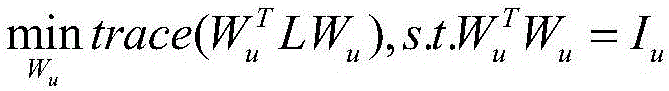Semi-supervised face recognition method based on local information and group sparse constraints
A local information and face recognition technology, applied in the field of semi-supervised face recognition, can solve the problems of low recognition accuracy, only consideration, and large consumption of time and space resources, so as to achieve excellent learning effect, improve accuracy, Effect of suppressing disturbance of noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0056] The technical solutions of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
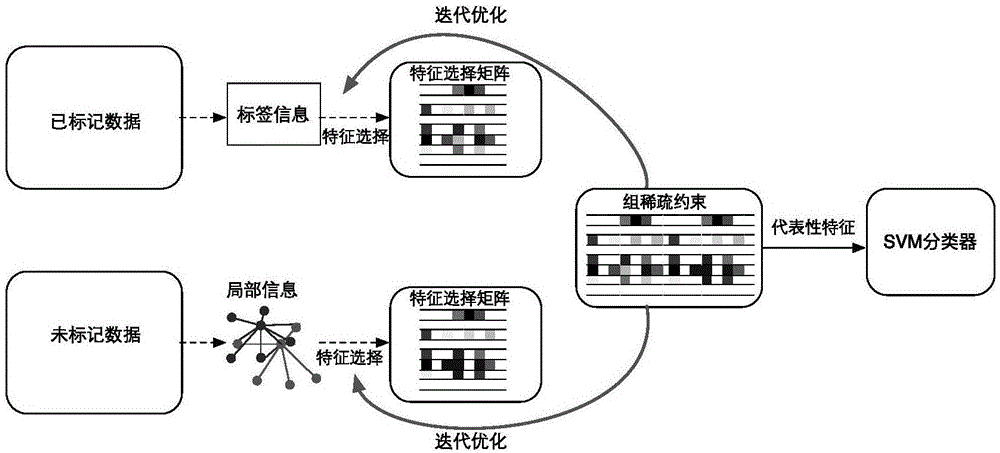
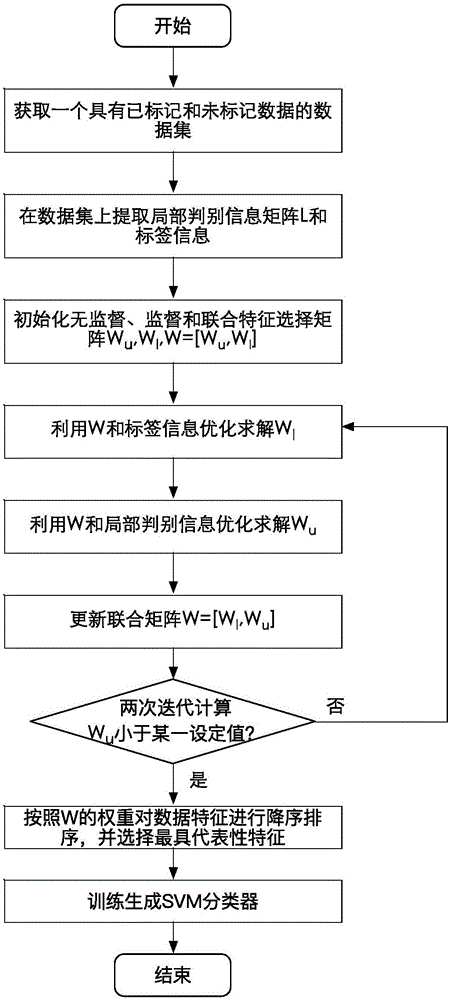
[0057] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the present invention provides a semi-supervised face recognition method based on local information and group sparse constraints, comprising the following steps:
[0058] (1) Obtain a face dataset X∈R containing n high-dimensional datad×n , where d is the data dimension, the face dataset contains m labeled datasets X l ∈ R d×m and the corresponding label matrix Y l ∈ R m x c , where c is the classification number of face data.
[0059] (2) On the data set X, construct an unsupervised face feature selection model based on local information constraints;
[0060]
[0061] Among them, I u ∈ R c×c is the identity matrix of order c, and L is defined as follows:
[0062]
[0063] Among them, I d ∈ R d×d is the identity matrix of order d, is the i-th data x in the data set X i A d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com