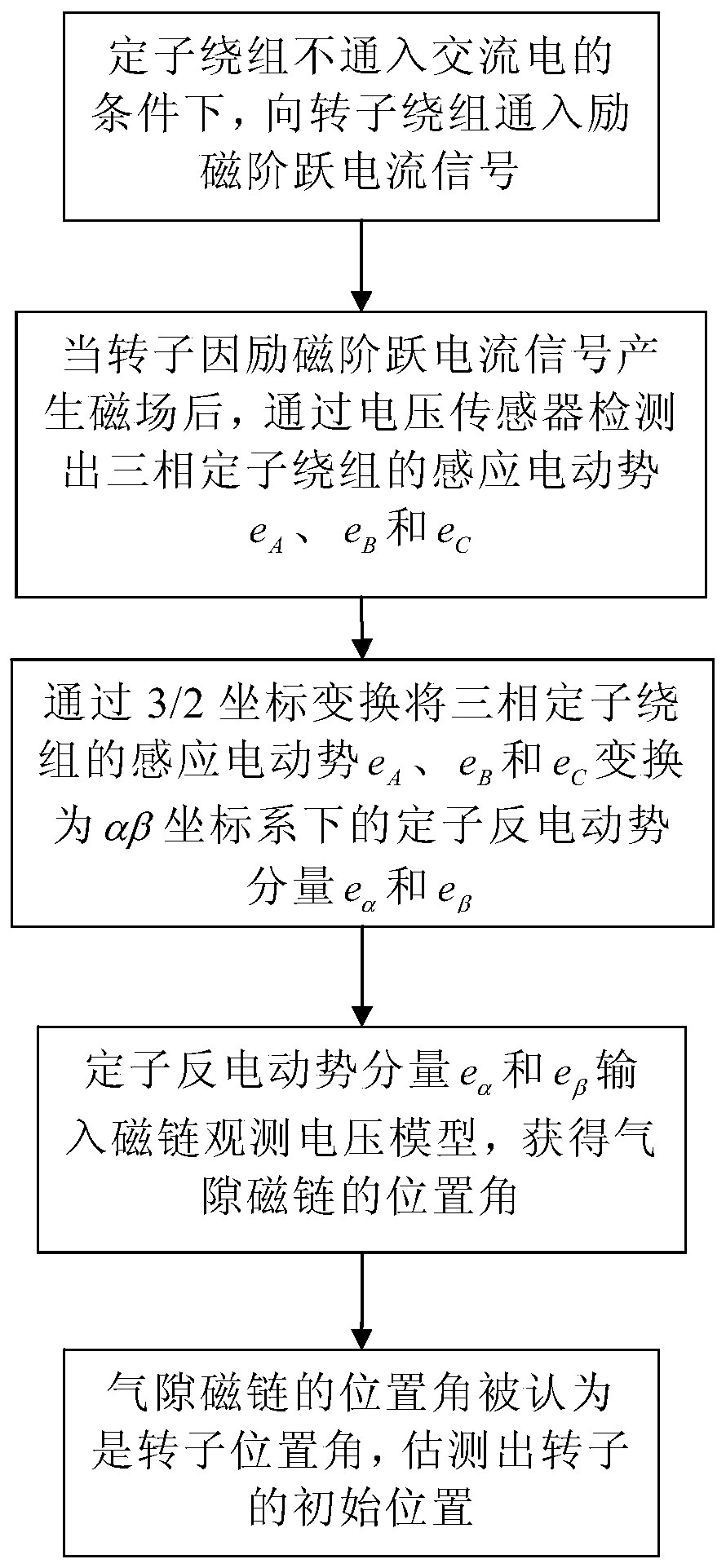
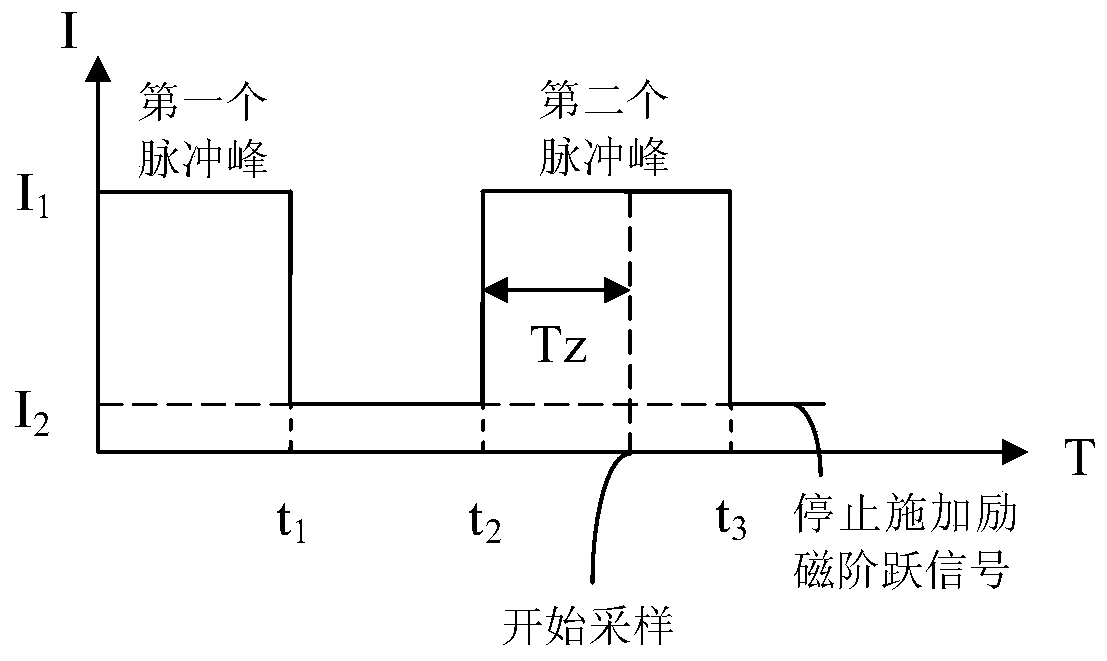
Estimation Method of Initial Rotor Position of Electrically Excited Synchronous Motor
A technology of rotor initial position and synchronous motor, applied in the direction of motor generator control, electronic commutation motor control, control generator, etc., can solve the problems of reduced system reliability, complex algorithm, and inability to guarantee the accuracy of estimation results, etc., to achieve The algorithm is simple and practical, there is no hardware signal interference problem, and the effect of expanding the scope of application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
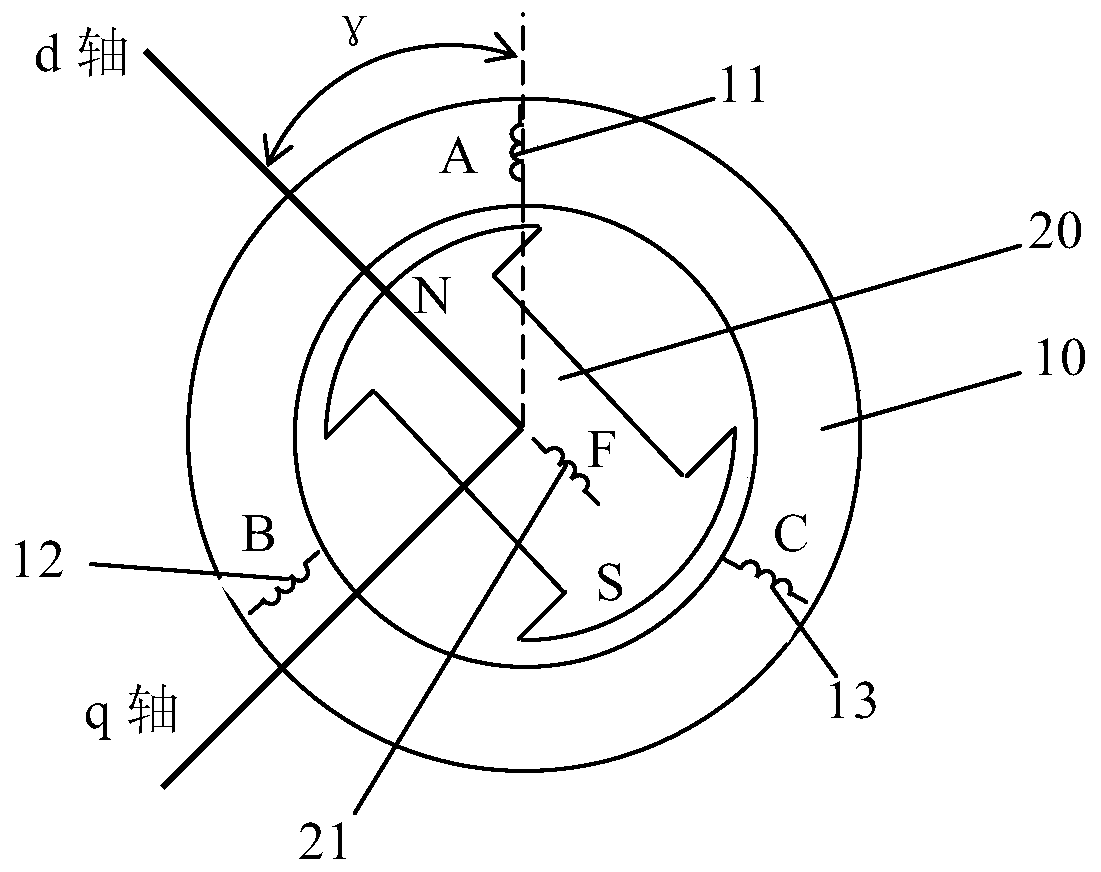
[0025] The estimation method of the present invention is designed for various types of electric excitation synchronous motors, figure 1 The structure diagram of a three-phase two-pole electric excitation synchronous motor is given as an example. Since the electric excitation synchronous motor is a well-known device in the field, it will not be described in detail here, but only briefly introduced. like figure 1 , the electric excitation synchronous motor includes a stator 10 and a rotor 20, and the stator winding includes an A-phase stator winding 11, a B-phase stator winding 12 and a C-phase stator winding 13, which are the same as the three-phase stator windings of an asynchronous motor, and the rotor 20 is provided with a through The rotor winding 21 (excitation winding) with DC current (excitation current) is input, and the DC current is passed into the rotor 20 through a static rectifier via a slip ring, a brush, or through a brushless excitation method. In addition, a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com