Data transmission protection method and apparatus thereof
A data transmission and protection device technology, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency, inability to protect multicast data, and excessive protection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
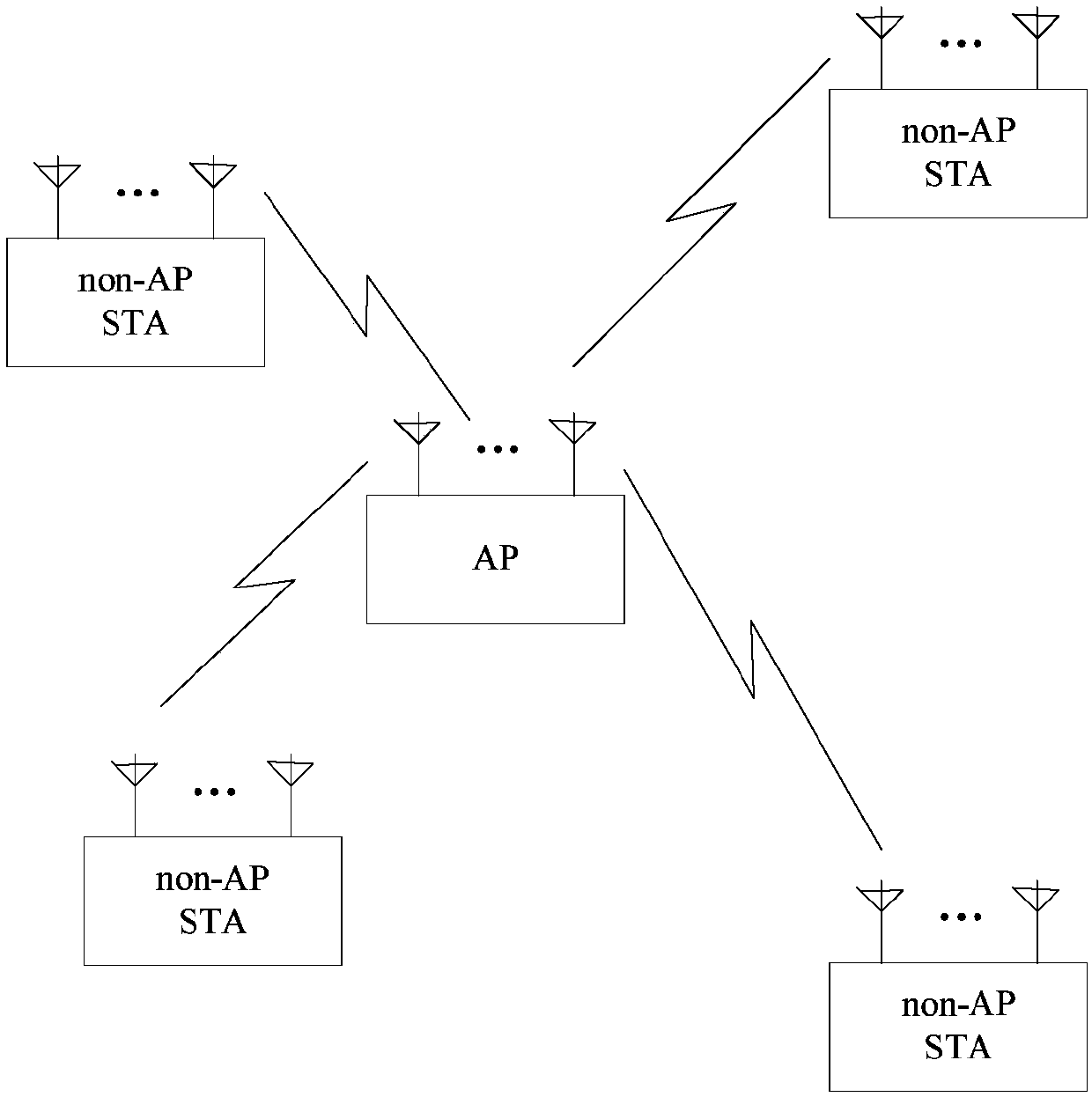
[0186] The AP and multiple stations STA1~STA10 form a BSS. The AP establishes a multicast service 1 with STA1~STA8, and assigns a multicast MAC address to identify the multicast service. The multicast MAC address and the unicast MAC address ( For example, the main difference between the MAC addresses of STA1 to STA10 is that the multicast address sets the I / G bit of the address to 1, and the unicast address sets this bit to 0. For example, in the 802.11 standard, the MAC address of 48 bits (B0 to B47) The B40 is the I / G bit. As an implementation manner, the multicast service may also be identified by other bits of the MAC address.
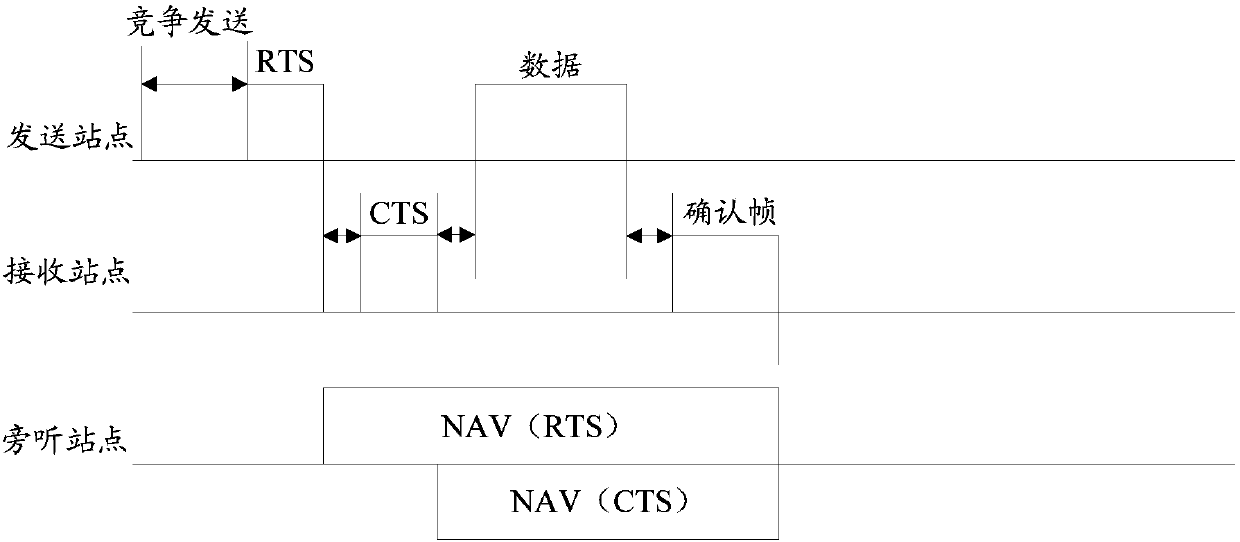
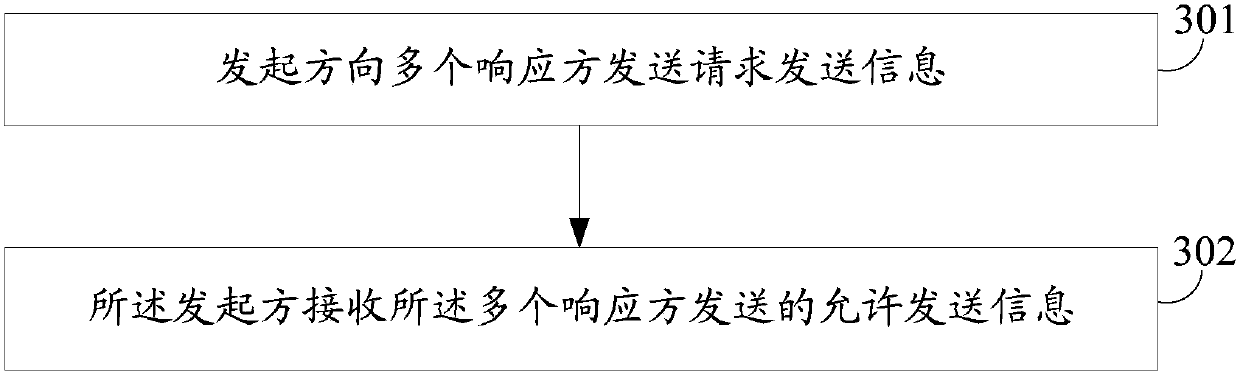
[0187] The AP gets the sending opportunity to send multicast data, such as Figure 5 As shown, in order to protect the multicast data to be sent, the AP performs RTS / CTS interaction before sending the multicast data. Different from the traditional RTS / CTS interaction, the AP sends an RTS frame whose receiving address is set to the multicast addres...
Embodiment 2
[0195] This embodiment describes different response factors and the case of judging whether the CTS can be sent. Similar to the first embodiment, the AP and multiple stations STA1-STA10 form a BSS, the AP and STA1-STA8 establish a multicast service, and assign a group The multicast MAC address is used to identify the multicast service.
[0196] The AP sends an RTS frame whose receiving address is set to the multicast address. The multicast address is the multicast address corresponding to the multicast service negotiated with STA1 to STA8 in advance, and the corresponding I / G bit is set to 1, indicating that the receiving address is multicast. address, STA1 finds that it belongs to the receiver of the multicast service, then STA1 is a station that may need to respond, but whether to respond needs further judgment, STA1 generates the probability P of sending CTS, and the probability P can be related to many factors. For example, it can be inversely proportional to the energy of...
Embodiment 3
[0205] This embodiment describes different response factors and the case of judging whether the CTS can be sent. Similar to the first embodiment, the AP and multiple stations STA1-STA10 form a BSS, the AP and STA1-STA8 establish a multicast service, and assign a group The multicast MAC address is used to identify the multicast service.
[0206] Suppose that the multicast data receiver uses the random backoff mechanism to decide whether to send CTS. Specifically, the station generates a random number a, where a is a non-negative integer that obeys the uniform distribution of [0, CW]. Each received address is a group In the RTS frame of the multicast service associated with itself, the random number a is subtracted by 1 or n, and if a becomes 0, the CTS can be sent, and the CW is the contention window. Specifically, as follows:
[0207] The AP sends an RTS frame whose receiving address is set to the multicast address. The multicast address is the multicast address corresponding...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com