Buffer hip joint
A technology of hip joints and inner holes, applied in the direction of hip joints, joint implants, joint implants, etc., can solve problems such as mechanical strength, uneven elastic modulus, affecting functions, hidden quality problems, etc., and achieve good structural mechanics Performance, slow down severe impact, prevent the effect of excessive load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
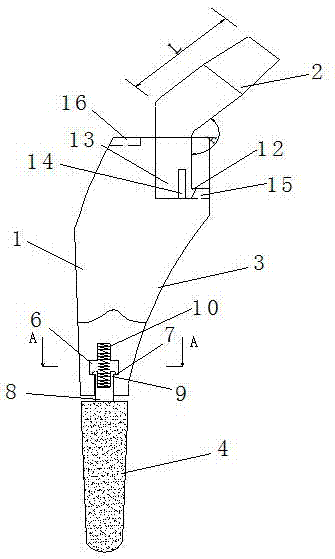
[0031] As attached Figure 1-3 As shown, a cushioning hip joint includes a femoral stem 1, a femoral neck 2 and a spring 10; the femoral stem 1 is split into two parts, a proximal end 3 and a distal end 4; the proximal end 3 has a head An L-shaped through hole 5, and a positioning hole 16 is additionally provided on the head of the proximal end 3; the lower part of the femoral neck 2 is in the shape of a positive cylinder, and the upper part is set as an offset inclined column; the lower end of the femoral neck 2 consists of two parts The lower part of the femoral neck 2 is inserted into the L-shaped through hole 5, and the barb 12 and the column 13 are provided with a gap 14 between the barb 12 and the column 13; The 12 hook is clamped in the transverse hole 15 on the L-shaped through hole 5; the lower part of the proximal end of the femoral stem 1 is provided with an inner hole 6. The middle cavity of the inner hole 6 is cylindrical, and the inner diameter of the middle cavity...
Embodiment 2
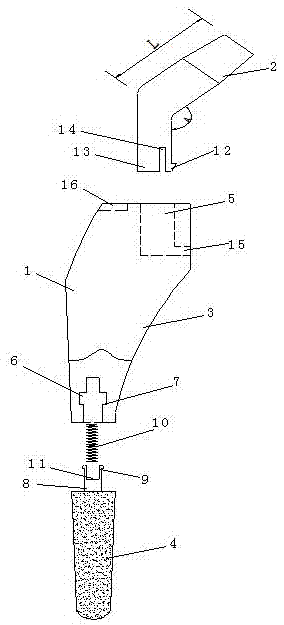
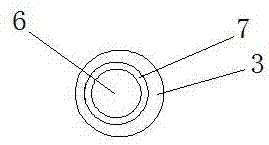
[0043] As attached Figure 4-5 As shown, a cushioning hip joint includes a femoral stem 1, a femoral neck 2 and a spring 10; the femoral stem 1 is split into two parts, a proximal end 3 and a distal end 4; the proximal end 3 has a head L-shaped through hole 5; the lower part of the femoral neck 2 is in the shape of a positive cylinder as a whole, and the upper part is set as an offset inclined column; the lower end of the femoral neck 2 is composed of two parts, one of which is a barb 12 and the other is a columnar body 13, and a gap 14 is provided between the barb 12 and the column 13; the lower part of the femoral neck 2 is inserted into the L-shaped through hole 5, and the barb 12 is hooked to the transverse hole 15 on the L-shaped through hole 5. The lower part of the proximal end of the femoral stem 1 is provided with an inner hole 6, which is provided with two symmetrically distributed intermittent stepped surfaces 7; its distal end 4 is made of multi-level hole material,...
Embodiment 3
[0054] As attached Image 6 As shown, a cushioning hip joint includes a femoral stem 1 and a femoral neck 2. The femoral stem 1 is split into two parts, a proximal end 3 and a distal end 4; the head of the proximal end 3 is provided with an L-shaped pass Hole 5; the lower part of the femoral neck 2 is in the shape of a positive cylinder as a whole, and the upper part is set as an offset inclined column; the lower part of the femoral neck 2 is inserted into the L-shaped through hole 5 through an interference fit; the proximal end of the femoral stem 1 The lower part is provided with an inner hole 6, which is provided with a continuous annular stepped surface 7; its distal end 4 is made of multi-stage hole material, and the head of the distal end 4 is additionally provided with a connecting rod 8. The end of the rod 8 is provided with an elastic barb 9; the connecting rod 8 is inserted into the inner hole 6, and the elastic barb 9 is hooked at the stepped surface 7 in the inner ho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com