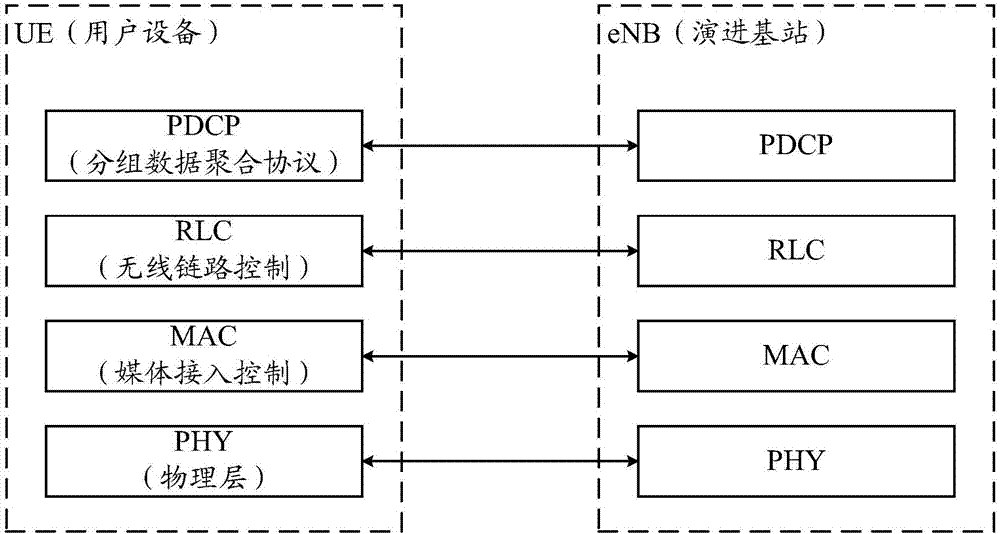
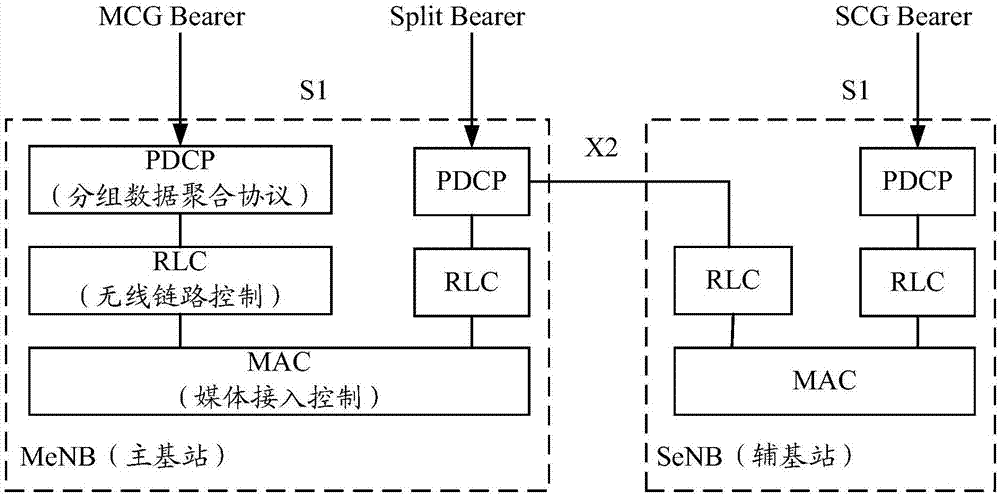
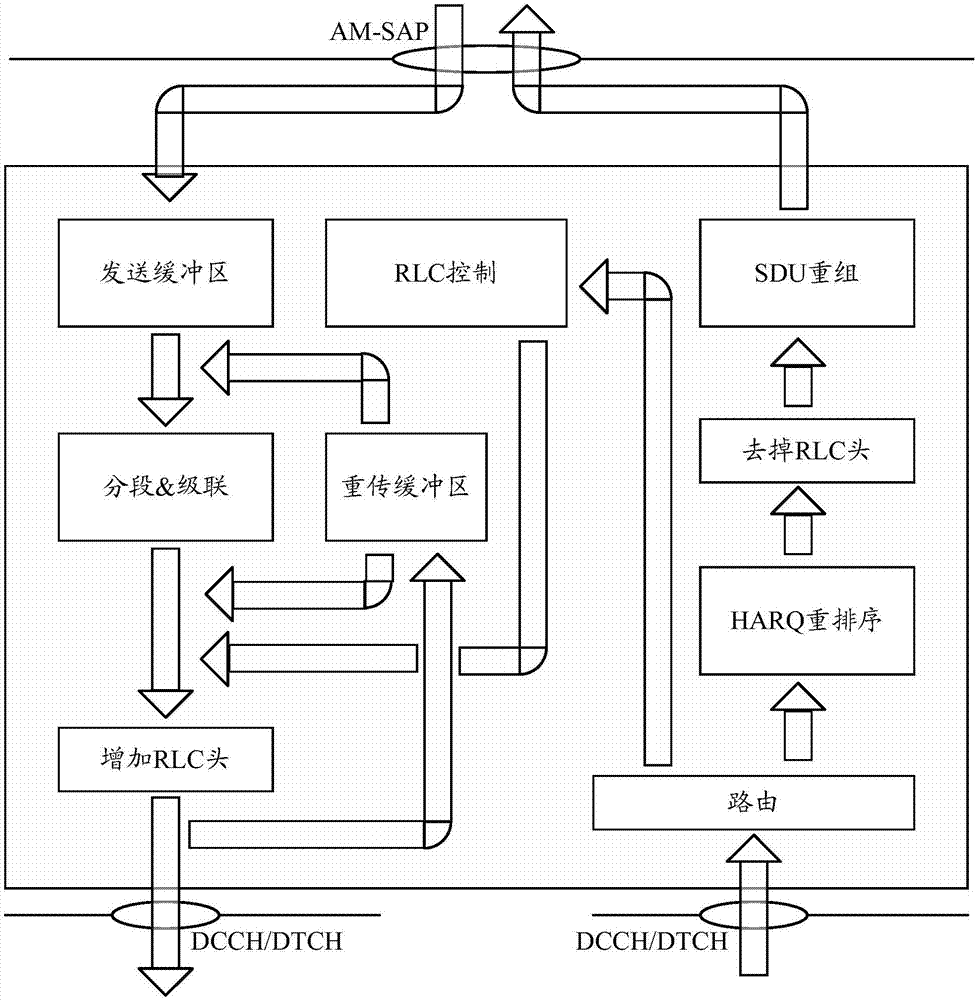
Data receiving method and device
A data receiving method, data technology, applied in digital transmission system, using return channel for error prevention/detection, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as ambiguity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0150] In this example, it illustrates the implementation of no packet loss, and the variable does not record segment information.
[0151] At the receiving end of AM, the following variables need to be maintained:
[0152] Next_receive_SN: The variable that records the highest received SN is equal to the current highest received SN plus 1 in LTE, but since NR RLC cancels the concatenation, the SN value of the next data packet to be received may still be equal to the current highest SN The value is nothing more than receiving the subsequent segment corresponding to the current SN;
[0153] Con_receive_SN: Record the highest value of SN received continuously, that is, the lower boundary of the receiving window. The part below this boundary is the PDU received continuously, which has exceeded the window and does not need to record the state;
[0154] T_reorder_SN: Record the upper boundary of the interval corresponding to the T_reordering timer, and the lower boundary is the lo...
Embodiment 2
[0162] In this example, the implementation of variable logging segment information without packet loss is illustrated.
[0163] For the variables at the receiving end, if the NR contains not only the SN but also segmented SO information, the variable maintenance and update mechanism for continuous sequence reception is as follows:
[0164] For the Next_receive_SN variable, if a latest complete PDU or the last segment packet of the latest PDU is received, Next_receive_SN is updated to the SN value +1 corresponding to the latest complete PDU, and SO=0; if received A latest PDU segment packet and this segment is not the last segment, then Next_receive_SN is updated to the SN value corresponding to the complete PDU, and the SO record is the SO value of the next segment expected to be received, for example, 200 characters have been correctly received section, then the next expected received SO=200 bytes.
[0165] For the variable Con_receive_SN, which is the lower boundary of the re...
Embodiment 3
[0169] In this example, the implementation of starting the reordering timer and not displaying the record segmentation information by the variable is illustrated.
[0170] Embodiments 1 and 2 give the simplest example of in-order reception, but in actual reception, out-of-order reception is often unavoidable due to poor link conditions. When the receiving end variable does not record segment information, This example shows how to deal with out-of-order reception.
[0171] In the case of out-of-order, the update of the lower boundary of the window is not affected, that is, Con_receive_SN is always equal to the SN of the oldest data to be received, and the update principle of Next_receive_SN is consistent with the above example. When the latest complete PDU or the latest The last segmented PDU of , then Next_receive_SN is updated to the latest SN+1, and when the latest segment received is not the last segment, Next_receive_SN is updated to the latest SN at this time, if it is fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com