Exploitation method of orchid microsatellite marker site, and detection method of length of microsatellite marker in microsatellite marker site
A technology of microsatellite markers and sites, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of inaccurate detection results, time-consuming and laborious, low resolution, etc., and achieve the effect of simple development and detection technology, ensuring versatility, and reducing workload
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
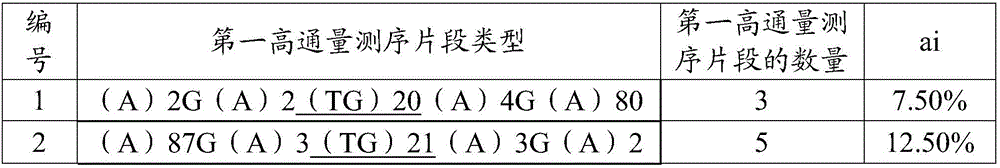
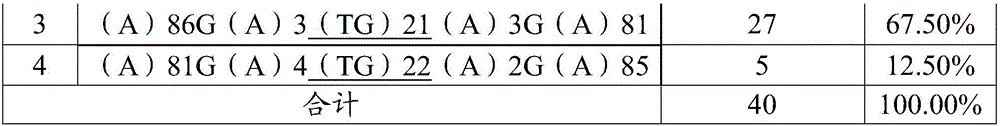
[0041] The development method of orchid microsatellite marker loci:
[0042] Mix n polymorphic orchid samples in equal amounts to obtain a mixed sample, where n>1.
[0043] Samples with polymorphism include: orchid samples that differ in external morphology (morphological polymorphism), orchid samples that differ in biological taxonomy (such as different varieties or varieties), orchid samples that differ from each other in other markers (such as protein markers) or different species. The orchid samples of wild resources in the ecological region, among them, the more orchid samples selected (the larger the n value), the more abundant the polymorphism, and the wider the applicability of the developed microsatellite marker loci. In this example, the species of the microsatellite marker site to be developed is orchid, and the selected orchids are different orchid varieties, which are: Baimo, Qihei, Jinzui, Xiaoxiang, Wandaifu, Huaguangdie, Peach, Jin Fu Cui, Wen Cai Lan, Peace G...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com