Generalized approximate modeling method based on fitting sensitivity for aero-engine performance, and model application
An aero-engine and approximate model technology, which is applied in the field of generalized approximate modeling and model application of aero-engine performance based on fitting sensitivity, can solve problems such as over-fitting and under-fitting, and achieve reasonable fitting and good generalization The effect of the ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0036] Specific implementation mode one: the specific process of the generalized approximate modeling method based on the aeroengine performance of fitting sensitivity is:
[0037] Fit Sensitivity Analysis
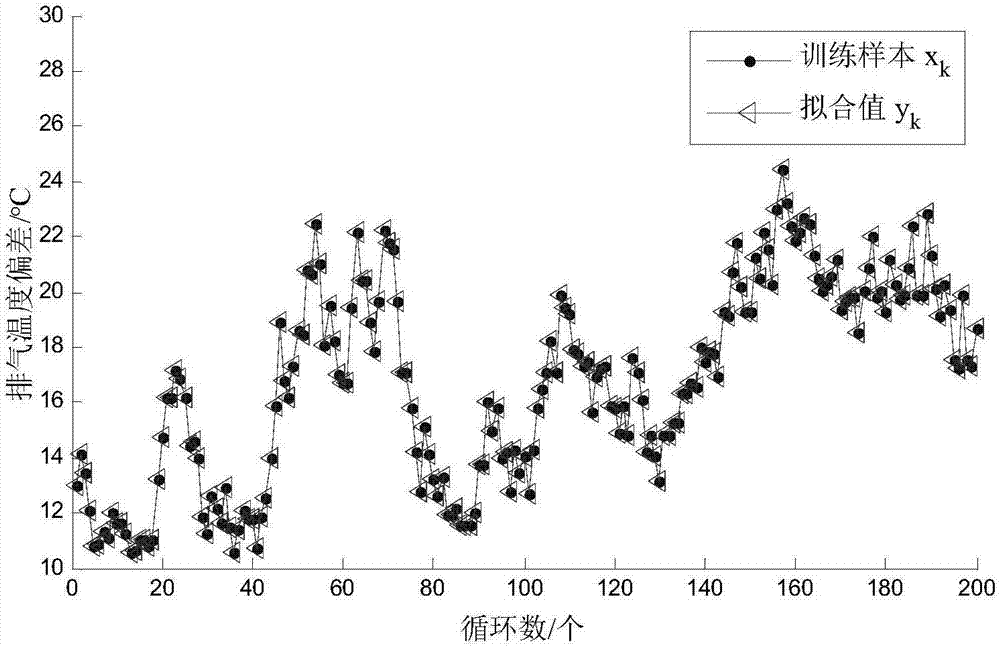
[0038] Denote the training samples as X=[x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x n ], the fitting value is expressed as Y=[y 1 ,y 2 ,...,y n ], then when X and Y have the same initial value (x 1 =y 1 ), the degree of fit can be expressed as the fitted sensitivity model dY / dX.
[0039] (a) When dY / dX→1, y k to x k Overfitting, that is, △Y≈△X. Fitted value y k The change trend of x k consistent, such as figure 1 shown.
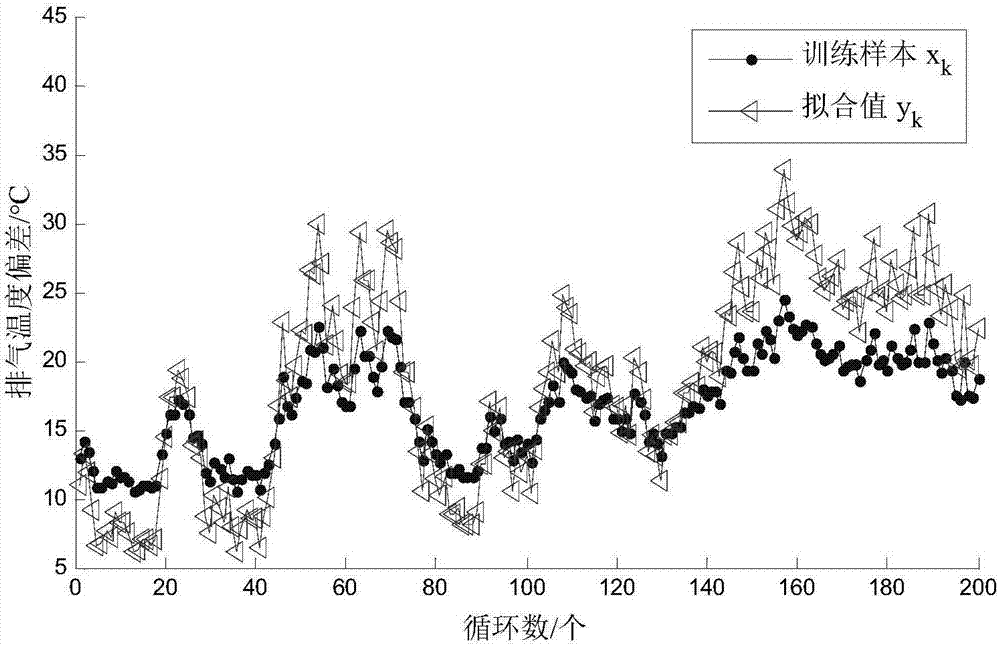
[0040] (b) When dY / dX>1, y k to x k Underfitting and △Y>△X, such as figure 2 shown. Fitted value y k Expanded training sample x k The trend of change, at this time y k is unstable and with x k Oscillation due to the change of , thus obtaining unstable prediction results. This state is called "over-underfitting".
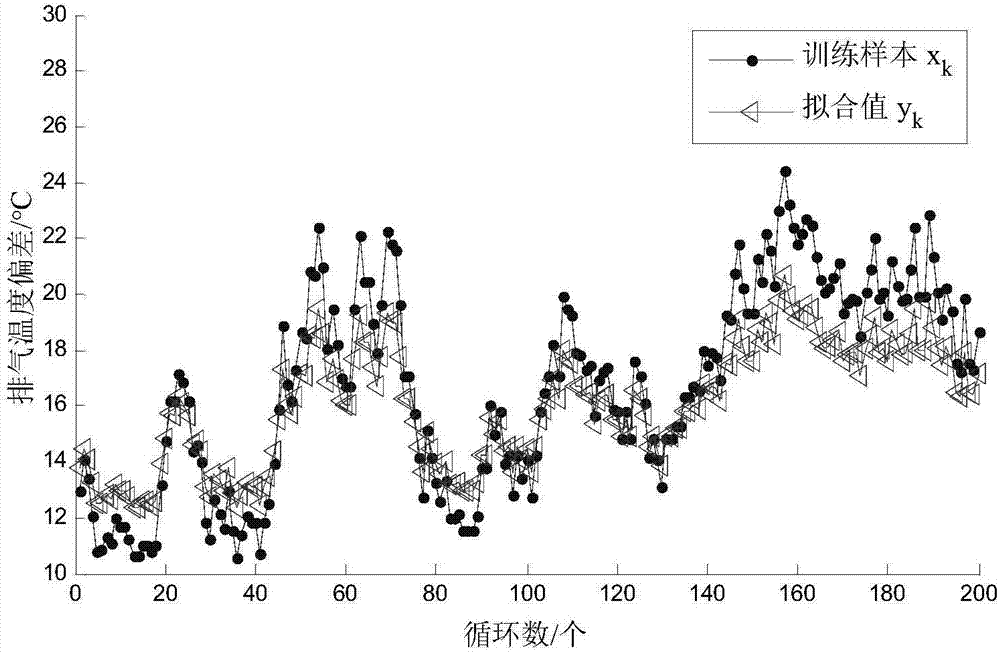
[0041] (c) When 0k to x k Underfitting an...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0068] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the specific process of establishing the generalized approximate model of the aeroengine performance based on the fitting sensitivity in the step one is:
[0069] Set the value of dY / dX in the interval (0, 1), when x 1 =y 1 When building a fitted sensitivity model:
[0070]
[0071] where X=[x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x n ] is the training sample, Y=[y 1 ,y 2 ,...,y n ] is the fitting value;
[0072] (a) when|x k -y k | becomes larger, the fitted value y k Deviate from the training sample x k . because the fitted value y k Should reflect the main trend of the training sample, so the training sample x k Contains strong noise and fluctuations. in order to make y k Get the slower main trend, y k to x k The sensitivity of dy k / dx k should be lowered.
[0073] (b) When|x k -y k | becomes smaller, the fitted value y k Approximate training samples x k . because the ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0089] Embodiment 3: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 in that the value of p is set in step 21: 1
[0090] When training the prediction model parameters, due to the large number of training samples, it is difficult to ensure that any sample segment will not be over-fitting. In order to improve the prediction accuracy, only the last p sample points of the training samples are constrained to satisfy the suppression of over-fitting. Underfitting constraints. The maximum length of p can be taken to the training sample length n, and the minimum can be taken to be 1, that is, p∈[1,n] and p∈N.
[0091] When p→1, the model only constrains the last few points, so that the fitted value of the training sample does not fall into overfitting and underfitting, but few points do not contain x k trend information, leading to inaccurate forecast results.
[0092] When p→n, the model constrains the entire training sample segment so that the fitted value of the tr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com