Decoupling four-degree-of-freedom telecentric mechanism for celiac minimally invasive surgery
A technology of minimally invasive surgery and degree of freedom, applied in the field of medical robots, can solve the problems of high processing precision, heavy end effector weight, and difficult control, etc., and achieve the effect of small moment of inertia, simple structure, and weight reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
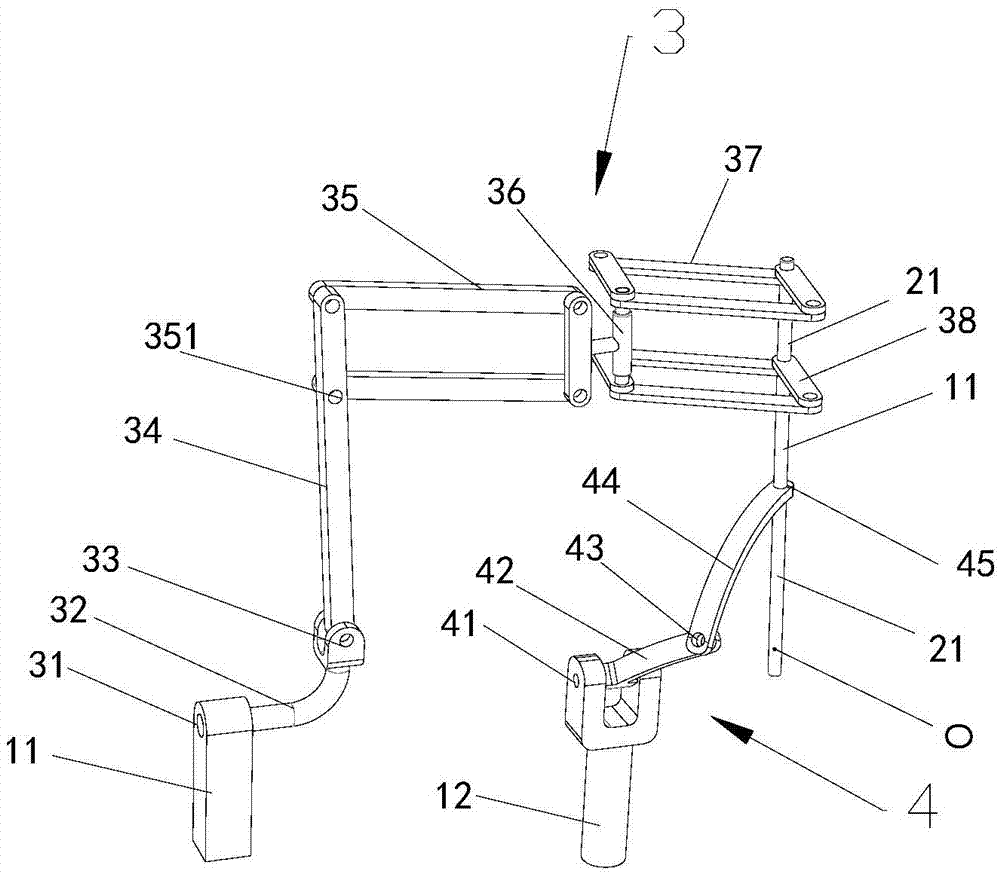
[0023] see figure 1 , with reference to figure 2 , image 3 , the decoupling four-degree-of-freedom telecentric mechanism used in abdominal minimally invasive surgery of the present invention includes a frame 1, an end effector 2, a first motion branch chain 3 and a second motion branch chain 4; the frame is provided with a first bracket 11 and the second bracket 12.
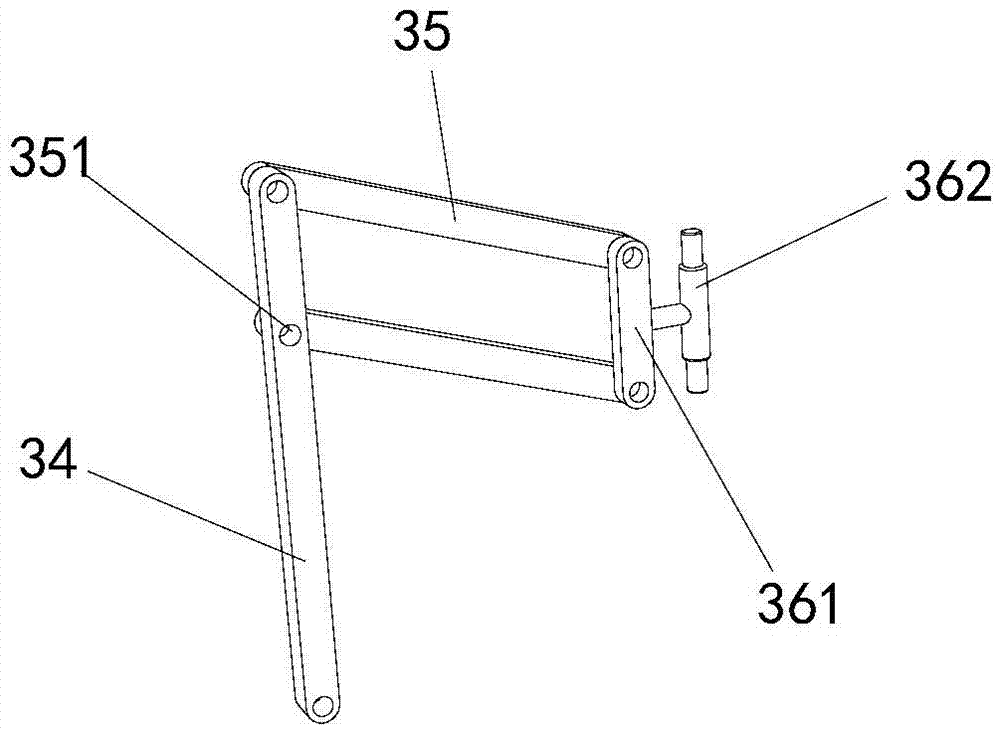
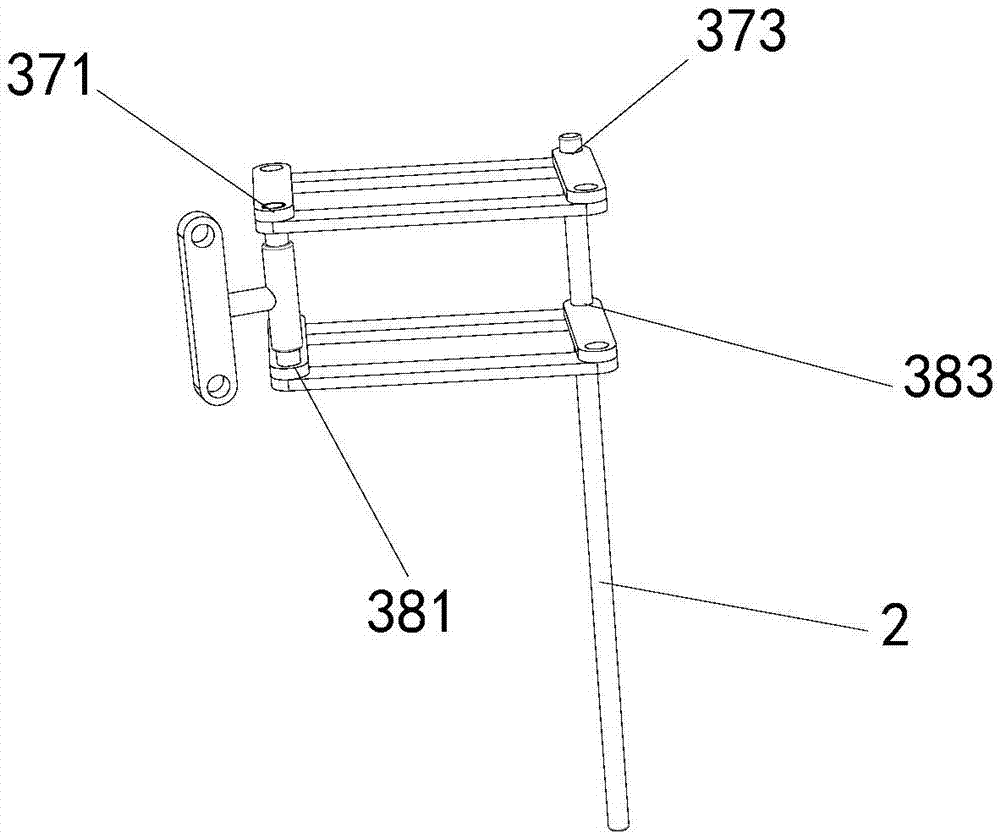
[0024] The first kinematic branch chain 3 in the present invention includes the first rotating pair 31, the first rod 32, the second rotating pair 33, the second rod 34, the first parallelogram structure 35, the third rod connected by sequential transmission. 36. The second parallelogram structure 37 and the third parallelogram structure 38; wherein the first rotating pair 31 is rotatably connected to the first bracket 11, the first parallelogram structure 35 is vertically arranged and can be vertically deformed, and the second parallelogram structure The structure 37 and the 3rd parallelogram structure 38 a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com