Random shortest path realization method based on hierarchical structure learning automaton
A technology of hierarchical structure and implementation method, applied in the field of information processing, to achieve the effect of high sampling cost, high accuracy and fast speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
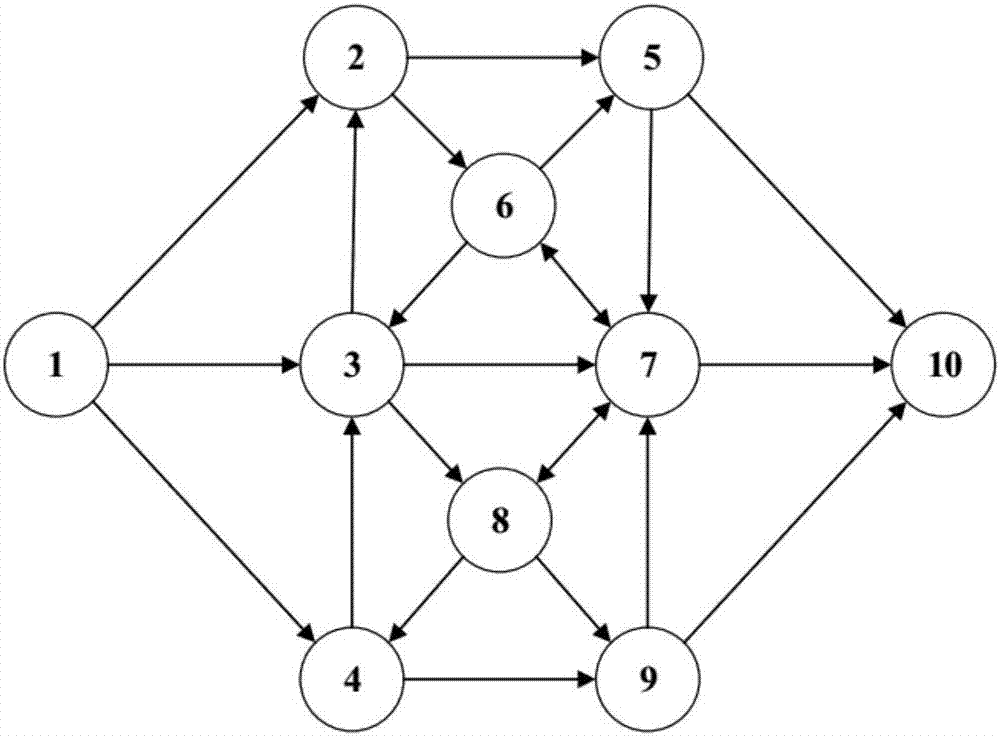
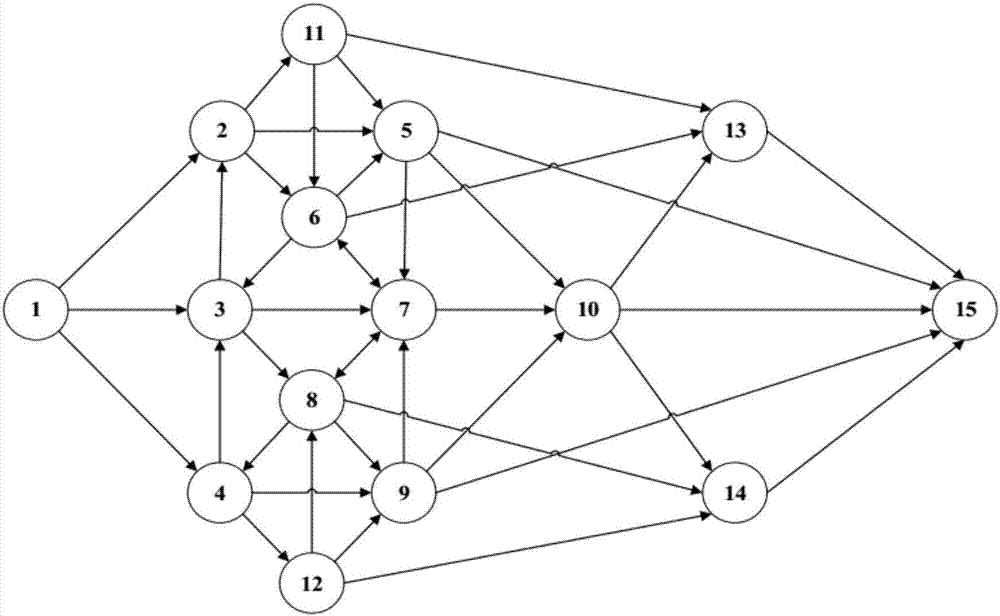
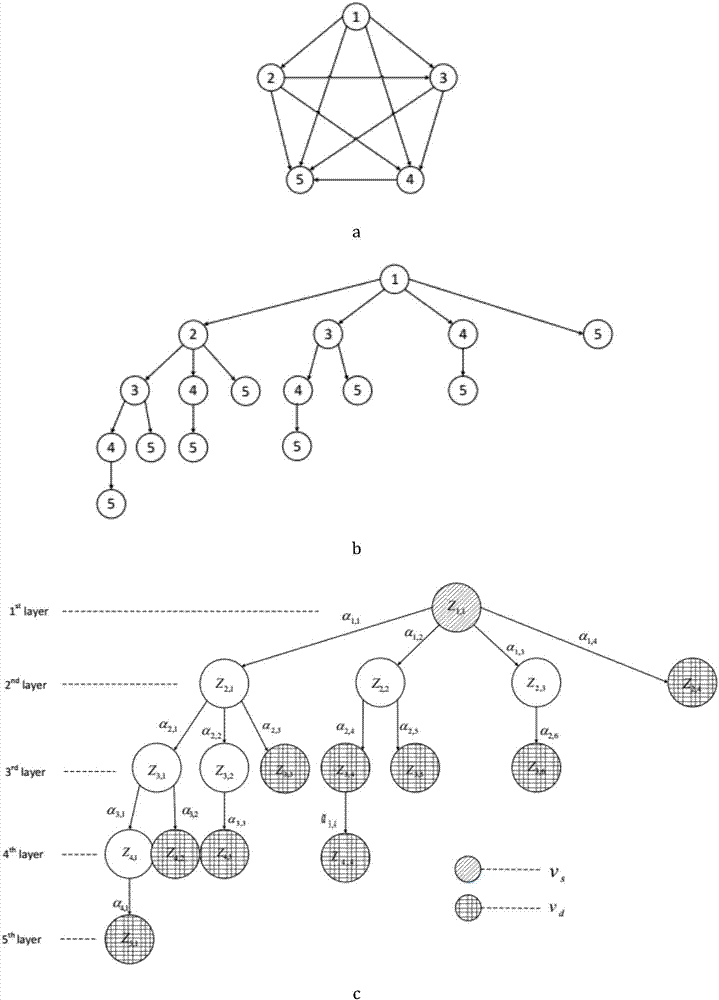
[0026] Such as image 3 a~ image 3 As shown in d, this method specifically implements the initialization of the hierarchical structure network in the following manner: with image 3 a as an example, from the source node v s set off at v s Deploy a learning automaton on , the number of behaviors of the learning automaton is equal to v s out degree; from v s Each neighbor node v of 2 Departure, in each v 2 Deploy a learning automaton on each of them, the number of behaviors is equal to v 2 out degree; then from v 2 Each neighbor node v of 3 Start, deploy the learning automata layer by layer in the same way until the target node v d The deployment of the learning automata is completed; finally delete the nodes that have not deployed the learning automata, thus forming a hierarchical network of learning automata, such as image 3 As shown in b; each learning automaton completes the initialization work independently, and initializes their respective probability vectors a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com