Cognitive base station-based railway communication spectrum sharing method and system
A spectrum sharing and cognitive base station technology, applied in the field of railway wireless communication, can solve the problems of passenger communication experience to be improved, spectrum status violation, and waste of spectrum resources, etc., to improve user experience, improve utilization, and reduce delay. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
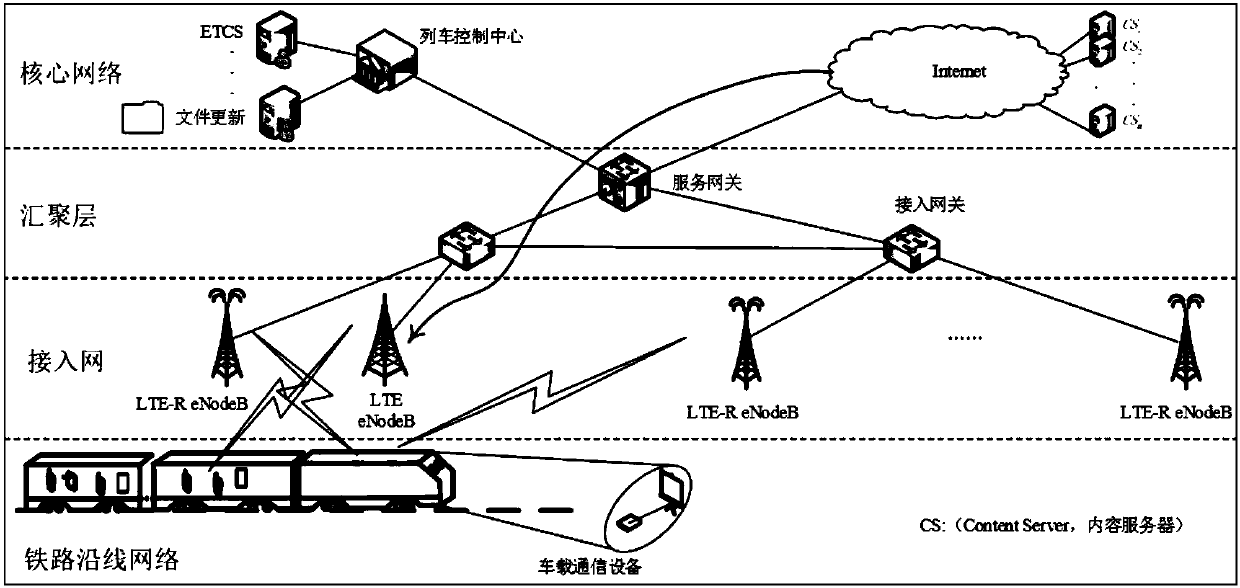
[0059] Through the above analysis, it is found that the LTE-R system based on RR scheduling not only wastes resources in idle time, but also wastes resources in TTI.
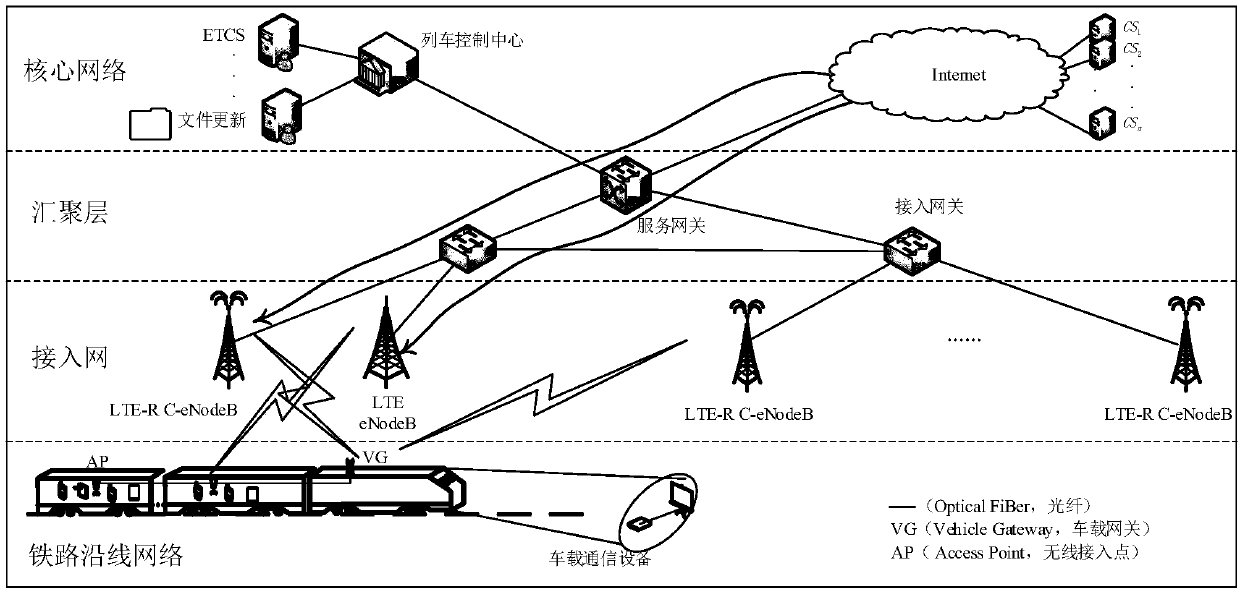
[0060] In order to improve the spectrum utilization rate of the LTE-R system, the present invention proposes to upgrade the LTE-R eNodeB to a C-eNodeB, and defines that the C-eNodeB has the following capabilities: 1. Accurately distinguish between PU and SU service data, ensure PU communication, and ensure Train operation is safe. 2. In the TTI with wasted RBs, allocate the wasted RBs to SU communication. 3. In the TTI where the SU has available RBs, the SU data of different services are processed differently according to the TOS value priority policy, reducing the delay of real-time services.
[0061] In order to reduce the complexity of the system, reduce the penetration loss and the interference of the SU to the vehicle-ground communication using the LTE-R authorized frequency band, the present invention ado...
Embodiment 2
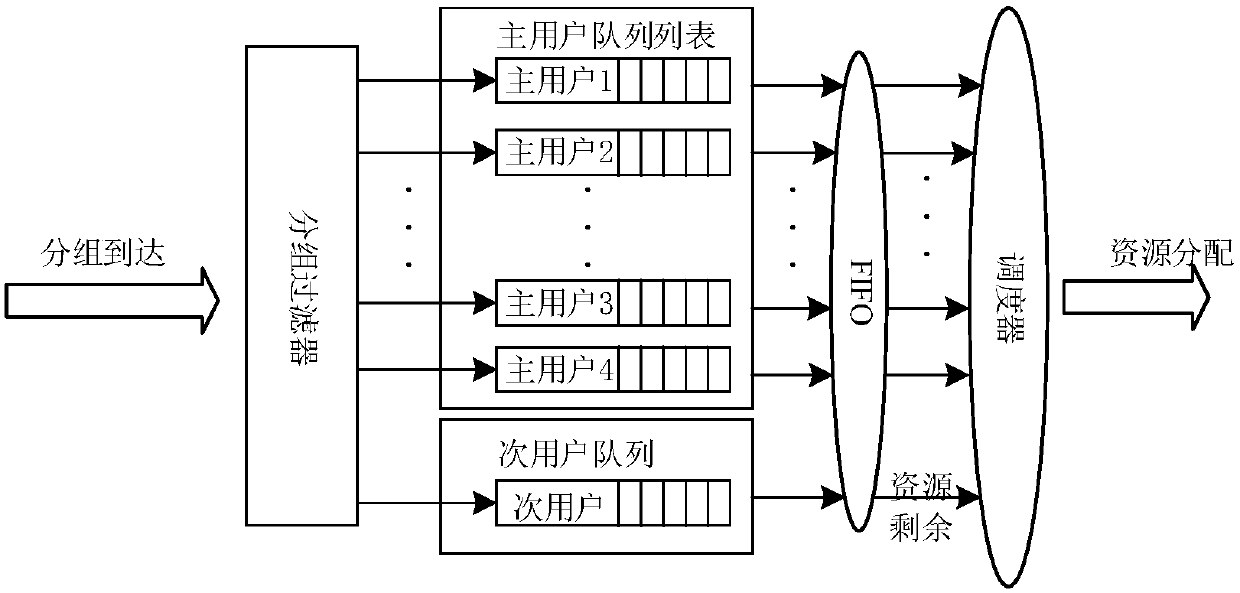
[0068] Figure 5 It is a flow chart of the railway communication spectrum sharing method based on the cognitive base station according to the present invention, and the method includes the following steps:
[0069] Step 1, the current transmission time interval starts;
[0070] Step 2: Cognitive LTE-R base station C-eNodeB traverses all radio bearers, and obtains the number of all active primary users in the current transmission time interval;
[0071] Step 3, C-eNodeB judges whether there is a primary user waiting for scheduling, if so, proceed to step 4, if not, proceed to step 9;
[0072] Step 4: C-eNodeB allocates the same amount of resource blocks to the primary user according to the scheduling strategy of average allocation in round-robin training, configures the corresponding downlink scheduling configuration instruction parameters and saves the relevant information of the primary user that has not been served, and waits for the next transmission time interval;
[007...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com