Robot realization method, control method, robot and electronic device
An implementation method and robot technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve the problems of many control instructions and high user requirements for video streaming, and achieve the effects of low control frequency, friendly interactive experience, and simple motion control.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
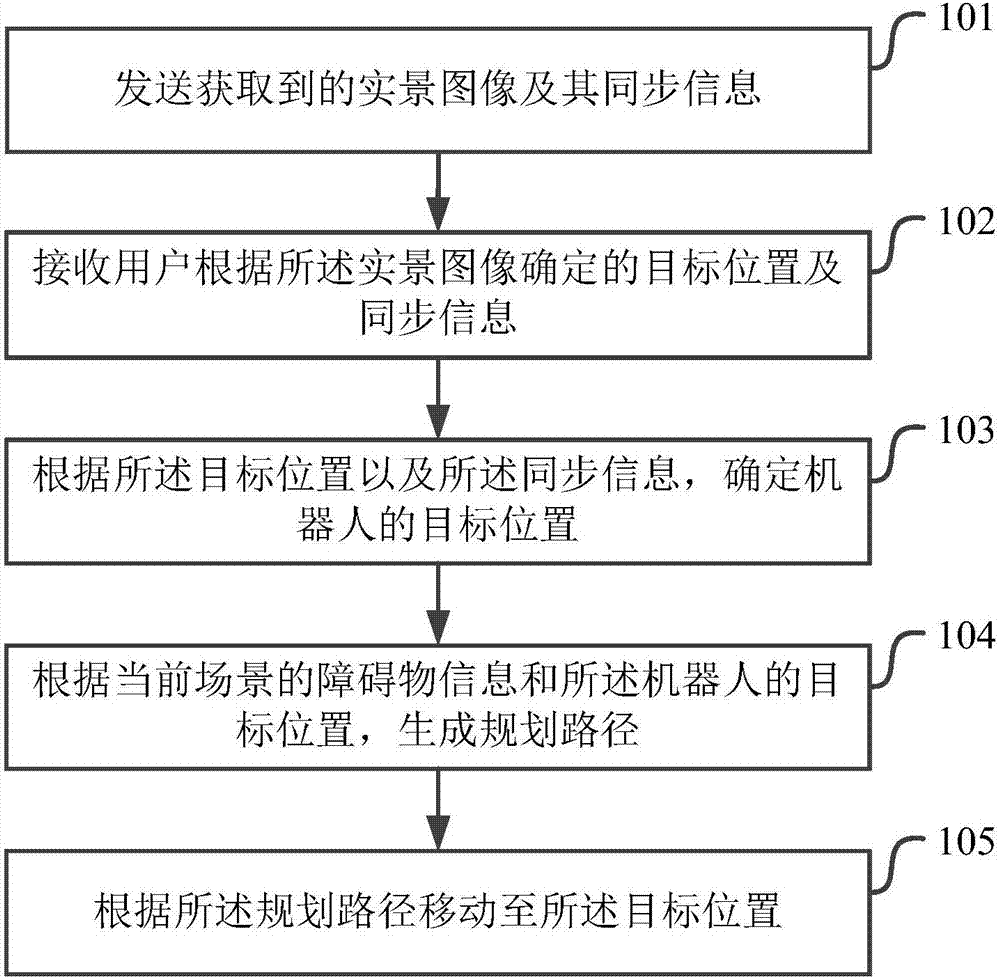
[0039] figure 1 It shows a schematic flowchart of the implementation of the robot implementation method in the embodiment of the present application. As shown in the figure, the robot implementation method may include the following steps:
[0040] Step 101, sending the acquired real scene image and its synchronization information;
[0041] Step 102, receiving the target position and synchronization information determined by the user according to the real-scene image;
[0042] Step 103. Determine the target position of the robot according to the target position and the synchronization information;
[0043] Step 104, generating a planned path according to the obstacle information of the current scene and the target position of the robot;
[0044] Step 105, move to the target location according to the planned route.
[0045] Wherein, the synchronization information may include odometer information, and the odometer information may include information such as starting from the ...
Embodiment 2
[0097] The embodiment of the present application also provides a robot control method, which is described as follows from the perspective of the control terminal.
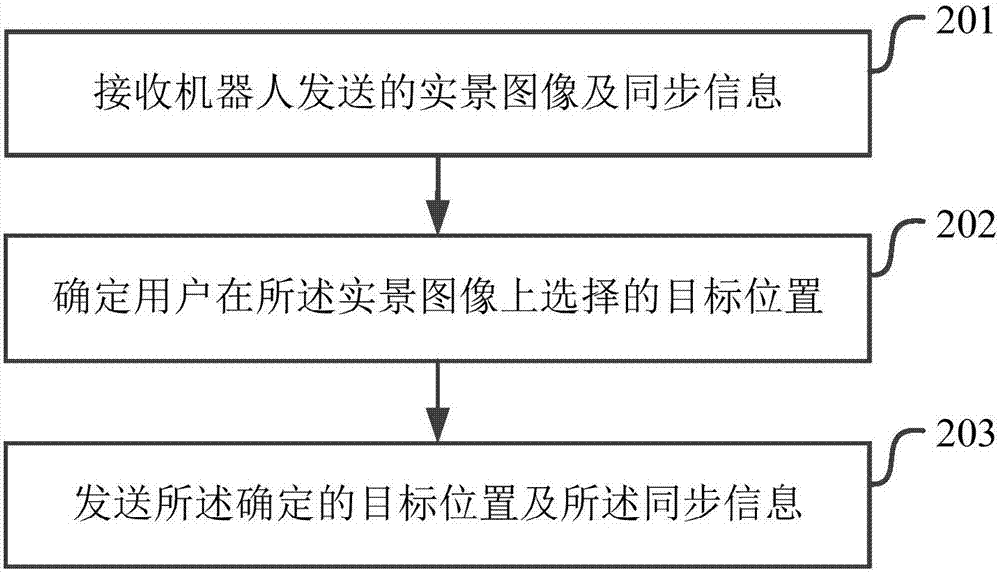
[0098] figure 2 It shows a schematic flowchart of the implementation of the robot control method in the embodiment of the present application. As shown in the figure, the robot control method may include the following steps:
[0099] Step 201, receiving the real scene image and synchronization information sent by the robot;
[0100] Step 202, determining the target position selected by the user on the real-scene image;
[0101] Step 203, sending the determined target location and the synchronization information.
[0102] In the embodiment of the present application, the control terminal only needs to receive the real-scene image sent by the robot, and select the target position by clicking on the real-scene image to realize the remote control of the robot to move to the designated position, without the need for th...
Embodiment 3
[0122] Assume that the robot takes a real-scene image every 10s while traveling according to the previously planned path.
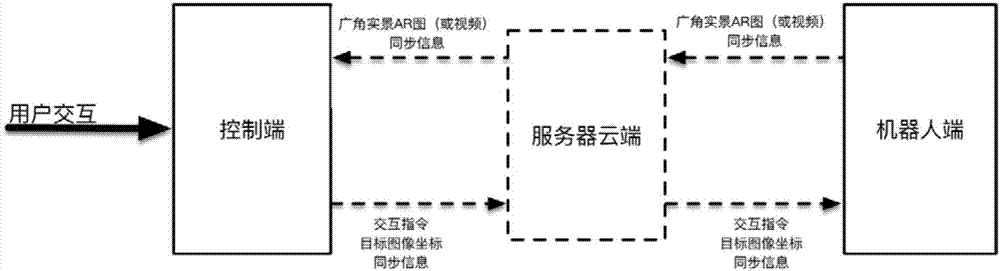
[0123] Image 6 A schematic diagram of the usage scene in the embodiment of the present application is shown. As shown in the figure, the robot interacts with the control terminal through the cloud in the three-dimensional real space, and the user of the control terminal views the displayed two-dimensional image and specifies the target point.
[0124] The robot uses the camera to capture the real scene image (or video) of the current scene, assuming that it is the first frame of the real scene image taken by the robot at 00:50, the real scene image can be an RGB two-dimensional image; and the attitude information of the current robot is obtained by using the odometer, For example: position (0m, 0m, 0m), facing 0rad, use obstacle sensing module (for example: ultrasonic, radar, infrared, depth camera, etc.) to perceive obstacle information, including obsta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com