Method for accelerating vBNN-IBS authentication in wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor and authentication method technology, applied in the field of vBNN-IBS authentication mechanism, can solve the problems of large energy consumption and slow authentication speed, and achieve the effect of reducing authentication time and improving life cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0031]Specific implementation mode one: a method for accelerating vBNN-IBS authentication in a wireless sensor network is implemented in the following steps:
[0032] System parameter establishment phase:
[0033] Give the security parameter k.
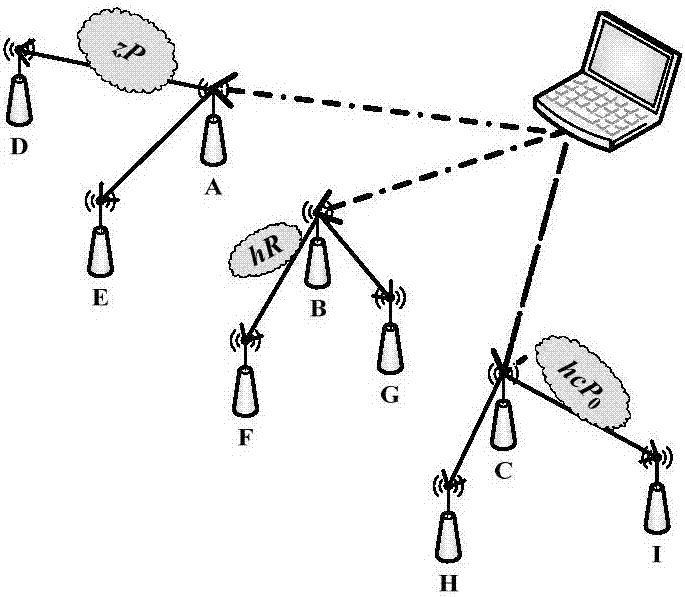
[0034] PKG specifies E / F q and a point P of order n. Among them, PKG refers to a trusted third party of Private Key Generator. We will define in the finite field F q The elliptic curve E in: y 2 =x 3 +ax+b is called E / F q , where q is a fairly large prime and both a and b are in the field F q middle. P is a point in the elliptic curve E, and its order is n.
[0035] in Z p randomly select a system private key x, and calculate the system public key P 0 =xP. where Z p Represents the field consisting of positive integers from 0 to p-1.
[0036] Defines the elliptic curve "add" and "multiply" operations. Take point P and point Q on elliptic curve E, l is a straight line passing through point P and point Q, and l intersects ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
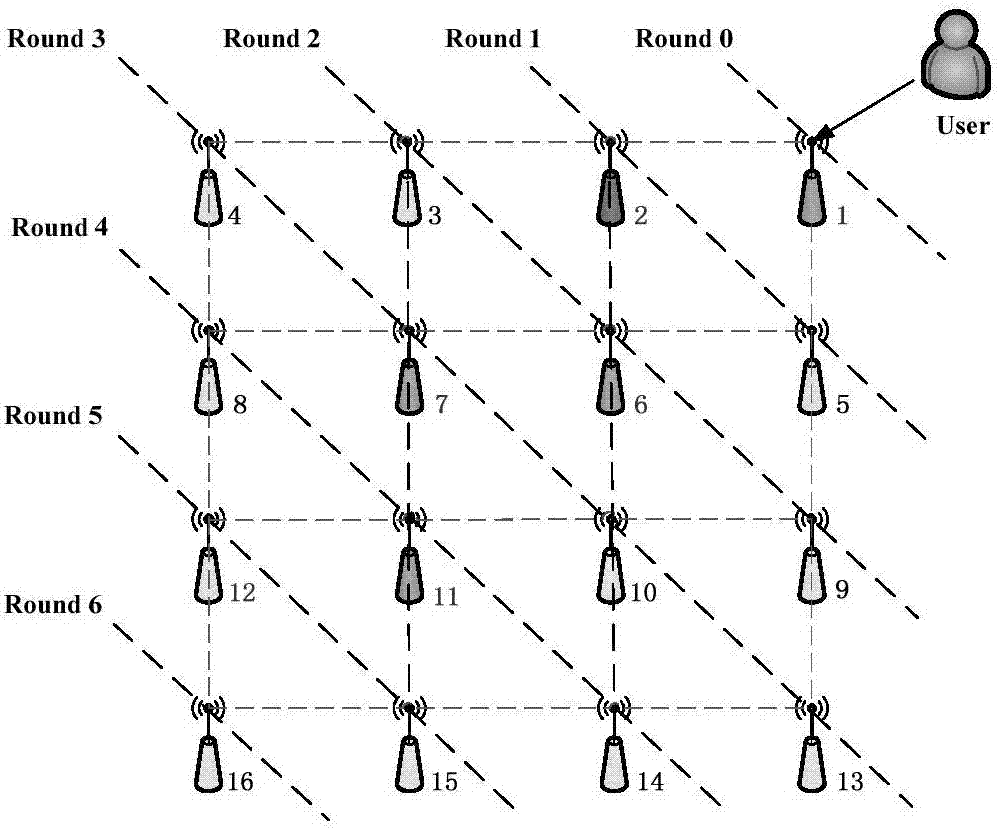
[0064] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment is that this embodiment is in the topological structure of 4*4 grid, and the simulation analysis is carried out from the function of the nodes of. The specific content is as follows:
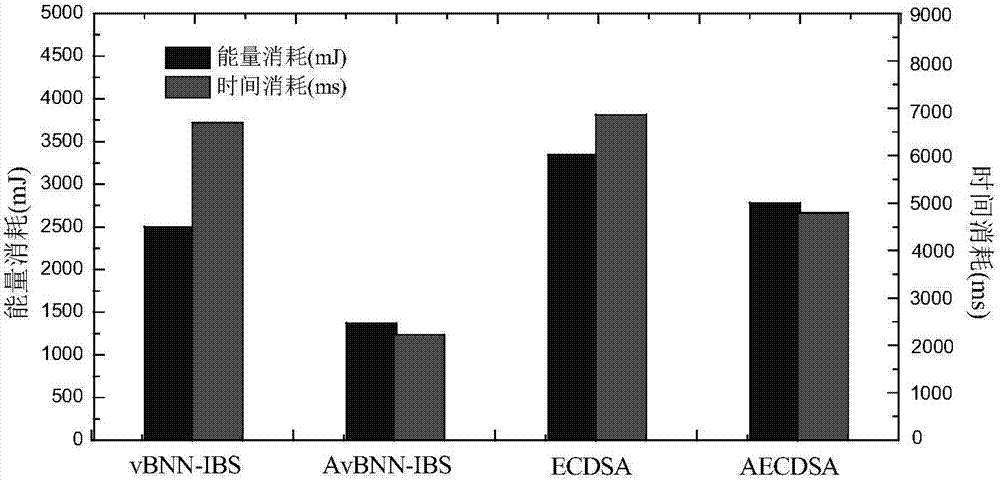
[0065] In order to get the energy value and time savings that AvBNN-IBS can reduce, we execute the NesC application in TinyOS system to send and receive 802.15.4 packets. Since the MICAz node can transmit up to 128 bytes at the physical layer, we need to split the data packet to transmit the 139 bytes data packet with intermediate calculation results. The first packet contains the user's information and the generated signature, represented by Sig, and the second data packet contains the intermediate calculation result, represented by INTER. We can conclude that the energy consumed when sending and receiving the data packet Sig...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0069] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that this embodiment is in the topological structure of 4*4 grid, the slave nodes The simulation analysis of the status is carried out. The specific content is as follows:
[0070] The state of the node is different, and the energy consumed is also different. A node in an active state means that the node sends, receives and transmits data packets; a node in an idle state keeps the radio transceiver on and is responsible for listening and authenticating data packets; a node in a dormant state cannot send, receive, or process any data packets. Initially, the nodes are idle. When it receives the authentication data packet, it is in an active state and waits for the node to complete the authentication work. It will be in a dormant state to reduce energy consumption until all nodes have complet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com