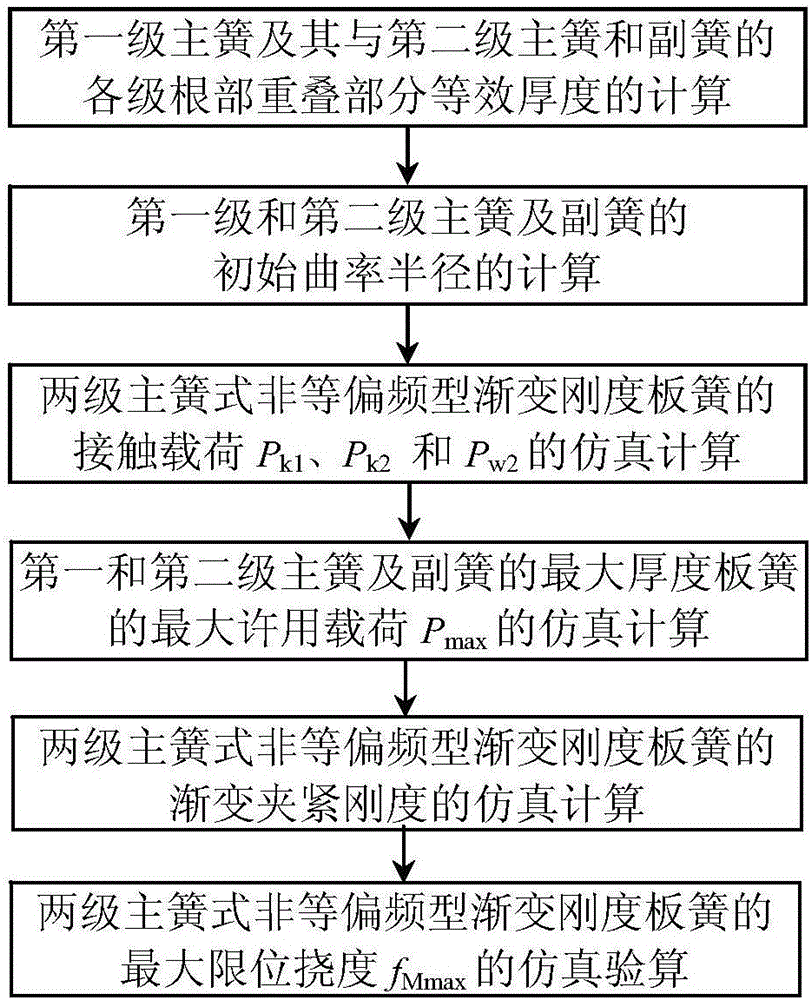
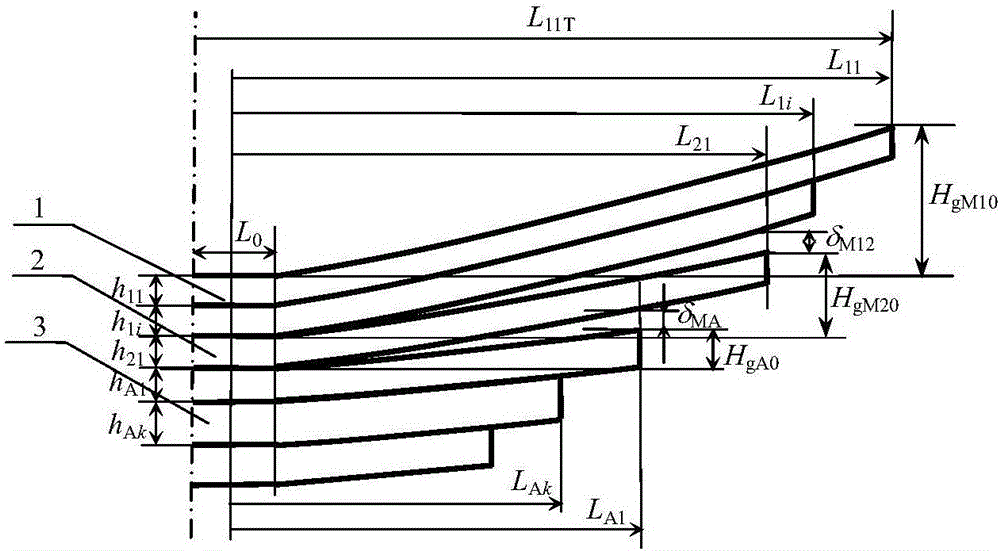
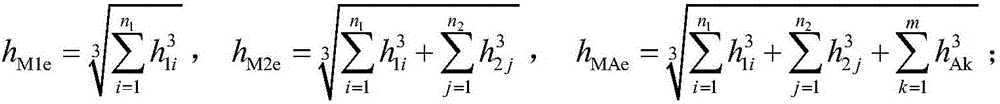Simulating checking calculation method for limiting flexibility of two-stage main spring type non-equal offset-frequency type gradual-change-rigidity plate spring
A main spring and leaf spring technology, which is applied in the field of simulation and test algorithm for the limit deflection of the offset-frequency gradient-stiffness leaf spring, which can solve the problems of complex and unsatisfactory deflection calculation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0052] Embodiment: The width b of a certain two-stage main spring type unequal-bias frequency gradual stiffness leaf spring is 63 mm, half of the clamping distance of the saddle bolt L 0 =50mm, elastic modulus E=200GPa, maximum allowable stress [σ]=800MPa. Number of primary reeds n 1 = 2, the thickness h of each piece of the first stage main spring 11 = h 12 =8mm, half of the effective length L of the first leaf of the first stage main spring 11T =525mm, half of the clamping length L 11 = L 11T -L 0 / 2=500mm. Second stage main reed number n 2 = 1, thickness h 21 =8mm, half the effective length L of the first leaf of the second-stage main spring 21T =350mm, half of the clamping length L 21 = L 21T -L 0 / 2=325mm. The number of secondary reeds m = 2, the thickness of each secondary reed h A1 = h A2 =13mm; half of the effective length L of the first leaf of the auxiliary reed A1T =250mm, half of the clamping length is L A1 = L A1T -L 0 / 2=225mm. The initial tan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com