A self-test method and device for non-volatile memory
A non-volatile memory technology, applied in the field of memory, can solve the problems of rising cost of memory products and high test cost, and achieve the effects of reducing requirements, improving output efficiency, and simplifying the burn-in test process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] refer to figure 2 , shows a flow chart of the steps of a non-volatile memory self-test method embodiment of the present invention, the non-volatile memory includes a self-test controller, the self-test controller can be embedded or integrated in the non-volatile memory, the non-volatile memory The volatile memory and the test equipment can be connected through a data interface, and the self-test method can specifically include the following steps:
[0028] S21, receiving a start-up self-test instruction sent by the test device through the non-volatile memory.
[0029] Wherein, the non-volatile memory (NVRAM, Non-volatile memory) refers to a memory whose stored information will not disappear when the system is shut down or there is no power supply. For example, EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory, Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory), EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory, Electronically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory, Flash m...
Embodiment 2
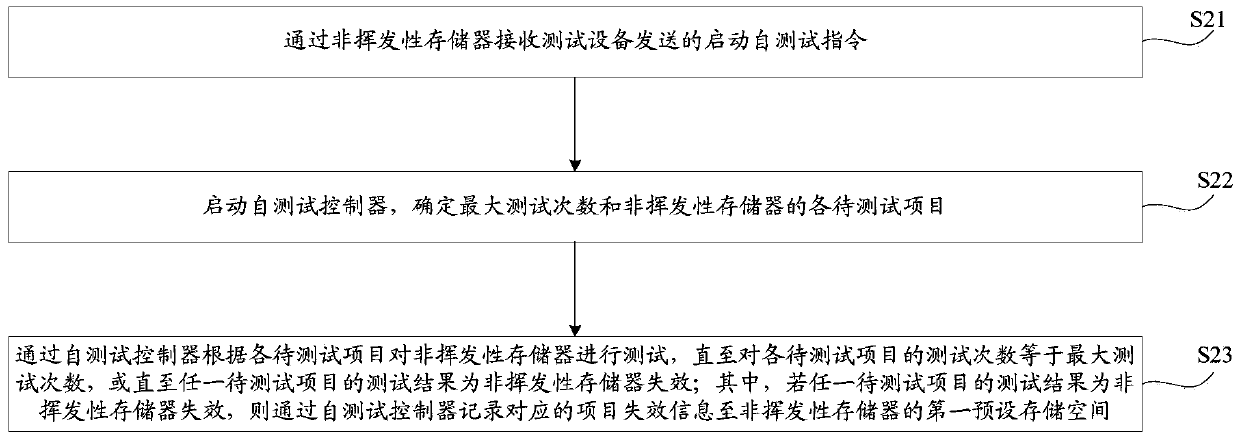
[0040] refer to image 3 , shows a flow chart of the steps of another non-volatile memory self-test method embodiment of the present invention, the non-volatile memory may include a self-test controller, the non-volatile memory is connected to the test equipment, and the self-test method may specifically be Including the following steps:
[0041] S31, receiving a start-up self-test instruction sent by the test device through the non-volatile memory.
[0042] S32, start the self-test controller, determine the maximum number of tests and each item to be tested of the non-volatile memory; determine the maximum number of tests and each item to be tested of the non-volatile memory, which may include:
[0043] S321. Obtain data corresponding to the maximum number of tests and data corresponding to each item to be tested from the second preset storage space of the non-volatile memory.
[0044] S322. Determine the maximum number of tests according to the data corresponding to the ma...
Embodiment 3
[0058] refer to Figure 4 , shows a flow chart of the steps of another non-volatile memory self-test method embodiment of the present invention, the non-volatile memory may include a self-test controller, the non-volatile memory is connected to the test equipment, and the self-test method may specifically be Including the following steps:
[0059] S41, receiving a start-up self-test instruction sent by the test device through the non-volatile memory.
[0060] S42, start the self-test controller, determine the maximum number of tests and each item to be tested of the non-volatile memory; determine the maximum number of tests and each item to be tested of the non-volatile memory, which may include:
[0061]S421. Obtain data corresponding to the maximum number of tests and data corresponding to each item to be tested from the instruction to start the burn-in self-test.
[0062] Specifically, the command to start the self-test may be any command sequence that causes the self-tes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com