Three-dimensional face identification method based on multi-scale covariance descriptor and local sensitive Riemann and sparse classification
A three-dimensional face, local sensitive technology, applied in the field of three-dimensional face recognition, can solve the problem of difficult to accurately describe the local features of the face and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
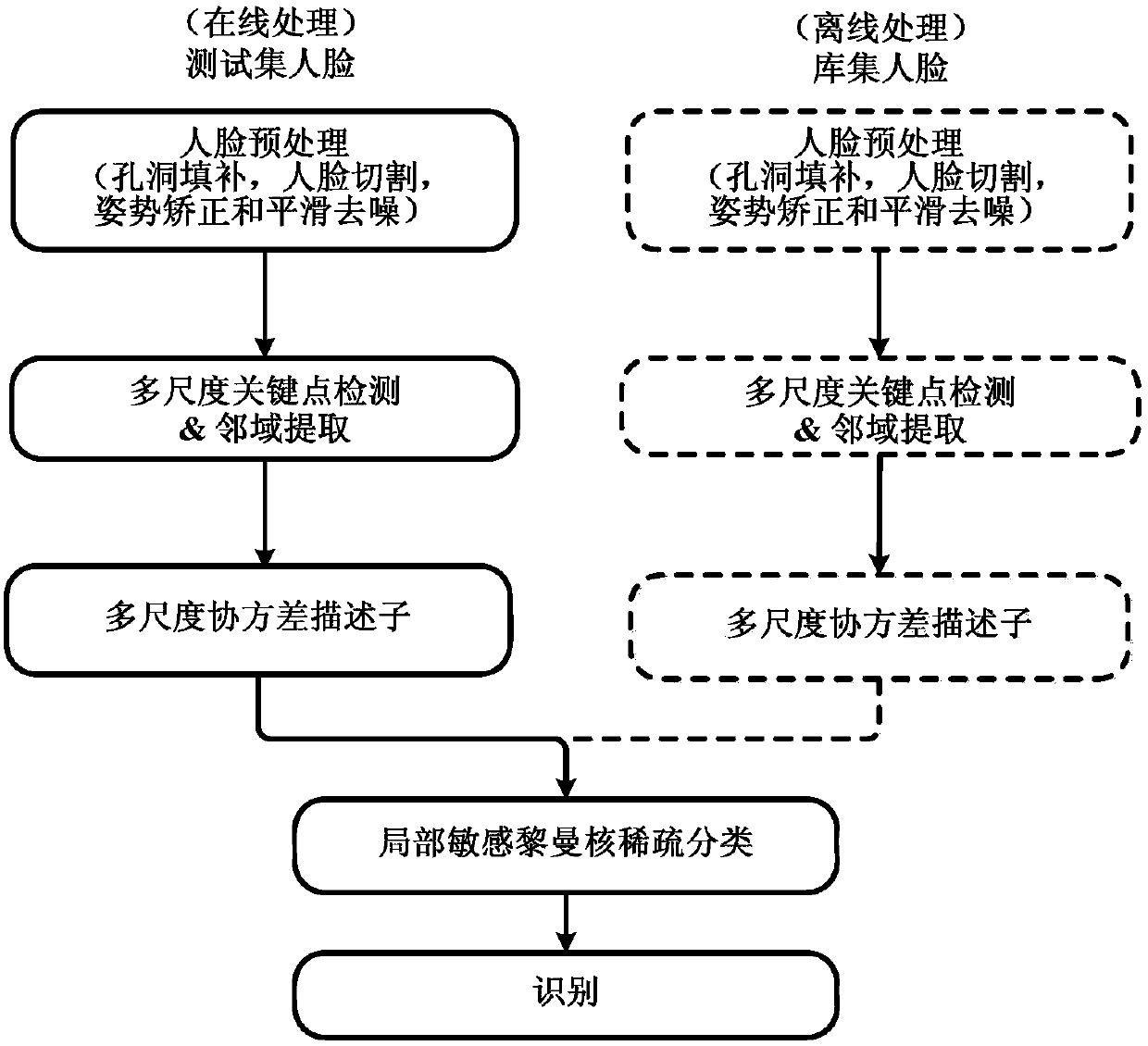
[0062] like Figure 1-4 As shown, a three-dimensional face recognition method based on multi-scale covariance descriptor and local sensitive Riemann kernel sparse classification of the present invention realizes three-dimensional face recognition process through Matlab R2015b programming tool in Windows operating system. The experimental data comes from the FRGC v2.0 3D face database, which contains 4007 3D face models of 466 individuals for testing.
[0063] Step 1: The specific process of automatic preprocessing of the original G face models in the library set and P test set face models is as follows:
[0064] Step 1.1: Some small holes in the face are filled by bicubic interpolation using the effective neighborhood of the adjacent three-dimensional point cloud coordinates (x, y, z);
[0065] Step 1.2: Cut the face, determine the position of the tip of the nose according to the shape index (Shape Index) feature and geometric constraints, point The shape index descriptor o...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Adopt the method of embodiment 1, carry out experimental verification. Specifically include the following steps:
[0113] Step 6: Identity recognition experiments, all experiments use R1RR (Rank-one Recognition Rate) as the recognition performance index.
[0114]Step 6.1: Experiment 1. This experiment uses the FRGC v2.0 database, which collects 4007 face point clouds of 466 objects, including faces with expressions such as smiling, surprised, and angry. Three recognition experiments were done on the database, and each experiment used the first neutral face of each object to form a library set of faces (466 in total). (1) Neutral vs. Others, the remaining 3541 faces constitute the test set; (2) Neutral vs. Neutral, the remaining neutral faces are used as the test set; (3) Neutral vs. Non-neutral, the remaining non-neutral faces as a test set. The three groups of experiments obtained the Rank-1 recognition rate of 98.3%, 100% and 95.7% respectively.
[0115] Step 6.2:...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com