Method and system for measuring terrain parameters of a legged robot
A robot and foot-type technology, applied in the field of robot parameter measurement, can solve the problems of large amount of calculation, robot overturning, high cost, etc., and achieve the effect of simplifying mathematical operation, high precision and reducing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
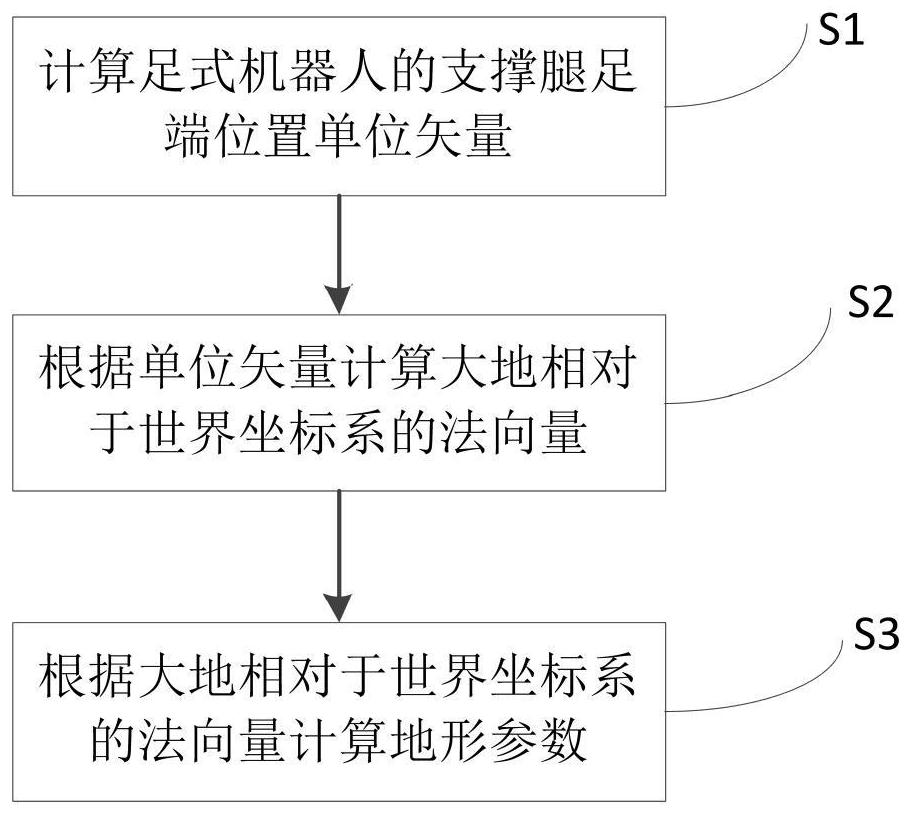
[0052] The invention provides a method for measuring terrain parameters of a legged robot, such as figure 1 Shown, is the flowchart of the inventive method, comprises the following steps:
[0053] S1: Calculate the unit vector of the foot end position of the supporting leg of the legged robot;
[0054] S101: When the legged robot is walking, under the condition that the supporting leg does not slip, the position vector of the foot end of the supporting leg of the legged robot in the fuselage coordinate system is obtained according to the sensor measurement. leg, the speed of the supporting leg being zero means that the supporting leg does not slip;
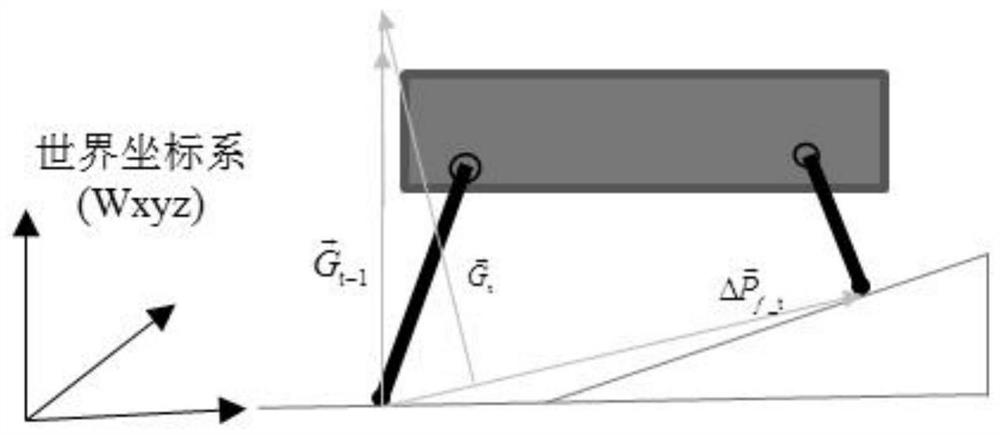
[0055] In this embodiment, a quadruped robot is taken as an example for description. Such as figure 2 As shown, the supporting legs are 1 leg and 2 legs, and the position vector of each leg can be obtained after kinematic calculation based on the sensor data installed on the legs.
[0056] S102: Calculate the position vector ...
Embodiment 2
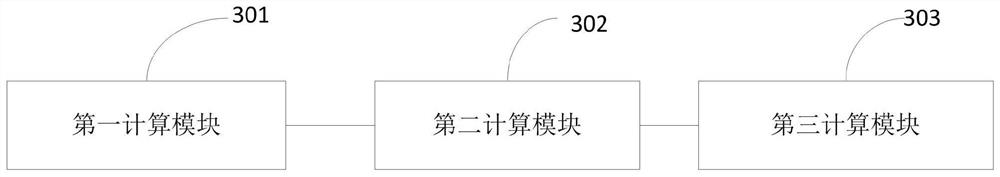
[0083] Based on the same inventive concept, the present invention also provides a measurement system for the topographical parameters of a legged robot, the structure diagram of which is as follows image 3 As shown, the system includes:
[0084] The first calculation module 301 is used to calculate the unit vector of the position of the foot end of the supporting leg of the legged robot;
[0085] The second calculation module 302 is used to calculate the normal vector of the earth relative to the world coordinate system according to the unit vector;
[0086] The third calculating module 303 is used for calculating terrain parameters according to the normal vector of the earth relative to the world coordinate system.
[0087] The first calculation module 301 further includes:
[0088] The measuring unit is used to obtain the position vector of the foot end of the supporting leg of the legged robot in the body coordinate system according to the sensor measurement;
[0089] T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com