Emulsion-based control of electrospun fiber morphology
a technology of electrospun fibers and morphology, applied in the field of emulsion-based control of electrospun fiber morphology, can solve the problems of inability to predict the formation of such fibers, the instability of liquid droplets, and few attempts to alter the geometry of electrospun fibers, so as to achieve the effect of controlling the morphology of fibers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
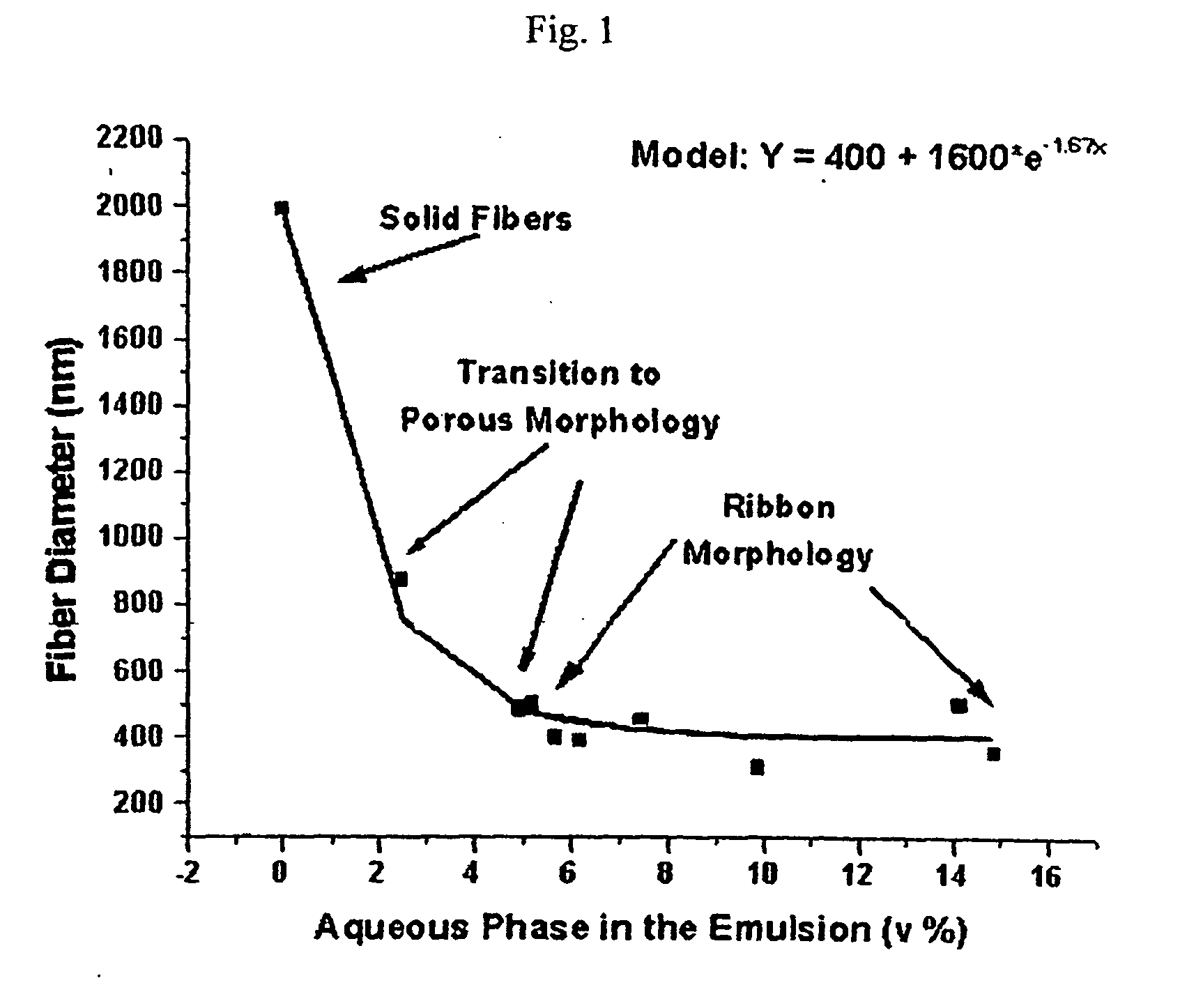
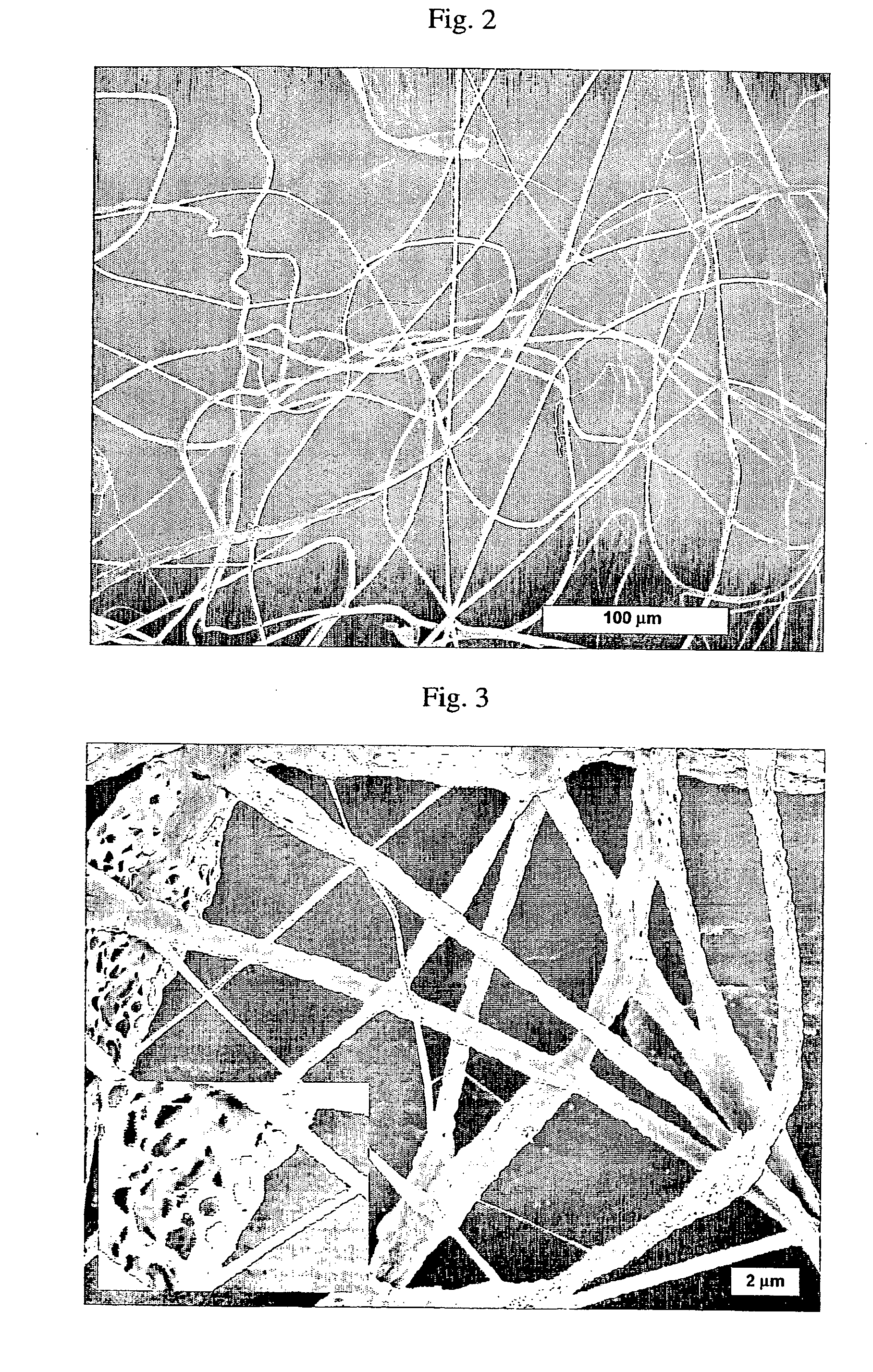
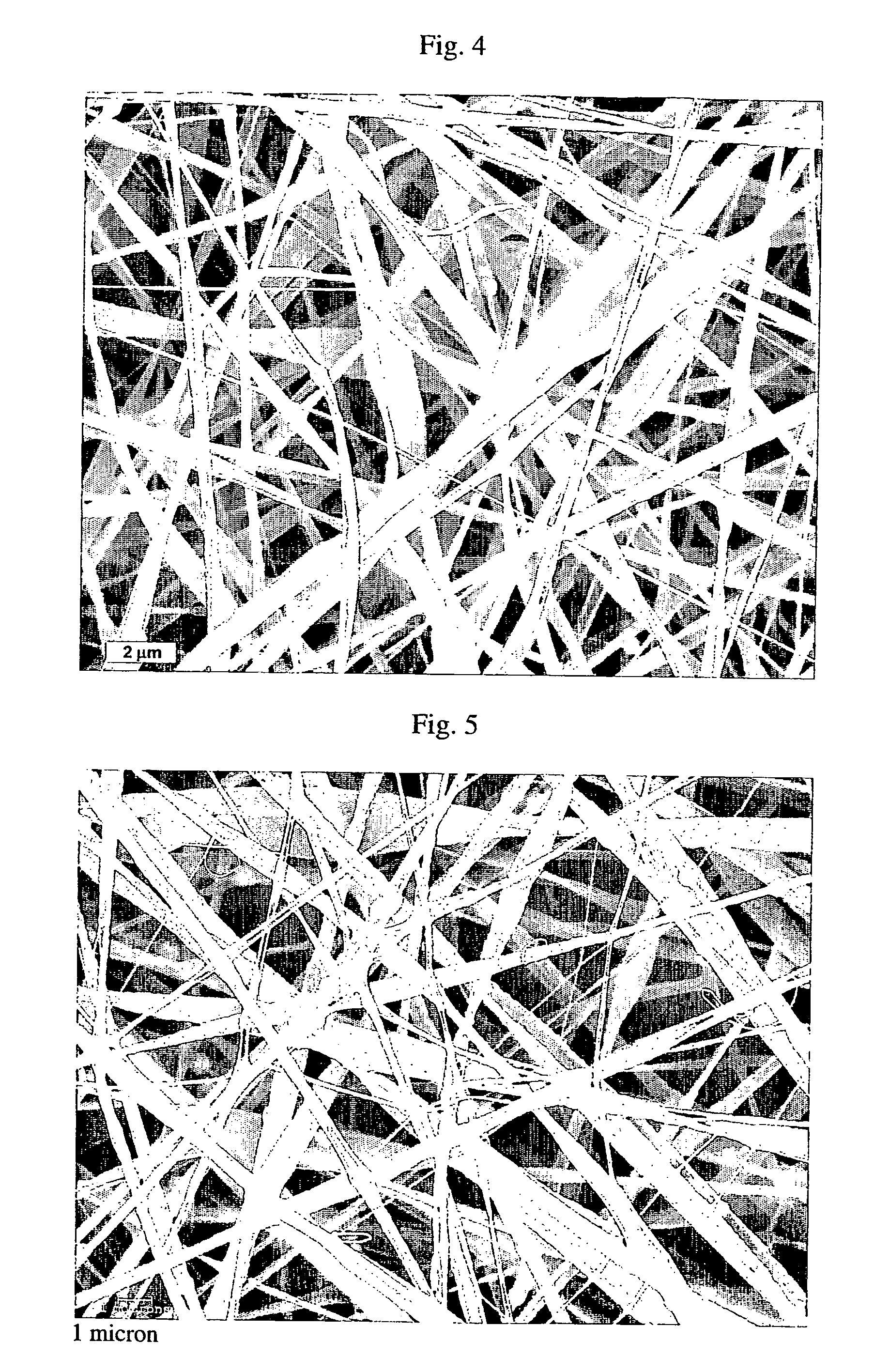
[0051] As a non-limiting example, the invention will be described based on the effect of a water / oil emulsion on the morphology of poly(L-lactic acid) (PLA) fibers obtained by ES.
[0052] Materials: Poly(L-lactic acid) (MW=300,000) (PLA) was purchased from Polysciences, Inc. (Warrington, PA). Poly(vinyl alcohol) (MW=10,000, 85% hydrolyzed) (PVA) and 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (99.5%) (NMP) were purchased from Aldrich Chemical Co (Milwaukee, Wis.). Chloroform (HPLC grade, 99.8%) was purchased from Fisher Scientific (Pittsburgh, Pa.). Poly(acrylic acid) coated Silica colloids 500 nm in diameter were produced by a sol-gel process. All chemicals were used as received without further purification unless otherwise noted.
[0053] Preparation of Polymer Solutions. Water-in-oil (W / O) emulsion of PLA was prepared by emulsifying a 2% stock of PLA in chloroform with 5% PVA solution in water and a fixed volume of NMP (Table 1). NMP was added to the mixture to serve as a phase compatibilizer (NMP is ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com