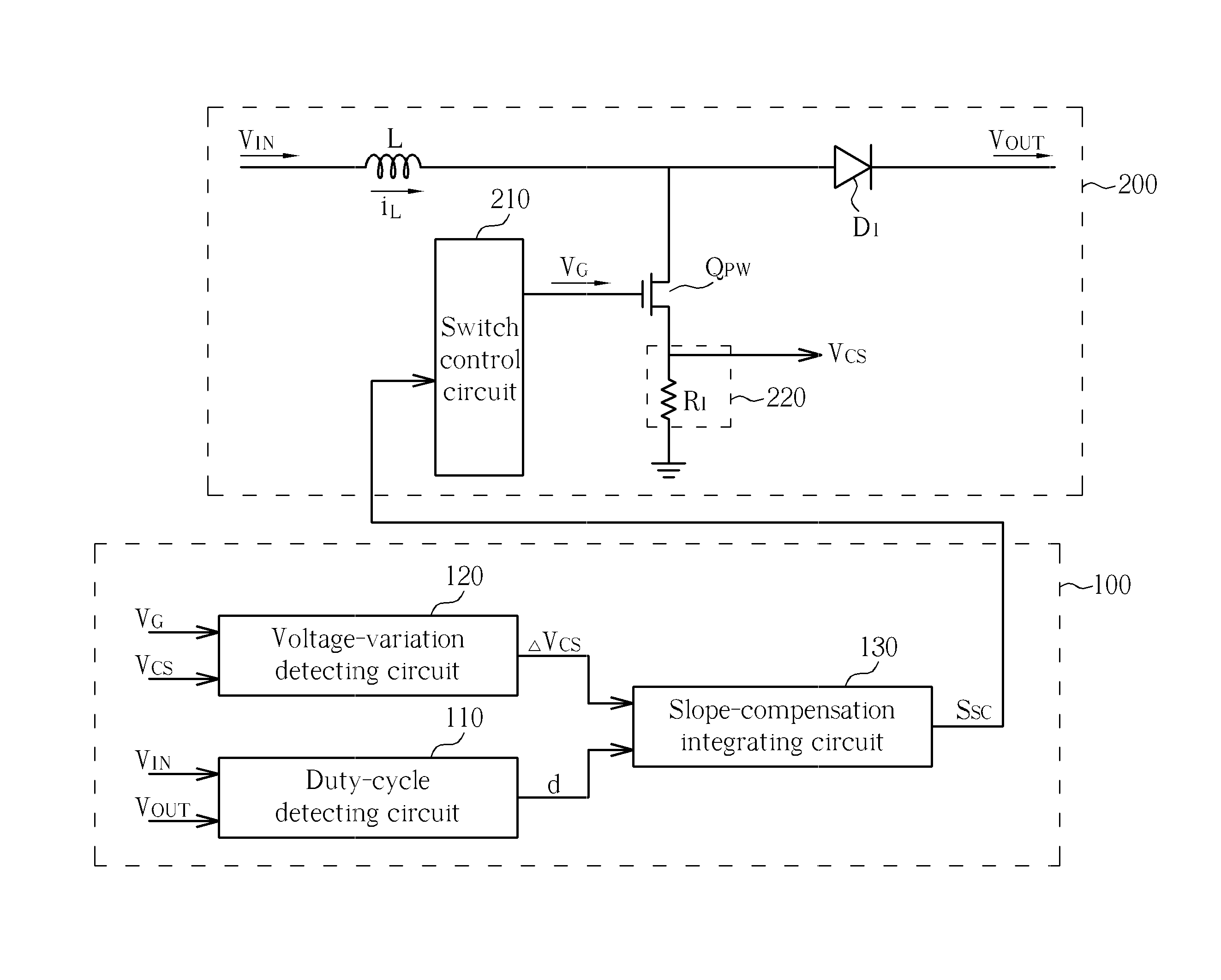
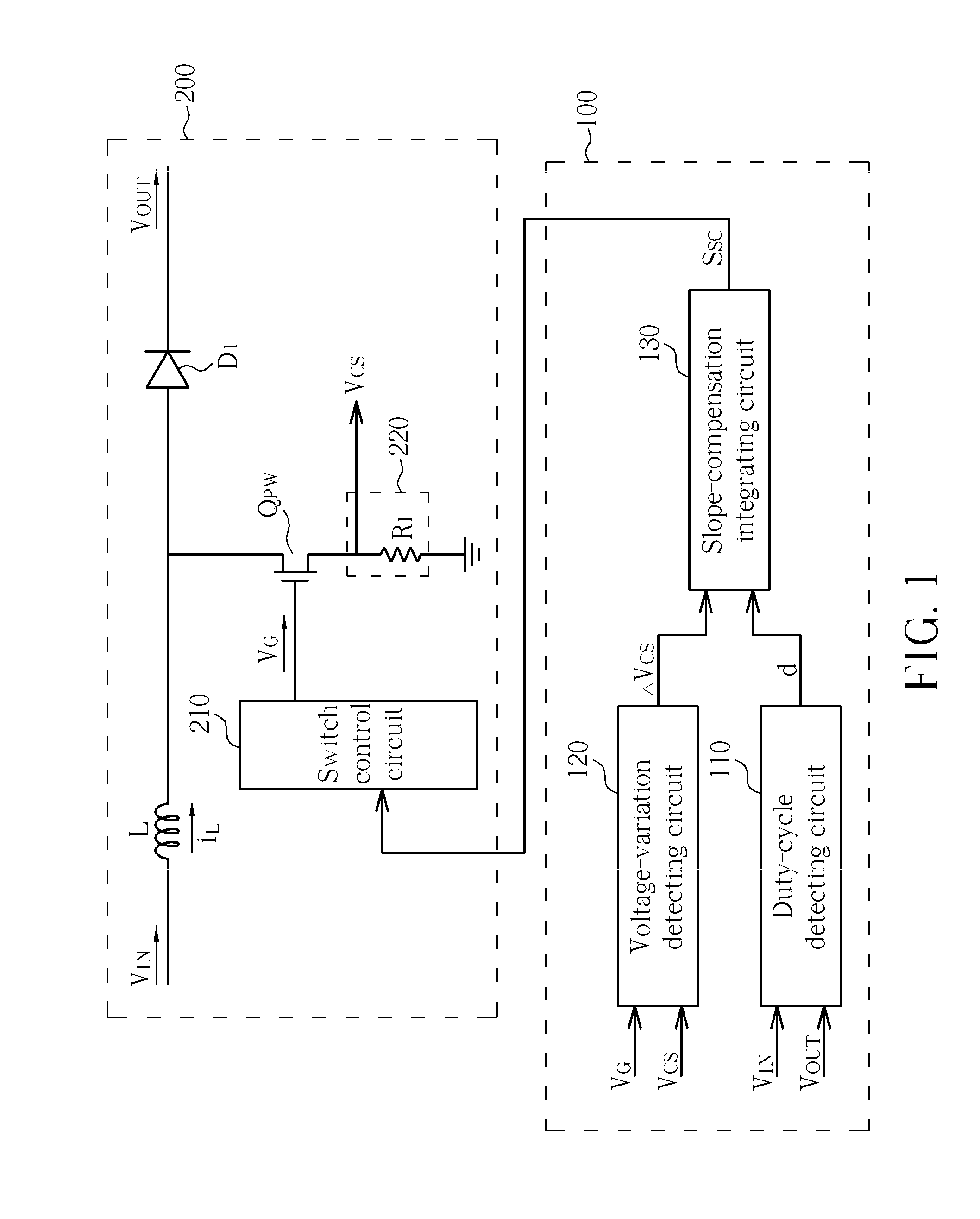
The invention provides an adaptive slope compensation method which is applied to a switched power supply unit. The switched power supply unit is provided with a power switch and an inductor which is coupled with an input power supply; and the power switch controls the inductor to store energies or release the energies so as to generate an output voltage. The adaptive slope compensation method comprises the following steps: detecting an inductive current flowing through the inductor and converting the inductive current into an inductive current detection voltage; detecting the duty cycle of the power switch; detecting the voltage difference of the inductive current detection voltage when the power switch is started; using the voltage difference of the duty cycle and the inductive current detection voltage to generate slope compensation signals; and utilizing the slope compensation signals to adjust the starting or the closing of the power switch. Therefore, although operation conditions of the input power supply or the output voltage are changed, the system can still respond quickly and does not generate sub-harmonic oscillation.
Owner:LEADTREND TECH
UPS frequency converter and line conditioner
ActiveUS7881079B2Less distortionImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc circuit to reduce harmonics/ripplesPower inverterTotal harmonic distortion
Systems and methods disclosed herein monitor and control input to a converter in one or more of a UPS, a frequency converter, or a line conditioner. Distortion due at least in part to ripple voltage can be removed from a control signal that controls input current to the converter. The systems and methods described herein afford a simple and effective way to reduce or eliminate one or more of subharmonic oscillation and total harmonic distortion from a converter input current during synchronous and asynchronous modes of operation. The converter may include one or more of a rectifier and an inverter.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IT CORP
Overcurrent/overpower protection method of switching power supply, protection circuit and switching power supply
InactiveCN103701310AOscillation suppressionPower conversion systemsTime rangeSubharmonic oscillation
The invention discloses an overcurrent / overpower protection method of a switching power supply. The protection method is applied to the switching power supply. The switching power supply comprises a control circuit used for controlling breakover and cut-off of a power tube, wherein the control circuit comprises an overcurrent / overpower protection module. The protection method comprises the following steps: a first signal is collected and kept to form a line voltage compensation signal which is constant in a preset time range, and the line voltage compensation signal is loaded to the overcurrent / overpower protection module, and the first signal is matched with the duty cycle of a PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) signal, so that a line voltage compensation value is kept constant in a certain time range by the method, and is not timely changing along with the PWM signal, so that the sub-harmonic oscillation is effectively restrained from the source.
Owner:BCD SEMICON MFG
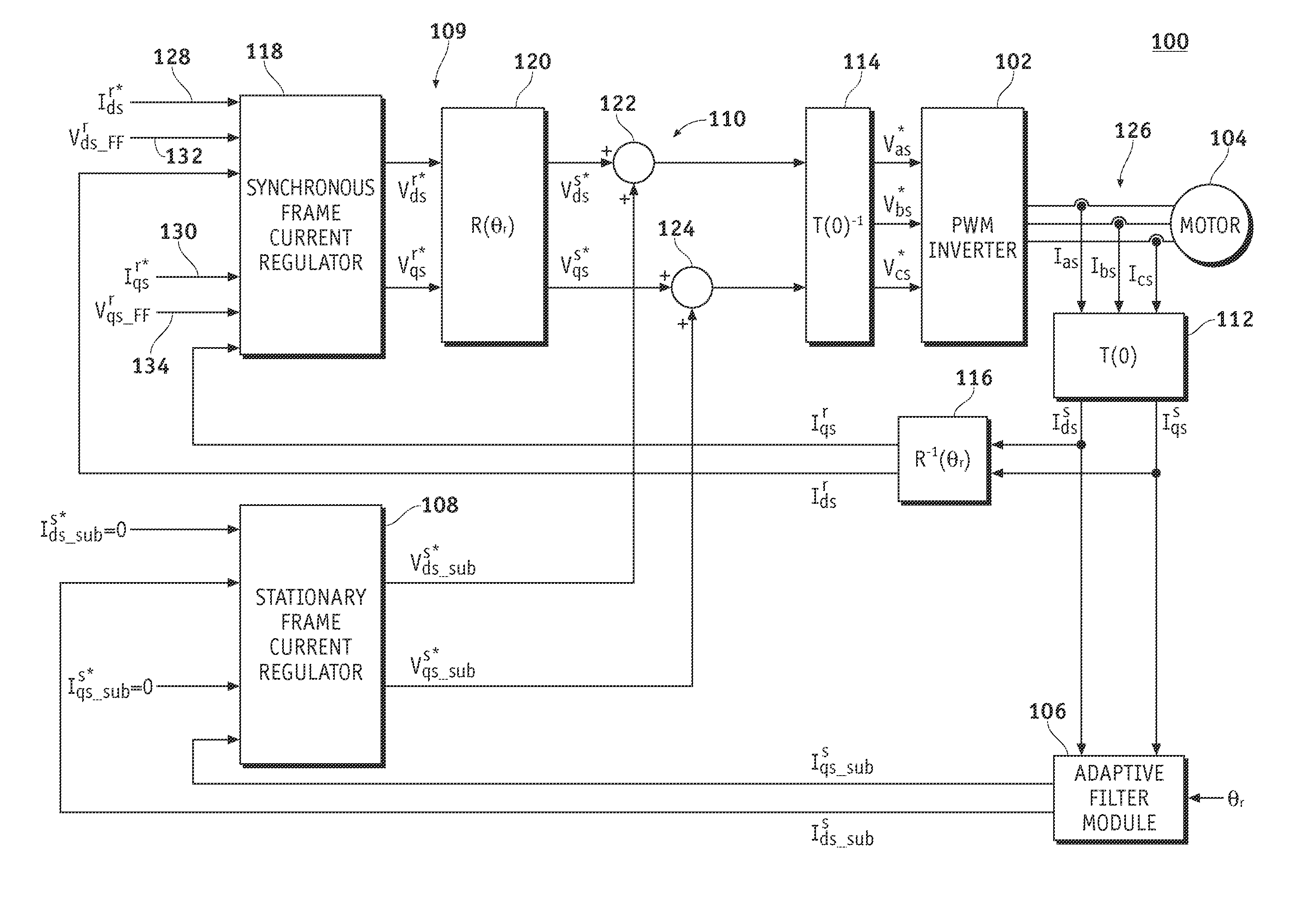
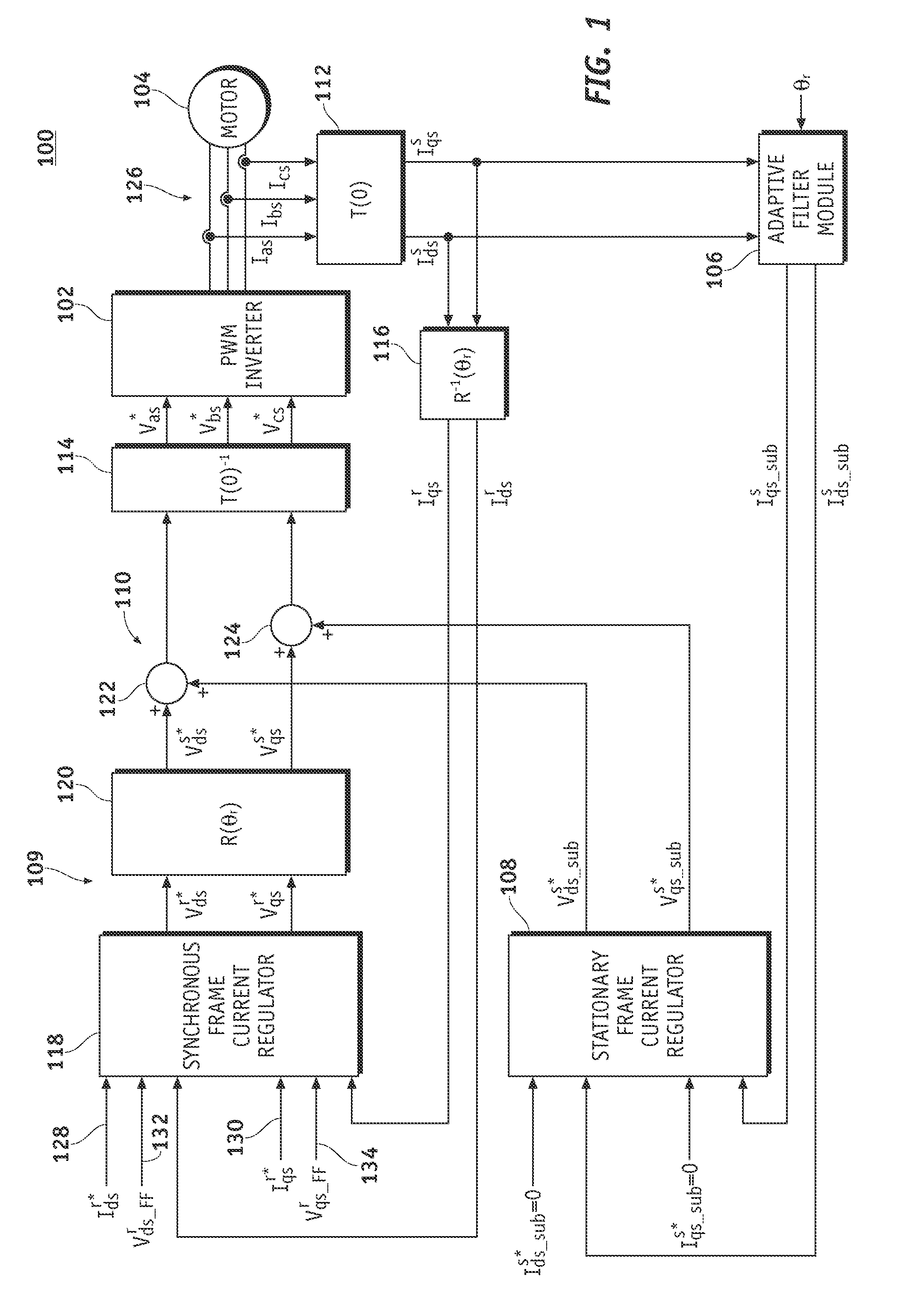
Reduction of subharmonic oscillation at high frequency operation of a power inverter
ActiveUS7449859B2Current errorEffective controlAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersPower inverterAdaptive filter
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Control circuit and control method of current mode control type DC-DC converter
ActiveUS7876077B2Prevent output from droppingAvoid oscillationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterCurrent mode control
The invention presents a control circuit and a control method of DC-DC converter capable of suppressing subharmonic oscillation of coil current even if the on-duty is over 50%. An error amplified signal V1 is an output voltage of an error amplifier ERA1. An offset voltage unit Ve2 outputs a lower limit set voltage V2 obtained by subtracting offset voltage e2 from error amplified signal V1. A voltage comparator COMP2 compares lower limit set voltage V2 output from offset voltage Ve2, and output voltage signal VIL. When the voltage value of output voltage signal VIL is decreased to lower limit set voltage V2 (region E2), the output of voltage comparator COMP2 changes from low level to high level. As a result, main transistor FET1 is set in conductive state. On the other hand, when the voltage value of output voltage signal VIL reaches an error amplified signal V1 (region E1), main transistor FET1 is set in non-conductive state.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Adaptive slope-compensation module and method thereof
An adaptive slope-compensation method is applied for a switch-mode power supply. The switch-mode power supply has a power switch, and an inductor coupled to an input power. The power switch controls the inductor storing energy or releasing energy to generate an output voltage. The adaptive slope-compensation method includes detecting an inductor current passing through the inductor and to generate an inductor-current detecting voltage, detecting a duty cycle of the power switch, detecting a voltage variation of the inductor-current detecting voltage when the power switch is turned on, generating a slope-compensation signal according to the voltage variation and the duty cycle, and adjusting the timing of turning the power switch on or off. In this way, even if the operation conditions of the input power and the output voltage change, the system still can quickly response and does not generate sub-harmonic oscillation.
Owner:LEADTREND TECH
Slope compensation control method and circuit for inverted welding power source with peak current control mode
InactiveCN104539157AAccurately reflectAvoid oscillationArc welding apparatusApparatus with intermediate ac conversionSubharmonic oscillationWave shape
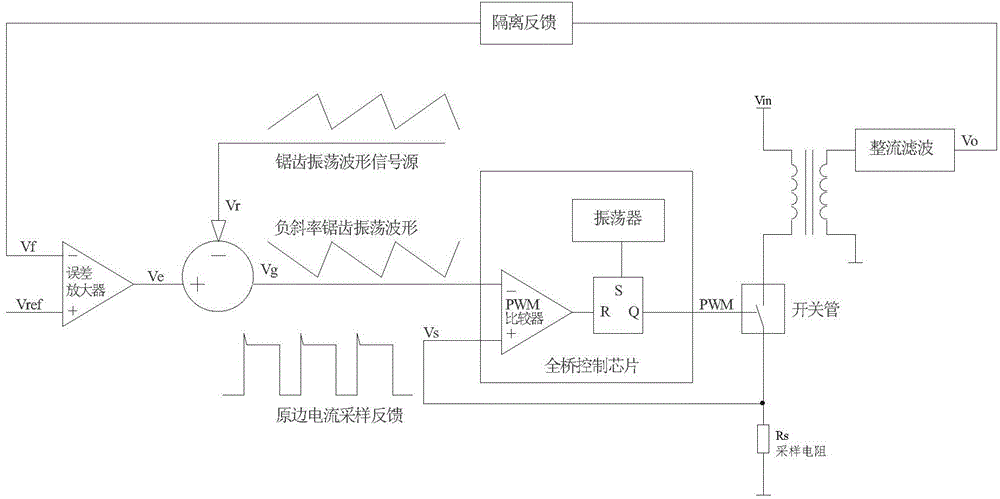
The invention relates to a slope compensation control method and a circuit for an inverted welding power source with a peak current control mode. The purpose of the slope compensation control method and the circuit is to effectively solve the sub-harmonic oscillation by providing a control method and a control circuit, to truly reflect the electric current of a power device, and to improve the anti-magnetic biasing capability of a system and the real-time protecting capability of the electric current of the power device. According to the technical scheme, the slope compensation control method and the circuit for the inverted welding power source with peak current control mode is characterized in that addition and subtraction are conducted between a saw-tooth oscillation waveform outputted by an input saw-tooth waveform signal source and a voltage signal outputted by an error amplifier, so that a voltage signal of a negative slope saw-tooth waveform is obtained. The voltage signal of the negative slope saw-tooth waveform is compared in real-time with a sampling feedback signal of a voltage input side current. Accordingly, the PWM pulse width output can be adjusted.
Owner:HANGZHOU KAIERDA ELECTRIC WELDING MACHINE
Peak current signal generating circuit, switching power supply circuit and method for generating peak current signals
ActiveCN102801305AReduce frequencyAchieve regulationApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceSubharmonic oscillation
The invention provides a peak current signal generating circuit, a switching power supply circuit and a method for generating peak current signals. The switching power supply circuit at least comprises a first power tube. The peak current signal generating circuit comprises a first current source, a peak capacitance, an LPF (Low-Pass Filtering) circuit, a first switch and a first voltage source, wherein the peak capacitance is connected and coupled with the first current source in parallel, and voltage signals at two ends of the peak capacitance are peak current signals; a first end and a second end of the LPF circuit are respectively coupled to the two ends of the peak capacitance, and a control end of the LPF circuit is used for receiving a pulse signal representing a switching period of the first power tube; a first end of the first switch is coupled to a third end of the LPF circuit, and a control end of the first switch is used for receiving a reset signal; and a first end of the first voltage source is coupled to a second end of the first switch, and a second of the first voltage source is coupled to the second end of the LPF circuit. According to the invention, the purposes of regulating the peak current signals according to a load condition, enabling the frequency of the switching power supply circuit to be lowered along with the lowering of the load and avoiding the generation of sub-harmonic oscillation can be realized.
Owner:CHENGDU MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
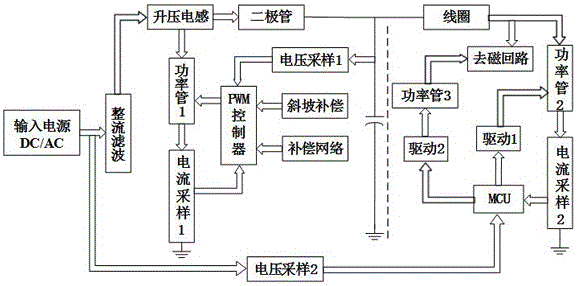
Intelligent electromagnetic switch control device for low voltage power supply system
ActiveCN104952667AStable working voltageWide operating voltage rangeRelaysLoop controlCurrent mode control
The invention aims to provide an intelligent electromagnetic switch control device for a low voltage power supply system. The intelligent electromagnetic switch control device is characterized by comprising a voltage conversion module and a current conversion module which are in cascade connection, wherein voltage conversion at the former stage adopts a current mode control manner, and working voltage supplied to the latter stage can be flexibly and quickly adjusted to be higher than the input voltage to conduct current monitoring; the latter stage conducts wave chopping on the output voltage at the former stage, and square-wave voltage is obtained at the two ends of an electromagnetic mechanism, so that an electromagnetic switch is subjected to current close-loop control. According to the device, the higher harmonic oscillation problem caused by boost inductive current instability is eliminated through slope compensation; the boosting conversion at the former stage can also play the power factor regulation function to purify a control power supply; through the adoption of the manner that an advanced control algorithm is coordinated with the ontology design of an electromagnetic mechanism, the optimum control duty cycle adjusting mode is automatically searched, and the optimum duty cycle is limited in a certain range, so that the harmonic component of the current in the retention stage is reduced, and the electromagnetic audio noise is reduced.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
High frequency oscillator using dielectric resonator
InactiveUS20050184818A1Improve stabilityEnhanced oscillationPulse automatic controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectromagnetic couplingAudio power amplifier
A second-harmonic oscillator based on push-push oscillation has a pair of amplifiers for oscillation, a high frequency transmission line for connecting inputs of the pair of amplifiers to each other and connecting outputs of the pair of amplifiers to each other, and an electromagnetic coupling member disposed between the inputs and outputs of the pair of amplifiers such that it is electromagnetically coupled to the high frequency transmission line. The electromagnetic coupling member includes at least a dielectric resonator. The pair of amplifiers, high frequency transmission line, and electromagnetic coupling member form two oscillation loops which oscillate in opposite phases to each other with respect to a fundamental wave of oscillation for generating a second harmonic of the fundamental wave.
Owner:NIHON DEMPA KOGYO CO LTD +1
LED dimming device based on PWM
InactiveCN104717778AChange duty cycleSmooth size adjustmentElectric light circuit arrangementEnergy saving control techniquesAverage currentPeak value
The embodiment of the invention discloses an LED dimming device based on PWM. The device comprises an LED driving unit, a current detecting unit and a hysteresis control unit, wherein the LED driving unit is composed of an inductor L and a fly-wheel diode, and LEDs are controlled to be turned on or off through an MOS transistor. The current detecting unit comprises a sampling resistor connected to an LED lamp in series and a differential amplifier connected to the sampling resistor in parallel; the hysteresis control unit is composed of an amplifier and a not-and gate; the negative input end of the amplifier is connected with the output end of the differential amplifier, a set threshold voltage is input to the positive input end of the amplifier, the output end of the not-and gate is connected with a gate pole of the MOS transistor, and the input of the not-and gate is connected with the output end of the amplifier and a digital dimming signal. Due to the adoption of the LED dimming device, a current hysteresis control mode is used for solving the problem that peak current and average current are not consistent during current peak control, the subharmonic oscillation phenomenon with the duty ratio larger than 0.5 occurring during peak current control is avoided, and therefore a slope compensation circuit is not needed, and the circuit structure is relatively simple.
Owner:吴汉肱
Double-edge modulation output voltage control method and device of boost converter
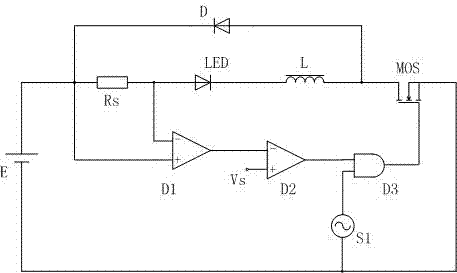
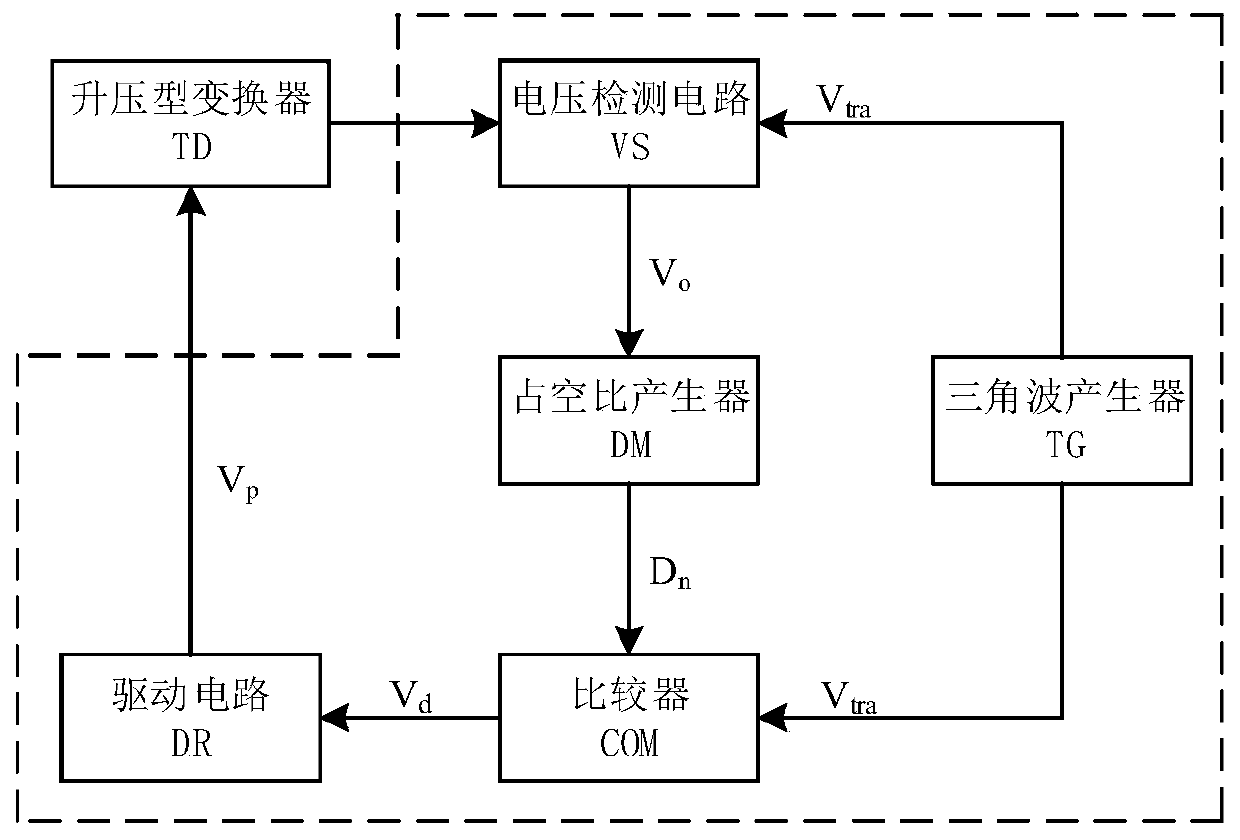
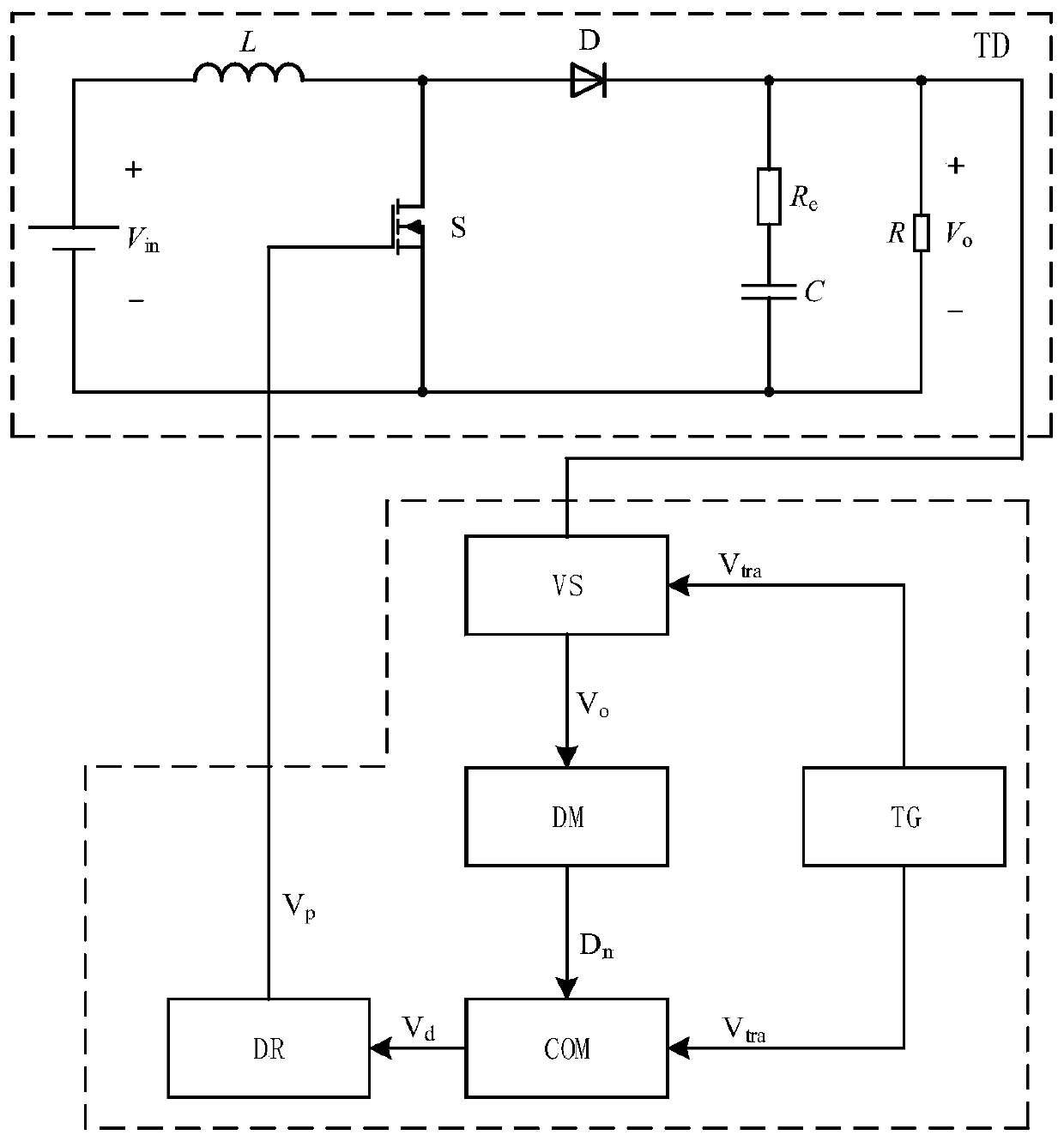
PendingCN109787473AImprove load transient performanceEffective regulationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationControl signalSwitching cycle
The invention discloses a double-edge modulation output voltage control method and device of a boost converter. The method comprises the following steps: sampling an output voltage at a starting moment of each switching cycle, and inputting the output voltage and a reference voltage value into a duty ratio generator to generate a duty ratio control signal Dn; comparing a triangular carrier signalVtra with the duty ratio control signal to generate a duty ratio signal Vd; and then inputting the duty ratio signal into a driving circuit to generate a switching tube driving signal, adopting one turn-on time and two turn-off times, and controlling the turn-off and the turn-on of a switching tube of the boost converter within each cycle by adopting a control time sequence composed of turn-off, turn-on and turn-off in sequence. The double-edge modulation output voltage control method and device disclosed by the invention can be used for controlling boost switching converters such as Boost converters, secondary Boost converters and the like, and have the beneficial effects that no compensation network is required, the control is simple, the precision is relatively high, stable work can beperformed within the entire duty ratio range, no subharmonic oscillation is generated, and the transient response speed is high.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
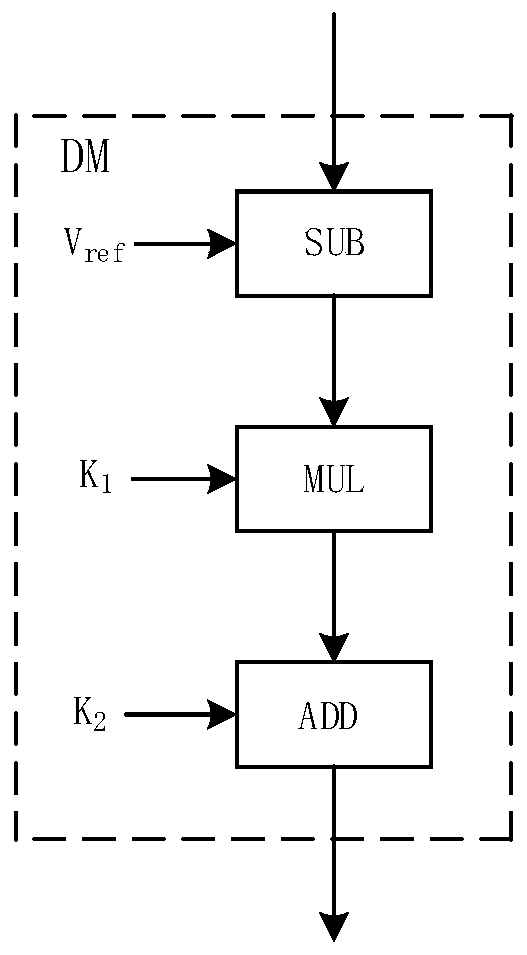
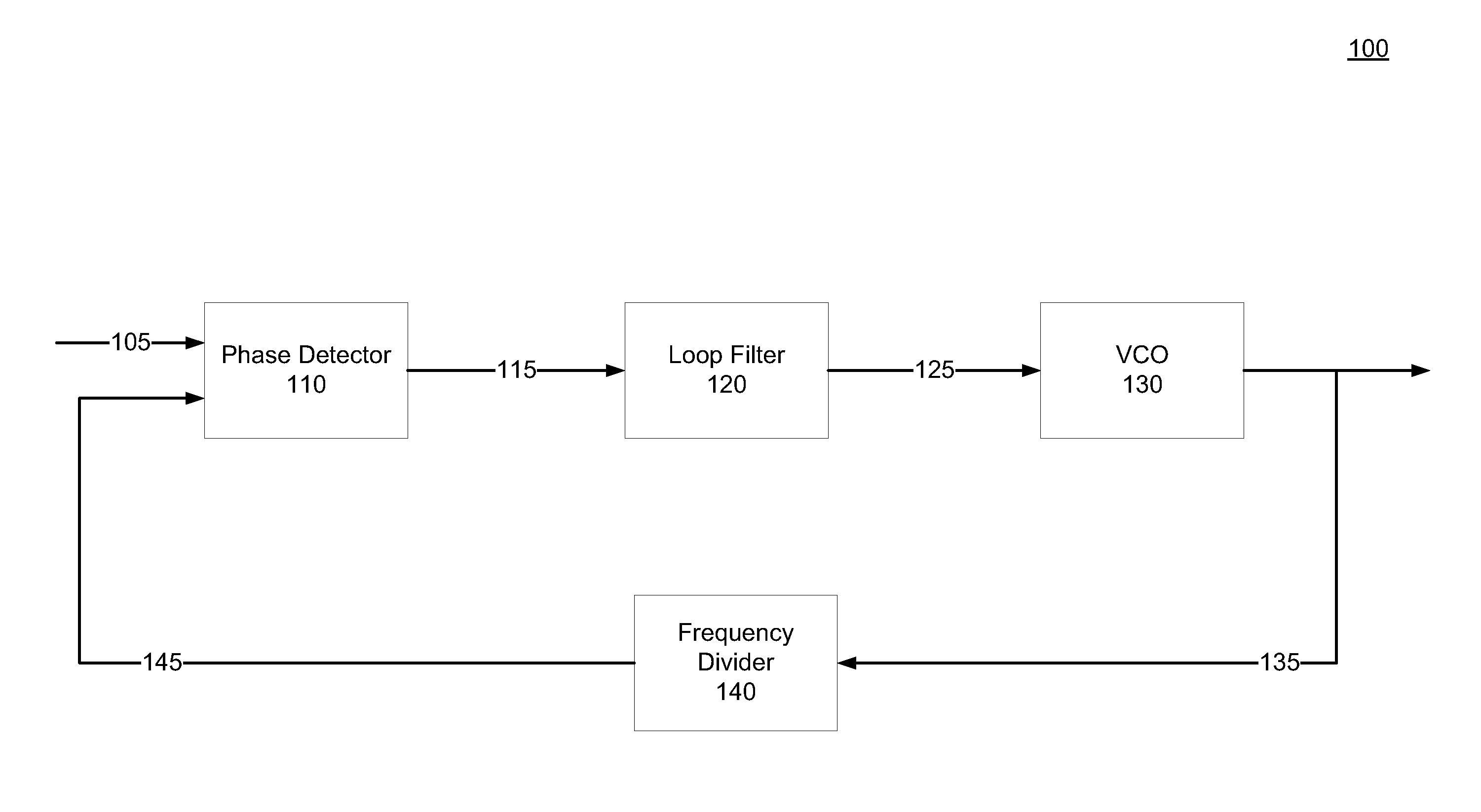
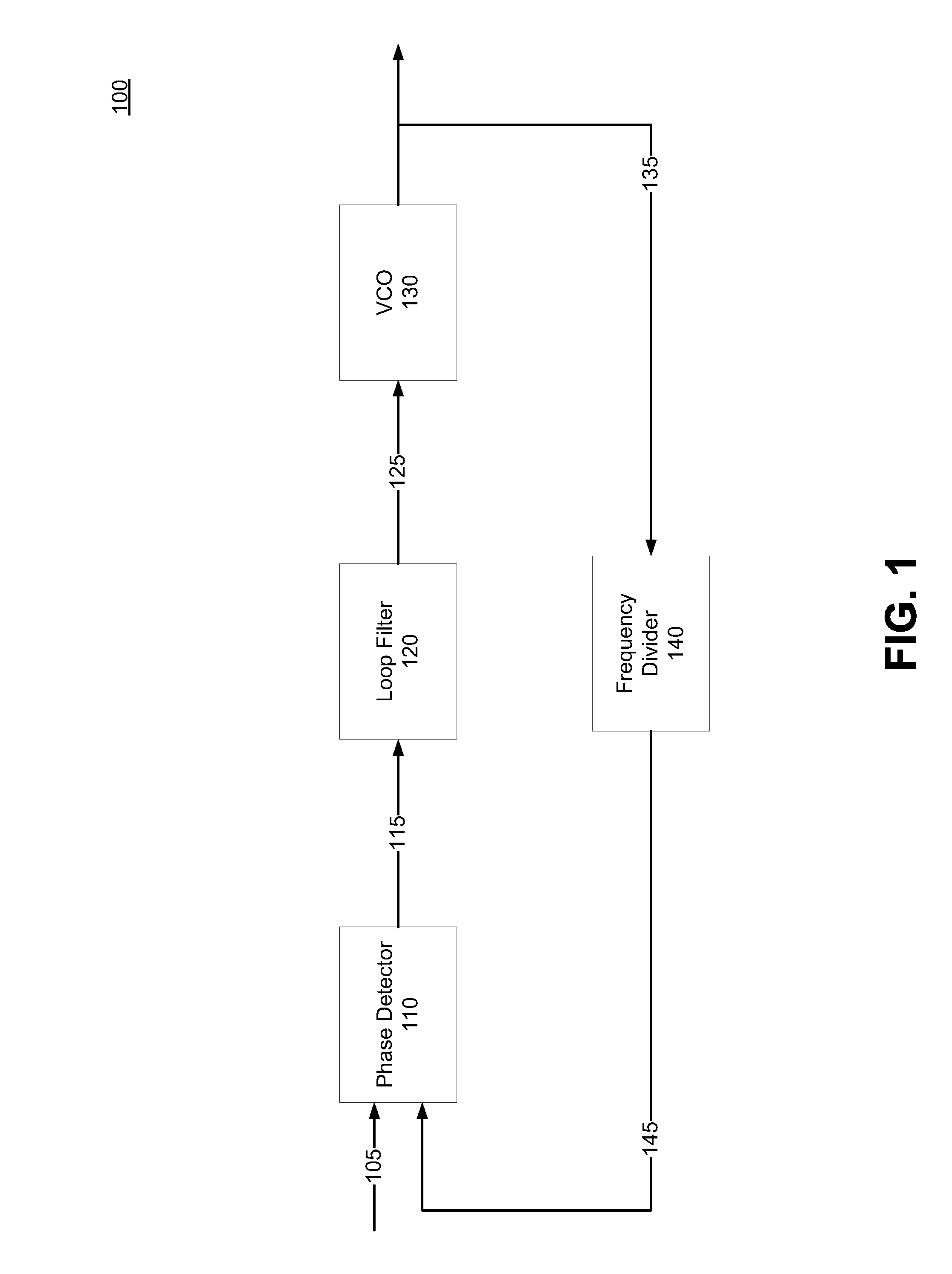
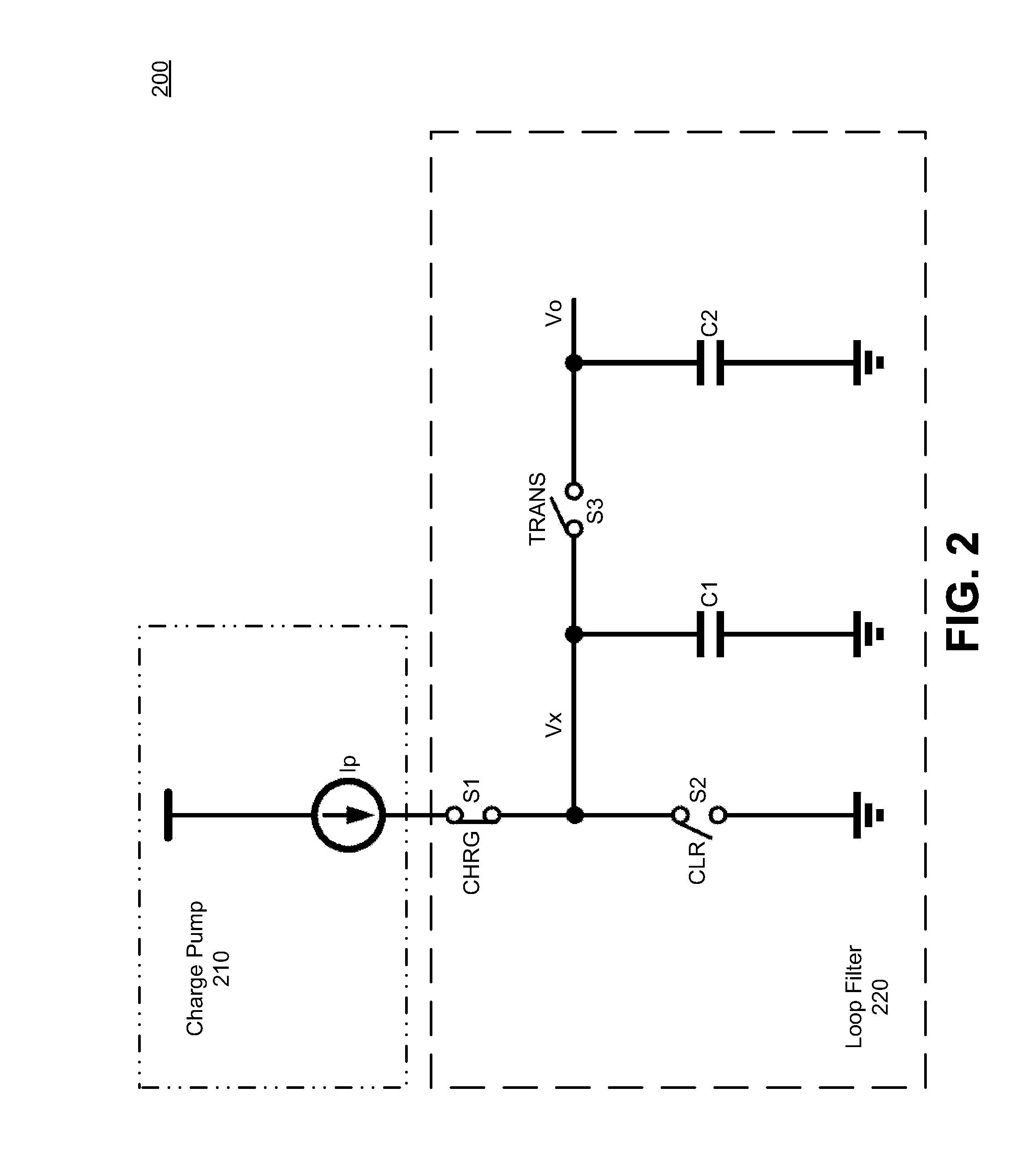
Phase Locked Loop with Sub-harmonic Locking Prevention Functionality
Embodiments relate to type-I PLLs that do not lock at a sub-harmonic frequency of a reference clock signal by controlling timing of charging or discharging of one or more capacitors in the PLLs. A phase frequency detector (PFD) of a type-I PLL can prevent sub-harmonic locking by generating a clear output signal to cause a sampling capacitor of PLL's loop filter to discharge only during a time period when the sampling capacitor is not being charged. For example, the PFD can include a gating element to control the time during which the clear output signal is generated. By ensuring that the sampling capacitor is not discharged during a time period while it is being charged, the PLL's voltage-controlled oscillator is controlled to oscillate at an intended frequency rather than at a sub-harmonic of the intended frequency.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
A fully differential Class D clamp recovery circuit
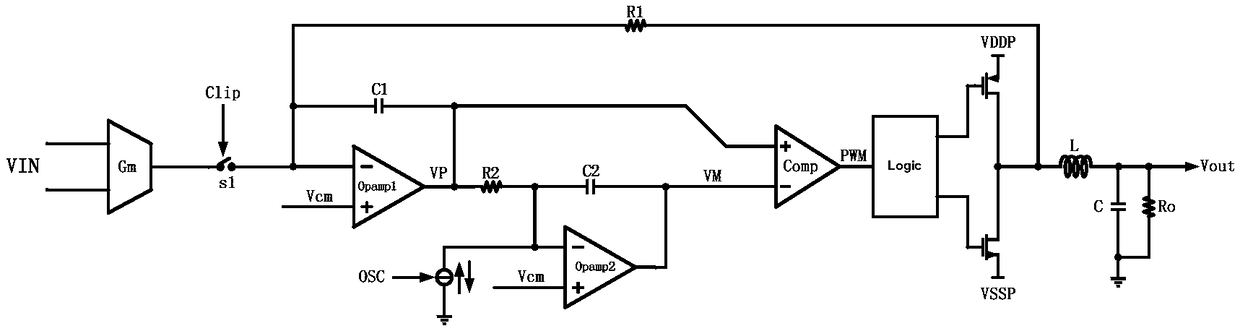
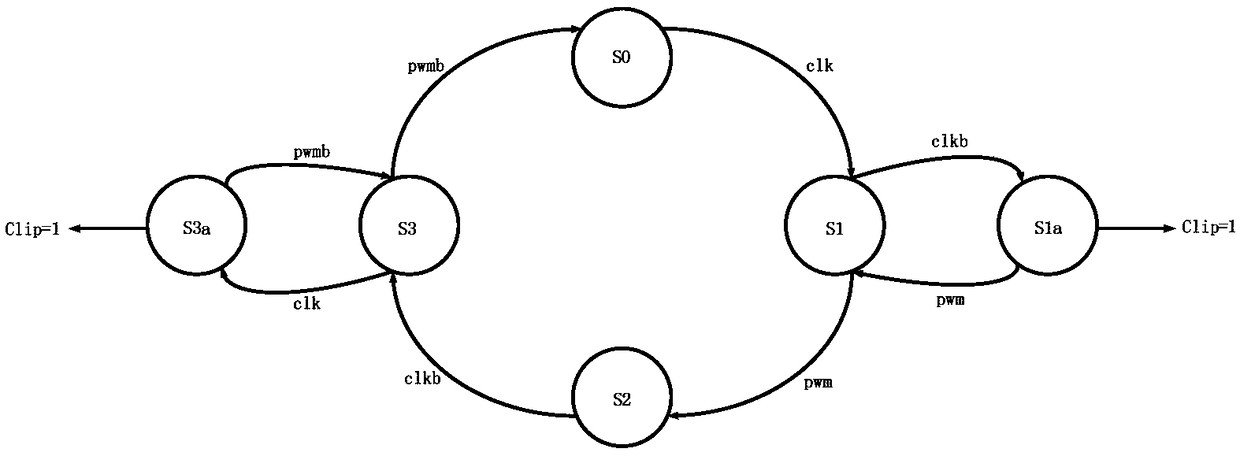
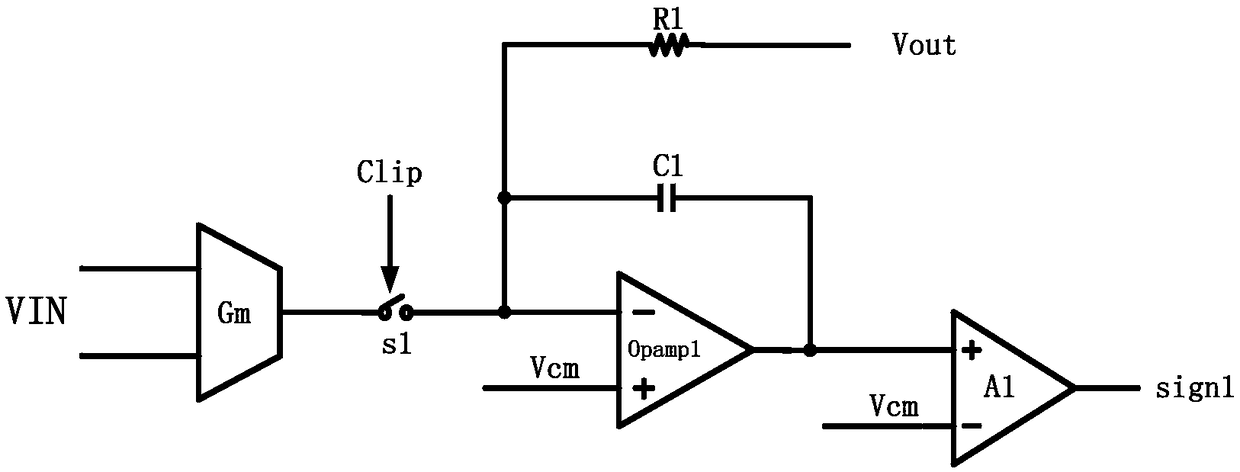
ActiveCN109167588AAvoid false triggersSmooth entryElectric pulse generatorPulse duration/width modulationIntegratorSubharmonic oscillation
An embodiment of the present invention provides a fully differential Class D clamp recovery circuit, As to whet that pwm signal between the two clk rising edge becomes high and whether the pwm signalbetween the two clk falling edge becomes low, whether the system enters the Clipping state or not can be judged according to whether the system enters or exits the Clipping state smoothly, which can avoid the false triggering of the Clipping state caused by the delay of the comparator Comp in the loop. By clamping the two outputs of the second integrator in the loop to a reference voltage slightlyabove the peak value of the triangular wave and slightly below the valley value of the triangular wave in the Clipping state, the subharmonic oscillation of the system in the Clipping state is prevented.
Owner:WUHAN JUXIN MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
COT control-based internal ripple compensation circuit and control method thereof
PendingCN109742945AImprove consistencyHigh precisionDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
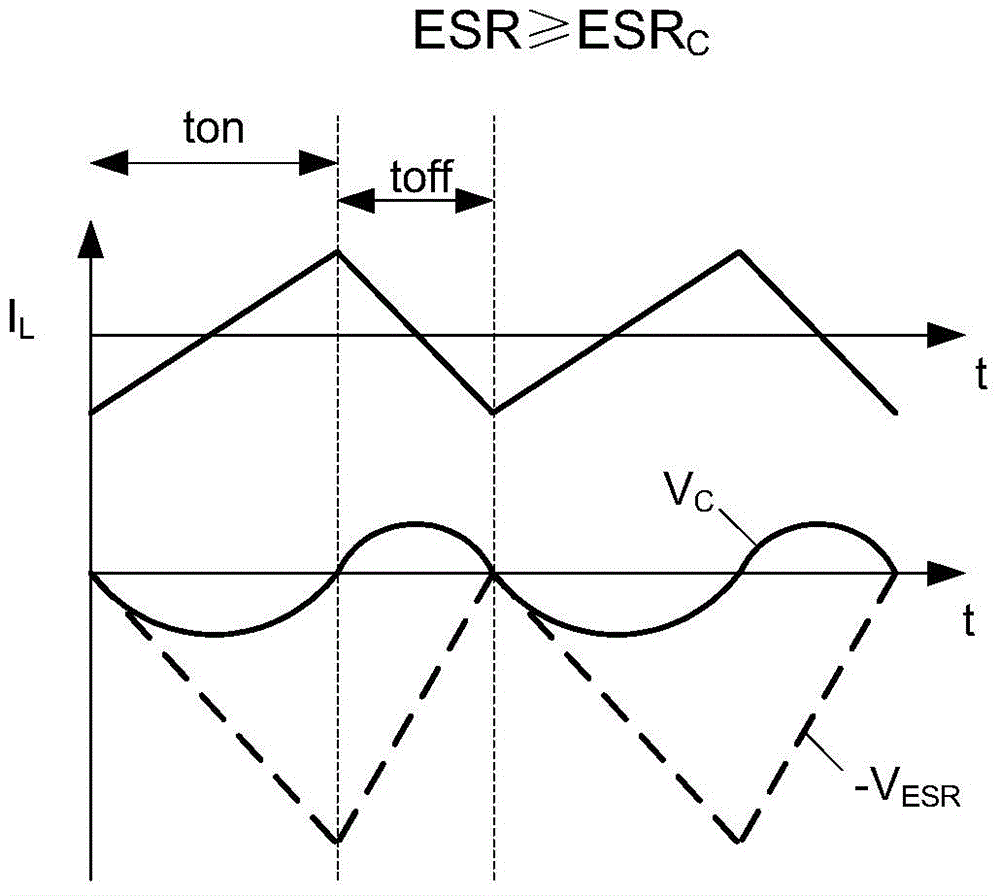
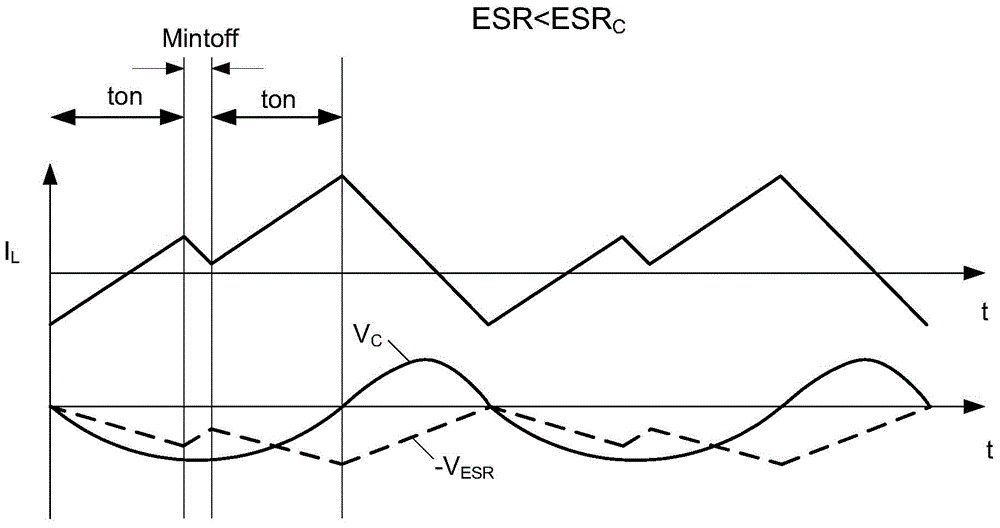
The invention relates to a COT control-based internal ripple compensation circuit and a control method thereof. A division voltage of an output end voltage of the circuit is used as a feedback voltagefor being acted on a comparator, the feedback voltage is compared with a reference voltage of the comparator, an output signal obtained by the comparator is acted on a RS trigger to control conduction of a power tube or a rectification tube, the power tube is conducted, the rectification tube is cut off and energy is stored in an inductor when the output end voltage is lower than a preset voltageand the feedback voltage is lower than the reference voltage, a conduction time control circuit starts to time, the RS trigger is controlled by the conduction time control circuit after preset time is reached, so that the power tube is cut off, the rectification tube is conducted, energy is released to an output capacitor from the inductor, the ripple compensation circuit generates a ripple voltage, the feedback voltage is larger than the reference voltage by the ripple voltage, and subharmonic oscillation of the circuit caused by excessively small series resistance of the output capacitor isprevented.
Owner:QX MICRO DEVICES
Phase-shifting control method of a boost converter and implementing circuit
ActiveCN101753014APhenomenon that prevents subharmonic oscillationApparatus without intermediate ac conversionPhase shift controlSubharmonic oscillation
The present invention relates to a phase-shifting control method of a boost converter and an implementing circuit, wherein the boost converter is provided with a main energy storing loop and at least one second energy storing loop connected with the main energy storing loop in parallel; a main loop current passing through the main energy storing loop has main loop charging time distance and main loop discharging time distance; and a second loop current passing through the second energy storing loop has second loop charging time distance and second loop discharging time distance. An ideal switching time sequence of judging value when the second loop current decreases to zero current is calculated, an actual switching time sequence of the second loop charging time distance is started, break-over error time distance of the phase differences of the ideal switching time sequence and the actual switching time sequence is obtained, and the second loop charging time distance is decided by the break-over error time distance and the main loop charging time sequence. Thus, the break-over error time distance of the nest period is avoided to enlarge, and further, a problem that the second loop current generates subharmonic oscillation is avoided.
Owner:SPI ELECTRONICS
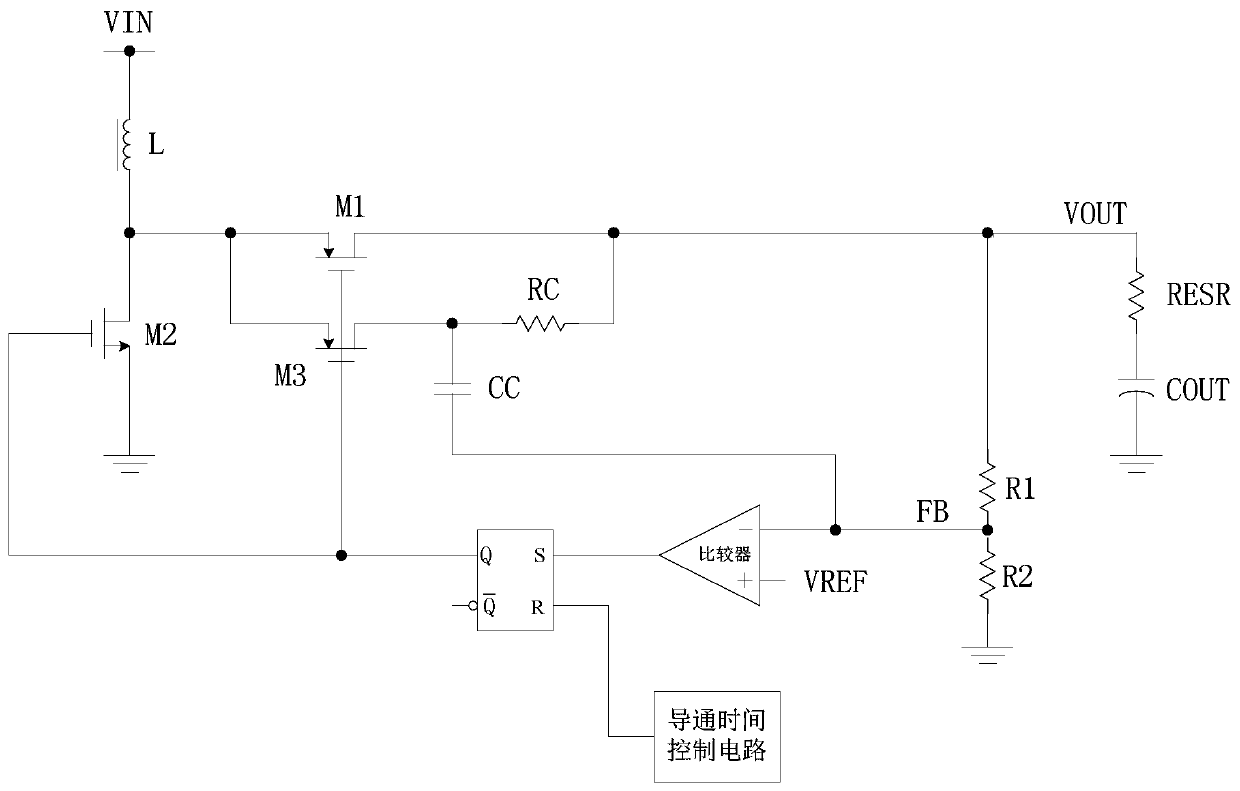
Control circuit and control method for DC-DC converter
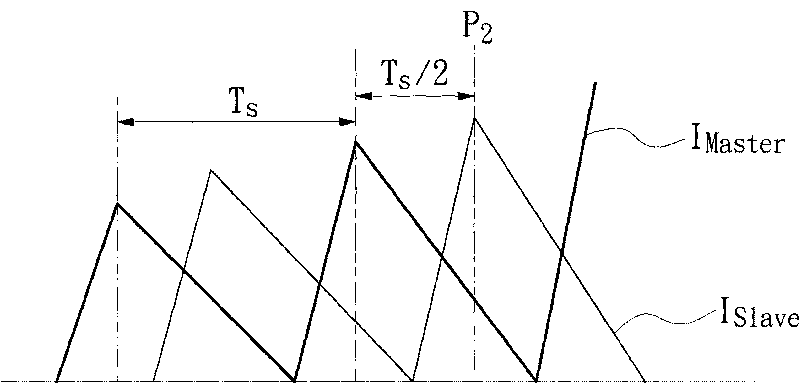
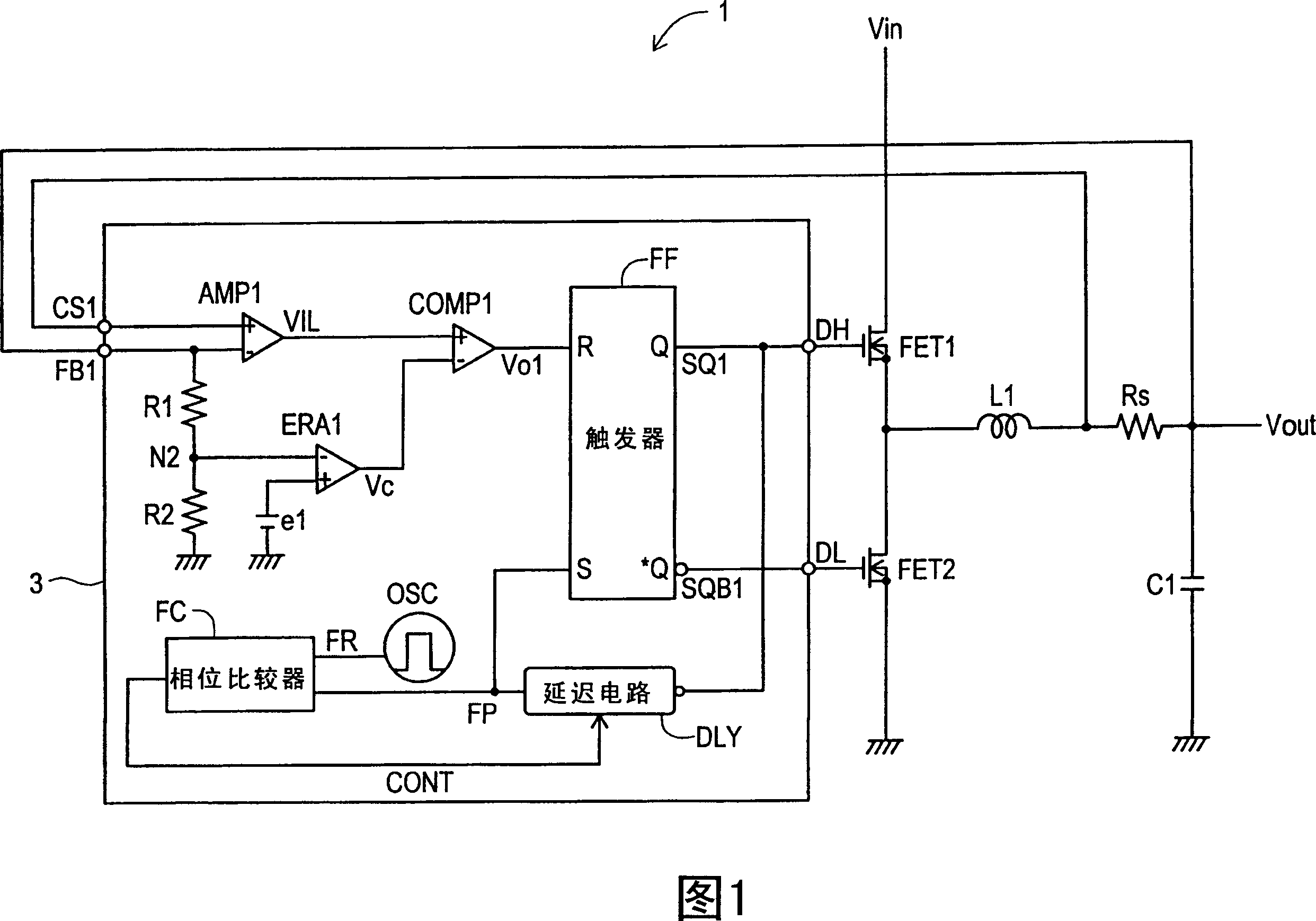
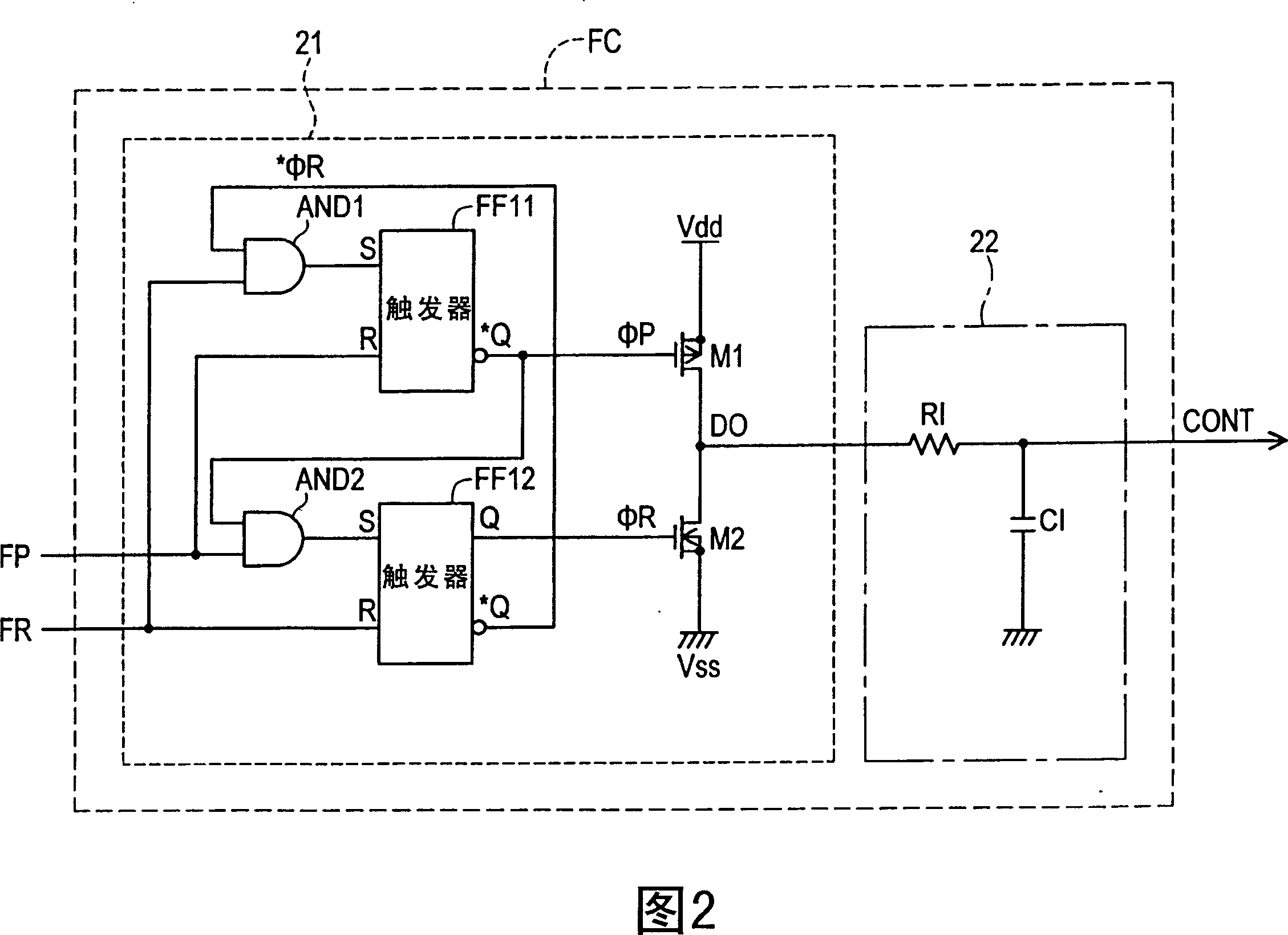
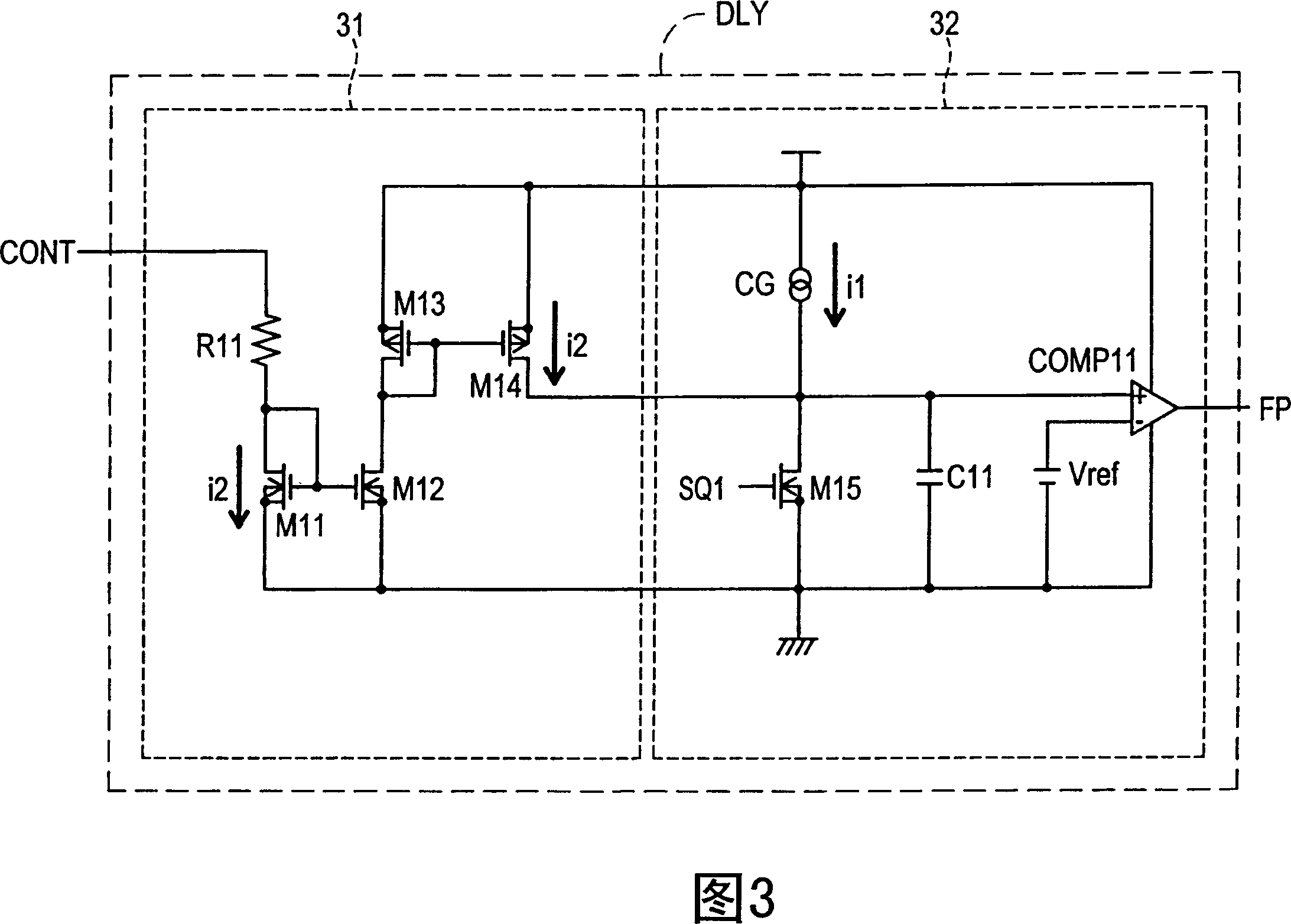
ActiveCN1980026APrevent subharmonic oscillationPrevents output current from droppingEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCurrent mode controlDc dc converter
The object of the present invention to provide a control circuit and a control method for a current mode control type DC-DC converter capable of preventing a subharmonic oscillation even if an on-duty is not less than 50% and capable of preventing a switching frequency from fluctuating depending on an input voltage. When a high-level output signal Vo 1 is inputted to a reset input terminal R of a flip-flop FF, a transistor FET 1 is turned off. A phase comparator FC outputs a comparison result signal CONT in accordance with a phase difference between a delay signal FP and a reference signal FR. A delay circuit DLY outputs a high-level delay signal FP after the passage of a delay time DT adjusted in accordance with the comparison result signal CONT from the turn-off of the transistor FET 1 . The transistor FET 1 is turned on in accordance with an input of the high-level delay signal FP.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
On-off timer circuit for use in dc-dc converter
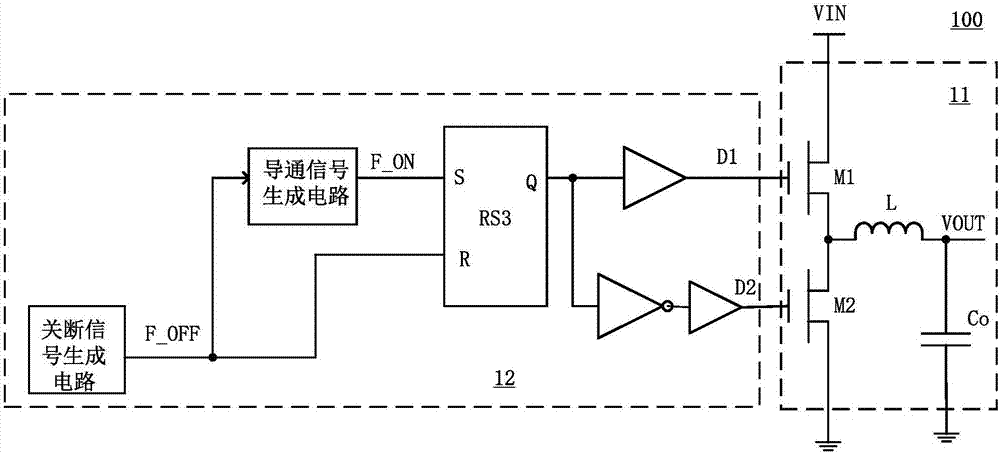
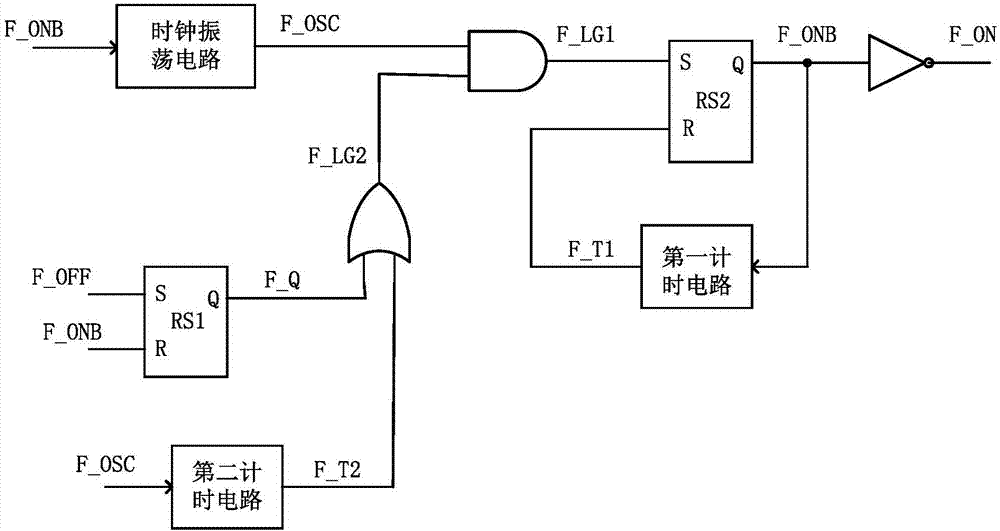
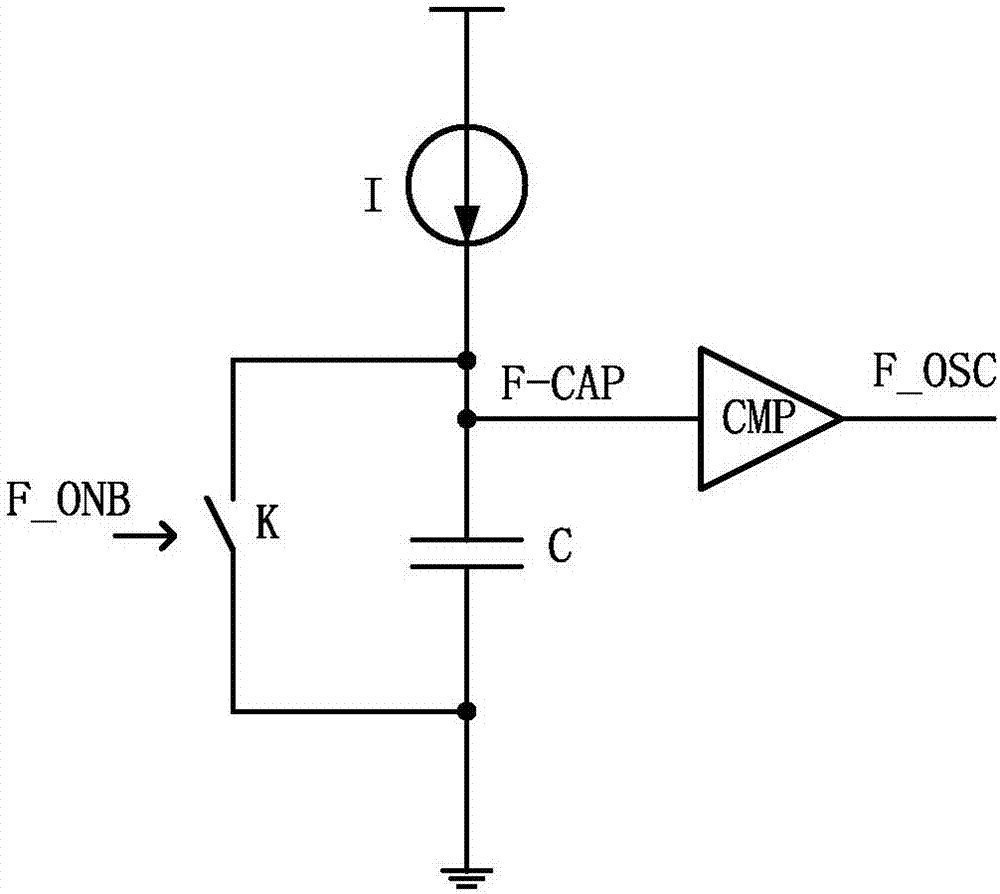
InactiveUS20110215786A1Minimize and eliminate riskDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationDc dc converterSubharmonic oscillation
An ON-OFF timer circuit for use in a DC-DC converter to minimize or eliminate the risk of developing sub-harmonic oscillations that may cause the dc-dc system to be unstable is presented. The apparatus controls and limits the ‘On’ time duration and ‘Off’ time duration within one pulse cycle.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Current mode controlled BOOST converter
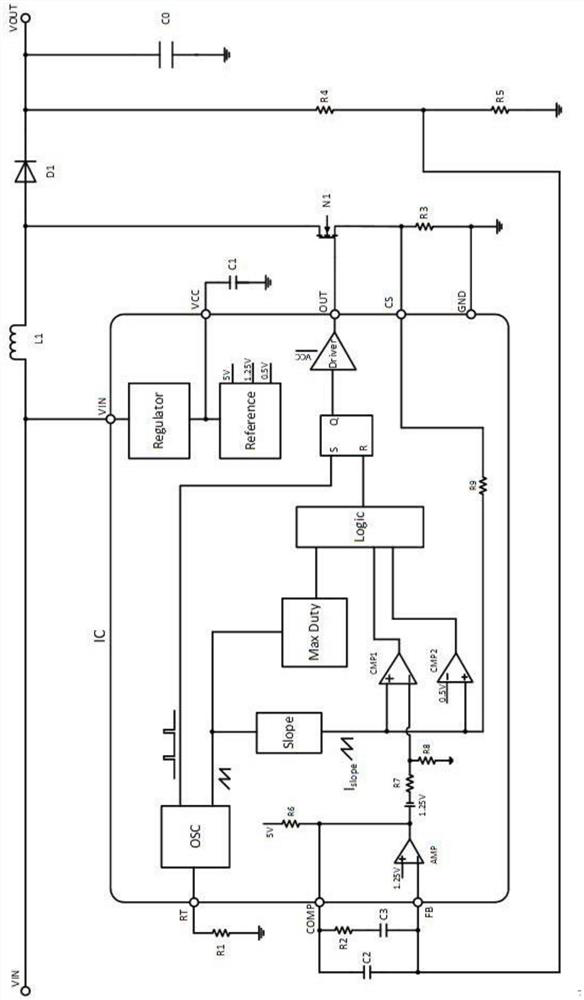
PendingCN112117899AWide input voltageImplementing Current Mode ControlDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceCurrent mode control
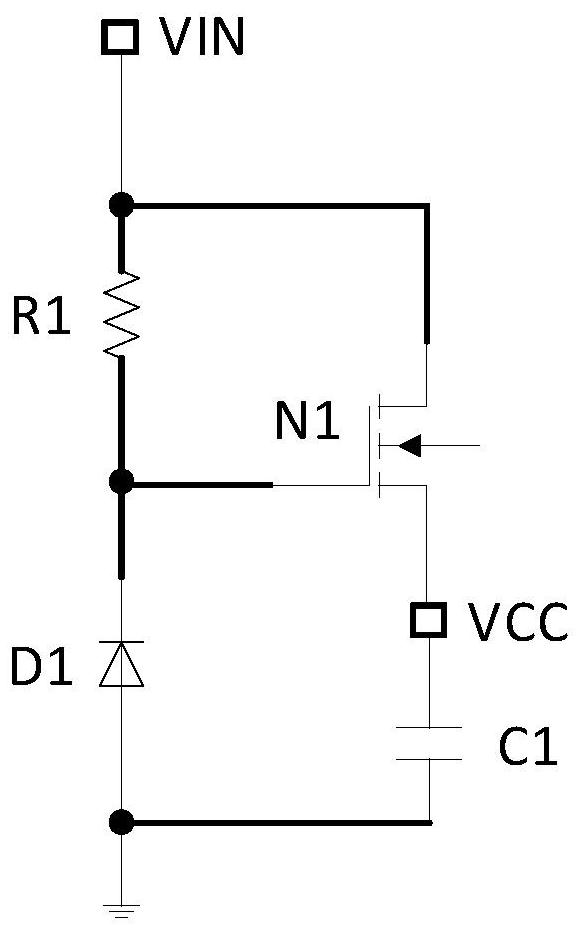
The invention relates to a current mode controlled BOOST converter, and the converter comprises a control IC and a peripheral circuit, wherein the IC peripheral circuit comprises VIN which is an inputvoltage of a system; VOUT which is the output voltage of the system; L1 which is an inductor; D1 which is a fly-wheel diode; C0 which is an output filter capacitor; an N1 power switch tube; C1 whichis a VCC pin plug-in capacitor of the IC; R1 which is a resistor, is connected with an RT pin of the IC and is used for controlling the working frequency of the system; R2, C2 and C3 which are FB pinand COMP pin compensation networks of the IC and play a role in deciding the stability of the system; R3 which is a current sampling resistor; R4 and R5 which form a sampling network of the output voltage, wherein the proportion of R4 and R5 determines the magnitude of the output voltage. The current mode BOOST converter provided by the scheme has wide input voltage, output ripples are easy to reduce, subharmonic oscillation is eliminated, and loop stability is convenient to adjust.
Owner:SUZHOU KAIWEITE SEMICON
Laser module
Disclosed is a laser module for generating laser light without a wavelength shift during a direct modulation of high frequency. The laser module includes: a laser light source for generating a first light; a nonlinear crystal for secondary harmonic generation for wavelength-converting the first light into a second light; and a multi-mode interferometer placed between the laser light source and the secondary harmonic generation, for modulating the intensity of the first light.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Control circuit, control method and switching power supply
ActiveCN107394998AIncrease duty cycleEasy to implementPower conversion systemsSubharmonic oscillationFrequency conversion
The invention provides a control circuit, a control method and a switching power supply. A frequency for controlling a conduction signal conducted by a main switch tube is a preset frequency when a switch-off time required by the main switch tube is larger than minimum switch-off time and is a frequency positively related to the switch-off time required by the main switch tube when the switch-off time required by the main switch tube is smaller than the minimum switch-off time, so that smooth switching between a fixed-frequency working mode and a variable frequency fixed switch-off working mode can be achieved, a mode switching signal is provided without a special mode judgment circuit, the control circuit is simple in implementation mode, and the expansion of a duty ratio of a switch control signal of the main switch tube can be stably and continuously achieved; and moreover, during the frequency conversion process, the power supply is still in the constant switch-off time working mode, so that the problem of subharmonic oscillation caused by insufficient subharmonic compensation due to frequency conversion is prevented.
Owner:SILERGY SEMICON TECH (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
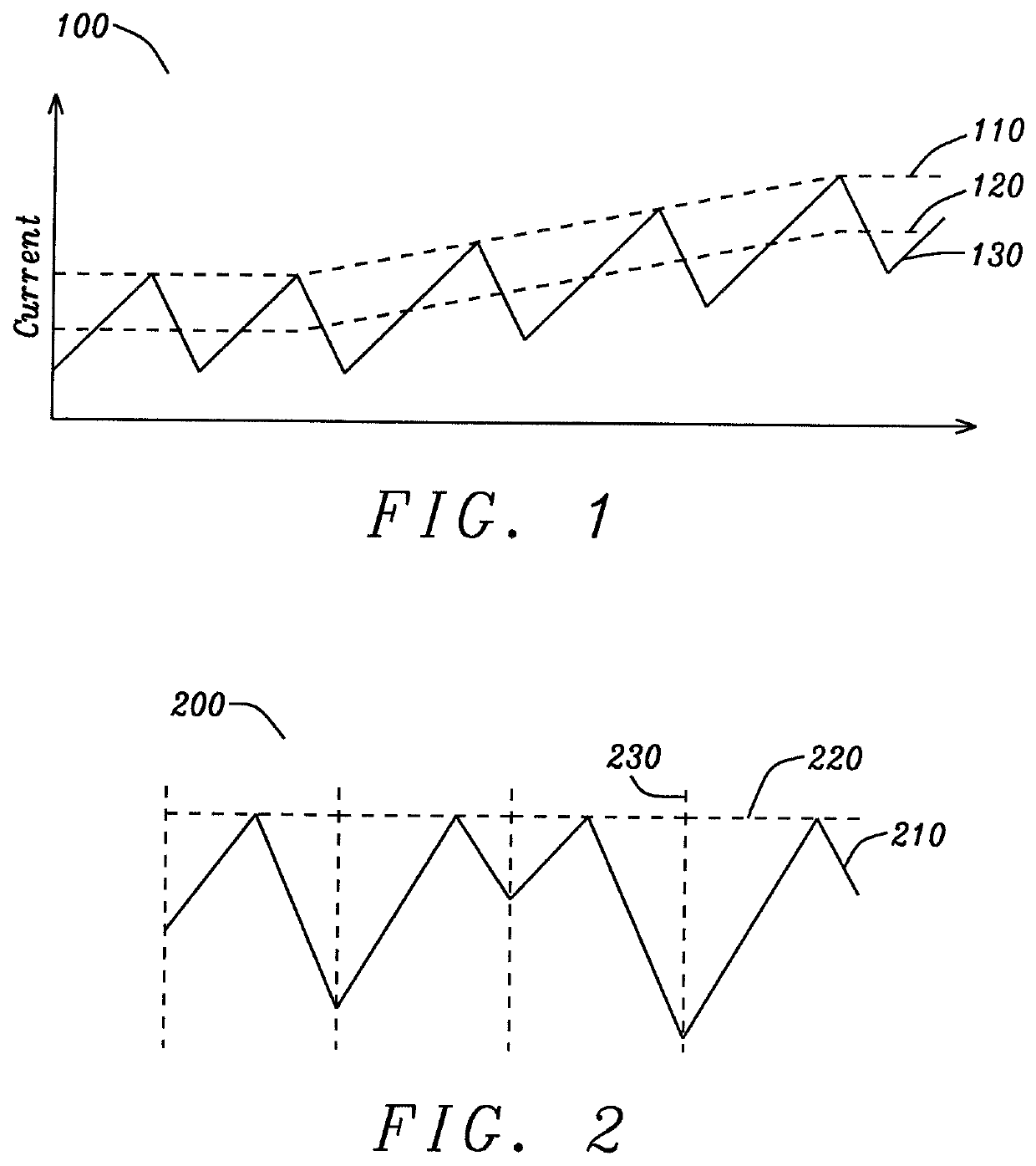
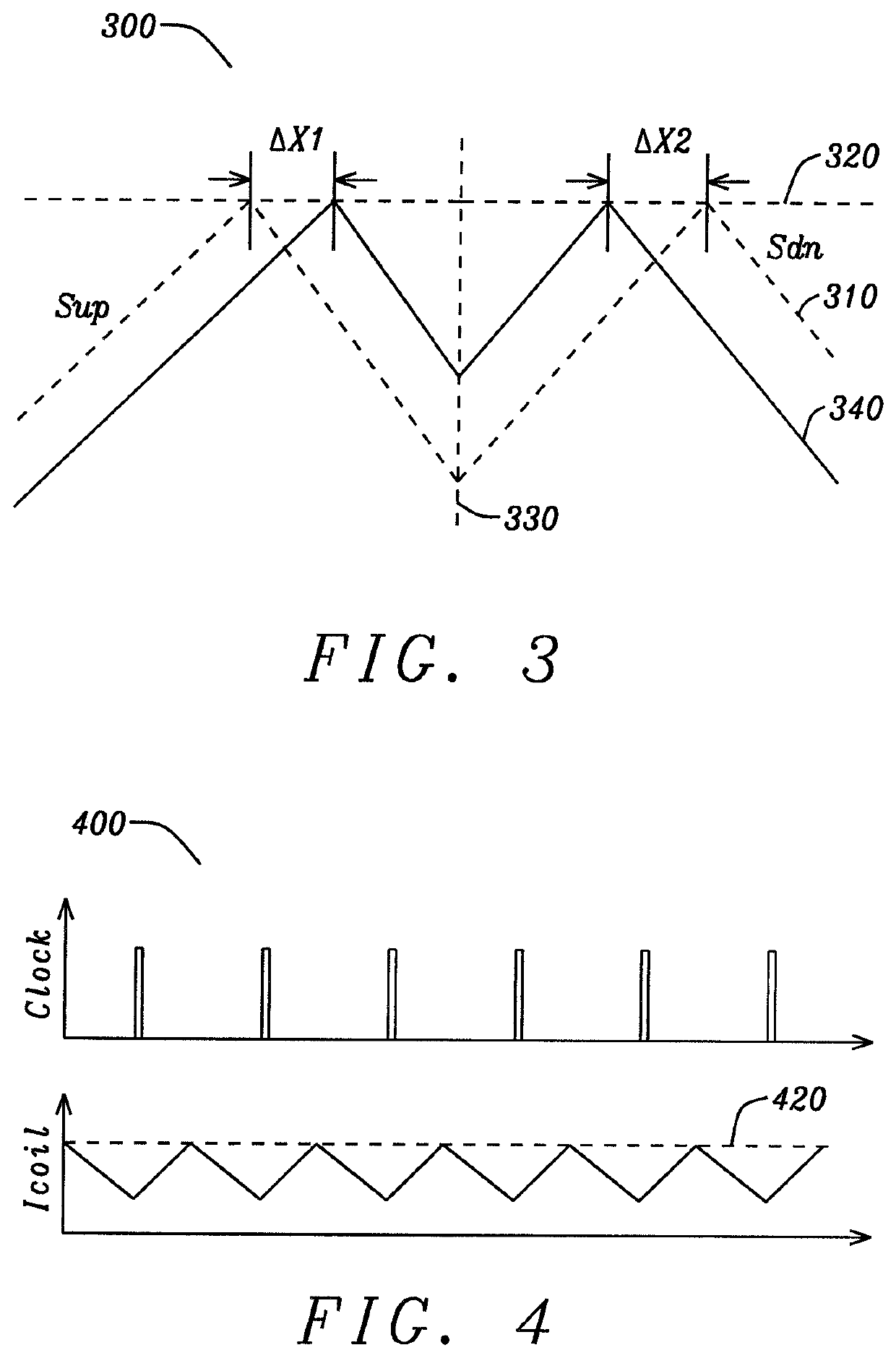
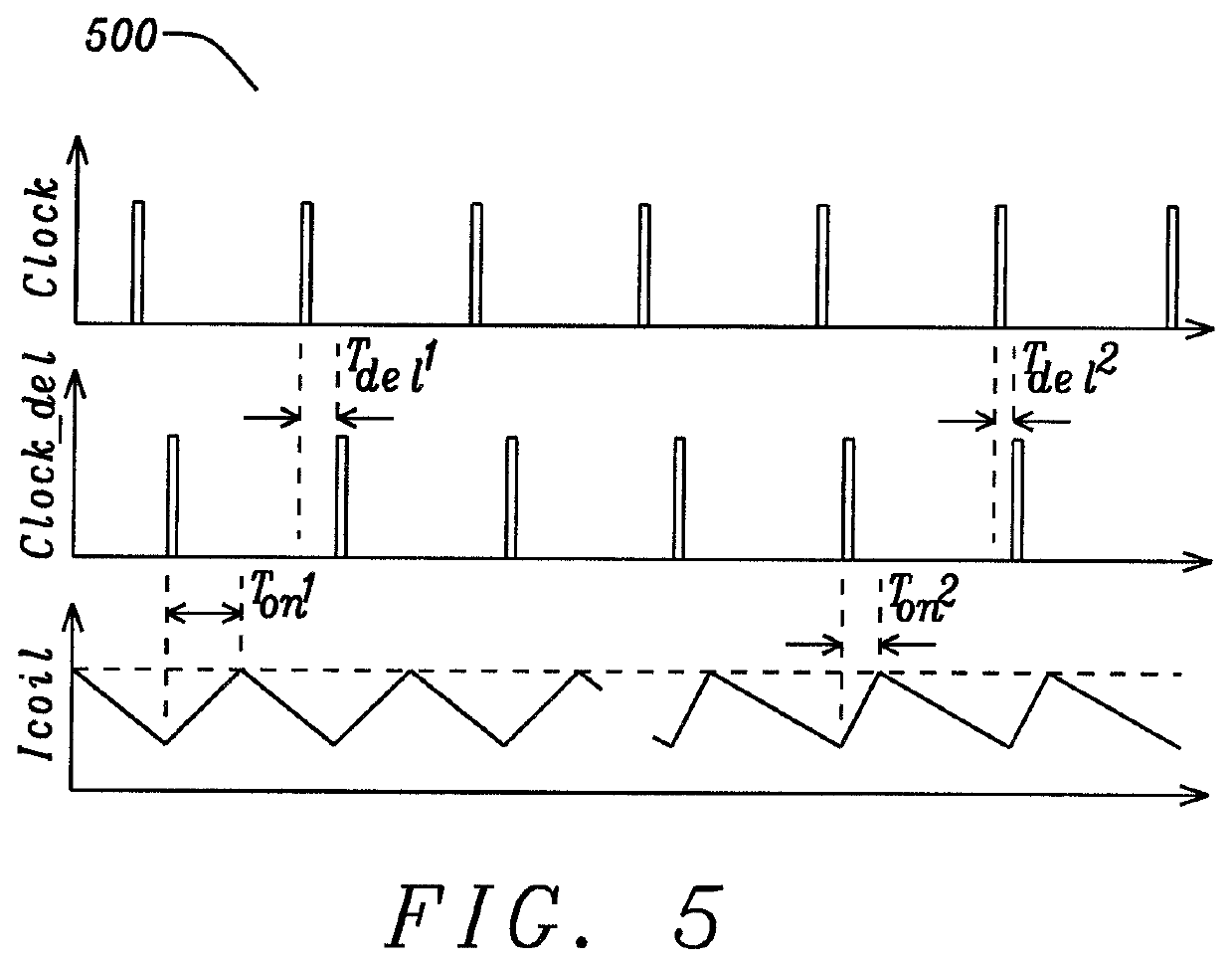
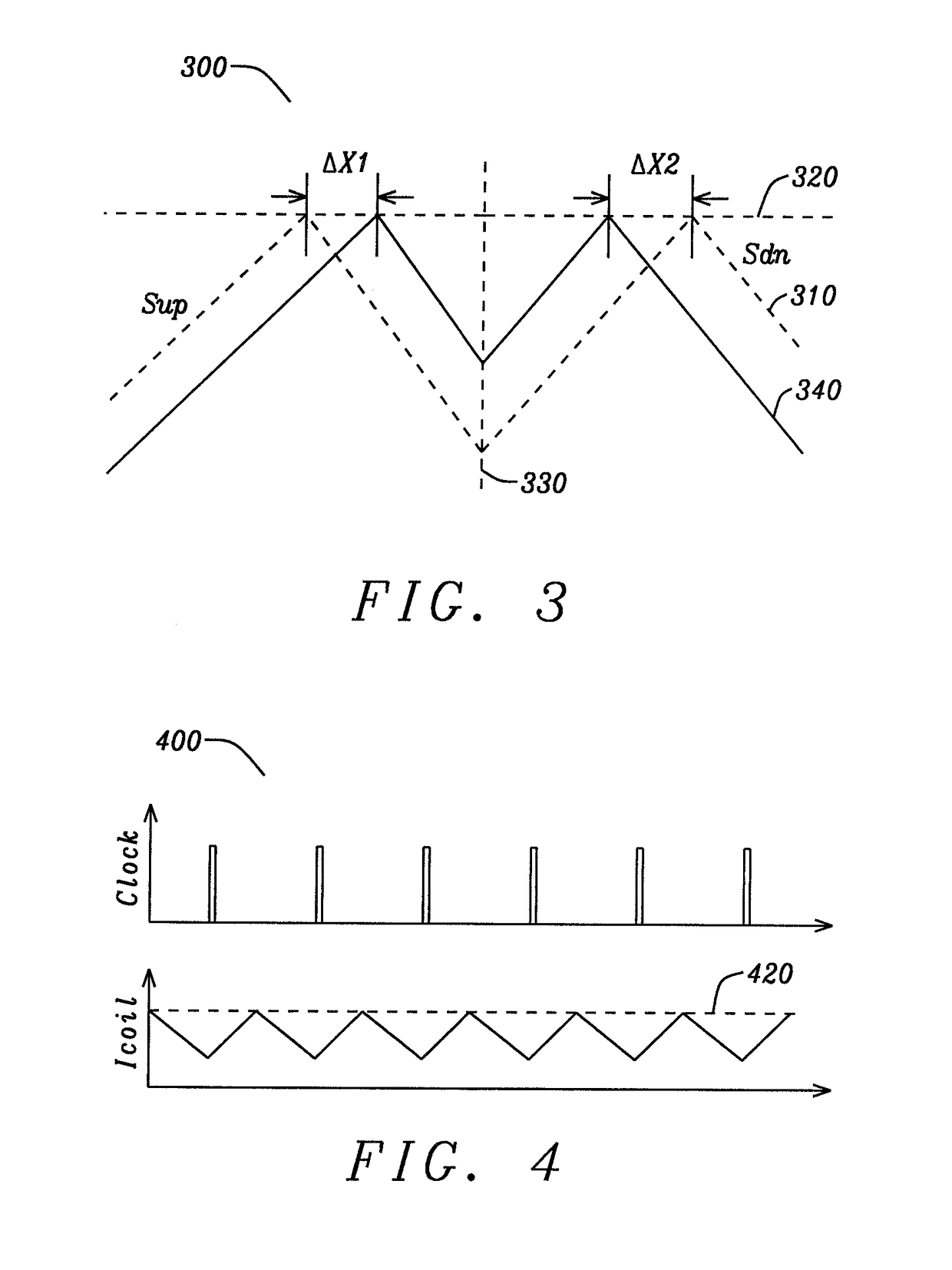
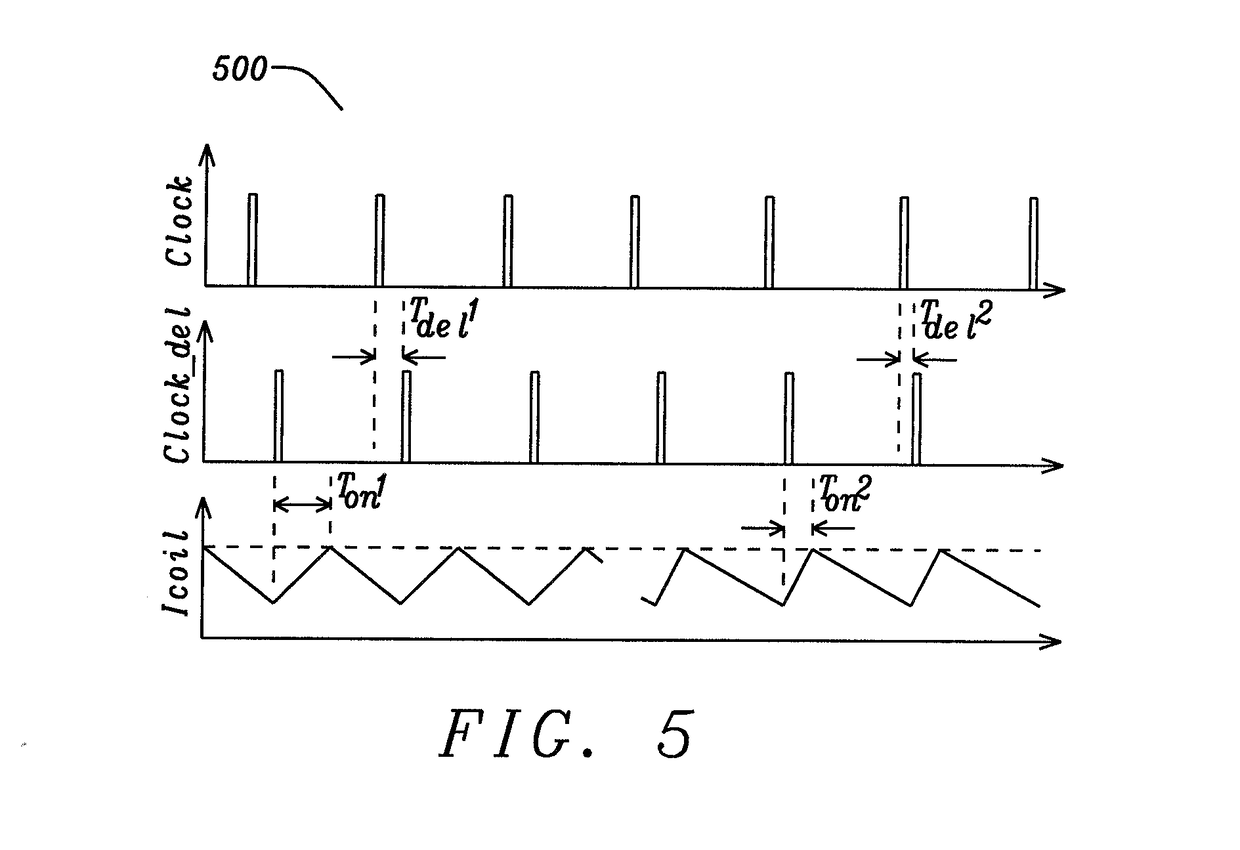
Preventing sub-harmonic oscillation with clock delay compensation, in a DC-DC switching converter
ActiveUS10840806B2Avoid oscillationDc-dc conversionPulse manipulationProportional controlClock offset
The clock input of a buck converter is delayed, and the delay is controlled proportionally to the preceding high-side output switch on time. In the steady state, the high-side switch on time is uniform, and the clock is offset by a fixed amount. When sub-harmonic oscillation begins to occur, the high-side switch on time may increase during a cycle. The longer high-side on time causes the clock to be delayed by an increased amount. This has the effect of increasing the following low-side output switch on time. This further increases the subsequent high-side on time, and counteracts the effects of sub-harmonic oscillation. If the system is properly controlled, loop compensation is implemented correctly and sub-harmonic oscillation is prevented. In addition, the scheme may also be configured for the delay to be controlled proportionally to the preceding low-side output switch on time of the buck converter.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICON UK
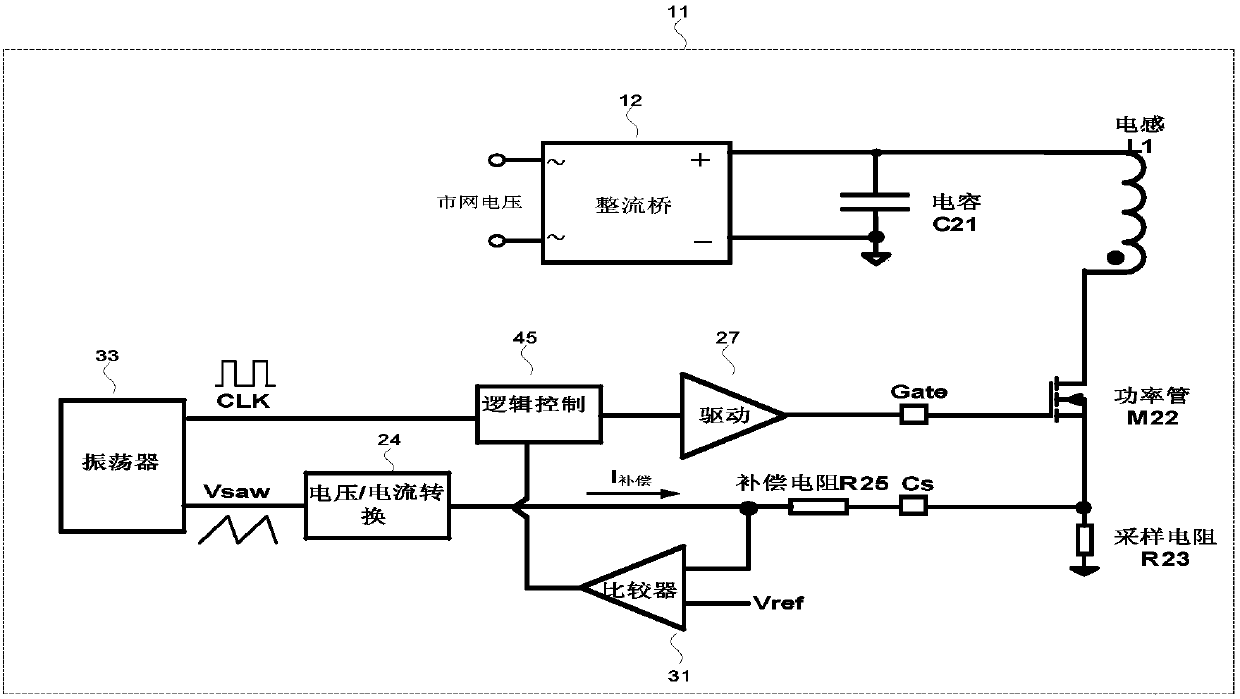
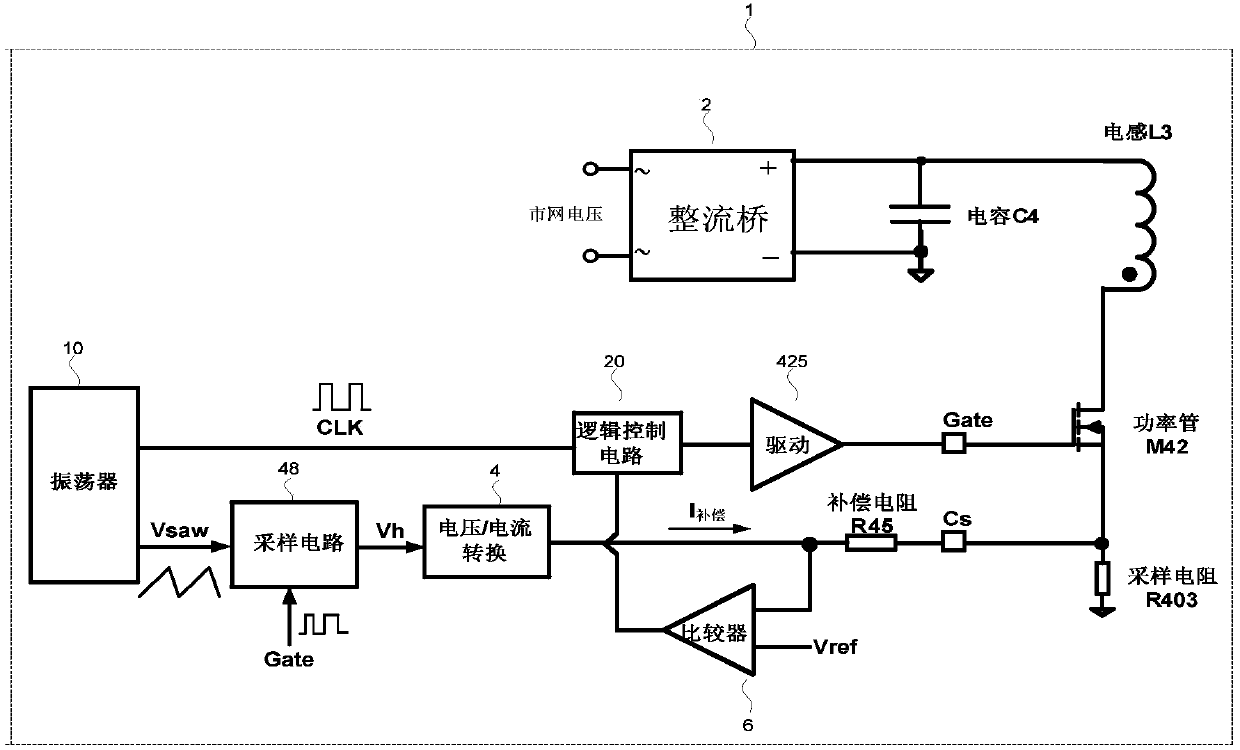
Constant power compensation circuit
The invention provides a constant power compensation method, which is applied to an AC / DC controller. The AC / DC controller includes a rectifier bridge, a filter capacitor, an inductor, an oscillator,a logic controller, a compensation resistor, a power transistor, a drive circuit, an over-current comparator, a sampling resistor, a sampling circuit and a voltage / current converter. The constant power compensation method includes the steps of collecting the sawtooth wave voltage of the oscillator and holding and sending the collected sawtooth wave voltage to the voltage / current converter. According to the method, the constant power compensation value is kept unchanged in a certain time range instead of transiently changing with the AC / DC drive switching signal, and the occurrence of sub-harmonic oscillation is suppressed.
Owner:NANJING BAIYA INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Peak-current-mode Buck circuit sub-harmonic oscillation elimination method based on slope compensation method
InactiveCN106411129AImprove stabilitySubharmonic Oscillation CancellationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSubharmonic oscillationHarmonic
The invention discloses a peak-current-mode Buck circuit sub-harmonic oscillation elimination method based on a slope compensation method. The peak-current-mode Buck circuit subharmonic oscillation elimination method relates to the Buck circuit sub-harmonic oscillation elimination technology, and aims to solve the problem that current disturbance can cause a steady-state oscillation phenomenon and damage the stability of the system when a PWM duty ratio of a PWM controller Uc3842 is greater than 50%. A non-inverting input end of a PWM comparator inputs a reference voltage signal, an inverting input end of the PWM comparator inputs a current feedback signal, and the inverting input end of the PWM comparator further inputs a positive-slope voltage signal used for compensating for a slope of the current feedback signal. The peak-current-mode Buck circuit sub-harmonic oscillation elimination method is suitable for eliminating the sub-harmonic oscillation of a Buck circuit.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Current mode synchronous rectification PWM control circuit
InactiveCN105680708ASolve the problem of slow response speedFast transient responseAc-dc conversionSoftware engineeringHemt circuits
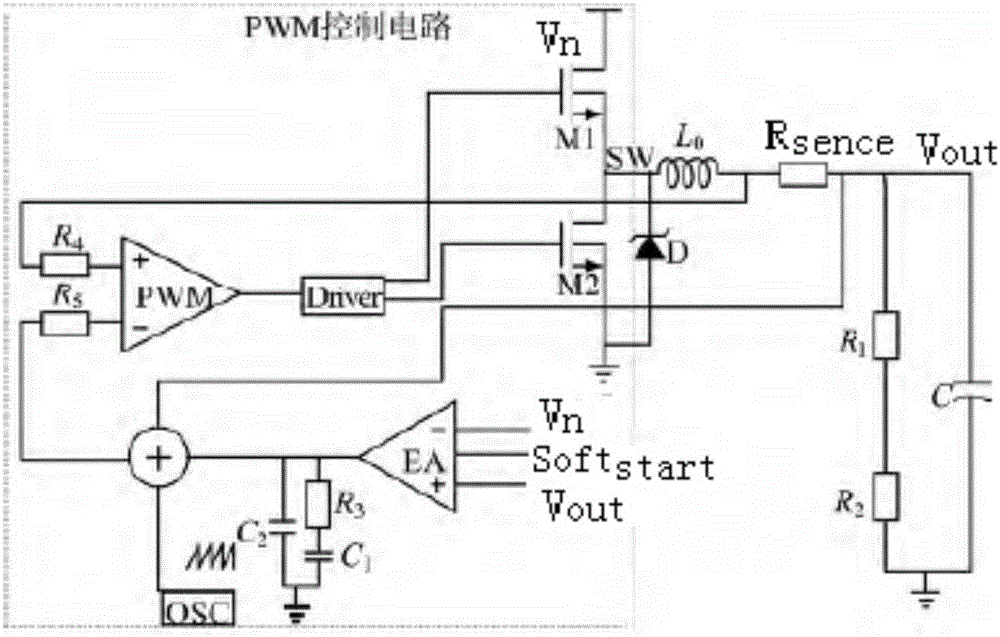
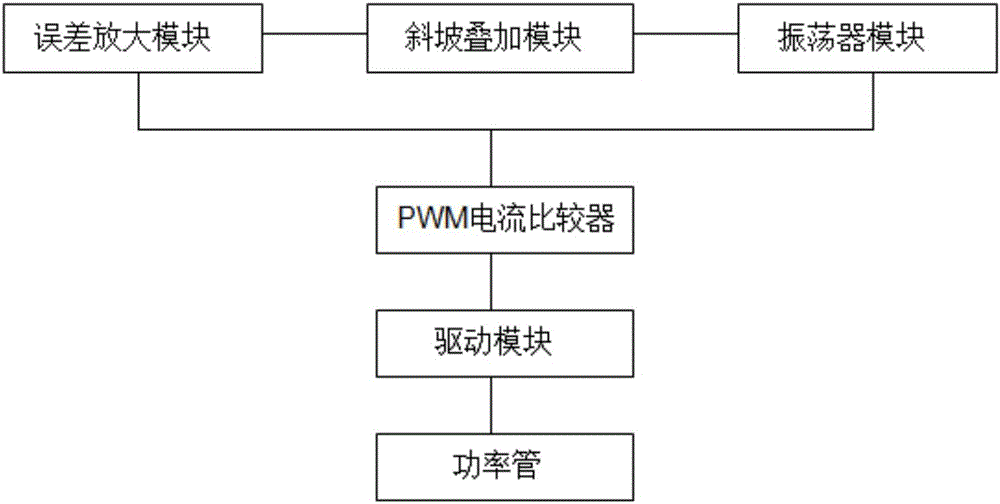
The invention discloses a current mode synchronous rectification PWM control circuit. A PWM comparison module and a current sampling amplification module are merged into a PWM current comparer, so that the circuit structure can be simpler, the circuit scale is smaller, and the circuit is easily integrated; the PWM current comparer is internally provided with an inverted tube, so that the problem that the reaction speed of the control circuit is slow caused by comparer delay can be solved; a slope superposition module is arranged between an error amplification module and an oscillator module, so that the problem of subharmonic oscillation in a current mode can be solved; when the output voltage variable quantity is 100 mV, the stability time is 90-100 us, the output voltage ripple of the control circuit is + / -4 mV, and the output voltage accuracy is + / -1%, so that the control circuit is high in output voltage accuracy and quick in transient response, and has extremely high application value.
Owner:WUHU RUIXIN ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Second harmonic oscillator
InactiveUS7629857B2Reduce outputWithout deteriorating phase noiseGenerator stabilizationFrequency analysisSubharmonic oscillationLeg length
A second harmonic oscillator has a series positive feedback configuration, suppresses output of a fundamental signal, and outputs a second harmonic signal having a frequency in a range from 1 GHz to 200 GHz generated inside of a circuit. The second harmonic oscillator includes: a transistor having a base terminal, a first emitter terminal, a second emitter terminal, and a collector terminal; a resonator circuit connected to the base terminal; a first transmission line shod-circuiting stub connected to one of the two emitter terminals; and a second transmission line short-circuiting stub connected to the other of the two emitter terminals and having a line length obtained by adding one-fourth of one wavelength of the fundamental signal to an integer multiple of one-half wavelength of the fundamental signal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Clock Delay Compensation
ActiveUS20180342952A1Avoid oscillationDc-dc conversionPulse manipulationStable stateSubharmonic oscillation
The clock input of a buck converter is delayed, and the delay is controlled proportionally to the preceding high-side output switch on time. In the steady state, the high-side switch on time is uniform, and the clock is offset by a fixed amount. When sub-harmonic oscillation begins to occur, the high-side switch on time may increase during a cycle. The longer high-side on time causes the clock to be delayed by an increased amount. This has the effect of increasing the following low-side output switch on time. This further increases the subsequent high-side on time, and counteracts the effects of sub-harmonic oscillation. If the system is properly controlled, loop compensation is implemented correctly and sub-harmonic oscillation is prevented. In addition, the scheme may also be configured for the delay to be controlled proportionally to the preceding low-side output switch on time of the buck converter.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICON UK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com