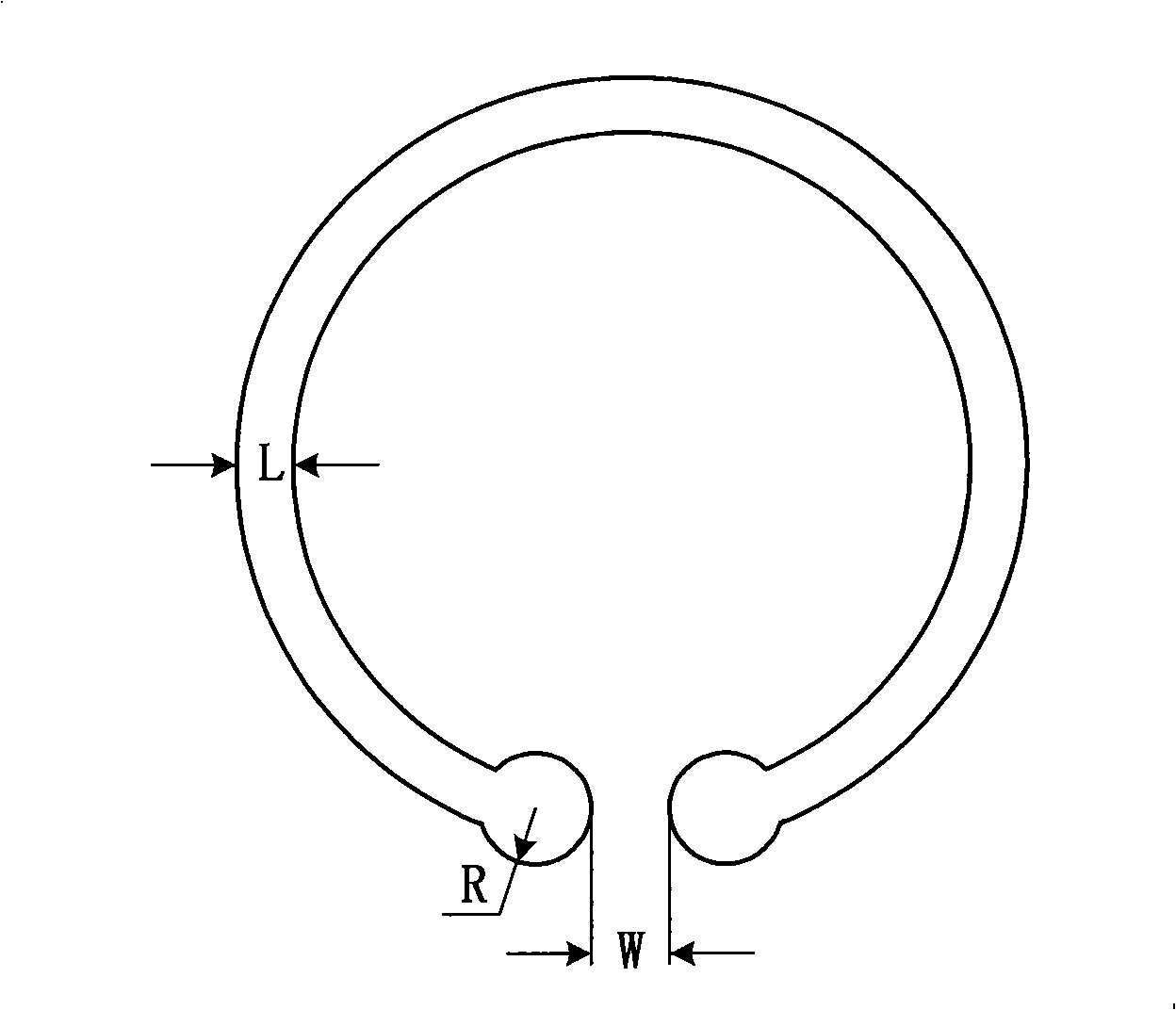
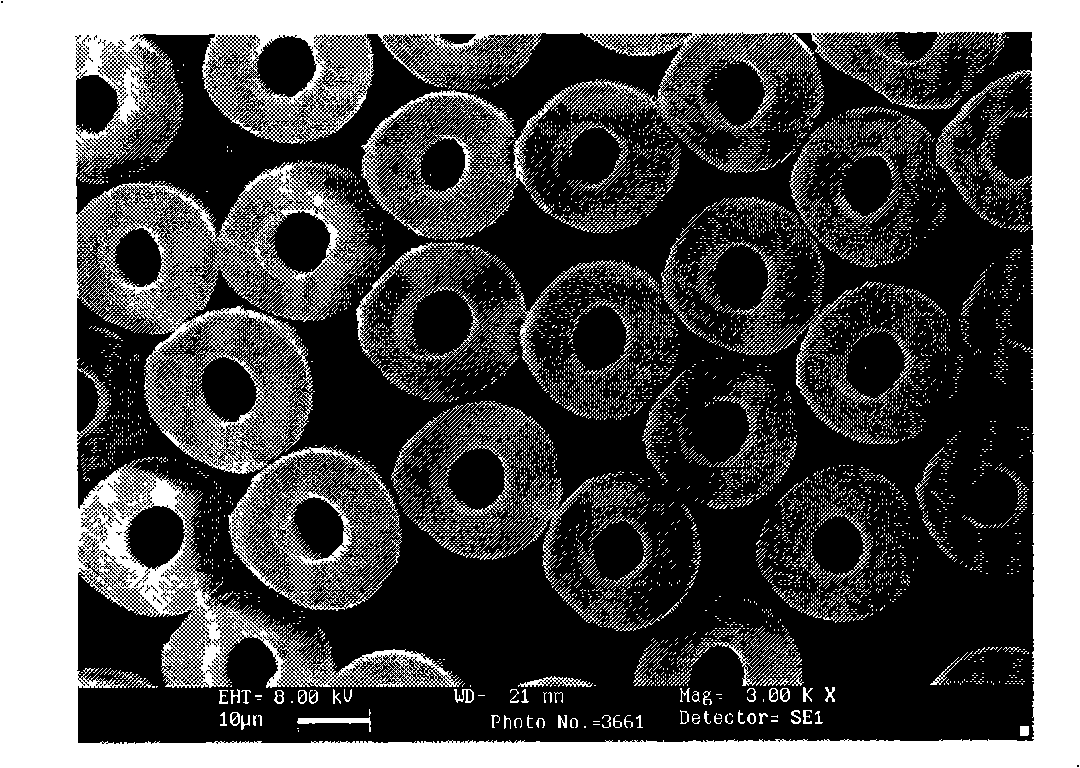
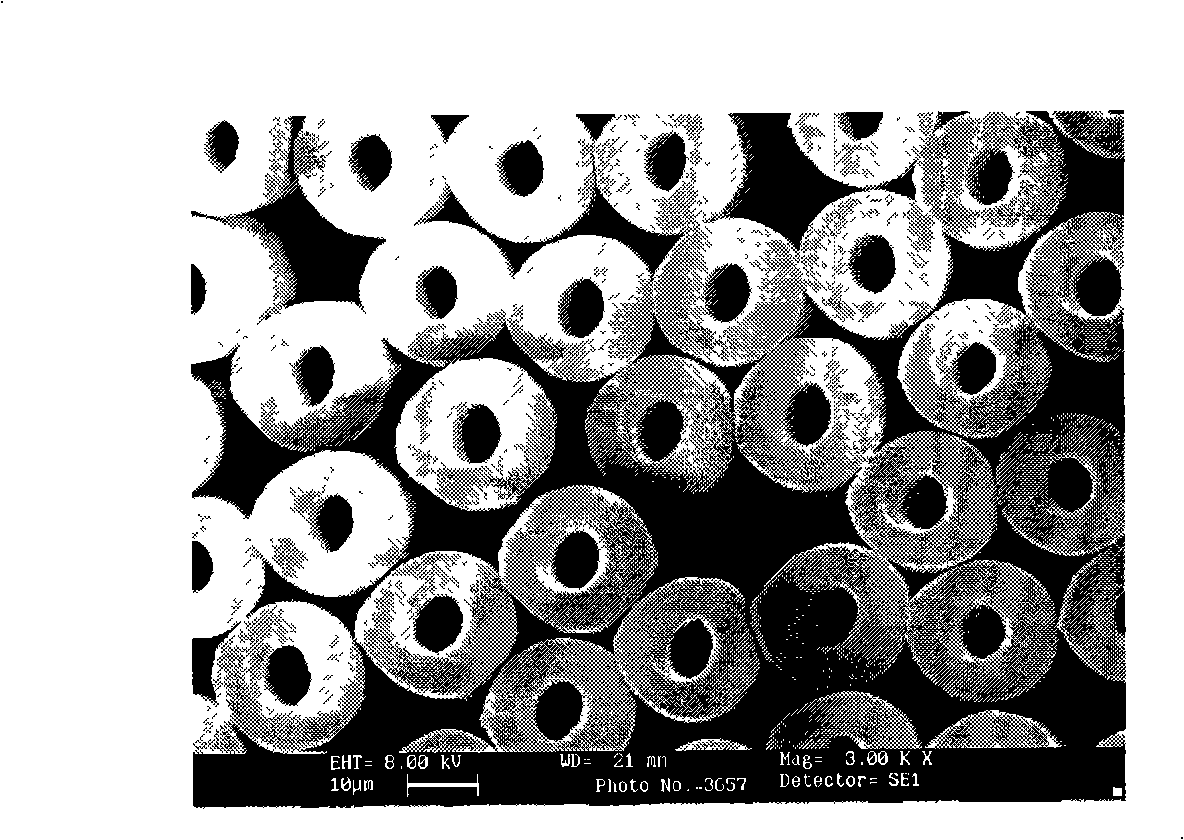
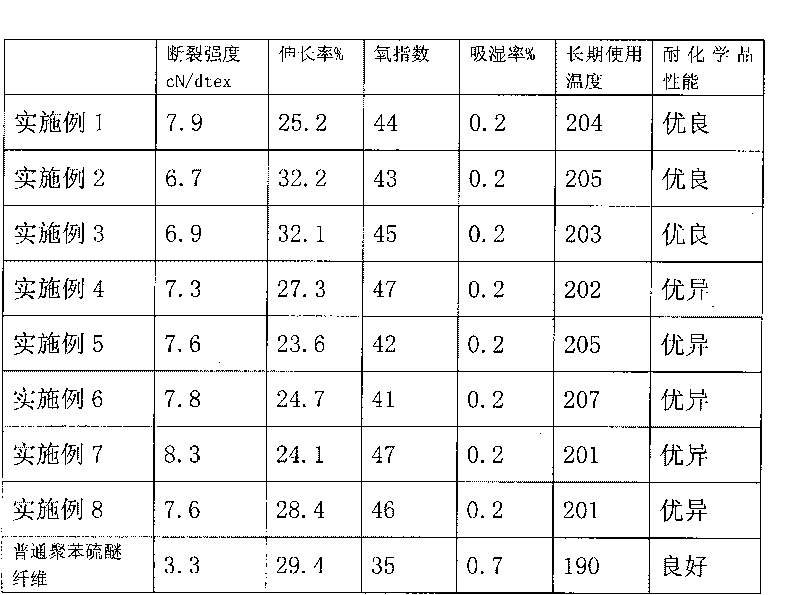
Patents
Literature
202results about "Staple fibre formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
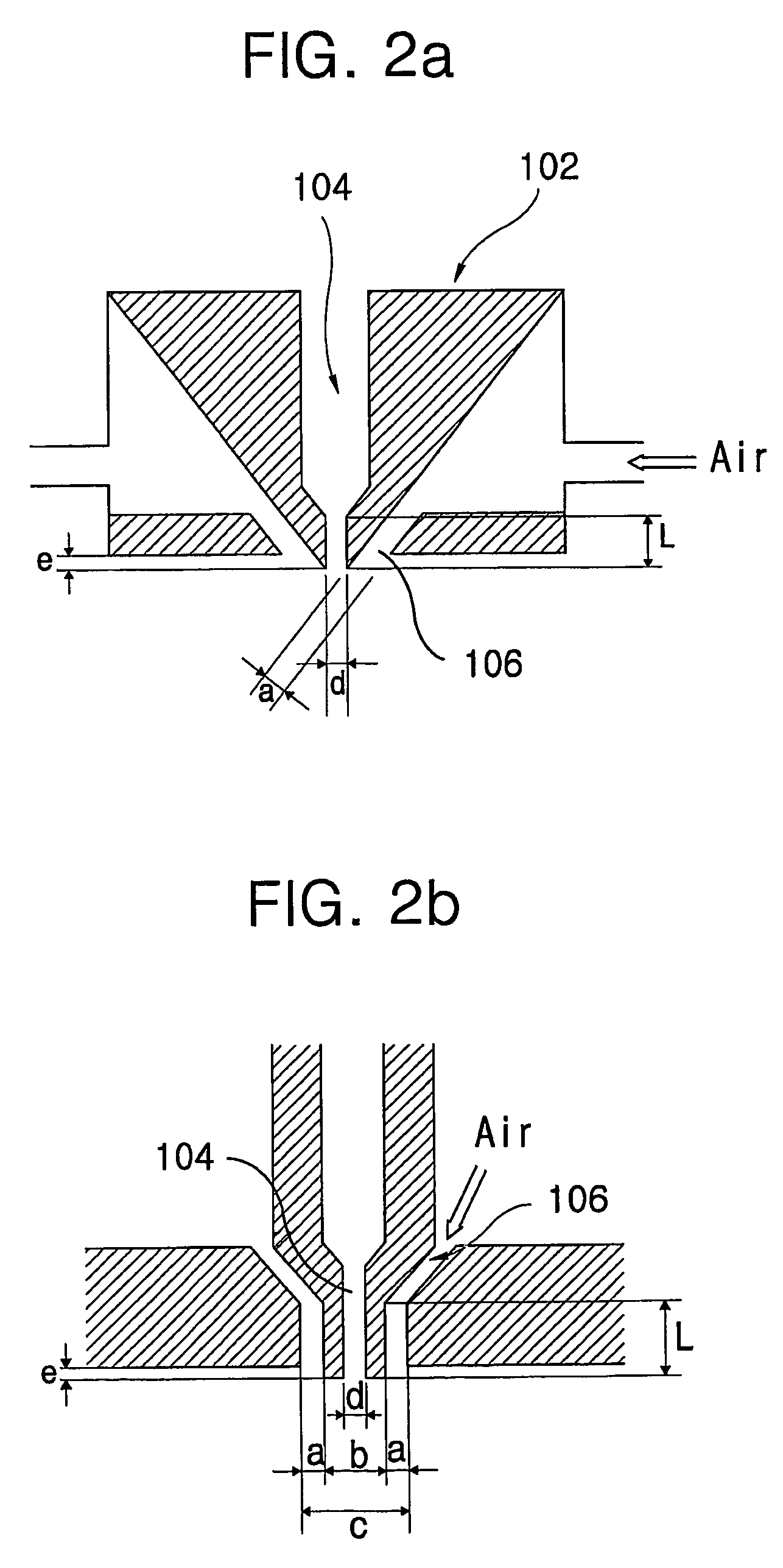
Nanofibers, and apparatus and methods for fabricating nanofibers by reactive electrospinning
ActiveUS20070018361A1Broaden applicationEasy to controlElectric discharge heatingInorganic material artificial filamentsFiberElectrospinning
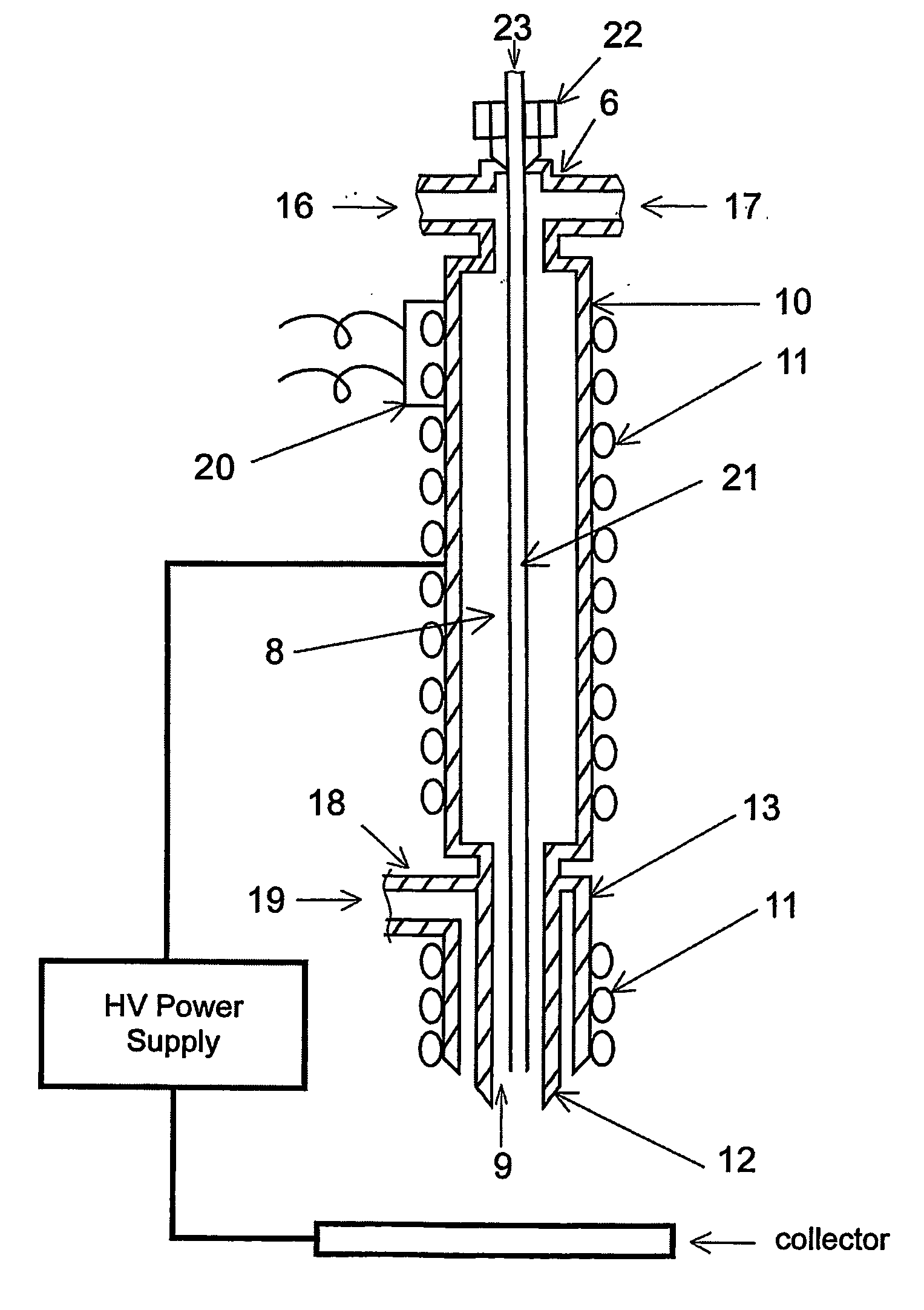
Apparatus and methods for fabricating nanofibers by reactive electrospinning are described. An electrospinning process is coupled with an in-line reactor where chemical or photochemical reactions take place. This invention expands the application of the electrospinning and allows the production of nanofibers of crosslinked polymers and other new materials, such as gel nanofibers of ceramic precursors.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Electro-blowing technology for fabrication of fibrous articles and its applications of hyaluronan
InactiveUS20050073075A1Improve the situationHigh productElectric discharge heatingFibre chemical featuresFiberNanofiber
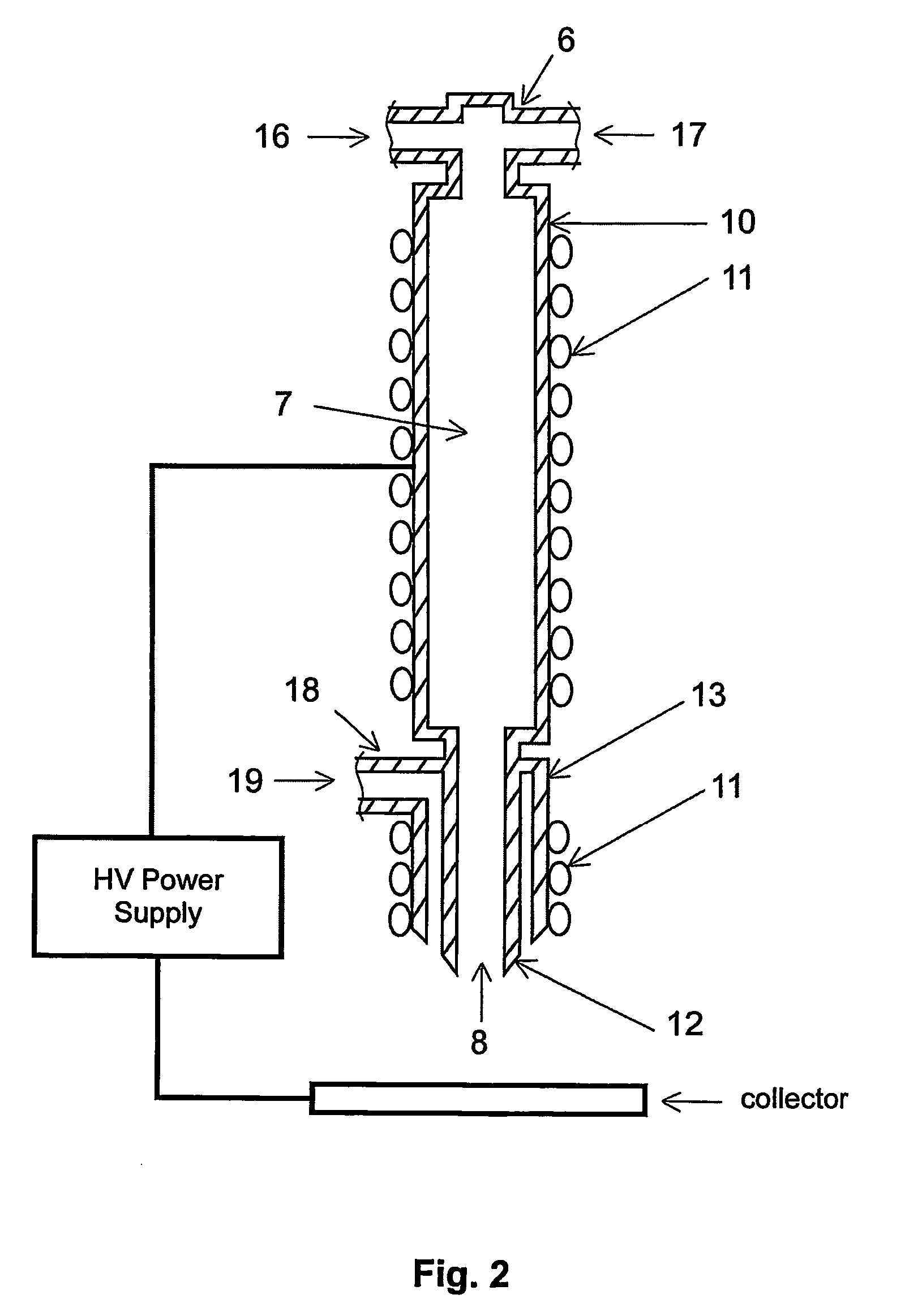
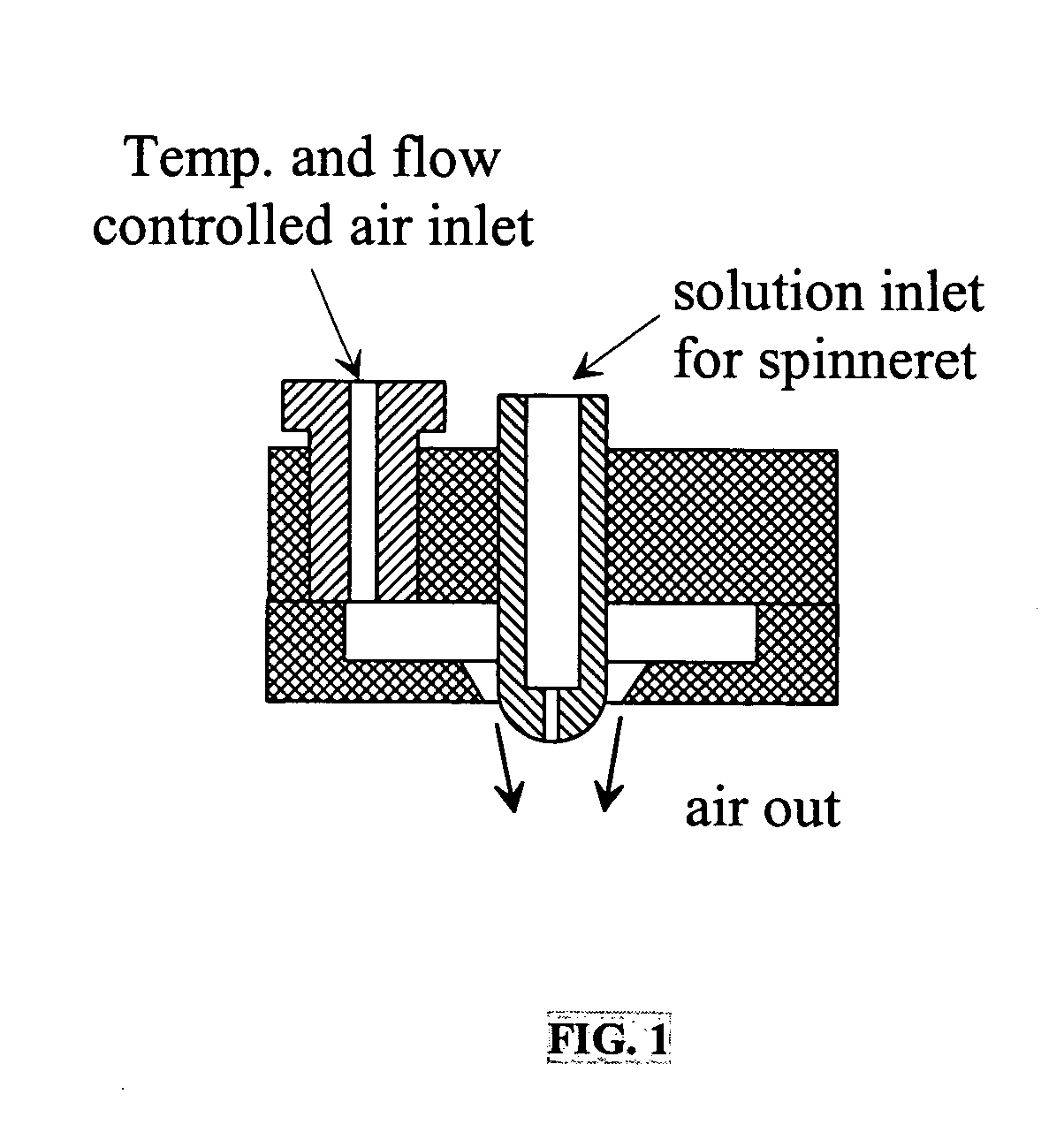
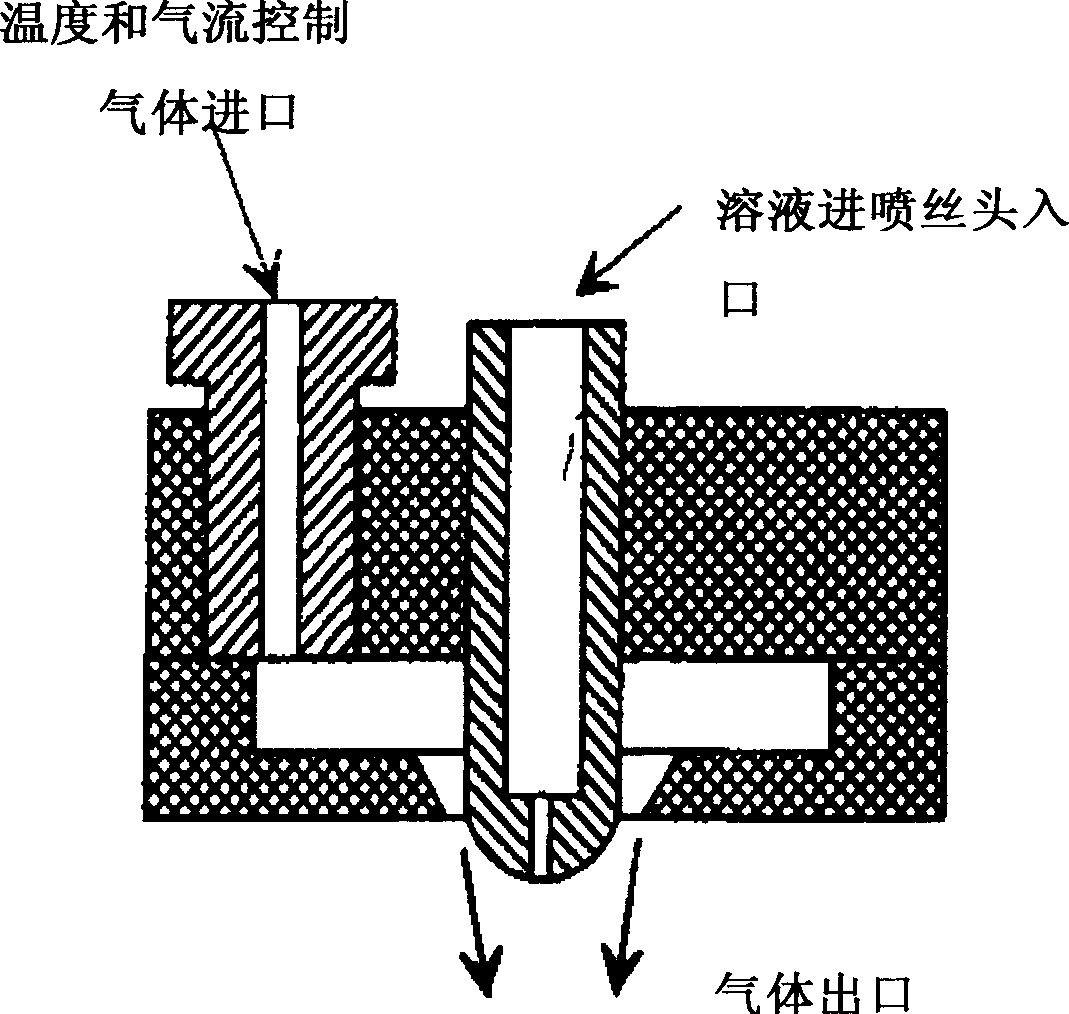
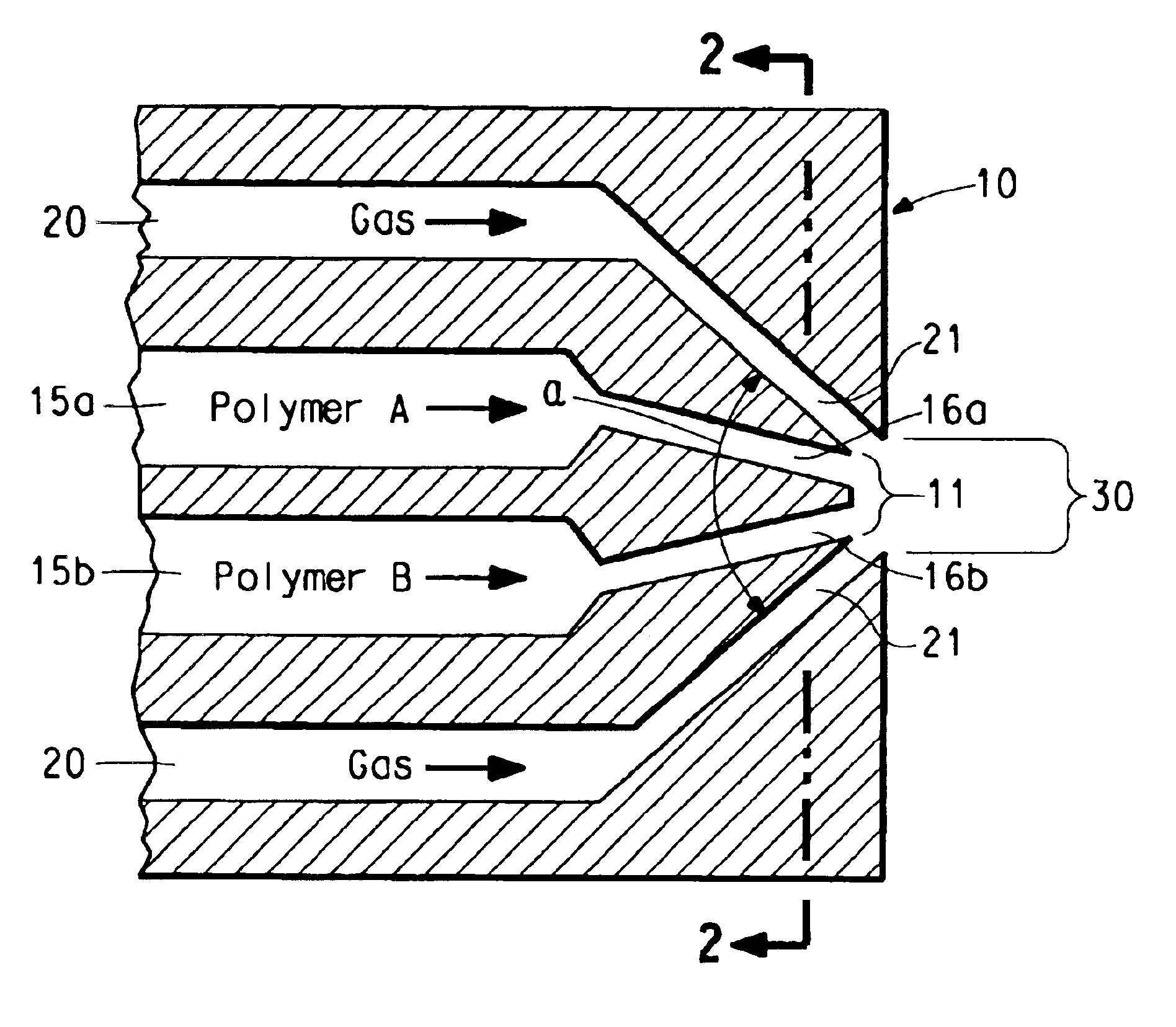
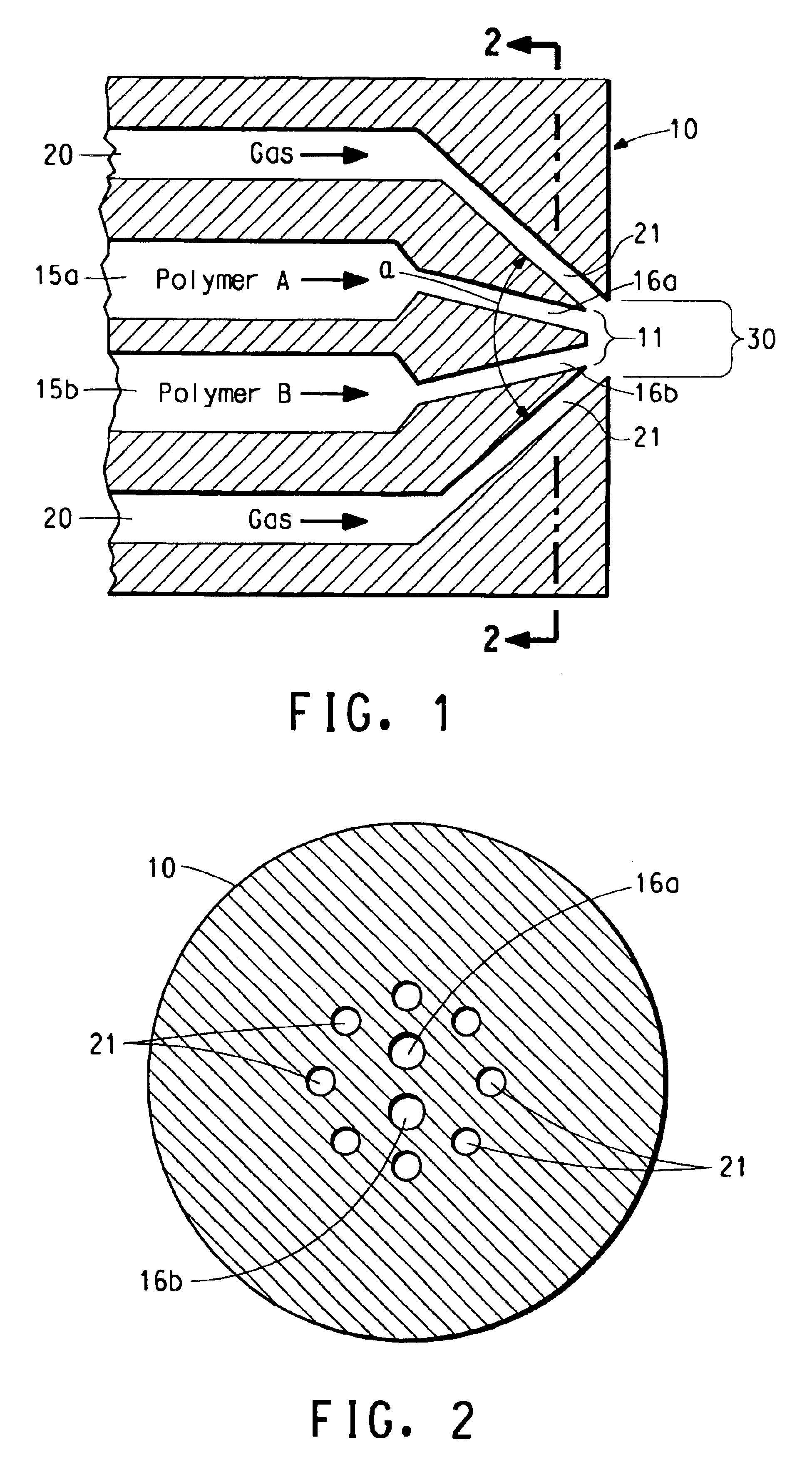
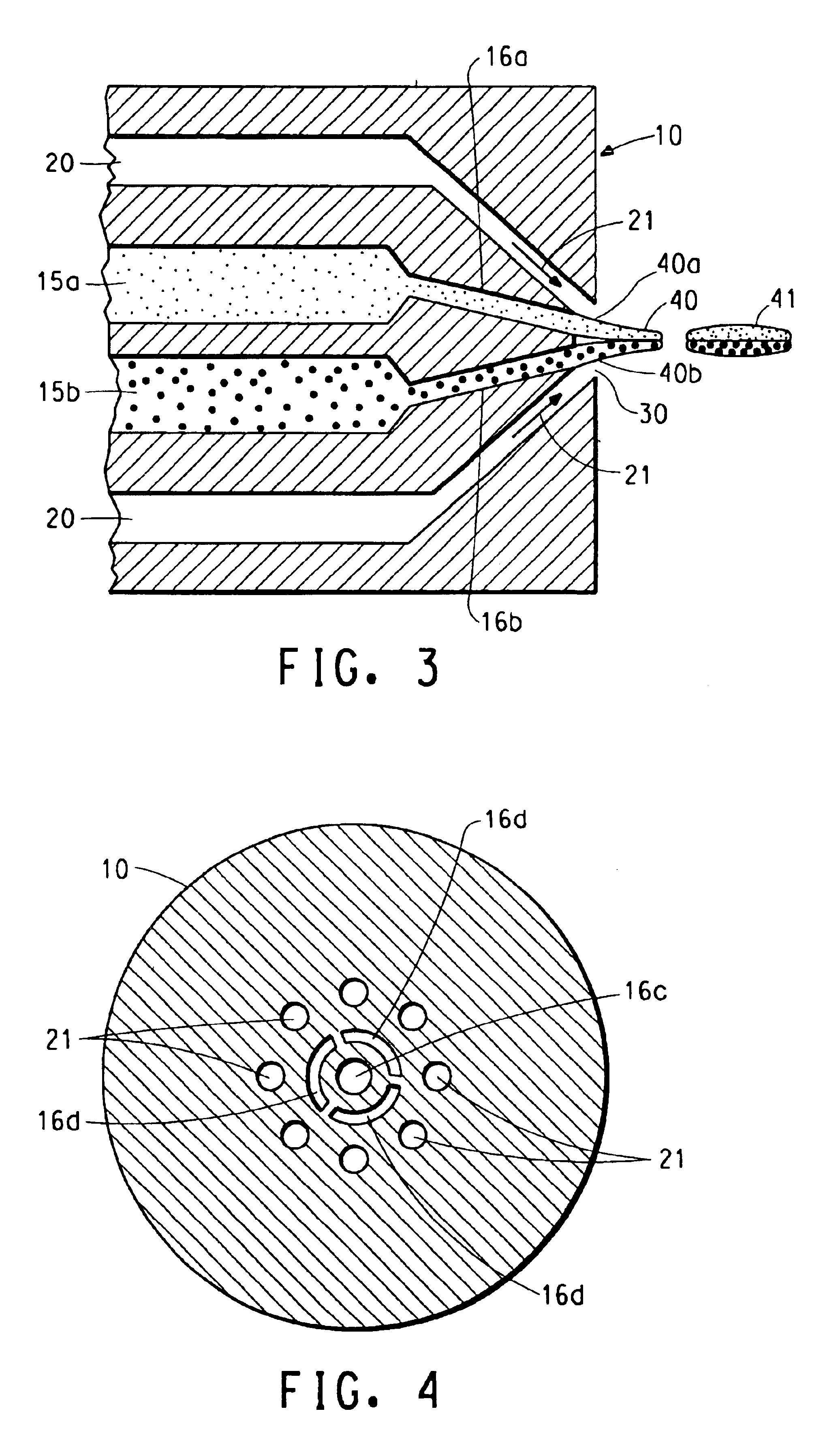
A method for electroblowing fibers is provided which involves the steps of: forcing a polymer fluid through a spinneret in a first direction towards a collector located a first distance from the spinneret, while simultaneously blowing a gas through an orifice that is substantially concentrically arranged around the spinneret, wherein the gas is blown substantially in the first direction; wherein an electrostatic differential is generated between the spinneret and the collector; and collecting the fibers, and its use in preparing submicron scale fibers of various types, particularly hyaluronan fibers, and the hyaluronan nanofibers thus formed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
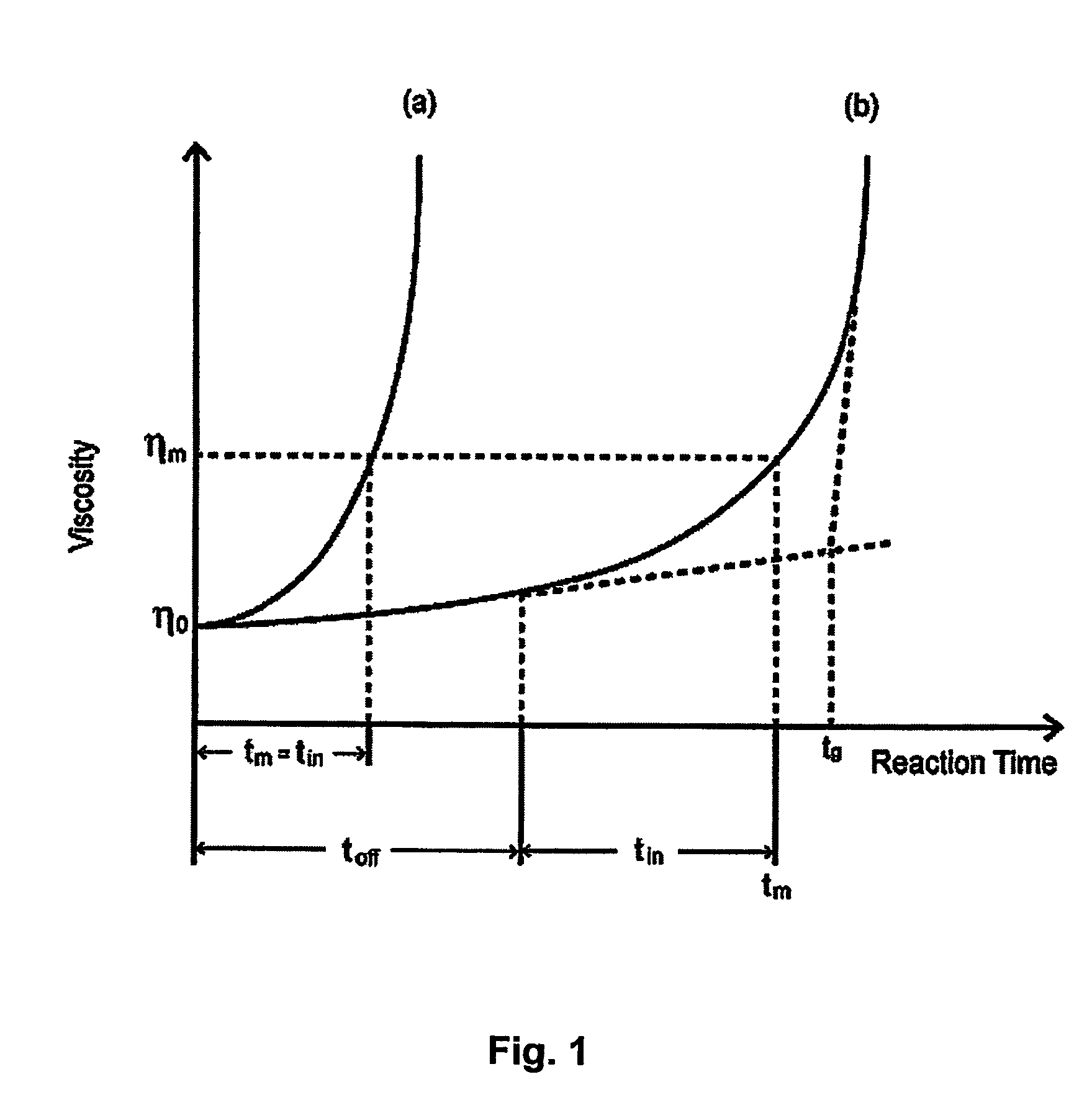
Process for forming polymeric micro and nanofibers
Polymers that have extremely high melt viscosities are very difficult to extrude and stretch making it difficult to synthesize fibers of such polymers via conventional methods. A process is provided for producing a polymer fiber which involves blowing a mixture of a polymer and a gas through a nozzle such that polymer micro- and / or nano-fibers are produced. The polymer fibers are characterized in that they have a diameter less than the diameter of the outlet aperture of the nozzle.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method of manufacture of nonwoven fabric
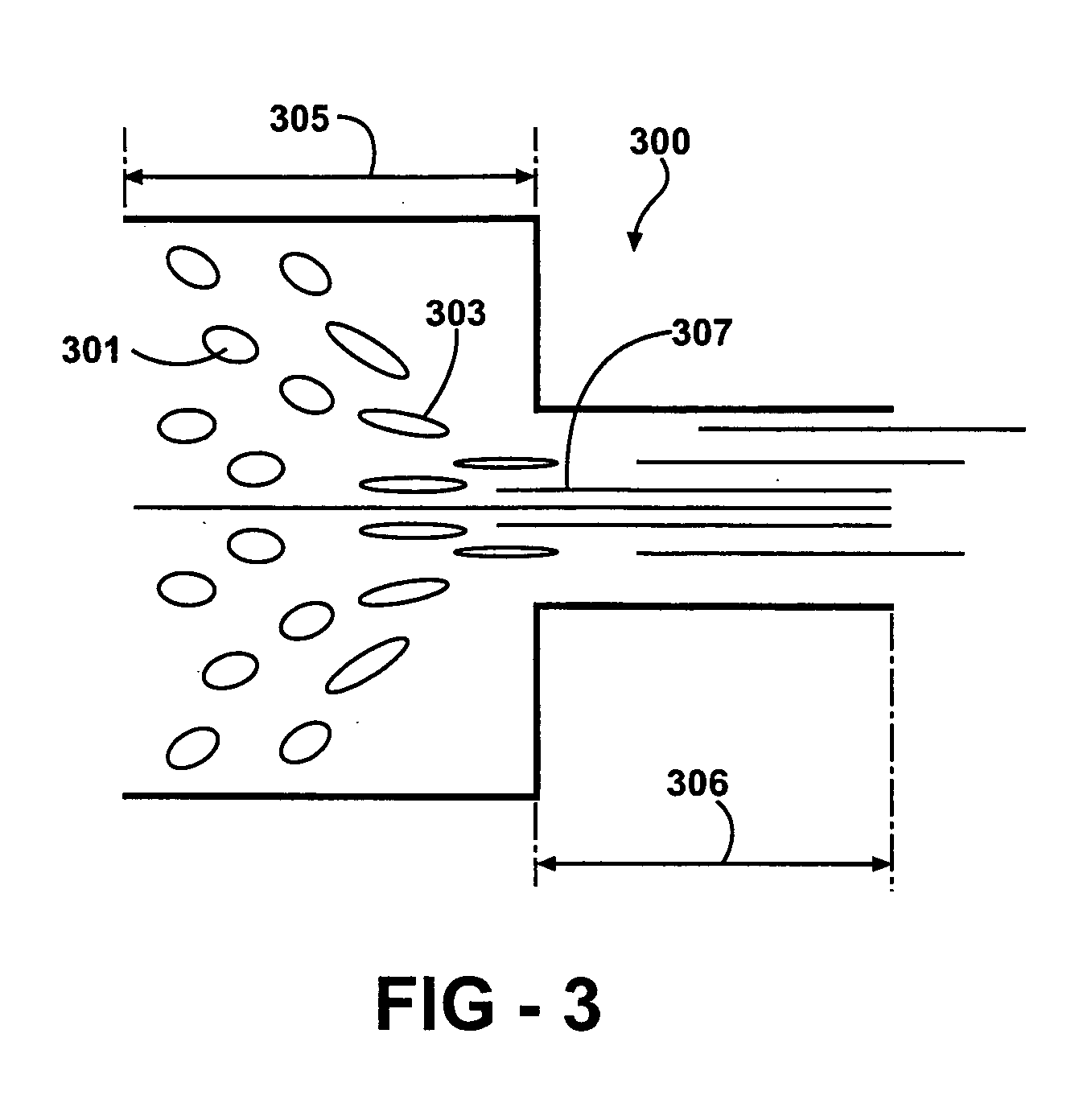
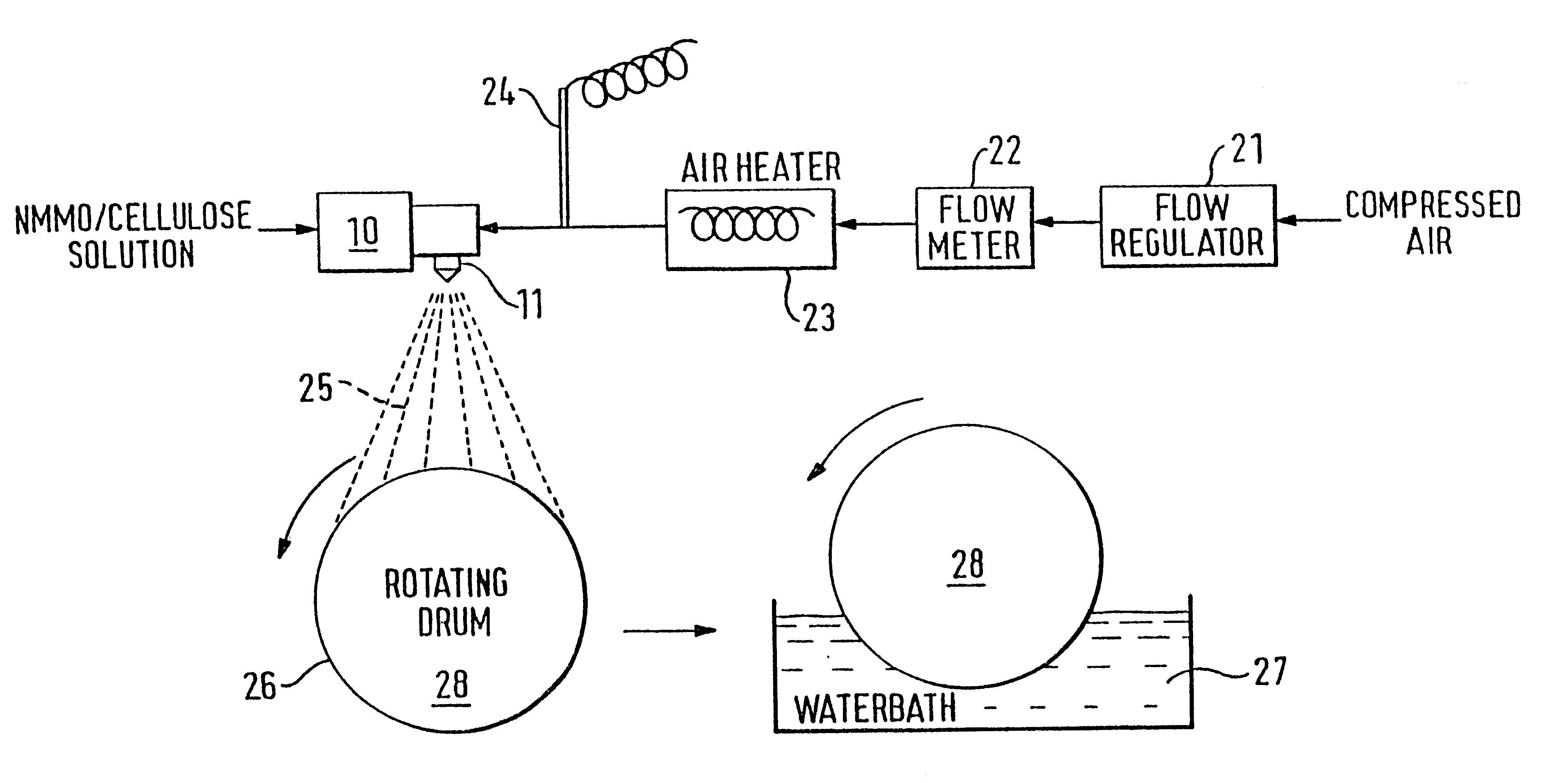
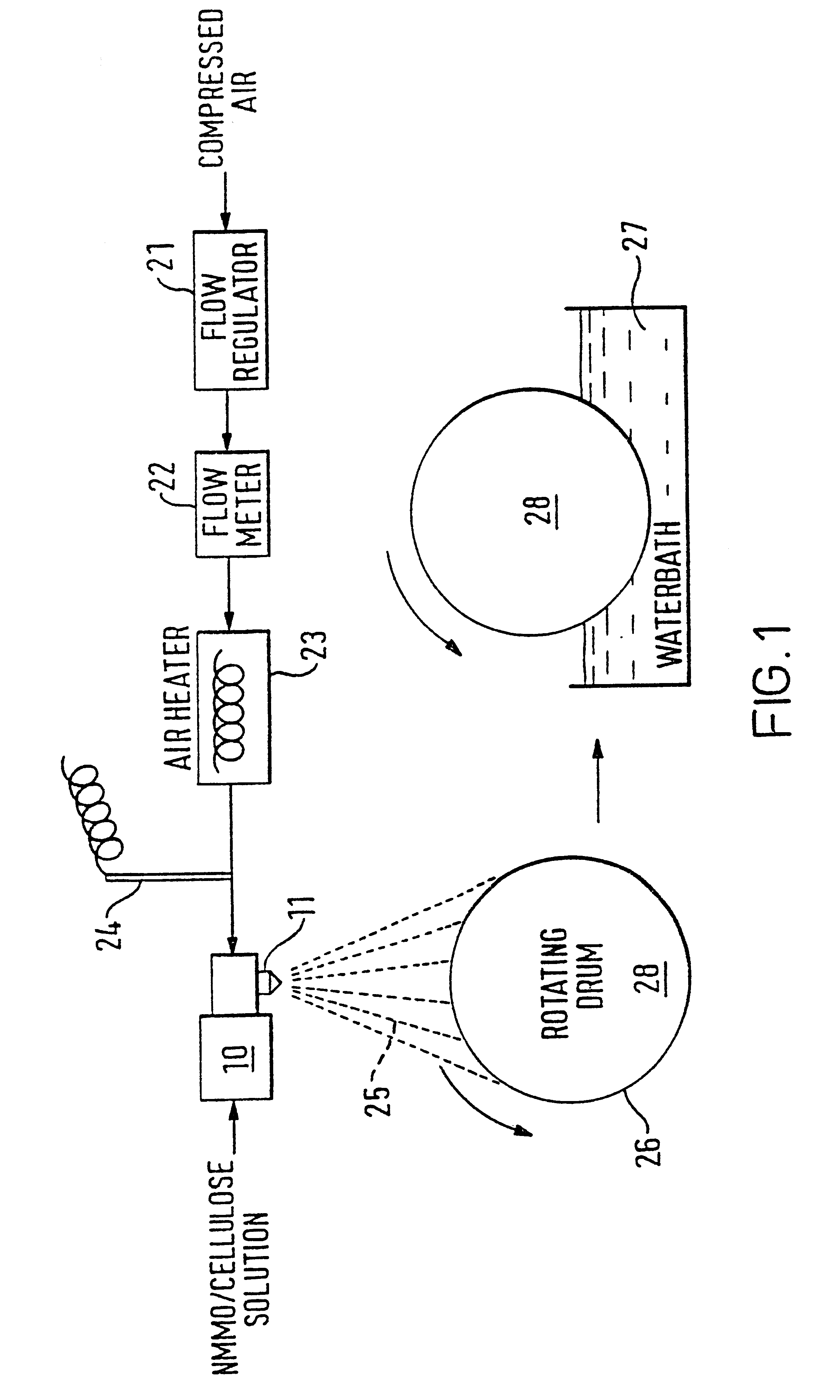
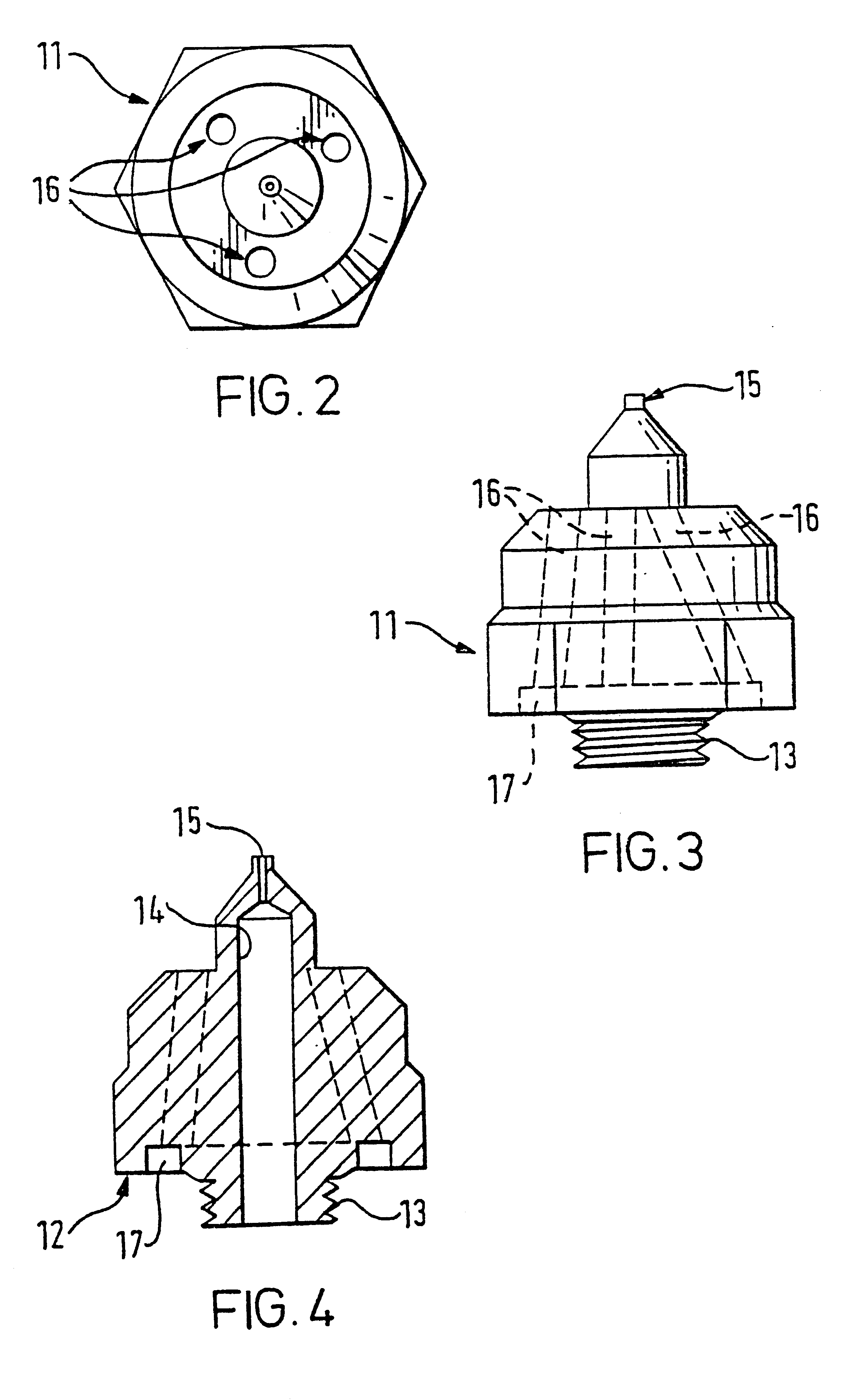
InactiveUS6358461B1Artificial filaments from cellulose solutionsCeramic shaping apparatusCelluloseEngineering
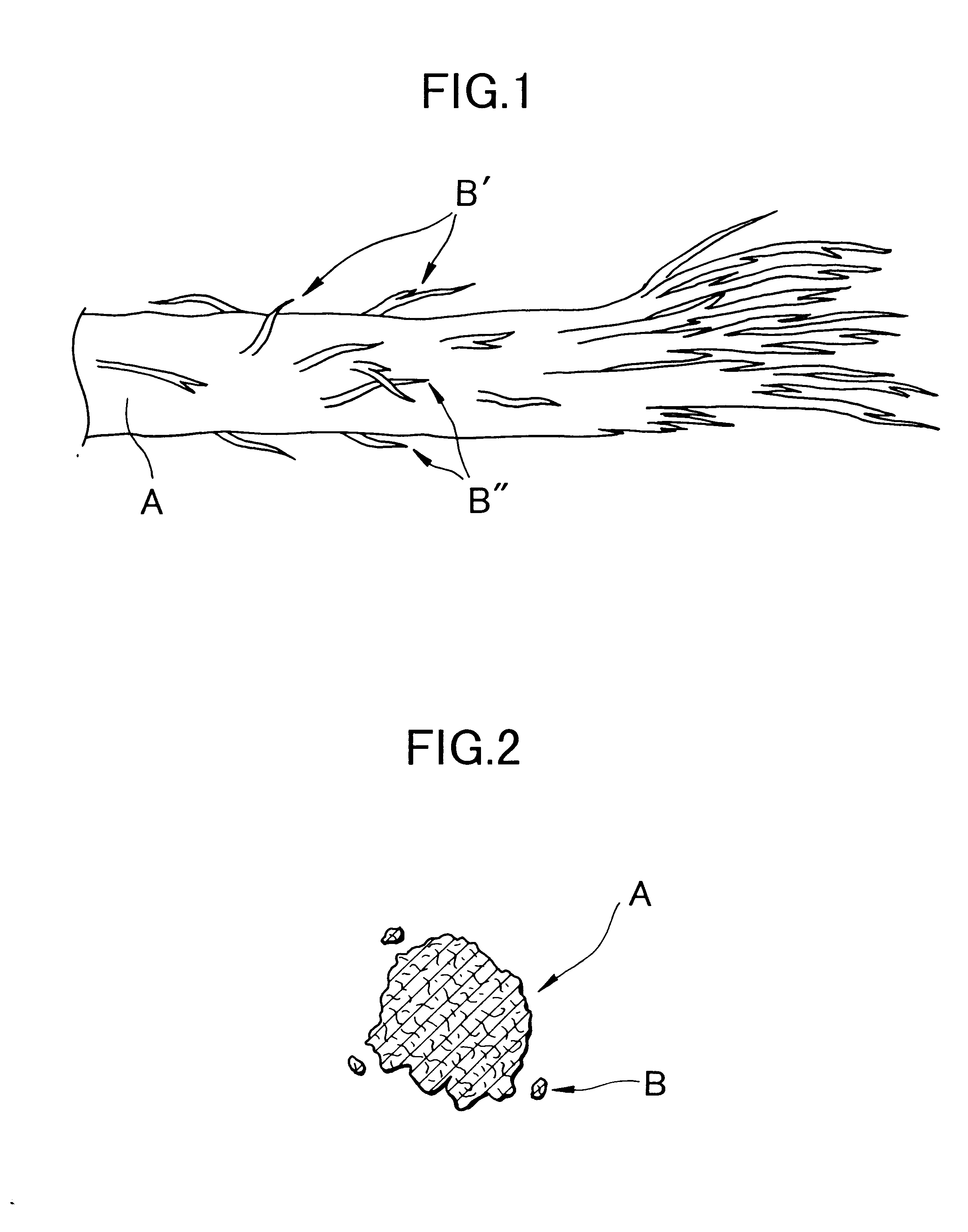
A method of manufacture of a nonwoven cellulose fabric is disclosed. The fabric is made from fibers formed by extrusion of a solution of cellulose through a spinning jet. The extruded fiber is attenuated with a high velocity gas flow, and the attenuated fiber is collected on a surface (such as the curved surface of a rotating drum) on which the fiber web is subsequently coagulated. Apparatus for carrying out the method is also disclosed. The method and apparatus permit the manufacture of a nonwoven lyocell fabric web in which fibers are bonded together without the use of a binder.
Owner:LENZING AG
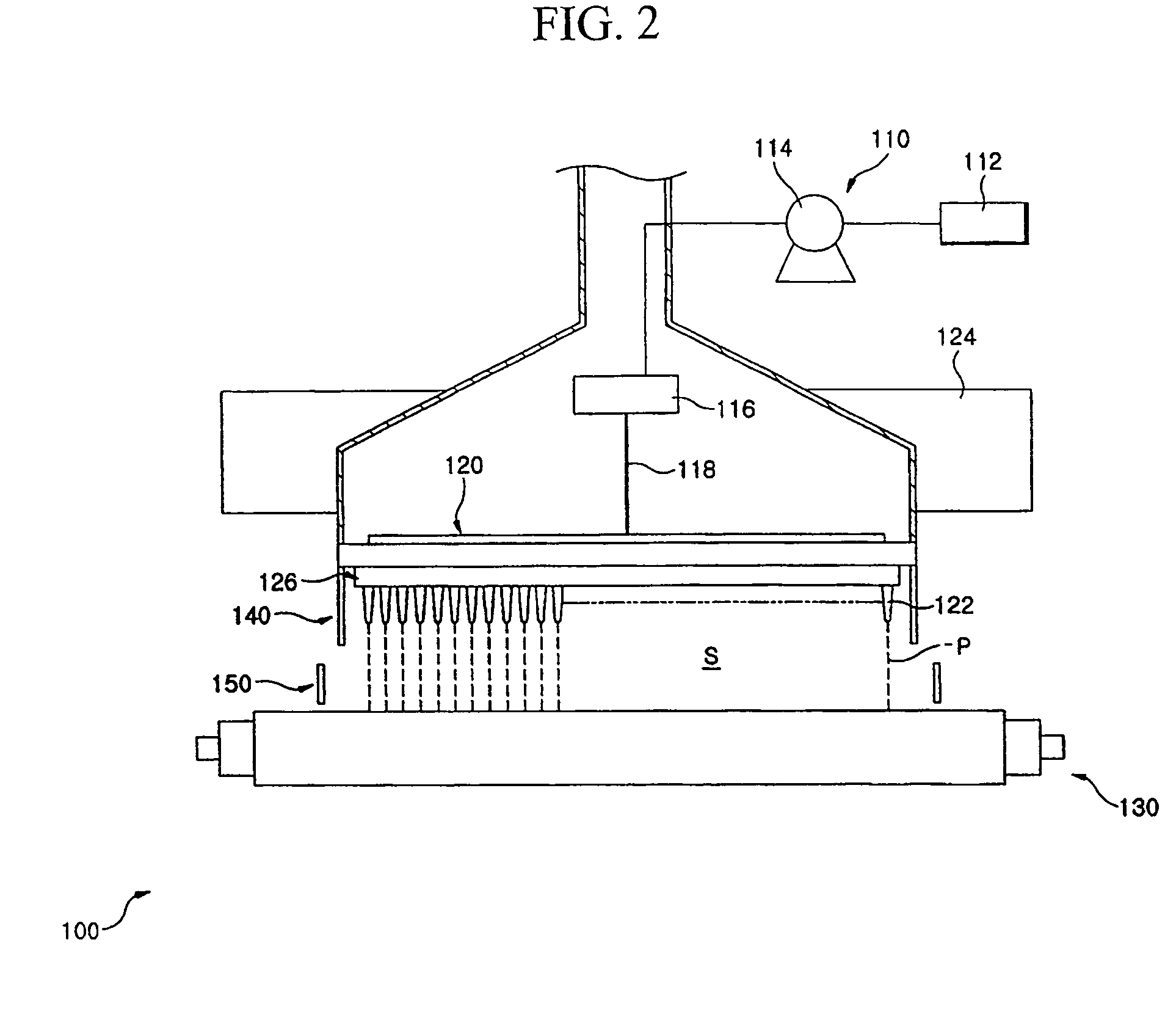
Manufacturing method and device for electret processed product
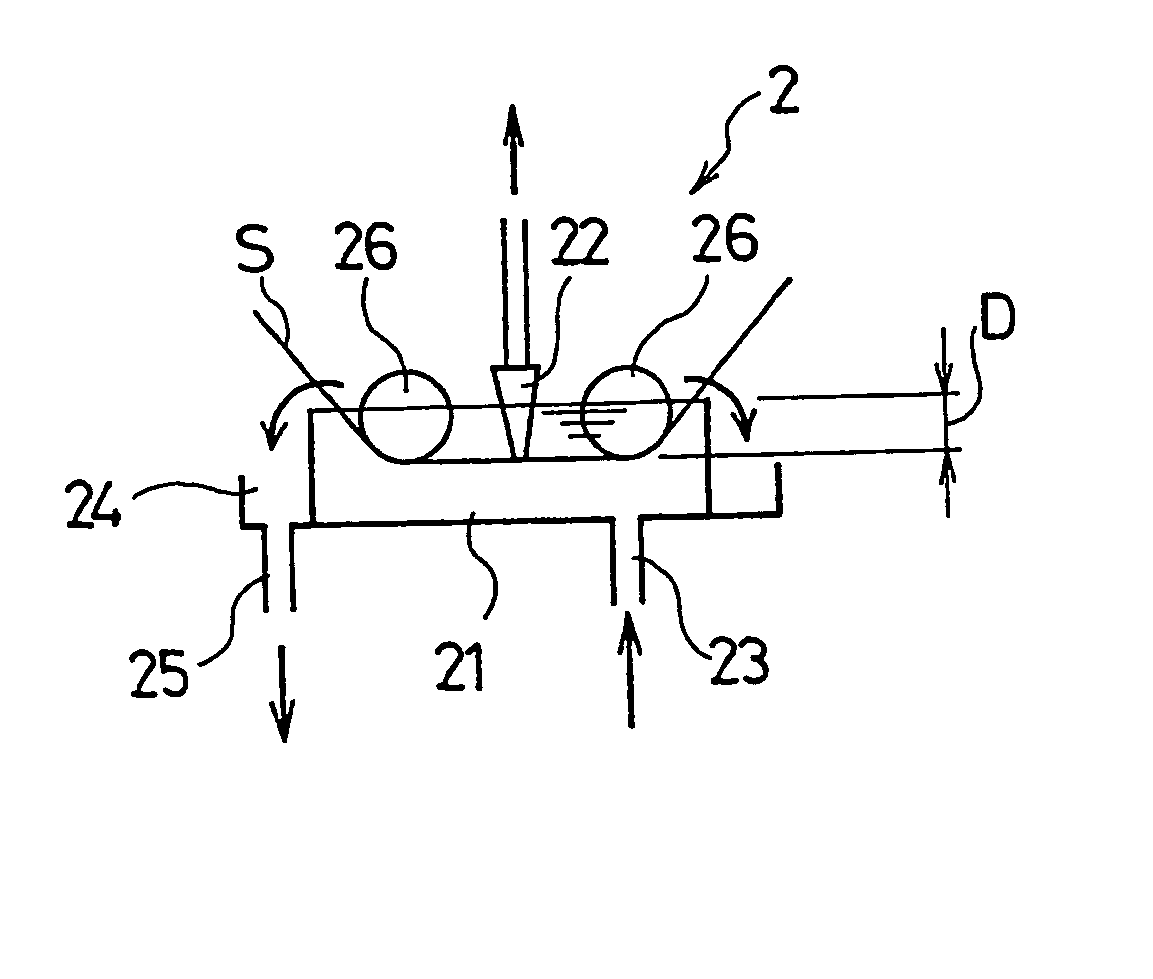
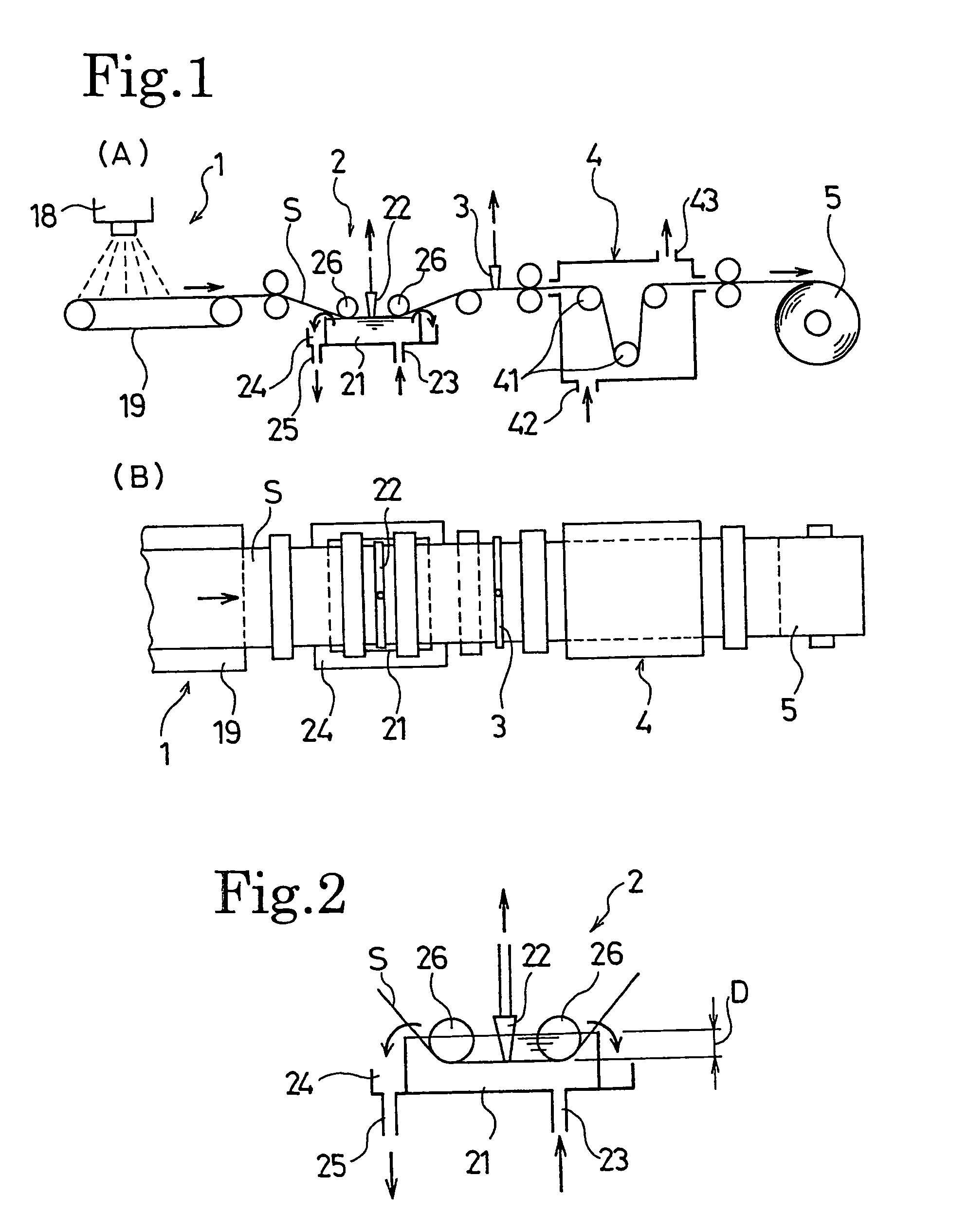
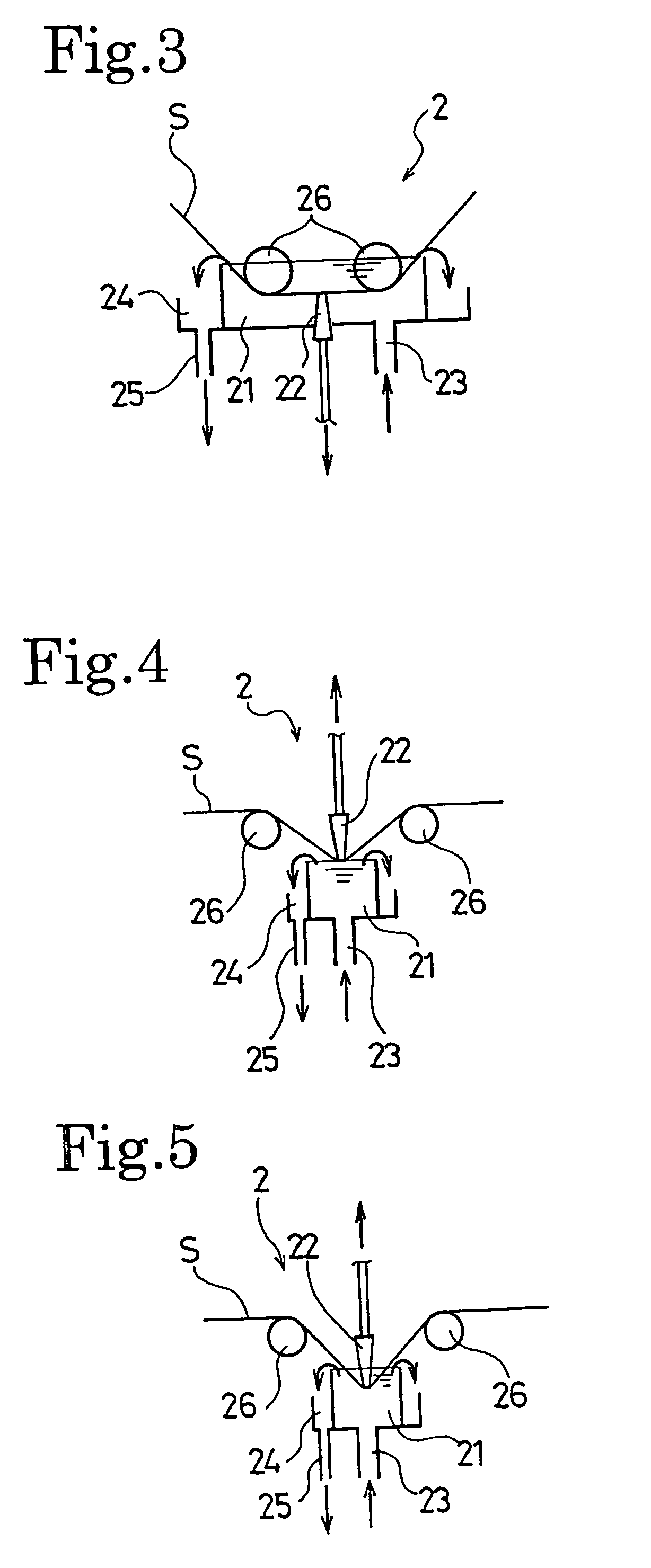
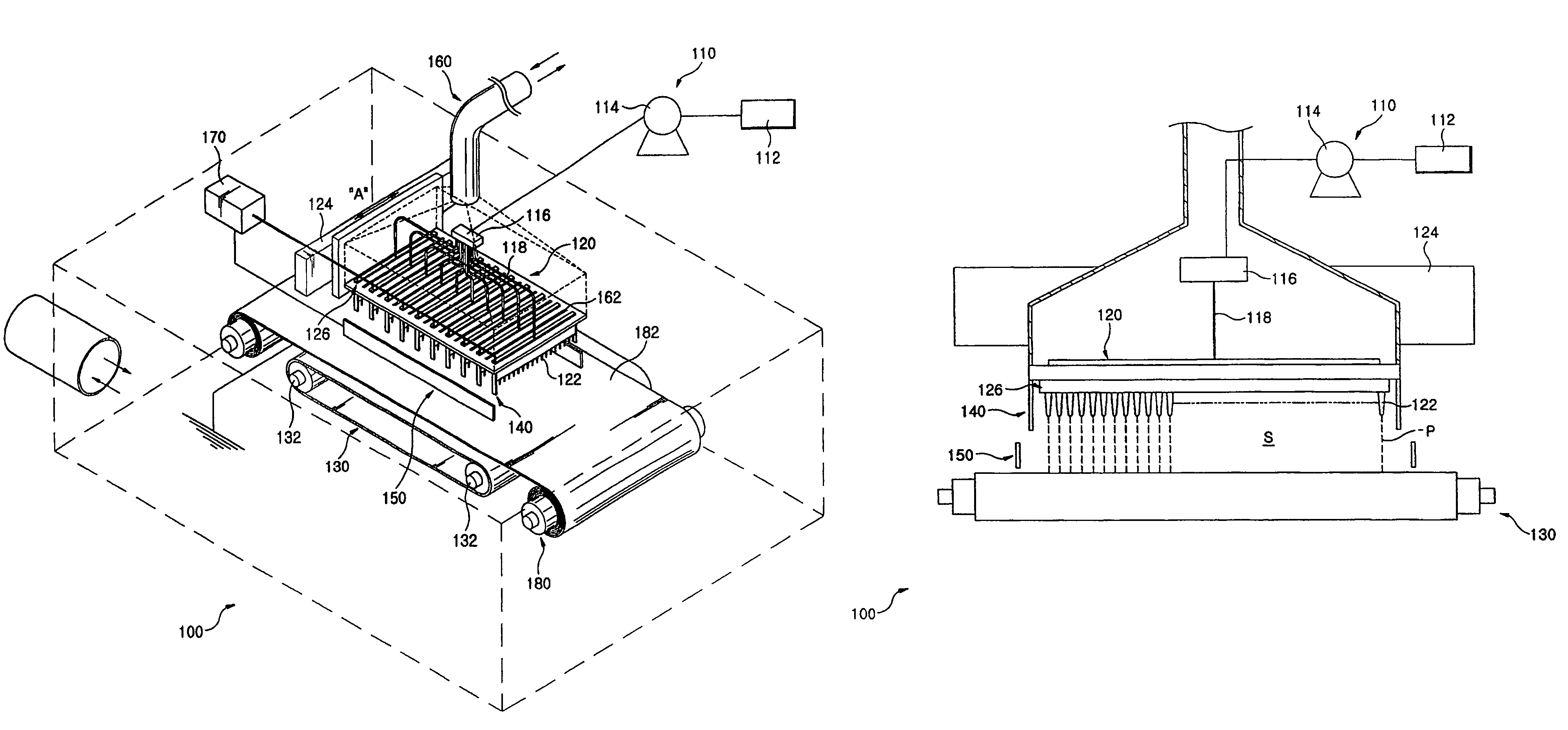
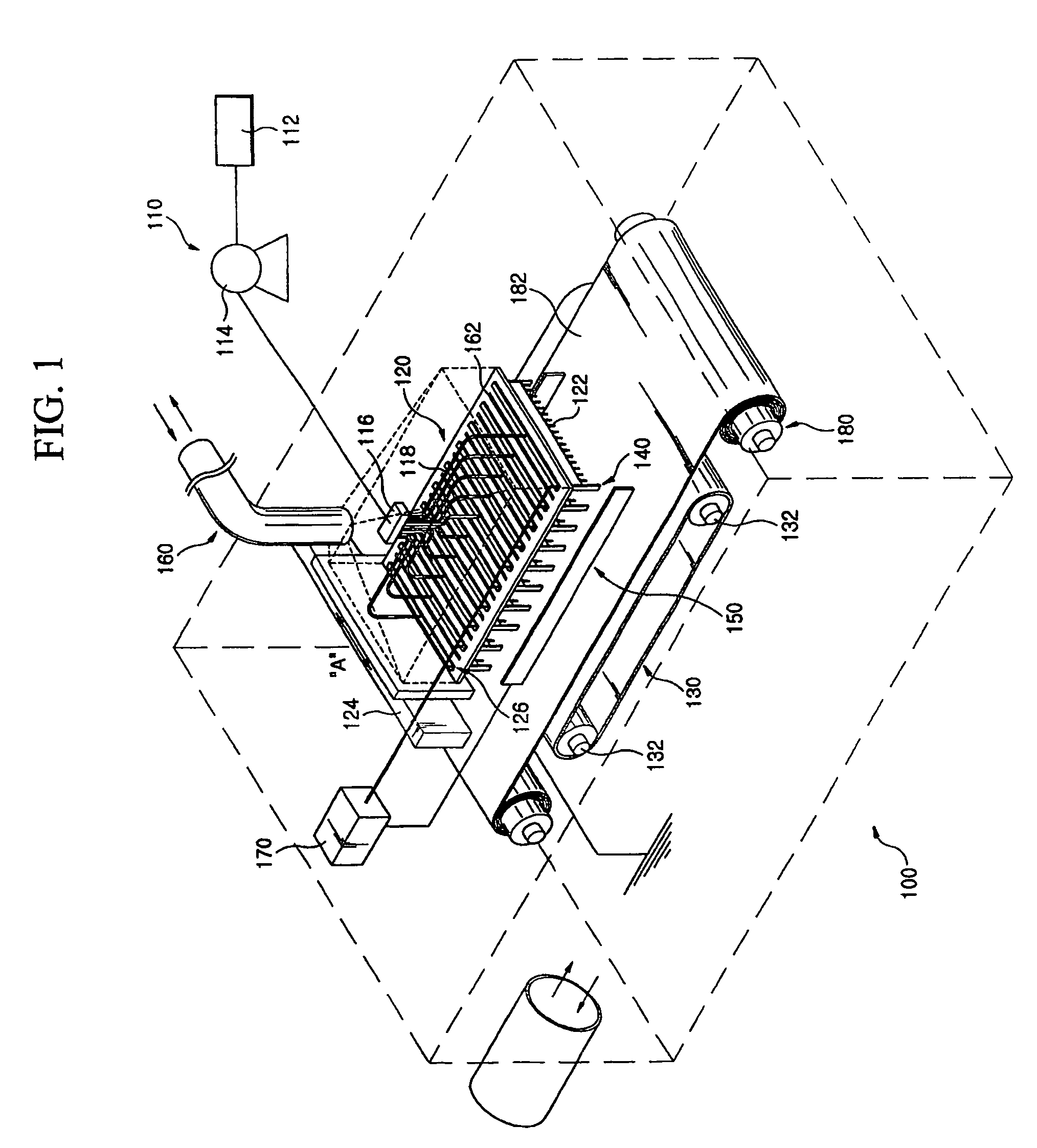
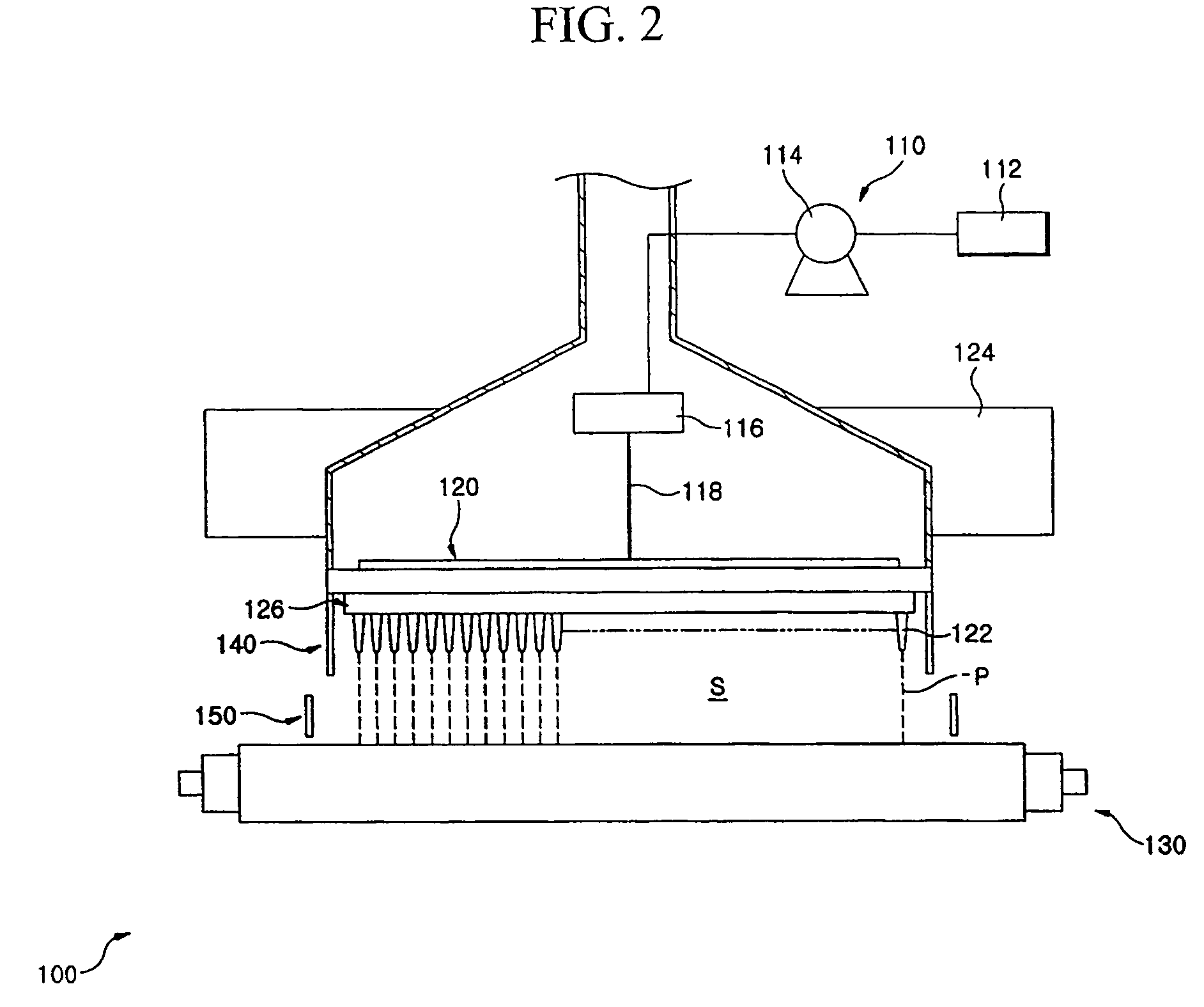
A manufacturing method of an electret processed product, comprising the steps of allowing a section nozzle (22) to come into contact with a nonconductive fiber sheet (S) so as to cross in the lateral direction of the sheet while running the sheet, allowing the surface of the sheet on the opposite side of the contact portion to come into contact with or to immerse into a water surface, sucking water from the suction nozzle (22) so that the water can be passed through the sheet in the thickness direction of the sheet to penetrate the water into the nonconductive fiber sheet (S), and drying the nonconductive fiber sheet (S), whereby a high quality and high performance electret processed product can be manufactured at a low cost.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
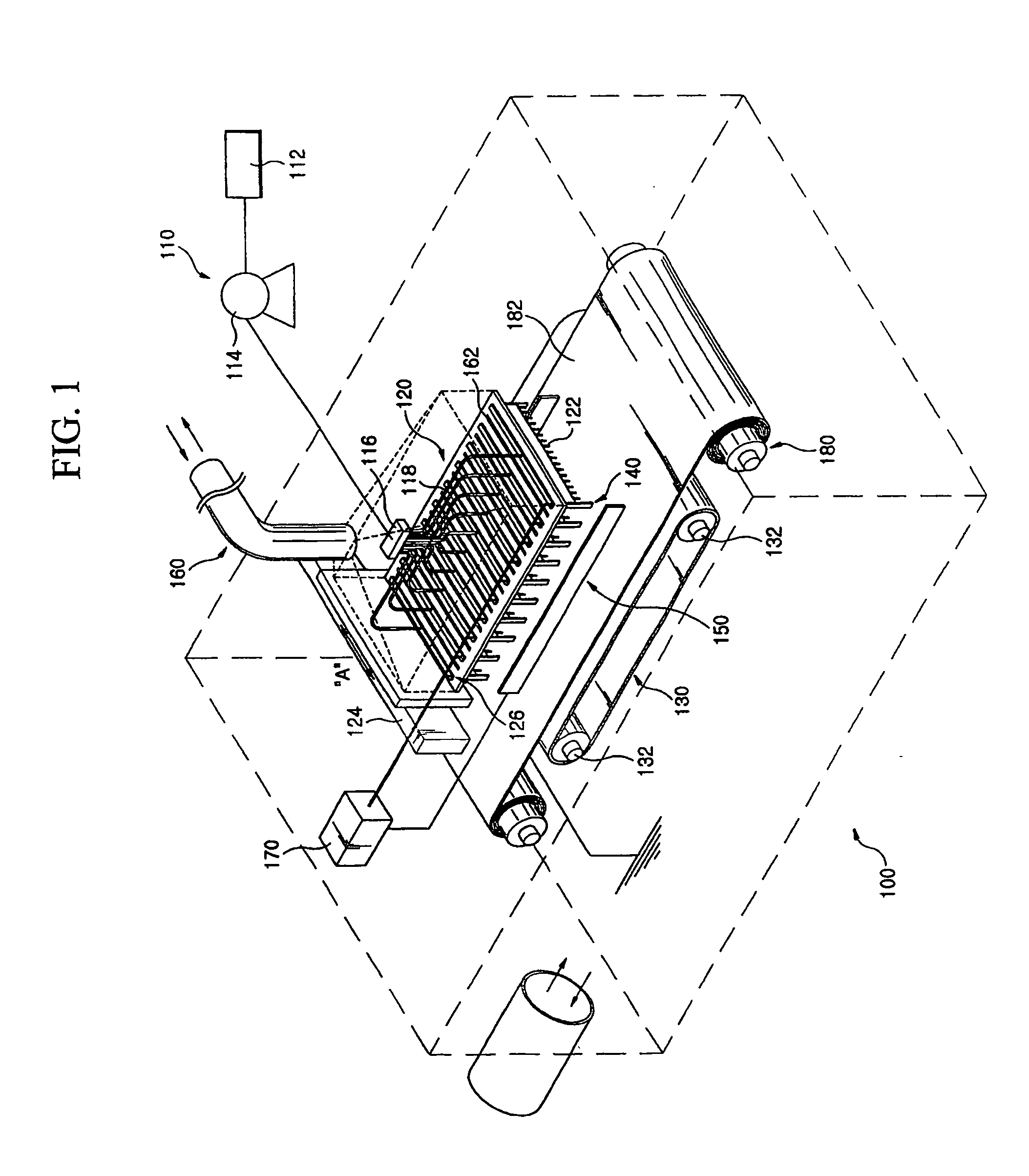
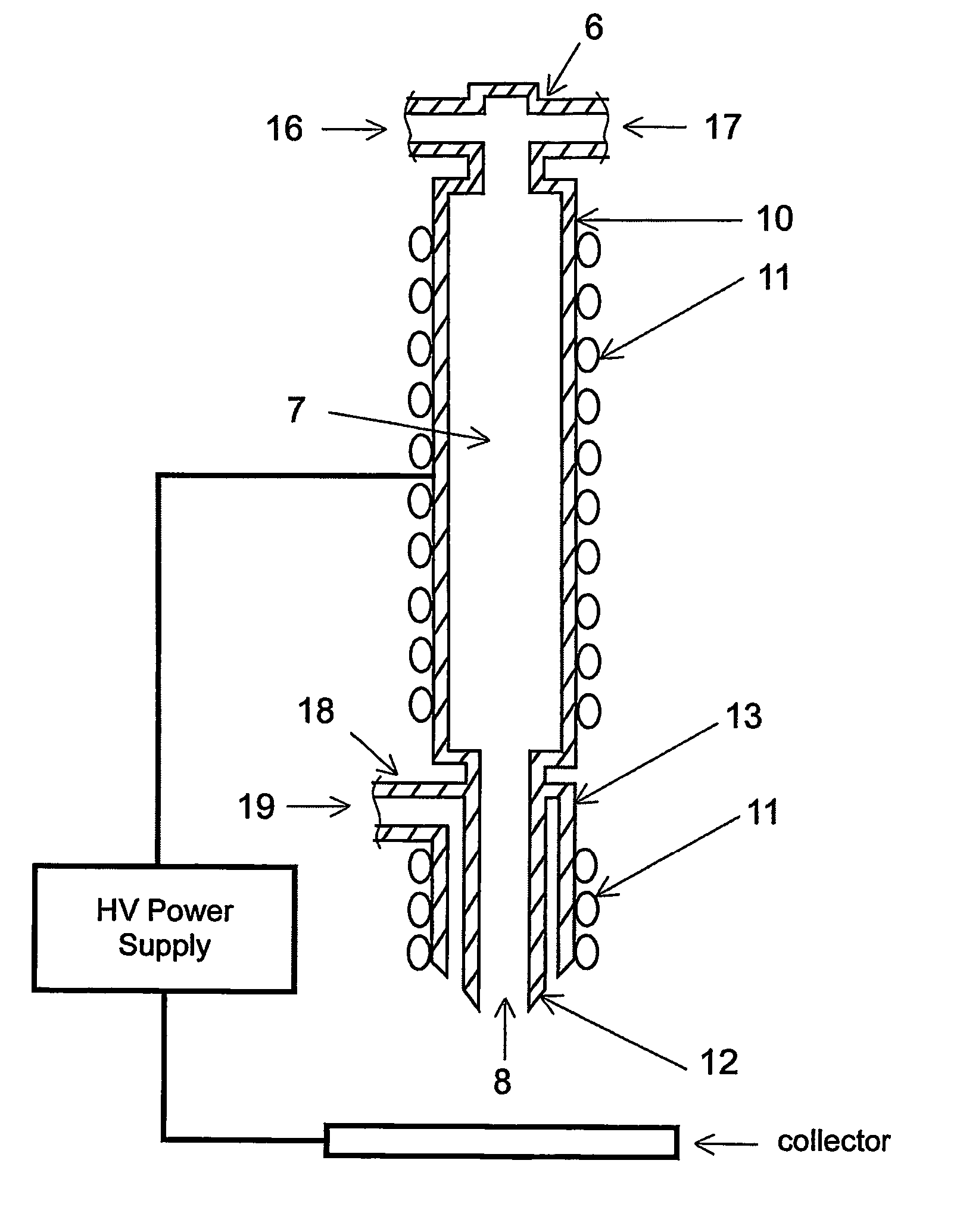
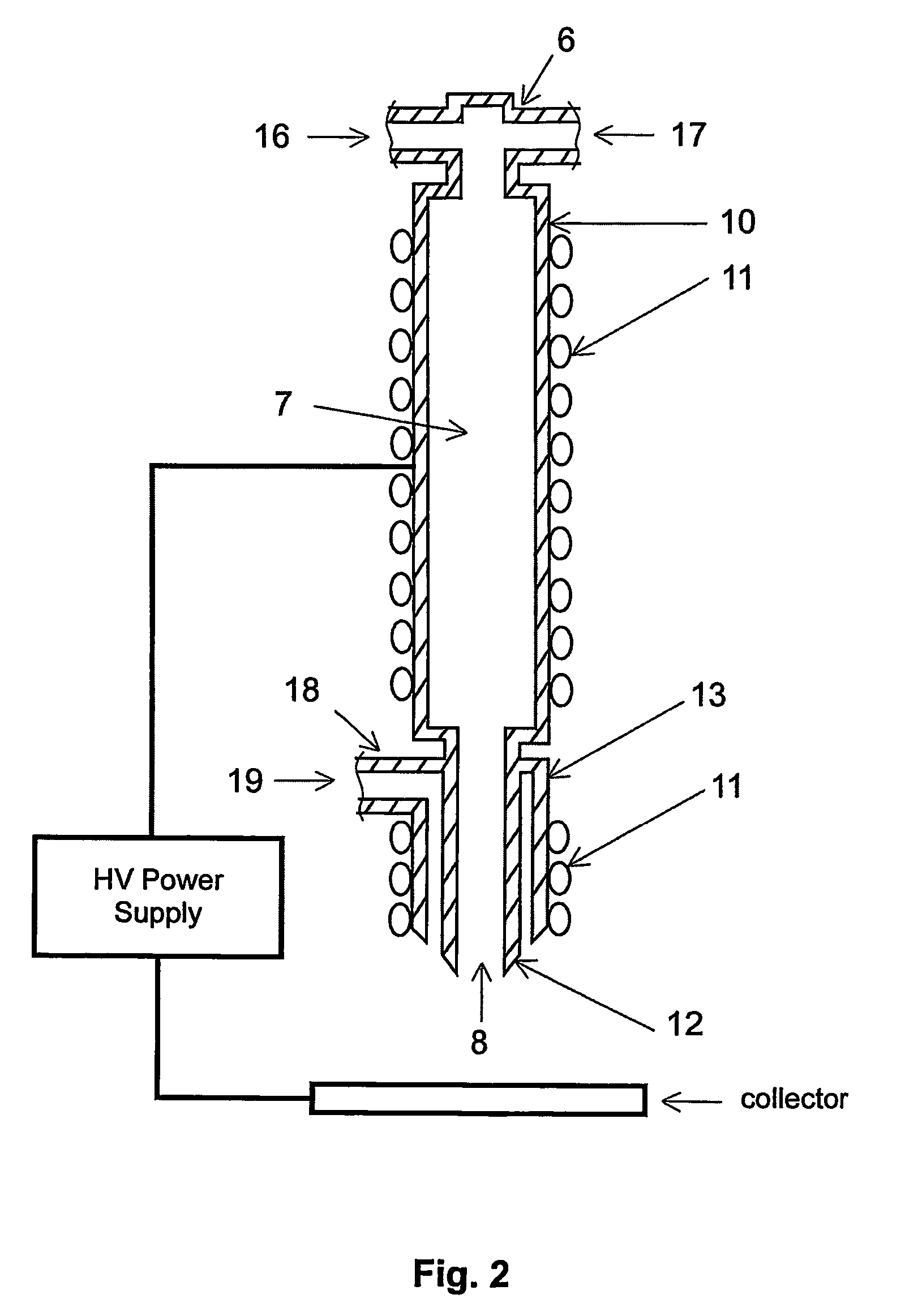
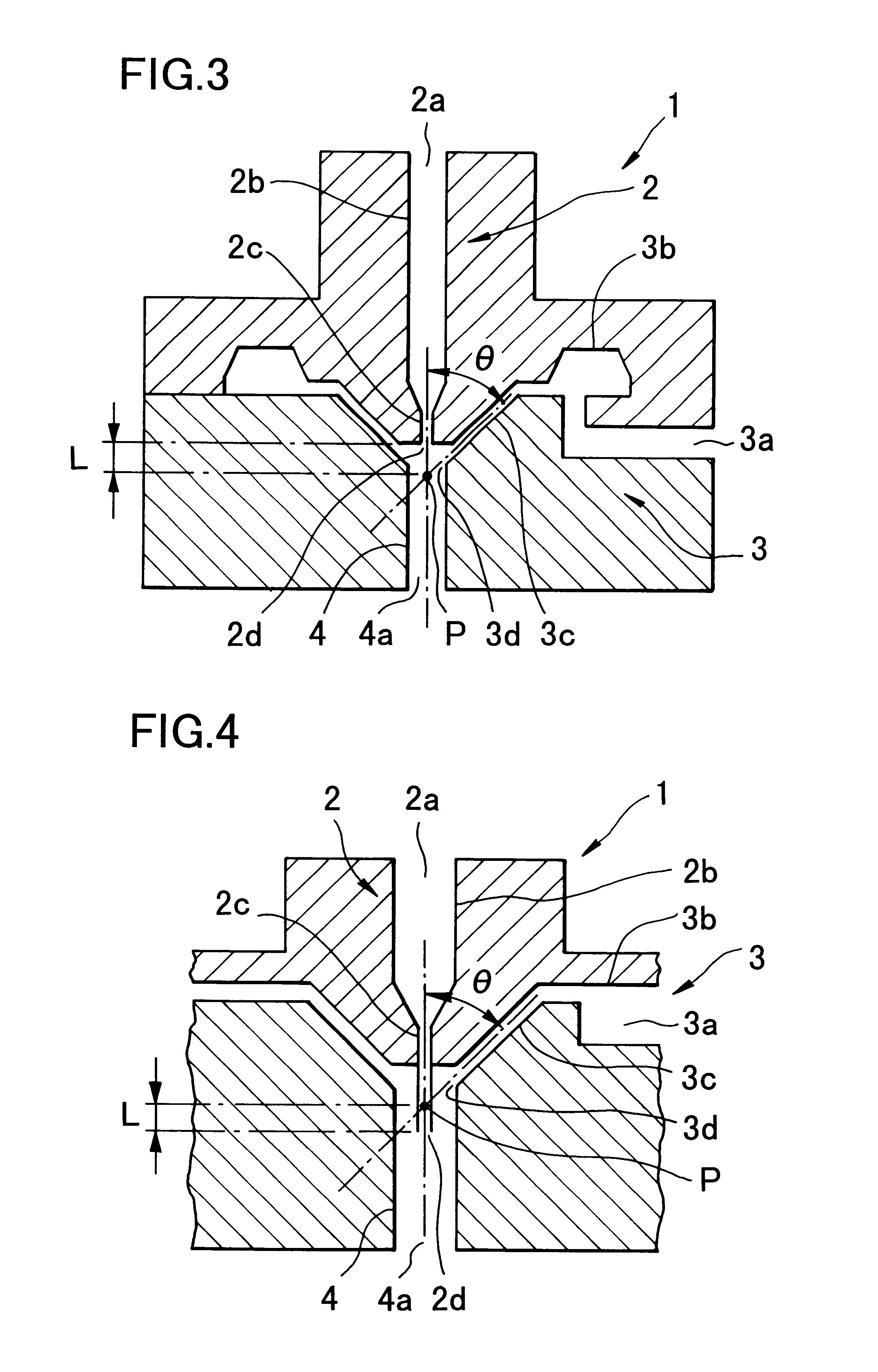
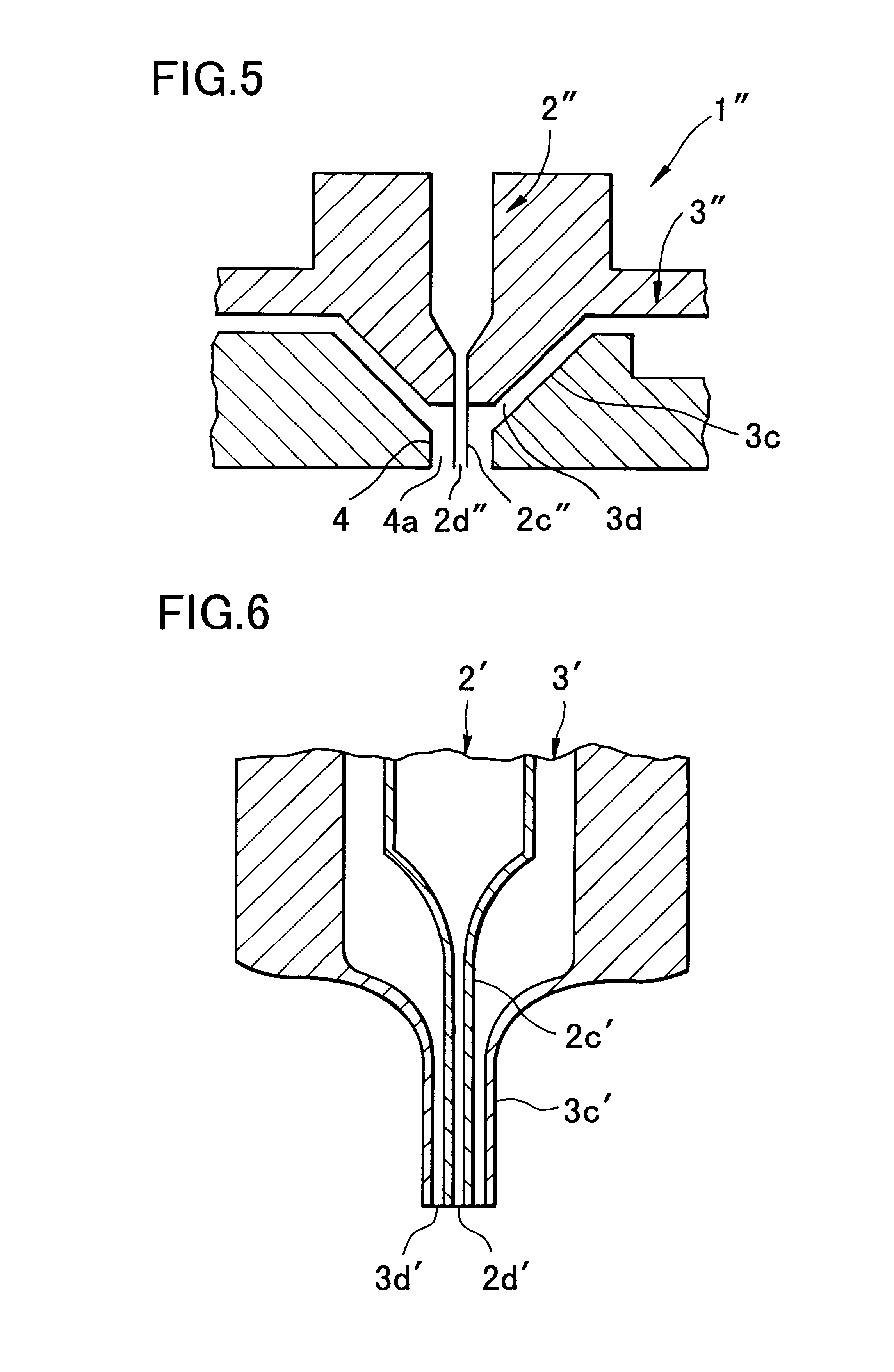
Apparatus for producing nanofiber utilizing electospinning and nozzle pack for the apparatus
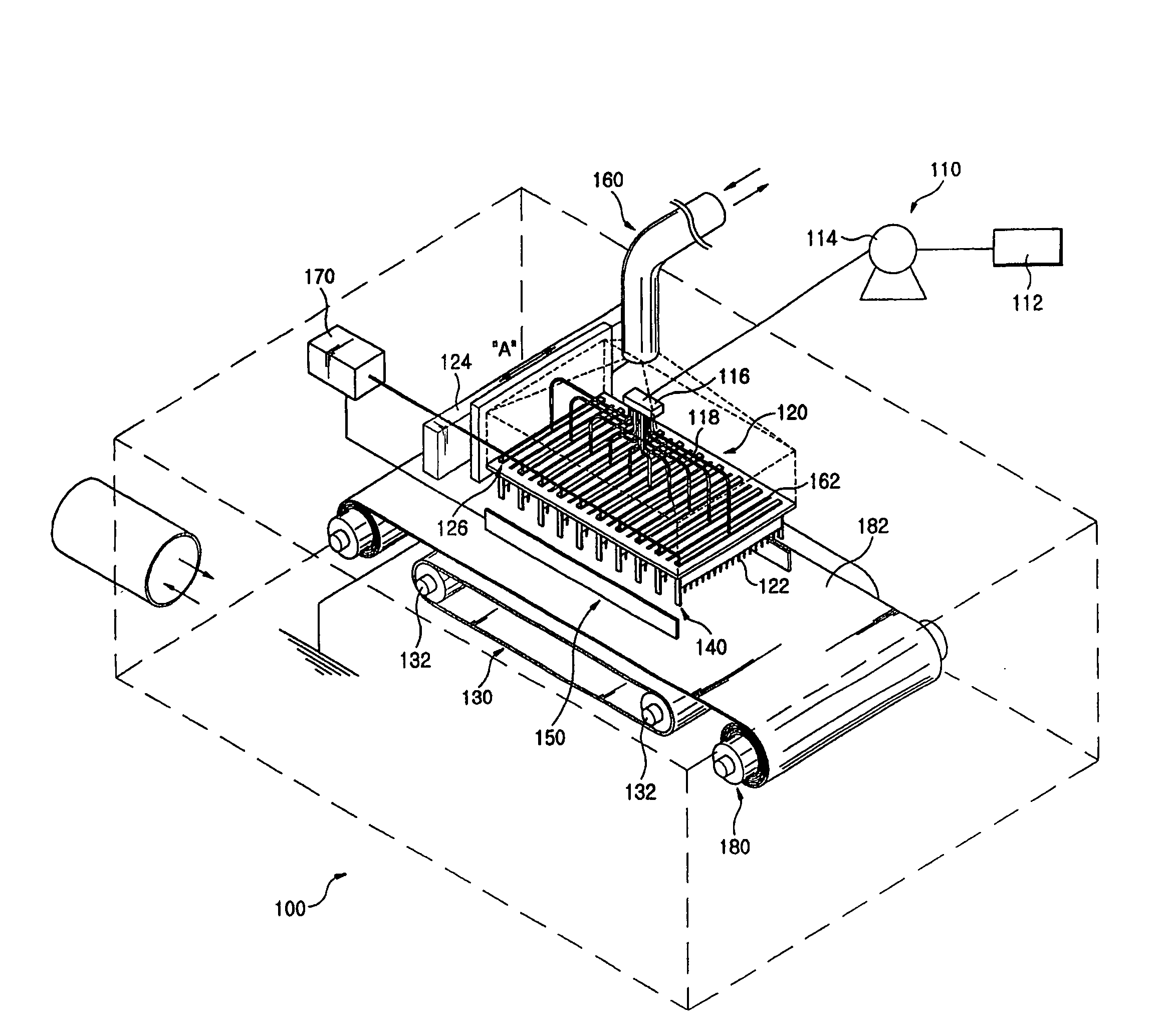
The apparatus for producing a nanofiber includes a supply unit (110) for supplying melted polymer for fiber material, a spinning unit (122) having several radiation nozzles (122) to which first voltage having a polar is applied to discharge the polymer solution supplied from the supply unit in a filament form, a collector (130) spaced apart form the spinning nozzles in order to pile the filament from the spinning unit and applied to second voltage having opposite polar to the first voltage, and a control unit (140) applied to the first voltage having the same polar as the charged filament and extended from an end of the spinning nozzle toward the collector at least at both sides of the spinning unit in order to prevent repulsion and dispersion of the filament stream radiated from each spinning nozzle.
Owner:NANOPHIL
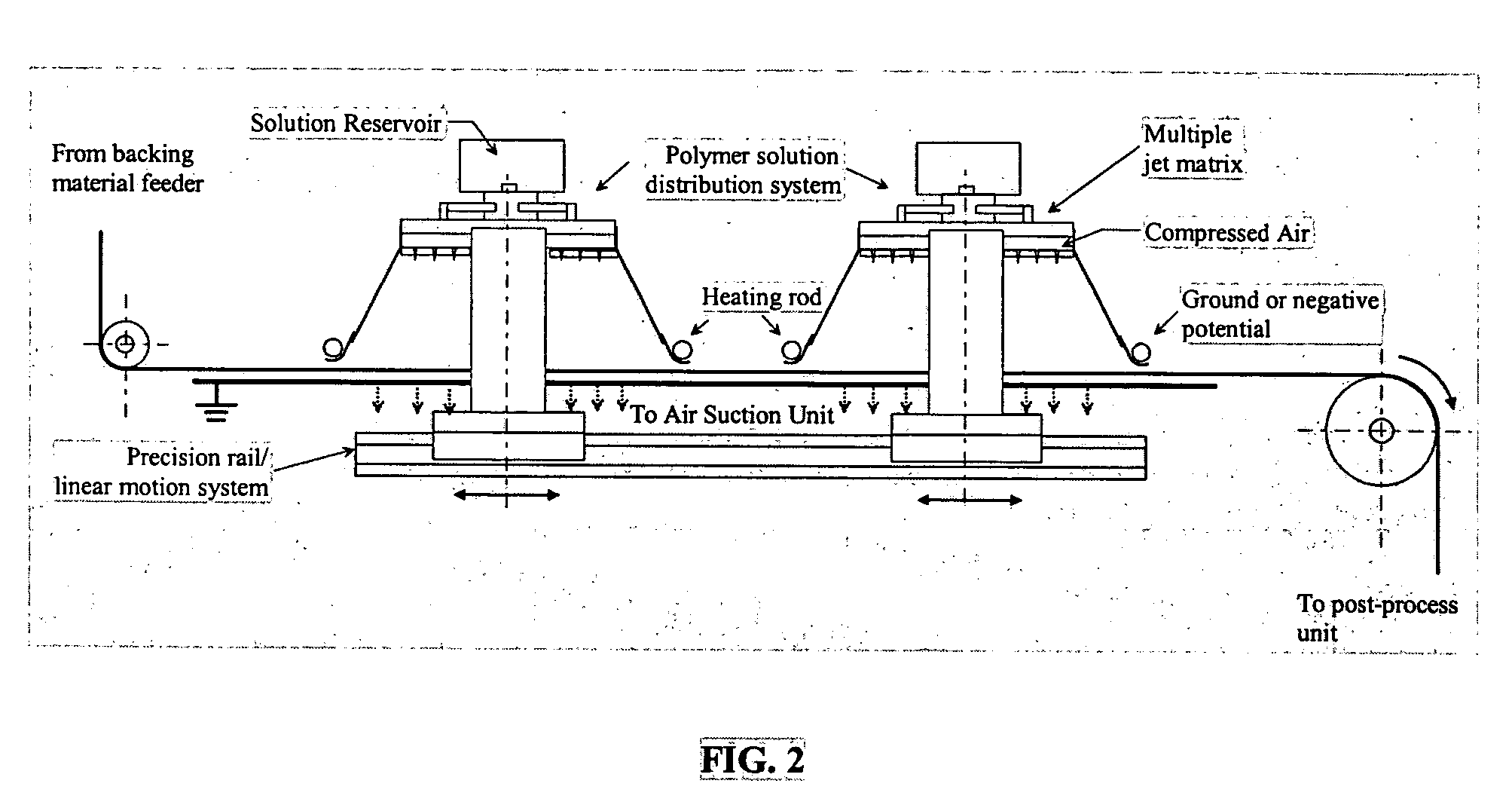
Manufacturing device and the method of preparing for the nanofibers via electro-blown spinning process
ActiveUS7618579B2Easily realizedElectric discharge heatingWood working apparatusThermoplasticNanofiber
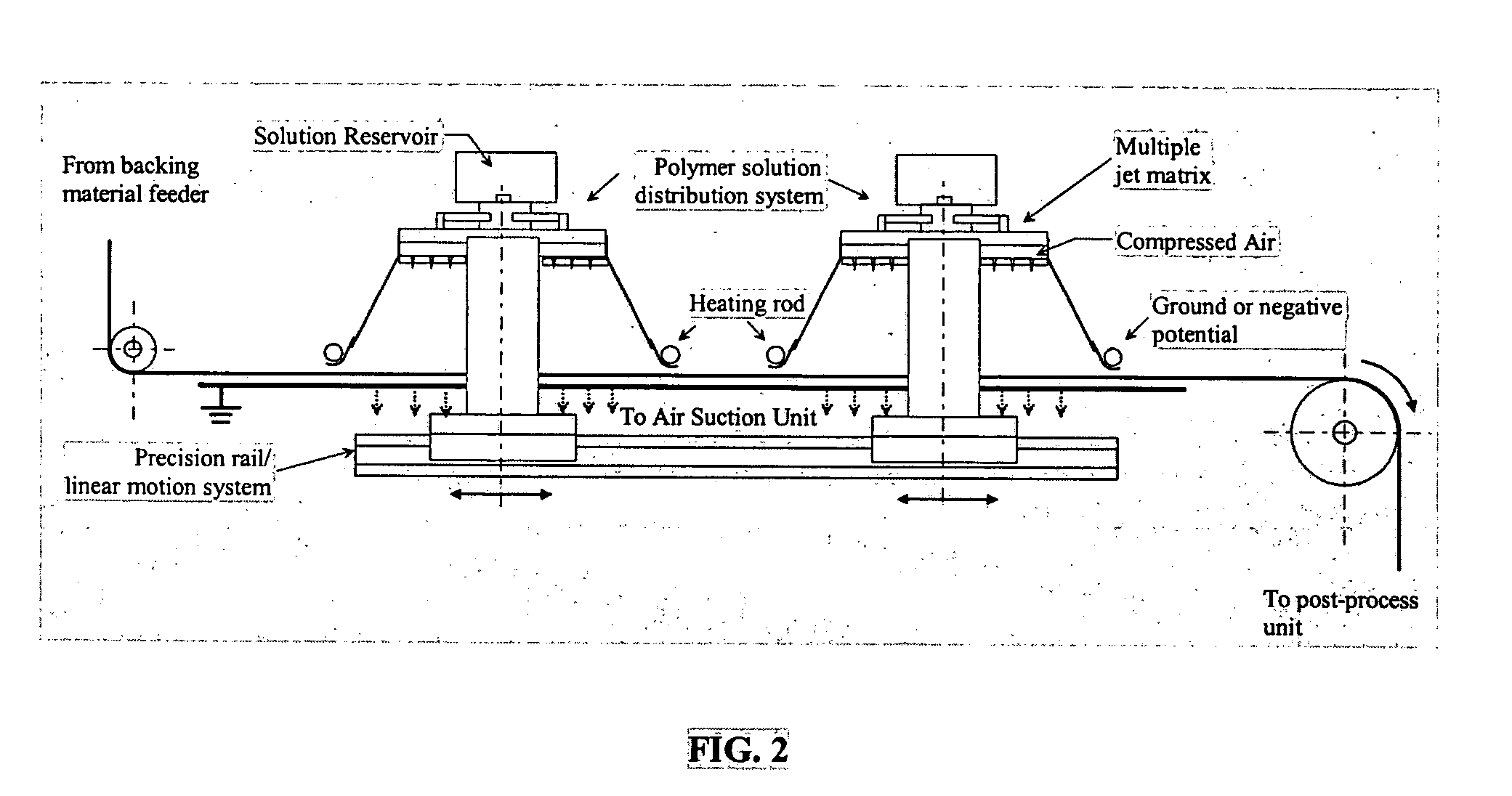
The invention relates to a nanofiber web preparing apparatus and method via electro-blown spinning. The nanofiber web preparing method includes feeding a polymer solution, which is a polymer dissolved into a given solvent, toward a spinning nozzle, discharging the polymer solution via the spinning nozzle, which is charged with a high voltage, while injecting compressed air via the lower end of the spinning nozzle, and collecting fiber spun in the form of a web on a grounded suction collector under the spinning nozzle, in which both of thermoplastic and thermosetting resins are applicable, the solution does not need to be heated and electrical insulation is readily realized.
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Method of preparing melamine formaldehyde resin/polyvinyl alcohol flame-proof fiber
InactiveCN101016658AImprove spinnabilityIncrease productivityFlame-proof filament manufactureWet spinning methodsFiberLimiting oxygen index
The invention discloses a method for producing melamine formaldehyde resin / polyvinyl alcohol flameproof fiber. The invention is characterized in that composing melamine and formaldehyde at the mole ratio as 1:1.2-1:6 and 50-100Deg. C into melamine formaldehyde resin water solution, to be mixed with the polyvinyl alcohol water solution at the solid content ratio as 2:8-8:2 to obtain spinning original liquid, then spinning and shaping the original liquid via general wet method, and treating solidifying bath via acid sodium sulfate saturated water solution, and the primary fiber is drawn, shaped via wet and heat method, washed, coiled, oiled, dried, and heated in dry condition to obtain the final melamine formaldehyde resin / polyvinyl alcohol flameproof fiber. The titer of said flameproof fiber is 10detex, while the strength is 1-3cN / dtex, the crack extended rate is 5-15%, the regain ratio is 5-10%, and the limit oxygen index is 30-45.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Bamboo pupa protein fiber long-short yarn and method for making same
ActiveCN101117737AConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsStaple fibre formationYarnCellulose
The present invention belongs to the spinning field and provides a long or short filament of bamboo pupa protein fiber. The long or short filament comprises 10-40wt percent silkworm pupa protein spinning liquid and 60-90wt percent bamboo cellulose viscose as the raw materials. The present invention also provides a method for preparing of the long or short filament. With bamboo cellulose as the raw material, the present invention can still meet the quality standard. Since bamboo cellulose can be acquired easily, the present invention provides a new choice for spinning product-pupa protein fiber.
Owner:YIBIN GRACE
Process of fabricating nanofibers by reactive electrospinning
ActiveUS8066932B2Easy to controlHigh voltageElectric discharge heatingInorganic material artificial filamentsNanofiberCrosslinked polymers
Apparatus and methods for fabricating nanofibers by reactive electrospinning are described. An electrospinning process is coupled with an in-line reactor where chemical or photochemical reactions take place. This invention expands the application of the electrospinning and allows the production of nanofibers of crosslinked polymers and other new materials, such as gel nanofibers of ceramic precursors.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Copolyester section or fiber and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101357981ASoft touchSoft lusterMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentMelt spinning methodsFiberAlcohol
The invention relates to copolyester sheets or a copolyester fiber, which comprises terephthalic acid, m-phthalic acid, glycol and 2-methyl-1, 3-propanediol; the mol ratio of dibasic acids to diatomic alcohols is 1 to 1.7-2.4. The preparation method of the copolyester sheet or fiber comprises the following steps: (1) the terephthalic acid, the m-phthalic acid, the glycol and the 2-methyl-1,3-propanediol are mixed for esterification for 1 to 5 hours together with a catalyzer and a heat stabilizer at 220 to 275 DEG C under the pressure of zero to 0.5MPa; (2) pre-polycondensation follows; the pressure is reduced and the temperature is raised to complete polycondensation, thus getting the copolyester sheets; the copolyester sheets are dried in vacuum, thus getting dry copolyester sheets capable of spinning; and the dry copolyester sheets are spun to get the copolyester fiber. The dyeing behaviour of the copolyester fiber is improved; and the copolyester fiber has the characteristics of resisting roughing and pilling and high contractibility. The preparation method is designed rationally and can be industrialized easily, which is safe for the environment.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for manufacturing fibril system fiber
InactiveUS6248267B1Shorten fiber lengthIncrease the diameterArtificial filaments from cellulose derivativesMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentFiberFibril
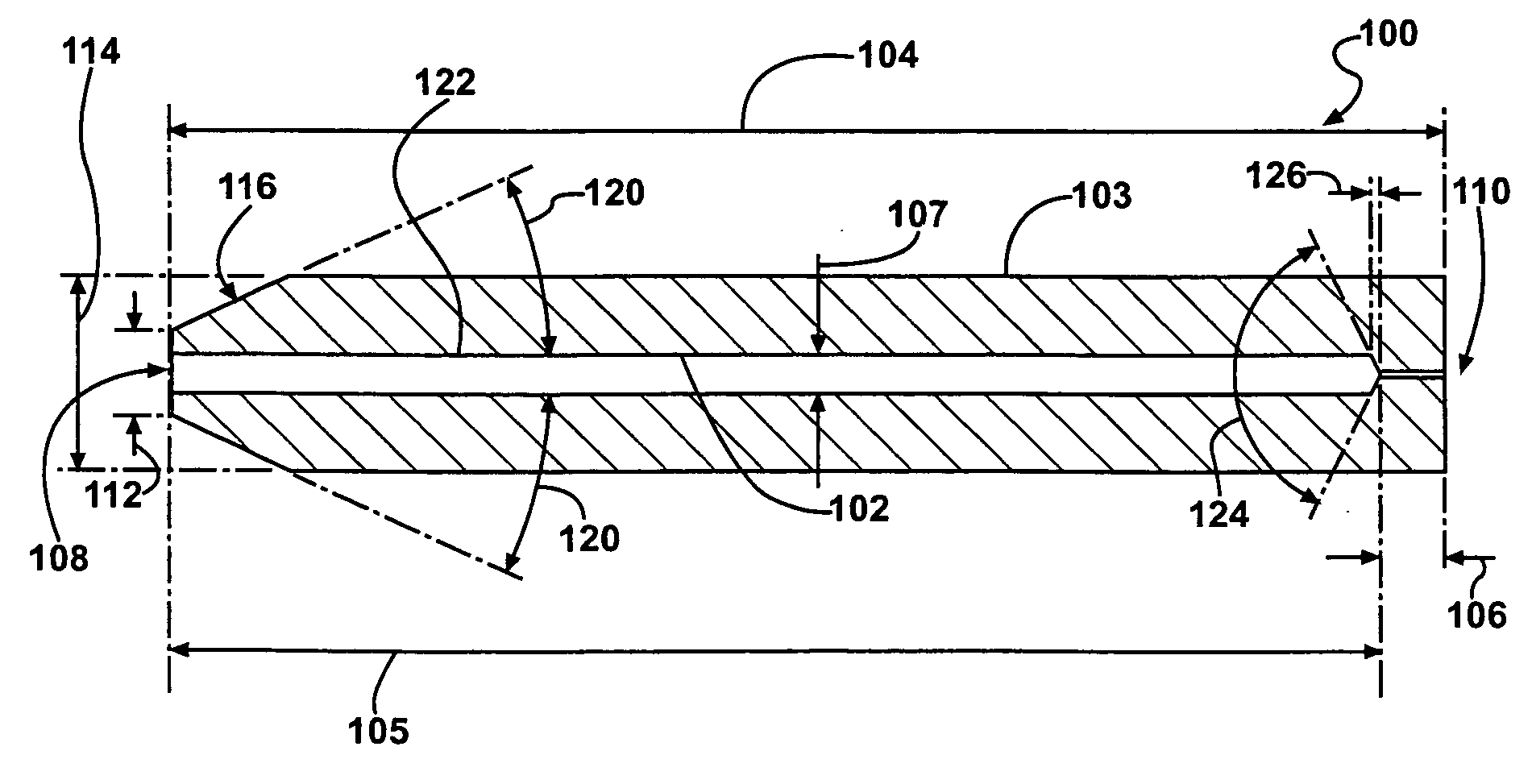
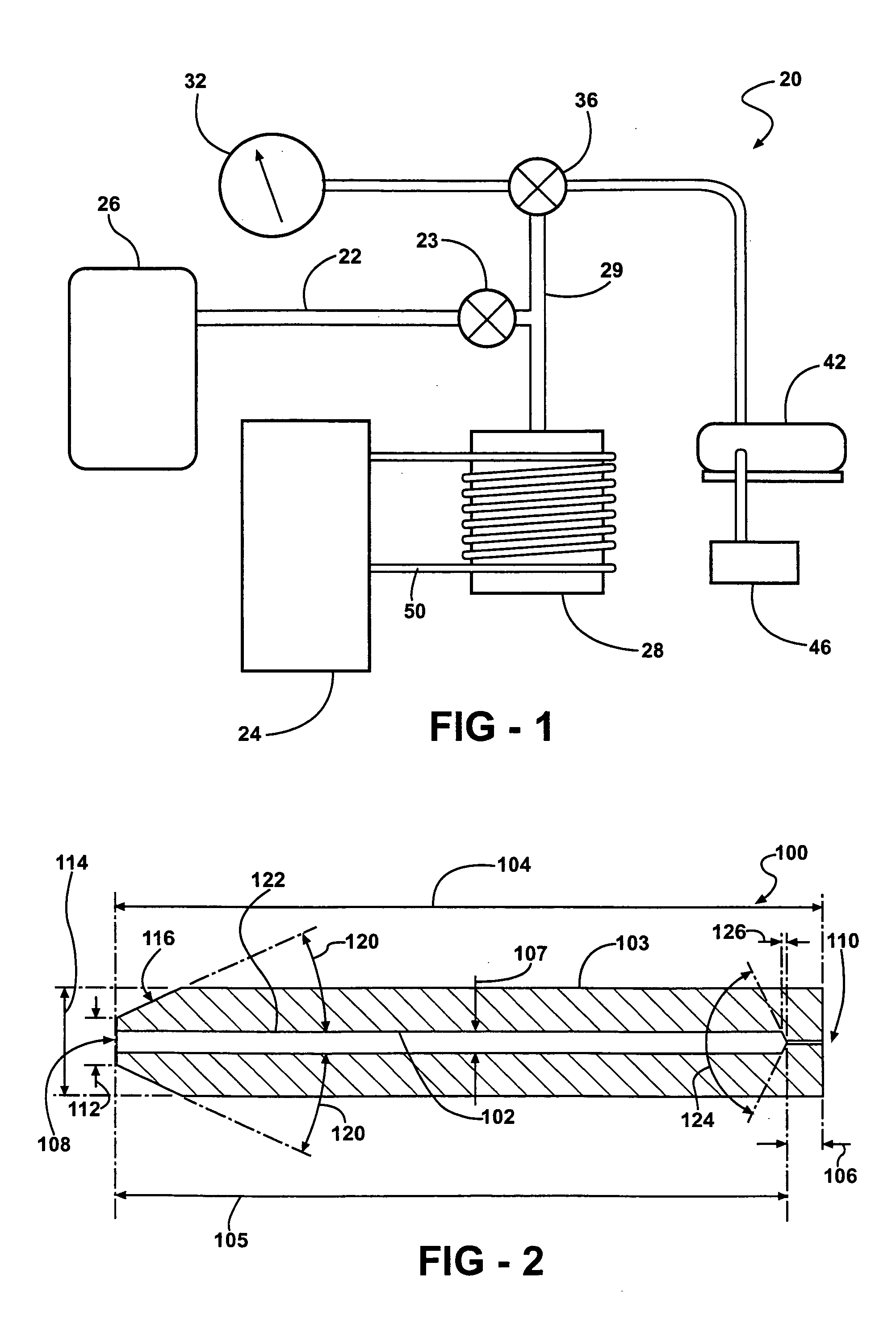
The present invention provides fibril system fibers which may be employed in filter applications and in artificial leather applications, and also provides an industrially superior manufacturing method for such fibril system fibers, and a spinning nozzle. The fibril fibers of the present invention include at least one macromolecular polymer having a film forming ability, and they have a structure in which fibrillated fibers having a diameter of 10 micrometers or less branch from main fibers having a width within a range of 0.1 micrometers-500 micrometers, and a length within a range of 10 micrometers-10 cm.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Production for of melting point polyester short staple
InactiveCN1644771APrevent softening adhesionStaple fibre formationMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentPolyesterPolymer science
A process for preparing the polyster staple fibres with low fusing point (120-130 deg.C) includes such steps as low-temp vacuum drying of polyester chips, fusing, spinning, winding, bundling, drafting three times, hot tension-setting curling, hot shrink-setting, cutting and opening.
Owner:中国石化集团天津石油化工公司
Electro-blowing technology for fabrication of fibrous articles and its applications of hyaluronan
InactiveCN1823184AIncrease varietyRelax viscosityElectric discharge heatingFibre chemical featuresFiberPolymer science
A method for electroblowing fibers is provided which involves the steps of: forcing a polymer fluid through a spinneret in a first direction towards a collector located a first distance from the spinneret, while simultaneously blowing a gas through an orifice that is substantially concentrically arranged around the spinneret, wherein the gas is blown substantially in the first direction; wherein an electrostatic differential is generated between the spinneret and the collector; and collecting the fibers, and its use in preparing submicron scale fibers of various types, particularly hyaluronan fibers, and the hyaluronan nanofibers thus formed.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for processing high shrinkage superfine denier polyester staple fiber
InactiveCN101503832AFeel goodGood water absorption and breathabilityMelt spinning methodsStaple fibre formationPolyesterYarn
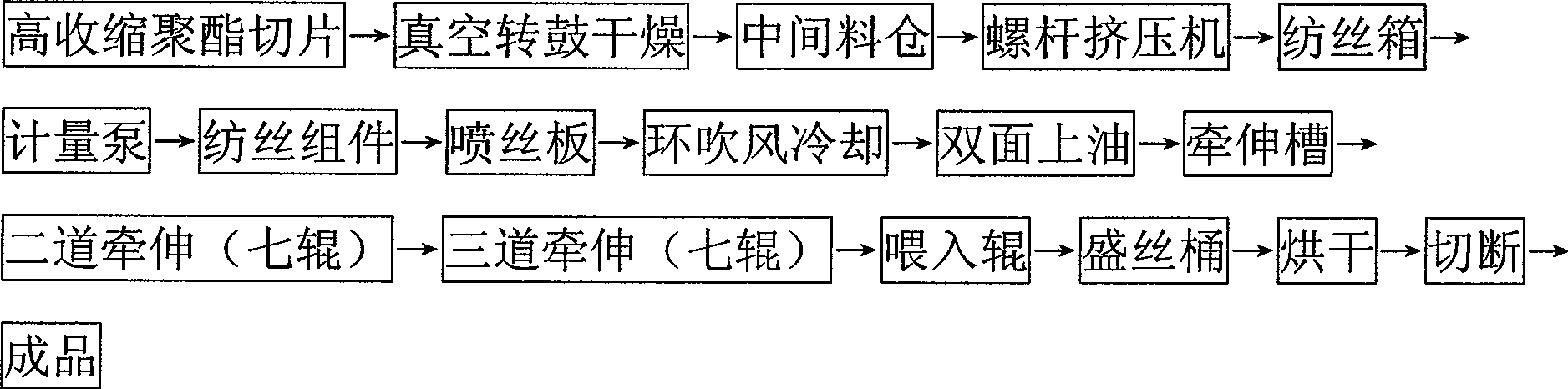
The invention relates to a processing method of high-shrinkage ultrathin polyester short fiber. The process flows of the method comprise: high-shrinkage polyester slicing, vacuum rotary drum drying, intermediate bunker, screw extruder, spinning box, metering pump, spinning component, spinneret plate, circular blowing cooling, double side oiling, drawing groove, second drawing (seven rollers), third drawing (seven rollers), feeding roller, yarn containing drum, drying, cutting and obtaining finished product. The technological parameter of the method is characterized in that slice drying adopts a vacuum rotary drum low-temperature longtime process; spinning temperature and preliminary drawing multiple are properly lowered; low-temperature drawing and unshaped drawing process are adopted; and the spinneret plate adopts a finishing spinneret plate which has 0.2*0.5mm aperture and is matched with a corresponding component. Due to adopting high-shrinkage functional polyester slice as a raw material, the processing method can realize production on common polyester short fiber spinning equipment without changing the prior spinning equipment during production.
Owner:JIANGSU SHENGHONG CHEM FIBRE CO LTD
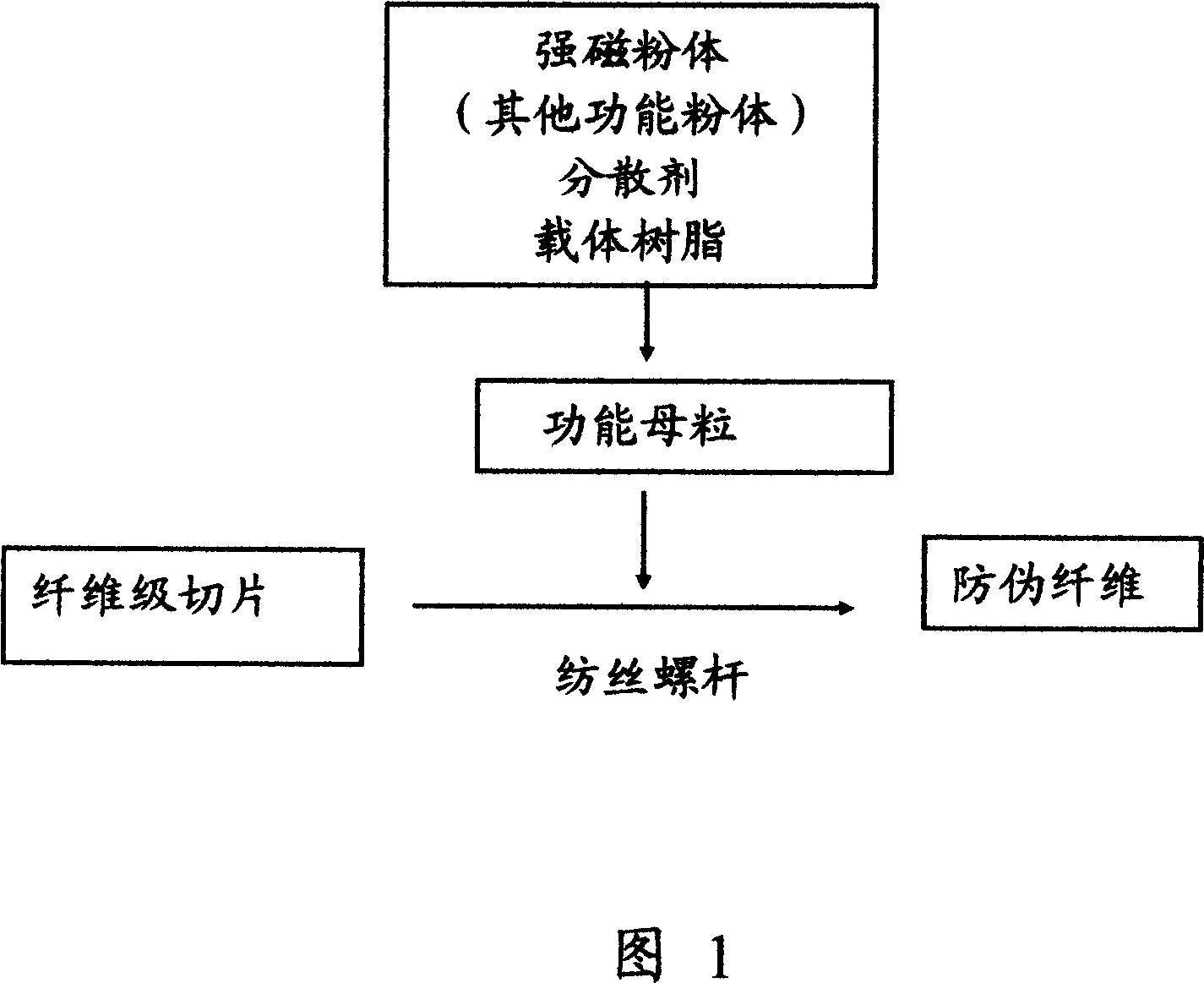
Chinlon 6 anion short fiber and producing method thereof
InactiveCN1772982AImprove surface activityTo promote metabolismStaple fibre formationArtifical filament manufactureFiberNylon 6
The present invention relates to a nylon 6 negative ion staple and its production method. Said staple includes negative ion function mother granules and nylon 6 chips, their weight ratio is 1:5-10. The described negative ion function mother granules include function powder body, carrier chip, dispersing agent, coupling agent and antioxidant, their weight ratio is 20:79.5:0.2:0.1:0.2. Besides, said invention also provides the concrete steps of its production method.
Owner:天津市发博纺织材料有限责任公司
Fibre-forming process and fibres produced by the process
ActiveCN104024494AMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentMonocomponent fibroin artificial filamentFiberPolymer science
Owner:HEIQ
Capron 6 bamboo charcoal staple fiber, and fabricating method
InactiveCN1760413AWith far infraredFunctionalStaple fibre formationArtifical filament manufactureNylon 6Extrusion Granulation
The present invention relates to a nylon 6 bamboo carbon staple and its production method. Said staple includes bamboo carbon function mother granules and nylon 6 chips, their weight ratio is 1:5-10; and the described bamboo carbon function mother granules include function powder body, carrier chips, dispersing agent, coupling agent and antioxidant, their weight ratio is 20:79.5:0.2:0.1:0.2. The present invention also provides the concrete steps of its production method. Said method includes the steps of preparing raw materials, mixing them, spinning, end winding, tow collecting, drafting, dewatering, crimpting, finalizing design and cutting.
Owner:天津市发博纺织材料有限责任公司
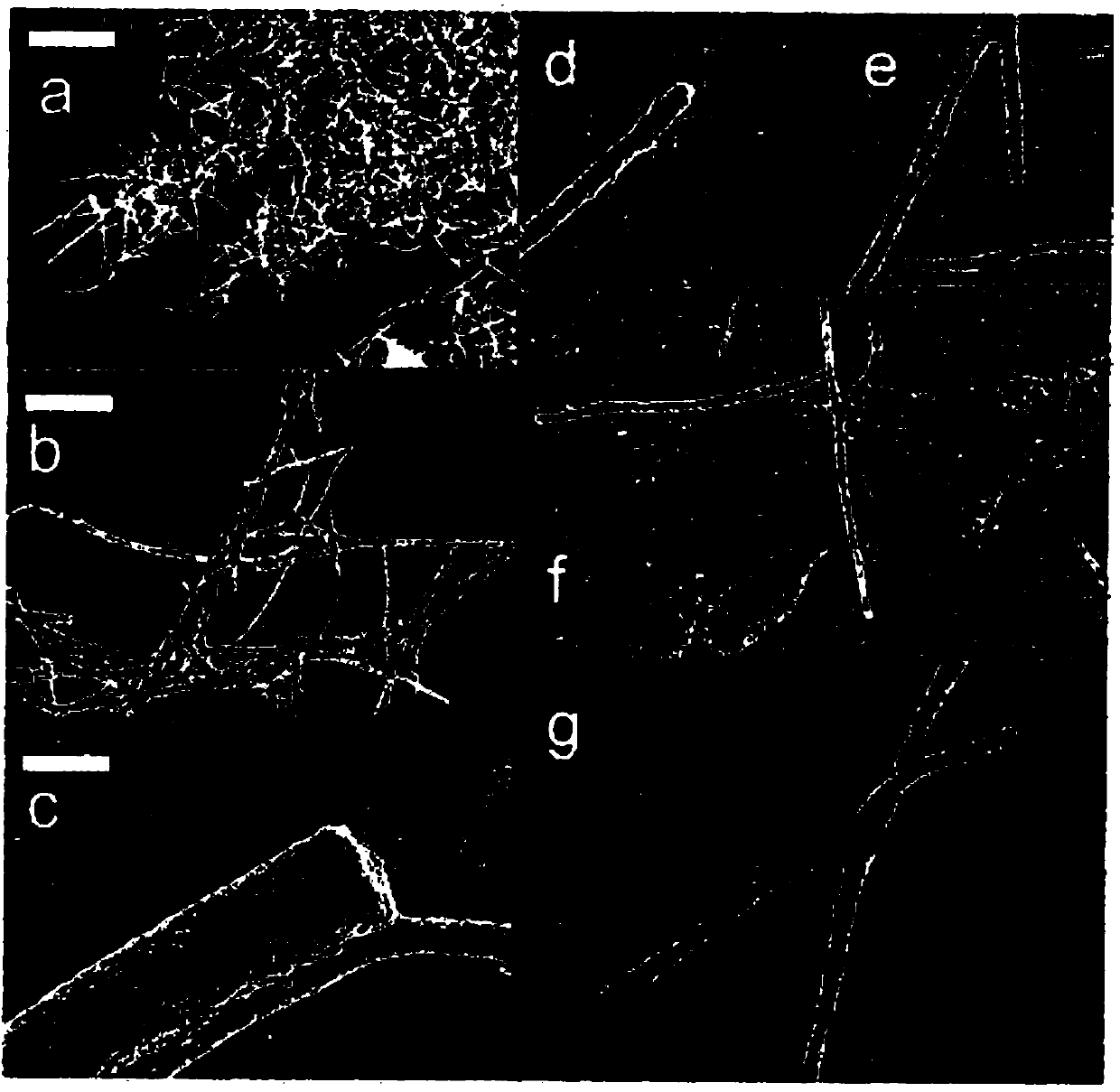
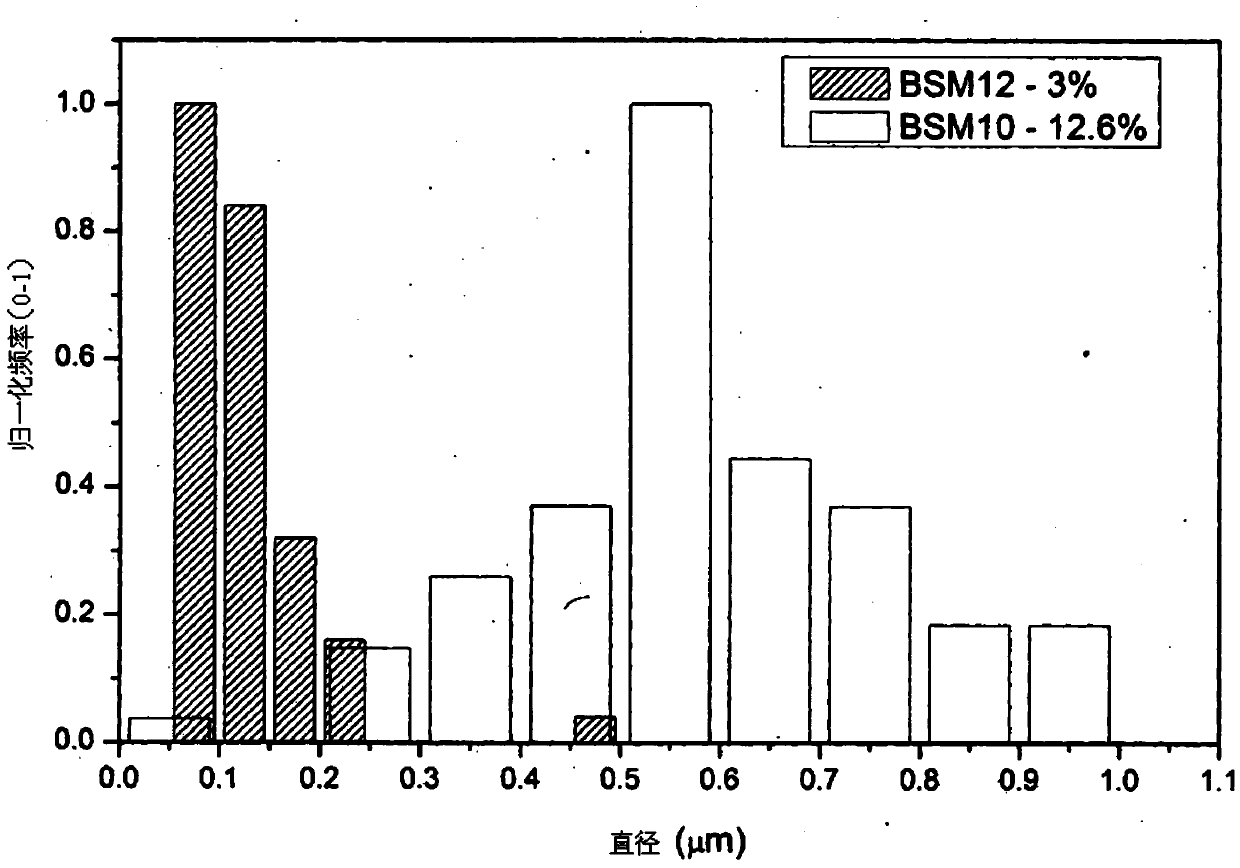
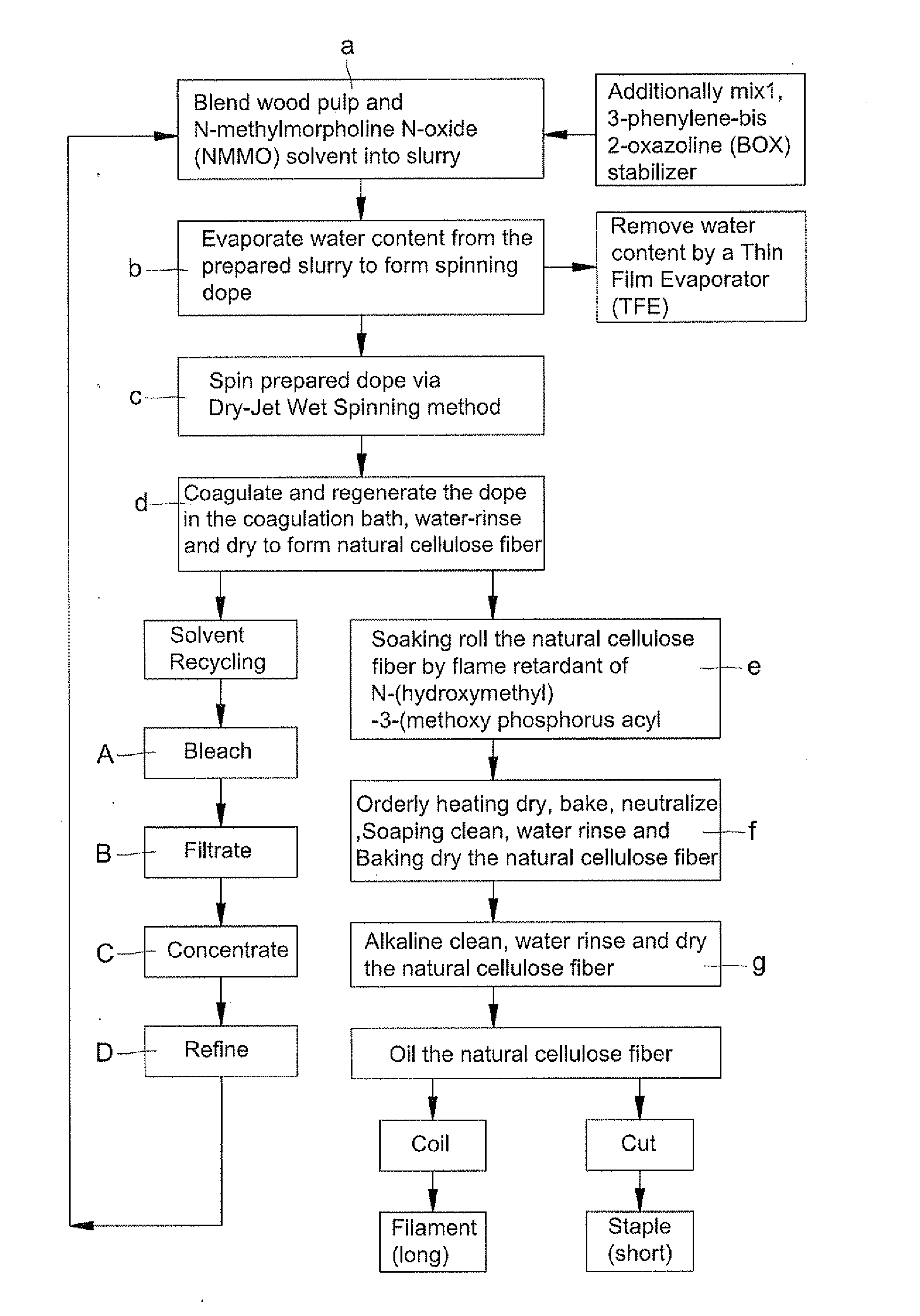
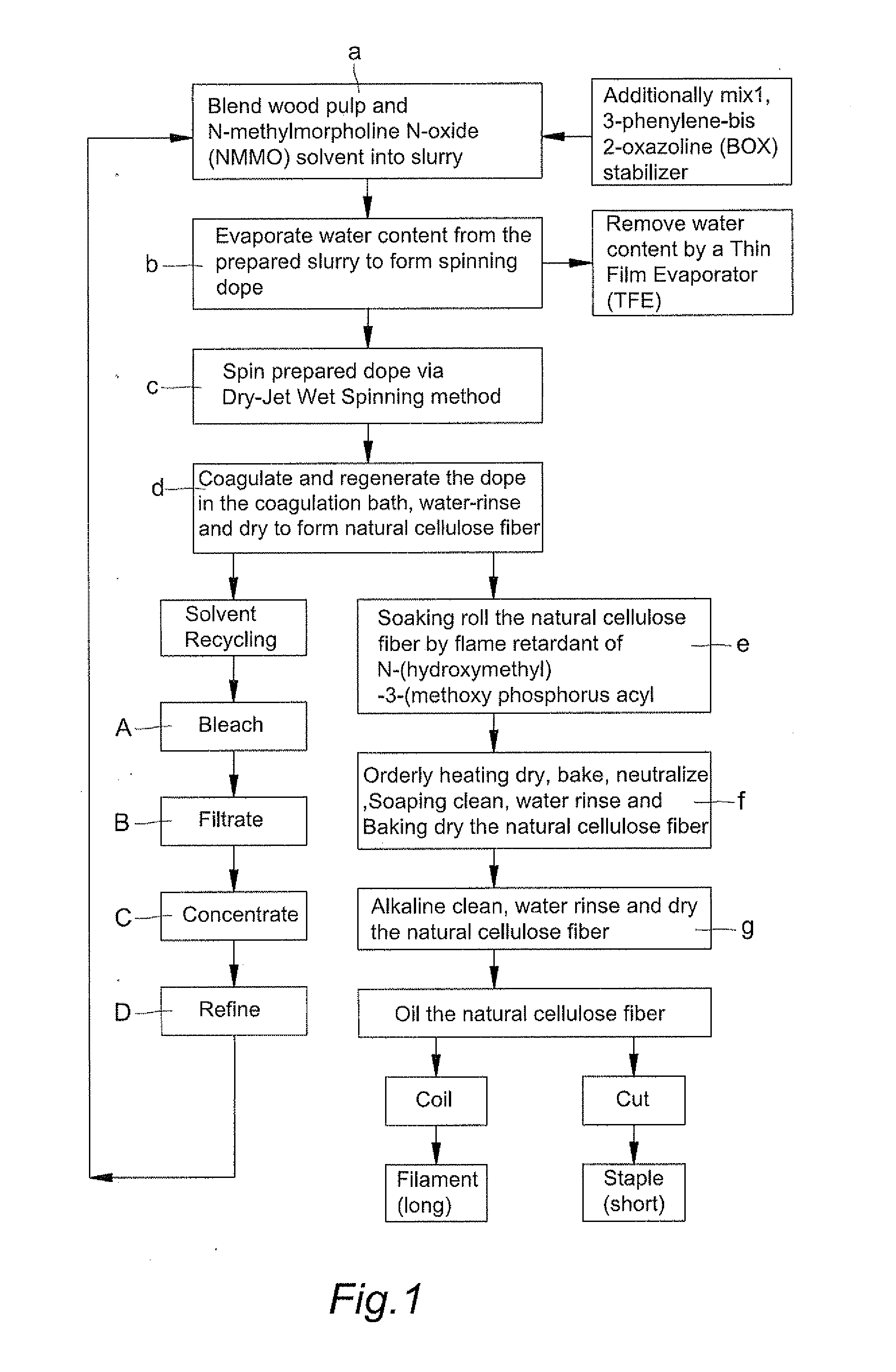
Fabrication of natural cellulose fiber with flame-retarding capability
ActiveUS20130228949A1Reduce solvent recycling costSimple facilitiesArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsFlame-proof filament manufactureCross-linkSlurry
A fabrication of natural cellulose fiber with flame-retarding capability comprises following steps. Blend pulp and solvent of N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) to form slurry. Evaporate extra water content from slurry by a Thin Film Evaporator (TFE) to form dope. By Dry-Jet Wet Spinning, spin and extrude dope for coagulating and regenerating. Water-rinse and dry to form natural cellulose fiber. Soaking roll natural cellulose fiber by flame retardant of N-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(methoxy phosphorus acyl). Orderly dry, bake, neutralize, soaping clean, water rinse, baking dry, soaking rolled, alkaline clean, water rinse, dry and oil the natural cellulose fiber to produce natural cellulose fiber of flame retarding capacity. Because of cross-linking reaction for the flame retardant of N-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(methoxy phosphorus acyl) with natural cellulose fiber, the flame-retarding capability thereof meet requirements of testing standards in American ASTM D6413-1999 and ASTM D2863-1995. Moreover, the wastes thereof meet the requirements of environment protections without harm.
Owner:ACELON CHEM & FIBER
Apparatus for making multicomponent meltblown fibers and webs
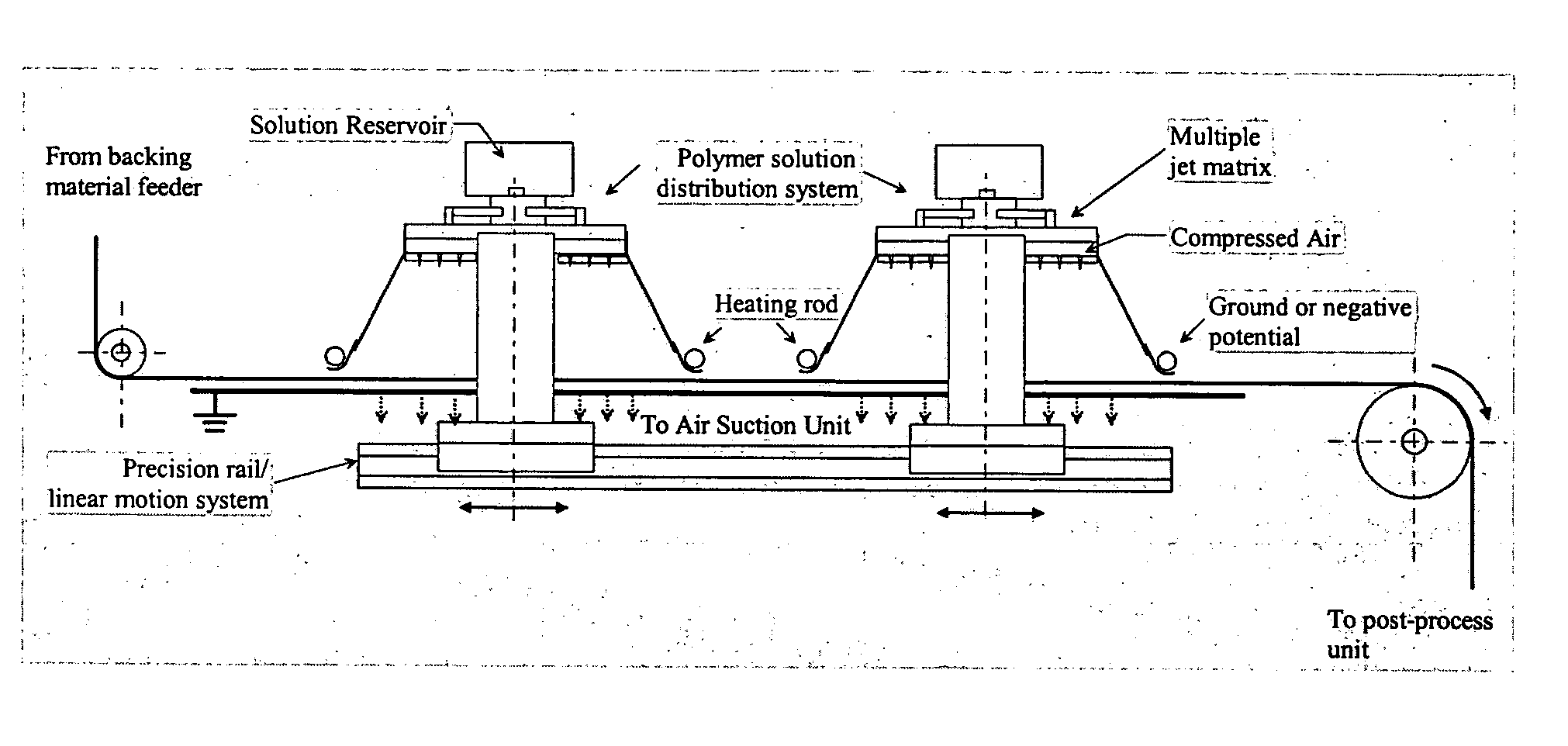
An extrusion die for meltblowing molten polymers having a row of die orifices each having at least two separate polymer supply ports entering from an entrance portion of the die, each of the polymer supply ports communicating with separate rows of extrusion capillaries having exit openings at an exit portion of the die, gas supply ports entering from the entrance portion of the die and arranged laterally to the polymer supply ports, the gas supply ports communicating with gas jets extending through the die and arranged laterally to the exit openings of the extrusion capillaries, wherein the rows of extrusion capillary exit openings and the gas jets communicate with a blowing orifice in the exit portion of the die.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Polyester superfine fibre villus, flocked plus material stuck with the same, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101240459AIncreased durabilityImprove performanceLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsPolyesterFiber
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV +1
Production method of fine denier hollow polyester staple fiber
ActiveCN101302656AStable productionImprove the success rate of closureHollow filament manufactureStaple fibre formationPolyesterFiber
The invention provides a production method for fine denier hollow polyester staple fiber. The spinneret hole of the spinneret is a single opening C-shaped circle, the spinning temperature is 288-292 DEG C, the circular air blow speed is 0.8-1.3 m / s and the air blow temperature is 17-23 DEG C. The 0.8 dt-1.5 dt fine denier hollow polyester staple fiber is obtained by processing adopting the process route of conventional polyester staple fiber. The invention has the advantages of stable production process and high product closing success rate. The titer and modulus of fiber are decreased further on the precondition of ensuring physical properties of the fiber such as higher hollowness, excellent fracture strength and elongation at break, thus improving the flexibility of fiber and soft feeling of fabric effectively and meeting the market demand for further fine denier of hollow polyester staple fiber.
Owner:SINOPEC YIZHENG CHEM FIBER
Magnetic nylon-6 short fiber and its making process
InactiveCN1740413AHigh strengthImprove featuresStaple fibre formationArtifical filament manufactureFiberNylon 6
The magnetic nylon-6 short fiber is made with magnetic functional agglomerate and nylon chip in the weight ratio of 1 to 5-10. The magnetic functional agglomerate includes functional powder, carrier chip, dispersant, coupler and antioxidant in certain weight proportion. The making process of the magnetic nylon-6 short fiber includes the following steps: 1. preparing the magnetic functional agglomerate through preparing functional powder of Fe3O4, drying and activating the functional powder, mixing the functional powder with carrier chip, dispersant, coupler and antioxidant in certain weight proportion via high speed stirring, cooling the mixture to room temperature, and extruding and pelletizing in extruder; and 2. producing magnetic nylon-6 short fiber through mixing magnetic functional agglomerate and nylon chip, spinning the mixture, winding, bundling, drafting, dewatering, crimping, setting and cutting.
Owner:任晓林
Method for manufacturing polyphenylene sulfide meltblown fiber products
ActiveCN101736418AElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentPolymer scienceAntistatic agent
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing polyphenylene sulfide meltblown fiber products, which is characterized in that polyphenylene sulfide resin meltblown fibers are used as the raw materials, undergo resin premixing and are melted, pelletized, chipped, melted, extruded and blown by a double-screw extruder after high-speed stirring and mixing and then are cut by 30-40MPa of high pressure nitrogen to obtain polyphenylene sulfide meltblown short fibers which are rapidly cooled by the nitrogen at 8-10 DEG C; and in the process of resin premixing, 98.5-99.5% of polyphenylene sulfide resins with weight-average molecular weight between 50 thousand and 60 thousand and molecular weight distribution coefficient between 1.8 and 19, and 0.5-1.5% of antistatic agents are employed. The polyphenylene sulfide meltblown fibers, non-woven fabrics and fiber paper manufactured by the invention are widely used in such high technology fields as environmental protection, electronics, aviation and the like.
Owner:德阳科吉高新材料有限责任公司
Method for producing color and differential polyester short fibre by melting body directly spinning online adding technology
InactiveCN1944719AImprove product qualityQuality improvementMelt spinning methodsStaple fibre formationPolyesterPolymer science
The present invention relates to synthetic fiber producing technology, and is direct melt spinning and on-line adding process for producing color and differential short polyester fiber. Technologically, the process includes injecting modifying material through drying, melting, filtering and metering to the polyester melt before entering to the spinning tank; mixing with the melt homogeneously in the static mixer, and spinning the mixture. The said process makes the agglomerate permeating into the inside of fiber easily to produce color fiber and other differential fibers with high quality, high fastness, high water washing resistance, excellent wear resistance, etc.
Owner:ANXING ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION COLOR FIBER CHUZHOU
Electro-blowing technology for fabrication of fibrous articles and its applications of hyaluronan
InactiveUS7662332B2Improve the situationHigh productElectric discharge heatingFibre chemical featuresFiberNanofiber
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Antiforge fibre, its antiforge use and yarn with health-care function using the fibre
The present invention relates to an anti-false fiber, its anti-false to an anti-false fiber, its anti-false application and anti-false yarn adopting said fiber and having health-care function. Specially, it relates to an anti-false fiber with residual magnetic property, its anti-false application and health-care type anti-false yarn made up by adopting said fiber. It is characterized by that in the described anti-false fiber a strong magnetic powder body with enough quantity is contained, 25 wt%-50 wt% of said fiber and other fiber are blended and spun so as to obtain the invented health-care anti-false yarn. Said anti-false yarn can be checked by utilizing bill-checking machine.
Owner:王铁琦
Water-disintegrable composite fiber and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20150284879A1High proppant dispersibilityMelt spinning methodsDrilling compositionFiberPolymer chemistry
A water-disintegrable composite fiber comprising a phase containing a polyglycolic acid resin and a phase containing a polylactic acid resin with a D-lactic acid unit ratio of at least 1.0%; the two phases extending continuously in a lengthwise direction; and the composite fiber having a cross sectional area formed by the phase containing the polyglycolic acid resin having an area ration of at most 50%; and the content of the polyglycolic acid resin being from 2 to 100 parts by mass per 1 part by mass of the D-lactic acid units in the polylactic acid resin.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Antibacterial terephthalic acid trimethylene glycol ester staple fiber and production method thereof
The invention discloses a short and antibacterial polytrimethylene terephthalate fiber and production method thereof, which adds master batches with antibacterial functions and amounting for 0.2-2 percent in mass to fiber during the spinning fiber smelting. The invention mixes antibacterial silver nanoparticle master batches to PTT slice for mixed spinning. The produced short fiber can be spun purely or spun with other various long or short fibers into blended yarns. The finished yarn has an antibacterial rate above 95 percent and can effectively kill most harmful bacteria. The antibacterial effect can not be changed after even a plurality of washing and the invention is also provided with excellent performance of ordinary PTT fiber product and is ideal spinning material in fields such as medical treatment, sanitation and sports, etc.
Owner:QUANZHOU HAITIAN MATERIAL TECH CORP
Apparatus for producing nanofiber utilizing electospinning and nozzle pack for the apparatus
The apparatus for producing a nanofiber includes a supply unit (110) for supplying melted polymer for fiber material, a spinning unit (122) having several radiation nozzles (122) to which first voltage having a polar is applied to discharge the polymer solution supplied from the supply unit in a filament form, a collector (130) spaced apart form the spinning nozzles in order to pile the filament from the spinning unit and applied to second voltage having opposite polar to the first voltage, and a control unit (140) applied to the first voltage having the same polar as the charged filament and extended from an end of the spinning nozzle toward the collector at least at both sides of the spinning unit in order to prevent repulsion and dispersion of the filament stream radiated from each spinning nozzle.
Owner:NANOPHIL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com