Semiconductor device
A technology of semiconductors and substrates, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as slow switching speed, reduce surge voltage, and operation errors, and achieve the effect of easing potential changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0051] 1. Semiconductor device
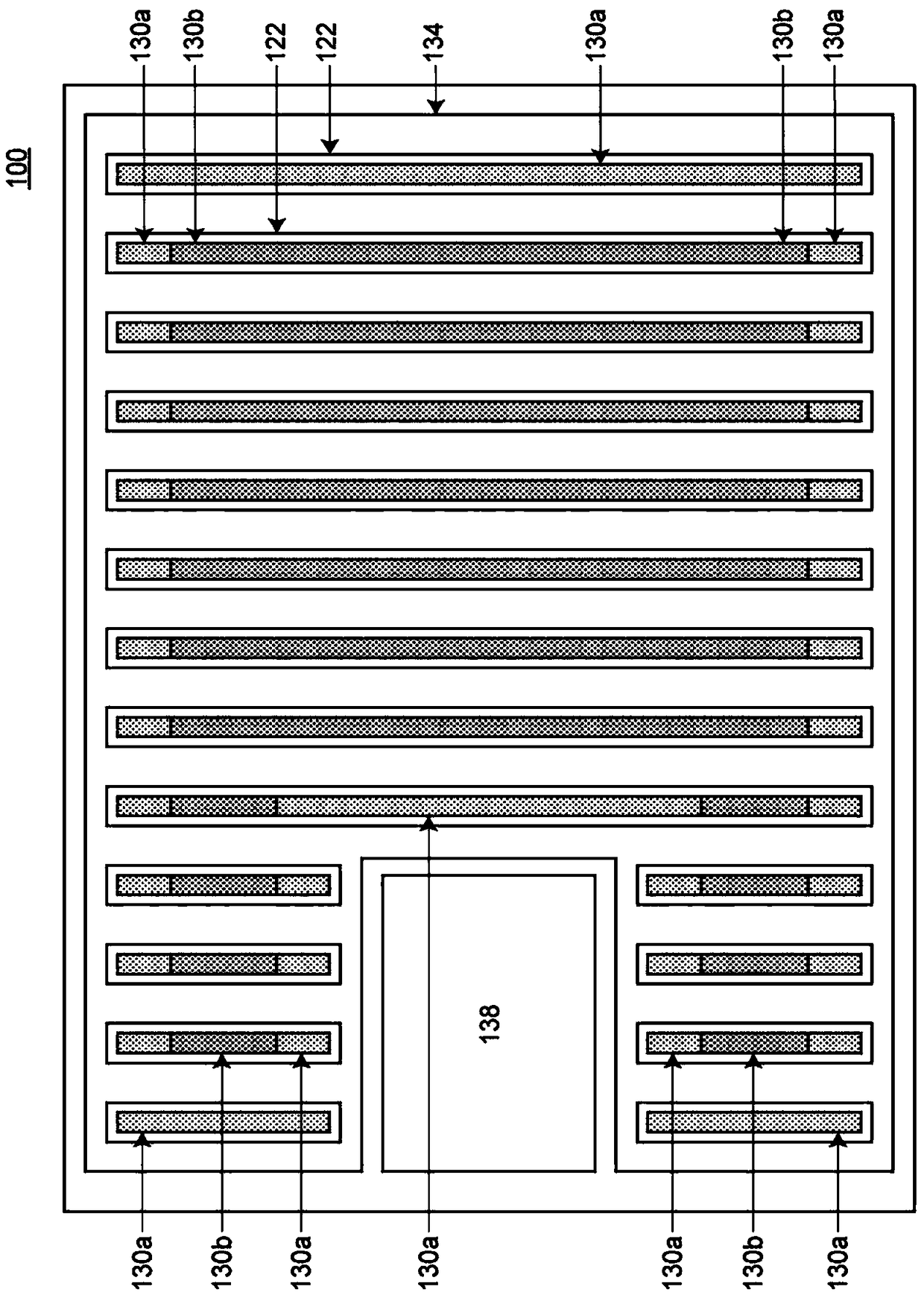
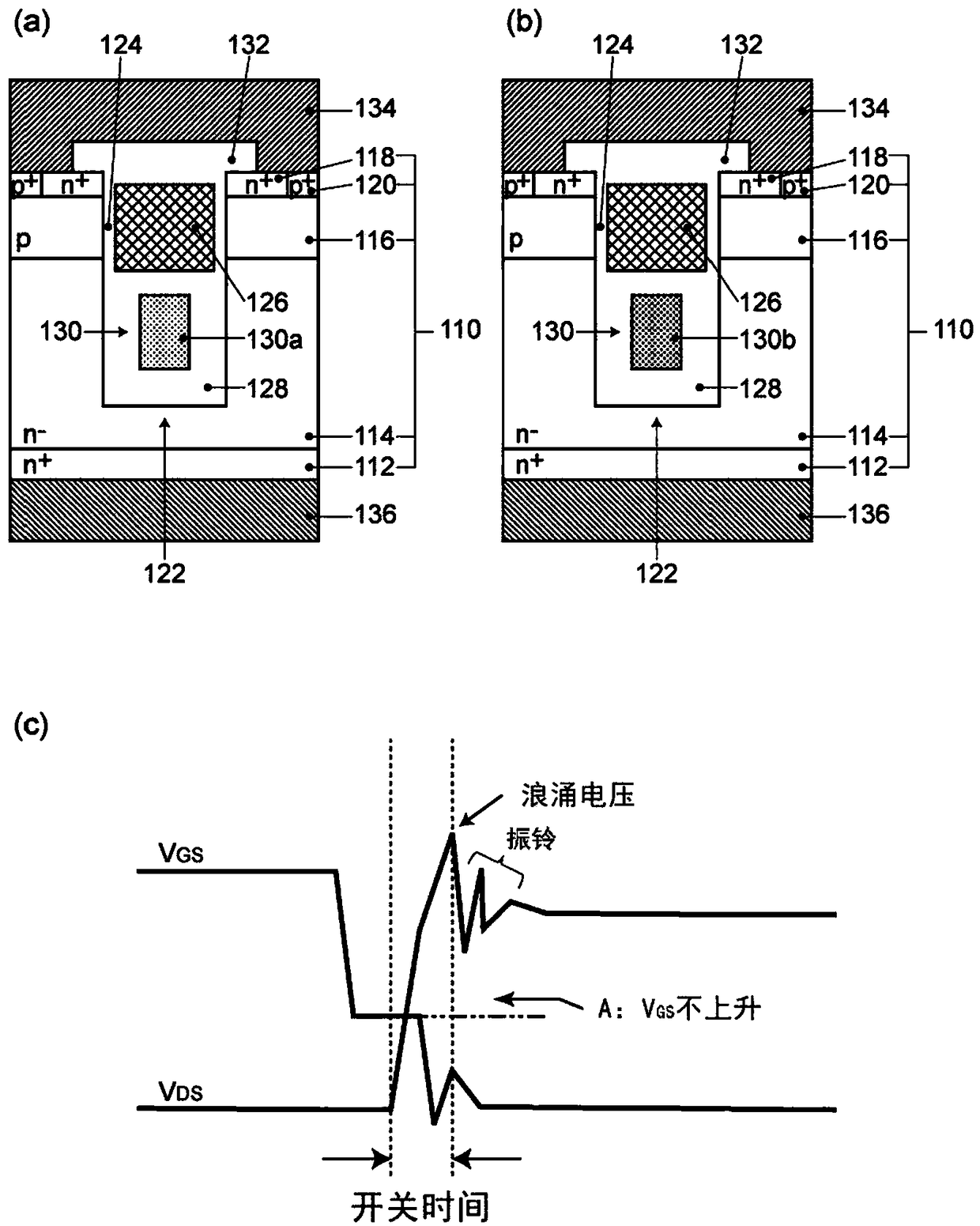
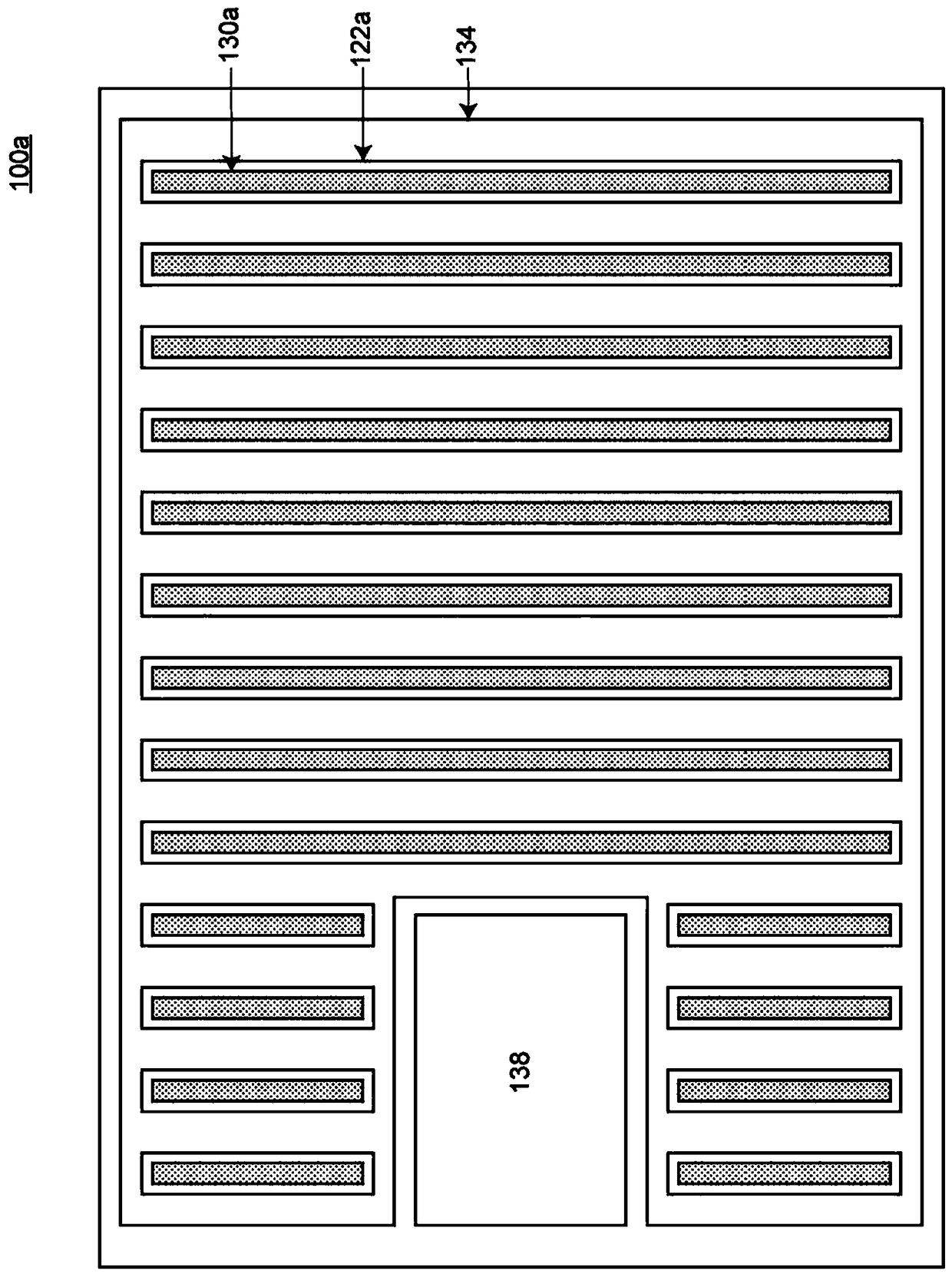
[0052] The semiconductor device 100 involved in the first embodiment is such as figure 1 , figure 2 (a) and figure 2 As shown in (b), it includes: a semiconductor substrate 110 containing: an n+ type drain region (first conductivity type drain region) 112, and an n-type drift region (first conductivity type) adjacent to the n+ type drain region 112 Type drift region) 114, a p-type base region (second conductivity type base region) 116 adjacent to the n-type drift region 114, and an n+ type source region adjacent to the p-type base region 116 (First conductivity type source region) 118; trench 122, formed in the semiconductor base 110, having a groove bottom adjacent to the n-type drift region 114, and the p-type base region 116 and the n-type drift The sidewalls of the region 114 adjacent to each other are formed in a stripe shape when viewed in plan; the gate electrode 126 is arranged in the trench 122, and the sidewall is connected to the p-t...
Embodiment approach 2
[0100] The semiconductor device according to the second embodiment basically has the same configuration as the semiconductor device 100 according to the first embodiment, but is different from the semiconductor device 100 according to the first embodiment in the configuration of the shield electrode 130. That is, as Picture 12 As shown, in the shield electrode 130 included in the semiconductor device according to the second embodiment, the high resistance region 130a and the low resistance region 130b are made of different materials, and the resistivity of the material constituting the low resistance region 130b is lower than The resistivity of the material constituting the high resistance region 130a.
[0101] As a material constituting the high-resistance region 130a, for example, high-resistance polysilicon formed by a CVD method can be used. In addition, as a material constituting the low resistance region 130b, for example, a metal with a high melting point (for example, W,...
Embodiment approach 3
[0105] The semiconductor device 102 according to the third embodiment basically has the same configuration as the semiconductor device 100 according to the first embodiment, but is different from the semiconductor device 100 according to the first embodiment in the configuration of the shield electrode 130. That is, as Figure 13 as well as Figure 14 As shown, in the shield electrode 130 included in the semiconductor device 102 according to the third embodiment, the high-resistance region 130a and the low-resistance region 130b are made of the same material, and are cut in a plane perpendicular to the longitudinal direction of the trench 122 The cross-sectional area of the subsequent high-resistance region 130a is smaller than the cross-sectional area of the low-resistance region 130b cut in a plane perpendicular to the longitudinal direction of the trench 122.
[0106] In this way, although the semiconductor device 102 according to the third embodiment is different from the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com