Top-loading two-axis automatic setting robot
A robotic and automatic technology, applied in transportation and packaging, stacking of objects, de-stacking of objects, etc., can solve the problems of heavy fixture weight, long maintenance time and high maintenance cost, achieve low mechanical vibration, low maintenance cost, The effect of high work efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
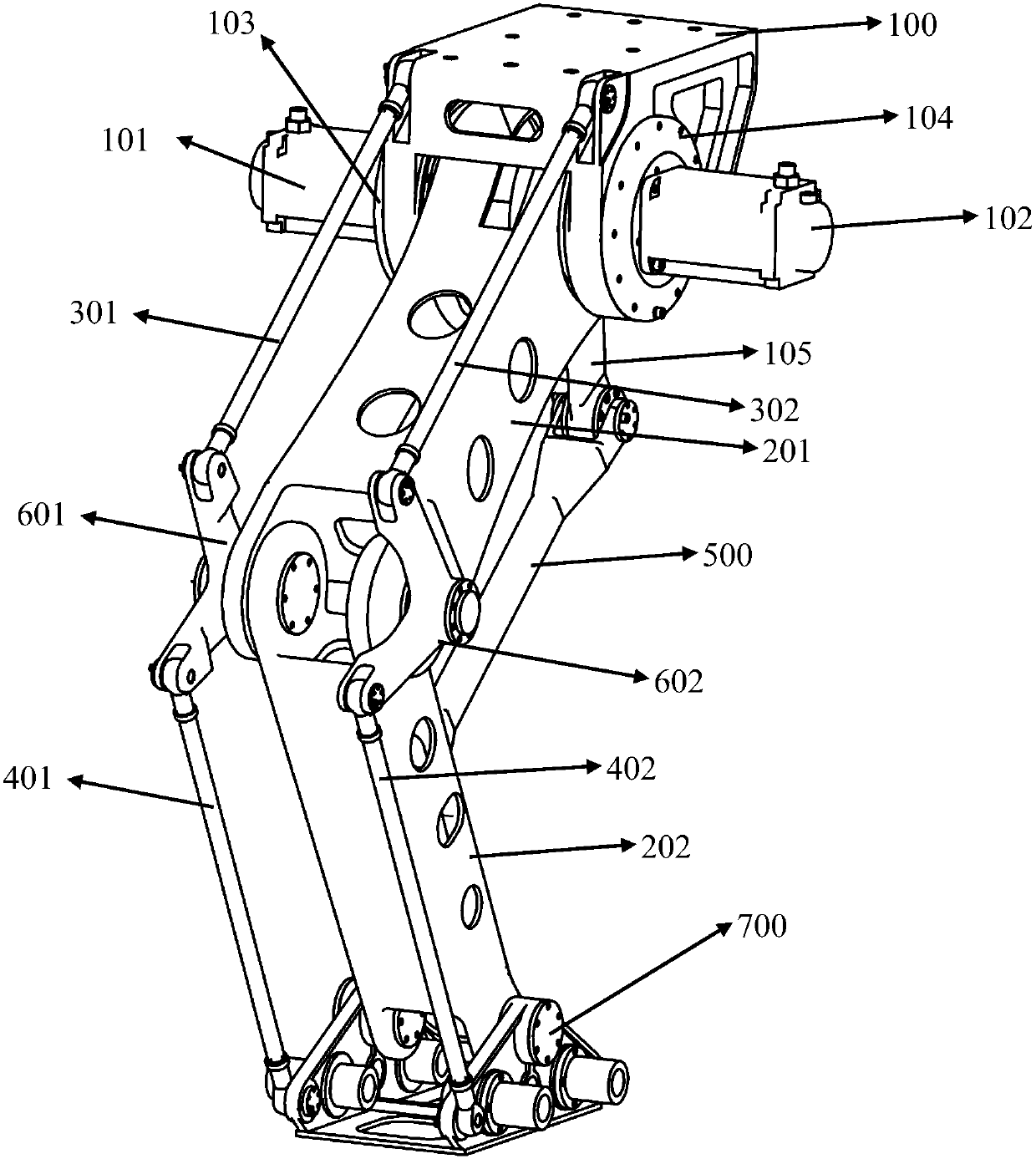
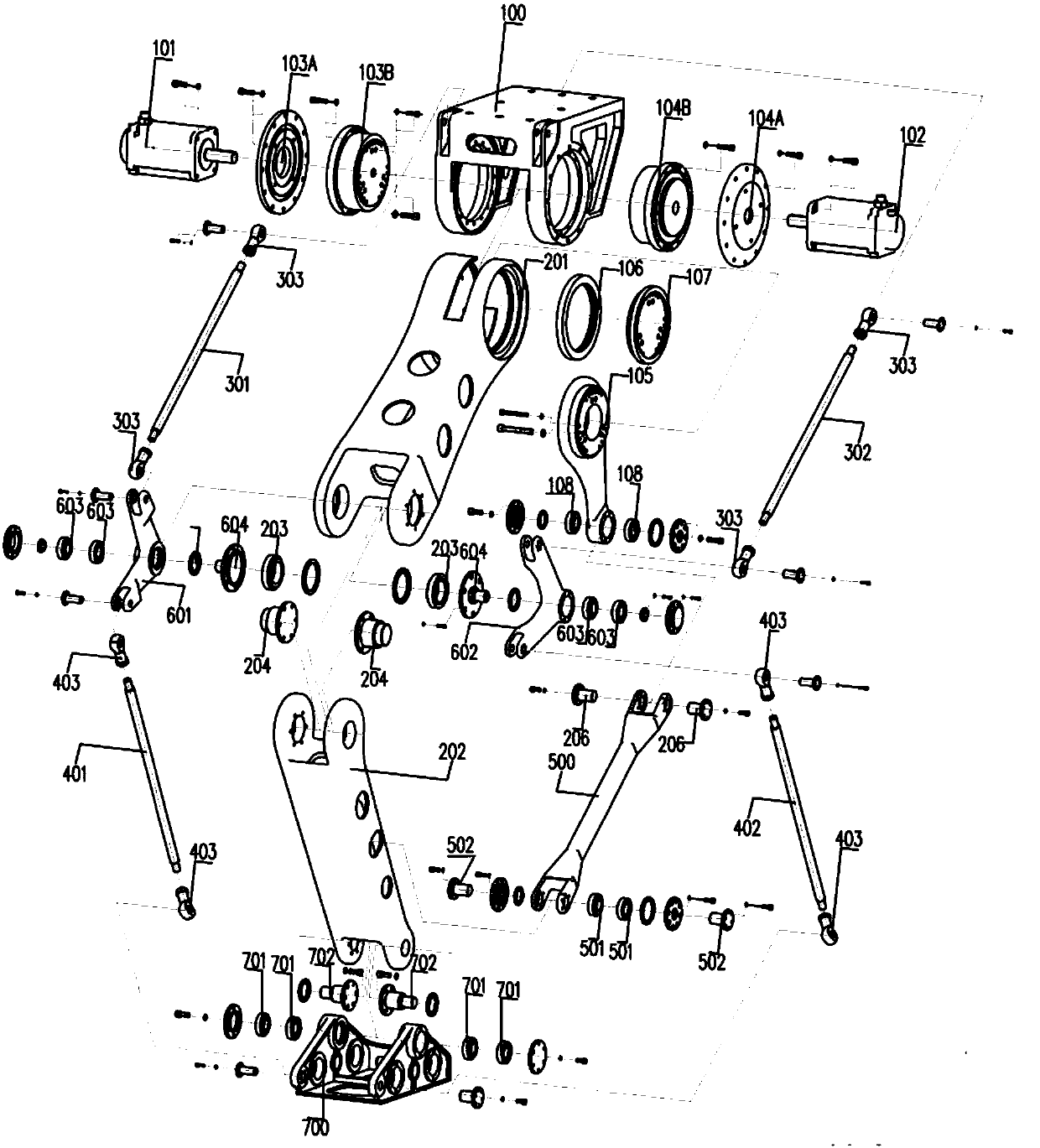
[0022] According to an embodiment of the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, a top-mounted two-axis automatic code blank robot includes: base 100, servo motor 101, servo motor 102, transmission device 103, transmission device 104, crank 105, mechanical arm I201, mechanical arm II202, upper connecting rod 301 and 302 , lower links 401 and 402 , drive link 500 , corner corners 601 and 602 and fixture mounting head 700 . Wherein, the motor 101 is fixedly mounted on the transmission device 103 , the transmission device 103 is fixedly mounted on the left side of the base 100 , the motor 102 is fixedly mounte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com