Semiconductor device
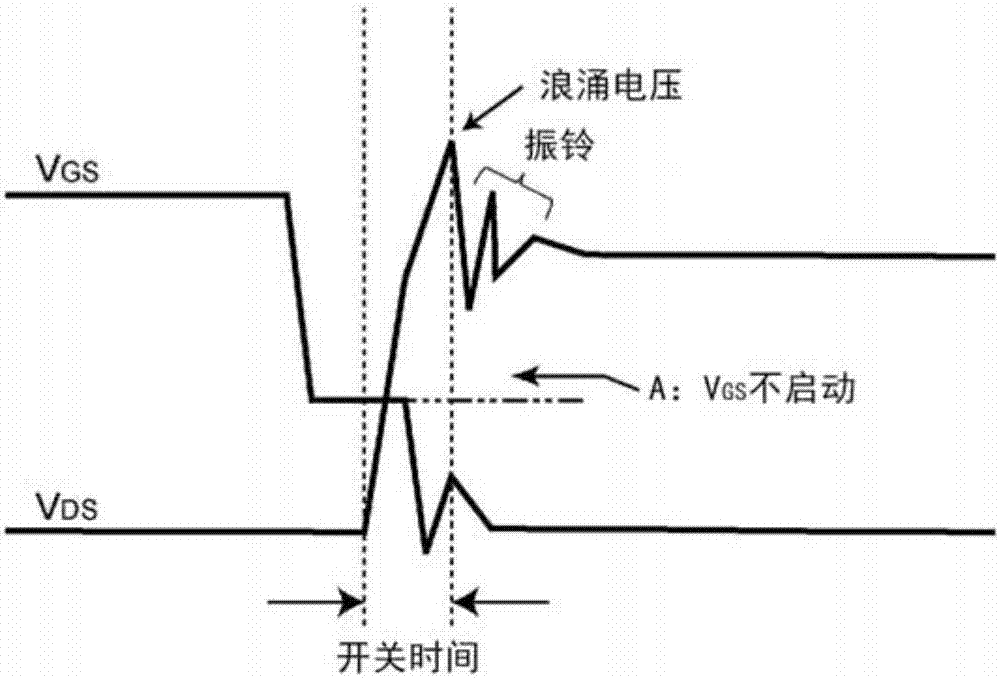
A semiconductor and substrate technology, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of reducing surge voltage, slowing switching speed, increasing switching loss, etc., to prevent the increase of switching loss and speed up switching speed , The effect of reducing the surge voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
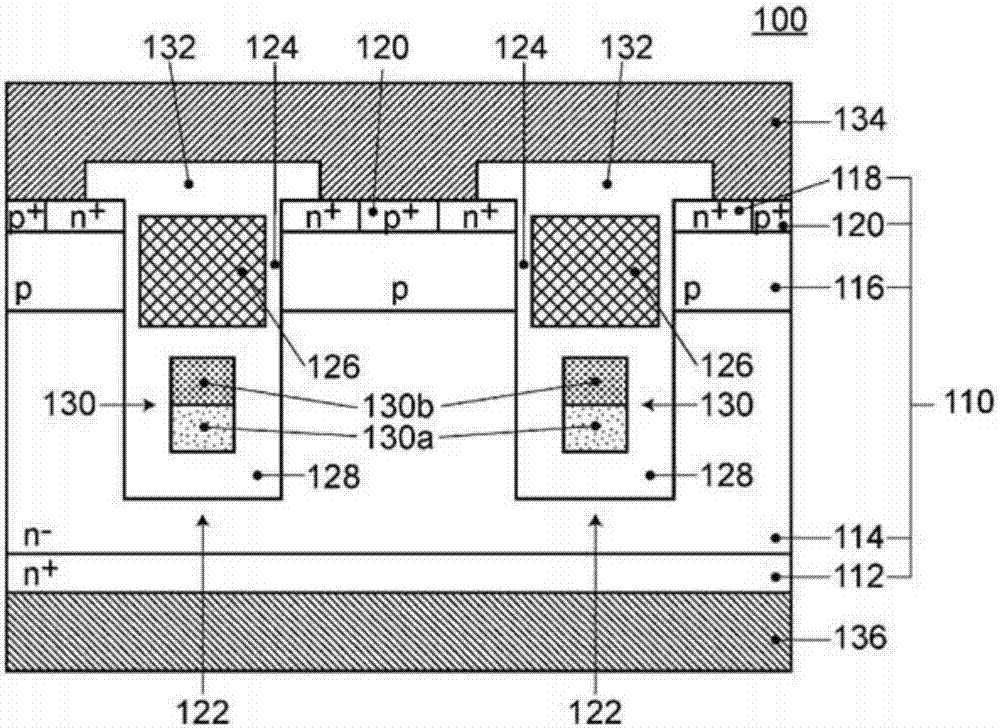
[0045] 1. Semiconductor device
[0046] The semiconductor device related to Embodiment 1, as shown in FIG. The adjacent n-type drift region (first conductivity type drift region) 114, the p-type base region (second conductivity type base region) 116 adjacent to the n-type drift region 114, and the p-type base region An n+ type source region (first conductivity type source region) 118 adjacent to the pole region 116; a trench 122, formed in the semiconductor base 110, having a groove bottom adjacent to the n-type drift region 114, and The sidewall adjacent to the p-type base region 116 and the n-type drift region 114 is formed in a stripe shape when viewed from the plane; The gate insulating film 124 is opposite to the p-type base region 116; the shielding electrode 130 is arranged in the trench 122, and is located between the gate electrode 126 and the bottom of the trench 122; the electrically insulating region in the trench 122 128, extending between the gate electrode 126...
Embodiment approach 2
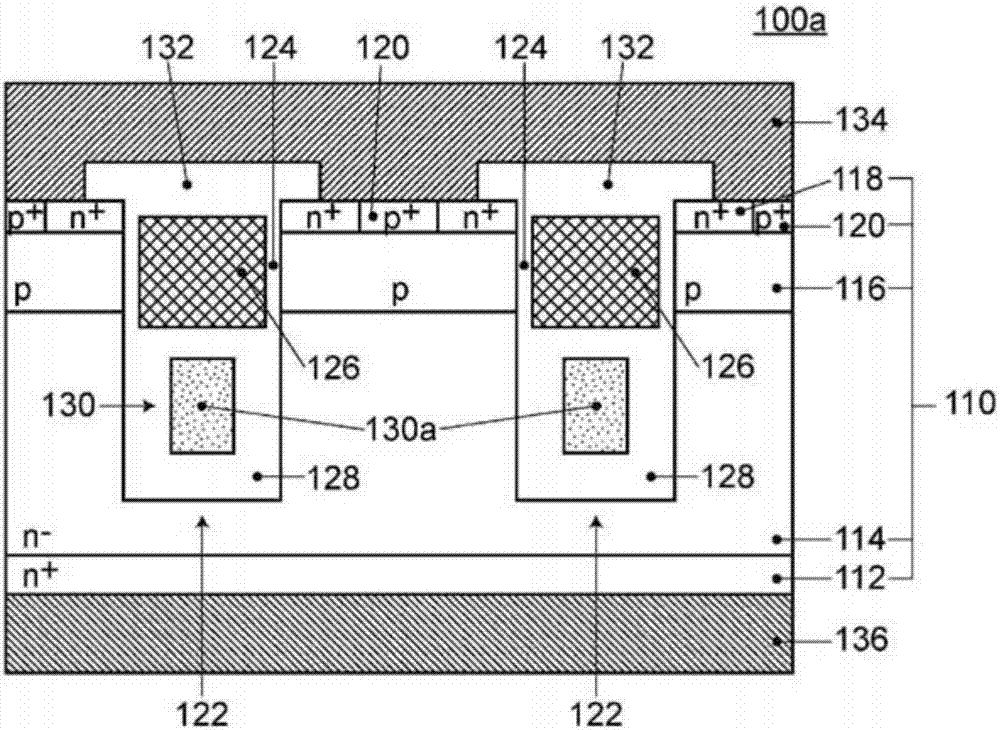
[0088] The semiconductor device 101 according to the second embodiment basically has the same configuration as the semiconductor device 100 according to the first embodiment, but differs from the semiconductor device 100 according to the first embodiment in the configuration of the shield electrode. That is, if Figure 9 As shown, in the semiconductor device 102 according to Embodiment 2, the high-resistance region 130a and the low-resistance region 130b are made of different materials, and the resistivity of the material constituting the low-resistance region 130b is lower than that of the material constituting the high-resistance region 130a. The resistivity of the material (see Figure 9 ).
[0089] As a material constituting the high-resistance region 130a, for example, high-resistance polysilicon formed by CVD can be used. In addition, as a material constituting the low-resistance region 130b, for example, a metal with a high melting point (eg, W, Mo, Ta, Nb, etc.) and ...
Embodiment approach 3
[0093] The semiconductor device according to the third embodiment basically has the same configuration as the semiconductor device 100 according to the first embodiment, but differs from the semiconductor device 100 according to the first embodiment in the configuration of the shield electrode. That is, if Figure 10 As shown, in the semiconductor device 102 according to the third embodiment, the high-resistance region 130 a and the low-resistance region 130 b are located at positions separated from each other via the electrically insulating region 128 .
[0094] The interval between the high-resistance region 130a and the low-resistance region 130b can be appropriately set, for example, it can be set to 1 μm.
[0095] In this way, although the semiconductor device 102 according to the third embodiment is different from the semiconductor device 100 according to the first embodiment in the configuration of the shield electrode, it has the high resistance region 130a located on ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com