Flash spun plexifilamentary strands and sheets
A strand and flash-spinning technology, applied in the field of fabrics or fiber webs, and flash-spun plexifilament sheets, can solve the problems of not being durable enough, expensive and uncomfortable for medical clothes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
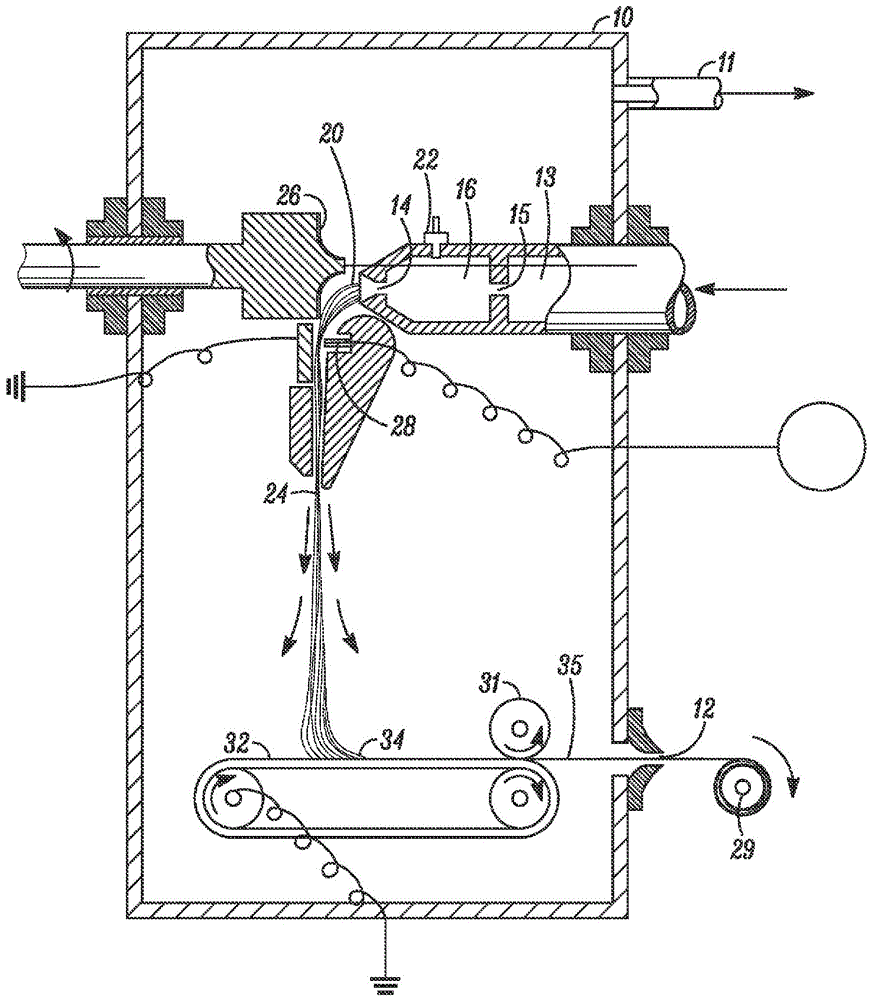
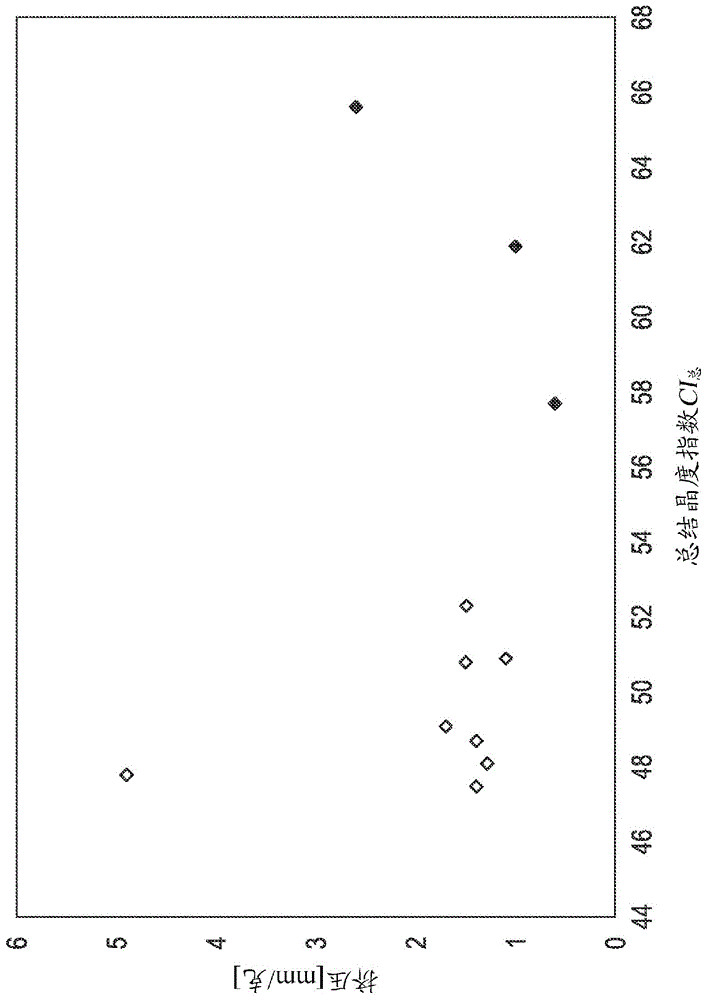
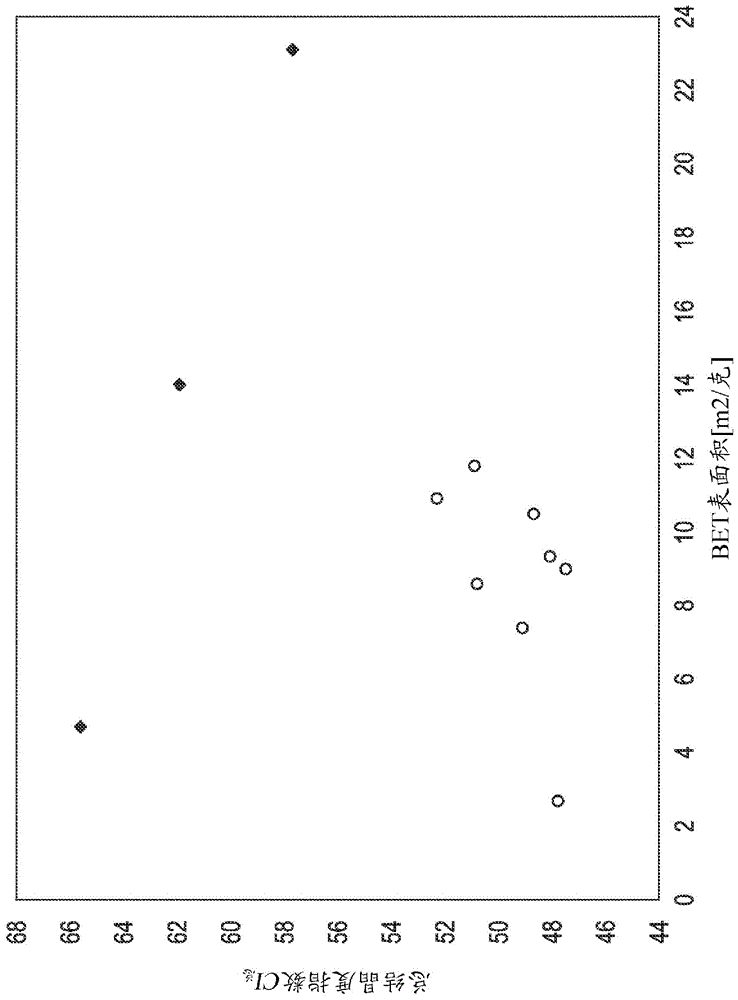
[0026] In one embodiment, the present invention is directed to flash spun plexifilamentary fiber strands having an overall crystallinity index of less than or equal to 55%.
[0027] In another embodiment, the fiber strands have less than 12m 2 / g BET surface area, extrusion value greater than or equal to 0.9mm / g. In another embodiment, the fiber strand consists essentially of fibers formed from polyethylene.
[0028] In another embodiment, the fiber strand comprises fibers formed primarily of polyethylene, the fibers having a total crystallinity index of less than 52%.
[0029] The fiber strands of the present invention may also have a monoclinic structure and an orthorhombic structure as determined by X-ray analysis described herein, and the crystallinity index of the monoclinic structure is equal to or higher than 1%.
[0030] In another embodiment, any of the embodiments of plexifilamentary fiber strands disclosed herein may be consolidated into a sheet structure. The sh...
Embodiment
[0041] testing method
[0042] In the specification, examples and claims, the following test methods were used to determine the various properties and properties reported.
[0043] The surface area of the plexifilamentary fiber strand product is a measure of the degree of fibrillation and fineness of the flash spun product. Surface area is measured by the BET nitrogen absorption method of S. Brunauer, P. H. Emmett and E. Teller, J. Am. Chem.Soc., Vol. 60, pp. 309-319 (1938), and is expressed in square meters per gram (m 2 / g) is reported in units.
[0044] The squeeze value indicates the ability of a fiber strand to recover its original shape after compression. It was determined using the following procedure: from Reemay ® Three plexifilamentary fiber strands of different sizes were drawn from the sheet. Three samples weighed approximately one gram, two grams and three grams. The reported extrusion values are the average of the values measured for three samples. Ea...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bet surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melt index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com