Time-dependent fatigue reliability analysis method based on bilinear cumulative damage
A technology of cumulative damage and analysis methods, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the load sequence effect without consideration, cannot reveal the physical nature of the failure process, and cannot reflect the dispersion and uncertainty of cumulative damage reliability and other issues to achieve the effect of reliability prediction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] In order to facilitate those skilled in the art to understand the technical content of the present invention, the content of the present invention will be further explained below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
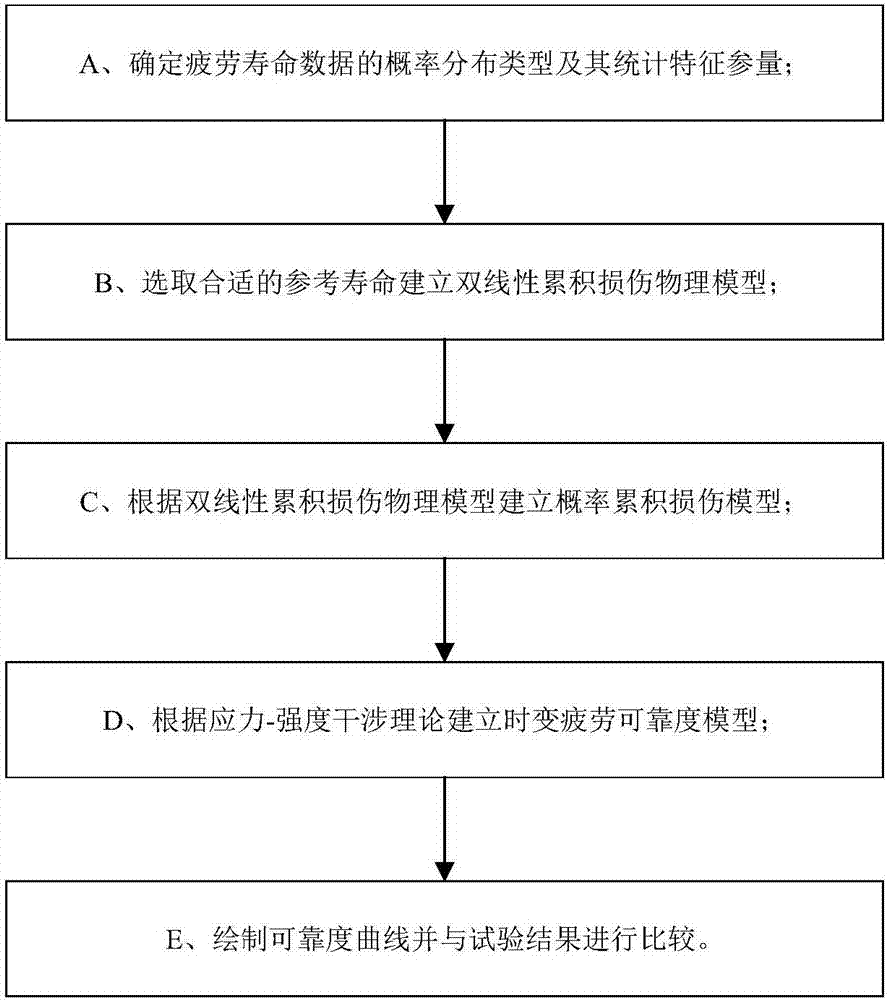
[0040] Take the 45 steel friction welded joint fatigue test with notch as an example to further illustrate the present invention, as figure 1 Shown is a flow chart of a time-varying fatigue reliability analysis method based on bilinear cumulative damage provided by the present invention, which specifically includes the following steps:
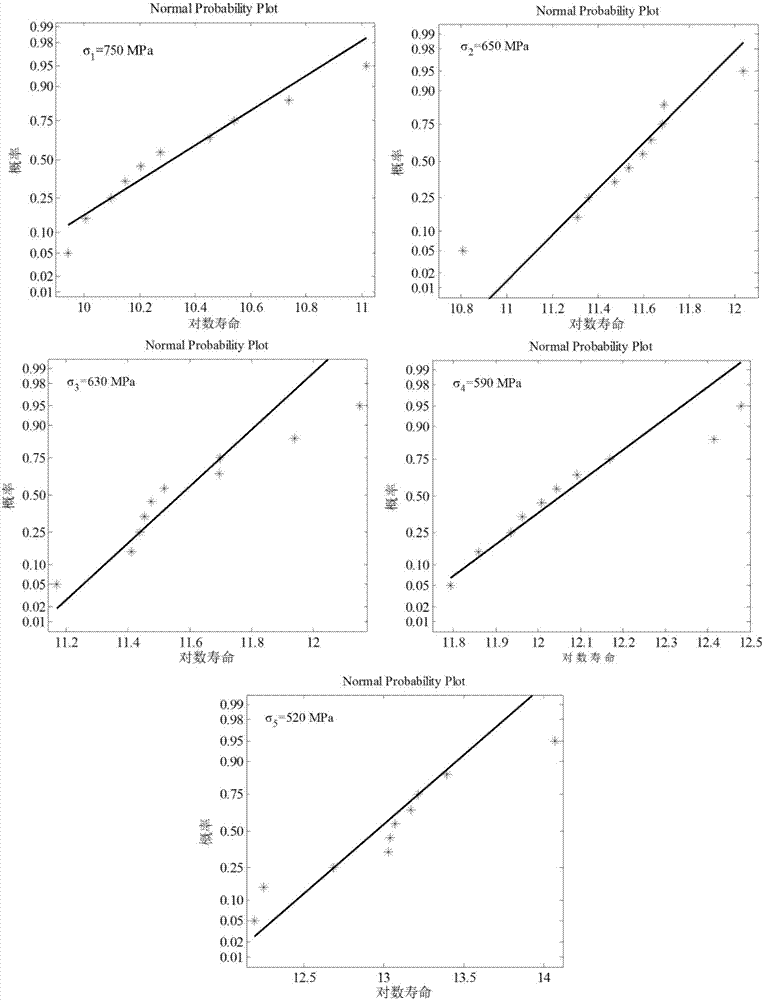
[0041] A. Determine the probability distribution type of fatigue life data and its statistical characteristic parameters;
[0042] B. Select an appropriate reference life to establish a bilinear physical model of cumulative damage;
[0043] C. Establish a probabilistic cumulative damage model based on the bilinear cumulative damage physical model;
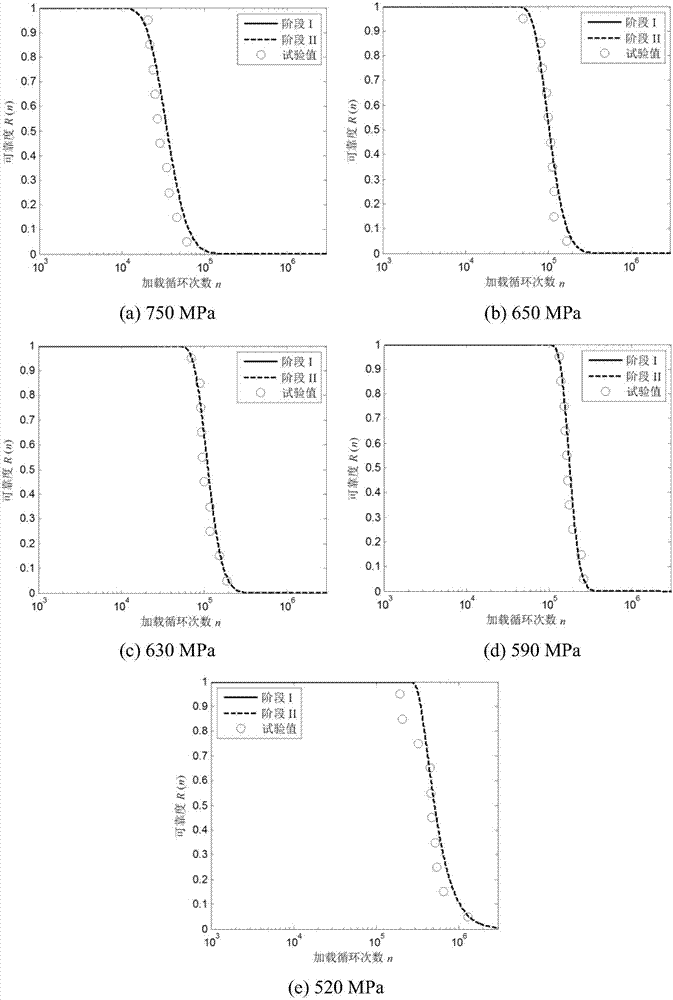
[0044] D. Establish a time-varying fatigue reliability model b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com