Fluidic devices with at least one actionnable fiber
A fluid and fiber technology, applied in the field of micron-scale, small-scale, nano-scale and millimeter-scale fluid systems, can solve problems such as difficult and restrictive system operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0717] - Preparation of removable fibers:
[0718] As noted above, the fibers of the present invention can be made from any type of material, and in fact, various types of materials that have been formed into fibers can be purchased and used. This has been demonstrated, for example, in Example 6: the movable fibers are nylon fibers, the catheters are prepared by punching with needles, and the PDMS chip already contains microchannels. The PDMS chip was fabricated by conventional soft lithography.
[0719] In some cases, however, the present invention must alter the shape of pre-existing fibers, or must construct new fibers with a predetermined shape.
[0720] In some embodiments, the present invention further comprises the step of adjusting the shape of the manipulable fiber over a portion of its length. Non-limiting means include:
[0721] A: Compresses fibers in one direction
[0722] B: locally stretch the fiber
[0723] C: Locally cast other materials on fibers
[0...
Embodiment 1
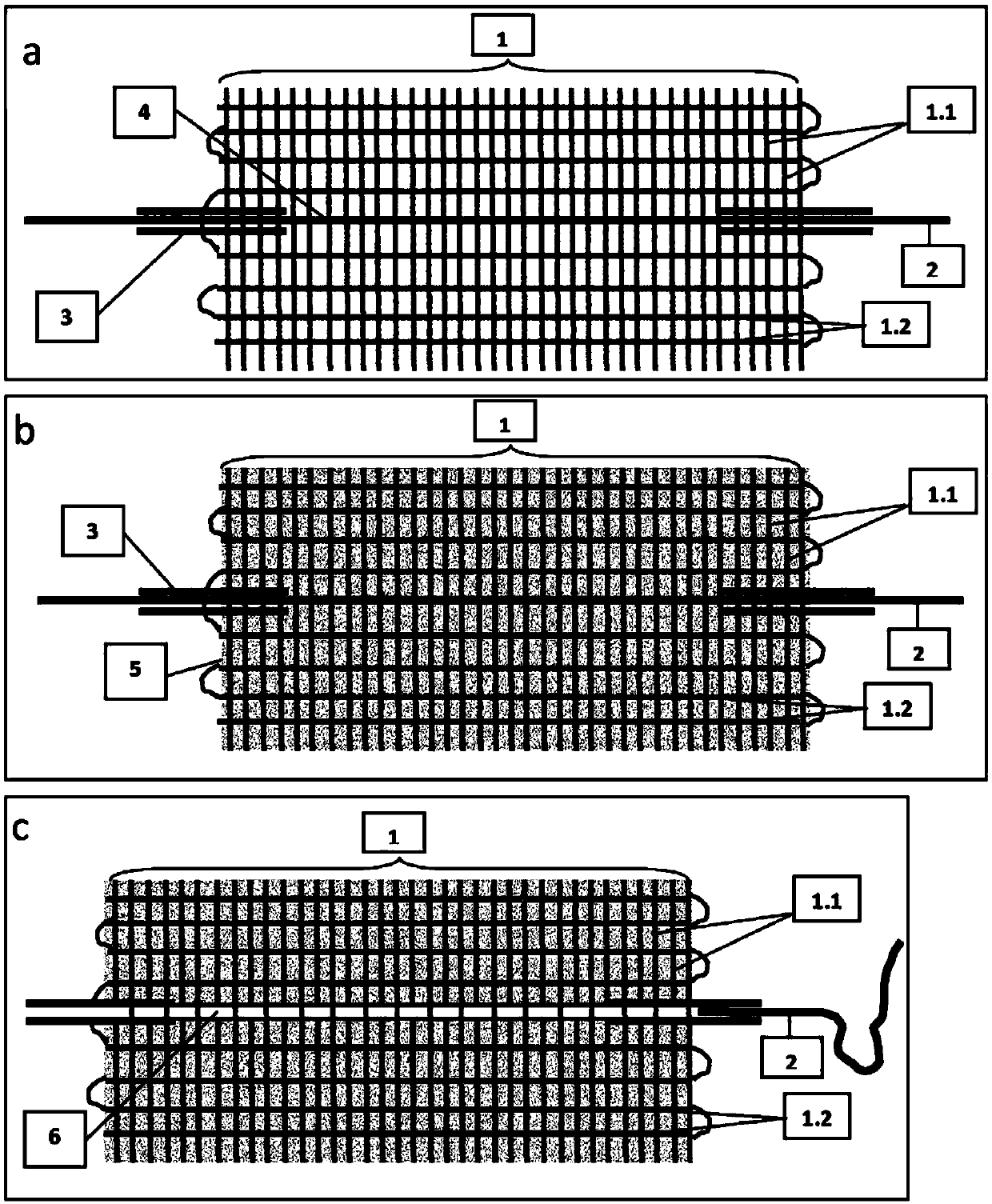
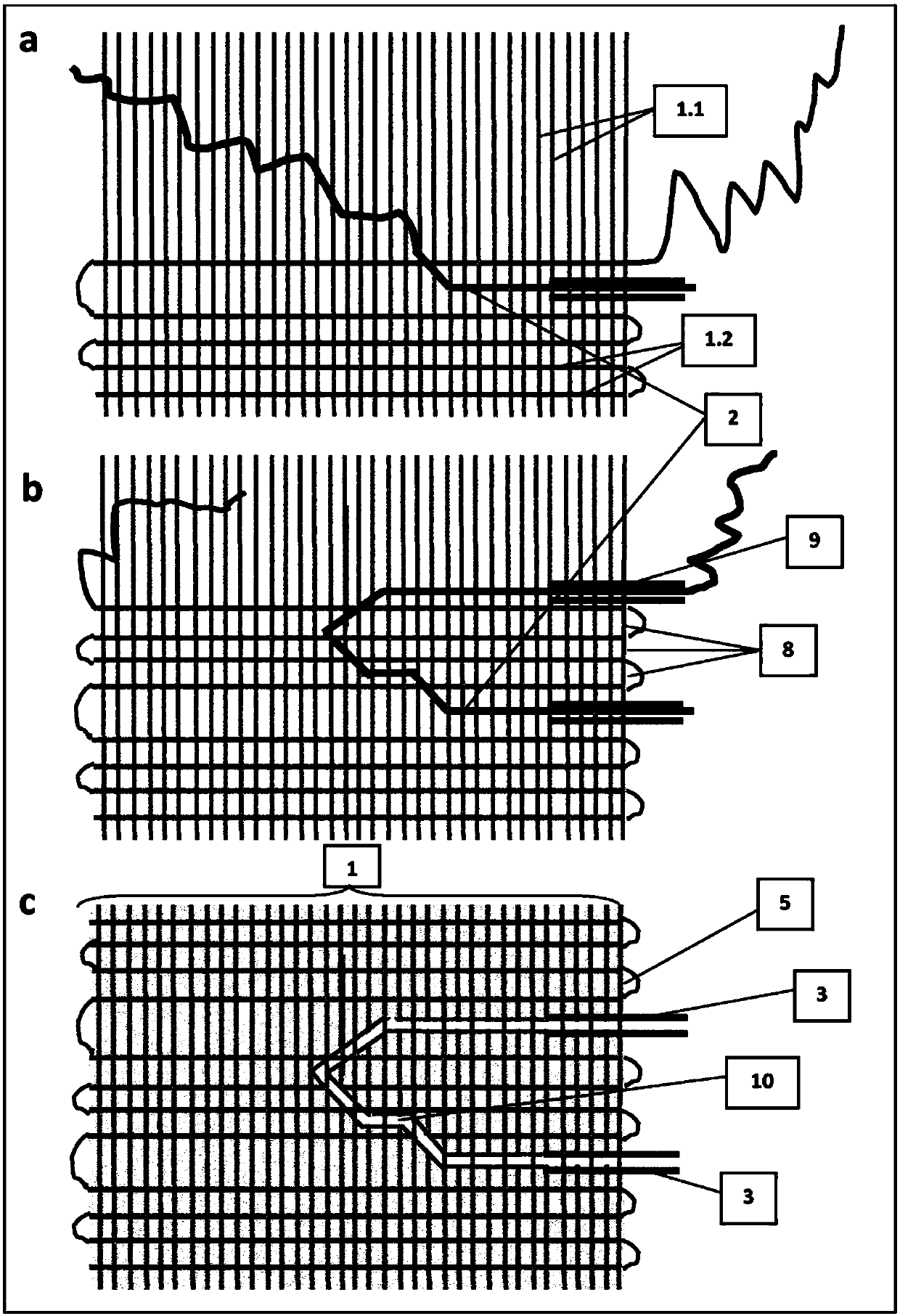
[0813] figure 1 The first example given in shows the use of a fabric support [1], one of the preparation methods for producing an inventive component or chip comprising a A single straight conduit [4] that contains movable fibers. First, a fiber fabric [1] made from support fibers [1.1] was mid-woven with a loom (Ashford, NZ). In addition to weaving, movable fibers [2] are inserted into two short silicone tubes [3], which serve as external ports in the resulting chip. Together with the tube [3], the movable fiber [2] is then added along the weft thread support fiber [1.2], by replacing a section of the weft thread fiber, to the end of half of the fabric fiber, as figure 1 As shown in a, the other half of the fabric fibers are still woven.
[0814] After weaving is completed, the fiber fabric [1] is separated from the loom and dipped into matrix precursor material [5]. Before being hardened, the matrix precursor material wicks the support fibers [1.1, 1.2], and its spatia...
Embodiment 2
[0816] Embodiment 2: the purposes of the present invention as integrated pump
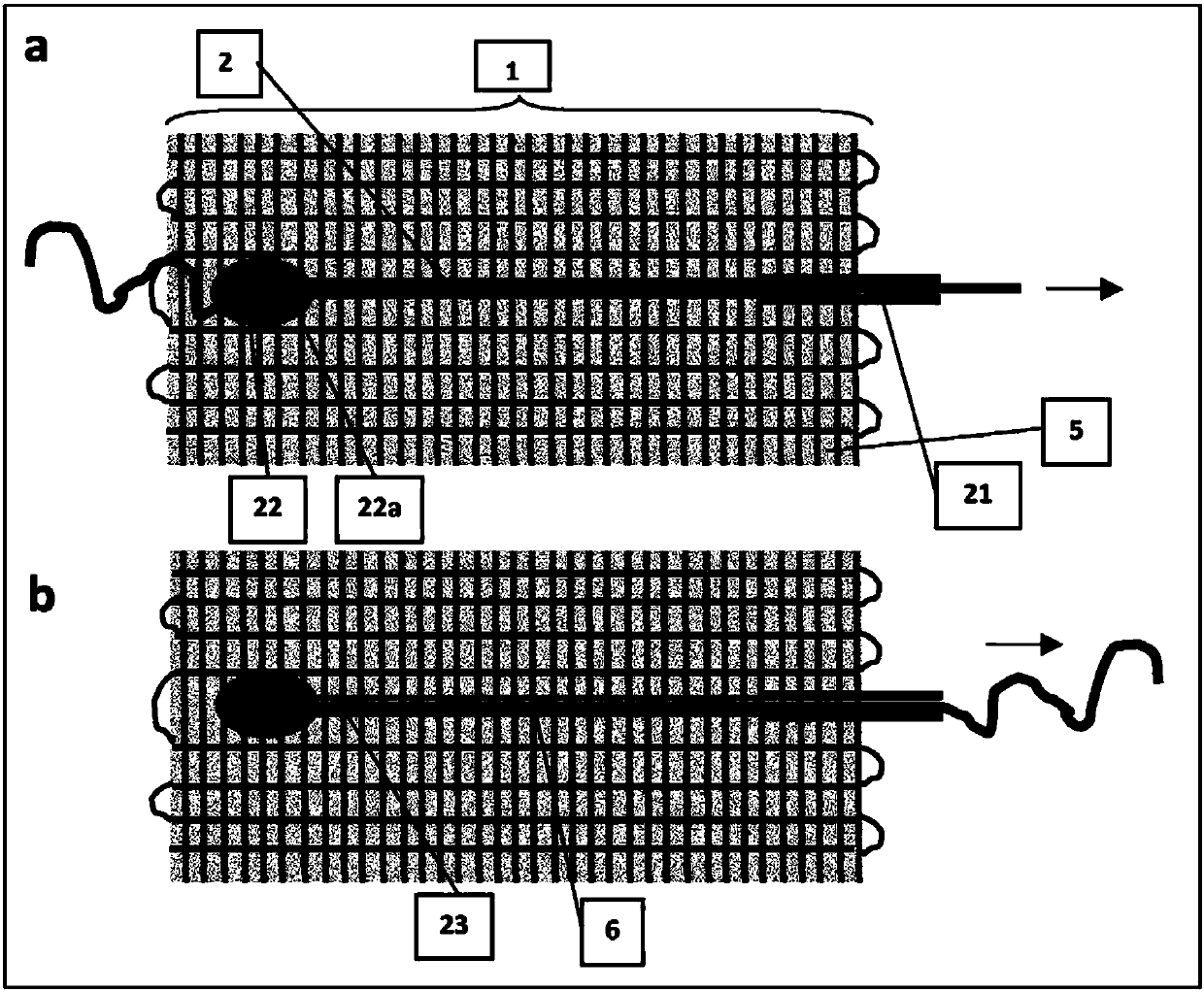
[0817] Prepare in the same manner as in Example 1 figure 2 device, except for the following two features:
[0818] First, insert only one end of the movable fiber [2] into the silicone tube [21]. During picking, the other end is partially inserted into the shed and thus protrudes from the surface of the fabric [1]. After the matrix [5] has hardened, the movable fibers [2] protrude from the matrix [5]. A drop of colored water [22a] is placed on the fabric at a location [22] where the movable fiber [2] exits the fabric and defines a fluid drop zone [22]. The movable fiber [2] is then pulled and partially removed, which allows fluid to enter the conduit [23], the space created by the fiber [2], similar to a microsyringe (see figure 2 b).
[0819] For this example, the supporting fibers of the fabric [1] were white cotton threads (n°7, Phildar, FR). The movable fiber [2] was a fluorocarbon mo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com