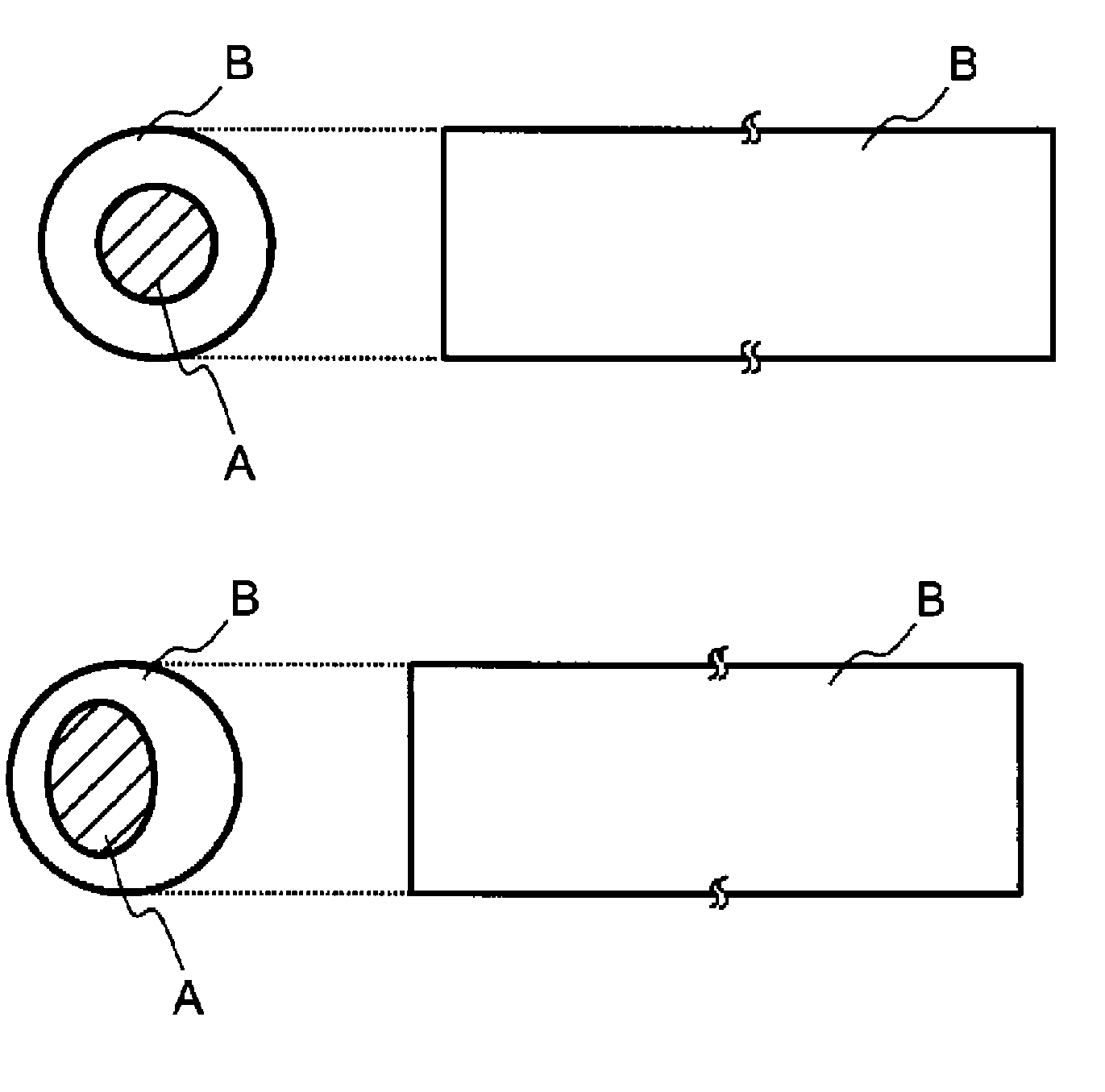
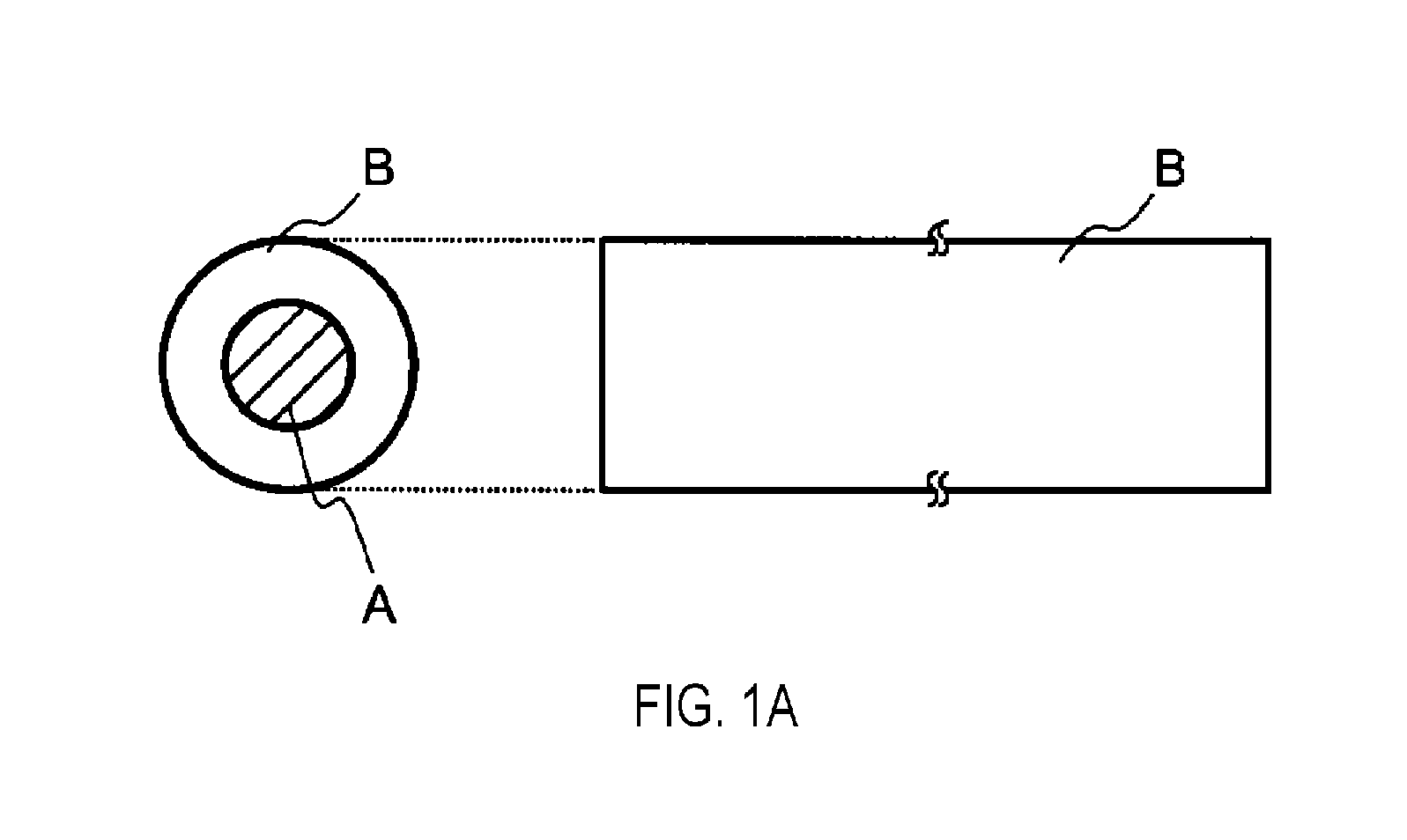
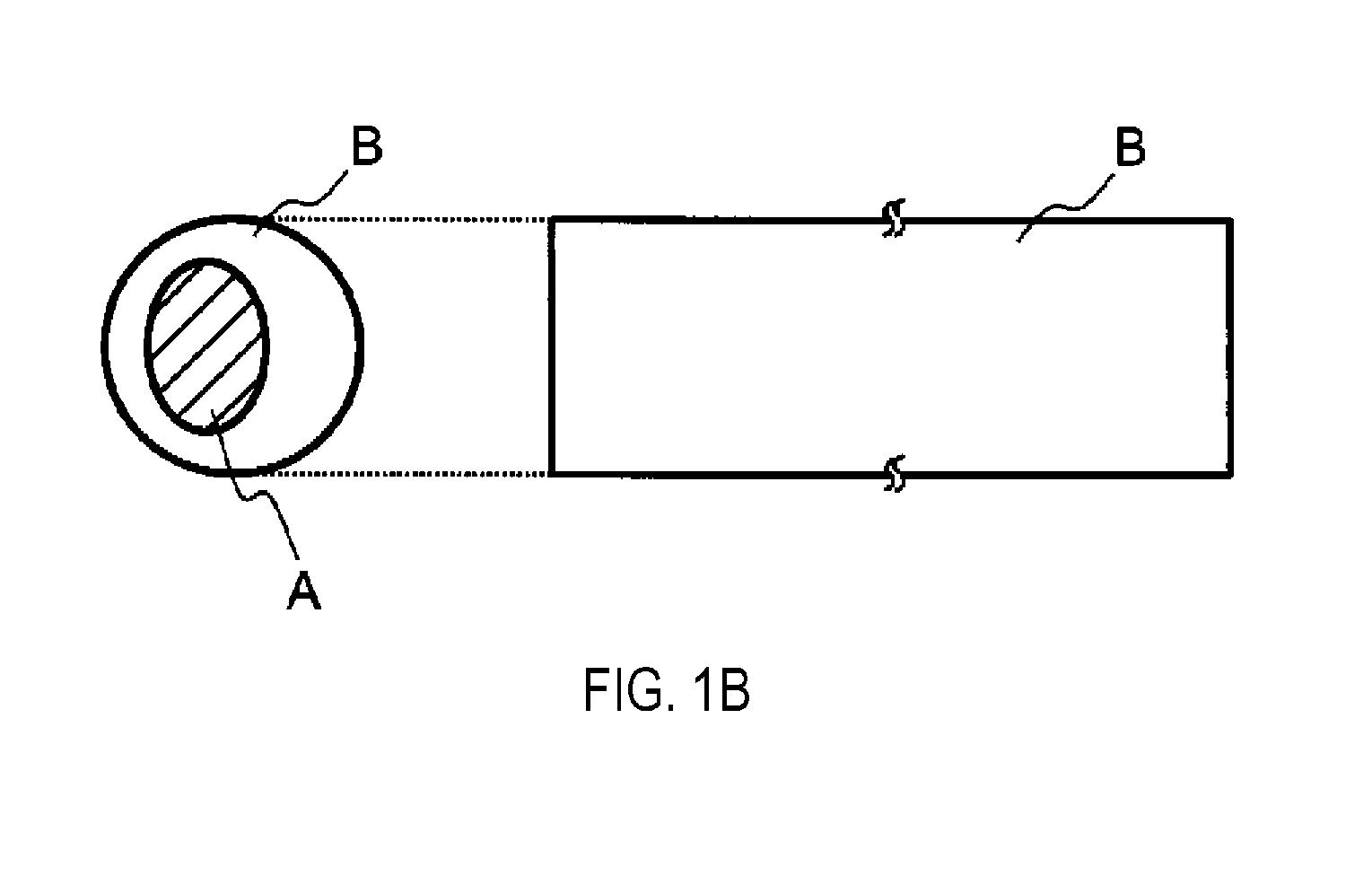
Water-disintegrable composite fiber and method for producing the same
a composite fiber and water disintegration technology, applied in the direction of yarn, melt spinning methods, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems that single fibers of polylactic acid resins or polyglycolic acid resins cannot be considered to have sufficient water disintegrability or mechanical characteristics, and the short fibers remain in the ground after well treatment, etc., to achieve high proppant dispersibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
working example 1
[0086]A PGA / PLA composite undrawn yarn was produced by using the melt spinning device illustrated in FIG. 2. A temperature-controllable heat sleeve 5 with a length of 150 mm and an inner diameter of 100 mm was mounted beneath a spinneret 4 for composite fibers of the melt spinning device. In the following explanations and drawings, elements that are identical or equivalent are labeled with the same symbols, and duplicate explanations will be omitted.
[0087]First, a pellet-formed PGA resin (made by the Kureha Corporation, weight average molecular weight: 180,000, glass transition temperature: 43° C., melting point: 220° C., melt viscosity (temperature: 240° C., shear rate: 122 sec−1: 790 Pa·s, size: 3 mm in diameter×3 mm in length) was loaded into a single-screw extruder 2a (made by Plagiken Co., Ltd., cylinder diameter: 30 mm, L / D=24) from a raw material hopper la and melted at 215 to 250° C. The cylinder temperature of the extruder 2a was set to 215 to 250° C., and the adapter tempe...
working example 2
[0092]A core-sheath type PGA / PLA composite undrawn yarn (core part: PGA resin, sheath part: PLA resin) was produced in the same manner as in Working Example 1 with the exception of regulating the volume of the molten PGA resin and the molten PLA resin so that the cross-sectional area ratio of the core part to the sheath part of the discharge port was core part / sheath part=35 / 65. The content of the PGA resin in the resulting core-sheath type PGA / PLA composite undrawn yarn is 5.7 parts by mass per 1 part by mass of the D-lactic acid units in the PLA resin.
[0093]A core-sheath type PGA / PLA composite drawn yarn (core part: PGA resin, sheath part: PLA resin) was then produced in the same manner as in Working Example 1 with the exception of changing the draw ratio to 2.5 times, and a core-sheath type PGA / PLA staple fiber (core part: PGA resin, sheath part: PLA resin) was further produced. The single fiber fineness of the resulting PGA / PLA composite drawn yarn and the mass loss and proppant...
working example 3
[0094]A core-sheath type PGA / PLA composite undrawn yarn (core part: PGA resin, sheath part: PLA resin) was produced in the same manner as in Working Example 1 with the exception of regulating the volume of the molten PGA resin and the molten PLA resin so that the cross-sectional area ratio of the core part to the sheath part at the discharge port was core part / sheath part=50 / 50. The content of the PGA resin in the resulting core-sheath type PGA / PLA composite undrawn yarn is 10.5 parts by mass per 1 part by mass of the D-lactic acid units in the PLA resin.
[0095]A core-sheath type PGA / PLA composite drawn yarn (core part: PGA resin, sheath part: PLA resin) was then produced in the same manner as in Working Example 1 with the exception of changing the draw ratio to 2.5 times, and a core-sheath type PGA / PLA staple fiber (core part: PGA resin, sheath part: PLA resin) was further produced. The single fiber fineness of the resulting PGA / PLA composite drawn yarn and the mass loss and proppan...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com