Parallel and highly efficient grid-and-density-based multi-dimensional spatial data clustering algorithm (GRIDEN)
A multi-dimensional space and data clustering technology, which is applied in the field of data mining and big data analysis, can solve the problems of insufficient precision of spatial data clustering algorithms and insufficient efficiency of spatial data clustering algorithms, and achieve powerful parallel computing capabilities and reduce time effect of complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
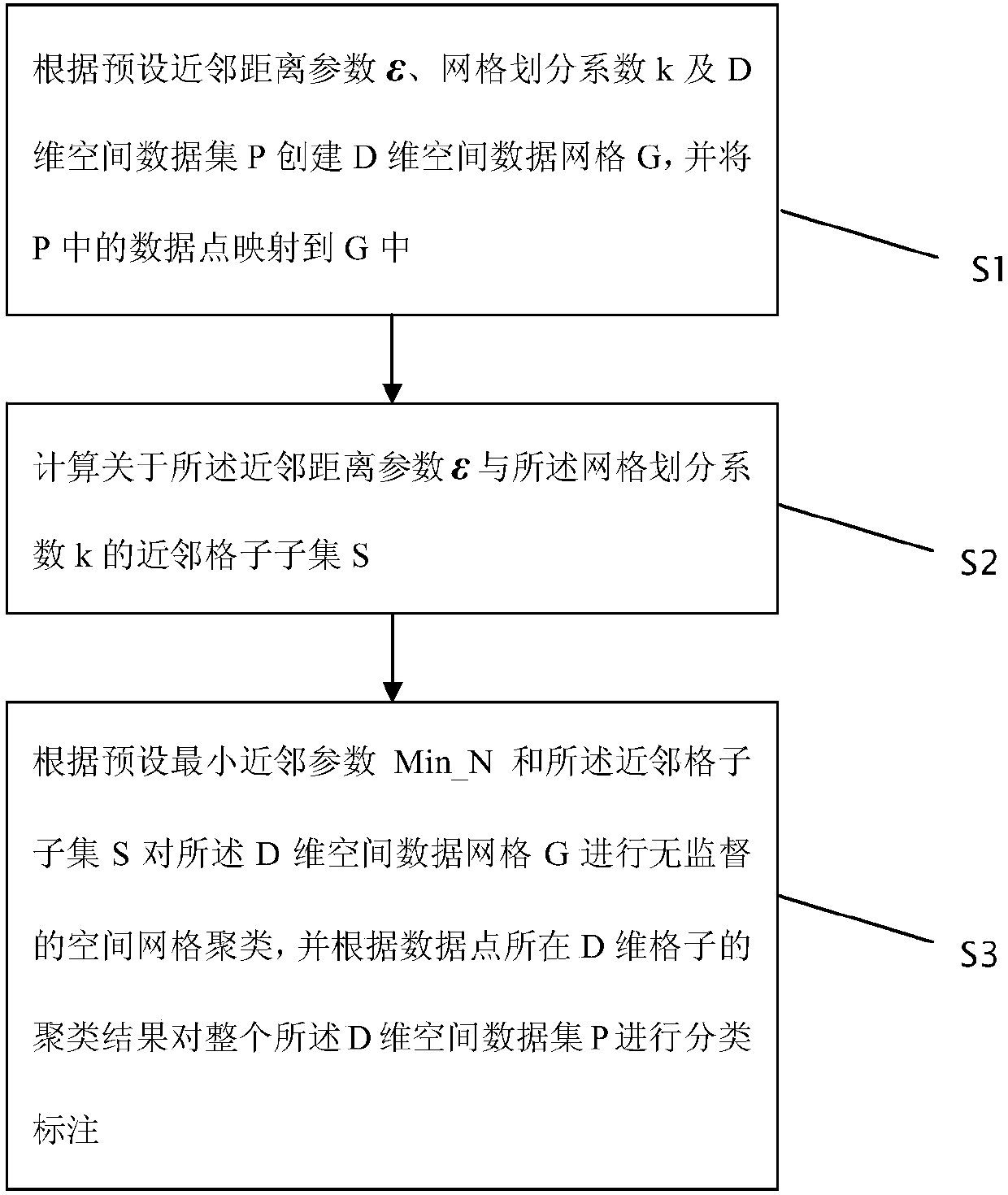
[0037] This embodiment provides a multi-dimensional spatial data clustering algorithm GRIDEN based on grid and density, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0038] S1: Create a D-dimensional spatial data grid G according to the preset neighbor distance parameter ε, grid division coefficient k, and D-dimensional spatial data set P, and map the data points in P to G.
[0039] S2: Calculate the neighbor grid subset S with respect to the neighbor distance parameter ε and the grid division coefficient k.
[0040] S3: Perform unsupervised spatial grid clustering on the D-dimensional spatial data grid G according to the minimum neighbor parameter Min_N and the neighbor grid subset S, and perform unsupervised spatial grid clustering on the entire D-dimensional grid according to the clustering results of the data points. The above D-dimensional spatial data set P is classified and labeled.
[0041] In the above scheme, first create a D-dimensional spatial data grid G composed of ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] In the above step S3, four sequential steps may be adopted to realize the parallel calculation of the unsupervised spatial grid clustering process. An implementation is provided in this embodiment, including:
[0044] Specifically, such as figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0045] S31: According to the preset minimum neighbor parameter Min_N, for any grid in which the number of data points in the D-dimensional spatial data grid G is not empty, calculate the sum of the number of data points in the subset S of adjacent grids in parallel, and calculate the total Grids larger than the minimum neighbor parameter Min_N are marked as core grids and given independent class labels;
[0046] S32: iteratively traversing and calculating all core grids in the D-dimensional spatial data grid G in parallel, and merging the core grid and all other core grids in the adjacent grid subset S into one class, if the iteration process has not ended Then continue the iter...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of the hardware structure of the electronic equipment of the multi-dimensional spatial data clustering algorithm GRIDEN based on the grid and density provided in this embodiment, as Figure 5 As shown, the equipment includes:
[0051] one or more processors 701 and memory 702, Figure 5 A processor 701 is taken as an example.
[0052] The device for executing the grid-and-density-based multidimensional spatial data clustering algorithm GRIDEN may also include: an input device 703 and an output device 704 .
[0053] The processor 701, the memory 702, the input device 703 and the output device 704 may be connected via a bus or in other ways, Figure 5 Take connection via bus as an example.
[0054] As a non-volatile computer-readable storage medium, the memory 702 can be used to store non-volatile software programs, non-volatile computer-executable programs and modules, such as the grid-and-density-based multidimensional The progra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com