FPGA training and inquiry circuit achievement method based on perfect hash algorithm
A query circuit and hash algorithm technology, which is applied in computing, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems of large scale and low efficiency of second-order hashing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
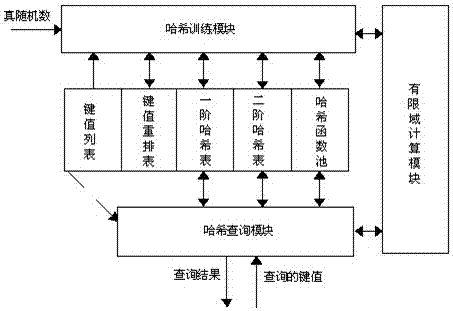
[0096] combined with Figure 1-3 As shown, a FPGA training and query circuit implementation method based on the perfect hash algorithm comprises the following steps:
[0097] S1) input the static key value and the hash index value of the static key value into the static key value table;
[0098] S2) performing a first-order hash calculation on the static key value and an input true random number to obtain a first-order hash table, and the entries of the first-order hash table include:
[0099] Address / Index: In the stage of rearranging static key values, it indicates the base address of the generated key value rearrangement table for static key values; after the second-order hash training is completed, that is, after the conflict group in the first-order hash table is resolved, If vld=1, col=0, it indicates the serial number of the static key value; if vld=1, col=1, it indicates the base address of the serial number of the static key value stored in the second-order hash tabl...
Embodiment 2
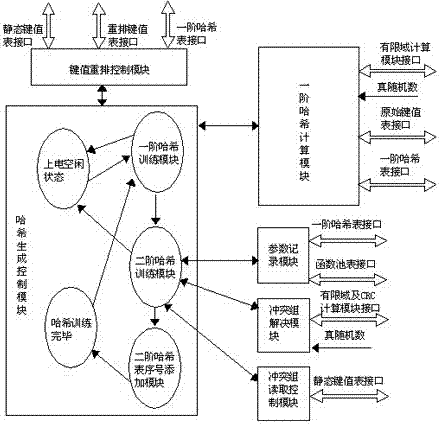
[0112] On the basis of Example 1, in conjunction with the attached Figure 1-3 and Figure 6 As shown, the step S2) is specifically:
[0113] S2.1) Empty the first-order hash table, so that the initial state of the first-order hash table is all 0;
[0114] S2.2) Perform a first-order hash calculation on the first static key value in the static key-value table and an input true random number to obtain the address index value of the first-order hash table, and write the serial number of the static key value into The address / index in the entry corresponding to the address index value of the first-order hash table, writing the col_cnt and col_rec of the entry into "1", and writing the valid indication vld of the entry into "1";
[0115] S2.3) Read the next static key value, perform first-order hash calculation, obtain the address index value of the first-order hash table corresponding to the static key value, and read the valid indication vld of the entry corresponding to the addr...
Embodiment 3
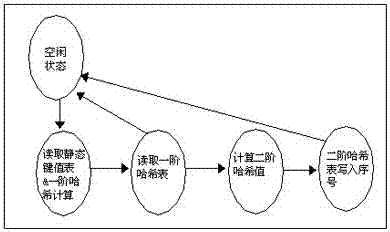
[0119] On the basis of embodiment 2, in conjunction with the attached Figure 1-3 and Figure 6 As shown, the step S3) is specifically:
[0120] S3.1) Set the FPGA internal counter base_addr_cnt to 0, read the first static key value in the static key value table, and read the col in the entry of the address index value corresponding to the static key value from the first-order hash table , if col is equal to 0, the static key value does not conflict, and the next static key value is directly read; otherwise, write the address / index of the entry corresponding to the static key value in the first-order hash table into base_addr_cnt= 0 as the base address in the key value rearrangement table, update base_addr_cnt=base_addr_cnt+col_rec, and use 0+col_cnt-1 as the absolute address of the static key value in the rearrangement table, copy the static key value to the Absolute address, at the same time, the col_cnt of the entry of the address index value corresponding to the static k...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com