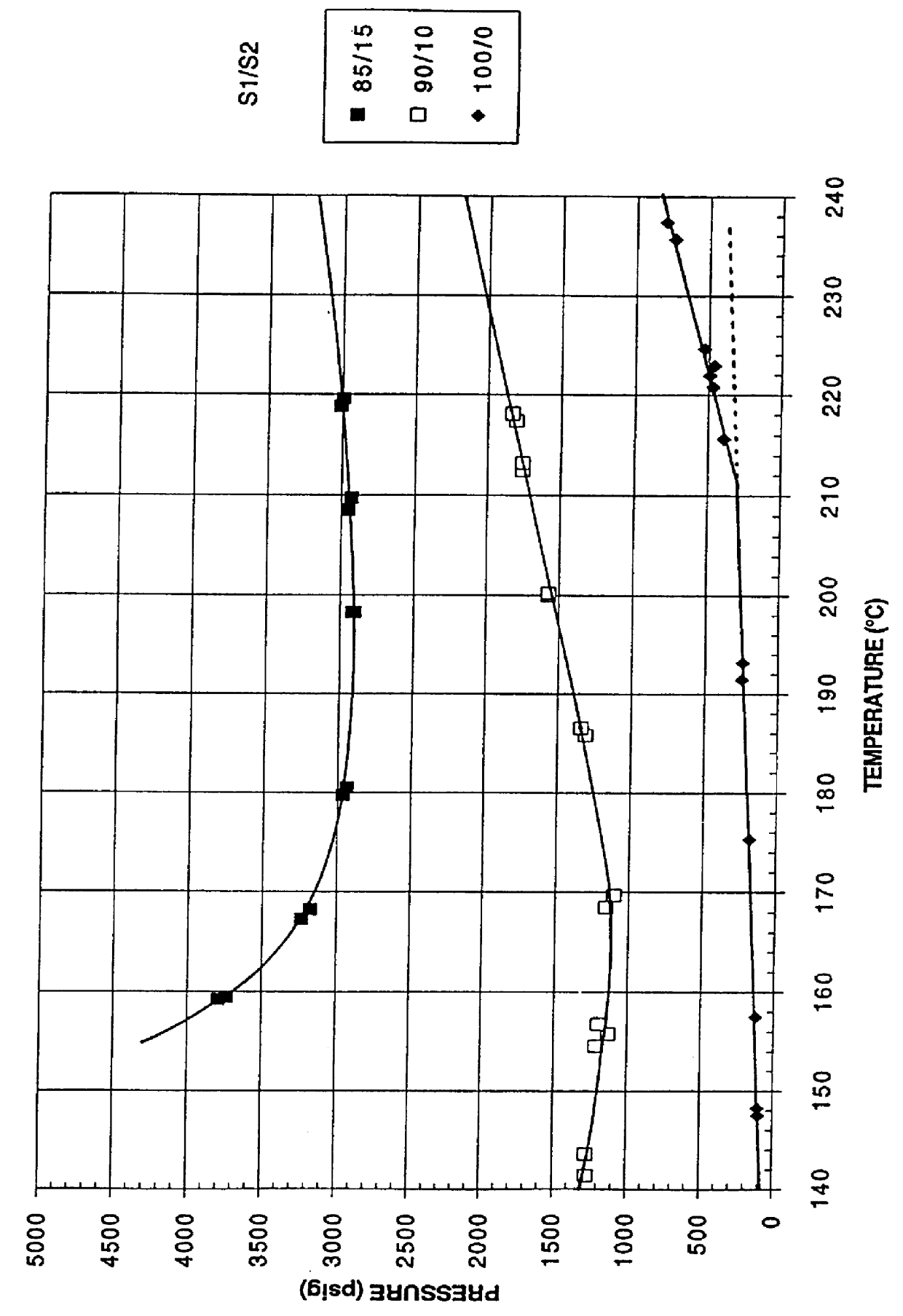
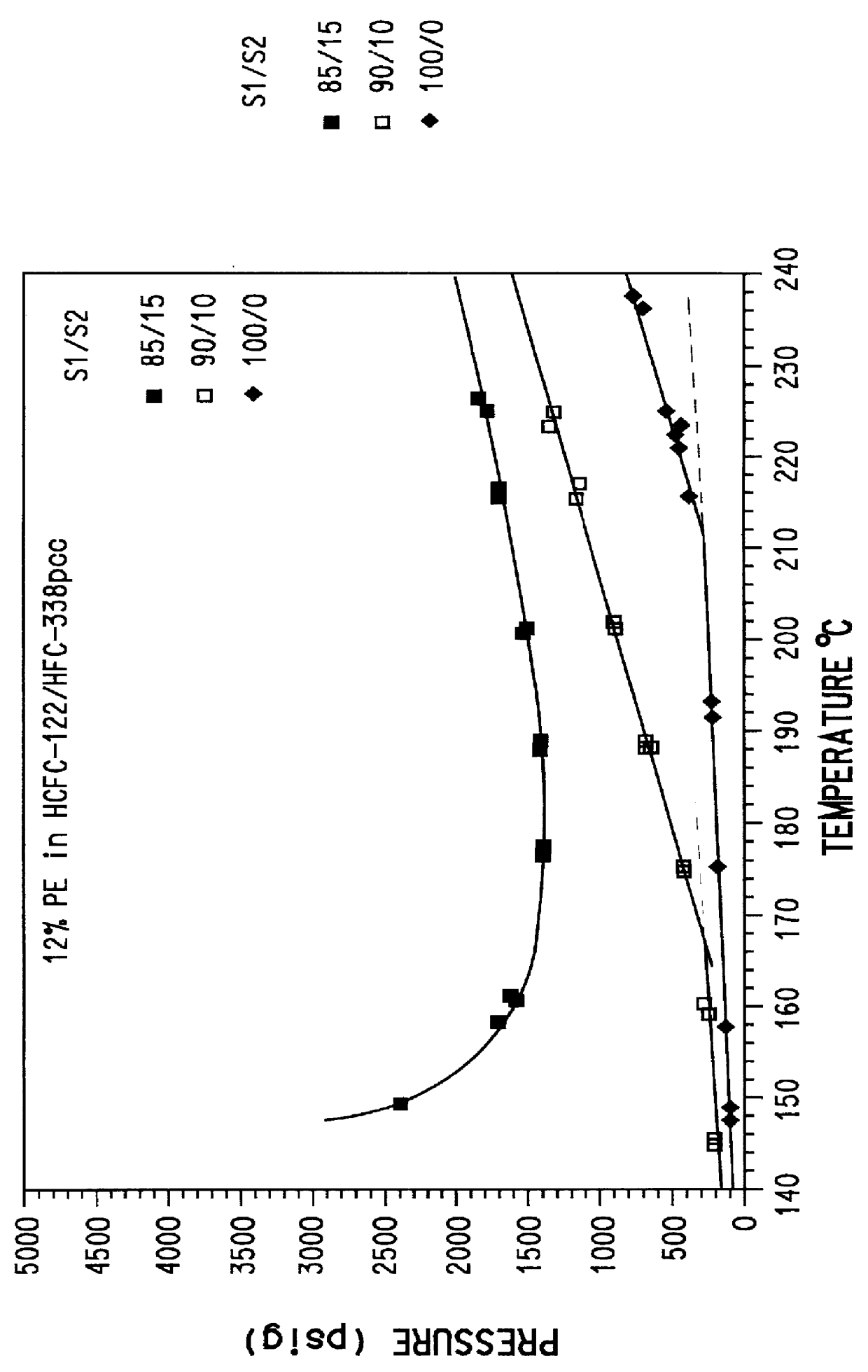
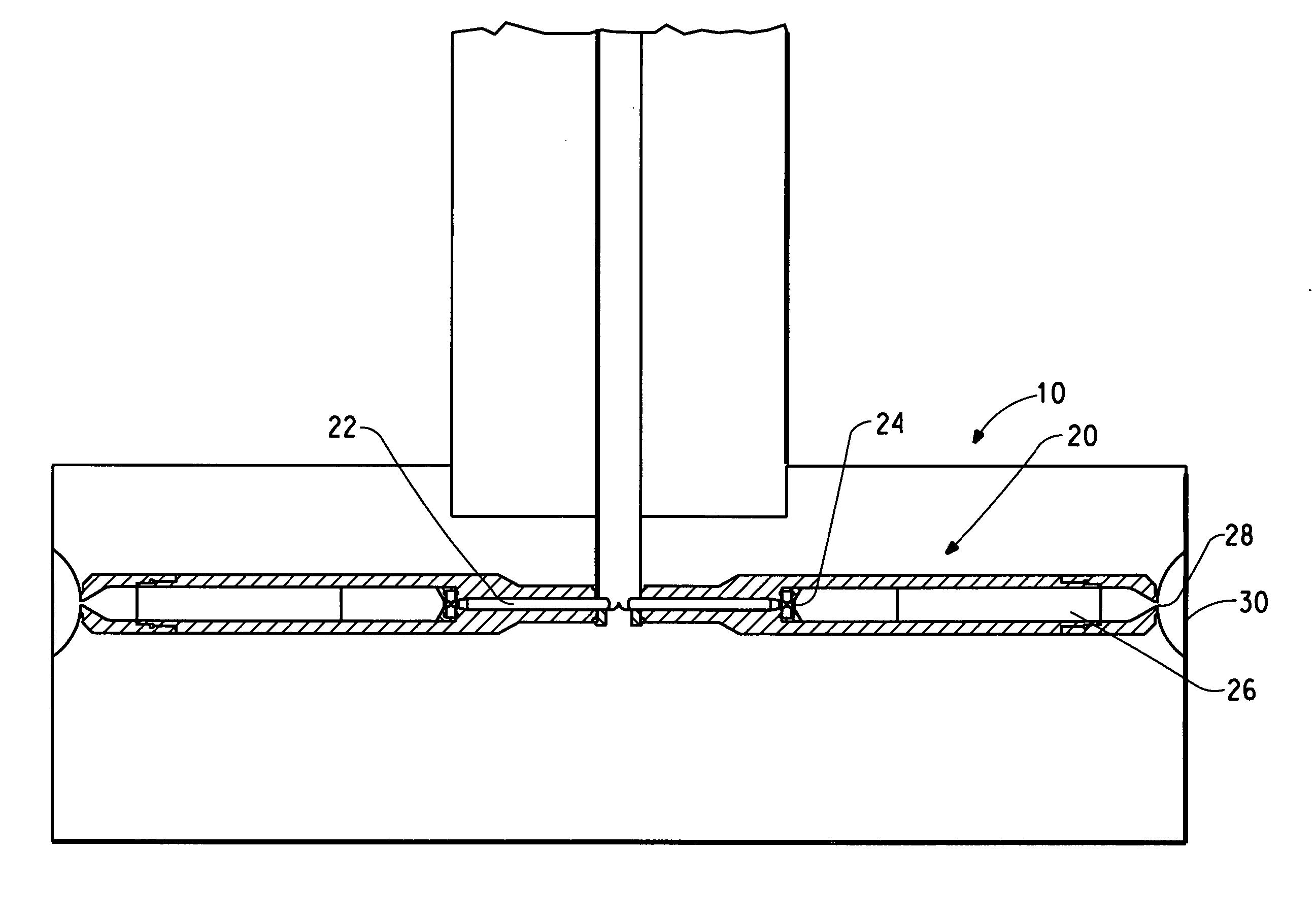
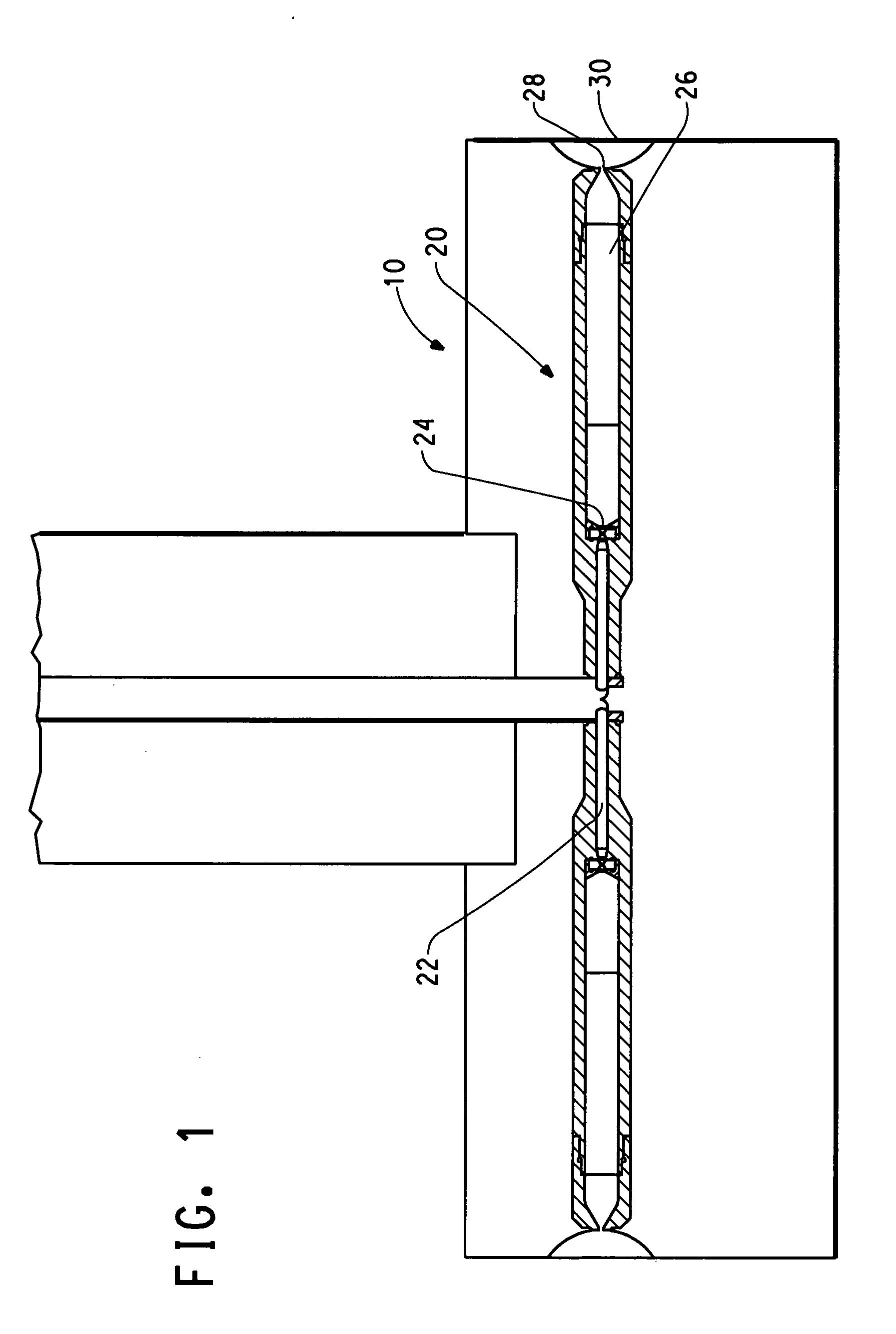
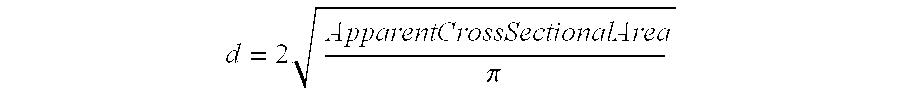Patents
Literature
77results about "Flash-spinning methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
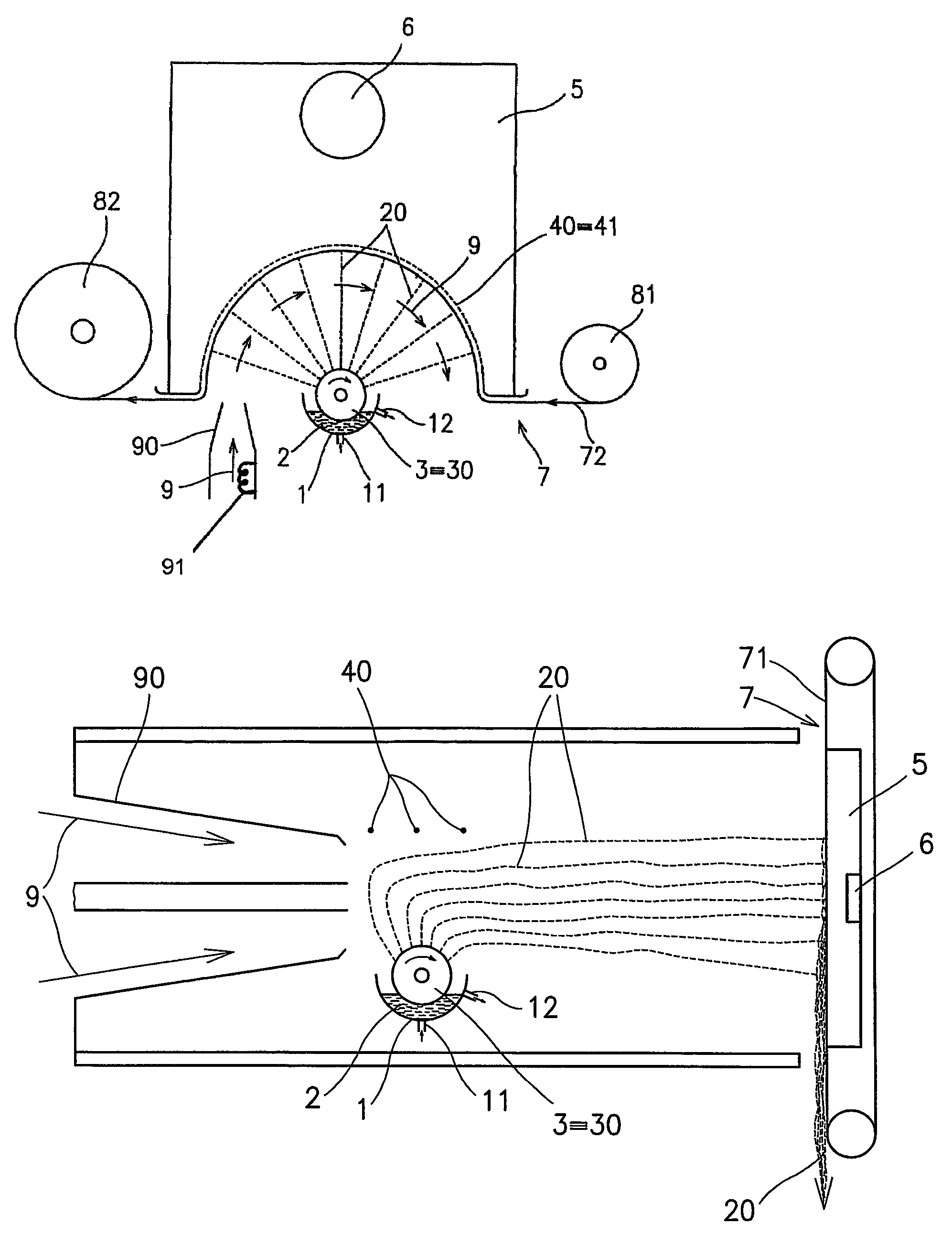
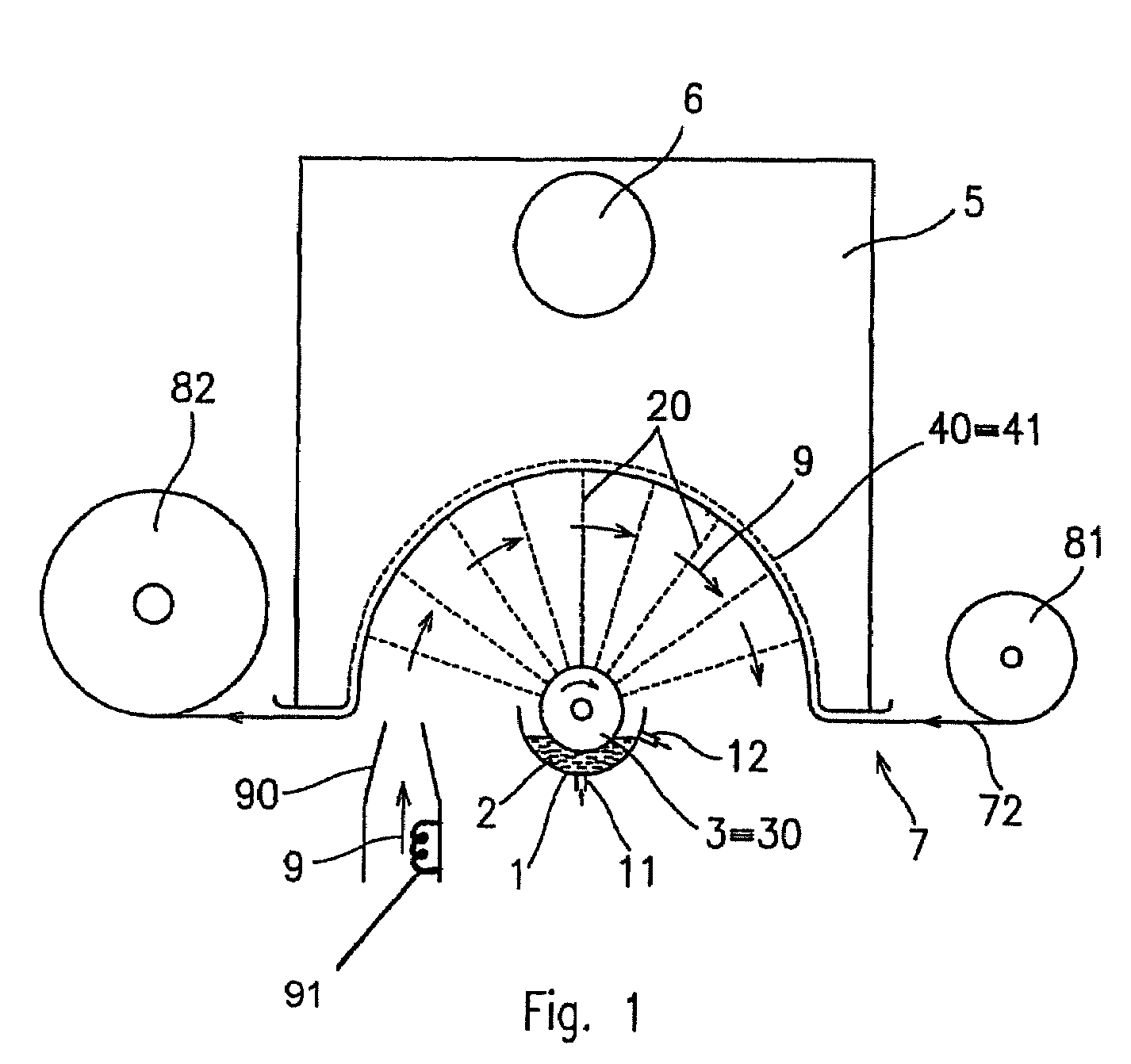
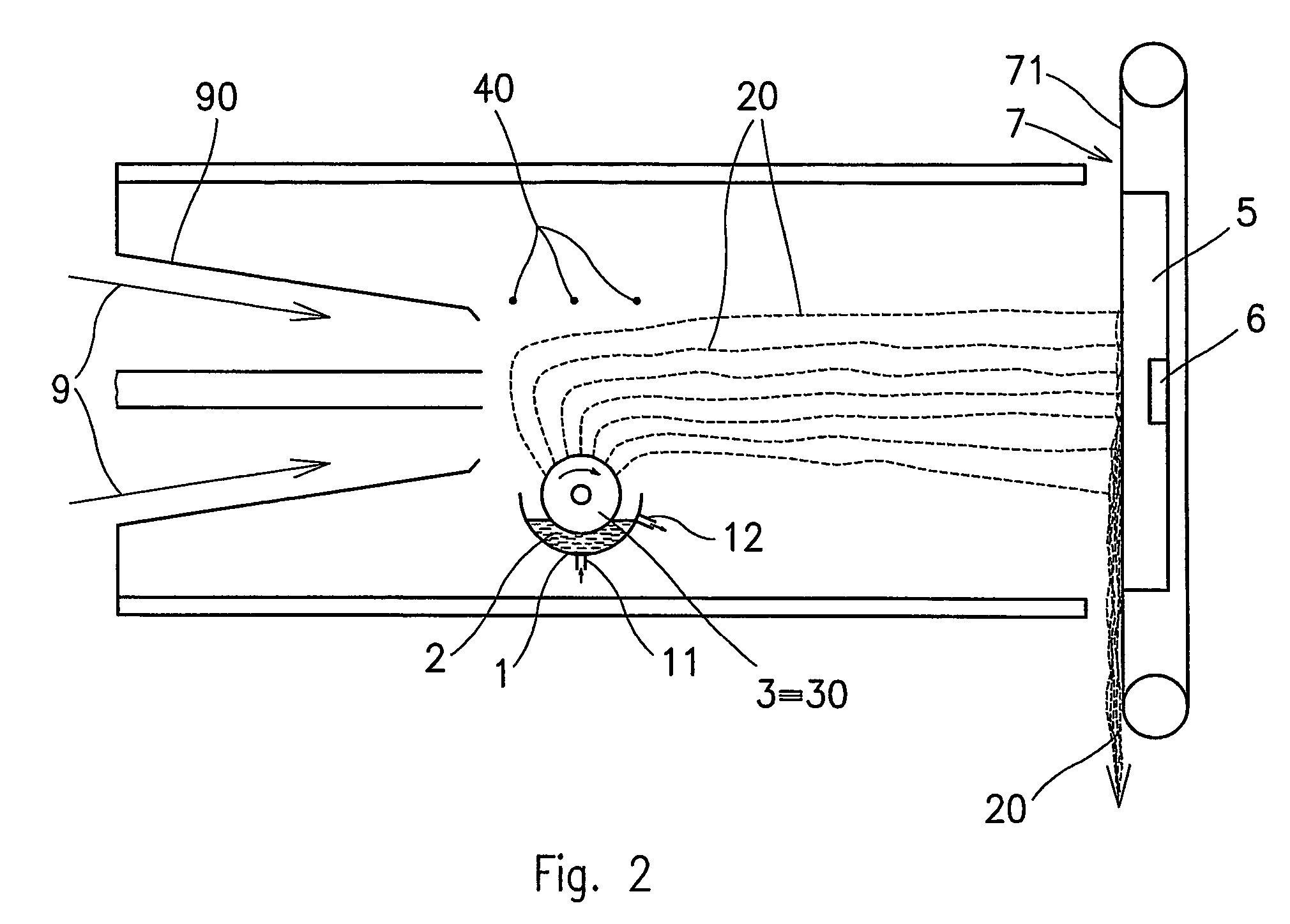
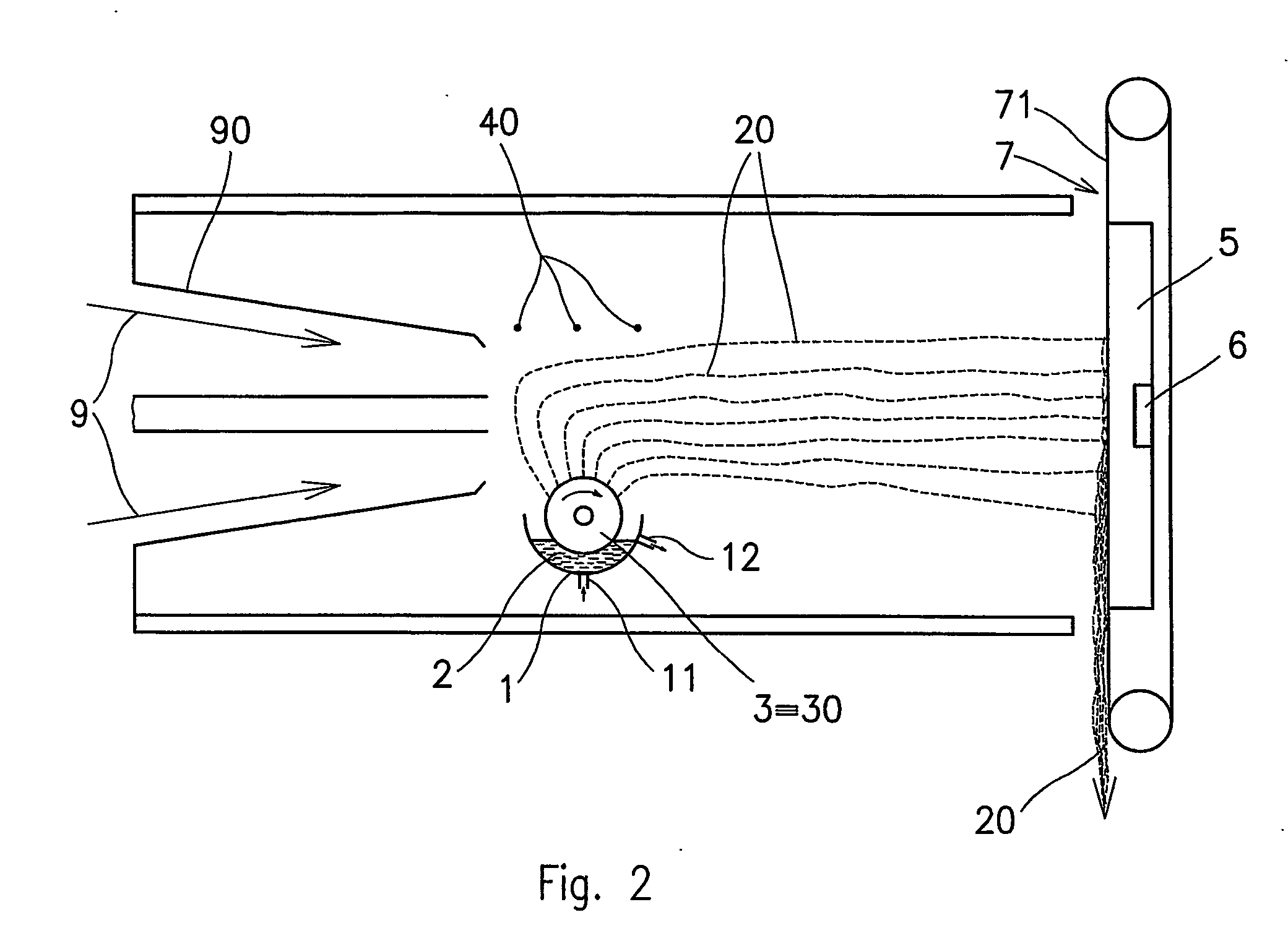
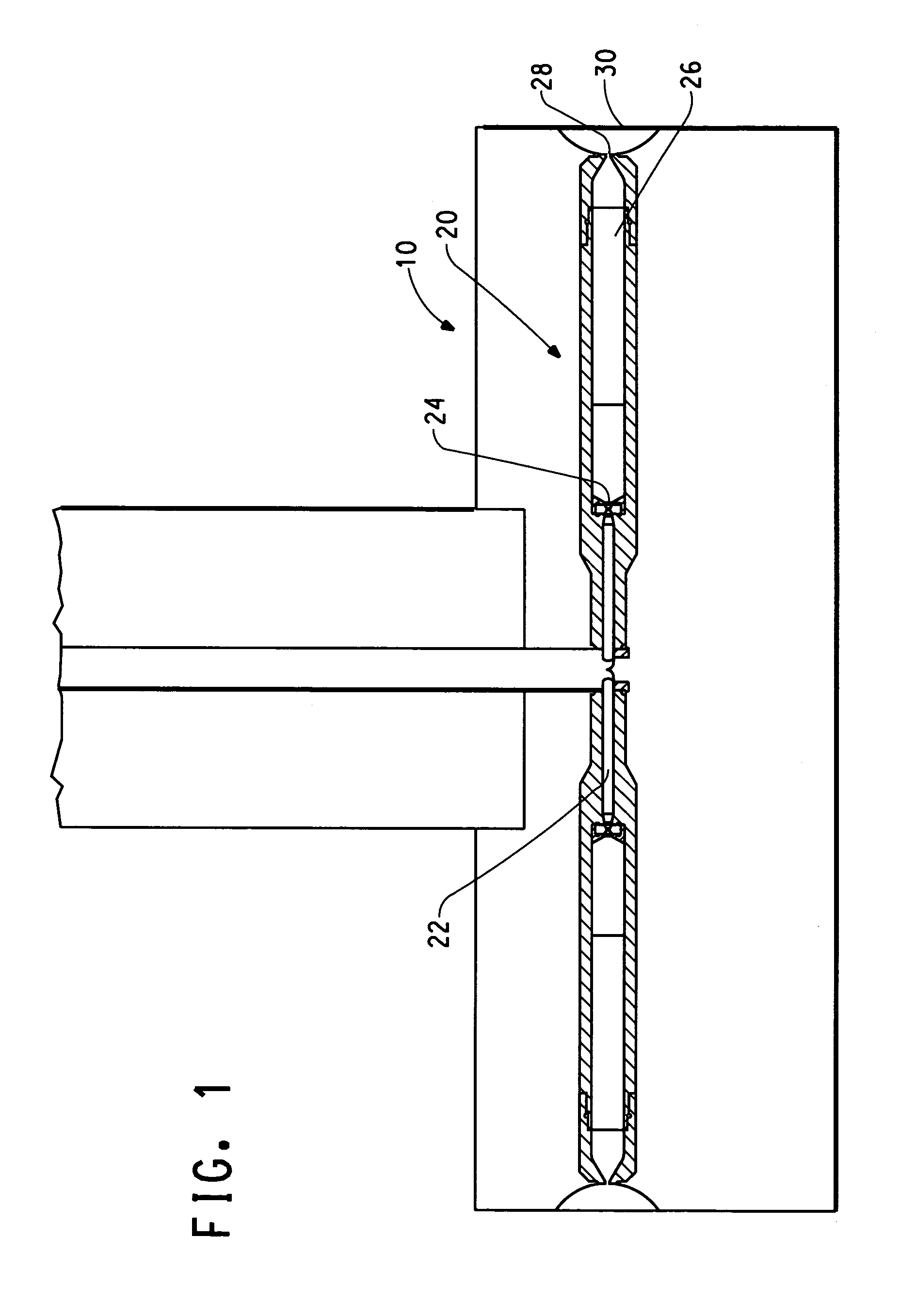
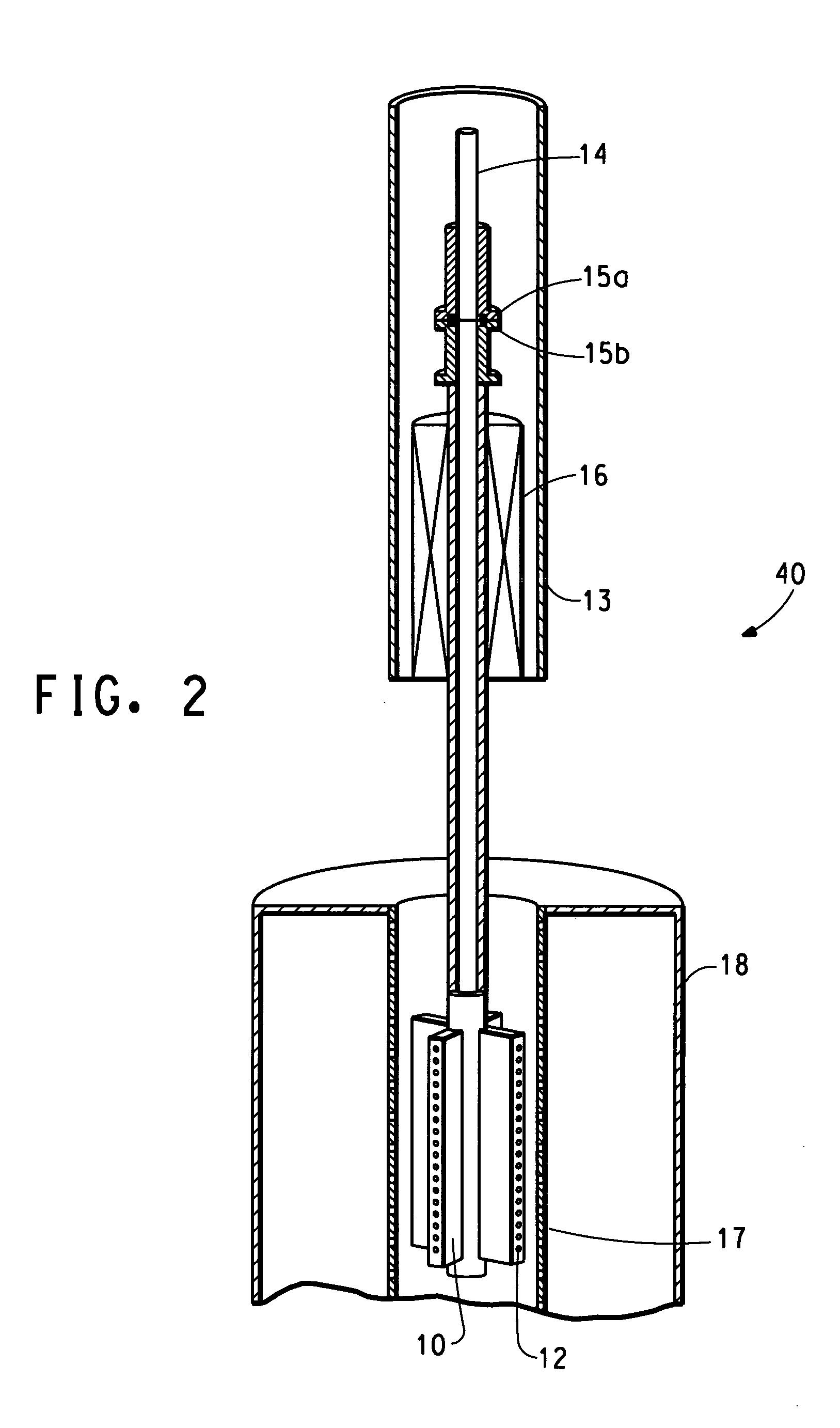
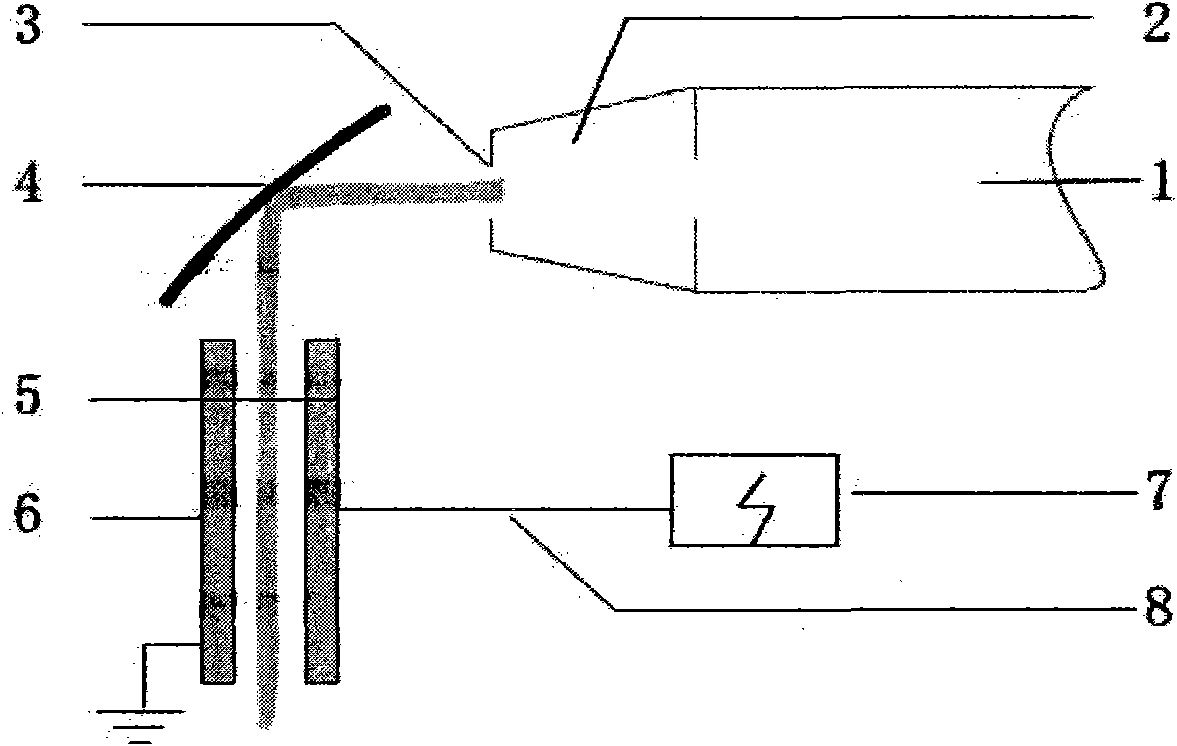
Method of nanofibres production from a polymer solution using electrostatic spinning and a device for carrying out the method
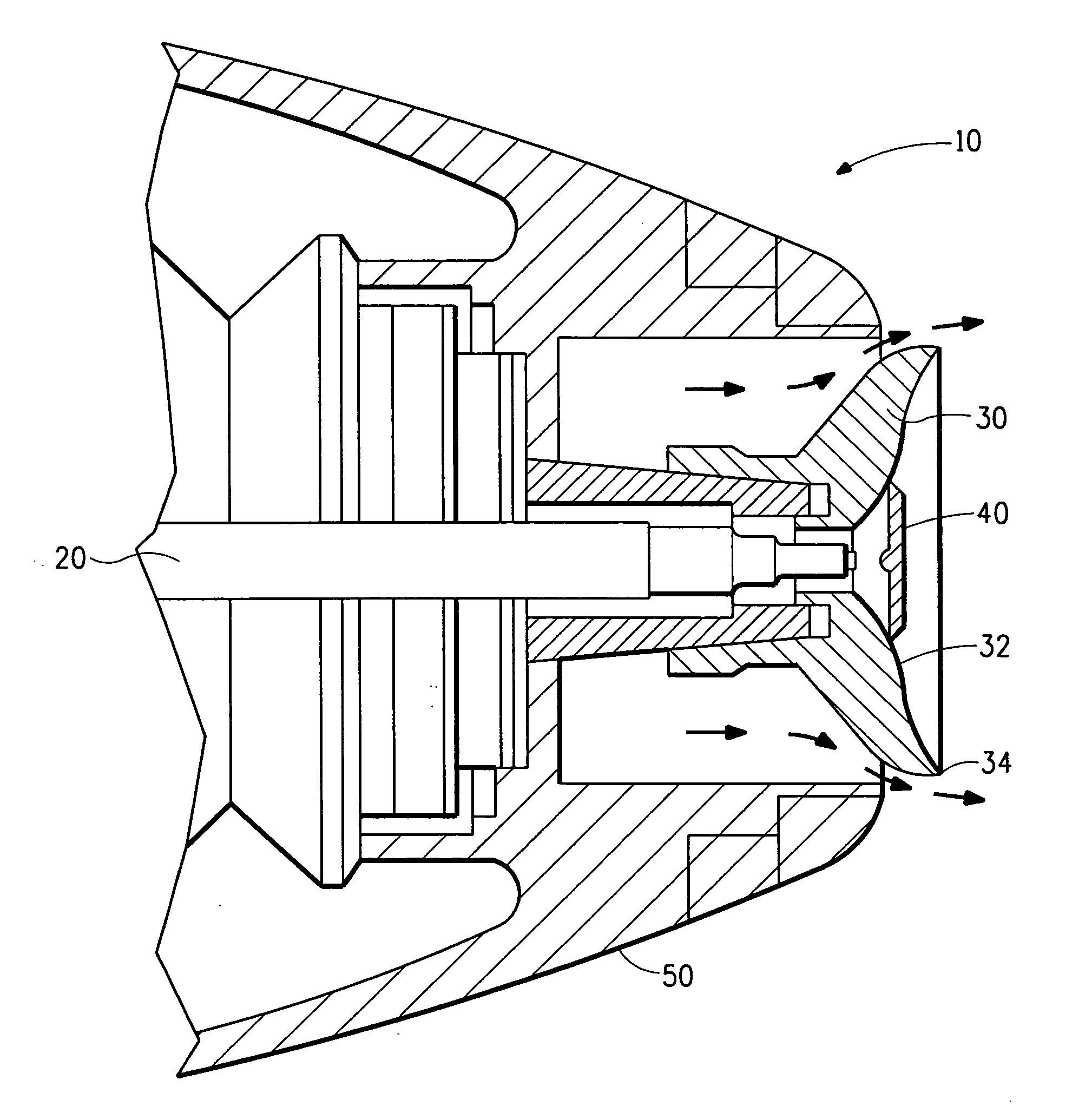
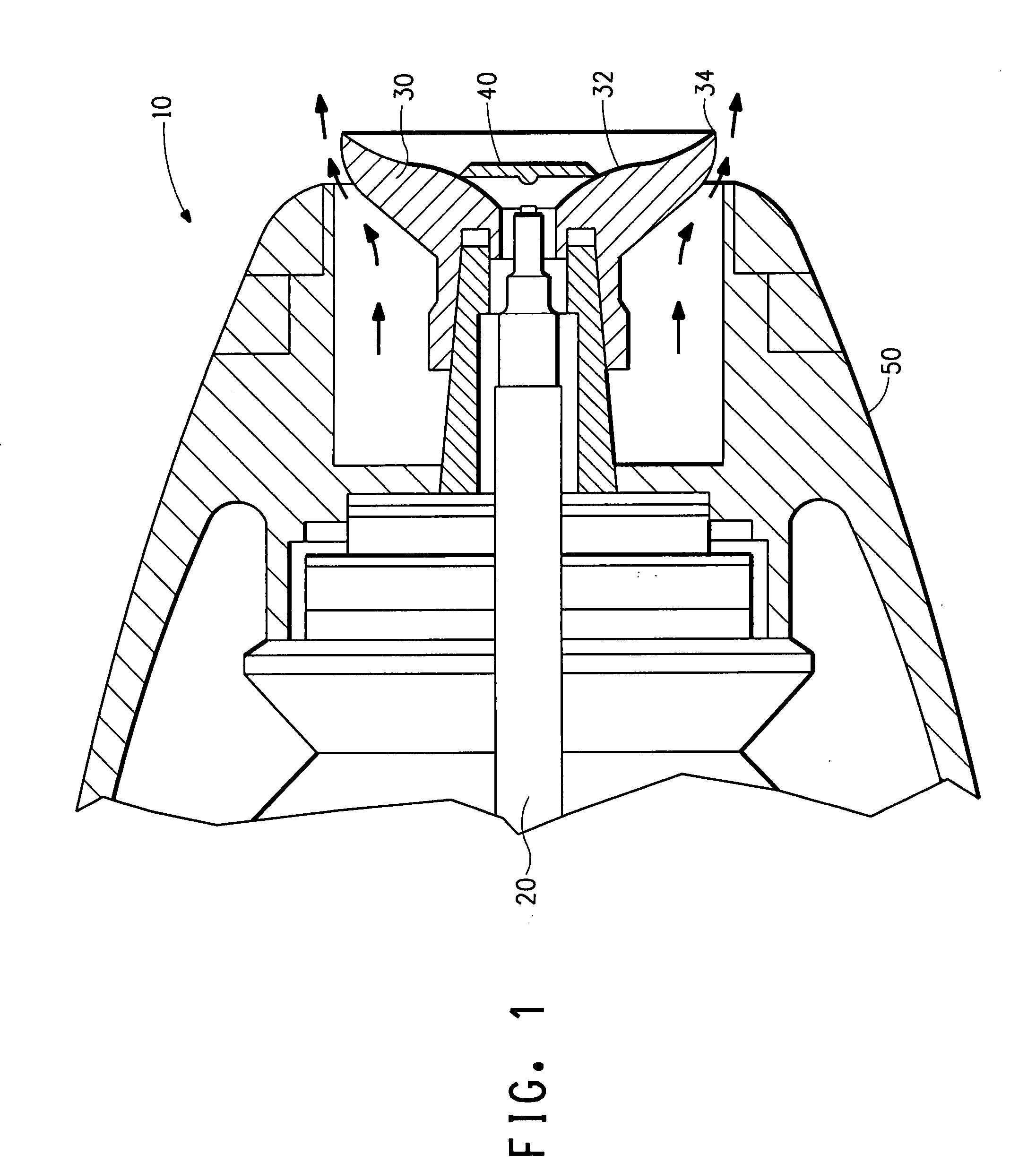
ActiveUS7585437B2High quality and uniformity of layerSpinnerette packsNanotechnologyPotential differenceElectrospinning
A method of nanofibers production from a polymer solution uses electrostatic spinning in an electric field created by a potential difference between a charged electrode and a counter electrode. The polymer solution for spinning is supplied into the electric field using the surface of a rotating charged electrode. On a part of the circumference of the charged electrode near to the counter electrode, a spinning surface is created for attaining a high spinning capacity. In a device for carrying out the method, the charged electrode is pivoted and part of its circumference is immersed in the polymer solution. The free part of the circumference of the charged electrode is positioned opposite the counter electrode.
Owner:TECHNICKA UNIVEZITA V LIBERCI
Process for forming polymeric micro and nanofibers
Polymers that have extremely high melt viscosities are very difficult to extrude and stretch making it difficult to synthesize fibers of such polymers via conventional methods. A process is provided for producing a polymer fiber which involves blowing a mixture of a polymer and a gas through a nozzle such that polymer micro- and / or nano-fibers are produced. The polymer fibers are characterized in that they have a diameter less than the diameter of the outlet aperture of the nozzle.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
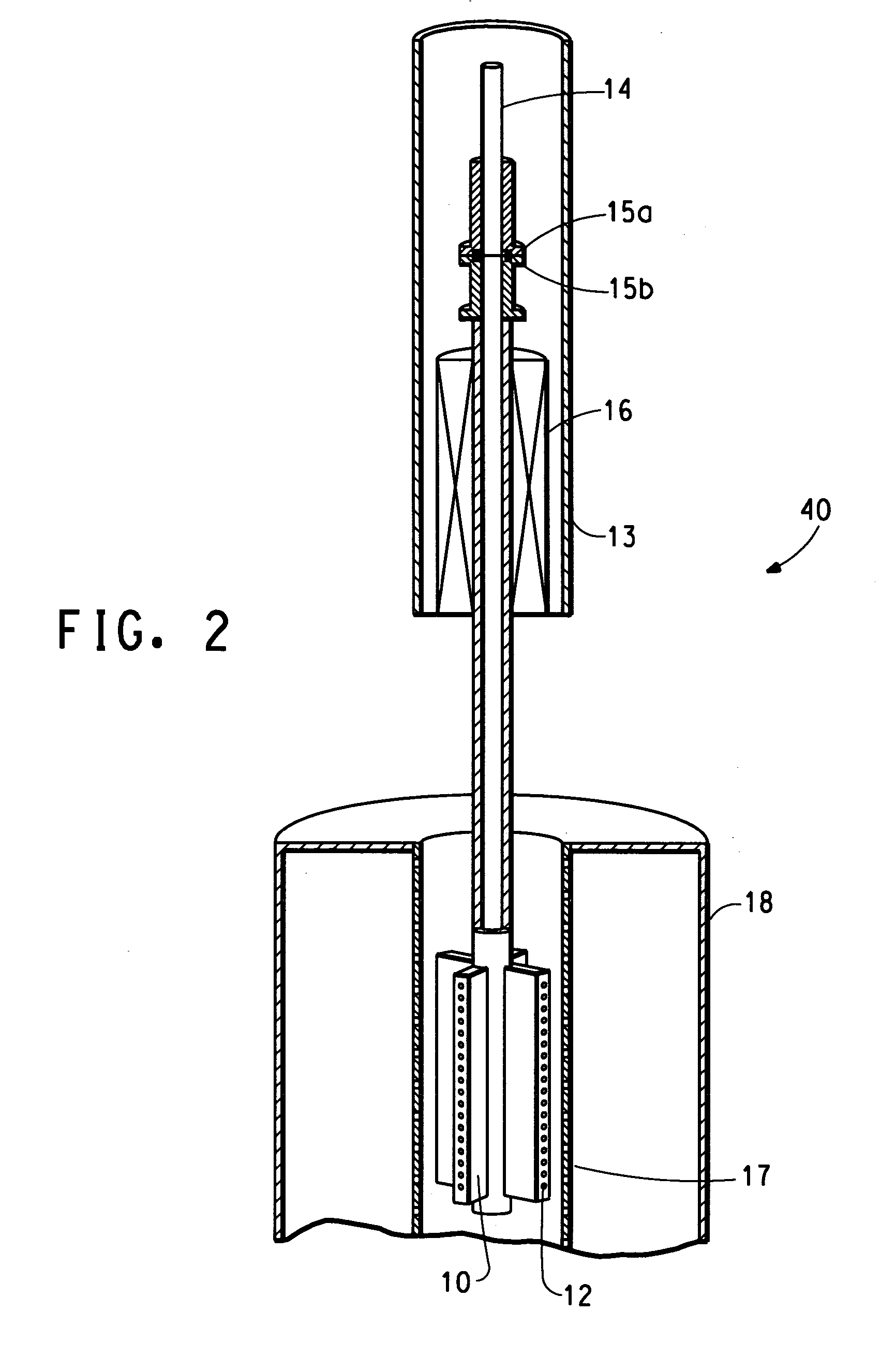
Method of nanofibres production from a polymer solution using electrostatic spinning and a device for carrying out the method
ActiveUS20060290031A1Quality improvementImprove uniformityElectric discharge heatingSpinnerette packsElectrospinningPotential difference
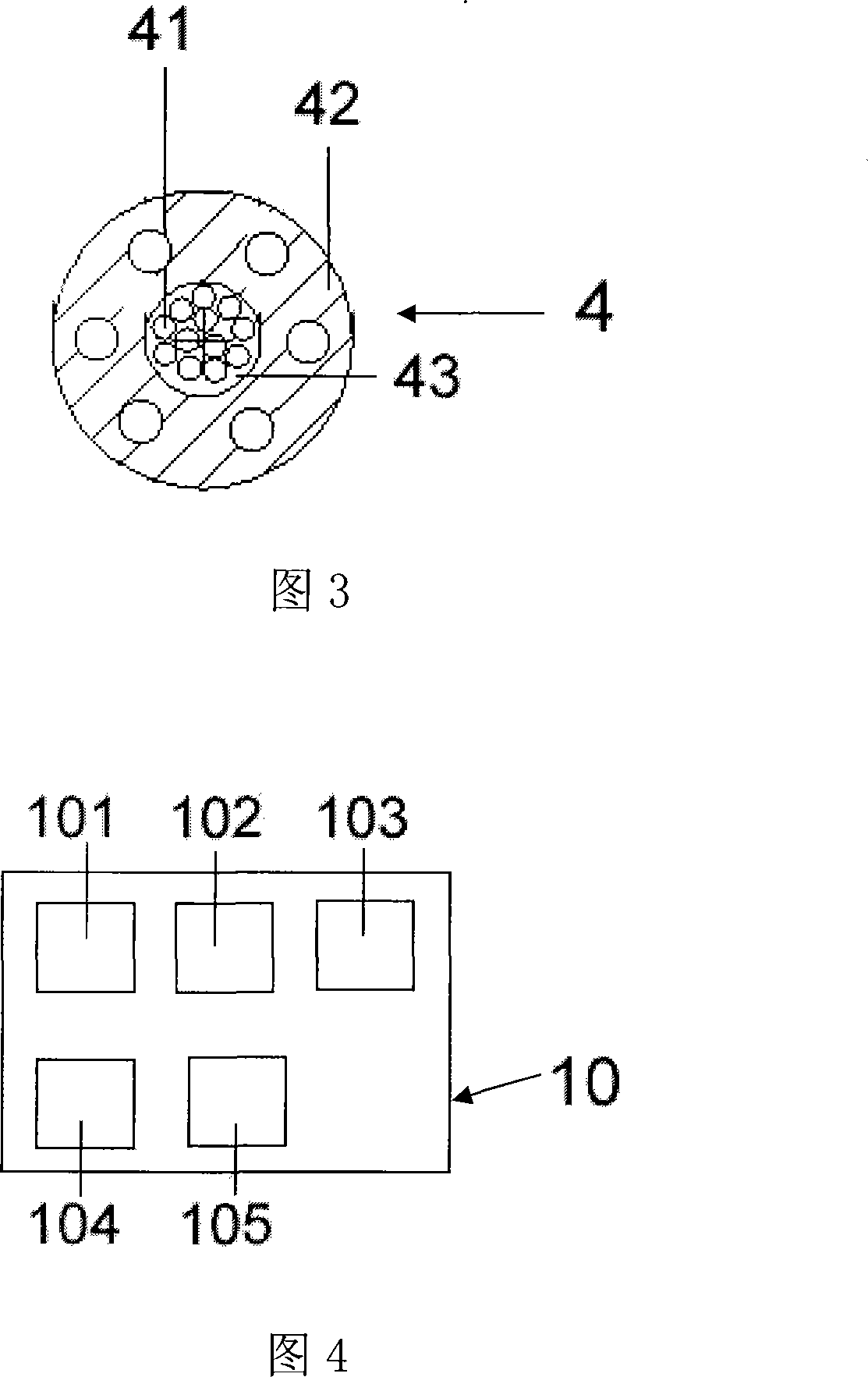
The invention relates to a method of nanofibres production from a polymer solution using electrostatic spinning in an electric field created by a potential difference between a charged electrode and a counter electrode. The polymer solution (2) is for spinning supplied into the electric field using the surface of the rotating charged electrode (30), while on a part of the circumference of the charged electrode (30) near to the counter electrode (40) is a spinning surface created, by which is a high spinning capacity reached. Further the invention relates to a device for carrying out the method, where the charged electrode (30) is pivoted and by its (bottom) part of its circumference it is immersed in the polymer solution (2), while against the free part of the circumference of the charged electrode (30) is positioned the counter electrode (40).
Owner:TECHNICKA UNIVEZITA V LIBERCI
Flash spun web containing sub-micron filaments and process for forming same
A nonwoven fibrous structure and process for forming it, which is an interconnecting web of polyolefin filaments having filament widths greater than about 1 micrometer which are further interconnected with webs of smaller polyolefin filaments having filament widths less than about 1 micrometer, wherein the smaller polyolefin filaments comprise a majority of all filaments.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
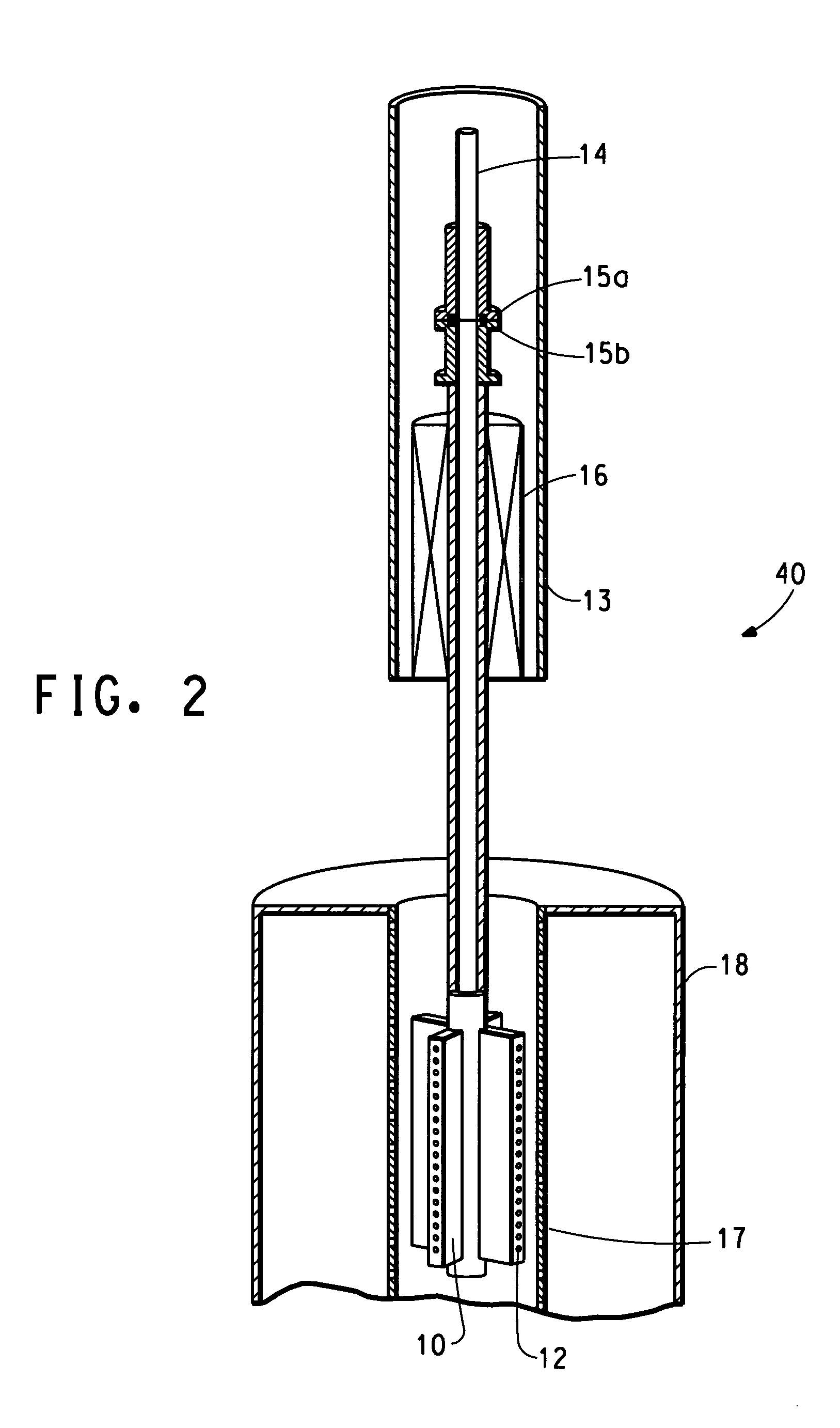
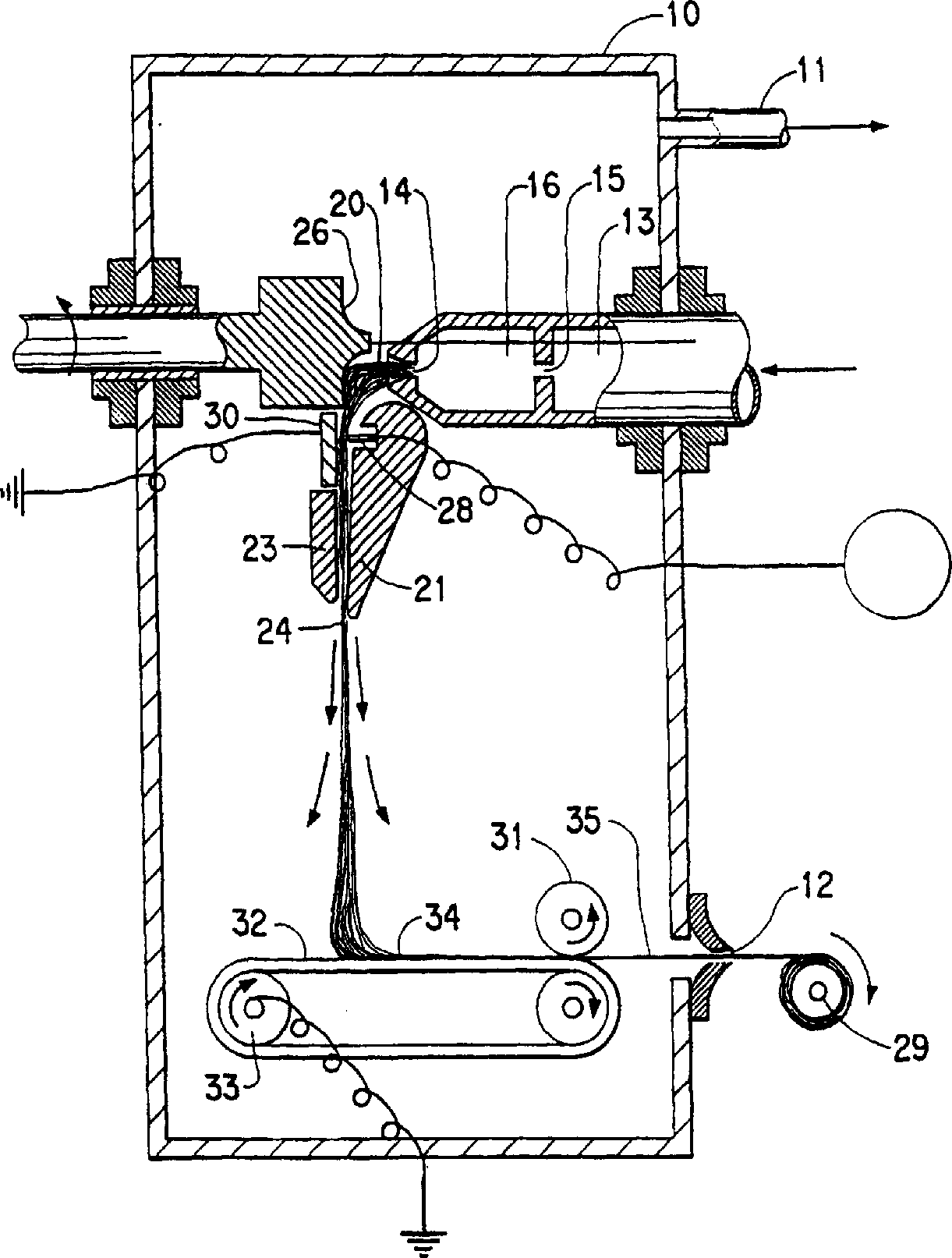
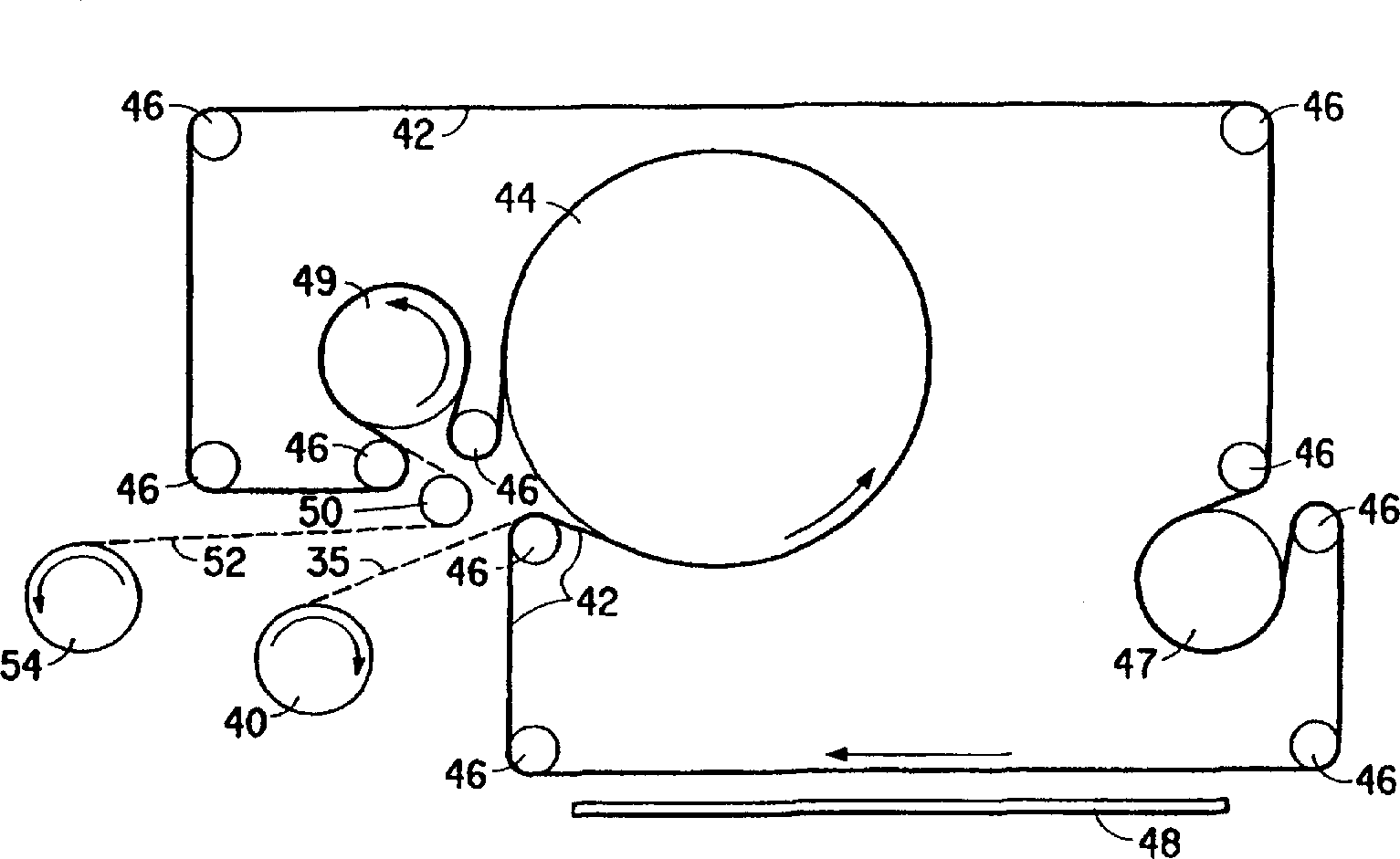
Rotary process for forming uniform material
ActiveUS7118698B2Synthetic resin layered productsMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentFiberDiscrete particle
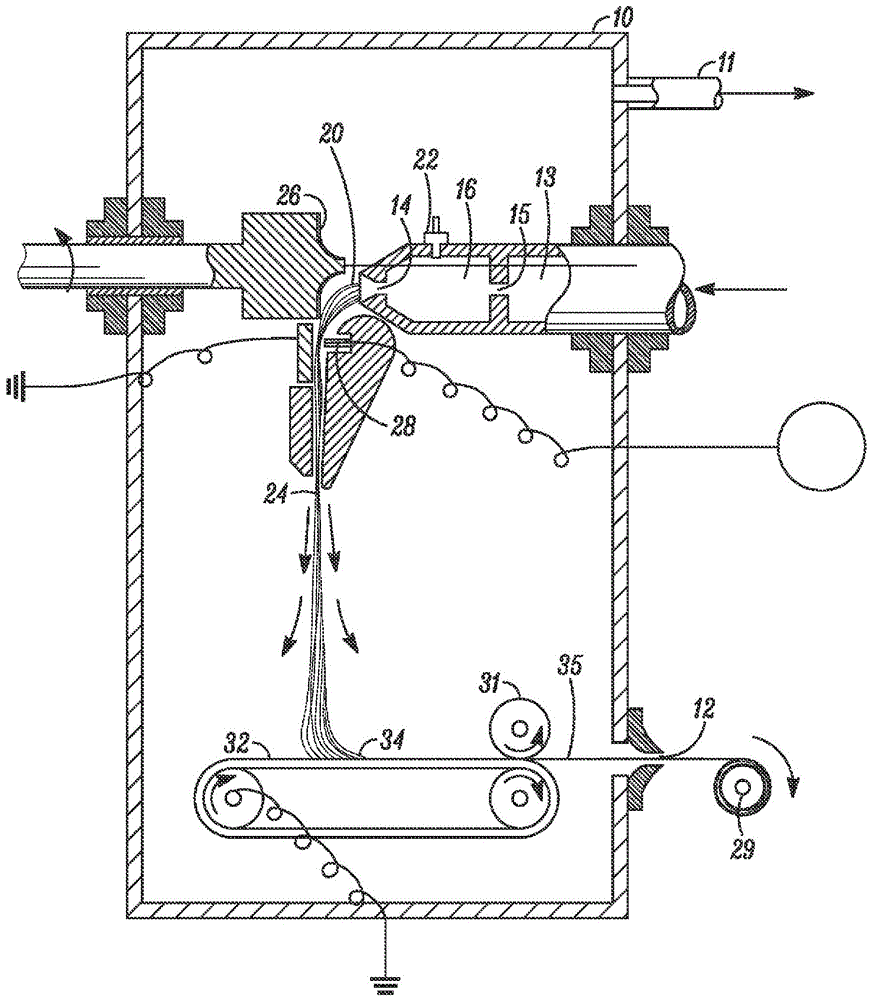
A process is provided for issuing material from a nozzle in a rotor rotating at a given rotational speed wherein the material is issued by way of a fluid jet. The material can be collected on a collector concentric to the rotor. The collector can be a flexible belt moving in the axial direction of the rotor. The collected material can take the form of discrete particles, fibers, plexifilamentary web, discrete fibrils or a membrane.
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
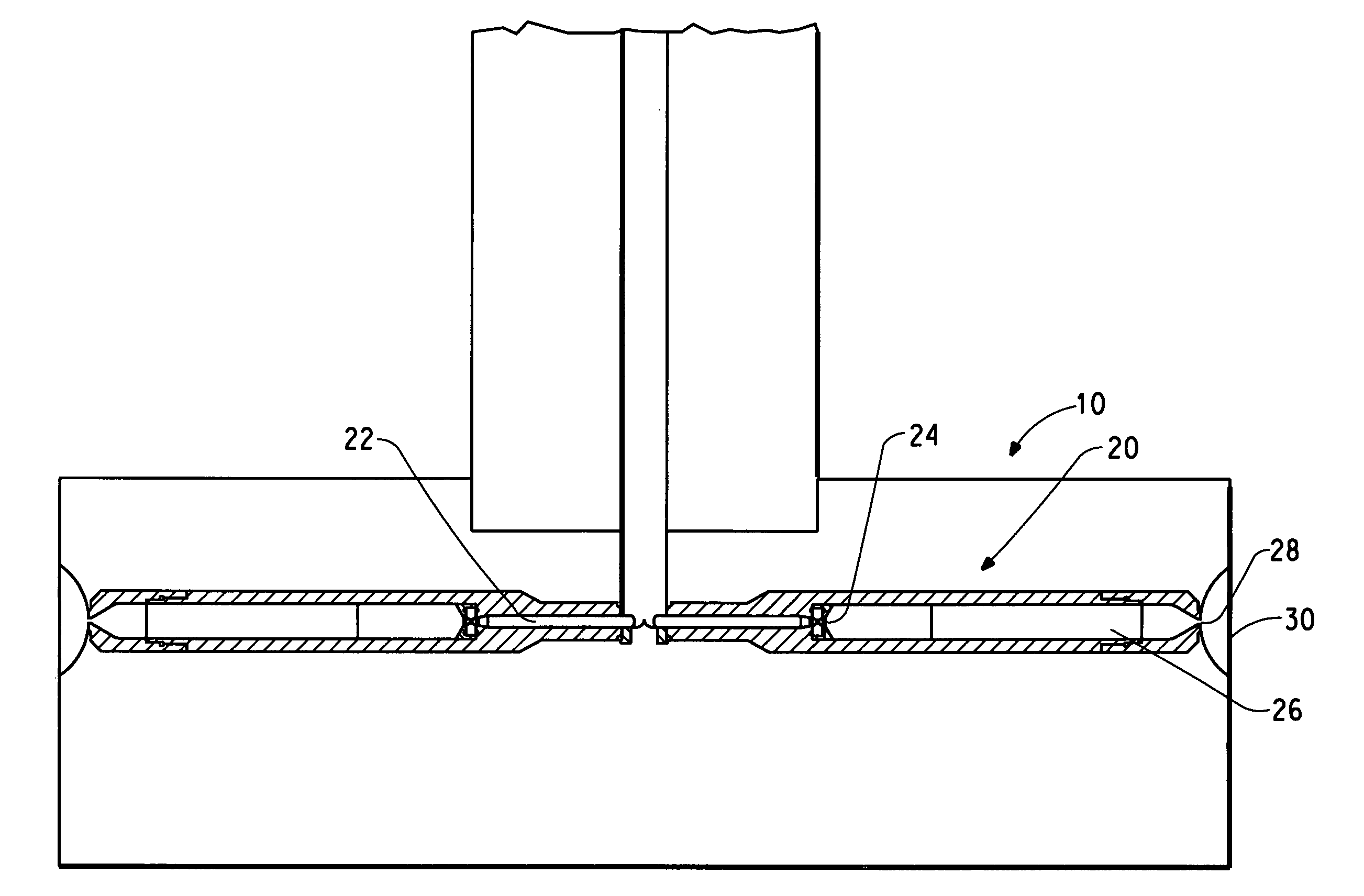
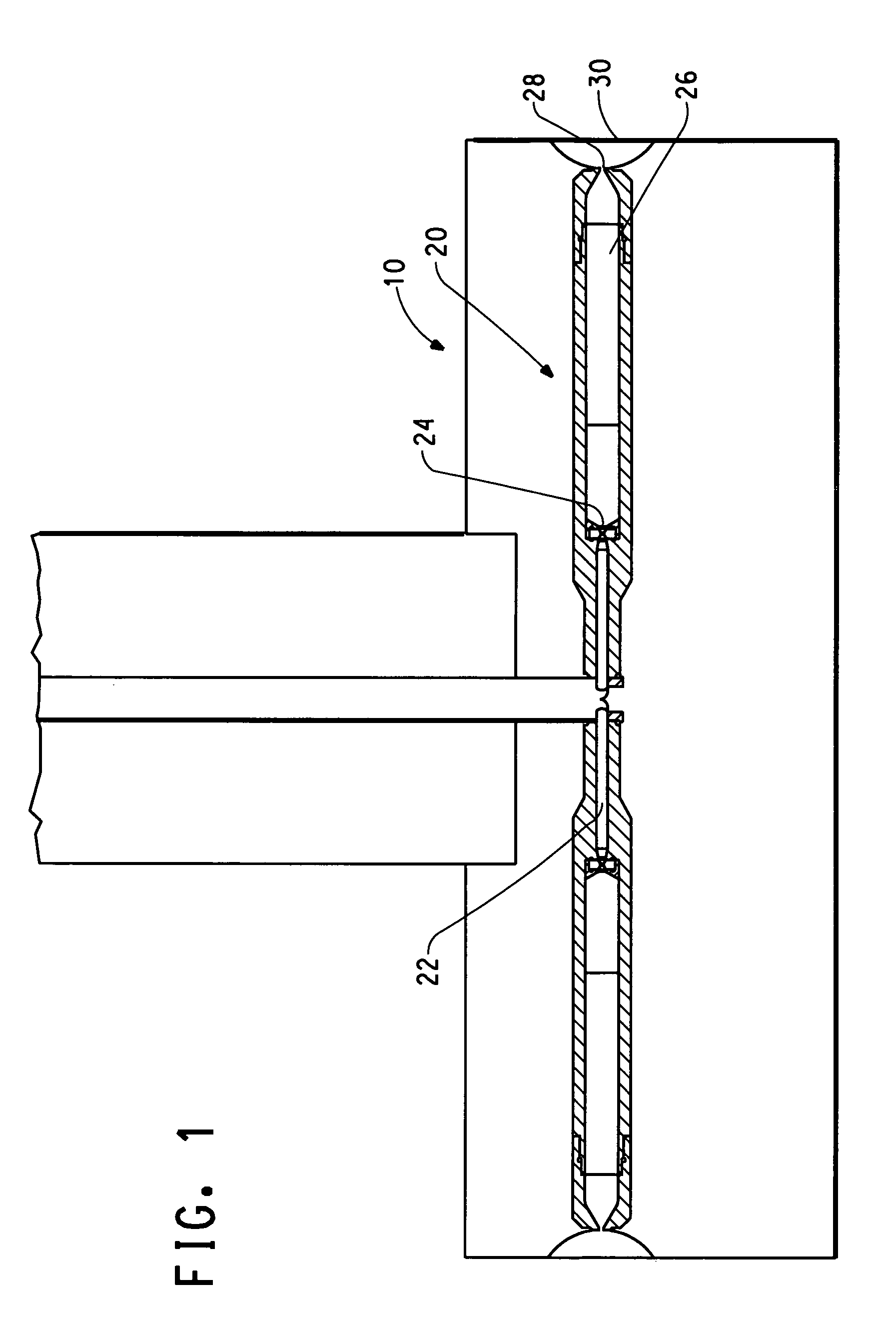
Flash-spun sheet material
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Flash spun sheet material having improved breathability
A process is disclosed for flash spinning a nonwoven fibrous sheet from a polymeric solution containing about 12% to 33% by weight of filler particles. The filler is preferably insoluble in the polymer. The resulting plexifilamentary film-fibril sheet material has increased breathability with no decrease in liquid barrier.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Rotary process for forming uniform material
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
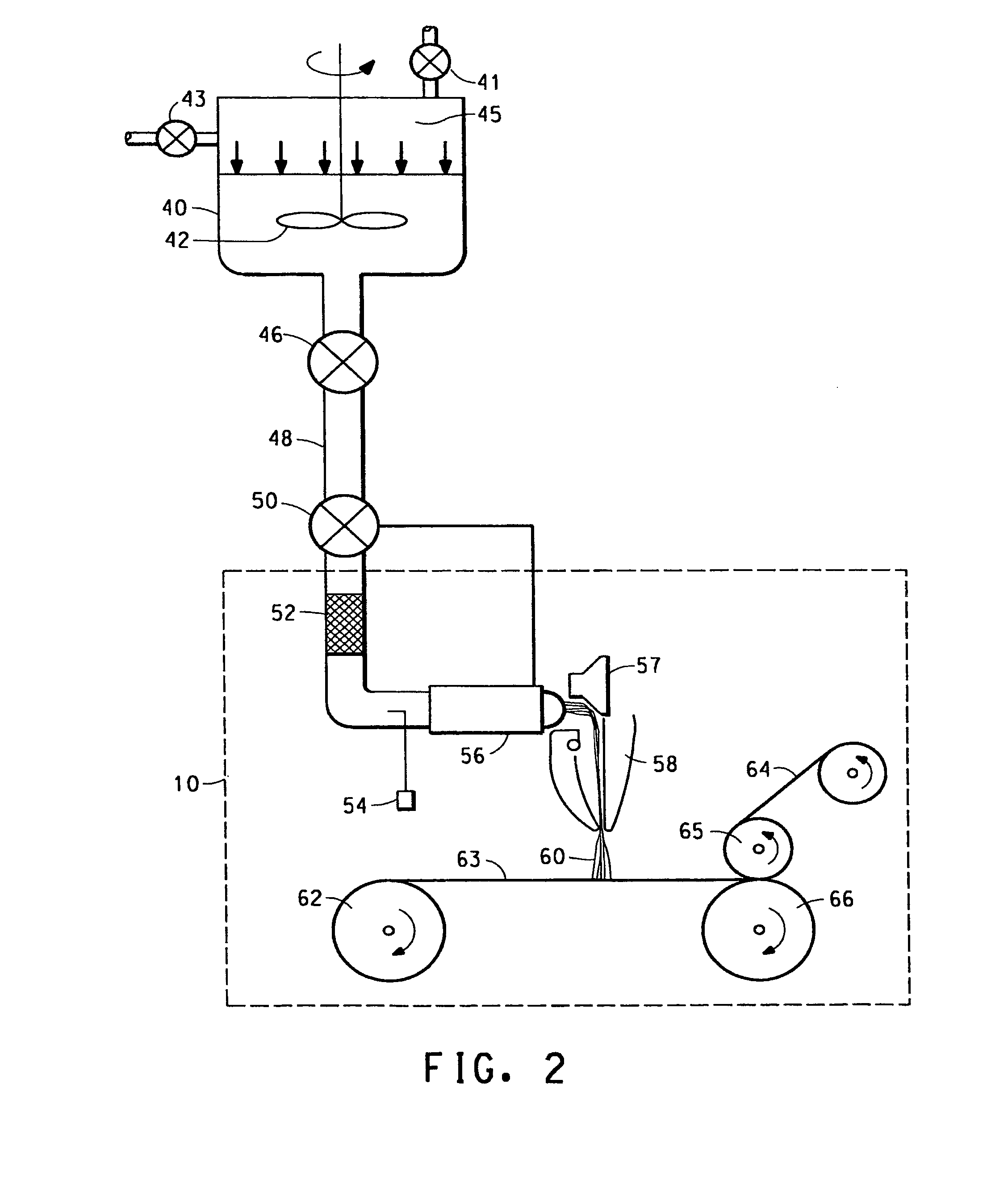
Composite-fiber nonwoven fabric
InactiveUS6355348B1Monocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsHigh intensityNonwoven fabric
The conjugate fiber nonwoven fabric of the present invention comprises conjugate fibers, preferably core-sheath-type or side-by-side-type conjugate fibers, composed of a polyethylene-based resin (A) having a higher melting point in the range of 120 to 135° C. and a lower melting point in the range of 90 to 125° C., which is lower than the above higher melting point at least by 5° C., and a high-melting point resin (B) whose melting point is higher than that of the above polyethylene-based resin (A) by 10° C. or more, the component ratio by weight of the polyethylene-based resin (A) to the high-melting point resin (B) (A / B) being in the range of 50 / 50 to 10 / 90, and the polyethylene-based resin (A) forming at least part of the surface of the fiber longitudinally continuously. This conjugate fiber nonwoven fabric has an excellent softness and a high strength, and it is suitably used as a nonwoven fabric for sanitary materials.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Flash spinning process and flash spinning solution
InactiveUS6162379ARaise cloud point pressureHigh dielectric strengthMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentMonocomponent polyolefin artificial filamentPolyolefinPhotochemistry
A process for producing plexifilamentary products by spinning from a spin fluid of a polyolefin dissolved in a primary spin agent selected from the group consisting of 1,1,2-trichloro-2,2-difluoroethane and isomers thereof; 1,1,3-trichloro-2,2,3,3-tetrafluoropropane and isomers thereof; 1,2-dichloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropane and isomers thereof; and 1,2-dichloro-1-fluoroethylene; and a co-spin agent; and also a spin fluid of a polyolefin dissolved in a primary spin agent selected from the group consisting of 1,1,2-trichloro-2,2-difluoroethane and isomers thereof; 1,1,3-trichloro-2,2,3,3-tetrafluoropropene and isomers thereof; 1,2-dichloro-3,3,30-trifluoropropane and isomers thereof; and 1,2-dichloro-1-fluoroethylene; and a co-spin agent.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Rotary process for forming uniform material
ActiveUS20050244639A1Electric discharge heatingSynthetic resin layered productsFiberMembrane configuration
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Flash spun sheet material having improved breathability
InactiveUS7338916B2Improve breathabilityLayered productsWoven fabricsPolymer sciencePolymer solution
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
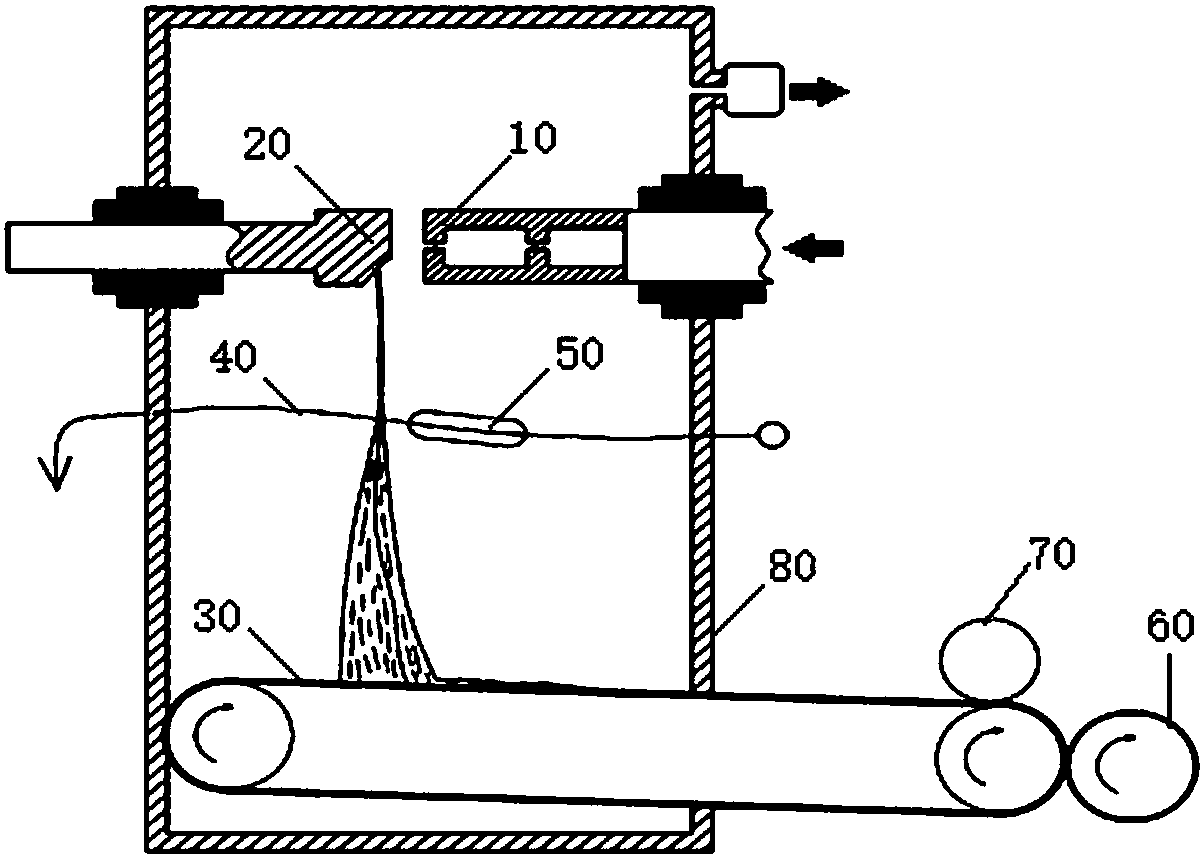
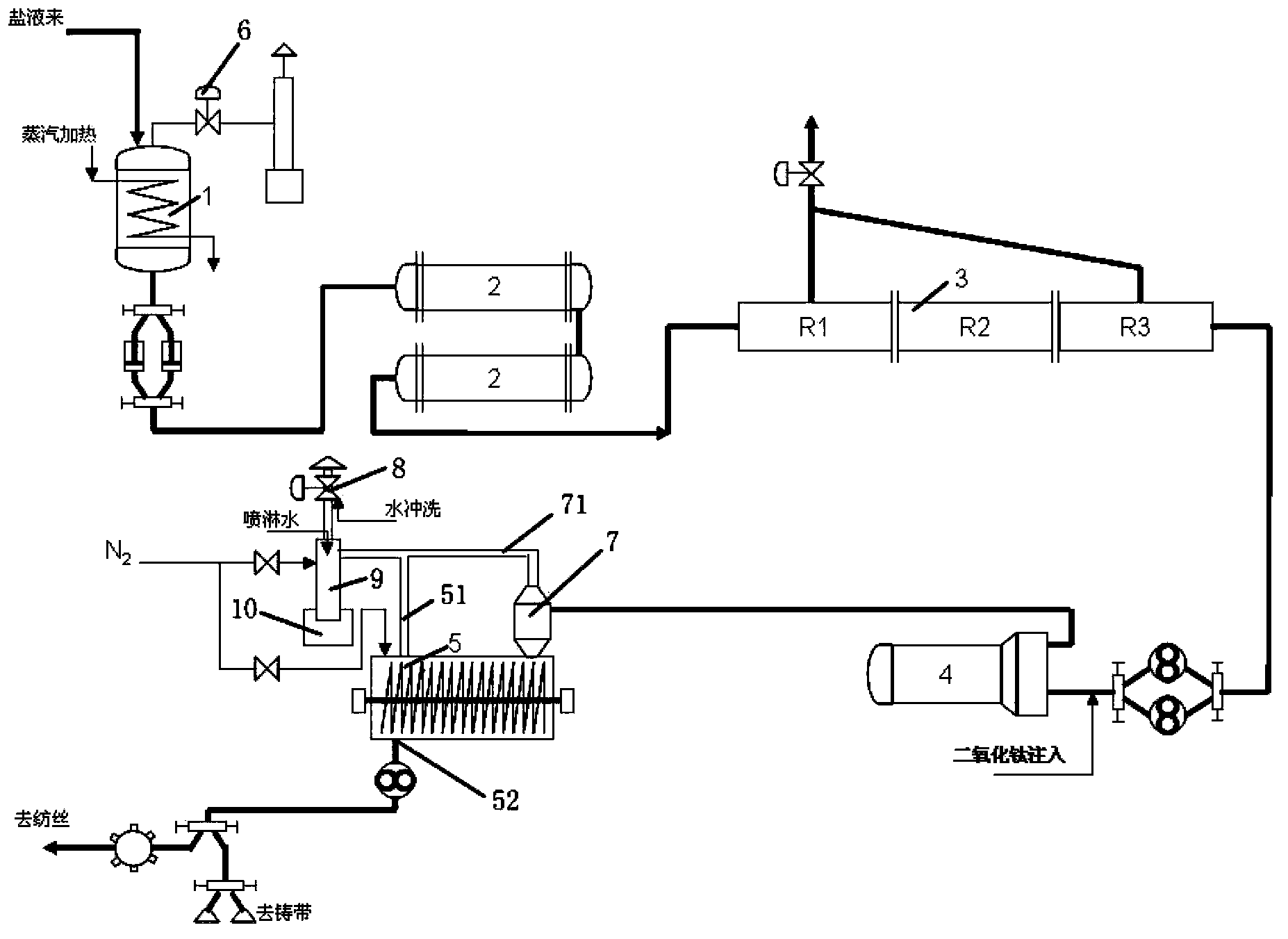
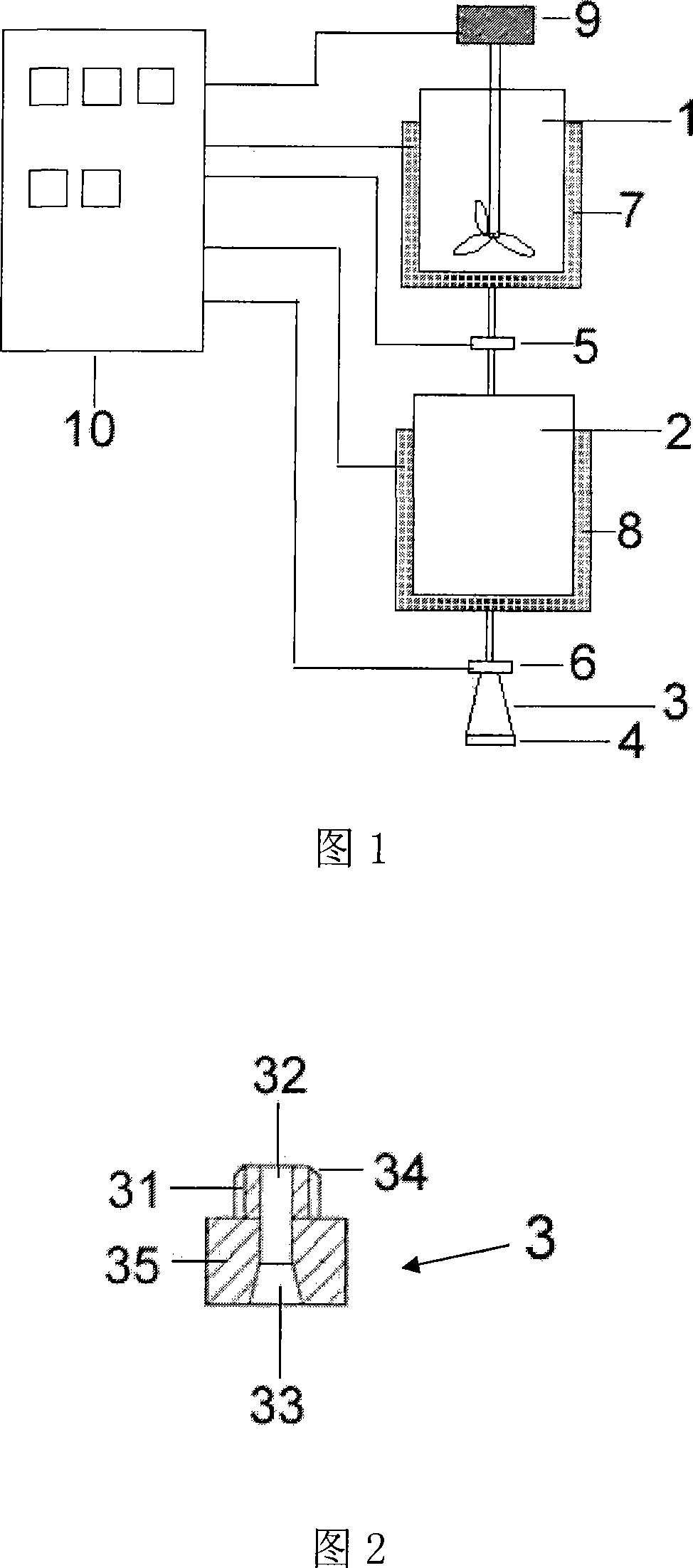
Flash spinning equipment and spinning method thereof
ActiveCN107740198AAvoid security issuesAchieve organic unityFlash-spinning methodsAudio power amplifierFiber bundle
The invention discloses flash spinning equipment. The equipment comprises a box, a spinning nozzle, a steering board and a conveying device, wherein a spinning solution inlet is formed in one side ofthe box, the spinning nozzle is arranged on the spinning solution inlet, the steering board is arranged on the other side of the box and opposite to the spinning nozzle, and the conveying device is arranged on the bottom of the box; the equipment further comprises an air amplifier, the air amplifier is arranged between the steering board and the conveying device, and high-pressure air with a fiberbundle led out by the steering board enters from a compressed air inlet of the air amplifier. The invention further discloses a spinning method of the flash spinning equipment. The method comprises the following steps that a spinning solution is sprayed from the spinning nozzle to form the fiber bundle, by means of the air amplifier, secondary drafting is conducted on the fiber bundle, and even splitting is conducted to form a fiber web. According to the equipment and the method, by adopting the air amplifier to replace traditional electrostatic apparatus for fiber splitting, the effect thatthe equipment and the method are more energy-saving and safer is achieved, the diameters of obtained fibers are small, and the strength is high.
Owner:XIAMEN DANGSHENG NEW MATERIAL CO LTD +1
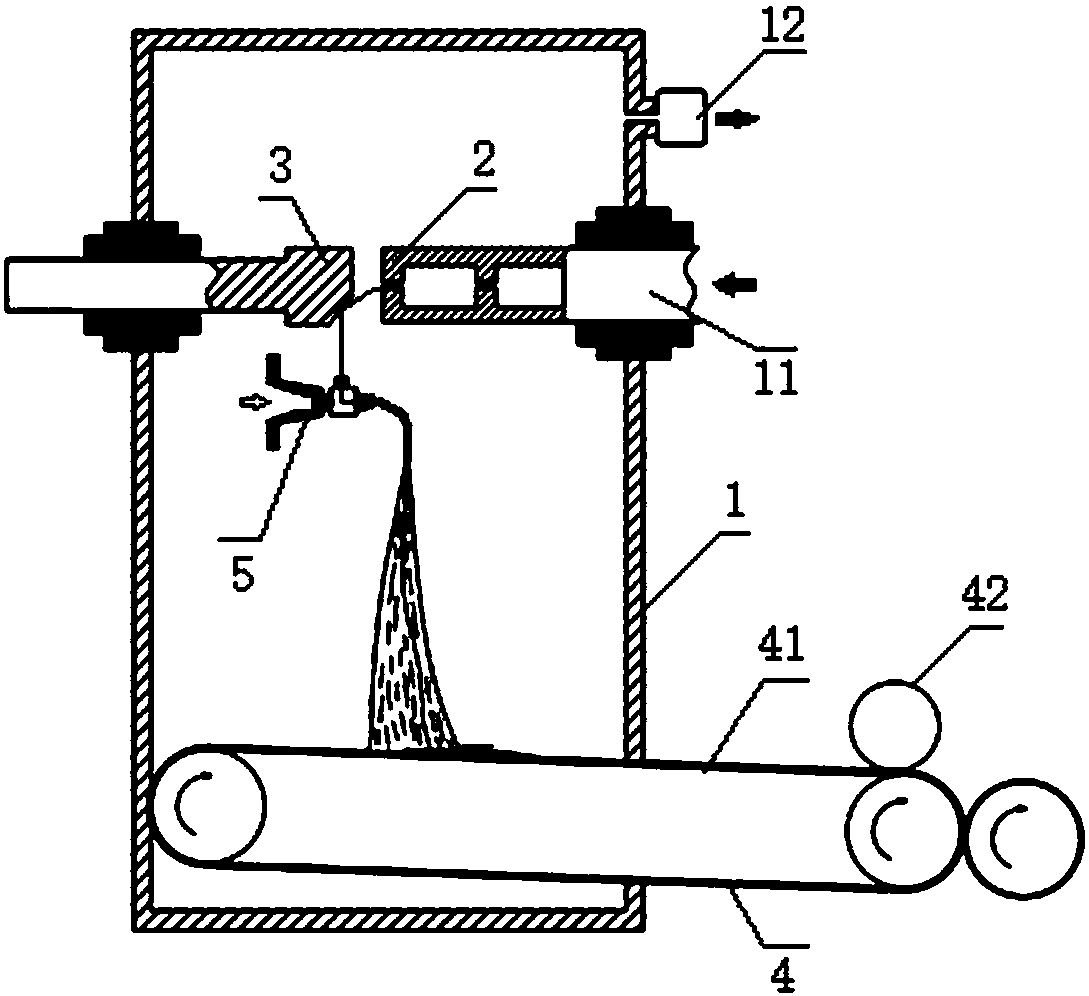
Safe solution spinning method
ActiveCN111286790AEmission reductionImprove production safetySpinnerette packsArtificial filament recoverySpinningNitrogen gas
The invention relates to a safe solution spinning method. The method is characterized in that in the solution spinning process, the oxygen content of mixed gas in a spinning box is controlled to be below 18vol%. By means of the method for introducing incombustible gas into the spinning box to reduce the oxygen content, the explosion risk in the solution spinning process is avoided, and the production safety is improved. The requirement for solvents can be reduced, the selection range of the solvents in the solution spinning process can be wider, the solvents are not limited to hydrocarbon solvents containing halogen, and hydrocarbon solvents (such as cyclopentane and cyclohexane) which have low flash points and only contain carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms can be adopted. In addition, by arranging a VOC-rich tail gas treatment system 8, the content of organic compounds in VOC-rich tail gas can be effectively reduced, and therefore low-VOC nitrogen is obtained, the tail gas in the spinning box can be recycled, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU QINGYUN NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Flash-spun sheet material
This invention relates to improved plexifilamentary sheet material useful in protective apparel and filtration media, which material is comprised of substantially continuous polyethylene plexifilamentary fiber strands and has a Frazier Permeability, normalized to 1.0 oz / yd2 basis weight, of at least 2 cfm / ft2.
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Separator media for electrochemical cells
InactiveUS20140134498A1Electrolytic capacitorsArtificial filament heat treatmentFiberPolymer science
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Nonwoven materials comprising low density fibers and absorbent articles comprising such fibers
InactiveUS20050090173A1Synthetic resin layered productsCircular knitting machinesPolymer scienceDesorption
Low density fibers and nonwoven materials comprising such fibers suitable for use in absorbent articles are disclosed. The nonwoven materials are in the form of a fibrous web and the fibers are made up of struts which define open and closed cells. The fibers have a fiber density that is less than the density of the polymer composition that is extruded to form the fibers. Depending on their final use in an absorbent article, the material can be either hydrophilic or hydrophobic. Hydrophilic materials, are suitable for topsheets and core components and have desirable fluid handling properties such as a liquid strike-through time of less than about 10 seconds, an absorptive capacity greater than about 4 grams per gram and a medium capillary desorption height of less than about 150 cm. The preferred materials for backsheets and cuffs are hydrophobic and have a repellency greater than 0 cm.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
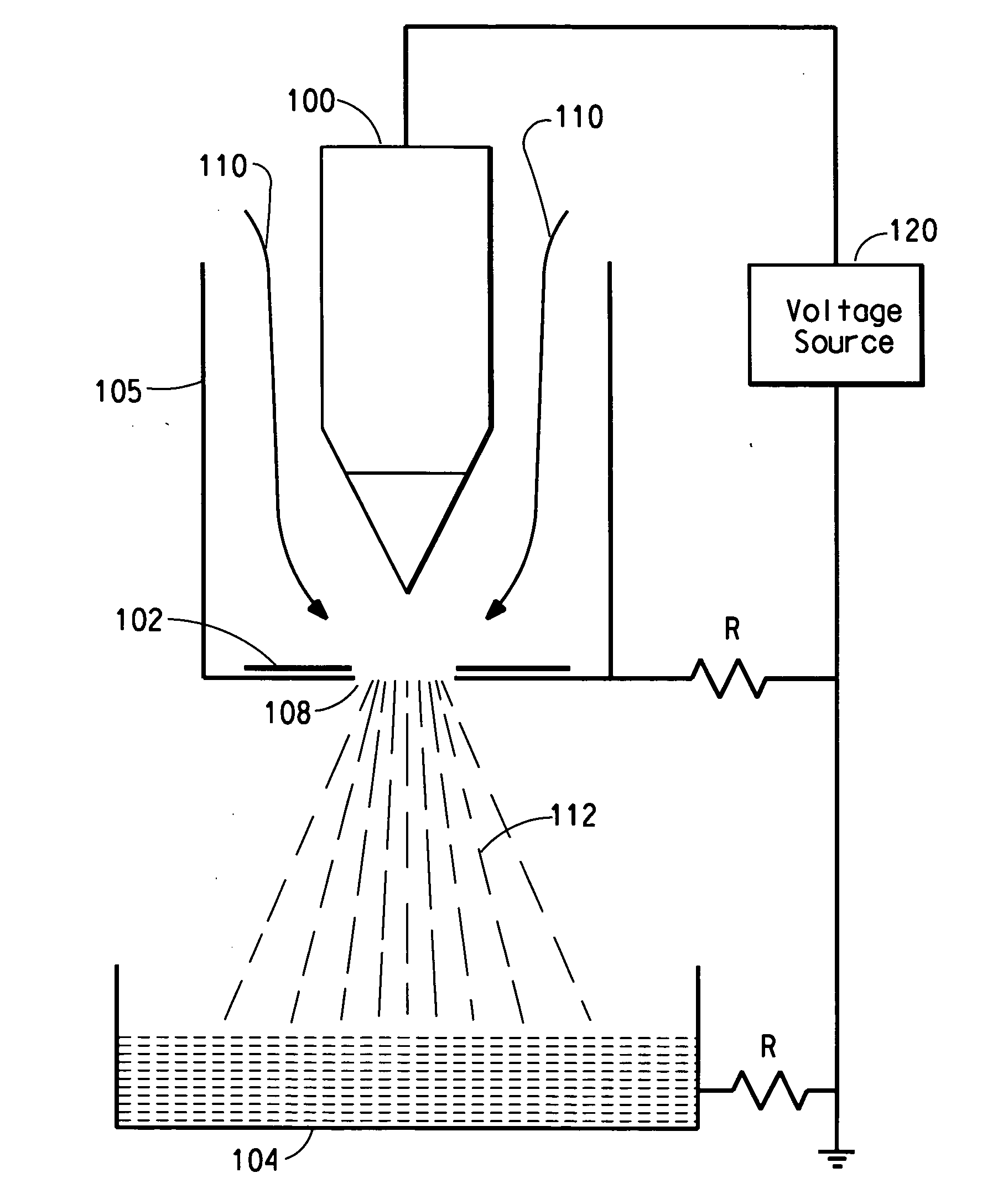
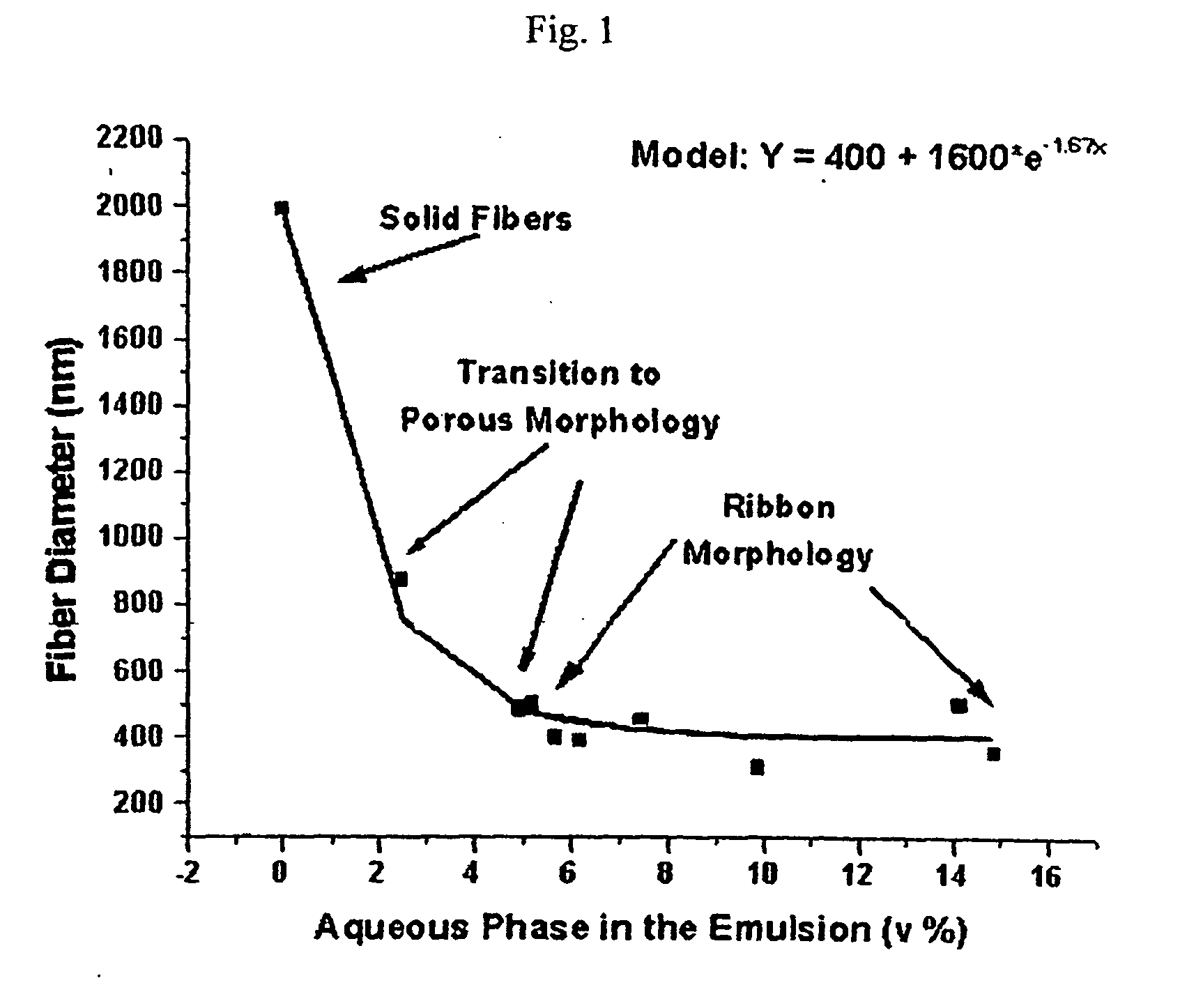
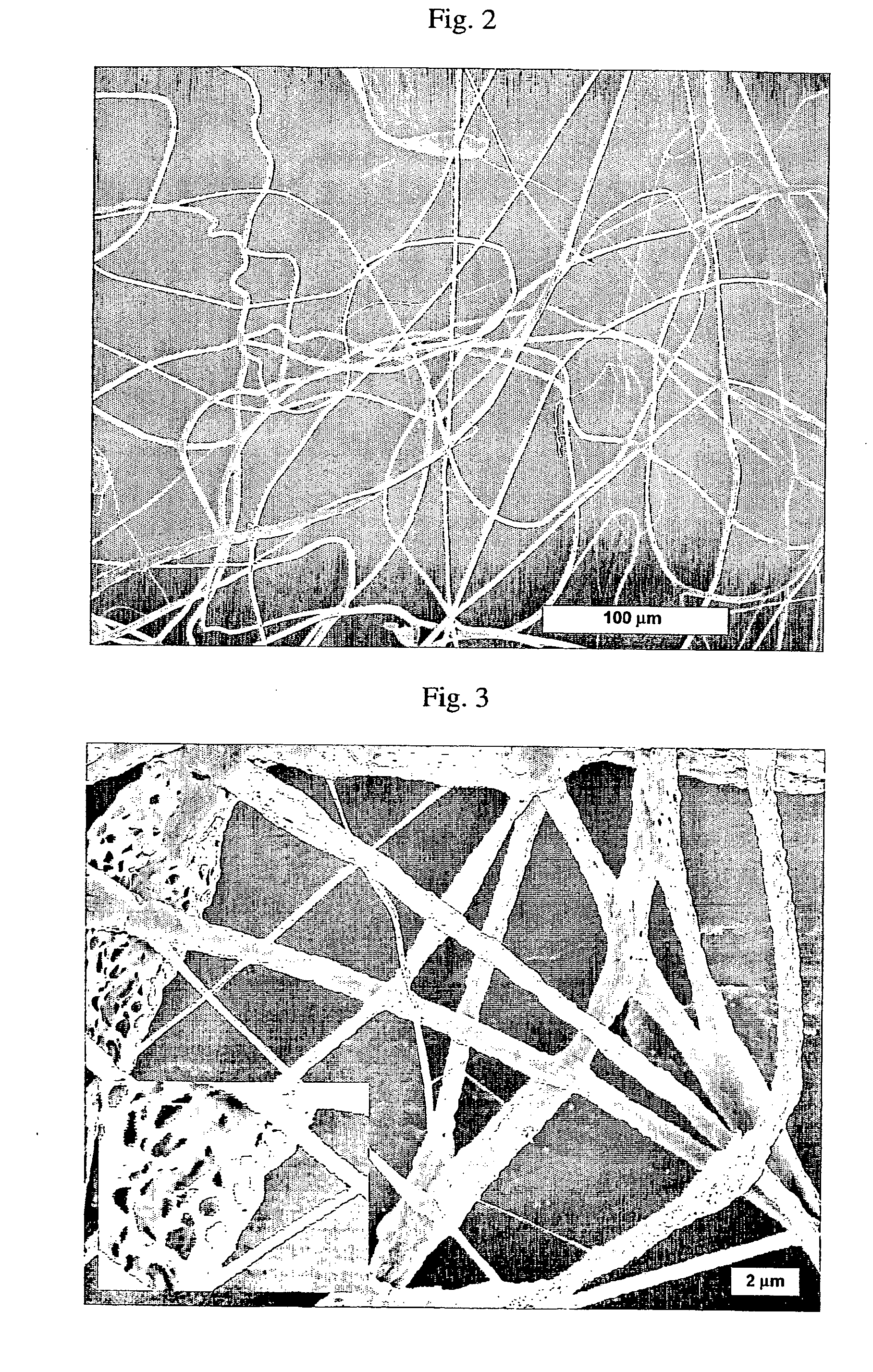
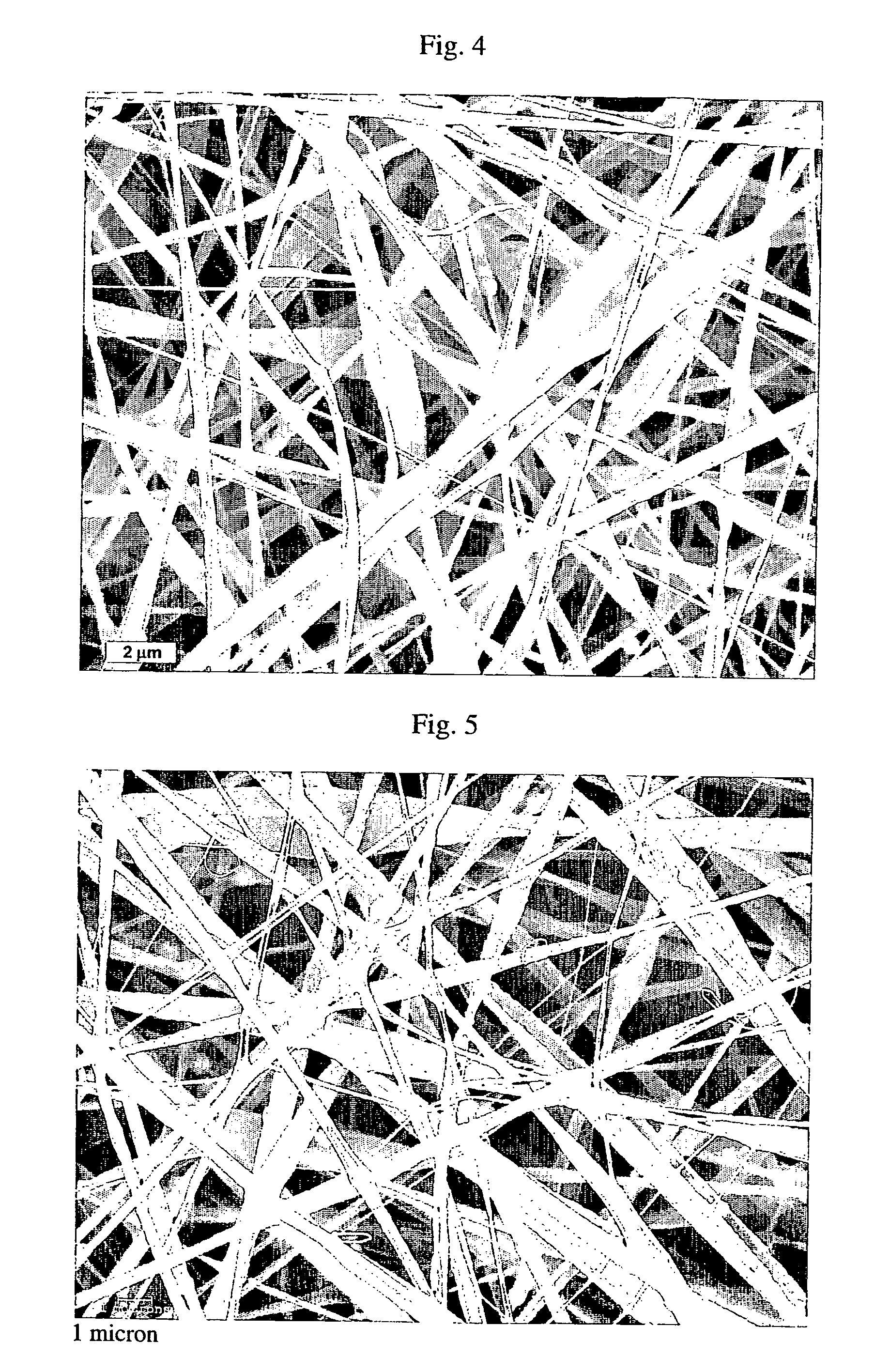
Emulsion-based control of electrospun fiber morphology
The invention provides a fiber having different morphology and a method of making such fiber in a predictable manner. The method includes providing a first component including water, wherein the first component has a first evaporation rate, providing a second component including a polymer, wherein the second component has a second evaporation rate, provided that the second evaporation rate is higher than the first evaporation rate, combining the first component and the second component to make an emulsion, applying a force to the emulsion, and extruding the emulsion to make the fiber, wherein the fiber has an outer surface, an internal cavity and a diameter of at most 10 micrometers.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
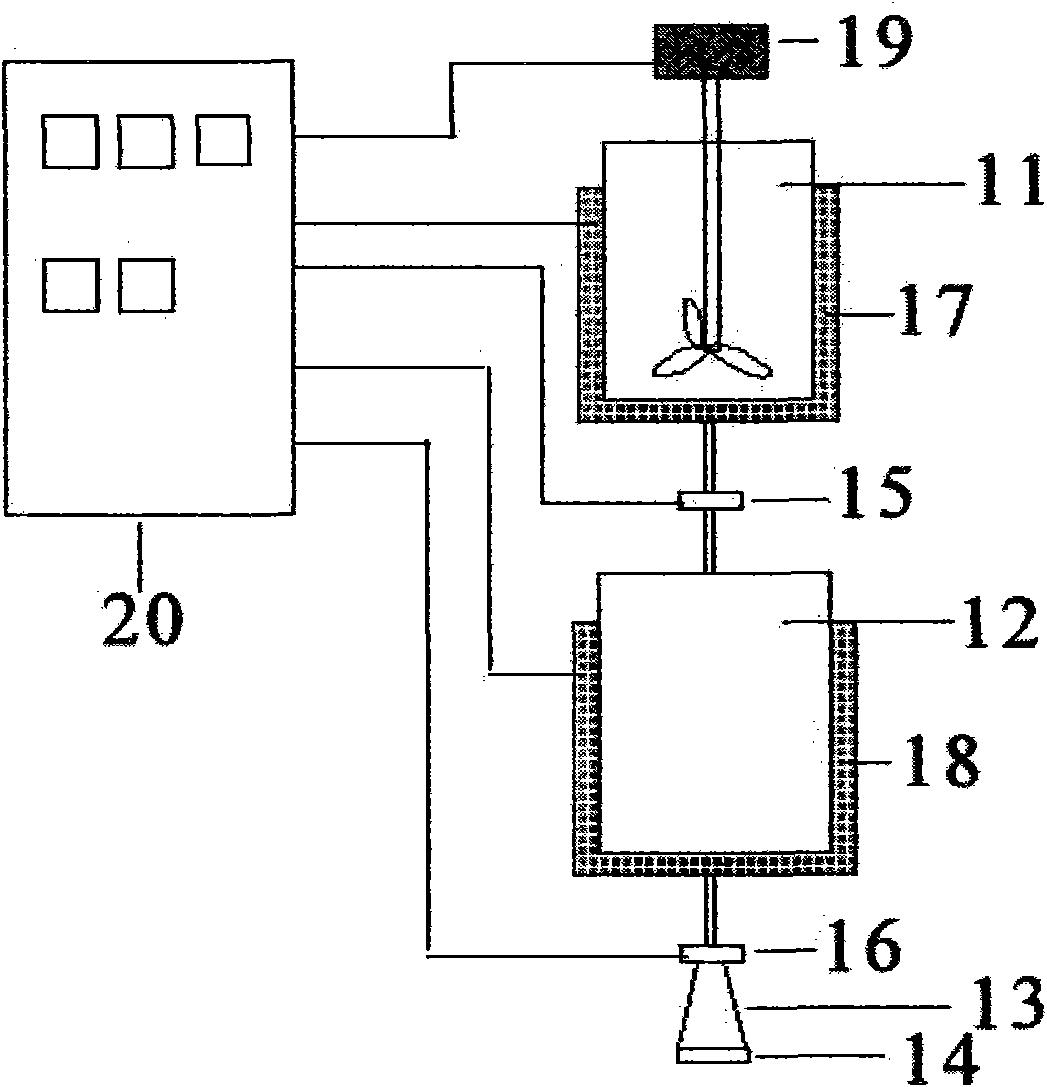
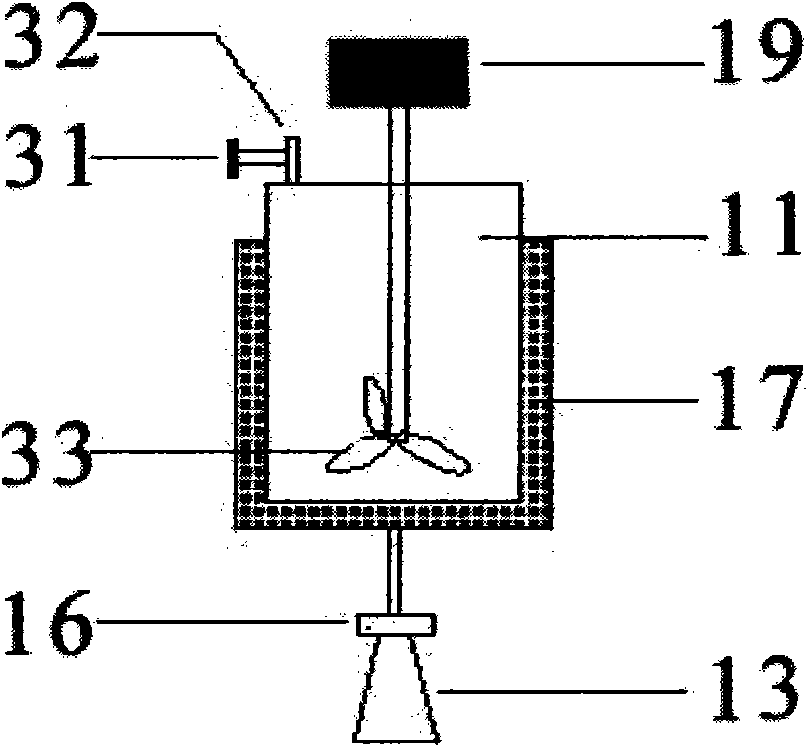
Preparation method of high strength polyethylene fiber and special device thereof
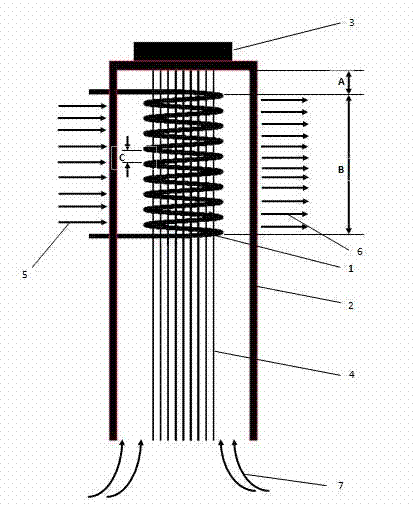
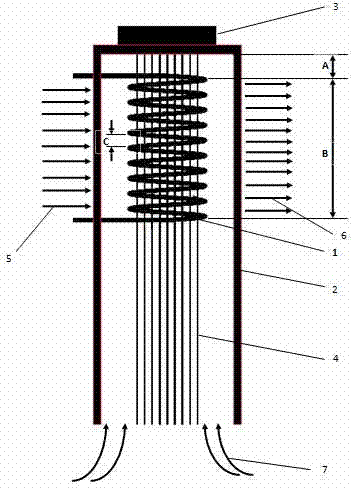
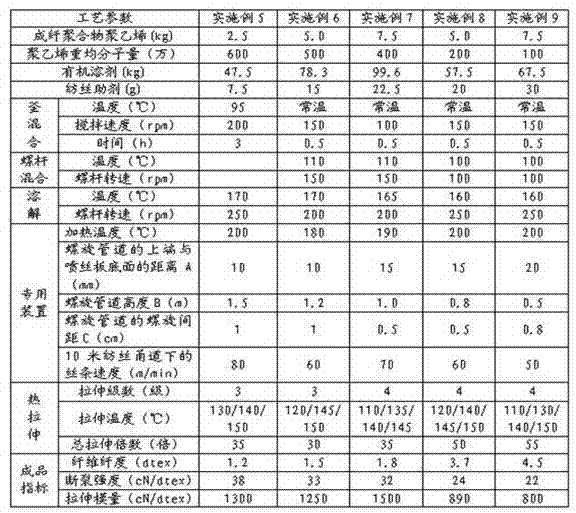
ActiveCN102226300AQuick drawSimple process routeArtificial filament washing/dryingArtificial filament heat treatmentState of artOrganic solvent
The invention provides a preparation method of high strength polyethylene fiber and a special device thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: fibre-forming polymer polyethylene and organic solvent are mixed with spinning aid, the mixture is dissolved to form organic solution, then the organic solution is extruded from a spinneret, liquid trickles enter a flashing heating area below the spinneret to ensure that the organic solvent in the liquid trickles is flashed fast, polyethylene is taken from the gap of spiral pipes of the special device arranged in the flashing heating area to form solid precursor with a fibrillated superfine reticular fiber structure; and the precursor performs hot drawing to prepare the high strength polyethylene fiber with the reticular structure. As the preparation method adopts the flashing technology and the special device, the problem of the prior art that the solvent in strand silk is difficult to volatilize owning to thick volatile solvent layer, can be effectively solved; and the process flow is shortened, the industrialized production is easy to realize, the production efficiency is increased and the product quality of the high strength polyethylene fiber can be ensured.
Owner:JIANGSU LIUJIA TECH CO LTD +1
Device and method for producing fine-denier or super-fine-denier nylon 66 filament
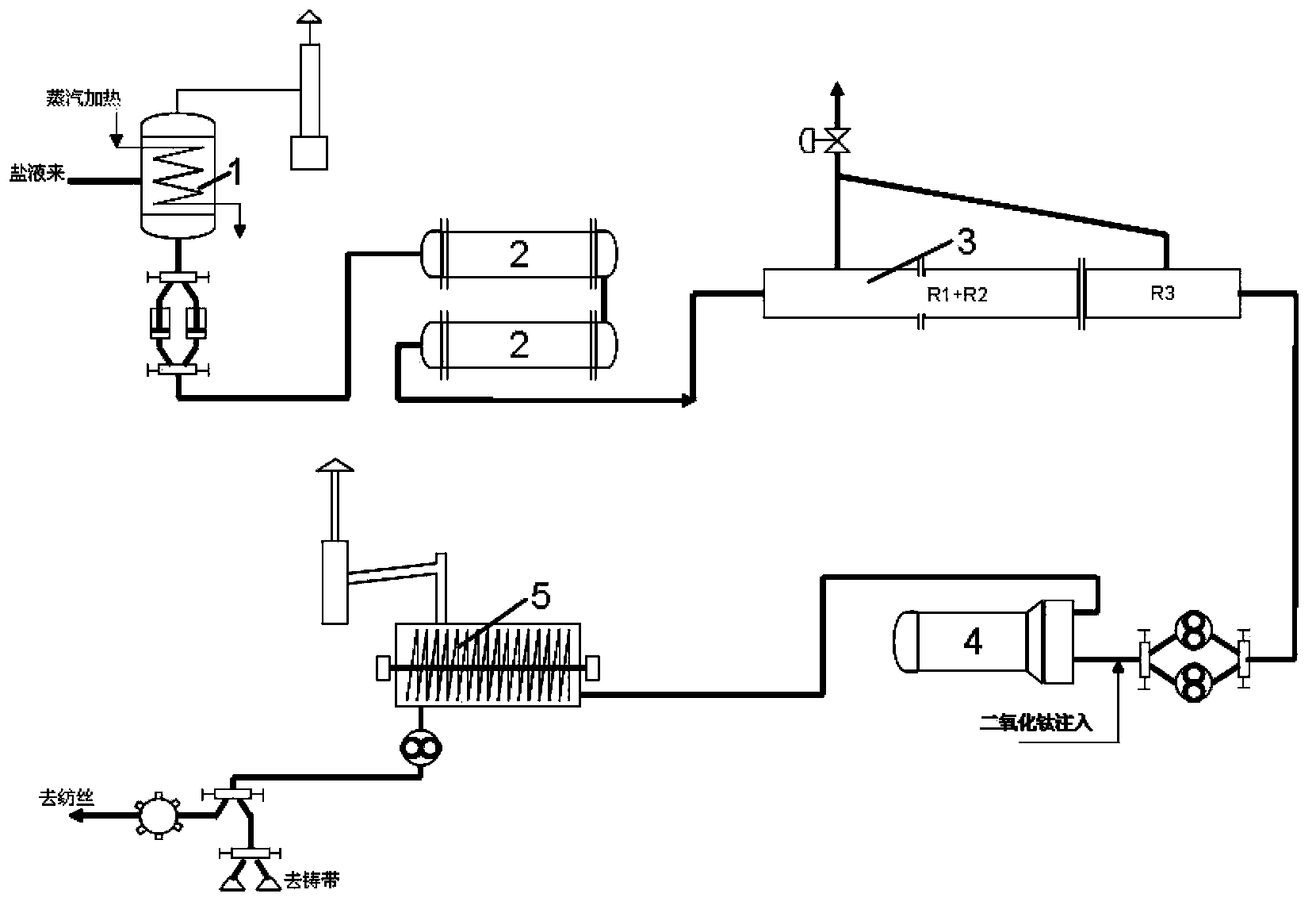
ActiveCN103668510AStabilize and improve qualityReliable working conditionsArtificial filament physical treatmentArtificial thread manufacturing machinesVapor–liquid separatorNylon 66
The invention discloses a device and method for producing a fine-denier or super-fine-denier nylon 66 filament and belongs to the technical field of textile materials. The device comprises an evaporator, a preheater, a reactor, a flash vessel and a polycondensation finisher system. A pressure adjusting valve is arranged on the evaporator. A three-section biphenyl secondary-circuit heating method is adopted by the reactor. The polycondensation finisher system comprises a polycondensation finisher, a vapor liquid separator, a vapor purifier device and a nitrogen injection system. A polycondensation reaction is conducted on a water solution of nylon 66 salt through the improved continuous polycondensation system, and then a nylon 66 resin melt is obtained. Spinning is directly conducted on the nylon 66 resin melt to manufacture the fine-denier or super-fine-denier nylon 66 POY filament. According to the device and method for producing the fine-denier or super-fine-denier nylon 66 filament, direct melt spinning is conducted by the adoption of a multi-hole spinneret plate, a POY melt spinning device and the accurate spinning technology through the technical improvement to an existing continuous polycondensation system and more reliable technology control, and therefore the nylon 66 POY filament with the dpf ranging from 0.8dtex to 1.0dtex is manufactured.
Owner:LIAONING YINZHU CHEMTEX GROUP
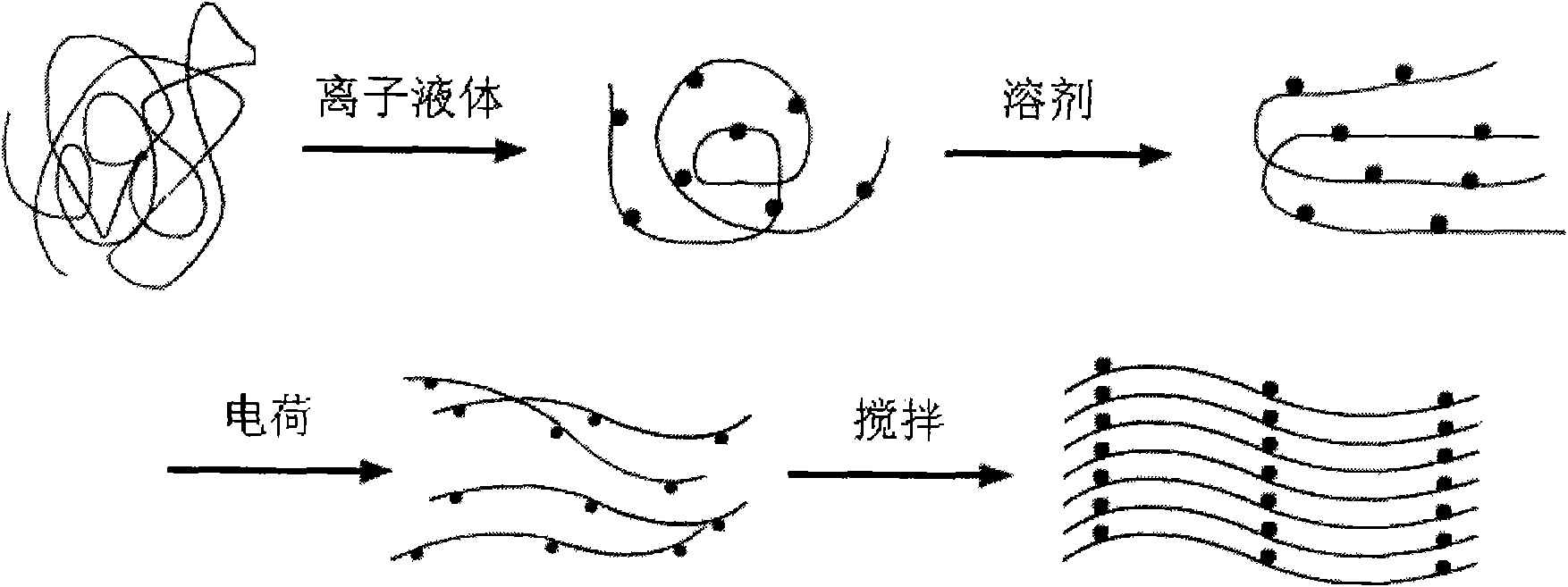
Method for fabricating superfine fiber by flash vaporization
InactiveCN101565861AReduce operational riskLow costSpinning solutions preparationFlash-spinning methodsViscous liquidPolyester
The invention relates to a fabricating method for fabricating superfine fiber by flash vaporization, of which the process is: polymers and ionic liquid are put into an autoclave according to a proportion of 10g of polymer to 5-20ml of ionic liquid and then is evenly stirred; then the standing pretreatment lasts for 0.5-3 hours under normal temperature so as to swell the polymer to be viscous liquid; polymer is added into the solvent in a ratio of 10g / 50-200ml and is stirred for 20-30min at the temperature of 150-350 DEG C and the pressure of 5-25MPa; after fully dissolving, a feeding control valve of the autoclave is opened so as to lead the filature to eject from a spinning nozzle to form the superfine fiber; devillication is automatically carried out; three-dimension network superfine fiber is formed on a receiving device by solidification; the polymer is polyolefine, polyester or polyvinylidene fluoride; the ionic liquid is 1-butyl-3-methyl-iminazole chloride or 1-allyl-3-methyll-iminazole chloride; and the solvent is 1, 2-dichloroethane, trichloromethane or cyclohexane.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Polyolefin synthetic pulp and use thereof
InactiveUS6338772B1Large fiber breaking lengthImprove internal bond strengthNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperPolymer sciencePolyolefin
A polyolefin synthetic pulp comprising a polyolefin resin graft-modified with an unsaturated carboxylic acid or a derivative thereof, and / or a polyolefin resin composition which comprises an ethylene / alpha,beta-unsaturated carboxylic acid copolymer and a polyethylene resin. Further, there is provided a heat sealing paper comprising a base fiber layer whose at least one surface is laminated and integrated with a layer of the polyolefin synthetic pulp. This polyolefin synthetic pulp has a large breaking length and an excellent internal bond strength, and exhibits stable heat sealing and hot tack properties over a wide temperature range from low to high temperature. The polyolefin synthetic pulp is suitable to use in battery separators, molding fiberboards, heat sealing papers and the like. The heat sealing papers have excellent heat sealing properties, and are characterized by having a large breaking length and an excellent internal bond strength and by exhibiting stable heat sealing and hot tack properties over a wide temperature range from low to high temperature.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
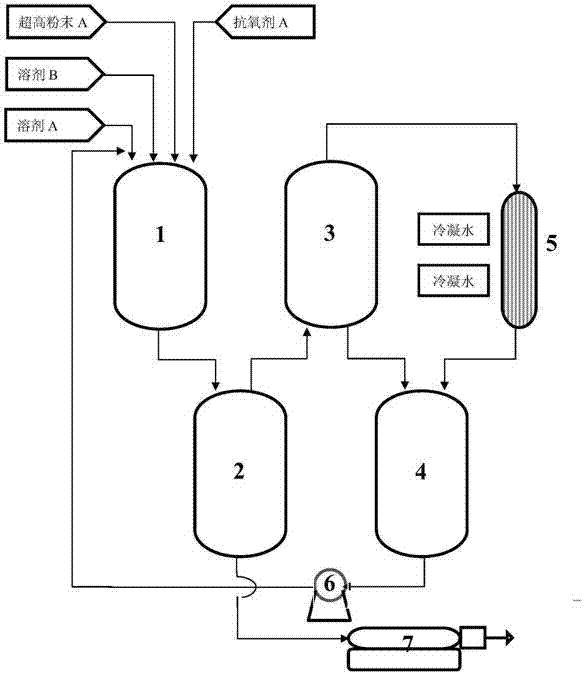
Preparation method of high concentration ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber spinning solution
ActiveCN106948022ALow costReduce dosageMonocomponent polyolefin artificial filamentSpinning solutions preparationHigh concentrationAntioxidant
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high concentration ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber spinning solution. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step one, subjecting polyethylene powder, a mixed solvent, and an antioxidant to pressurization, heating, stirring, and swelling to obtain suspension of swelled body; step two, subjecting the suspension obtained in the step one to reduced pressure flash evaporation, separating and storing a solvent A with a low boiling point in a buffer tank, and discharging the suspension after flash evaporation; and step three, feeding the suspension obtained in the step two into a double screw extruder to carry out high temperature dissolution to radically unwind molecular chains through mixing by double screws so as to obtain the high concentration polyethylene fiber spinning solution. Compared with the prior art, after the swelling process, the swelled suspension is rapidly cooled through flash evaporation so as to prevent excess swelling. The preparation method can prepare a uniform polyethylene spinning solution with a polyethylene mass percentage of 15 to 50%. The solvent extraction step is not needed, the production efficiency is largely improved, at the same time, the low boiling point solvent generated in flash evaporation can be condensed, recovered and reused, and the production cost is reduced greatly.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF CHEM IND
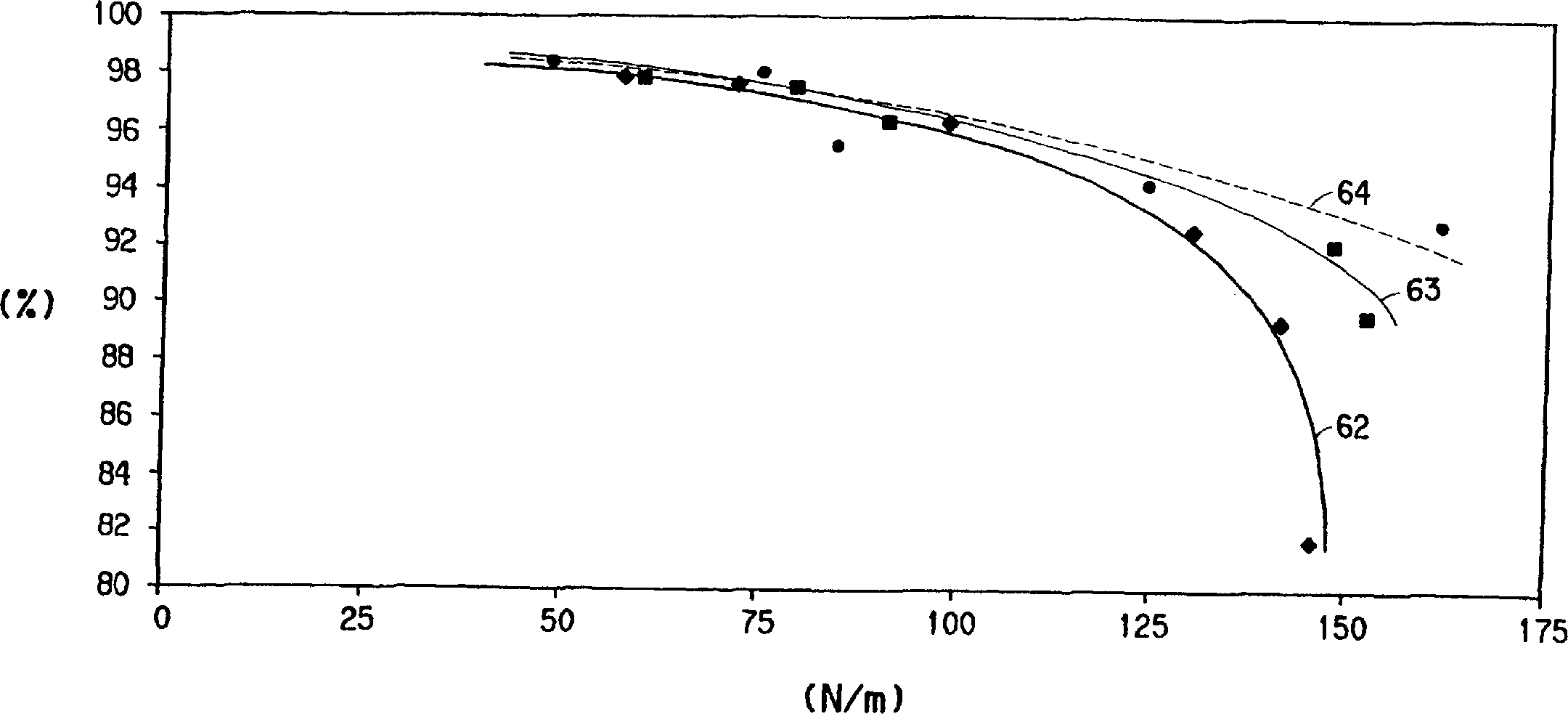
Improved flash-spun sheet material
InactiveCN1249791AControl devices for washing apparatusMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentFiberPolymer science
There is provided an improved sheet composed of bonded ultrafine plexifilamentary film-fibril bundles spun from polyolefin and pigment. The polyolefin accounts for at least 90% of the weight of the fibril bundle, and the pigment accounts for 0.05-10% of the weight of the fibril bundle. The sheet has high opacity even after bonding to a delamination strength greater than 120 N / m. The pigments in the sheet can be titanium dioxide, black pigments or colored pigments.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Device and method for flash evaporation textile of superfine fibre
ActiveCN101173374ASimple structureEasy to useSpinnerette packsFlash-spinning methodsPolyesterPolyolefin
The invention relates to a piece of equipment and a method for flash-spinning superfine fiber, which is characterized in that: the equipment comprises a high pressure boiler with a high pressure heating mantle, and a low pressure boiler with a low pressure heating mantle; wherein, a high pressure control valve is arranged between the high pressure boiler and the low pressure boiler which are communicated; an agitator is arranged in the high pressure boiler; the output pipe of the low pressure boiler is connected with a spinneret via a low pressure control valve, and a fiber splitting baffle is positioned at the outlet of the spinneret; the high pressure heating mantle, the low pressure heating mantle, the high pressure control valve, the low pressure control valve and the agitator are connected with a control device respectively; the method is applied to the equipment and the following process: polymer and solvent are put into the high pressure boiler for full dissolution; then the high pressure control valve is opened, and the solution flows into the low pressure boiler; after 15 to 30 minutes, the low pressure control valve is opened, the solution ejects from the spinneret and the fiber splitting baffle, and three dimension network shaped superfine fiber is obtained. The temperature and the pressure in both the high pressure boiler and low pressure boiler is 150 to 350 DEG C and 5 to 25MPa respectively; the polymer can be a polyolefin, a polyester or a polyvinylidene fluoride, and the solvent can be a 1, 2-dichloroethane, a chloroform or a cyclohexane corresponding to the polymer.
Owner:GUANGDONG KINGFA TECH CO LTD
Flash spun plexifilamentary strands and sheets
ActiveCN106574401AMonocomponent polyolefin artificial filamentFlash-spinning methodsFiberCrystallinity
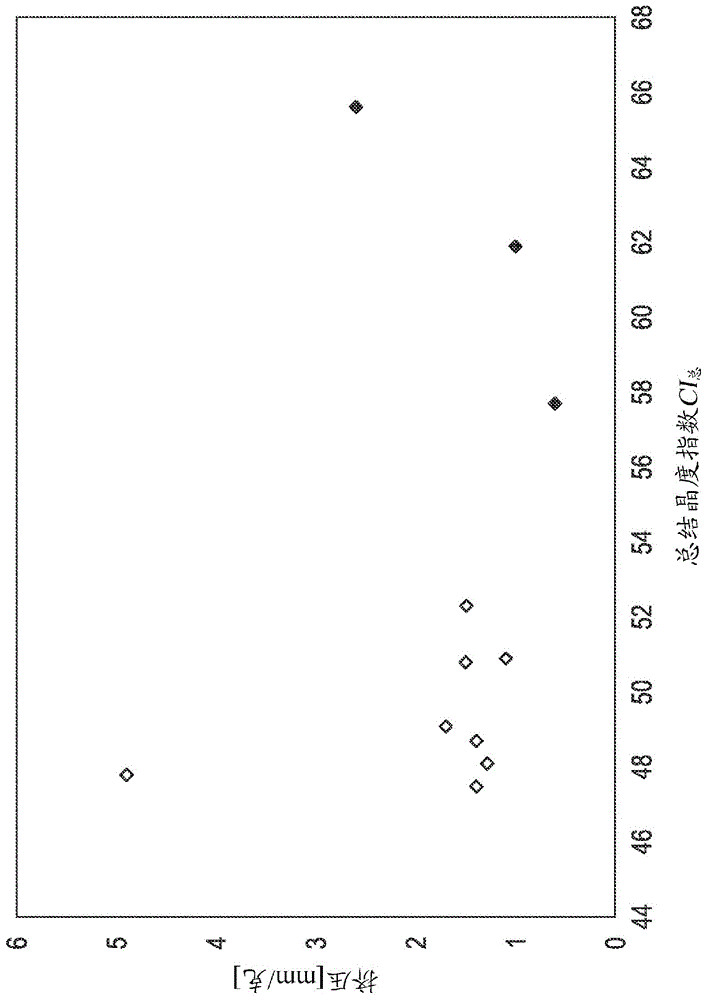
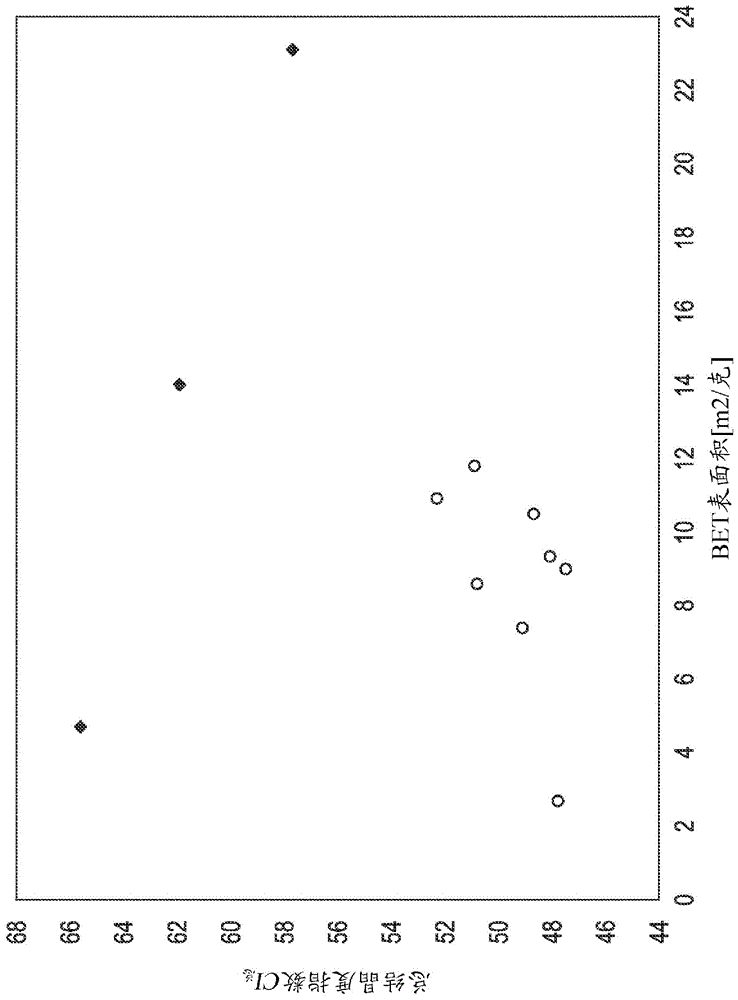
A flash-spun plexifilamentary fiber strand having a BET surface area of less than 12 m2 / g, a crush value of at least 0.9 mm / g wherein said fiber strand comprises predominantly fibers formed from polyethylene, said fibers having a total crystallinity index of less than 55 %, and sheets made thereof.
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Flash spinning equipment
InactiveCN101876089ARelieve pressureImprove solubilityFlash-spinning methodsHigh pressureHigh voltage
The invention discloses flash spinning equipment. The equipment mainly comprises a high pressure kettle, a heating sleeve of the high pressure kettle, a transmission motor, a stirrer, a high voltage electric valve and a spinning nozzle, and is characterized in that: a kettle cover of the high pressure kettle is provided with a pressure relief hole and a pressure relief valve, so the high pressure kettle simultaneously has the functions of a low pressure kettle; and the bottom of the high pressure kettle is in direct pipe connection with the spinning nozzle through the high pressure electric valve. The flash spinning equipment has the advantages of simple structure, easy control and the suitability for industrial use.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method of preparing ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene fiber through high-concentration gel spinning
PendingCN110158160AImprove swelling and dissolving effectIncrease temperatureArtificial filament heat treatmentMonocomponent polyolefin artificial filamentFiberHigh concentration
The invention relates to a method of preparing ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene fiber through high-concentration gel spinning. The method includes: stepwise rising temperature of a suspension of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene resin and a spinning solvent, allowing spinning dope obtained by treatment to go through a double-screw extruder and a spinning box to obtain gel fiber, and subjecting the gel fiber to solvent removing, drying and ultra-drawing to obtain the ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene fiber. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that by controlling temperature and emulsifying time, the problem of discharging difficulty due to excessive swelling can be solved while swelling dissolving effect is realized, and the method is suitable for industrial product and can obtain the UHMWPE fiber with excellent performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF CHEM IND
Preparation method of conducting fiber
InactiveCN101845679AHigh strengthReduces the chance of blemish breakageElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureMonocomponent polyolefin artificial filamentPolyesterFiber
The invention relates to a preparation method of conducting fiber, which adopts a flash evaporation method. The concrete process comprises the following steps of: firstly, adding a polymer and a solvent into a high-pressure kettle according to the proportion of 10g of the polymer to 50-200ml of the solvent; secondly, adding nanometer conducting powder according to a mass proportion that 5-30g of the nanometer conducting powder is added into every 100g of the polymer, uniformly stirring, and sufficiently stirring for 20-30 min under the condition that the temperature is 150-350 DEG C and the pressure is 5-25MPa; opening an emptying control valve of the high-pressure valve after the polymer is dissolved and the nanometer conducting powder is uniformly dispersed to enable spinning solution to be jetted out from a spinning nozzle and solidified on a receiving device to form three-dimensional network-shaped conducting fiber strips. The polymer is polyolefin, polyester or polyvinylidene fluoride, the solvent is 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform or cyclohexane, and the nanometer conducting powder is carbon black or antimony doped tin oxide.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com