Method for fabricating superfine fiber by flash vaporization
A superfine fiber and flash technology, which is applied in the direction of flash spinning, spinning solution preparation, etc., can solve the problems of increasing cost and not easy to control the process flow, and achieve cost reduction, simplification of spinning process and equipment, and reduction of The effect of operational risk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Use the method described in the invention to spin polyethylene ultrafine fibers.
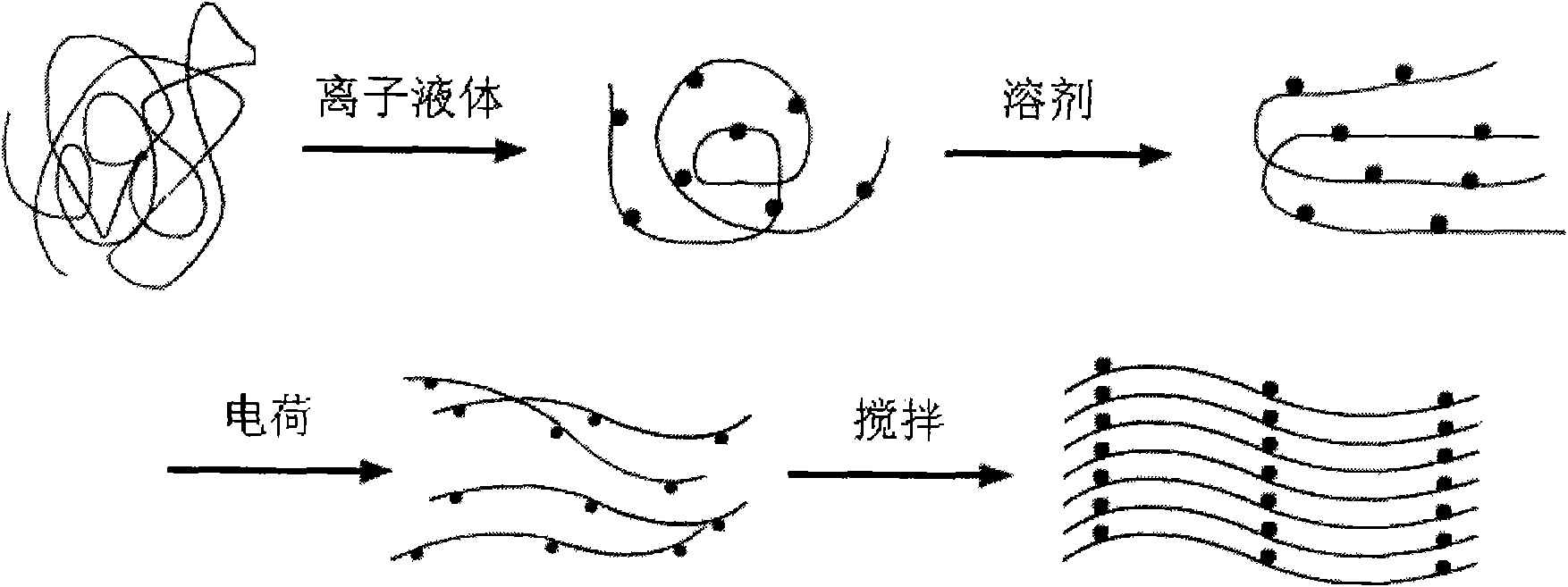
[0015] First put 10g of polyethylene monomer and 10ml of 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium chloride into the autoclave, stir evenly, and let it stand for pretreatment for 1 hour, then add 100ml of 1,2-dichloroethane, Heat and pressurize the autoclave, and stir for 20 minutes at a heating temperature of 200°C and a pressurization pressure of 15 MPa to fully dissolve the polyethylene; then open the autoclave discharge control valve to rapidly eject the spinning solution, and the solvent instantly Vaporization and high-stretching of polyethylene fibers, and self-separation, three-dimensional network polyethylene ultra-fine fiber filaments are obtained on the receiving device.
[0016] After inspection, the diameter of the polyethylene ultrafine fiber prepared in this embodiment is between 200 nm and 5 μm, with an average value of 1 μm, and the fiber strands have a cluster or three-dimensional net...
Embodiment 2
[0018] Use the method described in the present invention to spin polyester microfibers.
[0019] First put 6g of polyester monomer and 12ml of 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium chloride into the autoclave, stir evenly, and pre-treat for 2 hours, then add 150ml of chloroform, heat and pressurize the autoclave, Stir for 30 minutes at a temperature of 350°C and a pressure of 20 MPa to fully dissolve the polyester; then open the discharge valve of the autoclave to spray out the spinning solution quickly, and the solvent is instantly vaporized and the polyester fiber is stretched at a high rate and separated by itself. Silk, three-dimensional network polyester microfiber filaments are obtained on the receiving device.
[0020] After inspection, the diameter of the polyester ultrafine fiber prepared in this embodiment is between 100 nm-10 μm, with an average value of 1 μm, and the fiber strands are in a cluster or three-dimensional network structure.
Embodiment 3
[0022] The polyvinylidene fluoride superfine fiber is spun by using the method described in the invention.
[0023] First put 12g of vinylidene fluoride monomer and 25ml of 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium chloride into the autoclave, stir evenly, let it stand still for 1.5 hours, then add 140ml of cyclohexane; Stir for 25 minutes at a temperature of 220°C and a pressure of 16 MPa to fully dissolve the vinylidene fluoride; then open the discharge valve of the autoclave to spray out the spinning solution quickly, and the solvent is instantly vaporized and the polyvinylidene fluoride fiber is drawn at a high speed. Stretch and separate the filaments by itself, and obtain three-dimensional network polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafine fiber filaments on the receiving device.
[0024] After inspection, the diameter of the polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafine fibers prepared in this example is between 200 nm and 10 μm, with an average value of 1 μm, and the fiber strands are in a cluster or t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com