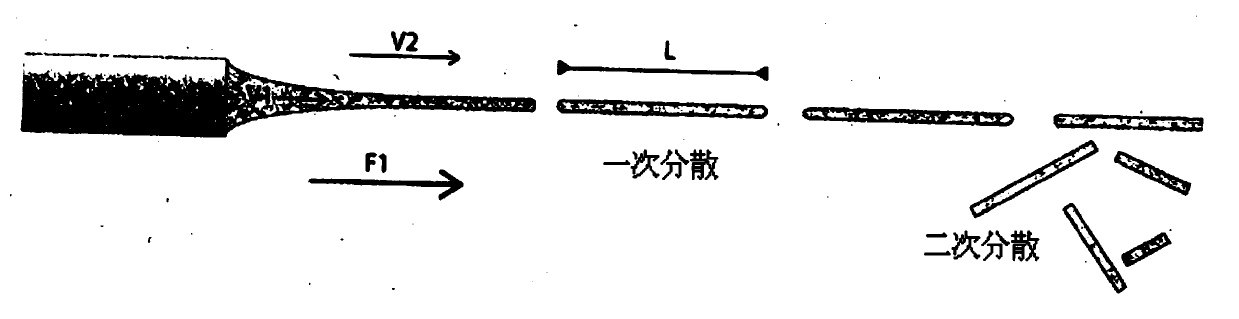
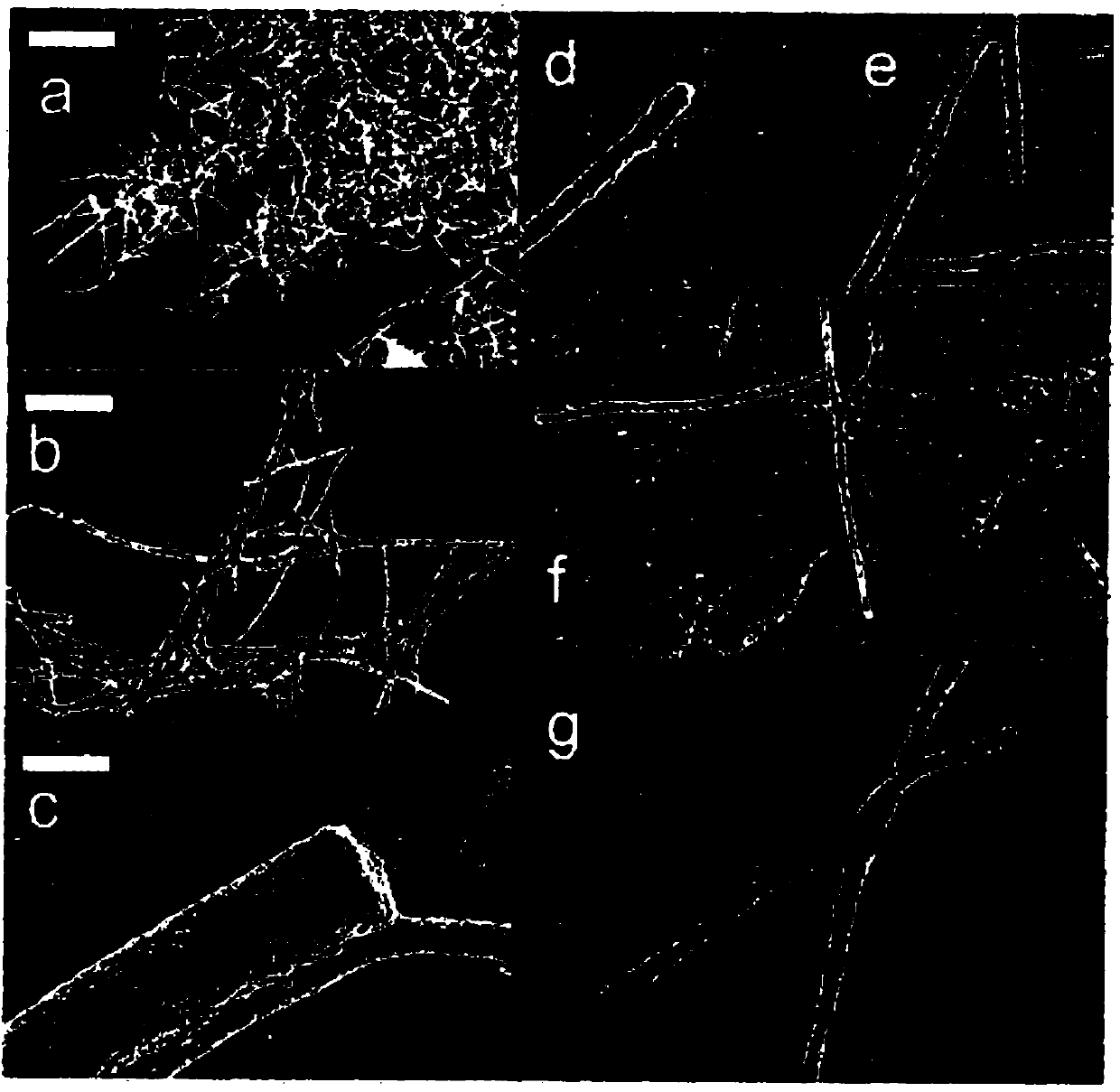
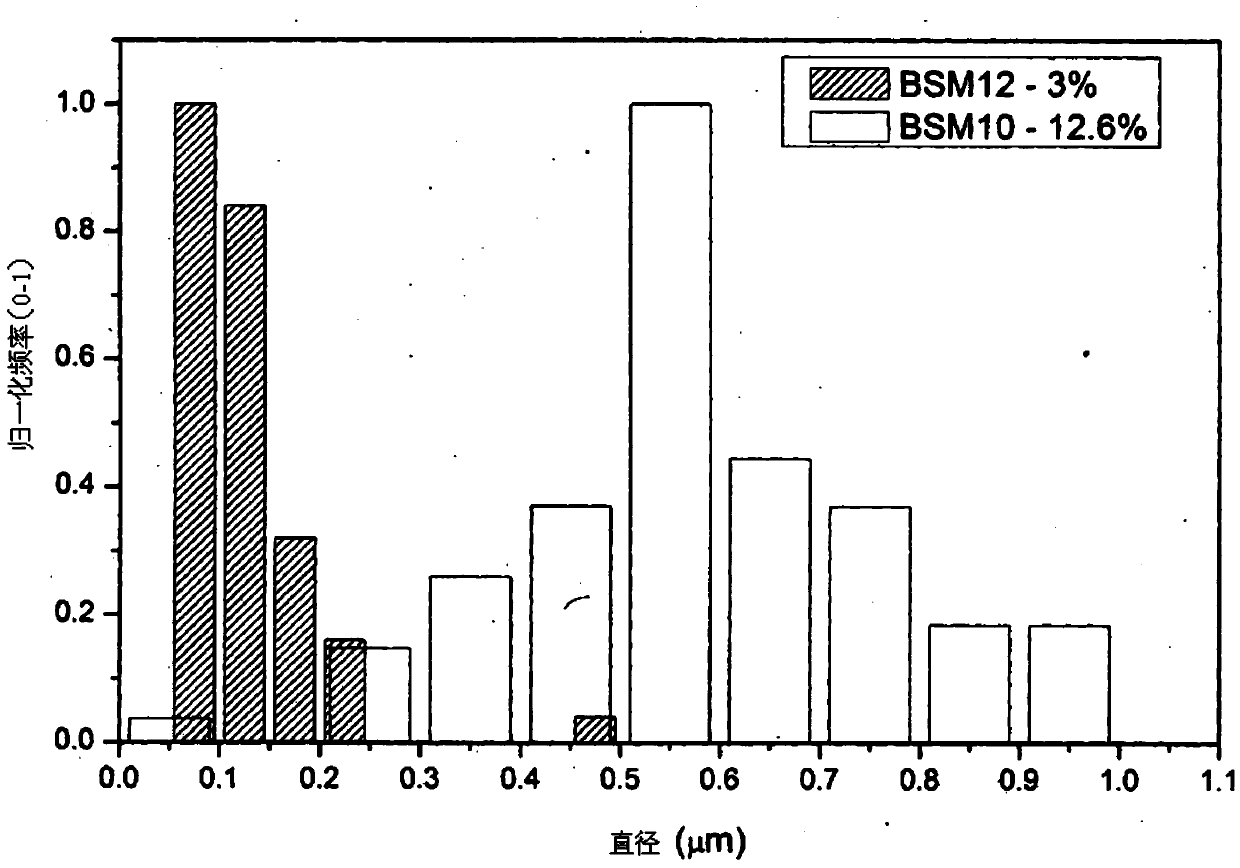
Fibre-forming process and fibres produced by the process
A fiber forming and fiber technology, applied in the direction of short fiber formation, fiber processing, fiber chemical characteristics, etc., can solve the problems of low productivity, difficult post-processing of polymer fibers, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0201] The following examples further illustrate the invention, but the examples should in no way be construed as limiting the scope of the invention as described herein.
[0202] General Experimental Procedure
[0203] Polymer solutions are prepared by dissolving the desired amount of polymer in a solvent with stirring. If necessary, the solution may be treated with heat, acid or base to aid dissolution of the polymer.
[0204] A volume of the selected dispersion medium (250-400ml) is introduced into a suitable vessel and a shear head with a high speed mixer (eg: T50 UltraTurrax - IKA fitted with a high shear impeller) is then submerged in it.
[0205] After starting stirring, the required volume of fiber forming liquid (eg 3-5 ml) is introduced into the gap between the mixer head and the beaker wall by means of injection (ie using a syringe pump). In the reported example, a 3 mL syringe with a 23G needle was used to inject the fiber forming liquid, and the injection speed ...
example 89
[0231] Preparation of Poly(ethylene-co-acrylic acid)(PEAA) Fibers from Magnetic Nanoparticles
[0232] Poly(ethylene-co-acrylic acid) (PEAA) (Dow Chemical, Primacor TM 59901) in a 20% wt / vol solution, stirred overnight at 95°C. Magnetic nanoparticles were then added to this solution, and then diluted with pH 12 ammonia to a final solution concentration of 8% (w / v) PEAA. 1-Butanol (250ml) was added to a beaker of a high speed mixer (T50 UltraTurrax-IKA) equipped with a high shear impeller. Insert the stir head into the beaker and start stirring. The polymer solution (3ml) with magnetic nanoparticles was then rapidly injected into the gap between the mixer head and the beaker wall using a 3mL syringe with a 27G needle, injection speed: 20mL / min. Stirring was continued for a certain period of time and then stopped. The resulting fibers were washed with the precipitation medium (n-butanol).
[0233] The magnetic nanoparticles were encapsulated with PEAA fibers, and as Figur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com